Sampling and Comparison of Extraction Techniques Coupled with Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) for the Analysis of Substrates Exposed to Explosives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Solvent Extraction of the Substrates
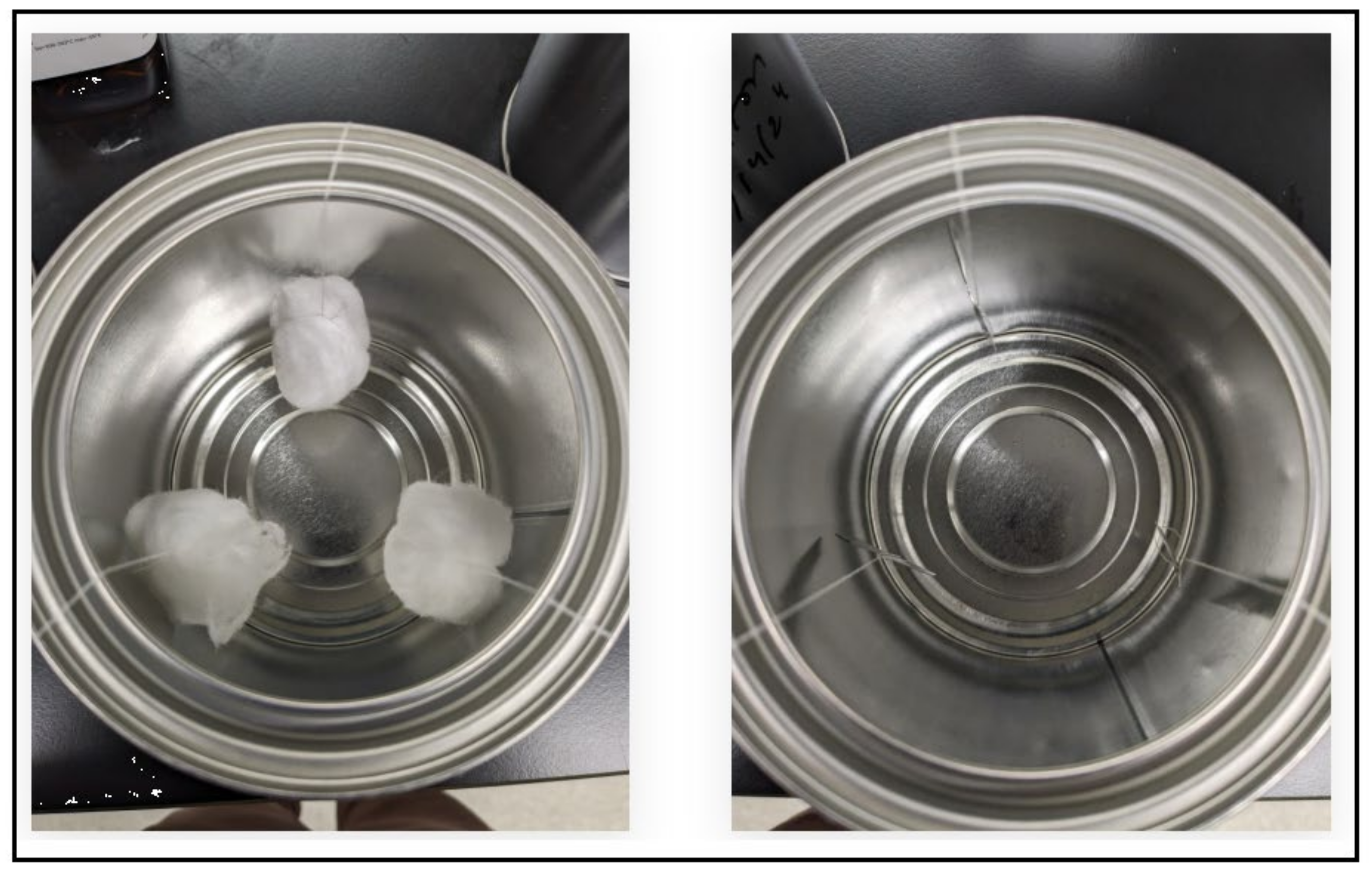
2.2.2. Swabbing of the Substrates
2.2.3. Direct SPME
2.2.4. Headspace
2.2.5. Change in Weight of the Substrate
2.3. GC-MS Parameters
2.3.1. Liquid Injection
2.3.2. Total Vaporization–Solid Phase Microextraction (TV-SPME) of the Swabs
2.3.3. Solid Phase Microextraction
2.3.4. Headspace Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
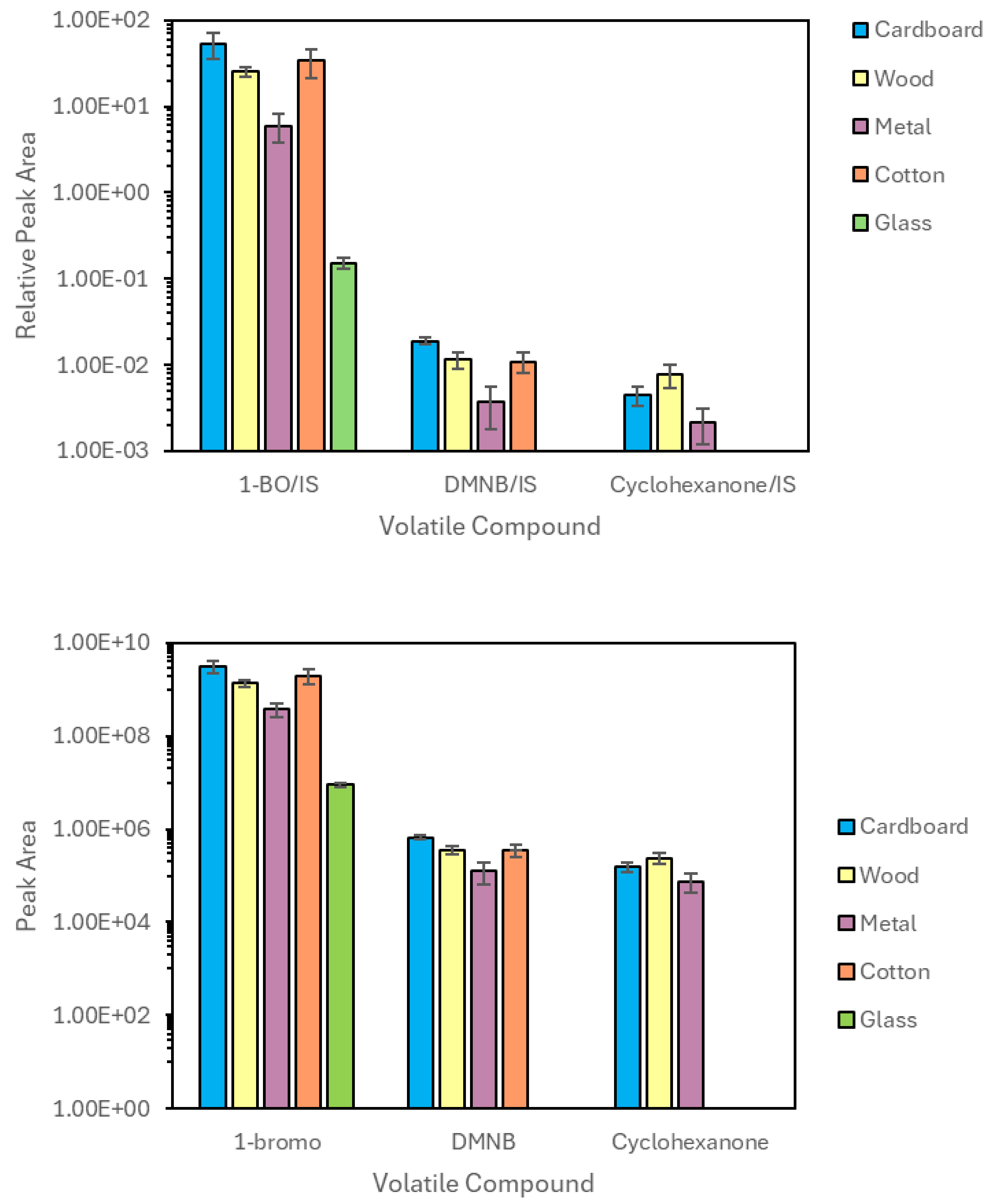
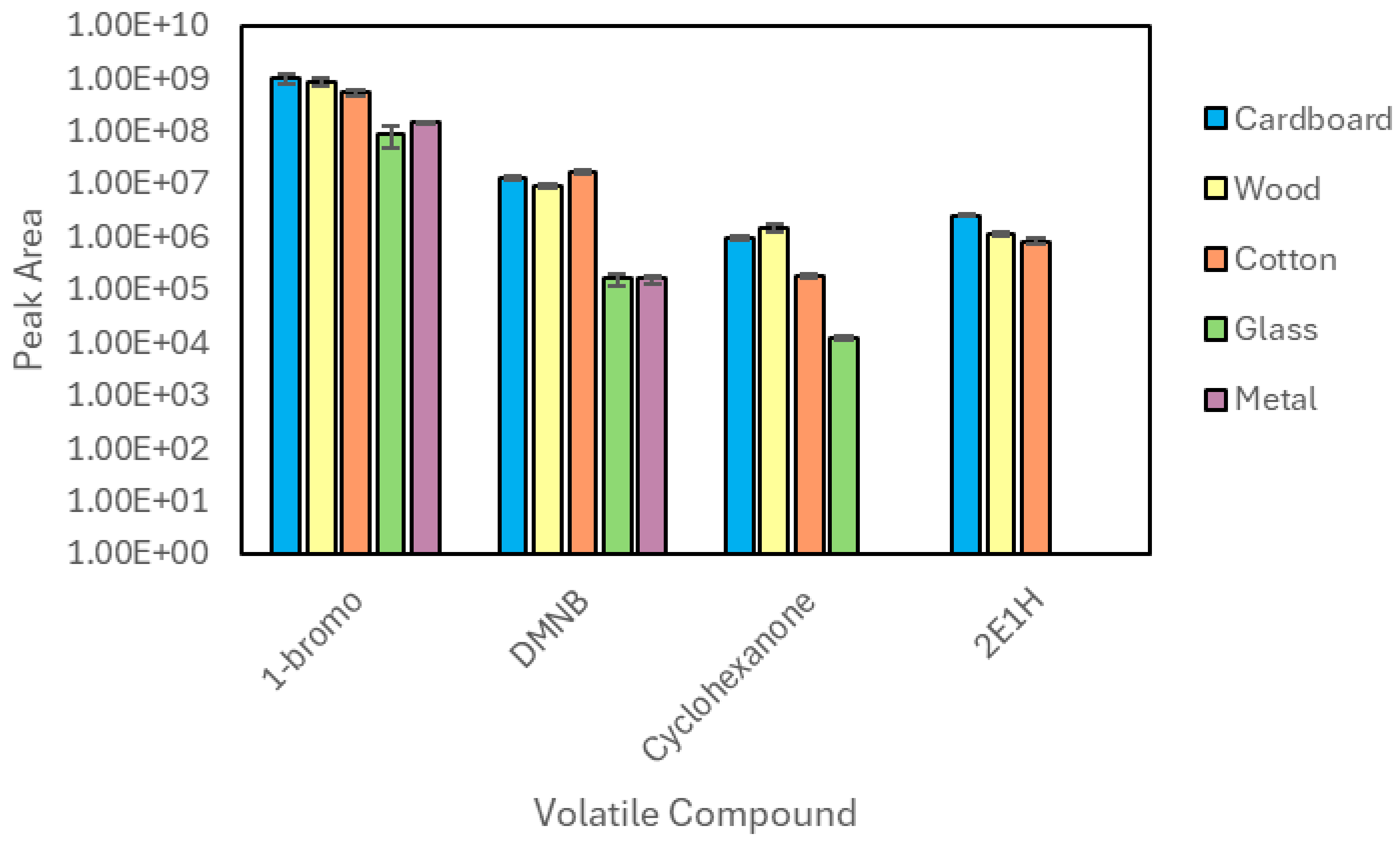
3.1. Liquid Injection
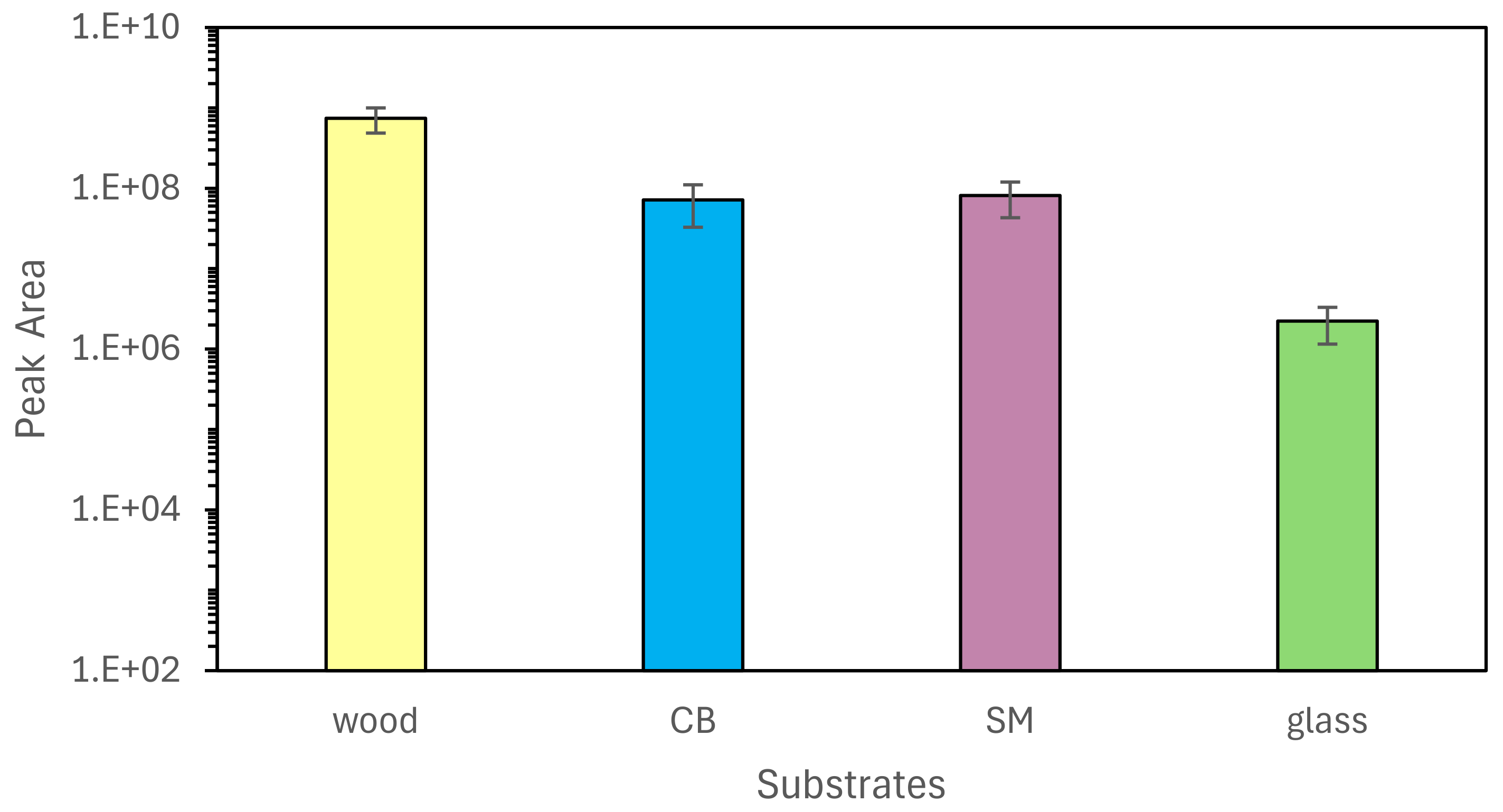
3.2. TV-SPME of Swabs
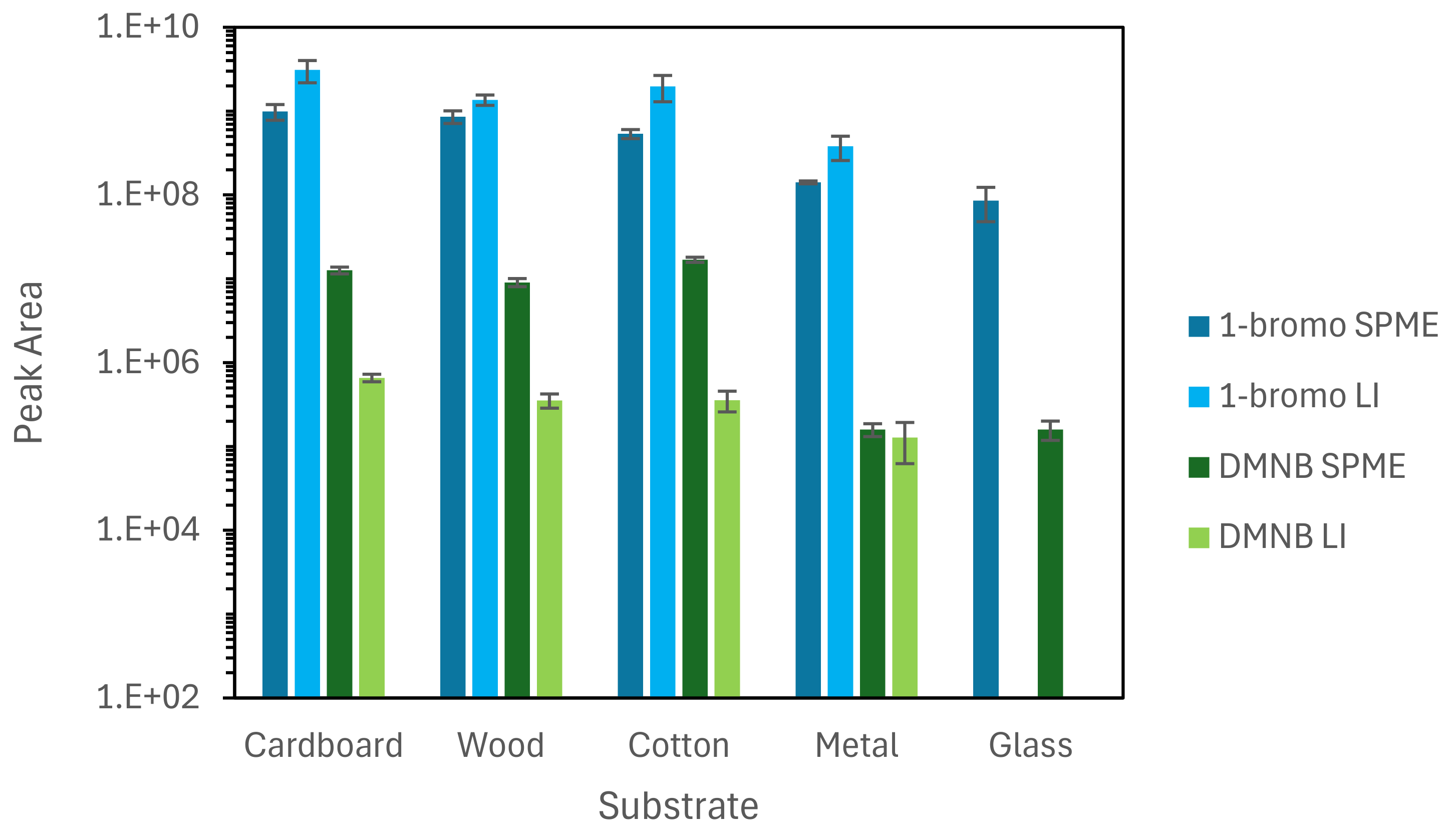
3.3. SPME
3.4. Change in Weight of the Substrate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aviles-Rosa, E.; Schultz, J.; Maughan, M.N.; Gadberry, J.D.; DiPasquale, D.M.; Farr, B.; Henderson, A.; Best, E.; Discepolo, D.R.; Buckley, P.; et al. A Canine Model to Evaluate the Effect of Exercise Intensity and Duration on Olfactory Detection Limits: The Running Nose. Front. Allergy 2024, 5, 1367669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTata, D.A.; Collins, P.A.; McKinley, A.J. A Comparison of Solvent Extract Cleanup Procedures in the Analysis of Organic Explosives. J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Goodpaster, J.V. Analysis