Flexible Humidity Sensor Based on Chemically Reduced Graphene Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. GO Synthesis and Characterization
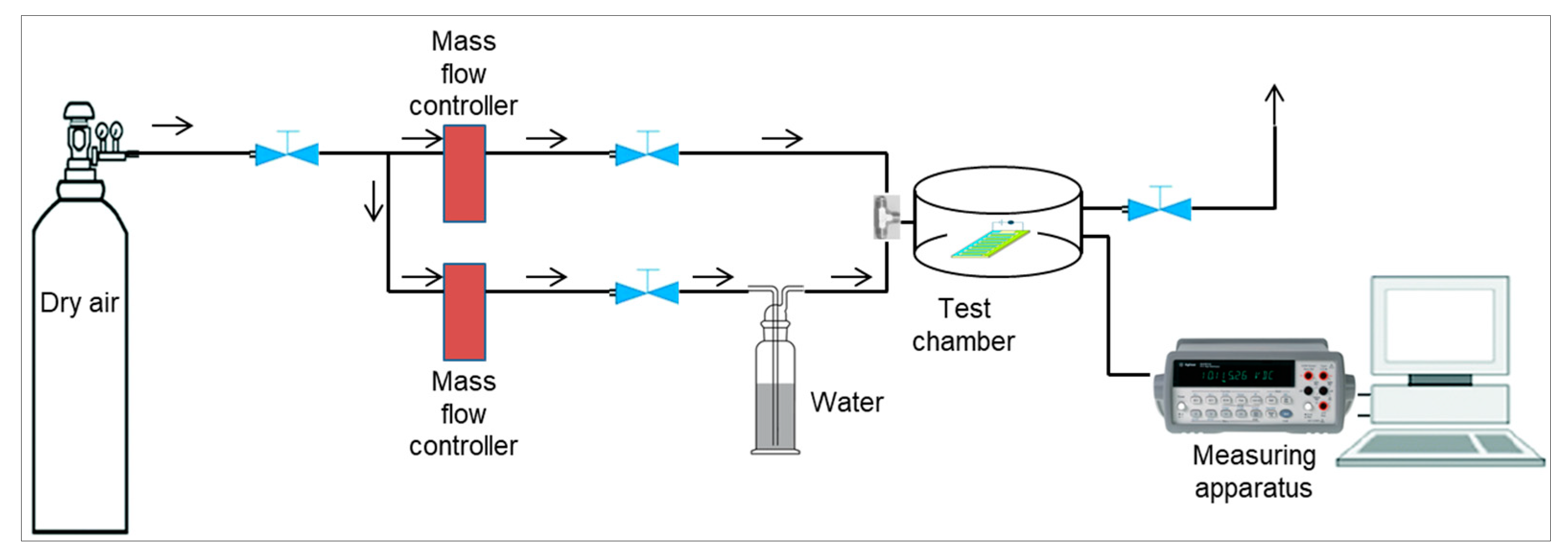
2.2. Chemiresistive Device Fabrication and Experimental Setup for Gas Sensing Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
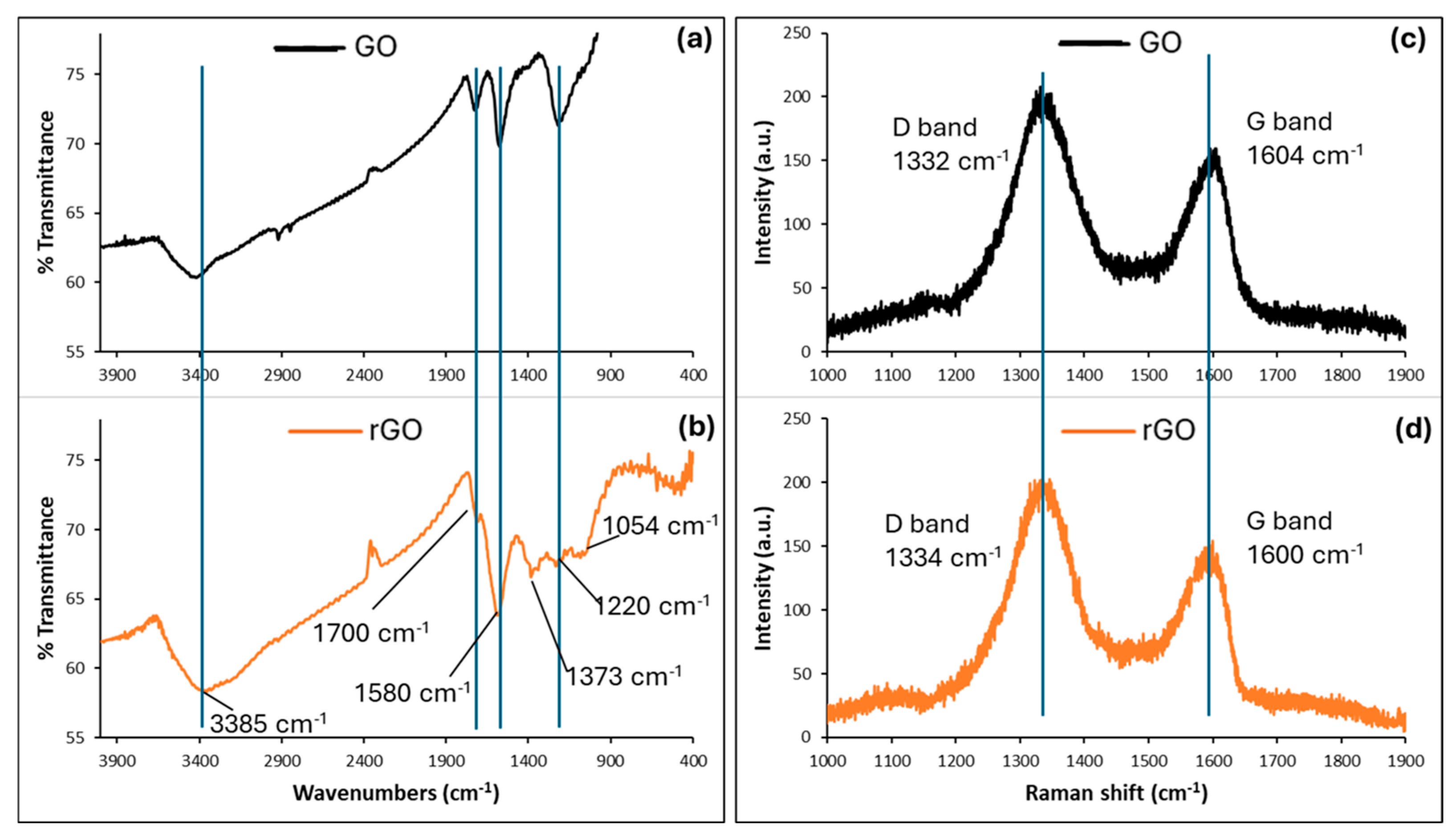
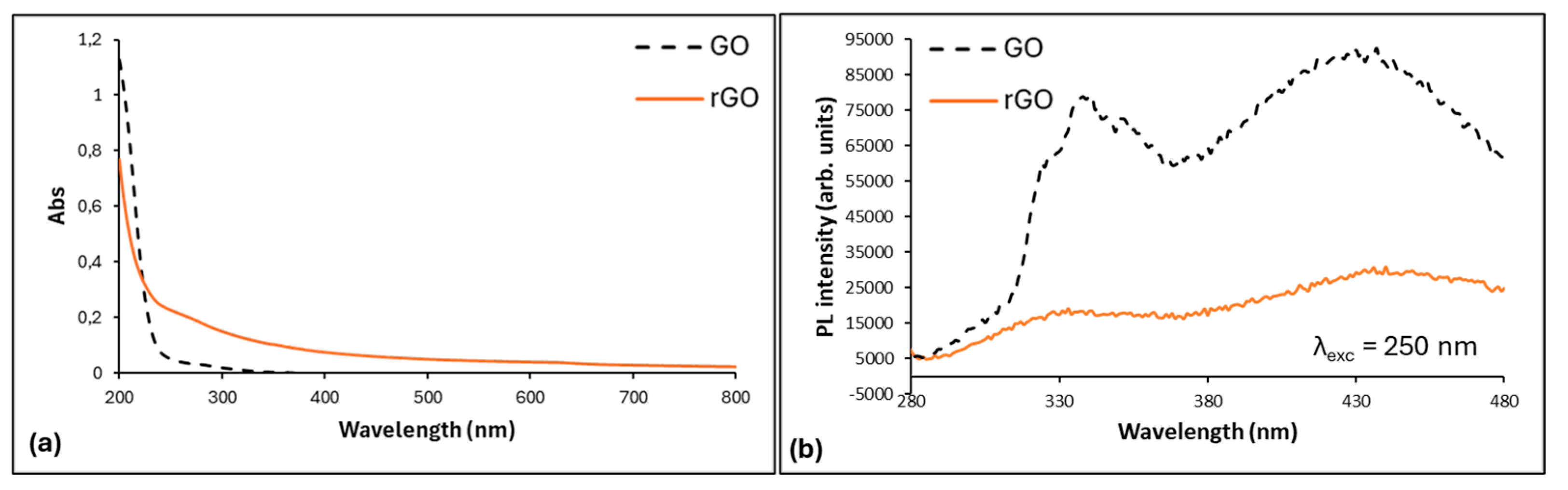
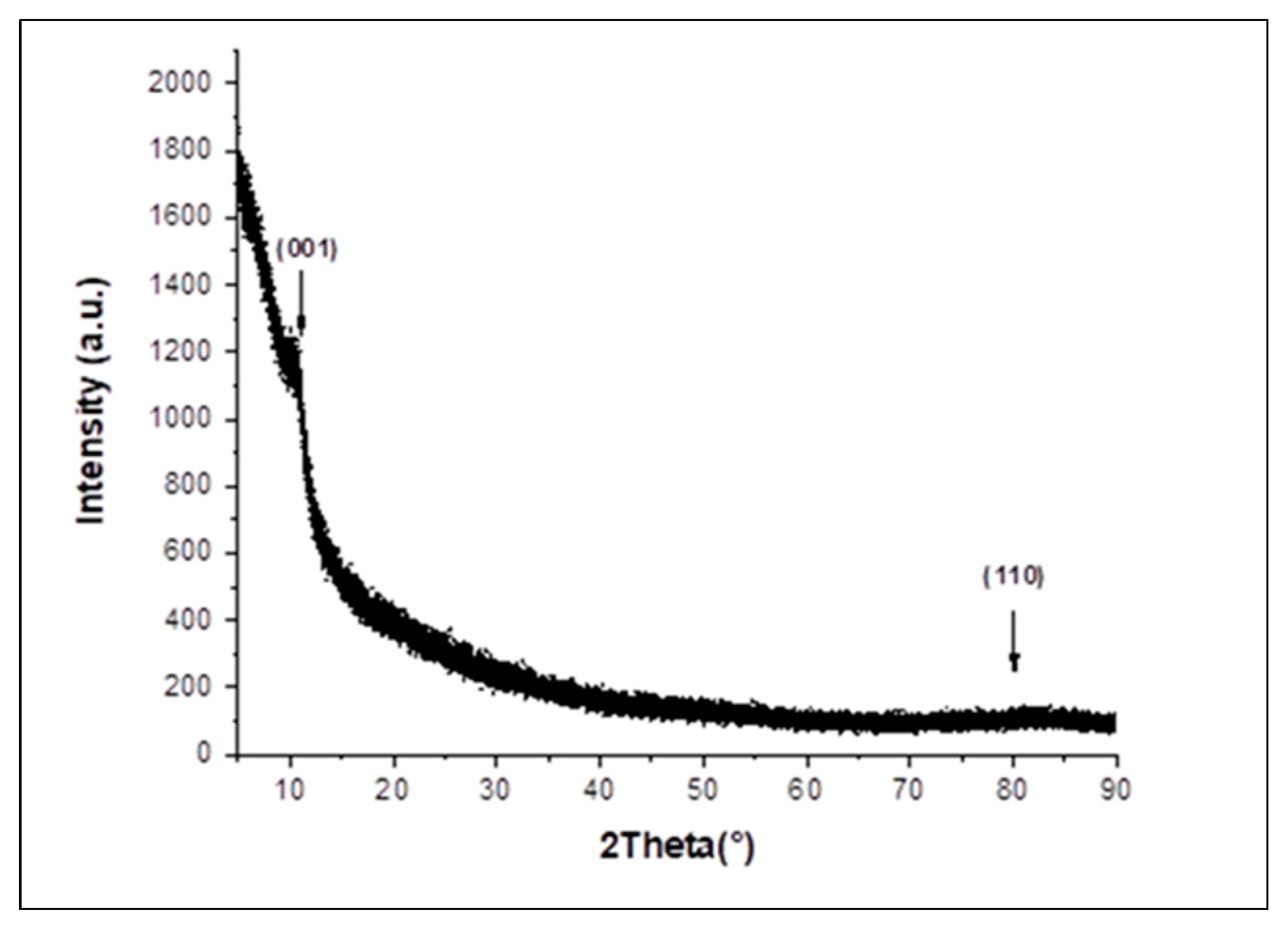
3.1. Material Characterization
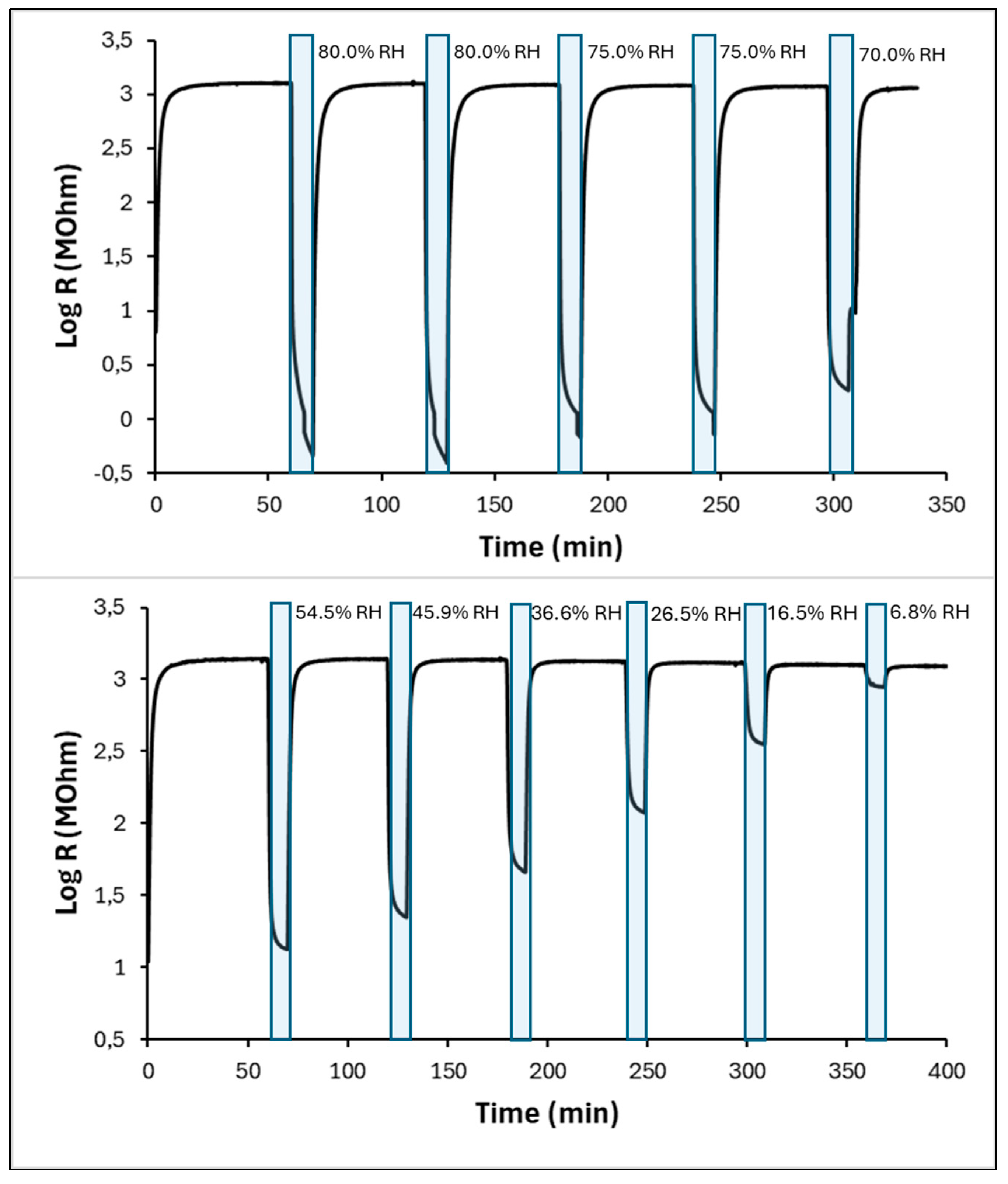
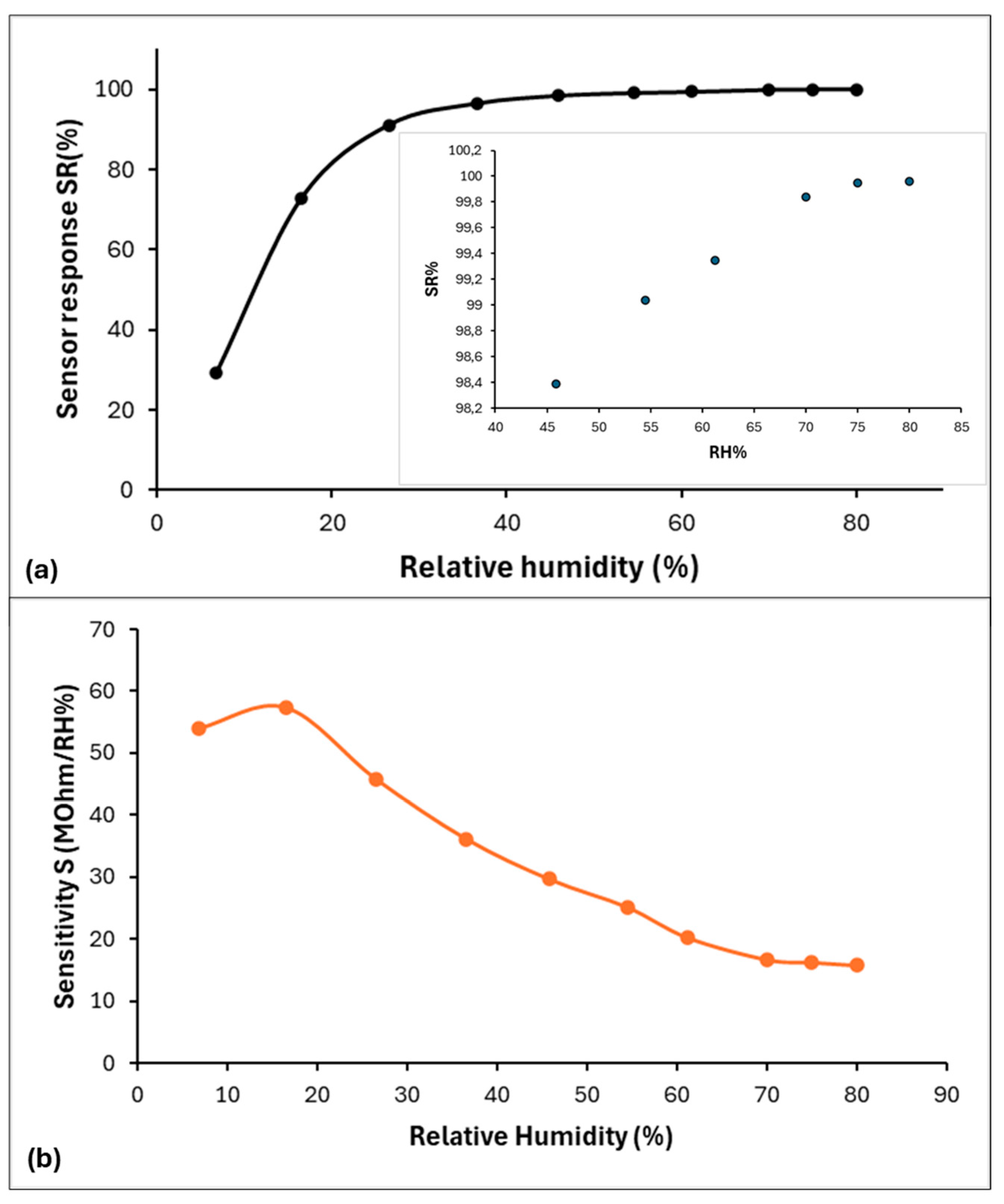
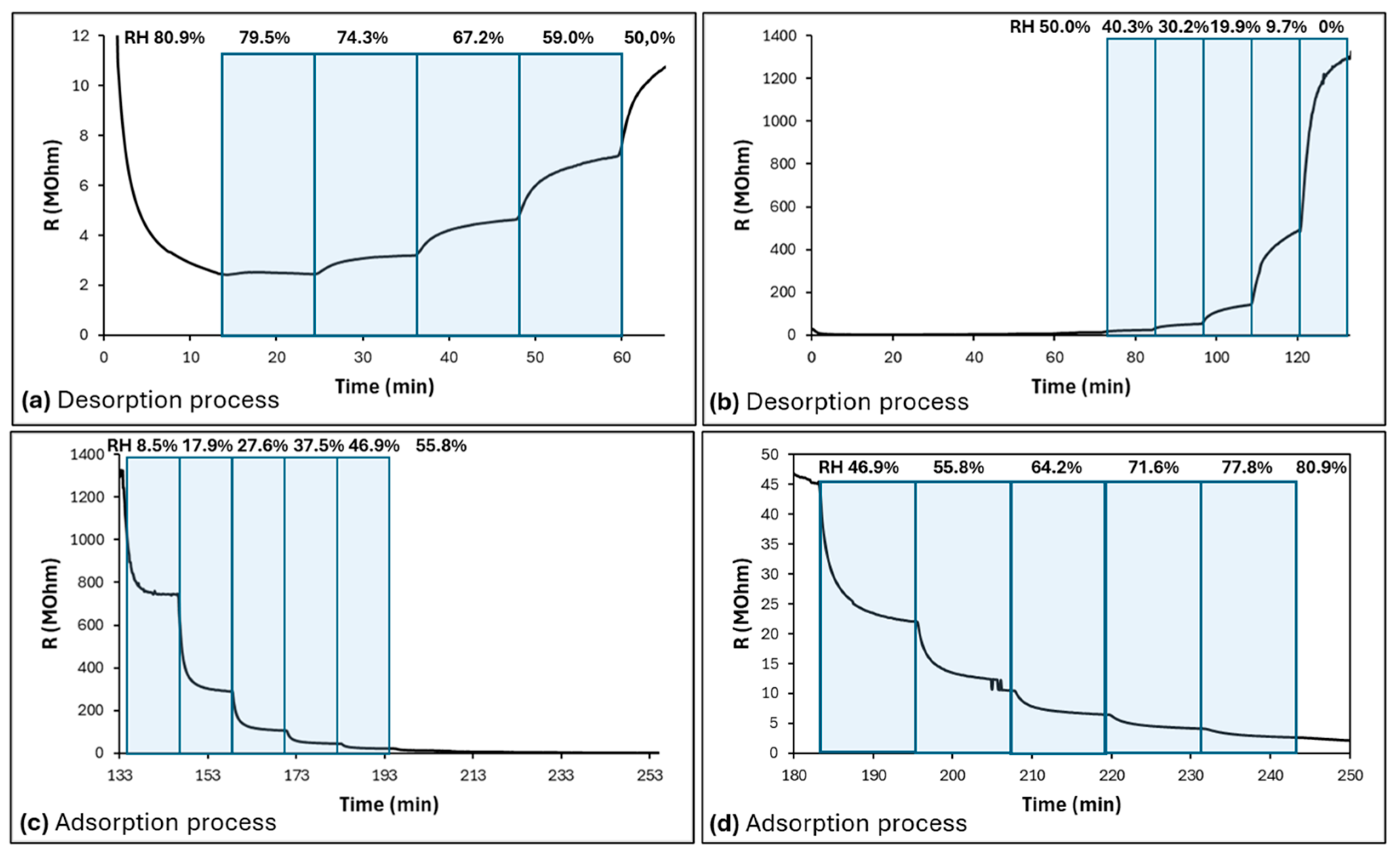
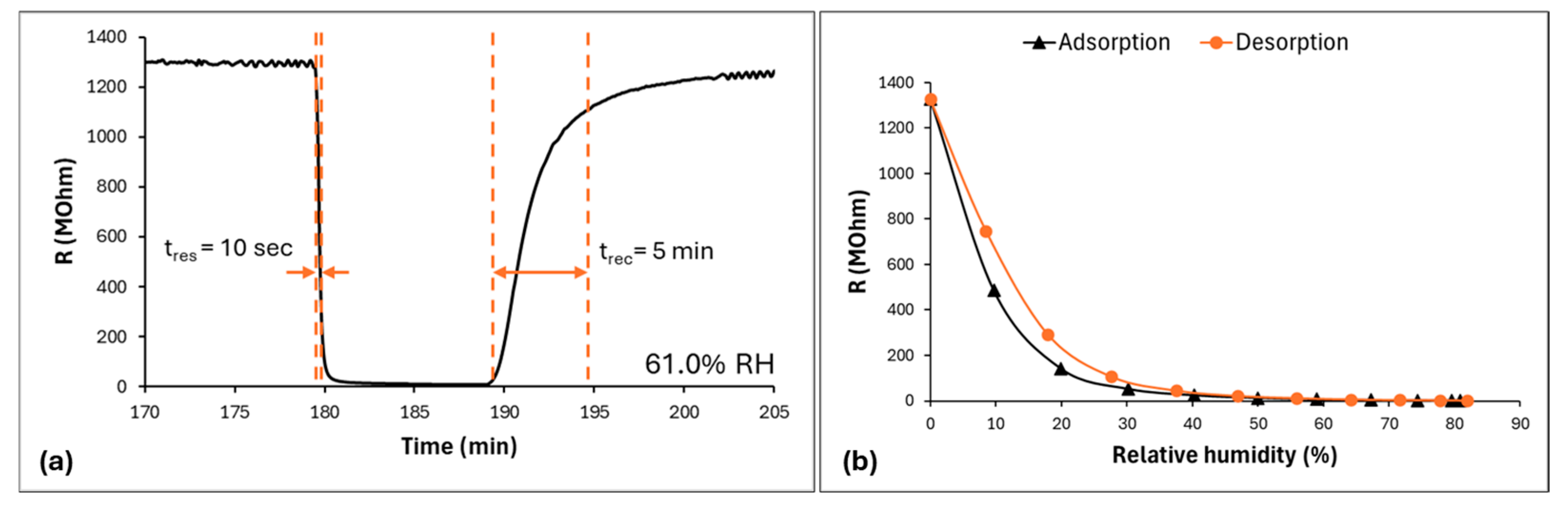
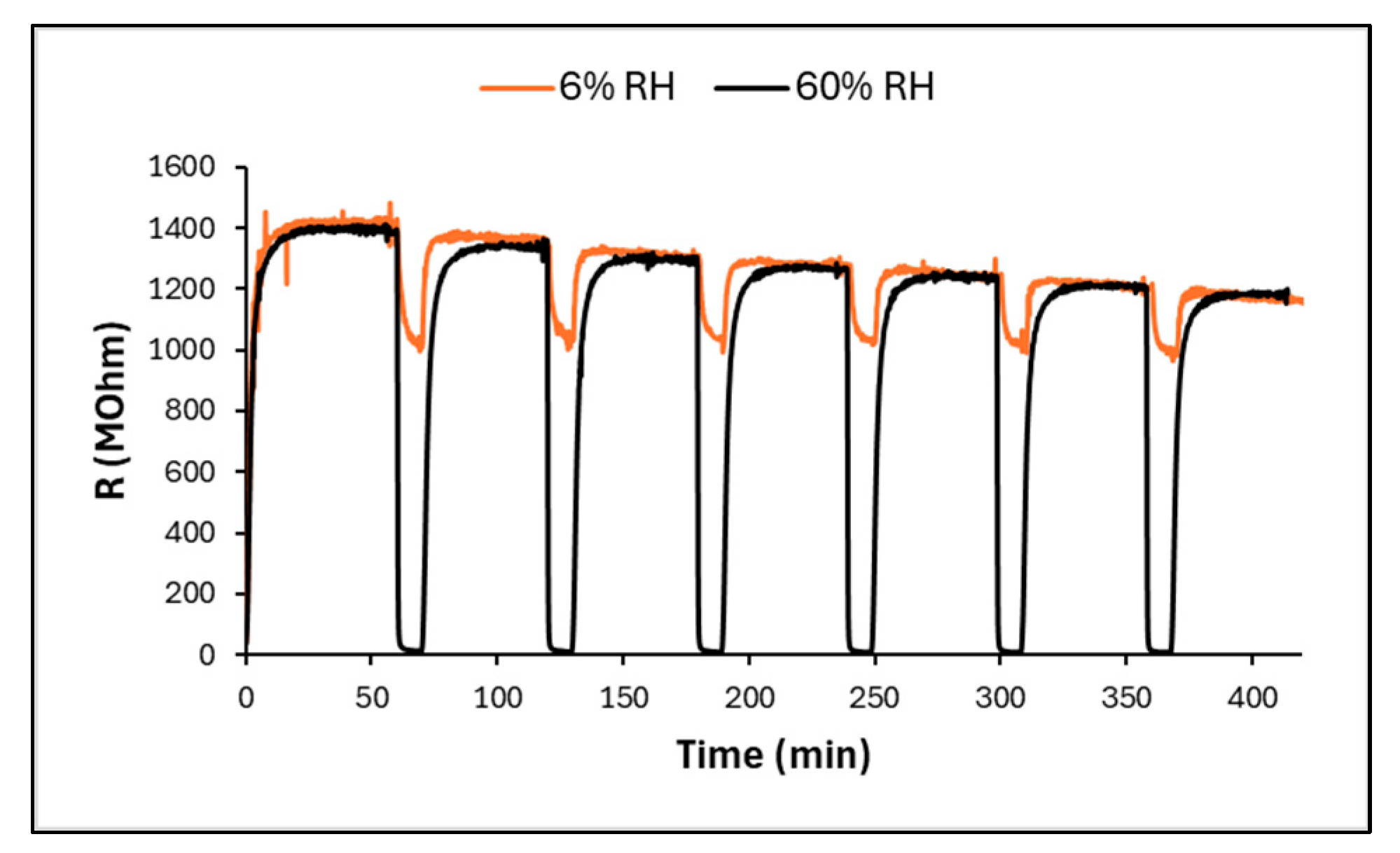
3.2. Sensing Properties and Mechanism Discussion
3.3. Sensitivity Toward Volatile Organic Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delipinar, T.; Shafique, A.; Goahr, M.S.; Yapici, M.K. Fabrication and materials integration of flexible humidity sensors for emerging applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 8744–8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, D.; Wang, M.; Tang, M.; Song, X.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Q. Recent progress of diversiform humidity sensors based on versatile nanomaterials and their prospective applications. Nano Res. 2022, 16, 11938–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, R.A.; Tamim, A.M.; Hwang, G.T.; Jeong, C.K. Humidity sensors using 2D and 3D nanmoaterials: From materials selection to technological aspects. