Investigating Sepsis-Associated Delirium Through Optical Neuroimaging: A New Frontier in Critical Care Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Sepsis-Associated Delirium Pathophysiology
1.2. Delirium Neuroimaging Studies
1.3. Optical Neuroimaging
2. Optical Neuroimaging in Sepsis-Associated Delirium
3. Challenges and Limitations
4. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torio, C.M.; Andrews, R.M. National Inpatient Hospital Costs: The Most Expensive Conditions by Payer, 2011. In Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2006. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK169005/ (accessed on 7 September 2024).
- Vincent, J.-L.; Marshall, J.C.; Namendys-Silva, S.A.; François, B.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Lipman, J.; Reinhart, K.; Antonelli, M.; Pickkers, P.; Njimi, H.; et al. Assessment of the worldwide burden of critical illness: The intensive care over nations (ICON) audit. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakr, Y.; Jaschinski, U.; Wittebole, X.; Szakmany, T.; Lipman, J.; Ñamendys-Silva, S.A.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Leone, M.; Lupu, M.-N.; Vincent, J.-L.; et al. Sepsis in Intensive Care Unit Patients: Worldwide Data From the Intensive Care over Nations Audit. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashyna, T.J.; Ely, E.W.; Smith, D.M.; Langa, K.M. Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA 2010, 304, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, J.R. Acute Brain Failure: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Management, and Sequelae of Delirium. Crit. Care Clin. 2017, 33, 461–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stollings, J.L.; Kotfis, K.; Chanques, G.; Pun, B.T.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Ely, E.W. Delirium in critical illness: Clinical manifestations, outcomes, and management. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, E.W.; Inouye, S.K.; Bernard, G.R.; Gordon, S.; Francis, J.; May, L.; Truman, B.; Speroff, T.; Gautam, S.; Margolin, R.; et al. Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: Validity and reliability of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU). JAMA 2001, 286, 2703–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, T.E.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Jung, E.; Swanson, A.; Ing, C.; Garcia, P.S.; Whittington, R.A.; Moitra, V. Association of Delirium With Long-term Cognitive Decline: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leighton, S.P.; Herron, J.W.; Jackson, E.; Sheridan, M.; Deligianni, F.; Cavanagh, J. Delirium and the risk of developing dementia: A cohort study of 12 949 patients. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, S.K.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; Saczynski, J.S. Delirium in elderly people. Lancet 2014, 383, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moine, P.; Abraham, E. Immunomodulation and sepsis: Impact of the pathogen. Shock 2004, 22, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, B.; Delmas, A.L.; Ozrazgat-Baslanti, T.; Vanzant, E.L.; Szpila, B.E.; Mohr, A.M.; Moore, F.A.; Brakenridge, S.C.; Brumback, B.A.; Moldawer, L.L.; et al. Human Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells are Associated With Chronic Immune Suppression After Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, W.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. Cytokines in sepsis: Potent immunoregulators and potential therapeutic targets--an updated view. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 165974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.A.; Gao, H. Sepsis, complement and the dysregulated inflammatory response. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 4154–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remick, D.G. Pathophysiology of sepsis. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Poll, T.; Opal, S.M. Host-pathogen interactions in sepsis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, F.B.; Chang, A.; Ruf, W.; Morrissey, J.H.; Hinshaw, L.; Catlett, R.; Blick, K.; Edgington, T.S. Lethal E. coli septic shock is prevented by blocking tissue factor with monoclonal antibody. Circ. Shock 1991, 33, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A.R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-Brain Barrier: From Physiology to Disease and Back. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 21–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, W.C. The role of the endothelium in severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood 2003, 101, 3765–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, J.R. Delirium pathophysiology: An updated hypothesis of the etiology of acute brain failure. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2018, 33, 1428–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, Y.; Kawamata, T.; Tamura, T.; Hovda, D.A.; Becker, D.P.; Tsubokawa, T. Calcium-dependent glutamate release concomitant with massive potassium flux during cerebral ischemia in vivo. Brain Res. 1991, 558, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, P.A.; Gibson, G.E. Dopamine and serotonin in rat striatum during in vivo hypoxic-hypoxia. Metab. Brain Dis. 1989, 4, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.E.; Blass, J.P. Impaired synthesis of acetylcholine in brain accompanying mild hypoxia and hypoglycemia. J. Neurochem. 1976, 27, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Liu, P.; Pascual, J.M.; Xiao, G.; Lu, H. Effect of hypoxia and hyperoxia on cerebral blood flow, blood oxygenation, and oxidative metabolism. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2012, 32, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, A.; Rogers, B.P.; Gunther, M.L.; Merkle, K.; Pandharipande, P.; Girard, T.D.; Jackson, J.C.; Thompson, J.; Shintani, A.K.; Geevarghese, S.; et al. The relationship between delirium duration, white matter integrity, and cognitive impairment in intensive care unit survivors as determined by diffusion tensor imaging: The VISIONS prospective cohort magnetic resonance imaging study. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2182–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, I.M.J.; de Bresser, J.; van Montfort, S.J.T.; Witkamp, T.D.; Walraad, B.; Spies, C.D.; Hendrikse, J.; van Dellen, E.; Slooter, A.J.C. BioCog consortium Postoperative delirium is associated with grey matter brain volume loss. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, Y.; Narumoto, J.; Shibata, K.; Matsuoka, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Hata, Y.; Yamada, K.; Yaku, H.; Fukui, K. White-matter hyperintensities predict delirium after cardiac surgery. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2013, 21, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitchingham, A.; Pereira, J.V.-B.; Wegner, E.A.; Oxenham, V.; Close, J.; Caplan, G.A. Regional cerebral hypometabolism on 18F-FDG PET/CT scan in delirium is independent of acute illness and dementia. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Montfort, S.J.T.; van Dellen, E.; Stam, C.J.; Ahmad, A.H.; Mentink, L.J.; Kraan, C.W.; Zalesky, A.; Slooter, A.J.C. Brain network disintegration as a final common pathway for delirium: A systematic review and qualitative meta-analysis. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 23, 101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Shin, J.E.; Yang, K.H.; Kyeong, S.; Lee, W.S.; Chung, T.-S.; Kim, J.-J. Cortical and subcortical changes in resting-state functional connectivity before and during an episode of postoperative delirium. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2019, 53, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Lee, H.; Chung, T.-S.; Park, K.-M.; Jung, Y.-C.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, J.-J. Neural network functional connectivity during and after an episode of delirium. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegand, T.L.T.; Rémi, J.; Dimitriadis, K. Electroencephalography in delirium assessment: A scoping review. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jöbsis, F.F. Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science 1977, 198, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luker, G.D.; Luker, K.E. Optical imaging: Current applications and future directions. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, E.M.C. Optical brain imaging in vivo: Techniques and applications from animal to man. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 051402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Guo, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Jiang, S.; Wu, D.; Jiang, H. Clinical photoacoustic/ultrasound dual-modal imaging: Current status and future trends. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1036621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Huang, L.; Jiang, M.S.; Jiang, H. Contrast agents for photoacoustic and thermoacoustic imaging: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23616–23639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morone, K.A.; Neimat, J.S.; Roe, A.W.; Friedman, R.M. Review of functional and clinical relevance of intrinsic signal optical imaging in human brain mapping. Neurophotonics 2017, 4, 031220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, Y.; Tamura, M. Detection of dynamic changes in cerebral oxygenation coupled to neuronal function during mental work in man. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 150, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, E.; Delpy, D.T. Near-infrared light propagation in an adult head model. II. Effect of superficial tissue thickness on the sensitivity of the near-infrared spectroscopy signal. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 2915–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpy, D.T.; Cope, M. Quantification in tissue near-infrared spectroscopy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1997, 352, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwell, C.E.; Cooper, C.E. Making light work: Illuminating the future of biomedical optics. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 4358–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.; Quaresima, V. A brief review on the history of human functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) development and fields of application. NeuroImage 2012, 63, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H. Diffuse Optical Tomography; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, Y.; Yamada, Y. Overview of diffuse optical tomography and its clinical applications. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 091312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, T.; Liu, T.T.; Miller, K.L.; Luh, W.M.; Wong, E.C.; Frank, L.R.; Buxton, R.B. Discrepancies between BOLD and flow dynamics in primary and supplementary motor areas: Application of the balloon model to the interpretation of BOLD transients. NeuroImage 2004, 21, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culver, J.P.; Durduran, T.; Furuya, D.; Cheung, C.; Greenberg, J.H.; Yodh, A.G. Diffuse optical tomography of cerebral blood flow, oxygenation, and metabolism in rat during focal ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2003, 23, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, J.P.; Siegel, A.M.; Franceschini, M.A.; Mandeville, J.B.; Boas, D.A. Evidence that cerebral blood volume can provide brain activation maps with better spatial resolution than deoxygenated hemoglobin. NeuroImage 2005, 27, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Wolf, U.; Toronov, V.; Michalos, A.; Paunescu, L.A.; Choi, J.H.; Gratton, E. Different time evolution of oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin concentration changes in the visual and motor cortices during functional stimulation: A near-infrared spectroscopy study. NeuroImage 2002, 16, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Rosas, E.E.; Zhao, H.; Nixon-Hill, R.W.; Smith, G.; Dunne, L.; Powell, S.; Cooper, R.J.; Everdell, N.L. Evaluating a new generation of wearable high-density diffuse optical tomography technology via retinotopic mapping of the adult visual cortex. Neurophotonics 2021, 8, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, H.; Wagoner, R.; Kozel, F.A.; Currier, G.; Jiang, H. Neuroimaging of depression with diffuse optical tomography during repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Carpenter, L.L.; Jiang, H. Optical neuroimaging: Advancing transcranial magnetic stimulation treatments of psychiatric disorders. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art. 2022, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Wagoner, R.; Yang, H.; Currier, G.; Jiang, H. Three-dimensional optical imaging of brain activation during transcranial magnetic stimulation. J. Xray Sci. Technol. 2021, 29, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Yang, H.; Czuma, R.; Yang, Y.; Kozel, F.A.; Jiang, H. Portable Diffuse Optical Tomography for Three-Dimensional Functional Neuroimaging in the Hospital. Photonics 2024, 11, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.; Siegemund, M.; Dell-Kuster, S.; Smielewski, P.; Rüegg, S.; Strebel, S.P.; Marsch, S.C.U.; Pargger, H.; Steiner, L.A. Cerebral perfusion in sepsis-associated delirium. Crit. Care 2008, 12, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, D.J.; Kumar, A.; Klar, G. Decreases in cerebral saturation in patients with septic shock are associated with increased risk of death: A prospective observational single center study. J. Intensive Care 2016, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, M.; Song, A.; Maslove, D.; Ferri, C.; Howes, D.; Muscedere, J.; Boyd, J.G. Brain Tissue Oxygenation in Patients with Septic Shock: A Feasibility Study. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 43, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaskó, A.; Siró, P.; László, I.; Szatmári, S.; Molnár, L.; Fülesdi, B.; Molnár, C. Assessment of cerebral tissue oxygen saturation in septic patients during acetazolamide provocation—A near infrared spectroscopy study. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2014, 101, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerebral Oxygenation and Neurological Outcomes Following Critical Illness (CONFOCAL) Research Group; Canadian Critical Care Trials Group; Wood, M.; Maslove, D.M.; Muscedere, J.G.; Day, A.G.; Gordon Boyd, J. Low brain tissue oxygenation contributes to the development of delirium in critically ill patients: A prospective observational study. J. Crit. Care 2017, 41, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.F.; Wood, M.D.; Maslove, D.M.; Muscedere, J.G.; Boyd, J.G. Dysfunctional cerebral autoregulation is associated with delirium in critically ill adults. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2019, 39, 2512–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, K.; Walker, K.A.; Goodson, C.; Olson, E.; Maher, D.; Brown, C.H.; Nyquist, P. Cerebral Autoregulation-Guided Optimal Blood Pressure in Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy: A Case Series. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, H.; Czuma, R.; Farley, L.; Cohen-Oram, A.; Hartney, K.; Chechotka, K.; Kozel, F.A.; Jiang, H. Diffuse optical tomography for mapping cerebral hemodynamics and functional connectivity in delirium. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 4032–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meagher, J.; Leonard, M.; Donoghue, L.; O’Regan, N.; Timmons, S.; Exton, C.; Cullen, W.; Dunne, C.; Adamis, D.; Maclullich, A.J.; et al. Months backward test: A review of its use in clinical studies. World J. Psychiatry 2015, 5, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzepacz, P.T.; Mittal, D.; Torres, R.; Kanary, K.; Norton, J.; Jimerson, N. Validation of the Delirium Rating Scale-revised-98: Comparison with the delirium rating scale and the cognitive test for delirium. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, F.; Tokumitsu, Y.; Hoshi, Y.; Tamura, M. Gender- and handedness-related differences of forebrain oxygenation and hemodynamics. Brain Res. 1993, 601, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strangman, G.E.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. Scalp and skull influence on near infrared photon propagation in the Colin27 brain template. NeuroImage 2014, 85 Pt 1, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, M.R. Shining light on the head: Photobiomodulation for brain disorders. BBA Clin. 2016, 6, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedford, C.E.; DeLapp, S.; Jacques, S.; Anders, J. Quantitative analysis of transcranial and intraparenchymal light penetration in human cadaver brain tissue. Lasers Surg. Med. 2015, 47, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroslavsky, A.N.; Schulze, P.C.; Yaroslavsky, I.V.; Schober, R.; Ulrich, F.; Schwarzmaier, H.J. Optical properties of selected native and coagulated human brain tissues in vitro in the visible and near infrared spectral range. Phys. Med. Biol. 2002, 47, 2059–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzschke, A.; Lovisa, B.; Seydoux, O.; Zellweger, M.; Pfleiderer, M.; Tardy, Y.; Wagnières, G. Red and NIR light dosimetry in the human deep brain. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 2921–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggebrecht, A.T.; Ferradal, S.L.; Robichaux-Viehoever, A.; Hassanpour, M.S.; Dehghani, H.; Snyder, A.Z.; Hershey, T.; Culver, J.P. Mapping distributed brain function and networks with diffuse optical tomography. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habermehl, C.; Holtze, S.; Steinbrink, J.; Koch, S.P.; Obrig, H.; Mehnert, J.; Schmitz, C.H. Somatosensory activation of two fingers can be discriminated with ultrahigh-density diffuse optical tomography. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 3201–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, F.; Tachtsidis, I. Clinical Brain Monitoring with Time Domain NIRS: A Review and Future Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havsteen, I.; Ohlhues, A.; Madsen, K.H.; Nybing, J.D.; Christensen, H.; Christensen, A. Are Movement Artifacts in Magnetic Resonance Imaging a Real Problem?—A Narrative Review. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, K.R.A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Buckner, R.L. The influence of head motion on intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigadoi, S.; Ceccherini, L.; Cutini, S.; Scarpa, F.; Scatturin, P.; Selb, J.; Gagnon, L.; Boas, D.A.; Cooper, R.J. Motion artifacts in functional near-infrared spectroscopy: A comparison of motion correction techniques applied to real cognitive data. NeuroImage 2014, 85, 10.1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarapicchia, V.; Brown, C.; Mayo, C.; Gawryluk, J.R. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: Insights from Combined Recording Studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Hong, K.-S.; Yang, D.; Huang, G. Motion artifacts removal and evaluation techniques for functional near-infrared spectroscopy signals: A review. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 878750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharshar, T.; Carlier, R.; Bernard, F.; Guidoux, C.; Brouland, J.-P.; Nardi, O.; de la Grandmaison, G.L.; Aboab, J.; Gray, F.; Menon, D.; et al. Brain lesions in septic shock: A magnetic resonance imaging study. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heming, N.; Mazeraud, A.; Verdonk, F.; Bozza, F.A.; Chrétien, F.; Sharshar, T. Neuroanatomy of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhun, G.; Esen, F.; Özcan, P.E.; Sencer, S.; Bilgiç, B.; Ulusoy, C.; Noyan, H.; Küçükerden, M.; Ali, A.; Barburoğlu, M.; et al. Neuroimaging Findings in Sepsis-Induced Brain Dysfunction: Association with Clinical and Laboratory Findings. Neurocrit Care 2019, 30, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, M.A.; Kumaran, K.R.; Ning, T.; Mansor, N.I.; Effendy, M.A.; Damodaran, T.; Lingam, K.; Wahab, H.A.; Nordin, N.; Liao, P.; et al. Insights into the neuropathology of cerebral ischemia and its mechanisms. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 31, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacalone, G.; Zanoletti, M.; Re, R.; Germinario, B.; Contini, D.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A.; Roveri, L. Time-domain near-infrared spectroscopy in acute ischemic stroke patients. Neurophotonics 2019, 6, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Kim, Y.; Chai, C.L.; Jeon, J.P. Application of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for the Detection of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia in Poor-Grade Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care 2021, 35, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Yang, Y.-R.; Tsai, Y.-A.; Wang, R.-Y.; Lu, C.-F. Brain Activation and Gait Alteration During Cognitive and Motor Dual Task Walking in Stroke-A Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Study. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yang, X.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, H. Intracerebral haemorrhage-induced injury progression assessed by cross-sectional photoacoustic tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 5814–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.R.; Snyder, A.Z.; Cohen, A.L.; Petersen, S.E.; Raichle, M.E.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Culver, J.P. Resting-state functional connectivity in the human brain revealed with diffuse optical tomography. NeuroImage 2009, 47, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggebrecht, A.T.; White, B.R.; Ferradal, S.L.; Chen, C.; Zhan, Y.; Snyder, A.Z.; Dehghani, H.; Culver, J.P. A quantitative spatial comparison of high-density diffuse optical tomography and fMRI cortical mapping. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.M. Precision psychiatry: A neural circuit taxonomy for depression and anxiety. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Cooper, R.J. Review of recent progress toward a fiberless, whole-scalp diffuse optical tomography system. Neurophotonics 2018, 5, 011012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.F.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, H.; Ding, L. Brain-wide functional diffuse optical tomography of resting state networks. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 046069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandharipande, P.; Shintani, A.; Peterson, J.; Pun, B.T.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Dittus, R.S.; Bernard, G.R.; Ely, E.W. Lorazepam is an independent risk factor for transitioning to delirium in intensive care unit patients. Anesthesiology 2006, 104, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikström, M.; Krab, K.; Sharma, V. Oxygen Activation and Energy Conservation by Cytochrome c Oxidase. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 2469–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Ma, X.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X. Mitochondria dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recent advances. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, E.; Musich, P.R.; Lin, F. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and the potential countermeasure. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis-induced multi-organ failure. Virulence 2014, 5, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, D.C.; Hulgan, T.; Fessel, J.P.; Billings, F.T.; Thompson, J.L.; Chandrasekhar, R.; Girard, T.D. Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroups and Delirium During Sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V. 20 years of the default mode network: A review and synthesis. Neuron 2023, 111, 2469–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemée, J.-M.; Berro, D.H.; Bernard, F.; Chinier, E.; Leiber, L.-M.; Menei, P.; Ter Minassian, A. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging versus task-based activity for language mapping and correlation with perioperative cortical mapping. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Makowski, C.; Hagler, D.J.; Garavan, H.P.; Thompson, W.K.; Greene, D.J.; Jernigan, T.L.; Dale, A.M. Task fMRI paradigms may capture more behaviorally relevant information than resting-state functional connectivity. NeuroImage 2023, 270, 119946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Techniques | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Bedside Capabilities | Patient and Safety Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOT | mm | ms | Yes | None |
| fNIRS | cm | ms | Yes | None |
| fMRI | mm | s | No | Ferromagnetic material |
| EEG | cm | ms | Yes | None |
| PET | mm | min | No | Fasting requirement |
| SPECT | cm | min | No | Ionizing radiation |
| Reference | Number of Patients | Optical Imaging Technique | Imaging Site(s) | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pfister et al., 2008 [59]. | 23 | NIRS | Frontal lobe and frontoparietal | No difference in oxygenation levels during delirium; however, Doppler-based blood flow velocity was diminished in delirious patients. |
| Funk et al., 2016 [60]. | 15 | NIRS | Frontal lobe | No difference in cerebral oxygenation in delirious patients. |
| Wood et al., 2016 [61]. | 10 | NIRS | Single forehead optode | Higher saturated oxygenation levels were observed in delirium. |
| Vasko et al., 2014 [62]. | 25 | NIRS | Frontal lobe | Lower cerebral oxygenation was reported in delirious patients consistently. |
| Wood et al., 2017 [63]. | 88 | NIRS | Single forehead optode | Longer duration of delirium was correlated with worse cerebral oxygenation values. |
| Lee et al., 2019 [64]. | 40 | NIRS | Single forehead optode | Duration of delirium and worse COx values associated with the development of delirium. |
| Rosenblatt et al., 2020 [65]. | 6 | NIRS | Frontal lobe | Severity of delirium was associated with COx values. |
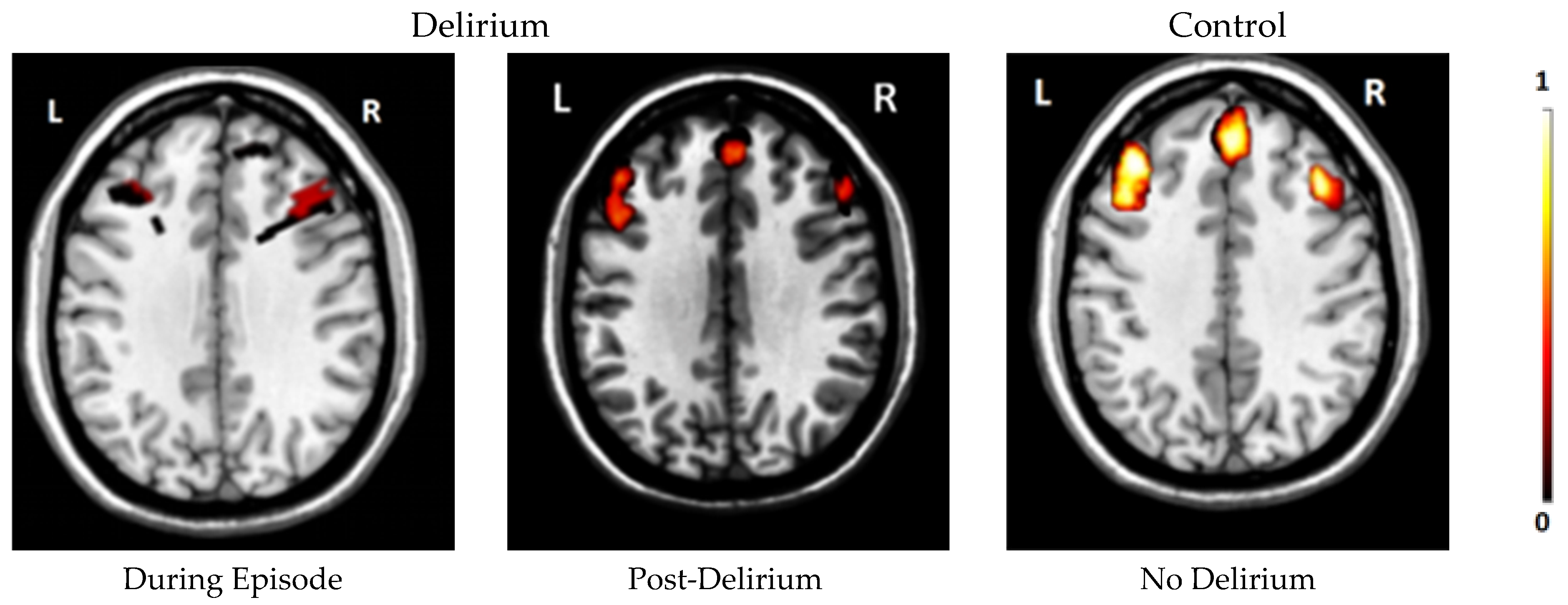
| Jiang et al., 2024 [66]. | 12 | DOT | Dorsolateral and dorsomedial prefrontal cortex | During delirium and post-delirium exhibited lower oxygenation levels compared to controls. Higher severity of delirium correlated with lower oxygenation levels. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Gunther, M.; Maldonado, J.R.; Efron, P.A.; DeKosky, S.T.; Jiang, H. Investigating Sepsis-Associated Delirium Through Optical Neuroimaging: A New Frontier in Critical Care Research. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120264
Jiang S, Gunther M, Maldonado JR, Efron PA, DeKosky ST, Jiang H. Investigating Sepsis-Associated Delirium Through Optical Neuroimaging: A New Frontier in Critical Care Research. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(12):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120264
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shixie, Matthew Gunther, Jose R. Maldonado, Philip A. Efron, Steven T. DeKosky, and Huabei Jiang. 2024. "Investigating Sepsis-Associated Delirium Through Optical Neuroimaging: A New Frontier in Critical Care Research" Chemosensors 12, no. 12: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120264
APA StyleJiang, S., Gunther, M., Maldonado, J. R., Efron, P. A., DeKosky, S. T., & Jiang, H. (2024). Investigating Sepsis-Associated Delirium Through Optical Neuroimaging: A New Frontier in Critical Care Research. Chemosensors, 12(12), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120264