of the Cross-Contamination of Explosive Canine Training Aids during Manufacturing and Storage. Forensic Chem. 2024, 38, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.; Oxley, J.C. Aspects of Explosives Detection; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, D.; Zach, R.; Matana, Y.; Elia, P.; Shustack, S.; Sharon, Y.; Zeiri, Y. Bomb Swab: Can Trace Explosive Particle Sampling and Detection Be Improved? Talanta 2017, 174, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnen, D.; Heuwieser, W.; Fischer-Tenhagen, C. Canine Scent Detection—Fact or Fiction? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 148, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, R.J.; Furton, K.G. Chapter 13—Biological Detection of Explosives. In Counterterrorist Detection Techniques of Explosives; Yinon, J., Ed.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 395–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, C.M.; Fahey, A.J.; Steffens, K.L.; Benner, B.A., Jr.; Lareau, R.T. Characterization of Composition C4 Explosives Using Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7237–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.L.; Almirall, J.R. Continuous Vapor Sampling of Volatile Organic Compounds Associated with Explosives Using Capillary Microextraction of Volatiles (CMV) Coupled to a Portable GC–MS. Forensic Chem. 2021, 26, 100380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, M.; Ma, C.-Y. Detection Limits for GC/MS Analysis of Organic Explosives. J. Forensic Sci. 2001, 46, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.; Benson, S.; Kelly, T.; Lennard, C. Determining the Effects of Routine Fingermark Detection Techniques on the Subsequent Recovery and Analysis of Explosive Residues on Various Substrates. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 233, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song-im, N.; Benson, S.; Lennard, C. Establishing a Universal Swabbing and Clean-up Protocol for the Combined Recovery of Organic and Inorganic Explosive Residues. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 223, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, B.D.; Otto, C.M.; Szymczak, J.E. Expert Perspectives on the Performance of Explosive Detection Canines: Operational Requirements. Animals 2021, 11, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-W.; Milam, S.J.; Tipple, C.A. Exploring the Analysis and Differentiation of Plastic Explosives by Comprehensive Multidimensional Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC × GC–MS) with a Statistical Approach. Forensic Chem. 2017, 6, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.; Sikes, J.; Prather, M. Explosive Detection Using High-Volume Vapor Sampling and Analysis by Trained Canines and Ultra-Trace Detection Equipment. In Sensors, and Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence (C3I) Technologies for Homeland Security and Homeland Defense III.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5403, pp. 