Application of Sensing Devices in the Detection of Oral, Pulmonary, and Gastrointestinal Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biochemical and Chemical Gas Sensors for the Detection of Oral Disease
2.1. Introduction to Oral Cancer
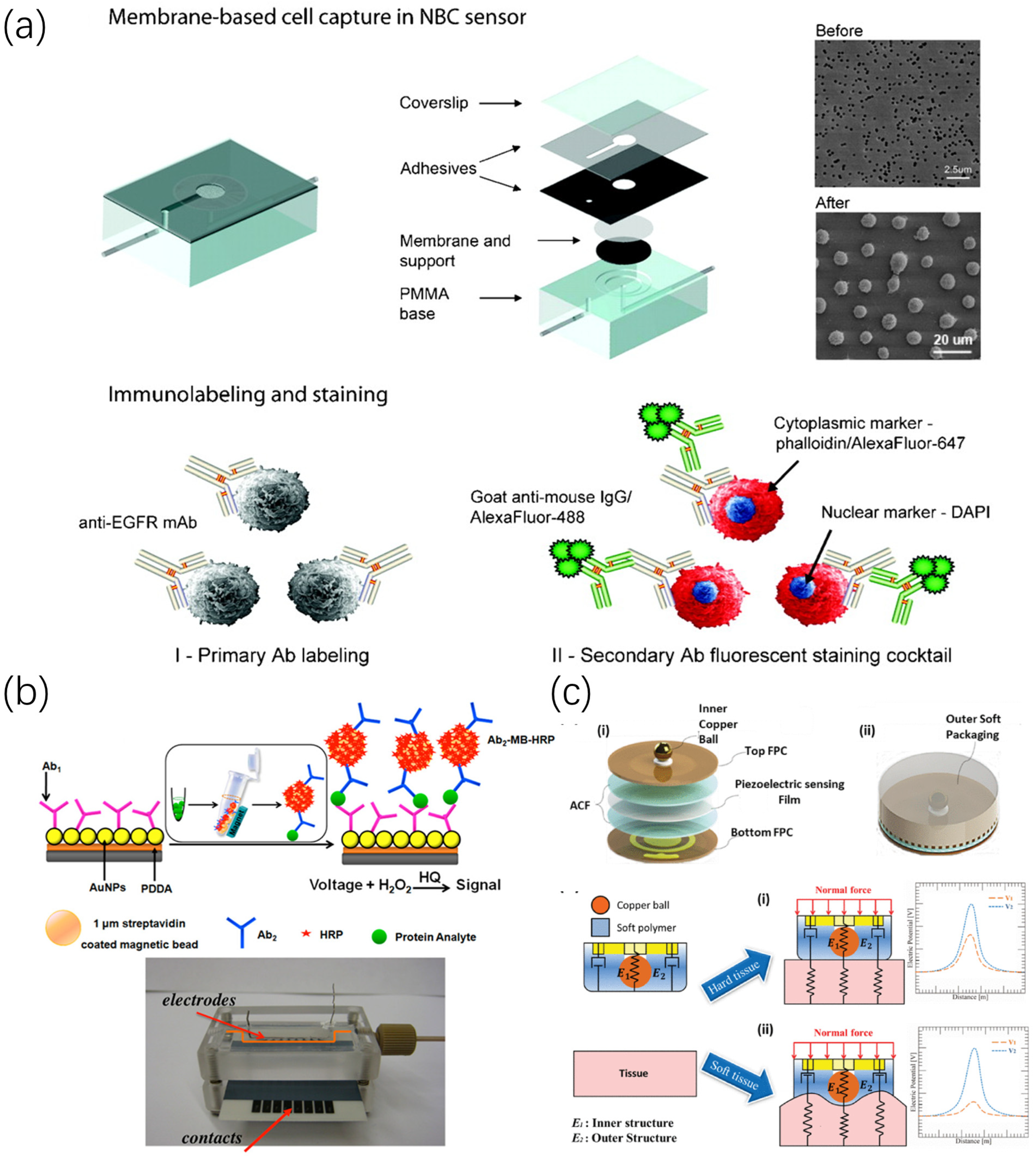
2.2. Development of Biochemical Sensors for Oral Cancer Markers
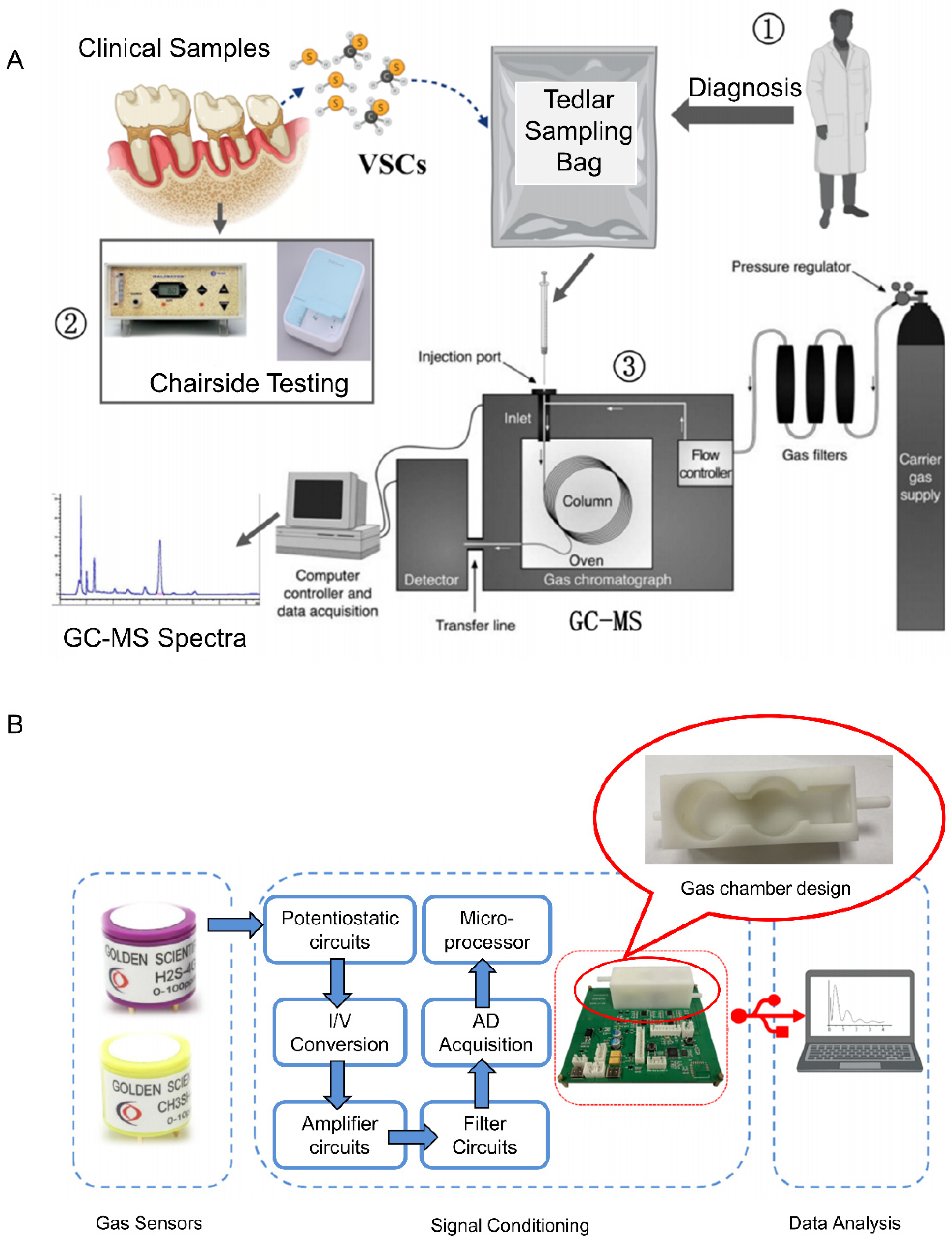
2.3. Halitosis and Periodontal Diseases
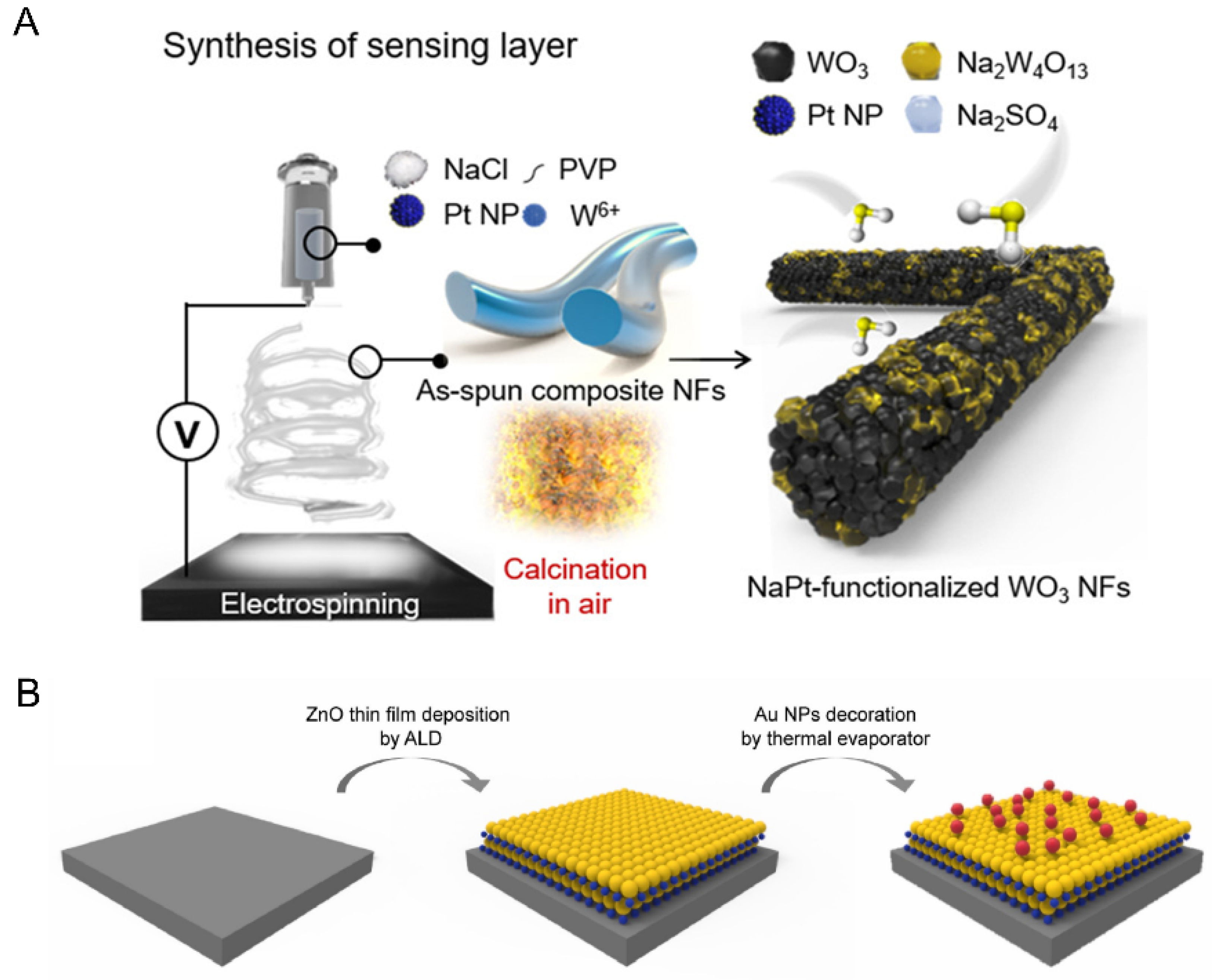
2.4. Chemical Gas Sensors for the Early Diagnosis of Orogenic Halitosis and Periodontal Diseases
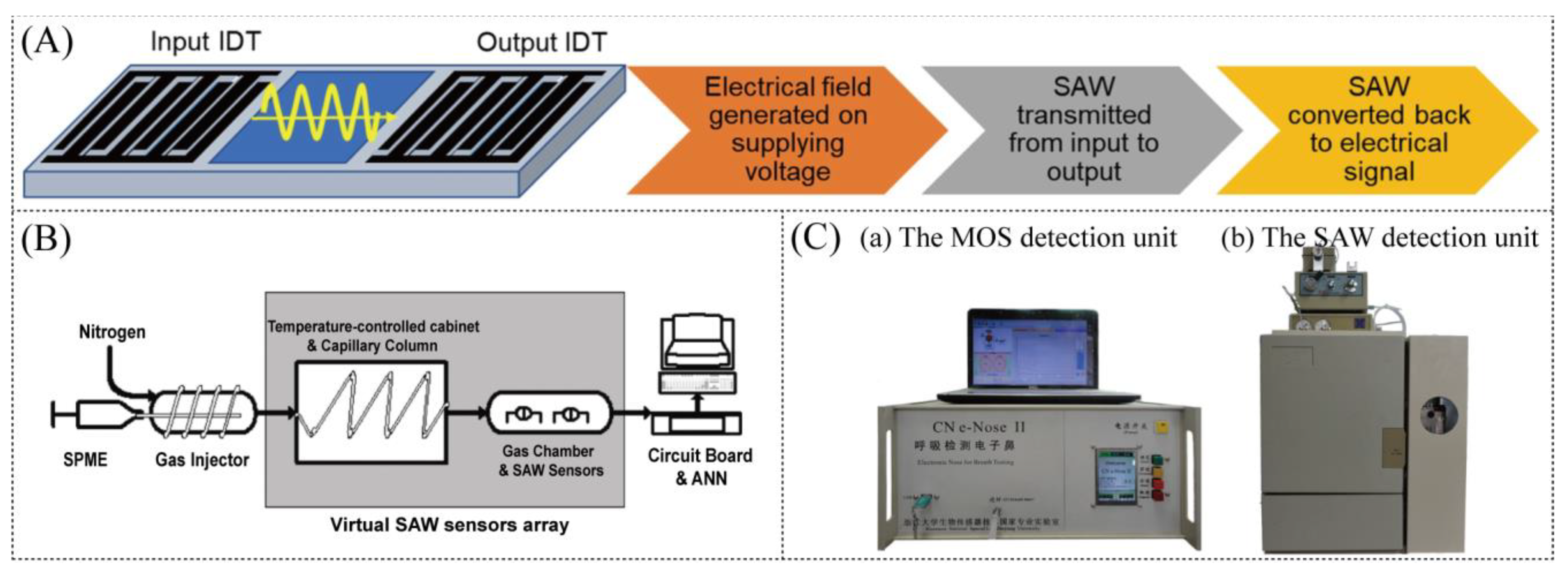
3. Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor (SAW) for Detecting Lung Diseases
3.1. Introduction to Lung Diseases
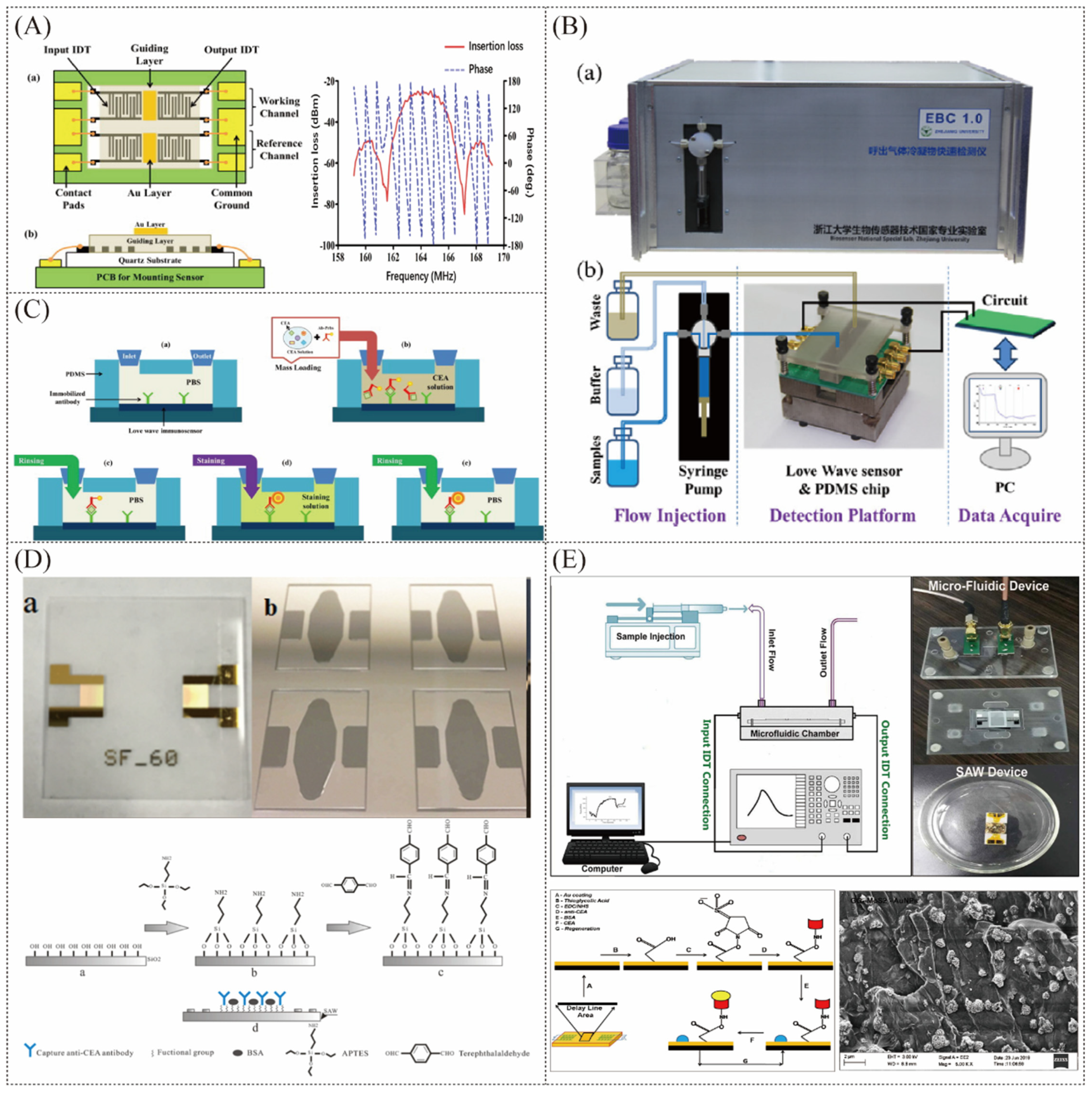
3.2. Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor
3.3. Detection of Lung Disease Markers
4. Sensors and an Electronic Nose for Detecting Gastrointestinal Diseases
4.1. Gastrointestinal Diseases
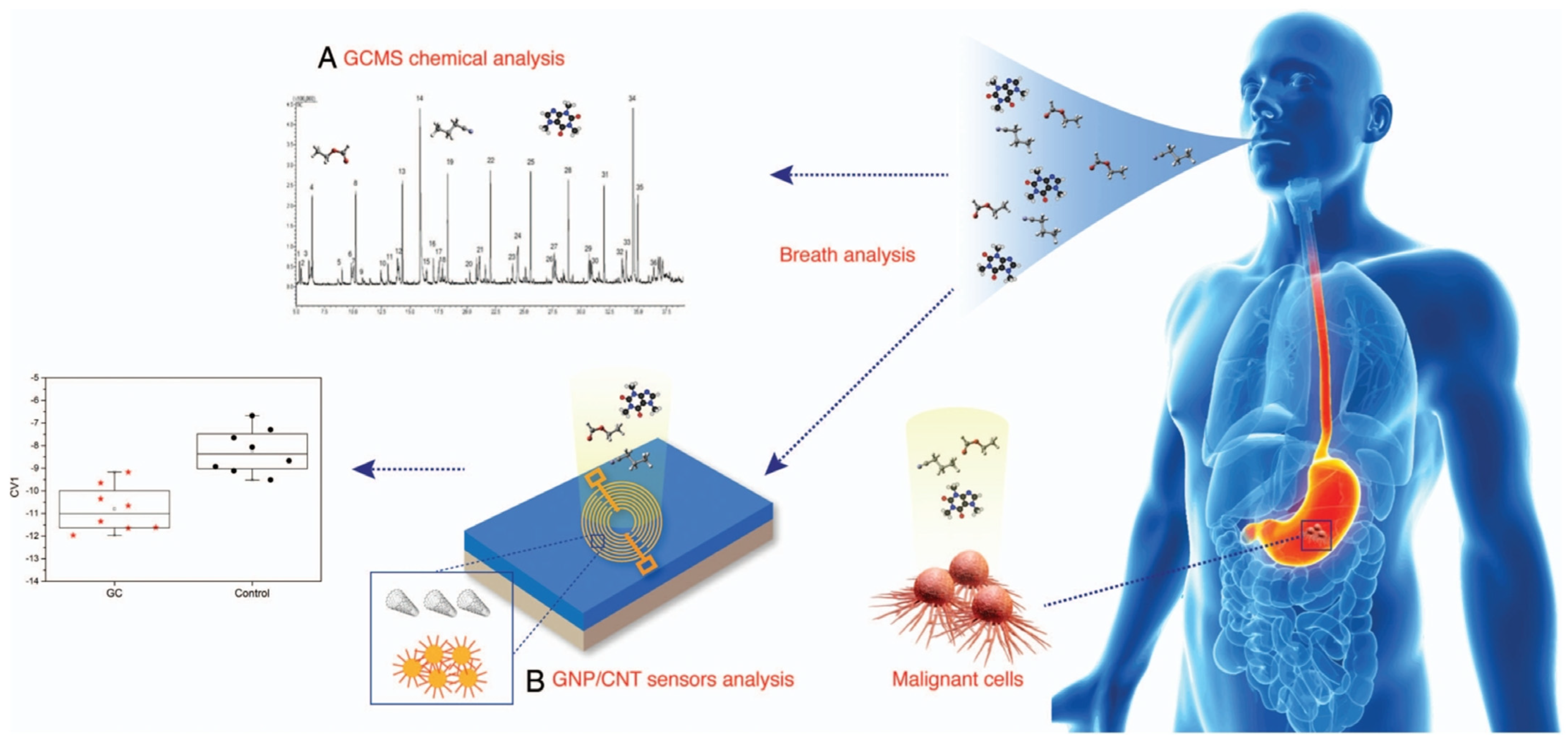
4.2. Gastric Disease Sensing and Detection
4.3. Detection of Intestinal Diseases
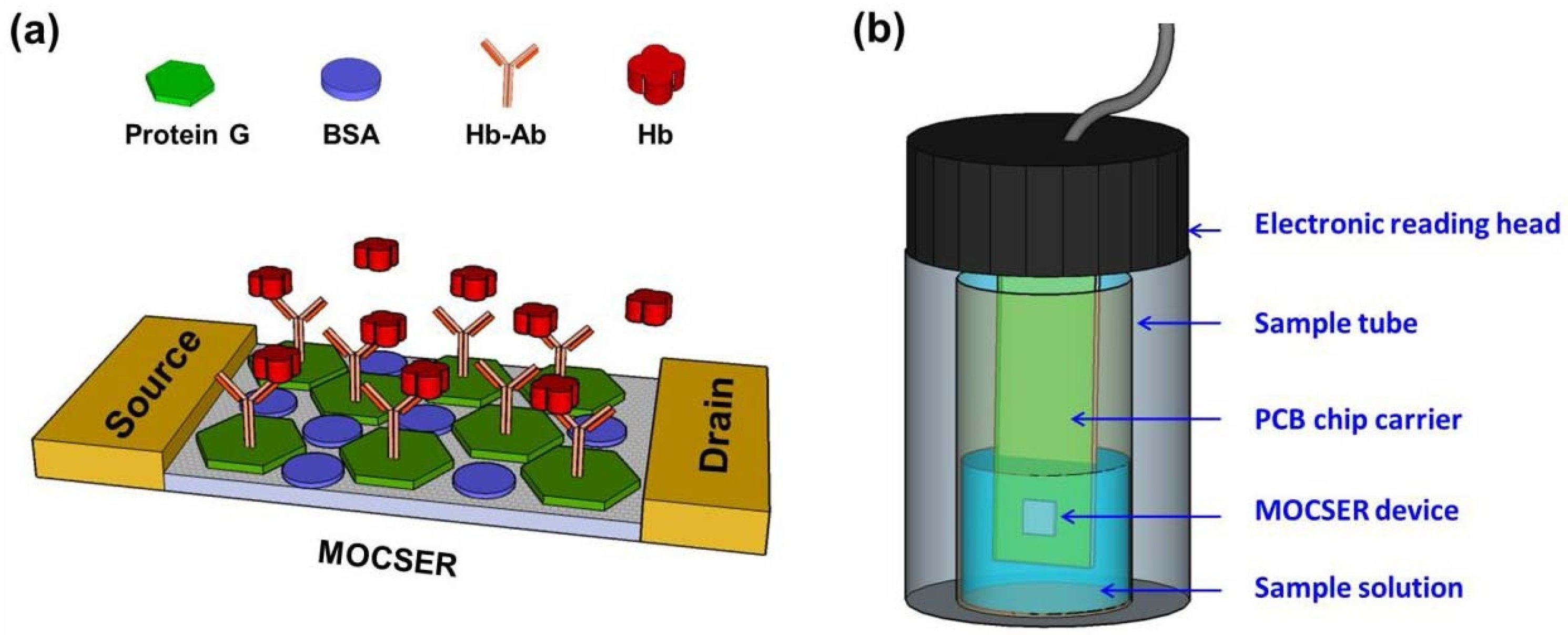
4.4. Ingestible Sensors
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, Y.-H.; Wong, D.T. Saliva: An emerging biofluid for early detection of diseases. Am. J. Dent. 2009, 22, 241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salek-Maghsoudi, A.; Vakhshiteh, F.; Torabi, R.; Hassani, S.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Hosseini, M.; Abdollahi, M. Recent advances in biosensor technology in assessment of early diabetes biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lino, C.; Barrias, S.; Chaves, R.; Adega, F.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Fernandes, J. Biosensors as diagnostic tools in clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Bai, M.; Gong, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D. Revolutionizing precision medicine: Exploring wearable sensors for therapeutic drug monitoring and personalized therapy. Biosensors 2023, 13, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waggoner, P.S.; Craighead, H.G. Micro-and nanomechanical sensors for environmental, chemical, and biological detection. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1238–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfe, P. Micro- and Nanosensors for Medical and Biological Measurement. Sens. Mater. 2012, 24, 275–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishinkin, R.; Haick, H. Nanoscale sensor technologies for disease detection via volatolomics. Small 2015, 11, 6142–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar-Lopez, F.J. Recent Progress in Micro-and Nanotechnology-Enabled Sensors for Biomedical and Environmental Challenges. Sensors 2023, 23, 5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varatharajan, R.; Manogaran, G.; Priyan, M.K.; Sundarasekar, R. Wearable sensor devices for early detection of Alzheimer disease using dynamic time warping algorithm. Clust. Comput. 2018, 21, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Gou, G.-Y.; Gao, F.; Yao, P.; Wu, H.; Guo, Y.; Yin, M.; Yang, J.; Wen, T.; Zhao, M. Multichannel Flexible Pulse Perception Array for Intelligent Disease Diagnosis System. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 5673–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geest, S.; Laleman, I.; Teughels, W.; Dekeyser, C.; Quirynen, M. Periodontal diseases as a source of halitosis: A review of the evidence and treatment approaches for dentists and dental hygienists. Periodontol. 2000 2016, 71, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S.; Khan, R.S.; Najeeb, S.; Slowey, P.D.; Rehman, I.U. Role of salivary biomarkers in oral cancer detection. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2018, 86, 23–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Berean, K.J.; Burgell, R.E.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. Intestinal gases: Influence on gut disorders and the role of dietary manipulations. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Luo, Z.; Qian, C.; Li, W.; Duan, Y. Breath volatile organic compound analysis: An emerging method for gastric cancer detection. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 044002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, T.; Li, T.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Q. Exhaled breath analysis in disease detection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 515, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, A.; Yan, F. Chemical Substances. In Seamless Healthcare Monitoring: Advancements in Wearable, Attachable, and Invisible Devices; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 335–365. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.; Pang, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Ibarlucea, B.; Liu, X.; Gemming, T.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H. Graphene biodevices for early disease diagnosis based on biomarker detection. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3841–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Shah, M.R.; Barek, J.; Malik, M.I. Cancer biomarkers and their biosensors: A comprehensive review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, M.; Hosseini, M.S.; Haghighi, A.M.; Misaghi, M. Nanosensors and their applications in early diagnosis of cancer. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2023, 41, 100569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Jain, R. MXene: An emerging material for sensing and biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, B.W.; Day, T.A. Oral cancer and precancerous lesions. CA-Cancer J. Clin. 2002, 52, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mork, J.; Lehtinen, M.; Dillner, J. Human papillomavirus infection as a risk factor for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck—Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 377. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, S.D.; Ferlito, A.; Takes, R.P.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Valentin, M.D.; Woolgar, J.A.; Bradford, C.R.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Rinaldo, A.; Hier, M.P.; et al. Advances and applications of oral cancer basic research. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, T.; Macey, R.; Kerr, A.R.; Lingen, M.W.; Ogden, G.R.; Warnakulasuriyas, S. Diagnostic tests for oral cancer and potentially malignant disorders in patients presenting with clinically evident lesions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 7, 1465–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowska, A.; Grzycka-Kowalczyk, L.; Trojanowski, P.; Klatka, J.; Drop, A. Computed tomography perfusion examination is helpful in evaluating the extent of oropharyngeal and oral cavity cancer. Pol. J. Radiol. 2011, 76, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Nae, A.; O’Leary, G.; Feeley, L.; Fives, C.; Fitzgerald, B.; Chiriac, E.; Sheahan, P. Utility of CT and MRI in assessment of mandibular involvement in oral cavity cancer. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 5, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolens, E.D.; Dourado, M.R.; Almangush, A.; Salo, T.A.; Rocha, C.A.G.; da Silva, S.D.; Brennan, P.A.; Coletta, R.D. The Impact of Histopathological Features on the Prognosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 784924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, S.; Chikazu, D.; Ochiya, T.; Yoshioka, Y. Extracellular vesicle-based liquid biopsies in cancer: Future biomarkers for oral cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 38, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldoni, R.; Scolaro, A.; Boccalari, E.; Dolci, C.; Scarano, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Ravazzani, P.; Muti, P.; Tartaglia, G. Malignancies and Biosensors: A Focus on Oral Cancer Detection through Salivary Biomarkers. Biosensors 2021, 11, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigum, S.E.; Floriano, P.N.; Christodoulides, N.; McDevitt, J.T. Cell-based sensor for analysis of EGFR biomarker expression in oral cancer. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigum, S.E.; Floriano, P.N.; Redding, S.W.; Yeh, C.K.; Westbrook, S.D.; McGuff, H.S.; Lin, A.; Miller, F.R.; Villarreal, F.; Rowan, S.D.; et al. Nano-Bio-Chip Sensor Platform for Examination of Oral Exfoliative Cytology. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, R.; Patel, V.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Munge, B.S.; Cheong, S.C.; Zain, R.B.; Abraham, M.T.; Dey, D.K.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Ultrasensitive Detection of Cancer Biomarkers in the Clinic by Use of a Nanostructured Microfluidic Array. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6249–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, M.O.; Lin, C.M.; Lee, D.H.; Chiang, W.F.; Chen, I.H.; Chuang, C.H. Portable Pen-Like Device With Miniaturized Tactile Sensor for Quantitative Tissue Palpation in Oral Cancer Screening. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 9610–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Sabet, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Klokkevold, P.R.; Wong, D.T.; Ho, C.M. Optical protein sensor for detecting cancer markers in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