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2024, 25, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, F.; Coudert, F.X.; Bocquet, M.L. Structure and chemistry of graphene oxide in liquid water from first principles. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.; Dikin, D.; Park, S.; Cai, W.; Mielke, S.L.; Ruoff, R.S. Effect of water vapor on electrical properties of individual reduced graphene oxide sheets. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 20264–20268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Tao, X.; Feng, B.; Yu, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, S.; Luo, J. A humidity sensor based on quartz crystal microbalance using graphene oxide as a sensitive layer. Vacuum 2017, 140, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Li, N. Investigation of the stability of QCM humidity sensor using graphene oxide as sensing films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, H.; Wu, Z. Graphene oxide thin film coated quartz crystal microbalance for humidity detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7778–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; He, M.; Meng, N.; He, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Shi, T.; Hasan, T.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Y.; et al. Fast response and high sensitivity ZnO/glass surface scoustic wave humidity sensors using graphene oxide sensing layer. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balashov, S.M.; Balachova, O.V.; Filho, A.P.; Bazetto, M.C.Q.; de Almeida, M.G. Surface acoustic wave humidity sensors based on graphene oxide thin films deposited with the surface acoustic wave atomizer. ECS Trans. 2012, 49, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Yin, K.; Xie, X.; Ji, J.; Wan, S.; Sun, L.; Terrones, M.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Ultrahigh humidity sensitivity of graphene oxide. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, X. Humidity sensing behaviors of graphene oxide-silicon bi-layer flexible structure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.J. Nanoarchitectonics of high-sensitivity humidity sensors based on graphene oxide films for respiratory monitoring. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 144, 110970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Lv, C.; Aoyagi, E.; Ogawa, S.; Watanabe, A. Laser direct writing of a high-performance all-graphene humidity sensor working in a novel sensing mode for portable electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 23987–23996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, N.; Su, T.; Wang, L.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Su, J.; Gao, Y. Self-powered graphene oxide humidity sensor based on potentiometric humidity transduction mechanism. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Pan, Q.; Huang, Z.; Gu, C.; Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, F.; Li, P.; Tu, Y.; et al. Ultrafast response of self-powered humidity sensor of flexible graphene oxide film. Mater. Des. 2023, 226, 111683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharie-Butucel, D.; Digianantonio, L.; Leordean, C.; Ressier, L.; Astilean, S.; Farcau, C. Flexible transparent sensors from