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, K.; Holness, H.; Furton, K.; DeGreeff, L. Explosives Detection by Dogs. In Counterterrorist Detection Techniques of Explosives; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 47–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glackin, J.M.E.; Gillanders, R.N.; Eriksson, F.; Fjällgren, M.; Engblom, J.; Mohammed, S.; Samuel, I.D.W.; Turnbull, G.A. Explosives Detection by Swabbing for Improvised Explosive Devices. Analyst 2021, 145, 7956–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, W.D.; Strange, N.A.; Goodpaster, J.V. “Fooling Fido”—Chemical and Behavioral Studies of Pseudo-Explosive Canine Training Aids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7817–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, R.J.; Almirall, J.R.; Furton, K.G. Identification of Dominant Odor Chemicals Emanating from Explosives for Use in Developing Optimal Training Aid Combinations and Mimics for Canine Detection. Talanta 2005, 67, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Leung, A.; Magee, M.; Almirall, J.R. Identification of Volatile Chemical Signatures from Plastic Explosives by SPME-GC/MS and Detection by Ion Mobility Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2997–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaidinho, J.; Freil, L.; Kelly, T.; Marland, K.; Wu, C.; Wittenbrook, B.; Valentin, G.; Jackson, M. Mobile Collaboration for Human and Canine Police Explosive Detection Teams. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing, CSCW ’17, Portland, OR, USA, 25 February–1 March 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.; Alexis, S.; Furton, K.G.; DeGreeff, L.E. Impact of Adsorption on the Vapor Availability of Contained Explosives and Drugs. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2024, e202400115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyett, P.C.; Chew, D.; Azevedo, V.; Blennerhassett, L.C.; Rosca, C.; Tomlinson, E. Optimizing SEM-EDX for Fast, High-Quality and Non-Destructive Elemental Analysis of Glass. J. Anal. Spectrom. 2024, 39, 2565–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbury, D.E.; Ritchie, N.W.M. Performing Elemental Microanalysis with High Accuracy and High Precision by Scanning Electron Microscopy/Silicon Drift Detector Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometry (SEM/SDD-EDS). J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 493–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyele, J.O.; Folorunsho, A.B. The Use of SEM/EDX Analysis to Investigate the Pore Effect on the Mechanical Properties of Some Selected Tropical Hardwoods. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2021, 56, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, T.; Kurimoto, Y.; Yamauchi, S. A Method for Visualizing Cesium Ions Adsorbed on Wood Charcoal Using SEM–EDX. Wood Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, W.; Kitts, K.; Strange, N.; Cummins, J.; Lotspeich, E.; Goodpaster, J. On the Smell of Composition C-4. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 236, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauzier, G.; Bors, D.; Ash, J.; Goodpaster, J.V.; Lewis, S.W. Optimisation of Recovery Protocols for Double-Base Smokeless Powder Residues Analysed by Total Vaporisation (TV) SPME/GC-MS. Talanta 2016, 158, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szomborg, K.; Jongekrijg, F.; Gilchrist, E.; Webb, T.; Wood, D.; Barron, L. Residues from Low-Order Energetic Materials: The Comparative Performance of a Range of Sampling Approaches Prior to Analysis by Ion Chromatography. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 233, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolla, P.; Hohenstatt, P. Stability of Explosives Traces on Different Supports. Forensic Sci. Int. 1993, 60, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furton, K.G.; Myers, L.J. The Scientific Foundation and Efficacy of the Use of Canines as Chemical Detectors for explosives. Invited Paper for the Special Issue of Talanta ‘Methods for Explosive Analysis and Detection’. Talanta 2001, 54, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodfin, R.L. Trace Chemical Sensing of Explosives; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, T.-H.; Mendum, T.; Geurtsen, G.; Kelley, J.; Ostrinskaya, A.; Kunz, R. Use of Mass Spectrometric Vapor Analysis to Improve Canine Explosive Detection Efficiency. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6482–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štejfa, V.; Kadlecová, K.; Růžička, K.; Fulem, M. Vapor Pressure and ThermophysicalProperties of Explosive Taggants. Chem. Thermodyn. Therm. Anal. 2021, 3–4, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Upadhyaya, H.; Hecker, A.J.; Goodpaster, J.V. Sampling and Comparison of Extraction Techniques Coupled with Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) for the Analysis of Substrates Exposed to Explosives. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120251
Upadhyaya H, Hecker AJ, Goodpaster JV. Sampling and Comparison of Extraction Techniques Coupled with Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) for the Analysis of Substrates Exposed to Explosives. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(12):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120251
Chicago/Turabian StyleUpadhyaya, Himanshi, Alexis J. Hecker, and John V. Goodpaster. 2024. "Sampling and Comparison of Extraction Techniques Coupled with Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) for the Analysis of Substrates Exposed to Explosives" Chemosensors 12, no. 12: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120251
APA StyleUpadhyaya, H., Hecker, A. J., & Goodpaster, J. V. (2024). Sampling and Comparison of Extraction Techniques Coupled with Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) for the Analysis of Substrates Exposed to Explosives. Chemosensors, 12(12), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120251




