A Review on Analytical Techniques for Quantitative Detection of Biogenic Amines in Aquatic Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Biogenic Amine | Relative Molecular Mass | Classification | Precursor | Chemical Structures | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tryptamine | 160.22 | Heterocyclic Amine | Tryptophan | 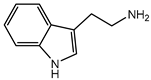 | [9] |
| Histamine | 111.15 | Heterocyclic Amine | Histidine | 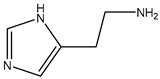 | [10] |
| Tyramine | 137.18 | Aromatic Amine | Tyrosine | 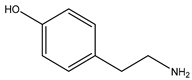 | [11] |
| β-Phenylethylamine | 121.18 | Aromatic Amine | Phenylalanine | 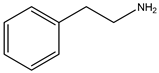 | [12] |
| Spermine | 202.34 | Aliphatic Amine | Arginine Ornithine | 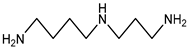 | [13] |
| Spermidine | 145.25 | Aliphatic Amine | Arginine Ornithine | 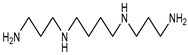 | [14] |
| Cadaverine | 102.18 | Aliphatic Amine | Lysine | 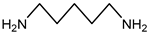 | [15] |
2. Biogenic Amines in Aquatic Products
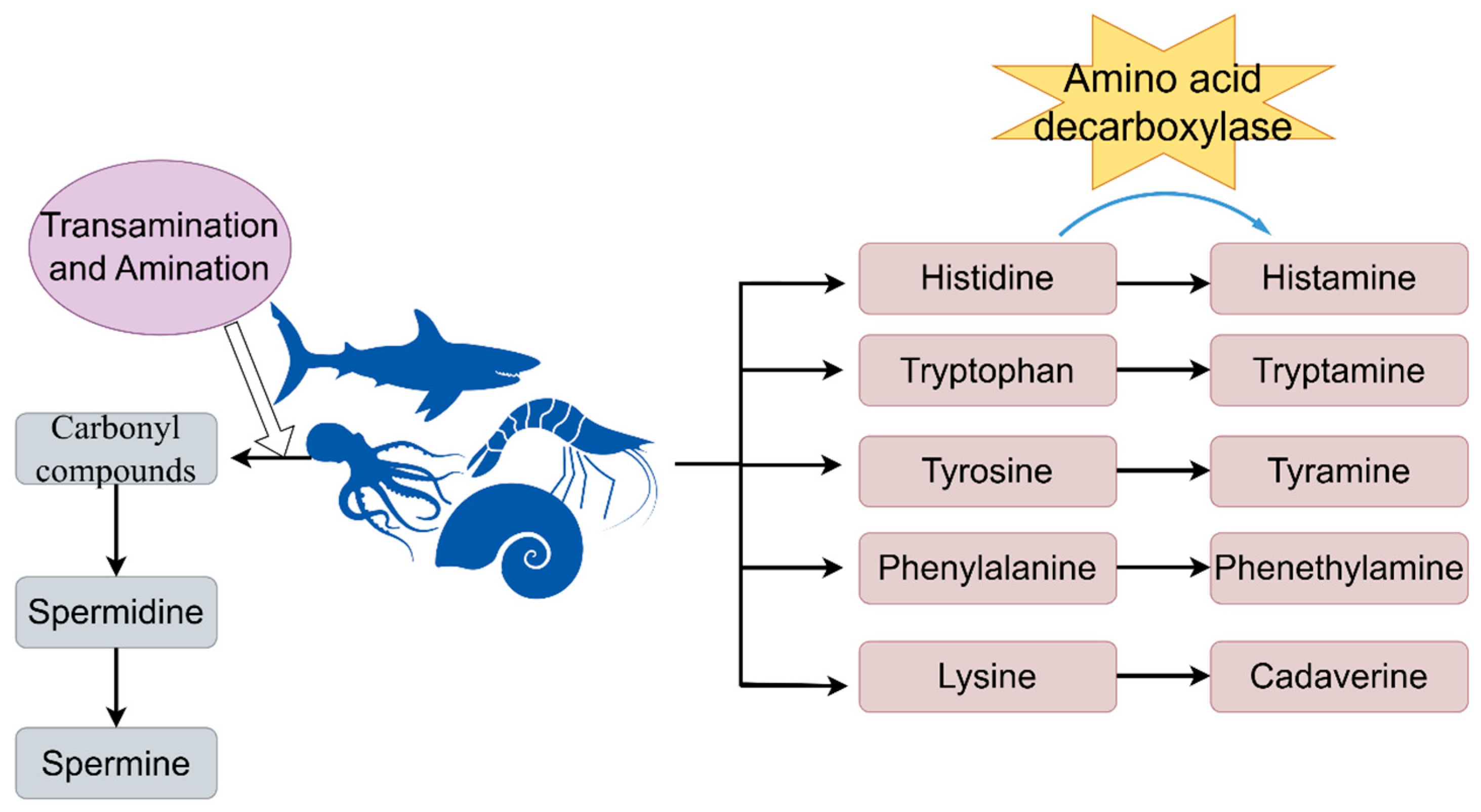
2.1. Classification and Sources of Biogenic Amines
2.2. Formation Mechanism and Influence Factors
2.3. Hazard of Biogenic Amines
2.3.1. Excessive Intake and Accumulation of Biogenic Amines
2.3.2. Poisoning of Biogenic Amines
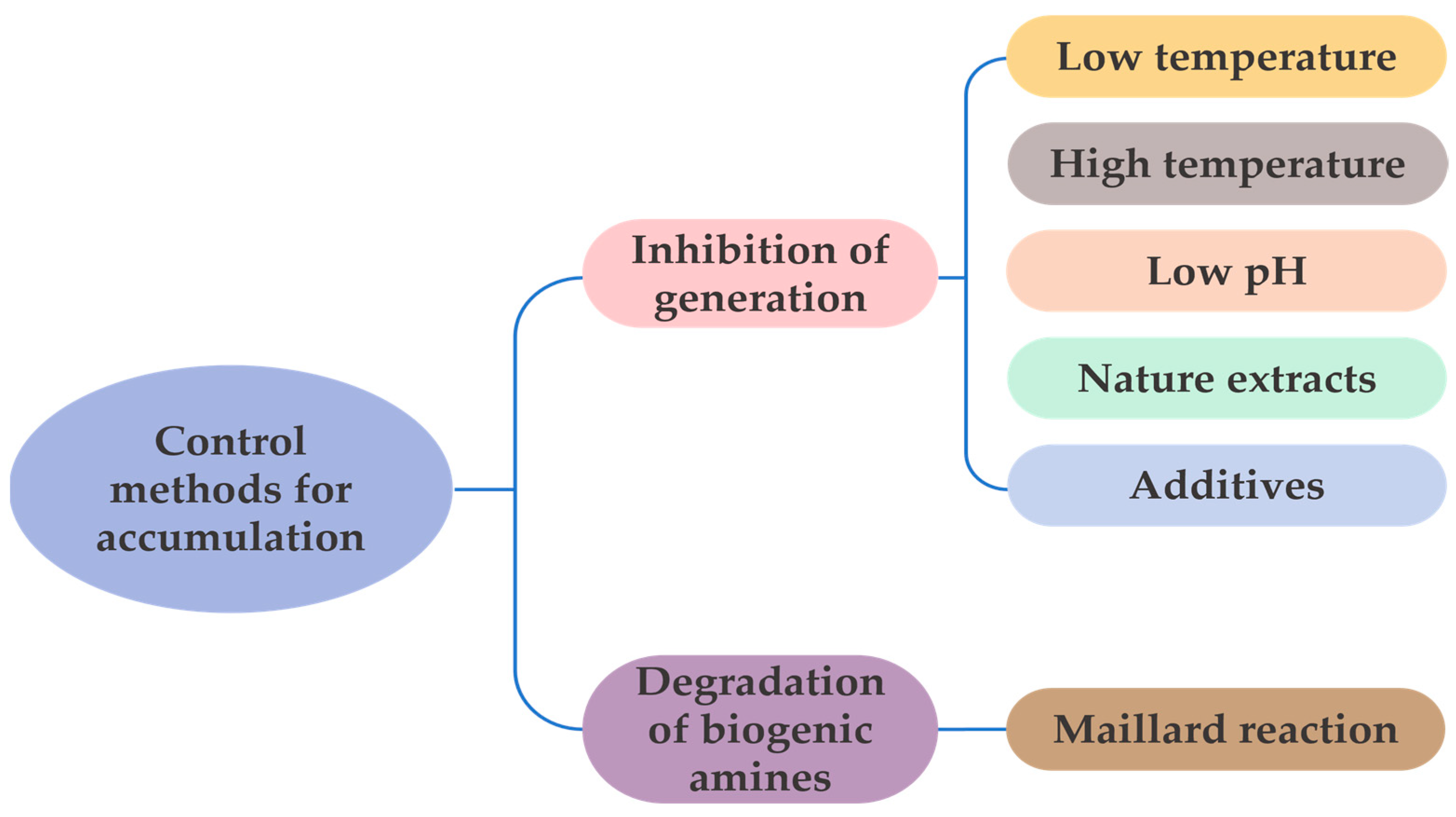
2.4. Control Methods for Biogenic Amines Excessive Accumulation in Aquatic Products
2.5. Maximum Residual Limits of Biogenic Amines in Water Bodies
3. Sample Pre-Treatment Technology
3.1. Liquid–Liquid Extraction
3.2. Solid-Phase Extraction
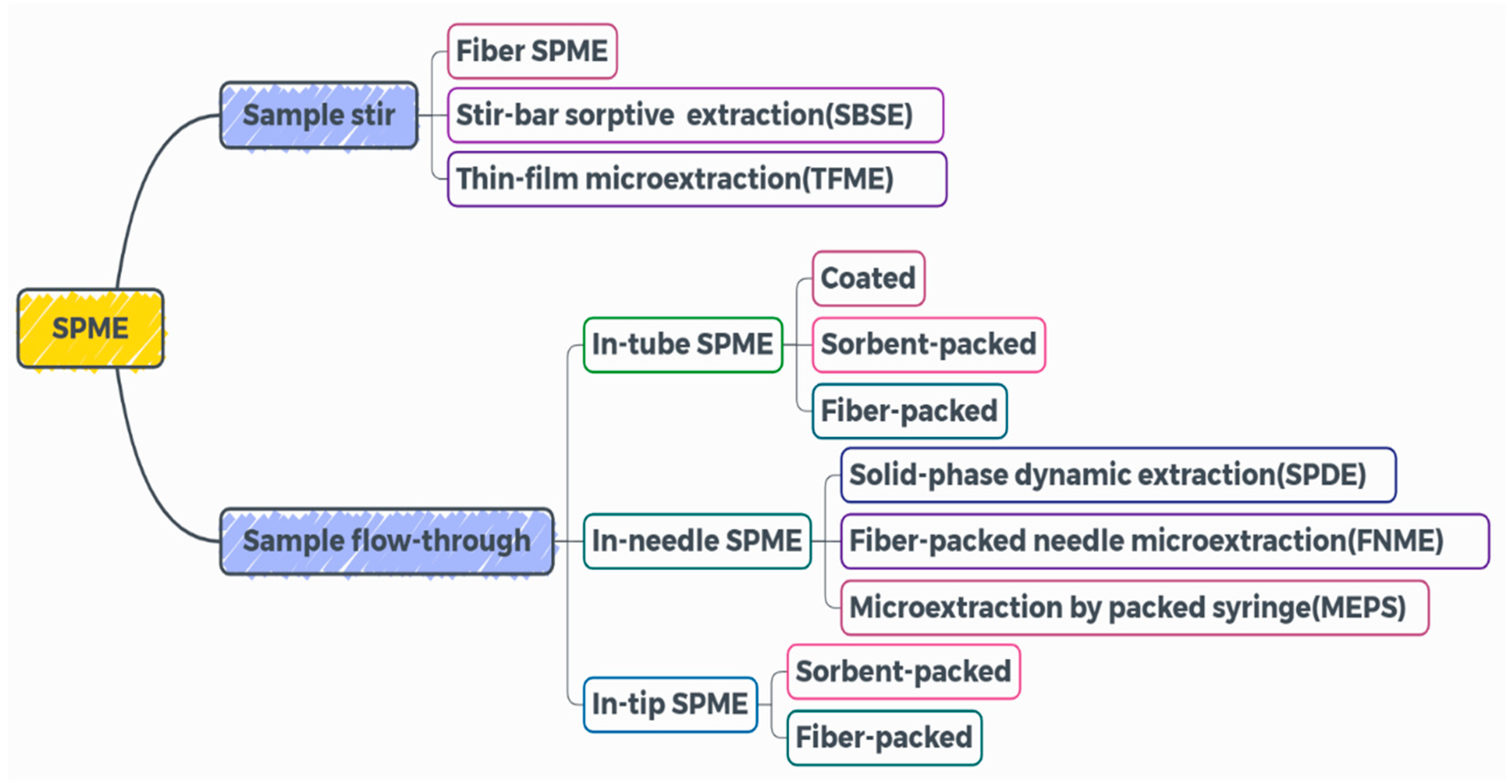
3.3. Solid-Phase Microextraction
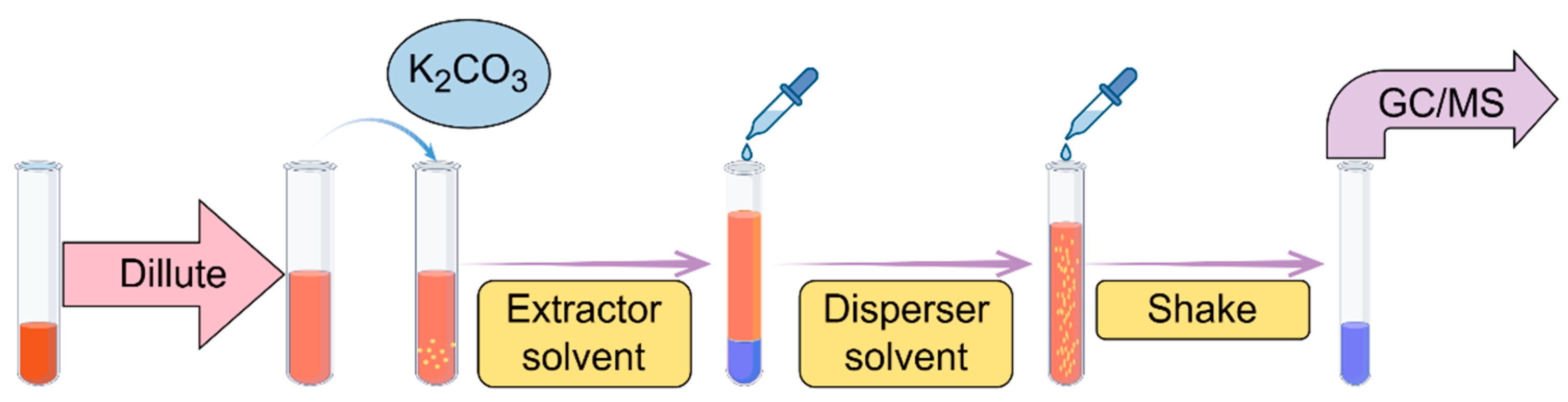
3.4. Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction
3.5. QuEChERS
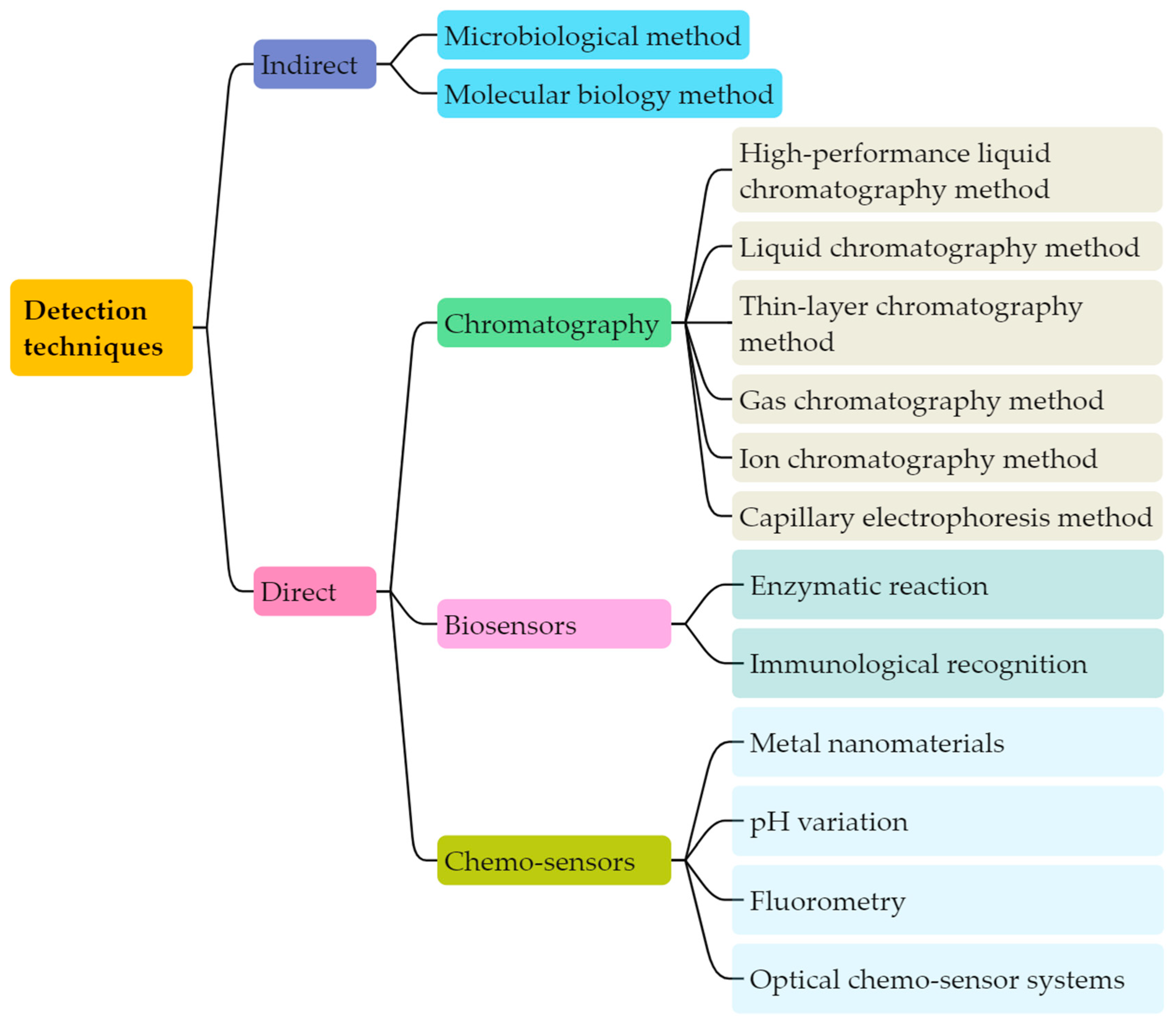
4. Detection Techniques of Biogenic Amines
4.1. Indirect Detection Technique of Biological Amines
4.1.1. Microbiological Method
4.1.2. Molecular Biology Method
4.2. Direct Detection Technique of Biological Amines
4.2.1. Chromatography
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method
Liquid Chromatography Method
Thin-Layer Chromatography Method
Gas Chromatography Method
Ion Chromatography Method
Capillary Electrophoresis Method
4.2.2. Biosensors
Enzymatic Reaction
Immunological Recognition
4.2.3. Chemo-Sensors
Nanomaterials
pH Sensors
Fluorometry
Optical Chemo-Sensor Systems
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GarridoGamarro, E.; Svanevik, C.S.; Lundebye, A.-K.; Sanden, M.; D’Agostino, E.; Kjellevold, M.; Pincus, L.; Pucher, J. Challenges in the implementation of food safety and quality assurance systems in small-scale fisheries. Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyad007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Jian, C.; Hu, M.Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, H.H.; Liu, Q.; Cao, R.; Xue, Y. Lipid changes and volatile compounds formation in different processing stages of dry-cured Spanish mackerel. Food Qual. Saf. 2024, 8, fyae026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeun, D.; Davaatseren, M.; Chung, M.S. Biogenic amines in foods. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Li, Y. Biogenic amines are important indices for characterizing the freshness and hygienic quality of aquatic products: A review. Lwt 2024, 194, 115793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Impact of Biogenic Amines on Food Quality and Safety. Foods 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krízek, M.; Pelikánová, T. Determination of seven biogenic amines in foods by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 815, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkadi, L.S. Amino acids and biogenic amines as food quality factors. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, R.; Wang, P. The Development of an Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Biogenic Amines in Fish Samples. Molecules 2023, 28, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, D.; Kaijun, X. Modified QuEChERS combined with ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry to determine seven biogenic amines in Chinese traditional condiment soy sauce. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuo, D.; Yuting, C.; Wenhui, L.; Changxin, L.; Chunxia, L.; Zhouping, W.; Shijia, W. Ratiometric SERS aptasensing for simultaneous quantitative detection of histamine and tyramine in fishes. Talanta 2023, 265, 124891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yifrach, Y.; Rahimi, R.; Baraban, J.H.; Bar, I. Ionization energies and ionization-induced structural changes in 2-phenylethylamine and its monohydrate. J. Chem. Phys. 2023, 158, 114305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaee, E.; Shareghi, B.; Farhadian, S. A comparative study of structural and dynamical properties of bovine serum albumin in the presence of spermine. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami-Farsani, R.; Farhadian, S.; Shareghi, B.; Asgharzadeh, S. Structural change of myoglobin structure after binding with spermidine. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 352, 118691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Shareghi, B.; Saboury, A.A.; Farhadian, S. The influence of Cadaverine on the structure, stability, and activity of acid phosphatase. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1247, 131372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, W.; Lukasiewicz-Mierzejewska, M.; Damaziak, K.; Bien, D. Biogenic Amines in Poultry Meat and Poultry Products: Formation, Appearance, and Methods of Reduction. Animals 2022, 12, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.H.S. Biogenic amines: Their importance in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 29, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirone, M.; Esposito, L.; D’Onofrio, F.; Visciano, P.; Martuscelli, M.; Mastrocola, D.; Paparella, A. Biogenic Amines in Meat and Meat Products: A Review of the Science and Future Perspectives. Foods 2022, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, J.E.; Hutkins, R.W.; Taylor, S.L. Biogenic Amines in Cheese and other Fermented Foods: A Review. J. Food Prot. 1991, 54, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio, B.; Fernandez, M.; Redruello, B.; Ladero, V.; Alvarez, M.A. New insights into the toxicological effects of dietary biogenic amines. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naila, A.; Flint, S.; Fletcher, G.; Bremer, P.; Meerdink, G. Control of Biogenic Amines in Food-Existing and Emerging Approaches. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, R139–R150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maijala, R.L.; Eerola, S.H.; Aho, M.A.; Hirn, J.A. The effect of GDL-induced pH decrease on the formation of biogenic amines in meat. J. Food Prot. 1993, 56, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karovicová, J.; Kohajdová, Z. Biogenic amines in food. Chem. Pap. 2005, 59, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasz, A.; Barath, A.; Simon-Sarkadi, L.; Holzapfel, W. Biogenic amines and their production by microorganisms in food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1994, 5, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conz, A.; Davoli, E.; Franchi, C.; Diomede, L. Seafood loss prevention and waste reduction. Food Qual. Saf. 2024, 8, fyae017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HernandezJover, T.; IzquierdoPulido, M.; VecianaNogues, M.T.; MarineFont, A.; VidalCarou, M.C. Biogenic amine and polyamine contents in meat and meat products. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1997, 45, 2098–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emborg, J.; Dalgaard, P. Formation of histamine and biogenic amines in cold-smoked tuna: An investigation of psychrotolerant bacteria from samples implicated in cases of histamine fish poisoning. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodmer, S.; Imark, C.; Kneubühl, M. Biogenic amines in foods: Histamine and food processing. Inflamm. Res. 1999, 48, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiaoqiao, L.; Ruoyu, S.; Pengfei, G.; Yutong, L.; Wei, C.; Chengtao, W. Biogenic amines in Huangjiu (Chinese rice wine): Formation, hazard, detection, and reduction. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 168, 113952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha Turna, N.; Chung, R.; McIntyre, L. A review of biogenic amines in fermented foods: Occurrence and health effects. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, F.; Montanari, C.; Gardini, F.; Tabanelli, G. Biogenic Amine Production by Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Review. Foods 2019, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comas-Baste, O.; Sanchez-Perez, S.; Veciana-Nogues, M.T.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.d.C. Histamine Intolerance: The Current State of the Art. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladero, V.; Calles-Enriquez, M.; Fernández, M.; Alvarez, M.J.C.N.A.; Science, F. Toxicological effects of dietary biogenic amines. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2010, 6, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.D.-P.; Flavia, B.C.; Maria, B.A.G. Health concerns associated with biogenic amines in food and interaction with amine oxidase drugs. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 54, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcobal, A.; De Las Rivas, B.; Maria Landete, J.; Tabera, L.; Munoz, R. Tyramine and Phenylethylamine Biosynthesis by Food Bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, L.; Smith, C. Aspalathus linearis (Rooibos) and Agmatine May Act Synergistically to Beneficially Modulate Intestinal Tight Junction Integrity and Inflammatory Profile. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.L.; Niu, Y.B.; Wei, H.M.; Lin, Y.M.; Lu, X.; Yamashita, T.; Yu, K.F.; Takaki, K.; Yuan, C.H. Effect of super-chilling storage on maintenance of quality and freshness of the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyad008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornsdottir-Butler, K.; Bencsath, F.A.; McCarthy, S.; Benner, R.A., Jr. Heat Resistance of Histidine Decarboxylase from Gram-Negative Histamine-Producing Bacteria in Seafood. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H. Formation, Analytical Methods, Change Tendency, and Control Strategies of Biogenic Amines in Canned Aquatic Products: A Systematic Review. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 2020–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardini, F.; Martuscelli, M.; Caruso, M.C.; Galgano, F.; Crudele, M.A.; Favati, F.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Suzzi, G. Effects of pH, temperature and NaCl concentration on the growth kinetics, proteolytic activity and biogenic amine production of Enterococcus faecalis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 64, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Niu, Y.; Wang, J.; Dao, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J. The Influence of Different Levels of Sodium Chloride, Sodium Nitrite, and Glucose on Biogenic Amines and Microbial Communities in Fermented Goat Meat Sausage. Foods 2024, 13, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jae-Hyung, M.; Han-Joon, H. Effects of food additives on biogenic amine formation in myeolchi-jeot, a salted and fermented anchovy (Engraulis japonicus). Food Chem. 2009, 114, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulgin, Y.P.; Lazhentseva, L.Y.; Shulgina, L.V.; Kalenik, T.K.; Matveeva, V.A.; Piekoszewski, W. Quality Improvement of Canned Fish with the Use of Cinnamon Oil Extract. Int. J. Food Eng. 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Ye, X.; Zhi, Z. Proanthocyanidins from Chinese Bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc.) Leaves Effectively Inhibit the Formation of Biogenic Amines in the Brewing Soy Sauce. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, C.; Huang, D.; Yang, G.; Tang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Kong, C.; Cao, P.; Cai, Y. Determination of 8 biogenic amines in aquatic products and their derived products by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry without derivatization. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, H. Concentrations of biogenic amines in fish, squid and octopus and their changes during storage. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2604–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young Mi, K.; Min Joo, K.; Sun Young, P.; Min Soo, H.; Jin-Soo, K. Survey and exposure assessment of biogenic amines in fish species commonly consumed in Korea. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Xia, G.; Cen, J.; Huang, H.; Hao, S. Biogenic amines in commercial fish and fish products sold in southern China. Food Control 2012, 25, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min-Ki, K.; Jae-Hyung, M.; Han-Joon, H. Biogenic amine formation and bacterial contribution in fish, squid and shellfish. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin Seok, M.; Yujin, K.; Keum Il, J.; Kyung-Ju, C.; Seung-Joon, Y.; Gun-Mook, Y.; So-Young, K.; Nam Soo, H. Analysis of biogenic amines in fermented fish products consumed in Korea. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, W. Pollution, Exposure and Risk of Biogenic Amines in Canned Sea Fish: Classification of Analytical Methods Based on Carbon Spheres QuEChERS Extraction Combined with HPLC. Molecules 2022, 27, 6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagratini, G.; Fernandez-Franzon, M.; De Berardinis, F.; Font, G.; Vittori, S.; Manes, J. Simultaneous determination of eight underivatised biogenic amines in fish by solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Han, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Determination of Biogenic Amines in Wine Using Modified Liquid-Liquid Extraction with High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detector. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Qi, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhao, Q. A Routine and Sensitive Quantification of 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline in Shrimp by DSPE-DLLME Coupled to HPLC-UV. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, S.; Kleeberg, K.; Fritsche, J. Recent Developments and Applications of Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME) in Food and Environmental Analysis—A Review. Chromatography 2015, 2, 293–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Amiri, A. Sample preparation and extraction methods for pesticides in aquatic environments: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Jia, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, Z.; Guo-Hui, L.; Wen-Zhen, Y.; Xue-Song, F. A review of pretreatment and analytical methods of biogenic amines in food and biological samples since 2010. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1605, 360361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis Ordonez, J.; Maria Troncoso, A.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.C.; Maria Callejon, R. Recent trends in the determination of biogenic amines in fermented beverages—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 939, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otles, S.; Kartal, C. Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE): Principles and Applications in Food Samples. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2016, 15, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasinghe, G.D.T.M.; Jinadasa, B.K.K.K.; Pawel, P.; Aydi, A. Critical review on microextraction techniques used in determination of histamine in food samples. Discov. Food 2022, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, G.I.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Alsibaai, A.A.; Alwael, H.; El-Shahawi, M.S. A critical overview on the chemistry, clean-up and recent advances in analysis of biogenic amines in foodstuffs. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 78, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Mayor, A.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.A. Updated overview of QuEChERS applications in food, environmental and biological analysis (2020–2023). TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 169, 117375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Lijie, X.; Ruifeng, L.; Xianyi, L.; Fei, Z.; Shiling, L. Modified QuEChERS combined with UPLC-MS/MS to determine eight biogenic amines in Xinjiang smoked horsemeat sausages. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e93521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarzadeh, M.; Heydari, R. Determination of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in environmental and food samples using salt-assisted liquid-liquid extraction coupled with micro-channel and high-performance liquid chromatography. Sep. Sci. Plus 2022, 5, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaili, A.; Heydari, R.; Rezaeepour, R. Monitoring the oleuropein content of olive leaves and fruits using ultrasound-and salt-assisted liquid-liquid extraction optimized by response surface methodology and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, S.; Tian, H.; Sun, B. Research progress in the use of liquid-liquid extraction for food flavour analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 132, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lan, H.; Pan, D.; Zhang, T. Hydrophobic Mesoporous Silica-Coated Solid-Phase Microextraction Arrow System for the Determination of Six Biogenic Amines in Pork and Fish. Foods 2023, 12, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, Z. Selection of nitrite-degrading and biogenic amine-degrading strains and its involved genes. Food Qual. Saf. 2020, 4, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakinaka, T.; Iwata, S.; Takeishi, Y.; Watanabe, J.; Mogi, Y.; Tsukioka, Y.; Shibata, Y. Isolation of halophilic lactic acid bacteria possessing aspartate decarboxylase and application to fish sauce fermentation starter. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 292, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LopezSabater, E.I.; RodriguezJerez, J.J.; HernandezHerrero, M.; MoraVentura, M.T. Incidence of histamine-forming bacteria and histamine content in scombroid fish species from retail markets in the Barcelona area. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 28, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landete, J.M.; de las Rivas, B.; Marcobal, A.; Muñoz, R. Molecular methods for the detection of biogenic amine-producing bacteria on foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic, J.T.; Butinar, L.; Marusic, M.B.; Korte, D.; Vodopivec, B.M. Determination of biogenic amines formation by autochthonous lactic acid bacteria from ’Refosk’ grapes using different analytical methods. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 156, 112908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Kimura, B.; Yoshikawa, M.; Fujii, T. Cloning and sequencing of the histidine decarboxylase genes of gram-negative, histamine-producing bacteria and their application in detection and identification of these organisms in fish. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2568–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalazek-Rudnicka, K.; Wasik, A. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the determination of biogenic amines in wines and beers. Monatsh Chem. 2017, 148, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Zheng, H.; Han, X.; Cao, L.; Sui, J. Development of a highly sensitive HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of eight biogenic amines in aquatic products. Acta Chromatogr. 2021, 33, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Dong, X.; Wang, D. Biogenic amines in commercially produced Yulu, a Chinese fermented fish sauce. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2014, 7, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Dong, L.; Wang, A.; Wang, W.; Hu, N.; You, J. Simultaneous determination of biogenic amines and estrogens in foodstuff by an improved HPLC method combining with fluorescence labeling. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurrahman Munir, M.; Haji Badri, K. The importance of derivatizing reagent in chromatography applications for biogenic amine detection in food and beverages. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 5814389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomke, S.; Seiwert, B.; Dudek, L.; Effkemann, S.; Karst, U. Determination of biogenic amines in food samples using derivatization followed by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veciana-Nogues, M.T.; Hernandez-Jover, T.; Marine-Font, A.; Vedal-Carou, M.D.C. Liquid chromatographic method for determination of biogenic amines in fish and fish products. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosma, I.; Badeka, A. Determination of six underivatized biogenic amines by LC-MS/MS and study of biogenic amine production during trout (Salmo trutta) storage in ice. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2021, 38, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, P.-L.; Lim, G.-K. A review on analytical techniques for quantitative detection of histamine in fish products. Microchem. J. 2023, 189, 108499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiono, K.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nabeshi, H.; Ikeda, A.; Yokoyama, J.; Akiyama, H. Simple and rapid determination of biogenic amines in fish and fish products by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using 2,4,6-triethyl-3,5-dimethyl pyrylium trifluoromethanesulfonate as a derivatization reagent. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1643, 462046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
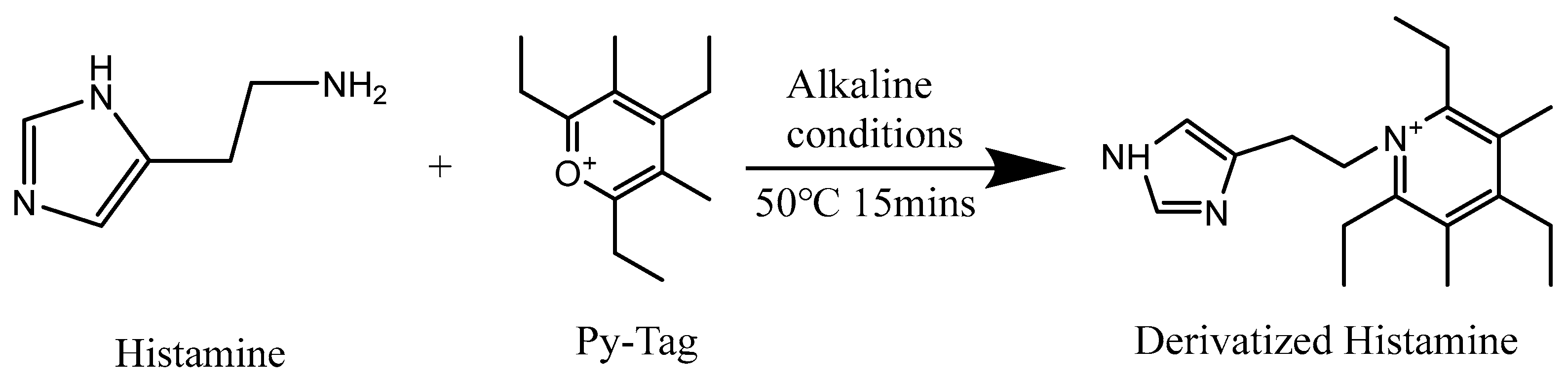
- Tatsuta, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Ikeda, A.; Matsukawa, S.; Katano, H.; Taira, S. Nanoparticle-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry (Nano-PALDI MS) with Py-Tag for the Analysis of Small Molecules. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 6, S0069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aladhadh, M.; Nasser Binjawhar, D.; Abd El-Kader Ebrahim, H.N.E.; Radhi, K.S.; Almatrafi, M.; Fayad, E.; Al-Saman, M.A.; Elsanhoty, R.M. Investigation of Biogenic Amine Levels and Microbiological Activity as Quality Markers in Some Dairy and Fish Products in Food Markets in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 19193–19202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls, J.E.; Bello, R.A.; Kodaira, M.S. Semiquantitative analysis by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) of biogenic amines in dried, salted and canned fish products. J. Food Qual. 2002, 25, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrul, H.A.; Inayatullah, A.; Munir, M.A. Fish Analysis Containing Biogenic Amines Using Gas Chromatography Equipped With Flame Ionization And Mass Spectrometer Detectors. Sci. Technol. Indones. 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.R. Significance of biogenic amines to food safety and human health. Food Res. Int. 1996, 29, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, M.; Enriquez, L.G.; McNair, H.M. Use of cold on-column injection for the analysis of putrescine and cadaverine by gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1997, 35, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavnicar, A.; Rogelj, I.; Kocar, D.; Kose, S.; Pompe, M. Determination of Biogenic Amines in Cheese by Ion Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry Detection. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1542–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocar, D.; Kose, S.; Tufan, B.; Scavnicar, A.; Pompe, M. Determination of Biogenic Amines in Fresh Fish and Processed Fish Products Using IC-MS/MS. Foods 2021, 10, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocar, D.; Köse, S.; Koral, S.; Tufan, B.; Scavnicar, A.; Pompe, M. Analysis of Biogenic Amines Using Immunoassays, HPLC, and a Newly Developed IC-MS/MS Technique in Fish Products-A Comparative Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yu, R.