CRDS Technology-Based Integrated Breath Gas Detection System for Breath Acetone Real-Time Accurate Detection Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Principles of CRDS Technology
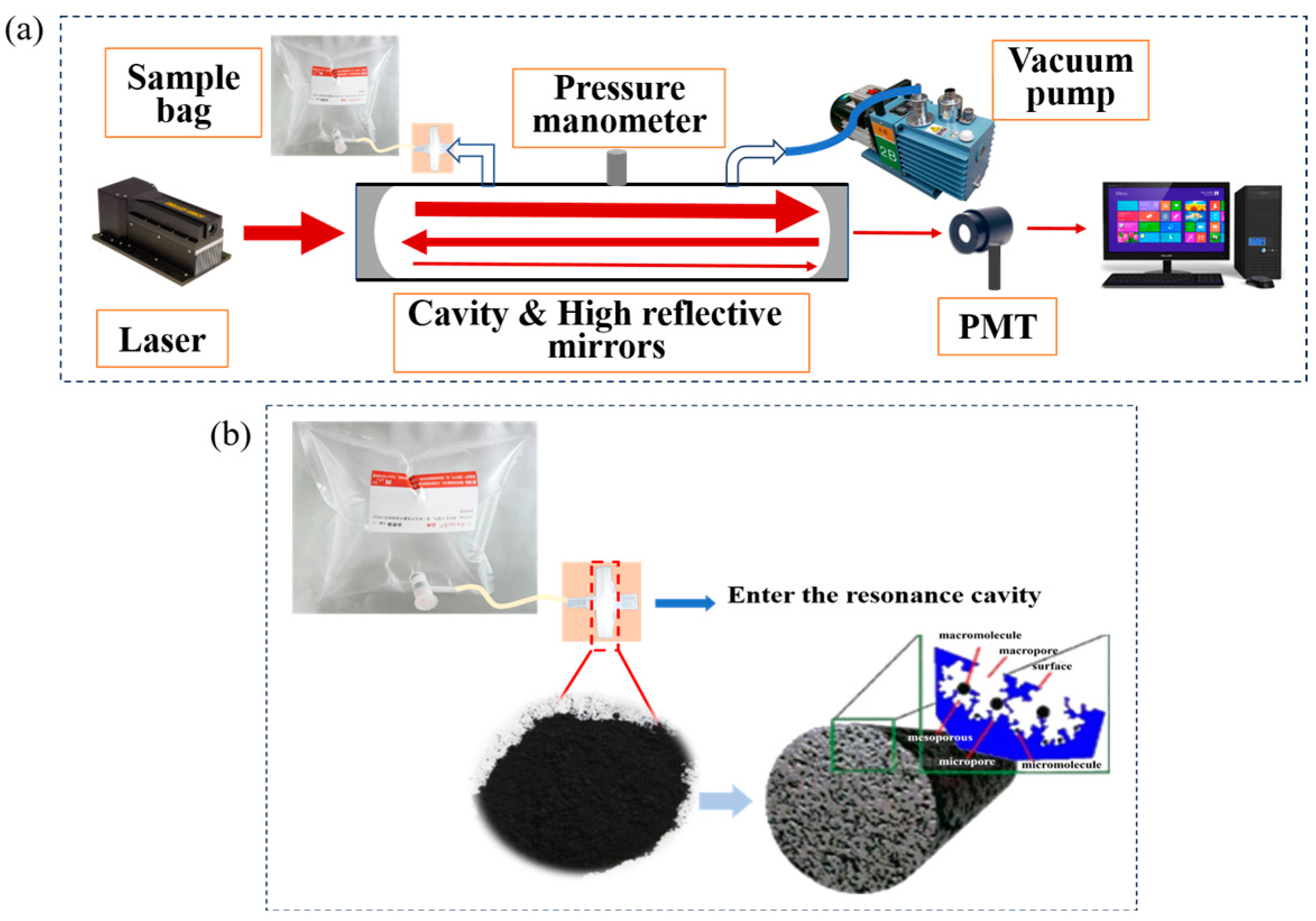
2.2. Construction of an Integrated Breath Gas Detection System Based on CRDS Technology
2.3. Preparation of Activated Carbon by Ester Hydrolysis for Breath Gas Pretreatment Unit
2.4. Calculation of Acetone Concentration Based on Single-Wavelength Background Deduction Method
2.5. Breath Sample Collection Program
2.6. Sample Test Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of Breath Gas Pretreatment Units
3.2. Performance of the Integrated Breath Gas Detection System
3.3. Application of Integrated Breathing Acetone Detection System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phelps, N.H.; Singleton, R.K.; Zhou, B.; Heap, R.A.; Mishra, A.; Bennett, J.E.; Barbagallo, C.M. Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2024, 403, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdomo, C.M.; Cohen, R.V.; Sumithran, P.; Clément, K.; Frühbeck, G. Contemporary medical, device, and surgical therapies for obesity in adults. Lancet 2023, 401, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, A.; Marrone, G.; Celotto, R.; Campo, M.; Vita, C.; Chiaramonte, C.; Carretta, A.; Di Daniele, N.; Noce, A. Utility of SIFT-MS to evaluate volatile organic compounds in nephropathic patients’ breath. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, P.-H.; Lin, Z.-L.; Pan, Y.-C.; Yang, H.-C.; Chang, C.-J.; Liang, S.-K.; Wen, Y.-F.; Chang, C.-H.; Chang, L.-Y.; Yu, K.-L.; et al. Exploring Volatile Organic Compounds in Breath for High-Accuracy Prediction of Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sana, S.R.G.L.; Lv, Y.; Chen, G.; Guo, L.; Li, E. Analysis of the volatile organic compounds of epidural analgesia-ameliorated metabolic disorder in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus based on untargeted metabolomics. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1009888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincentis, A.; Pennazza, G.; Santonico, M.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U.; Galati, G.; Gallo, P.; Vernile, C.; Pedone, C.; Antonelli Incalzi, R.; Picardi, A. Breath-print analysis by e-nose for classifying and monitoring chronic liver disease: A proof-of-concept study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Jia, Z.; Zou, J.; Liu, G.; et al. A novel non-invasive exhaled breath biopsy for the diagnosis and screening of breast cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Hanada, M.; Koda, H.; Sugimoto, M.; Takada, M.; Toi, M. Reduction of bacterial volatile sulfur compound production by licoricidin and licorisoflavan A from licorice. J. Breath. Res. 2022, 17, 016006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Sahay, P. Breath Analysis Using Laser Spectroscopic Techniques: Breath Biomarkers, Spectral Fingerprints, and Detection Limits. Sensors 2009, 9, 8230–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C. Measuring breath acetone for monitoring fat loss: Review. Obesity 2015, 23, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güntner, A.T.; Abegg, S.; Königstein, K.; Gerber, P.A.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Breath Sensors for Health Monitoring. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.A.; Baker, J.; Aggarwal, P.; Hughes, D.M.; Nwosu, A.C.; Boyd, M.T.; Mayland, C.R.; Mason, S.; Ellershaw, J.; Probert, C.S.; et al. GC-MS Techniques Investigating Potential Biomarkers of Dying in the Last Weeks with Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Sun, R.; Su, J.; Sun, Y.; Xia, K.; Cong, L.; Cui, H. Highly selective acetone detector based on a separation channel and semiconduc-tor gas analyzer. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 085102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MG, G.; Bastide, B.H.; Remund, A.L.; Oosthuizen, D.N.; Derron, N.; Gerberb, P.A.; Weber, I.C. Handheld device quantifies breath acetone for real-life metabolic health monitoring. Anal. Diagn. 2023, 2, 918–928. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, Q.; Lan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Liquid-crystal-based fiber laser ana-lyzer for non-invasive gas detection. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 4508–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Likhodii, S.S.; Cunnane, S.C. Breath acetone is a reliable indicator of ketosis in adults consuming ketogenic meals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Gao, M.; Cheng, K.; Shao, X.; Wu, H.; Dong, L.; Yin, X. Trace photoacoustic SO2 gas sensor in SF6 utilizing a 266 nm UV laser and an acousto-optic power stabilizer. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 6974–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, G.; Mei, J.; Liu, K.; Chen, W.; Gao, X. Simultaneous Detection of Major Greenhouse Gases with Multiresonator Photoacoustic Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 14877–14883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Y.; Lu, P. Differential photoacoustic spectroscopy for flow gas detection based on single microphone. Photoacoustics 2024, 38, 2213–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentaro, N.; Keisuke, H.; Naoko, N.; Ryuichiro, E.; Mariko, T.; Mai, N.; Hitomi, S.; Misaki, M.; Satoko, T.; Hisako, F.; et al. Ketogenic effects of medium chain triglycerides containing formula and its correlation to breath acetone in healthy volunteers: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, single dose-response study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1224740. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. A portable Real-Time Ringdown Breath Acetone Analyzer: Toward Potential Diabetic Screening and Management. Sensors 2016, 16, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Yuan, X.; Li, B.; Sun, K.; Liu, J. Air-mediated phosphoric acid activation strategy for preparation of oxygenated functional groups rich activated carbon for capacitive deionization. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 215, 118657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, A.; Deacon, D.A.G. Cavity ring-down optical spectrometer for absorption measurements using pulsed laser sources. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1988, 59, 2544–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, K.W.; Busch, M.A. Cavity Ringdown Spectroscopy: An Ultra-Trace Absorption Measurement Technique; ACS Symposium Series; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 1–720. [Google Scholar]
- Romanini, D.; Lehmann, K.K. Ring-down cavity absorption spectroscopy of the very weak HCN overtone bands with six, seven, and eight stretching quanta. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 6287–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, S.; Ai, J.; Yang, C.; Jia, Q.; Cao, B. Hierarchical Porous Activated Carbon Obtained by a Novel Heating-Rate-Induced Method for Lithium-Ion Capacitor. Chem. Sel. 2019, 4, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, S.H.; Li, S.S.; Cao, B.Q. Double-activated porous carbons for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes. Rare Met. 2017, 36, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Chen, Z.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Determination of breath acetone in 149 type 2 diabetic patients using a ringdown breath-acetone analyzer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, X.; Yin, H.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Study of breath acetone and its correlations with blood glucose and blood beta-hydroxybutyrate using an animal model with lab-developed type 1 diabetic rat. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71002–71010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.S.; Yang, R.T. Improved Horvath-Kawazoe equations including spherical pore models for calculating micropore size distribution. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1994, 49, 2599–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finqueneisel, G.; Zimny, T.; Weber, J.V. On the prediction of adsorption isotherms of methanol/water vapour mixtures on microporous activated carbon. Carbon 2005, 43, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.S.; Mevada, C.; Mukhopadhyay, M. Hydrophilic Carbon Cloth (Chemically Activated) as an Electrode Material for Energy Storage Device. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 5949–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangsathitkulchai, C.; Ngernyen, Y.; Tangsathitkulchai, M. Surface modification and adsorption of eucalyptus wood-based activated carbons: Effects of oxidation treatment, carbon porous structure and activation method. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Hwang, B.; Hong, L.; Yoo, S.J.; Chun, S.-E. Fabrication of hydrophilic porous carbon from polyvinylidene chloride-resin via synergetic activation of ZnO and tetrahydrofuran for aqueous supercapacitors. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 40, 103127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canete, S.J.P.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Kong, L.M.; Schlegel, V.L.; Plantz, B.A.; Dowben, P.A.; Lai, R.Y. Application of synchrotron FT-IR microspectroscopy for determination of spatial distribution of methylene blue conjugated onto a SAM via ‘‘click’’ chemistry. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11918–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, T.; Kitakaze, Y.; Sekida, T.; Hayashi, J.; Katoh, M. Characteristics and humidity control capacity of activated carbon from bamboo. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3964–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.H.; Li, A.M. Adsorption characteristics of water vapor on the hypercrosslinked polymeric adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 180, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, J.K.; Bandosz, T.J.; Thomson, K.T.; Gubbins, K.E. Water in porous carbons. Colloid. Surf. A 2001, 187, 539–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Shi, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Song, B.; Li, W.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Y.; Cao, B.; Jiang, C. CRDS Technology-Based Integrated Breath Gas Detection System for Breath Acetone Real-Time Accurate Detection Application. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120261
Sun J, Shi D, Wang L, Yu X, Song B, Li W, Zhu J, Yang Y, Cao B, Jiang C. CRDS Technology-Based Integrated Breath Gas Detection System for Breath Acetone Real-Time Accurate Detection Application. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(12):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120261
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jing, Dongxin Shi, Le Wang, Xiaolin Yu, Binghong Song, Wangxin Li, Jiankun Zhu, Yong Yang, Bingqiang Cao, and Chenyu Jiang. 2024. "CRDS Technology-Based Integrated Breath Gas Detection System for Breath Acetone Real-Time Accurate Detection Application" Chemosensors 12, no. 12: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120261
APA StyleSun, J., Shi, D., Wang, L., Yu, X., Song, B., Li, W., Zhu, J., Yang, Y., Cao, B., & Jiang, C. (2024). CRDS Technology-Based Integrated Breath Gas Detection System for Breath Acetone Real-Time Accurate Detection Application. Chemosensors, 12(12), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120261