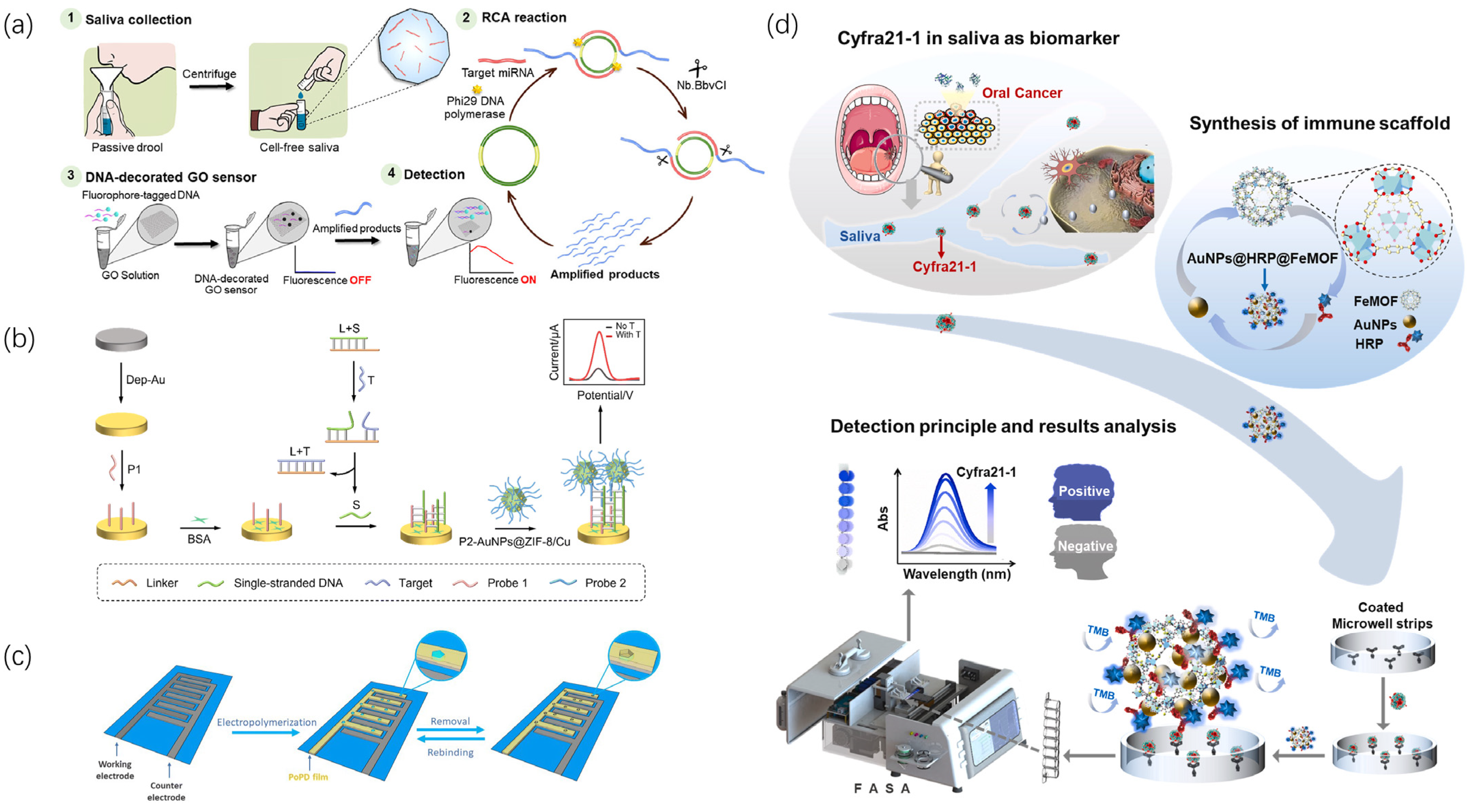
- Pitikultham, P.; Putnin, T.; Pimalai, D.; Sathirapongsasuti, N.; Kitiyakara, C.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, B.Q.; Japrung, D. Ultrasensitive Detection of MicroRNA in Human Saliva via Rolling Circle Amplification Using a DNA-Decorated Graphene Oxide Sensor. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 15266–15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, G.; Chiriacò, M.S.; Ferrara, F.; Turco, A.; Velardi, L.; Signore, M.A.; Esposito, M.; Gigli, G.; Primiceri, E. Development of an MIP based electrochemical sensor for TGF-β1 detection and its application in liquid biopsy. Analyst 2023, 148, 4447–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Qiu, D.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Li, J. Cu 2+-doped zeolitic imidazolate frameworks and gold nanoparticle (AuNPs@ ZIF-8/Cu) nanocomposites enable label-free and highly sensitive electrochemical detection of oral cancer-related biomarkers. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, J.G.; Maji, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Nanostructured zirconia decorated reduced graphene oxide based efficient biosensing platform for non-invasive oral cancer detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Kong, L.B.; Gan, Y.; Liang, T.; Zhou, S.Q.; Sun, J.D.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. Microfluidic-based fluorescent electronic eye with CdTe/CdS core-shell quantum dots for trace detection of cadmium ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1131, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Sun, X.Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Kong, L.B.; Huang, Z.R.; Hu, Y.J.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. Multifunctional AuNPs@HRP@FeMOF immune scaffold with a fully automated saliva analyzer for oral cancer screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 222, 114910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, S.; Sridharan, G.; Gadbail, A.; Poornima, V. Nitric oxide and oral cancer: A review. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, I.J.; Jung, T.Y.; Son, Y.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.H. Detection of volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) in exhaled breath as a potential diagnostic method for oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouza, M.; Gonzalez-Soto, J.; Pereiro, R.; de Vicente, J.C.; Sanz-Medel, A. Exhaled breath and oral cavity VOCs as potential biomarkers in oral cancer patients. J. Breath Res. 2017, 11, 016015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Yu, W.R.; Chen, Z.X.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.J.; Liu, S.H.; Li, L.Z.; Li, Y.X.; Huang, Y.Z. Early-stage oral cancer diagnosis by artificial intelligence-based SERS using Ag NWs@ZIF core-shell nanochains. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 13466–13472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apatzidou, A.; Bakirtzoglou, E.; Vouros, I.; Karagiannis, V.; Papa, A.; Konstantinidis, A. Association between oral malodour and periodontal disease-related parameters in the general population. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2013, 71, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.N.; Shinada, K.; Chen, X.C.; Zhang, B.X.; Yaegaki, K.; Kawaguchi, Y. Oral malodor-related parameters in the Chinese general population. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2006, 33, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.W.; Goh, R.; Cheong, E.; Guan, G.; Jin, C.; Cannon, R.D.; Farella, M.; Mei, L. Prevalence of halitosis among young adults in Dunedin, New Zealand. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2022, 20, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshome, A.; Derese, K.; Andualem, G. The prevalence and determinant factors of oral halitosis in northwest ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2021, 13, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, R.; Liu, J.; Wen, X.; Zhang, L. Halitosis: Etiology, prevention, and the role of microbiota. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 6383–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setia, S.; Pannu, P.; Gambhir, R.S.; Galhotra, V.; Ahluwalia, P.; Sofat, A. Correlation of oral hygiene practices, smoking and oral health conditions with self perceived halitosis amongst undergraduate dental students. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2014, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Wang, H.L. Association between oral malodor and adult periodontitis: A review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2001, 28, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Shin, S.I.; Hong, J.Y. Investigation of volatile sulfur compound level and halitosis in patients with gingivitis and periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylıkcı, B.U.; Çolak, H. Halitosis: From diagnosis to management. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2013, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Wang, H.L. Relationship between sulcular sulfide level and oral malodor in subjects with periodontal disease. J. Periodontol. 2001, 72, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Kim, D.-H.; Jung, W.; Jang, J.-S.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, Y.; Chang, K.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Namkoong, K. Surface activity-tuned metal oxide chemiresistor: Toward direct and quantitative halitosis diagnosis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14207–14217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, Z.; Zong, X. Flexible and highly sensitive H2S gas sensor based on in-situ polymerized SnO2/rGO/PANI ternary nanocomposite with application in halitosis diagnosis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 289, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.K.; D’Costa, J.V.; Sakhuja, N.; Bhat, N. MoSe2 nanoflakes based chemiresistive sensors for ppb-level hydrogen sulfide gas detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulemo, P.M.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, I.-D. Facile synthesis of Pt-functionalized meso/macroporous SnO2 hollow spheres through in situ templating with SiO2 for H2S sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 18183–18191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asres, G.A.; Baldoví, J.J.; Dombovari, A.; Järvinen, T.; Lorite, G.S.; Mohl, M.; Shchukarev, A.; Pérez Paz, A.; Xian, L.; Mikkola, J.-P. Ultrasensitive H2S gas sensors based on p-type WS 2 hybrid materials. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4215–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.; Jo, Y.-M.; Kim, S.; Yoon, J.-W.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, H.J.; Cho, Y.; Park, J.; Jeong, Y.W.; et al. Selective dual detection of hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan using CuO/CuFe2O4 nanopattern chemiresistors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.; Kim, M.; Lee, A.; Ji, S.; Jang, M.; Yim, S.; Song, W.; Lee, S.S.; Yoon, D.H.; An, K.-S. Nanometric lamination of zinc oxide nanofilms with gold nanoparticles for self-perceived periodontal disease sensors. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 230, 109490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, M.; Subha, P.; Aswathy, P.; Merin, K.; Jayaraj, M.; Kumar, K.R. Selective detection of hydrogen sulphide from the background of low concentration reducing gases. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 260, 124038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Choi, S.-J.; Koo, W.-T.; Kim, I.-D. Sub-parts-per-million hydrogen sulfide colorimetric sensor: Lead acetate anchored nanofibers toward halitosis diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8769–8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosolina, S.M.; Carpenter, T.S.; Xue, Z.-L. Bismuth-based, disposable sensor for the detection of hydrogen sulfide gas. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatty, H.K.; Stemme, G.; Roxhed, N. A miniaturized amperometric hydrogen sulfide sensor applicable for bad breath monitoring. Micromachines 2018, 9, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, M.; Hasanzadeh, M. Pharmacotherapy. Non-invasive bioassay of Cytokeratin Fragment 21.1 (Cyfra 21.1) protein in human saliva samples using immunoreaction method: An efficient platform for early-stage diagnosis of oral cancer based on biomedicine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Singh, A.; Shukla, A.; Kaswan, J.; Arora, K.; Ramirez-Vick, J.; Singh, P.; Singh, S.P. Anti-IL8/AuNPs-rGO/ITO as an immunosensing platform for noninvasive electrochemical detection of oral cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27462–27474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Das, S.R.; Brownlee, B.J.; Parate, K.; Davis, T.M.; Stromberg, L.R.; Chan, E.K.; Katz, J.; Iverson, B.D.; Claussen, J.C. CIP2A immunosensor comprised of vertically-aligned carbon nanotube interdigitated electrodes towards point-of-care oral cancer screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, S.; Moghadam, T.T.; Dabirmanesh, B.; Jabbari, S.; Khajeh, K. Development of a label-free SPR sensor for detection of matrixmetalloproteinase-9 by antibody immobilization on carboxymethyldextran chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, S.