reduced graphene oxide microstripes fabricated by convective self-assembly. Carbon 2017, 113, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Chung, G.S. Effects of rapid thermal annealing on humidity sensor based on graphene oxide thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril, H.A.; Mao, J.; Liu, Z.; Stoltenberg, R.M.; Bao, Z.; Chen, Y. Evaluation of solution-processed reduced graphene oxide films as transparent conductors. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laera, A.M.; Penza, M. Chemiresistive materials for alcohol vapor sensing at room temperature. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, C.K.; Pumera, M. Reduction of graphene oxide with substituted borohydrides. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Cui, X.; Lin, Y. Synthesis of graphene nanosheets via oxalic acid-induced chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Chen, F.; Tang, C.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, H.; Fu, Q. The preparation of high performance and conductive poly (vinyl alcohol)/graphene nanocomposite via reducing graphite oxide with sodium hydrosulfite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Peng, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F. Deoxygenation of exfoliated graphite oxide under alkaline conditions: A green route to graphene preparation. Adv. Mat. 2008, 20, 4490–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laera, A.M.; Cassano, G.; Burresi, E.; Protopapa, M.L.; Penza, M. A graphene oxide flexible sensor for humidity detection. Eng. Proc. 2023, 48, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphene oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, W.M.; Morsy, M.; Nada, N.A.; Ibrahim, M. Studying the humidity sensing behavior of MWCNTs boosted with Co3O4 nanorods. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 121, 108754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Q.; Wang, C.; Kim, N.Y. High-sensitivity and low-hysteresis porous MIM-type capacitive humidity sensor using functional polymer mixed with TiO2 microparticles. Sensors 2017, 17, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tai, H. Electrospun nanofiber-based humidity sensors: Materials, devices, and emerging applications. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2024, 12, 27157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudin, K.N.; Ozbas, B.; Schniepp, H.C.; Prud’Homme, R.K.; Aksay, I.A.; Car, R. Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, K.K.; Benayad, A.; Yoon, S.M.; Park, H.K.; Jung, I.S.; Jin, M.H.; Jeong, H.K.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, J.Y. Efficient reduction of graphite oxide by sodium borohydride and its effect on electrical conductance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yue, W.; Huang, D.; Chen, C.; Lin, H.; Yang, X. A facile green strategy for rapid reduction of graphene oxide by metallic zinc. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8827–8832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.A.; Xian, L.; Chou, M.Y. Structural and electronic properties of oxidized graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 086802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.T.; Li, S.S.; Lai, W.J.; Yeh, Y.C.; Chen, H.A.; Chen, I.S.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, K.H.; Nemoto, T.; Isoda, S.; et al. Tunable photoluminescence from graphene oxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6662–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Lin, Y.Y.; Mattevi, C.; Yamaguchi, H.; Chen, H.A.; Chen, I.S.; Chen, C.W.; Chhowalla, M. Blue photoluminescence from chemically derived graphene oxide. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerveny, S.; Barroso-Bujans, F.; Alegria, A.; Colmenero, J. Dynamics of water intercalated in graphite oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Singh, N.; Song, L.; Liu, Z.; Reddy, A.L.M.; Ci, L.; Vajtai, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, B.; Ajayan, P.M. Direct laser writing of micro-supercapacitors on hydrated graphite oxide films. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, R.; Kumar, R. Reactive events at the graphene oxide-water interface. Chem. Comm. 2021, 57, 11697–11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.D.; Elgammal, K.; Niklaus, F.; Delin, A.; Fischer, A.C.; Vaziri, S.; Forsberg, F.; Rasander, M.; Hugosson, H.; Bergqvist, L.; et al. Resistive graphene humidity sensors with rapid and direct electrical readout. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, M.; Salehi, A.; Vollebregt, S. Effect of humidity on gas sensing performance of carbon nanotube gas sensors operated at room temperature. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 5763–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, P.; Tiwary, P.; Chakraborty, A.K.; Mahapatra, R.; Thakur, A.D. Graphene oxide based free-standing films for humidity and hydrogen peroxide sensing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 15946–15956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jiang, H.B.; Shao, R.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xie, S.Y.; Wang, J.N.; Li, X.B.; Jiang, F.; Chen, Q.D.; Zhang, T.; et al. Two-beam-laser interference mediated reduction, patterning and nanostructuring of graphene oxide for the production of a flexible humidity sensing device. Carbon 2012, 50, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Chen, W.; Yan, L. Free-standing dried foam films of graphene oxide for humiditysensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.G.; Chiou, C.F. Electrical and humidity-sensing properties of reduced graphene oxidethin film fabricated by layer-by-layer with covalent anchoring onflexible substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 200, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.U.; Choi, B.I.; Kim, J.C.; Woo, S.B.; Kim, Y.G.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.W. Correlation between the sensitivity and the hysteresis of humidity sensors based on graphene oxides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| GO Reduction Method | Measured Property | Sensor Response or Sensitivity | Response/Recovery Time | Sensing Range | Hysteresis | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline treatment | Resistance | (Rdry − Rwet)/ Rdry × 100 99.7% (80% RH) | 10/300 s | 10–80% RH | 8.8% | This work |