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wang, R.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z. Development of a capillary electrophoresis method based on magnetic solid-phase extraction for simultaneous and sensitive detection of eight biogenic amines in foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 3256–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yu, R.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Xu, Z. A Capillary Electrophoresis Method Based on Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Histamine in Foods. Molecules 2022, 27, 6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.; Hooda, V.; Gahlaut, A.; Gothwal, A.; Hooda, V. Enzymatic biosensors for the quantification of biogenic amines: A literature update. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, H.; Coelho, L.C.C.; Matias, A.; Saraiva, C.; Jorge, P.A.S.; de Almeida, J.M.M.M. Biosensors for Biogenic Amines: A Review. Biosensors 2021, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Datta, S.; Prasad, R.; Singh, J. Biological biosensors for monitoring and diagnosis. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.; Wittmann, C. Enzyme sensor array for the determination of biogenic amines in food samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 372, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranifam, M. Analytical applications of chemiluminescence systems assisted by carbon nanostructures. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 387–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omanovic-Miklicanin, E.; Valzacchi, S. Development of new chemiluminescence biosensors for determination of biogenic amines in meat. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahangari, H.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Ehsani, A.; Uslu, B. Latest trends for biogenic amines detection in foods: Enzymatic biosensors and nanozymes applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
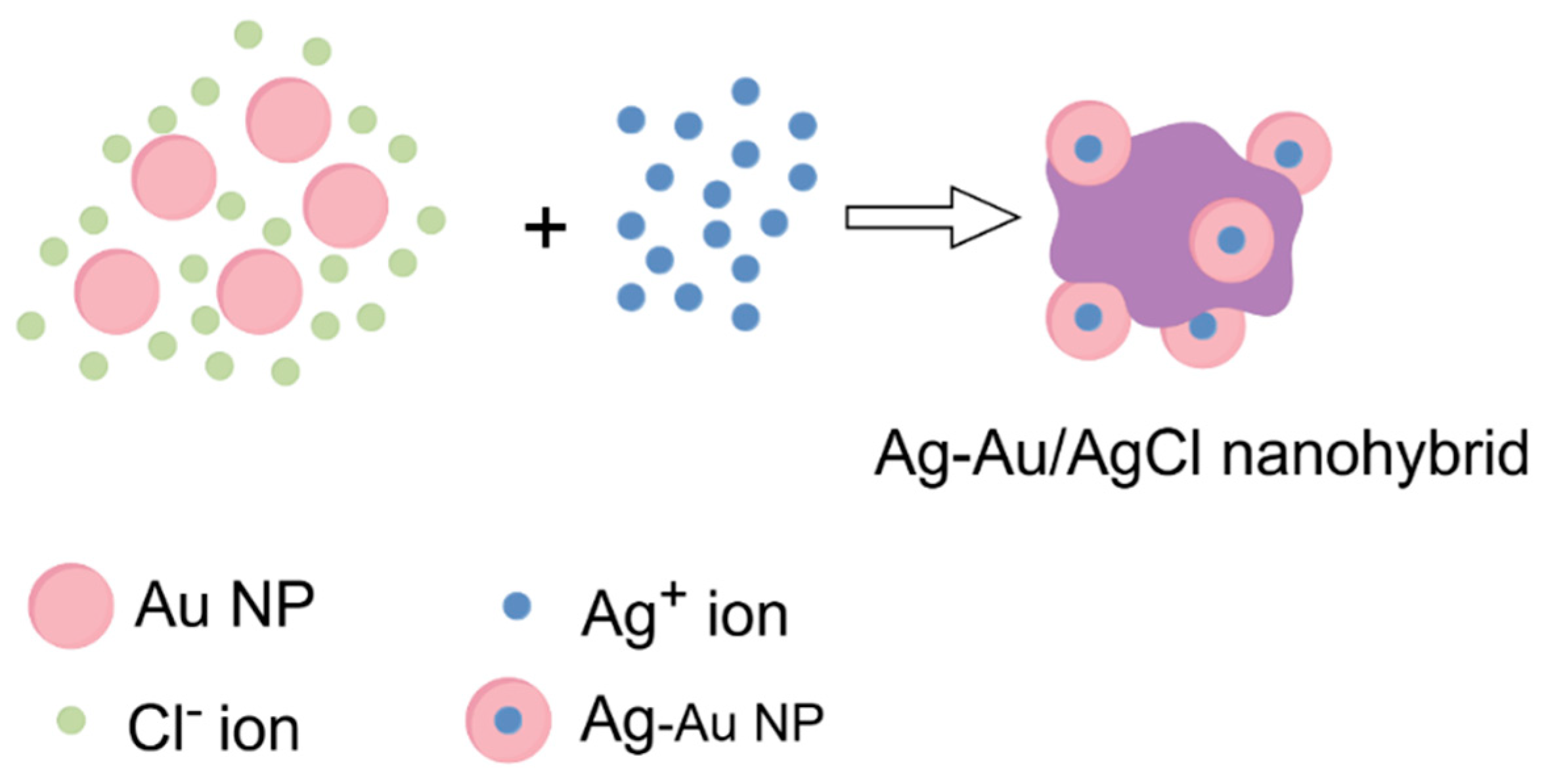
- Kuo, P.-C.; Lien, C.-W.; Mao, J.-Y.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Chang, H.-T.; Lin, H.-J.; Huang, C.-C. Detection of urinary spermine by using silver-gold/silver chloride nanozymes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1009, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Vicente, I.; Rivero, I.; Marcuello, L.; Montano, M.P.; de Marcos, S.; Galban, J. Portable colorimetric enzymatic disposable biosensor for histamine and simultaneous histamine/tyramine determination using a smartphone. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givanoudi, S.; Heyndrickx, M.; Depuydt, T.; Khorshid, M.; Robbens, J.; Wagner, P. A Review on Bio- and Chemosensors for the Detection of Biogenic Amines in Food Safety Applications: The Status in 2022. Sensors 2023, 23, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M. Aptamer-based assay of biomolecules: Recent advances in electro-analytical approach. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotariu, L.; Lagarde, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Bala, C. Electrochemical biosensors for fast detection of food contaminants trends and perspective. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, S.; Yeung, C.C.; Li, T.; Lau, S.C.; Sun, Q.J.; Li, L.Y.; Li, J.H.; Lam, M.H.W.; Roy, V.A.L. Portable molecularly imprinted polymer-based platform for detection of histamine in aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, J.; Eremin, S.; Dias, A.C.P.; Zhang, X. Development of ELISA and chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for quantification of histamine in drug products and food samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4739–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaxu, X.; Hongfei, Y.; Liangni, Q.; Jixiang, L.; Long, L.; Xiaohui, F.; Dapeng, P. Rapid detection of fluoroquinolone residues in aquatic products based on a gold-labeled microwell immunochromatographic assay. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 6, fyac033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkodra, B.; Abera, B.D.; Cantarella, G.; Douaki, A.; Avancini, E.; Petti, L.; Lugli, P. Flexible and Printed Electrochemical Immunosensor Coated with Oxygen Plasma Treated SWCNTs for Histamine Detection. Biosens. 2020, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degefu, H.; Amare, M.; Tessema, M.; Admassie, S. Lignin modified glassy carbon electrode for the electrochemical determination of histamine in human urine and wine samples. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 121, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.A.; Badri, K.H.; Heng, L.Y.; Inayatullah, A.; Badrul, H.A. A Modest Approach of Electrochemical Sensor to Determine Biogenic Amines in Food and Beverages. JSI 2020, 1, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, L.Y.; Badri, K.H.; Munir, M.A. Biogenic Amines Detection by Chromatography and Sensor Methods: A Comparative Review. Sci. Technol. Indones. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.; Freitas, A.C.; Pereira, R.; Duarte, A.C.; Santos, T.A.R. Recent developments in recognition elements for chemical sensors and biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 68, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervisevic, M.; Dervisevic, E.; Şenel, M. Recent progress in nanomaterial-based electrochemical and optical sensors for hypoxanthine and xanthine. A review. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Lao, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Lyu, X.; Gao, P.; Wu, S.; Minami, T.; Liu, Y. Freshness monitoring of raw fish by detecting biogenic amines using a gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric sensor array. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 6803–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, B.; Stoeva, S.I.; Sorensen, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J. Digestive ripening of thiolated gold nanoparticles: The effect of alkyl chain length. Langmuir 2002, 18, 7515–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Orouji, A.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M.R. Multiplex Detection of Biogenic Amines for Meat Freshness Monitoring Using Nanoplasmonic Colorimetric Sensor Array. Biosensors 2023, 13, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, T.; Li, Z.; Xue, C.; Xu, J. Ratiometric fluorescent nanosystem based on upconversion nanoparticles for histamine determination in seafood. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 133194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Y.; Hassan, M.M.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q. Lanthanide ion (Ln3+)-based upconversion sensor for quantification of food contaminants: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3531–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripongpreda, T.; Siralertmukul, K.; Rodthongkum, N. Colorimetric sensor and LDI-MS detection of biogenic amines in food spoilage based on porous PLA and graphene oxide. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.H.; Huo, D.Q.; Fa, H.B.; Luo, X.G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.N.; Hou, C.J. Rapid and ultrasensitive detection of biogenic amines with colorimetric sensor array. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 274, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Li, X.; Hu, L.C.; Zhang, Y.C.; Jiang, Y.; Mao, Z.P.; Xu, H.; Wang, B.J.; Feng, X.L.; Sui, X.F. A naked-eye detection polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose-based pH sensor for intelligent packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M. Fluorescence reaction for amino acids. Anal. Chem. 1971, 43, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanova, N.; Çelik, S.E.; Apak, R. Dithioerythritol functionalized gold nanoparticles−based fluorometric sensing of biogenic amines in food samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peat, M.A.; Gibb, J.W. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of indoleamines, dopamine, and norepinephrine in rat brain with fluorometric detection. Anal. Biochem. 1983, 128, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Jiang, L.; Chen, T.; Bao, G.-M.; Zeng, L.; Hu, X.; Yuan, H.-Q. A colorimetric and fluorescence lighting-up probe for the determination of biogenic primary diamine during the spoilage of fish. Dyes Pigm. 2021, 186, 108963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.-N.; Li, Z.-Y.; Chan, W.-H.; Lau, K.-C.; Crossley, M.J. Appending zinc tetraphenylporphyrin with an amine receptor at β-pyrrolic carbon for designing a selective histamine chemosensor. Supramol. Chem. 2010, 22, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Wu, W. Quantum dot biosensor combined with antibody and aptamer for tracing food-borne pathogens. Food Qual. Saf. 2021, 5, fyab019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarez, S.N.; Wongkaew, N.; Simsek, M.; Baeumner, A.J.; Duerkop, A. Dipsticks with Reflectometric Readout of an NIR Dye for Determination of Biogenic Amines. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotka-Wasylka, J.M.; Morrison, C.; Biziuk, M.; Namiesnik, J. Chemical Derivatization Processes Applied to Amine Determination in Samples of Different Matrix Composition. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4693–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danchuk, A.I.; Komova, N.S.; Mobarez, S.N.; Doronin, S.Y.; Burmistrova, N.A.; Markin, A.V.; Duerkop, A. Optical sensors for determination of biogenic amines in food. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4023–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, J.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Jia, Z.Q.; Pan, X.H.; Rani, K.K.; Zhou, J.Z.; Jiao, T.H.; Chen, Q.M.; Wu, D.Y. Rapid fabrication of large-area and uniform surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrate of Au nano-hemisphere array and its application in the detection of Malachite Green in tilapia. Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyac061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaude, C.; Meindl, C.; Froehlich, E.; Attard, J.; Mohr, G.J. Developing a sensor layer for the optical detection of amines during food spoilage. Talanta 2017, 170, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, L.; Rios, A.; Valcarcel, M. Selective and rapid determination of biogenic amines by capillary zone electrophoresis. Chromatographia 1997, 46, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Garai, B.; Prakasam, T.; Benyettou, F.; Varghese, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Gandara, F.; Pasricha, R.; Baias, M.; Jagannathan, R.; et al. Fluorescence turn on amine detection in a cationic covalent organic framework. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Mandal, S.; Sanmartin Matalobos, J.; Sahana, A.; Das, D. Interaction of water with a benzimidazole derivative: Fluorescence and colorimetric recognition of trace level water involving intramolecular charge transfer process. J. Mol. Recognit. 2016, 29, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
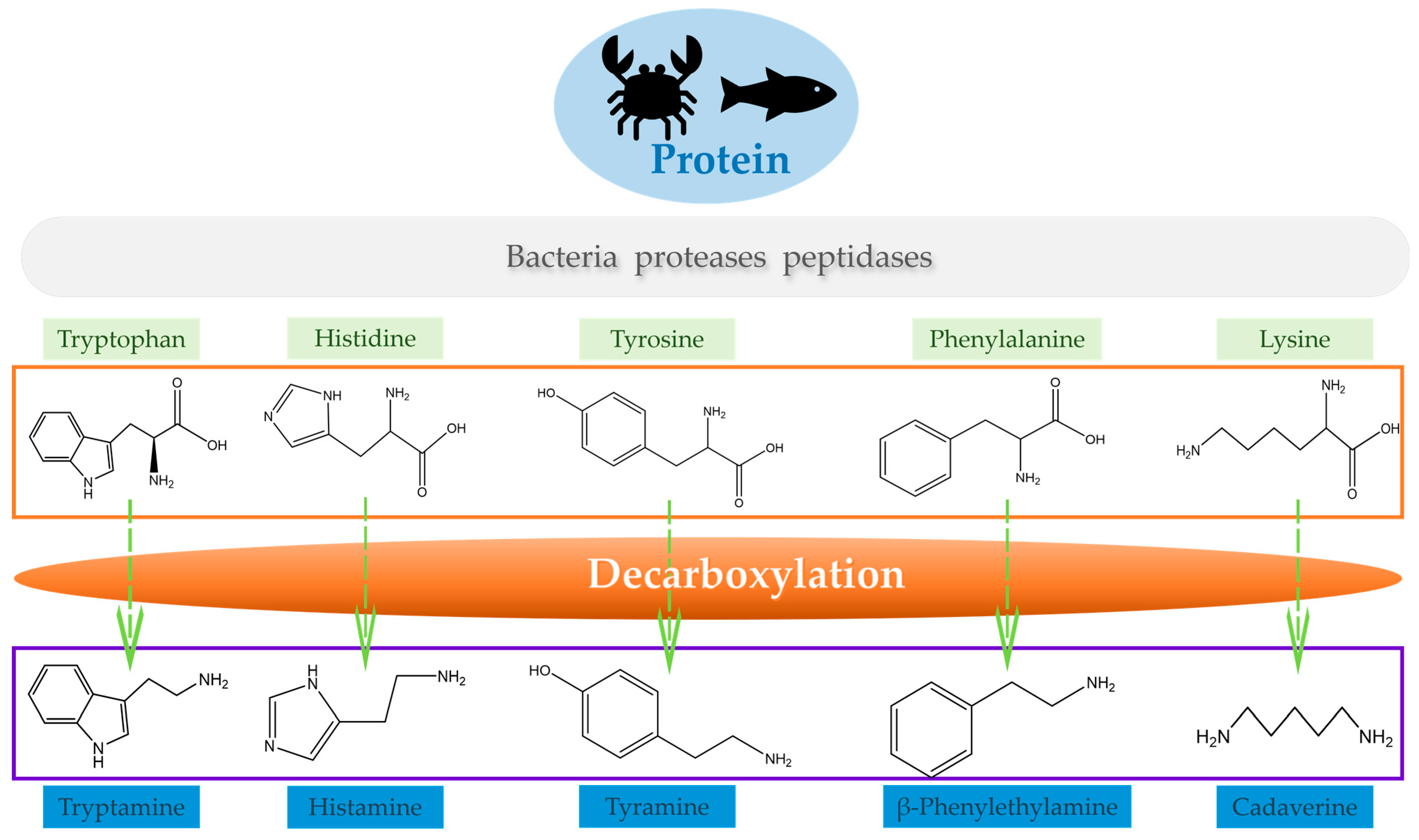
| Aquatic Products | Histamine | Cadaverine | Putrescine | Dopamine | Serotonin | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belt fish | 2.6 | 24.2 | 15.9 | [47] | ||
| Octopus | 3.2 | 25.5 | 18.3 | [47] | ||
| Common mackerel | 1.9 | 1.4 | 0.4 | <0.03 | [48] | |
| Common mullet | 1.7 | 1.7 | 0.4 | <0.03 | [48] | |
| Grass carp | 2.51 | 0.90 | 1.32 | [49] | ||
| Swimming crab | 2.1 | 10.6 | 17.3 | <0.1 | 0.1 | [50] |
| Common sea squirt | 3.4 | 18.7 | 12.5 | <0.1 | 1.6 | [50] |
| Chum salmon | 1.4 | <0.1 | 1.8 | 5.0 | <0.1 | [50] |
| Japanese scallop | <0.1 | 2.5 | 2.9 | <0.1 | <0.1 | [50] |
| Silver pomfret | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | [50] |
| Mackerel | 2.3 | 4.8 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.2 | [51] |
| Tuna | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 0.6 | [51] |
| Sample Pre-Treatment Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) | Minimal damage to the analyte; Easy to operate | Time consuming; Low extraction ability; High consumption of organic solvent | [58] |
| Solid-phase extraction (SPE) | Reduced analysis steps; Easy automation; Using no organic solvents | Time-consuming; Relatively expensive | [59] |
| Solid-phase microextraction (SPME) | Fast, universal; Solvent-less separation | Fibers used may be broken; Coating can be stripped off; Needle can be bent | [60] |
| Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) | Easy to operate; Fast; High preconcentration factor; Environmentally friendly | High consumption of solvents; Partition coefficient decrease | [61] |
| QuEChERS | Easy to operate; Fast; High cost-effectiveness; Less equipment required; Relatively small amounts of solvents | Limited scope of application; Not very suitable for traditional fermented meat products | [62] |
| Primer | Target Gene | Sequence | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUT1-F | ornithine decarboxylase | TWYMAYGCNGAYAARACNTAYYYTGT | 1440 |
| PUT1-R | ornithine decarboxylase | ACRCANAGNACNCCNGGNGGRTANGG | 1440 |
| HIS1-F | histidine decarboxylase | GGNATNGTNWSNTAYGAYMGNGCNGA | 372 |
| HIS2-R | histidine decarboxylase | TANGGNSANCCDATCATYTTRTGNCC | 531 |
| TDC-F | tyrosine decarboxylase | TGGYTNGTNCCNCARACNAARCAYTA | 825 |
| TDC-R | tyrosine decarboxylase | ACRTARTCNACCATRTTRAARTCNGG | 825 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Xie, J.; Mei, J. A Review on Analytical Techniques for Quantitative Detection of Biogenic Amines in Aquatic Products. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120274
Chen Z, Xie J, Mei J. A Review on Analytical Techniques for Quantitative Detection of Biogenic Amines in Aquatic Products. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(12):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120274
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zixin, Jing Xie, and Jun Mei. 2024. "A Review on Analytical Techniques for Quantitative Detection of Biogenic Amines in Aquatic Products" Chemosensors 12, no. 12: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120274
APA StyleChen, Z., Xie, J., & Mei, J. (2024). A Review on Analytical Techniques for Quantitative Detection of Biogenic Amines in Aquatic Products. Chemosensors, 12(12), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120274