-H.; Du, X.-Y.; Sun, J.-J. Plasmonic Ag nanocube enhanced SERS biosensor for sensitive detection of oral cancer DNA based on nicking endonuclease signal amplification and heated electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 338, 129854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Tao, Z.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wan, H.; Ye, W.; Wang, P. Study on the Screening and Diagnosis of Oral Diseases Based on Volatile Sulfur Compounds in Human Exhaled Breath. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 40, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Stout-Delgado, H.W. Aging and lung disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2020, 82, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookson, W.O.; Cox, M.J.; Moffatt, M.F. New opportunities for managing acute and chronic lung infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, A.; Vogelmeier, C.; Faner, R. COPD 2020: Changes and challenges. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 319, L879–L883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H. The immunology of asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, C.T.; Faubert, B.; Yuan, Q.; Lev-Cohain, N.; Jin, E.; Kim, J.; Jiang, L.; Ko, B.; Skelton, R.; Loudat, L. Metabolic heterogeneity in human lung tumors. Cell 2016, 164, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Humbert, M.; Souza, R.; Idrees, M.; Kawut, S.M.; Sliwa-Hahnle, K.; Jing, Z.-C.; Gibbs, J.S.R. A global view of pulmonary hypertension. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhaber, S.Z.; Bounameaux, H. Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. Lancet 2012, 379, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Muyinda, H.; Nyakoojo, G.; Kirenga, B.; Katagira, W.; Pooler, J. Does pulmonary rehabilitation alter patients’ experiences of living with chronic respiratory disease? A qualitative study. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 2375–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Agusti, A.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Bourbeau, J.; Celli, B.R.; Criner, G.J.; Frith, P.; Halpin, D.M.; Han, M. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease: The GOLD science committee report 2019. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1900164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, G.A.; Ghosh, S.; Gamboa, L.; Patriotis, C.; Srivastava, S.; Bhatia, S.N. Synthetic biomarkers: A twenty-first century path to early cancer detection. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziej, M.; de Veer, M.J.; Cholewa, M.; Egan, G.F.; Thompson, B.R. Lung function imaging methods in cystic fibrosis pulmonary disease. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devillier, P.; Salvator, H.; Naline, E.; Couderc, L.-J.; Grassin-Delyle, S. Metabolomics in the diagnosis and pharmacotherapy of lung diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodavanti, U.P. Respiratory toxicity biomarkers. In Biomarkers in Toxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 217–239. [Google Scholar]
- Hekiem, N.L.L.; Ralib, A.A.M.; Akmal, M.; Hattar, M.; Ahmad, F.B.; Nordin, A.N.; Rahim, R.A.; Za’bah, N.F. Advanced vapour sensing materials: Existing and latent to acoustic wave sensors for VOCs detection as the potential exhaled breath biomarkers for lung cancer. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2021, 329, 112792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, L.; Cao, M.F.; Chen, X.; Wang, P.; Jiao, J.W.; Wang, Y.L. Detection volatile organic compounds in breath as markers of lung cancer using a novel electronic nose. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors 2003, Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–24 October 2003; Volumes 1 and 2, pp. 1333–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Cao, M.F.; Li, Y.; Hu, W.J.; Wang, P.; Ying, K.J.; Pan, H.M. A study of an electronic nose for detection of lung cancer based on a virtual SAW gas sensors array and imaging recognition method. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Lu, D.; Cai, W.; Ying, K.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y. Development of electronic nose for diagnosis of lung cancer at early stage. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Special Topic Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine, Shenzhen, China, 30–31 May 2008; Volumes 1 and 2, p. 402. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Ying, K.; Feng-Juan, X.; Wang, P. A Novel Electronic Nose for Detection of Lung Cancer Based on Virtual SAW Gas Sensors Array. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 27, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Hu, Y.; Ying, K. A Study on Electronic Nose for Clinical Breath Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. In Proceedings of the Olfaction and Electronic Nose, Brescia, Italy, 15–17 April 2009; pp. 314–317. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Hu, Y.J.; Ying, K.J. Characterization of a Modified Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor Used in Electronic Nose for Potential Application in Breath Diagnosis. Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, K.; Wang, Y.S.; Hu, Y.J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Ying, K.J.; Wang, P. A Hybrid Electronic Noses’ System Based on Mos-Saw Detection Units Intended for Lung Cancer Diagnosis. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2012, 5, 1150006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; He, Y.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, S.; Fang, J.Y.; Zhang, X.A.; Peng, G. Sniffing lung cancer related biomarkers using an oxidized graphene SAW sensor. Front. Phys. 2016, 11, 116801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.N.; Rotello, V.M. Gold Nanoparticles in Chemical and Biological Sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zou, Y.C.; An, C.; Ying, K.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, P. A miniaturized immunosensor platform for automatic detection of carcinoembryonic antigen in EBC. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2014, 205, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, X.; An, C.; Ran, C.; Ying, K.; Wang, P. A point-of-care testing system with Love-wave sensor and immunogold staining enhancement for early detection of lung cancer. Biomed. Microdevices 2014, 16, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Xue, Y.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. Recent advances in acoustic wave biosensors for the detection of disease-related biomarkers: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1164, 338321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.M.; Wan, Y.; Su, Y.; Fan, C.H.; Bhethanabotla, V.R. Gold nanoparticle-based low limit of detection Love wave biosensor for carcinoembryonic antigens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 95, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ran, C. Love wave based portable sensing system for on-line detection of carcinoembryonic antigen in exhaled breath condensate. Biomed. Microdevices 2020, 22, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandas, P.J.; Luo, J.T.; Quan, A.J.; Qiu, C.H.; Cao, W.G.; Fu, C.; Fu, Y.Q. Highly selective and label-free Love-mode surface acoustic wave biosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen detection using a self-assembled monolayer bioreceptor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 518, 146061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandas, P.J.; Luo, J.T.; Prabakaran, K.; Chen, F.; Fu, Y.Q. Highly stable, love-mode surface acoustic wave biosensor using Au nanoparticle-MoS2-rGO nano-cluster doped polyimide nanocomposite for the selective detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 246, 122800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, H.; Yu, W.; Ying, K.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. The Love Wave Biosensor for the Detection of the Bacterial Pneumonia Biomarker C-reactive Protein. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Aveiro, Portugal, 29 May–1 June 2022; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.D. Application of electronic-nose technologies and VOC-biomarkers for the noninvasive early diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases. Sensors 2018, 18, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.q.; Broza, Y.Y.; Ionsecu, R.; Tisch, U.; Ding, L.; Liu, H.; Song, Q.; Pan, Y.y.; Xiong, F.x.; Gu, K.S.; et al. A nanomaterial-based breath test for distinguishing gastric cancer from benign gastric conditions. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amal, H.; Leja, M.; Funka, K.; Skapars, R.; Sivins, A.; Ancans, G.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Kikuste, I.; Lasina, I.; Haick, H. Detection of precancerous gastric lesions and gastric cancer through exhaled breath. Gut 2016, 65, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, H.; Tashkhourian, J.; Geramizadeh, B.; Ghohestani, E.; Zangouri, V.; Asadian, F.; Hemmateenejad, B. Metallic Nanocluster-Based Sniffing Device for Identification of Malignancy in Gastric Cancer Tissues. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 5578–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, B.; Anthis, A.H.; Zehnder, A.K.; Mergen, V.; Rosendorf, J.; Gerken, L.R.; Schlegel, A.A.; Korcakova, E.; Liska, V.; Herrmann, I.K. Surgical Sealant with Integrated Shape-Morphing Dual Modality Ultrasound and Computed Tomography Sensors for Gastric Leak Detection. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2301207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Shang, L. Developing sensor materials for screening intestinal diseases. Mater. Futures 2022, 1, 022401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, S.; McGuire, N.; de Lacy Costello, B.; Ewen, R.; Jayasena, D.; Vaughan, K.; Ahmed, I.; Probert, C.; Ratcliffe, N. The use of a gas chromatograph coupled to a metal oxide sensor for rapid assessment of stool samples from irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease patients. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 026001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.K.; Leggett, C.L.; Wang, K.K. Diagnosing gastrointestinal illnesses using fecal headspace volatile organic compounds. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, A.; Chandrapalan, S.; Bosch, S.; Bannaga, A.; De Boer, N.K.H.; De Meij, T.G.J.; Leja, M.; Hanna, G.B.; De Vietro, N.; Altomare, D.; et al. The Influence of Mechanical Bowel Preparation on Volatile Organic Compounds for the Detection of Gastrointestinal Disease—A Systematic Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalis, C.; Mesfin, F.M.; Manohar, K.; Liu, J.; Shelley, W.C.; Brokaw, J.P.; Markel, T.A. Volatile Organic Compound Assessment as a Screening Tool for Early Detection of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westenbrink, E.; Arasaradnam, R.P.; O’Connell, N.; Bailey, C.; Nwokolo, C.; Bardhan, K.D.; Covington, J.A. Development and application of a new electronic nose instrument for the detection of colorectal cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-K.; Capua, E.; Naaman, R. Application of a GaAs-based sensor for detecting hemoglobin in gastrointestinal environments. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 17, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonne, P.; Ruud, W.M.S.; Adriaan, C.T.; Sanne, K.B.; de Bart, J.; Peter, D.S. Detection of Barrett’s oesophagus through exhaled breath using an electronic nose device. Gut 2020, 69, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiele, A.; Wicaksono, A.; Kansara, J.; Arasaradnam, R.P.; Covington, J.A. Breath Analysis Using eNose and Ion Mobility Technology to Diagnose Inflammatory Bowel Disease—A Pilot Study. Biosensors 2019, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
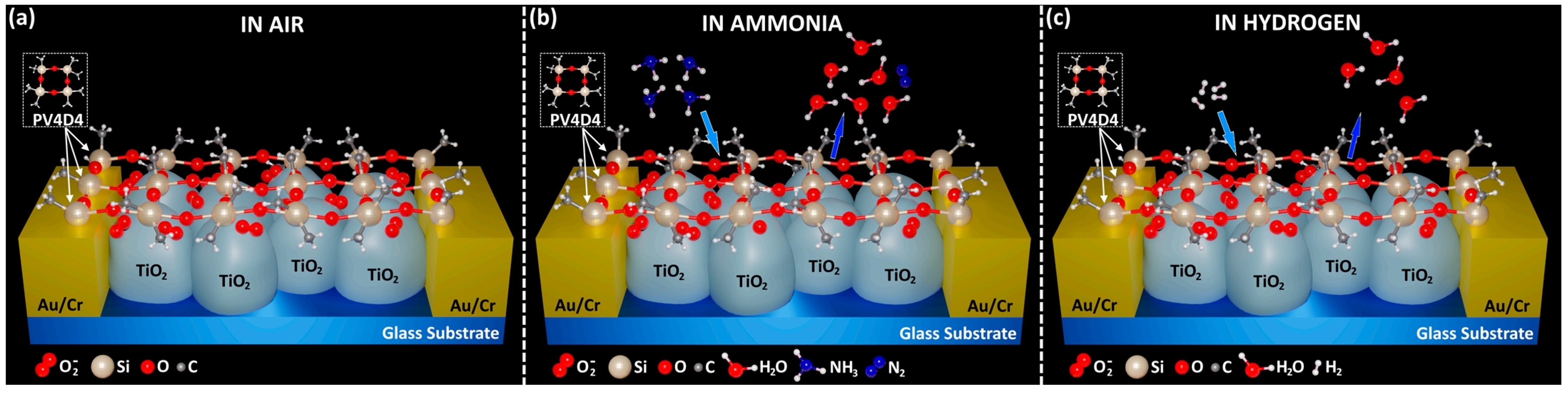
- Brinza, M.; Schröder, S.; Ababii, N.; Gronenberg, M.; Strunskus, T.; Pauporte, T.; Adelung, R.; Faupel, F.; Lupan, O. Two-in-One Sensor Based on PV4D4-Coated TiO2 Films for Food Spoilage Detection and as a Breath Marker for Several Diseases. Biosensors 2023, 13, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neetha, A.S.; Rao, K.V. Broccoli-shaped nano florets-based gastrointestinal diseases detection by copper oxide chitosan. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 30, 101503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, S.; Angeli, M.A.C.; Polo, A.; Costantini, A.; Petrelli, M.; Avancini, E.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M.; Gaiardo, A.; Valt, M.; et al. In vitro gastrointestinal gas monitoring with carbon nanotube sensors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
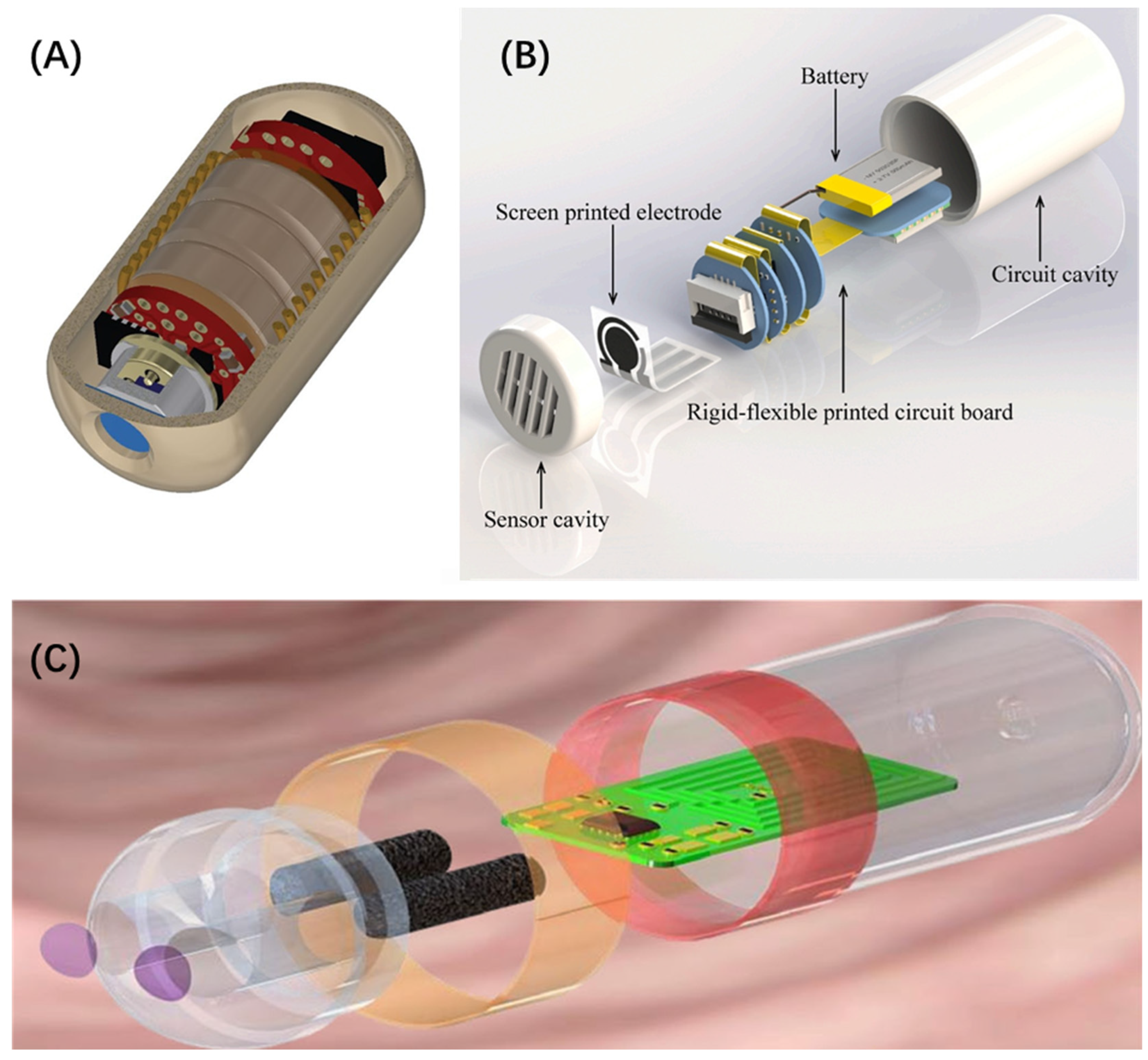
- Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Ha, N.; Ou, J.Z.; Berean, K.J. Ingestible Sensors. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, R.; Ibrahim, A.-B.; David, G.T.; Wayne, Y.; Leo, K.C.; Ebubekir, A. Smart capsules for sensing and sampling the gut: Status, challenges and prospects. Gut 2024, 73, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Berean, K.J.; Ha, N.; Chrimes, A.F.; Xu, K.; Grando, D.; Ou, J.Z.; Pillai, N.; Campbell, J.L.; Brkljača, R.; et al. A human pilot trial of ingestible electronic capsules capable of sensing different gases in the gut. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; An, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Su, B.; Liu, Q. A wireless, ingestible pH sensing capsule system based on iridium oxide for monitoring gastrointestinal health. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 349, 130781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, R.; Peng, Y.; Duan, F.; Huang, Y.; Guo, W.; Chen, X.; Nie, L. In Vivo Quantitative Photoacoustic Diagnosis of Gastric and Intestinal Dysfunctions with a Broad pH-Responsive Sensor. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9561–9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Paz, E.; Maganti, N.H.; Trifonov, A.; Jeerapan, I.; Mahato, K.; Yin, L.; Sonsa-ard, T.; Ma, N.; Jung, W.; Burns, R.; et al. A self-powered ingestible wireless biosensing system for real-time in situ monitoring of gastrointestinal tract metabolites. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | Principle | Disease | Target | Sensing Materials | Working Temperature (°C) | Response (Rair/Rgas or Rgas/Rair) | Sensitivity | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gas sensor | Chemoresistive | halitosis | H2S | Na2Pt-WO3 NFs | 350 | 780.8 (1 ppm) | / | / | [55] |
| Chemoresistive | halitosis | H2S | SnO2/rGO/PANI | RT | 23.9 (0.2 ppm) | / | 50 ppb | [56] | |
| Chemoresistive | halitosis | H2S | MoSe2 | 200 | 18.57 (50 ppb) | 5.57%/ppm | 6.73 ppb | [57] | |
| Chemoresistive | halitosis | H2S | Pt-SnO2 | 250 | 10.8 (1 ppm) | / | / | [58] | |
| Chemoresistive | halitosis | H2S | WS2 | 200 | 2.3 (1 ppm) | 0.043/ppm | 20 ppb | [59] | |
| Chemoresistive | halitosis | H2S,CH3SH | CuO/CuFe2O4 | 200 (H2S); 400 (CH3CH4) | 800 (5 ppm H2S); 32 (5 ppm CH3SH) | / | / | [60] | |
| Chemoresistive | halitosis | CH3SH | Au NPs/ZnO | 250 | 4.99 (50 ppb) | / | / | [61] | |
| Chemoresistive | halitosis | H2S | Au-doped SnO2 nanofibers | 370 | 121.05 (100 ppm) | / | 550 ppb | [62] | |
| Chemoresistive | halitosis | H2S | Lead(II) acetate [Pb(Ac)2] | RT | / | / | 400 ppb | [63] | |
| Chemoresistive | halitosis | H2S | alkaline bismuth hydroxide Bi(OH)3 or its derivatives | RT | / | / | 30 ppb | [64] | |
| Electrochemical | halitosis | H2S | a nanostructured Nafion | RT | / | 0.65 nA/ppb | 75 ppb | [65] | |
| Liquid sensor | Electrochemical | oral cancer | cyfra21-1 | CysA-GA/AuE | RT | / | / | 2.5 ng/mL | [66] |
| Electrochemical | oral cancer | cyfra21-1 | BSA/anti-CYFRA-21-1/APTES/ZrO2–RGO/ITO | RT | / | 0.756 µA mL/ng | 2 ng/mL | [38] | |
| Electrochemical | oral cancer | IL-8 | IL8/anti-IL8/AuNPs-rGO/ITO | RT | / | / | 72.73 pg/mL | [67] | |
| Electrochemical | oral cancer | CIP2A | 3D high-aspect-ratio vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays | RT | / | / | 0.24 pg/mL | [68] | |
| SPR | periodontitis | MMP-9 | anti-MMP-9 onto the CMD chip surface | RT | / | / | 8 pg/mL | [69] | |
| SERS | oral cancer | DNA | Nt.BstNBI/AgNCs/HAuE | RT | / | / | 3.1 fM | [70] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, W.; Mou, S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Xue, Y.; Xiong, H.; Hsia, K.J.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. Application of Sensing Devices in the Detection of Oral, Pulmonary, and Gastrointestinal Diseases. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12040057
Yu W, Mou S, Zhang X, Sun J, Xue Y, Xiong H, Hsia KJ, Wan H, Wang P. Application of Sensing Devices in the Detection of Oral, Pulmonary, and Gastrointestinal Diseases. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(4):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Weijie, Shimeng Mou, Xiaojing Zhang, Jiaying Sun, Yingying Xue, Hangming Xiong, K. Jimmy Hsia, Hao Wan, and Ping Wang. 2024. "Application of Sensing Devices in the Detection of Oral, Pulmonary, and Gastrointestinal Diseases" Chemosensors 12, no. 4: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12040057
APA StyleYu, W., Mou, S., Zhang, X., Sun, J., Xue, Y., Xiong, H., Hsia, K. J., Wan, H., & Wang, P. (2024). Application of Sensing Devices in the Detection of Oral, Pulmonary, and Gastrointestinal Diseases. Chemosensors, 12(4), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12040057