| Not Reduced | Resistance | (R40%RH − R)/R40%RH × 100 96.3% (80% RH) | Not given | 40–80% RH | Not given | [13] |
| UV lamp irradiation | Resistance | Rdry/Rwet 15.0 (90% RH) | 2.3/0.6 s | 26–90% RH | Not given | [42] |
| Two-beam-laser interference | Impedance | Not give | 3/10 s | 11–95% RH | 6.0% | [43] |
| Not reduced | Impedance | (Zwet1 − Zwet2)/(RH2 − RH1) 33.3% | 50/79 s | 11–95% RH | Not given | [44] |
| NaBH4 | Impedance | logZ/%RH −0.0423 | 28/48 s | 30–90% RH | 2.5% | [45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laera, A.M.; Cassano, G.; Burresi, E.; Protopapa, M.L.; Penza, M. Flexible Humidity Sensor Based on Chemically Reduced Graphene Oxide. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120245
Laera AM, Cassano G, Burresi E, Protopapa ML, Penza M. Flexible Humidity Sensor Based on Chemically Reduced Graphene Oxide. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(12):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120245
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaera, Anna Maria, Gennaro Cassano, Emiliano Burresi, Maria Lucia Protopapa, and Michele Penza. 2024. "Flexible Humidity Sensor Based on Chemically Reduced Graphene Oxide" Chemosensors 12, no. 12: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120245
APA StyleLaera, A. M., Cassano, G., Burresi, E., Protopapa, M. L., & Penza, M. (2024). Flexible Humidity Sensor Based on Chemically Reduced Graphene Oxide. Chemosensors, 12(12), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12120245






