WO3-LaFeO3 Nanocomposites for Highly Sensitive Detection of Acetone Vapor at Low Operating Temperatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Sensing Materials
2.2. Characterization of Sensing Materials
2.3. Fabrication and Measurement of Sensing Elements
3. Results and Discussion
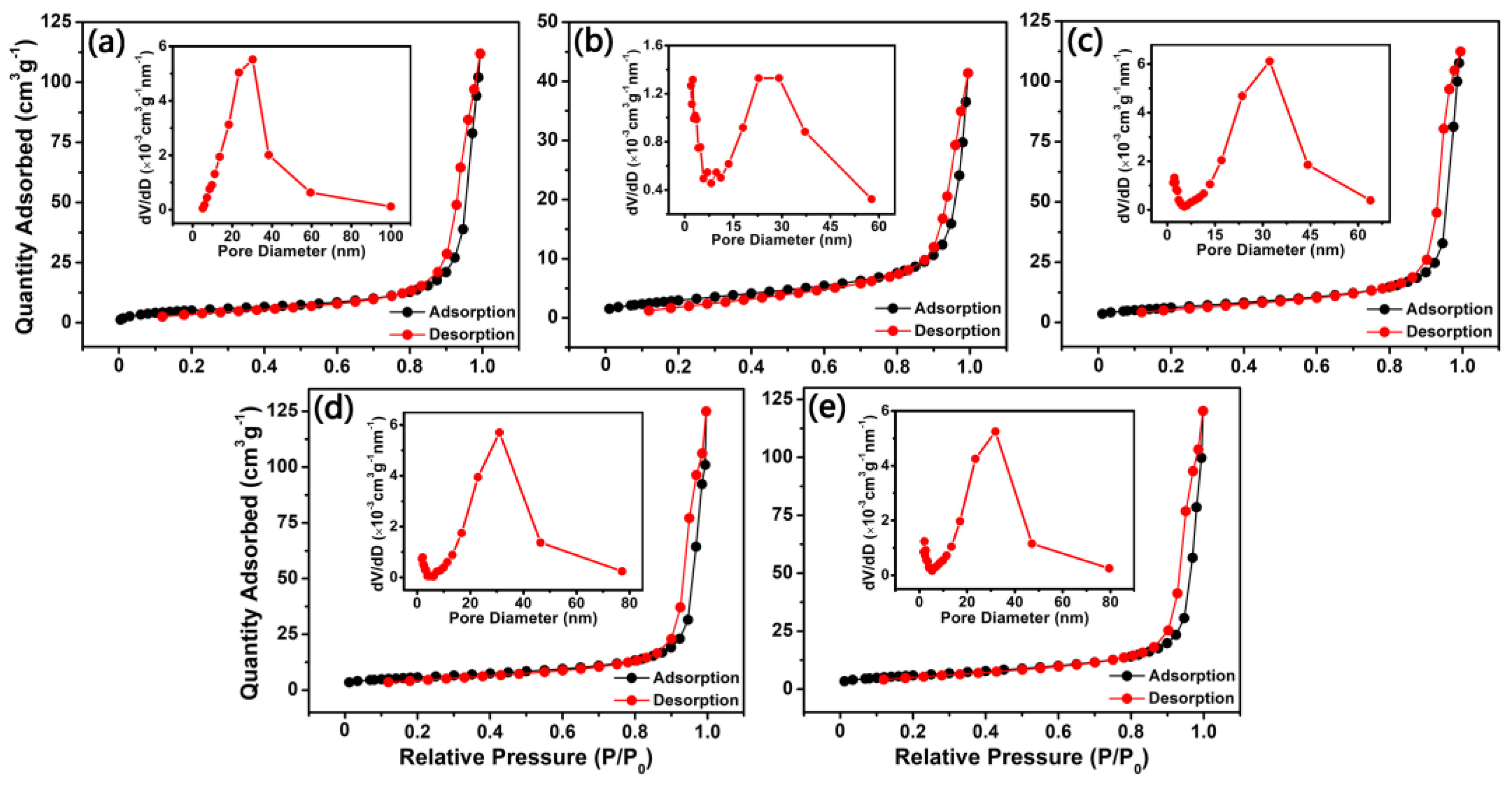
3.1. Characterization of Sensing Materials
3.2. Acetone Sensing Performance
3.3. Sensing Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howard, W.L. Acetone. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Righettoni, M.; Amann, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Breath analysis by nanostructured metal oxides as chemo-resistive gas sensors. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Miao, T.; Cheng, B.; Qin, H.; Hu, J. High performance of p-p heterojunction LaFeO3/YFeO3 planar electrode sensor for volatile organic compounds under multi-wavelength light illumination. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2023, 162, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, H.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Hu, J. Acetone sensing properties and mechanism of nano-LaFeO3 thick-films. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 235, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, H.; Han, D.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Q. Preparation of biomorphic porous LaFeO3 by sorghum straw biotemplate method and its acetone sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 196, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Sun, P.; Chuai, X.; Lu, G. Gas sensing with yolk-shell LaFeO3 microspheres prepared by facile hydrothermal synthesis. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 258, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Xue, C.; Song, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Preparation of porous LaFeO3 microspheres and their gas-sensing property. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 337, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Ruan, S.; Yin, Y.; Li, F.; Wen, S.; Chen, Y. Self-sacrificial template-driven LaFeO3/α-Fe2O3 porous nano-octahedrons for acetone sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 4671–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yu, Z.; Nie, Z.; Cao, E. Constructing p–p heterojunction with PANI to improve the acetone sensing performance of LaFeO3 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Meng, F.; Gong, X.; Tao, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, F.; Yan, X.; Sun, P.; Lu, G. A solution to boost acetone sensing performance of perovskite oxides chemiresistors: In-situ derived p-p heterostructures. Sens. Actuators B 2023, 378, 133092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, R.; Ibni Khursheed, A.; Song, J.; Sun, L.; Yu, Z.; Nie, Z.; Cao, E. A comparative study on the acetone sensing properties of ZnO disk pairs, flowers, and walnuts prepared by hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 591, 153218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murade, P.A.; Sangawar, V.S.; Chaudhari, G.N.; Kapse, V.D.; Bajpeyee, A.U. Acetone gas-sensing performance of Sr-doped nanostructured LaFeO3 semiconductor prepared by citrate sol-gel route. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Lin, Z.; Song, P.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Q. Hydrothermal preparation and acetone-sensing properties of Ni-doped porous LaFeO3 microspheres. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 6679–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, M.; Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Zi, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Duan, L.; et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of porous and hollow α-Fe2O3/LaFeO3 nanostructures for acetone gas sensing as well as photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 215601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Xiong, X.; Guan, W.; Long, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Self-templated flower-like WO3-In2O3 hollow microspheres for conductometric acetone sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2022, 361, 131705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, H.; Lu, H.; Li, G.; Gao, J.; Yang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; He, Z. Porous bimetallic Mo-W oxide nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning with enhanced acetone sensing performances. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 779, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, H.; Yan, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, G.; Gao, J.; Yin, F.; Wang, C. Fabrication of conductive graphene oxide-WO3 composite nanofibers by electrospinning and their enhanced acetone gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 264, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.; Qin, Y.; Cui, T.; Sun, L.; Hao, W.; Zhang, Y. Influence of Na doping on the magnetic properties of LaFeO3 powders and dielectric properties of LaFeO3 ceramics prepared by citric sol-gel method. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 7922–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Cao, E.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, W.; Sun, L.; Peng, H. The influence of nonstoichiometry on electrical transport and ethanol sensing characteristics for nanocrystalline LaFexO3−δ sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 230, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Song, P.; Wang, Q. Enhanced acetone sensing performance of an α-Fe2O3-In2O3 heterostructure nanocomposite sensor. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 120, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yu, Z.; Nie, Z. Hydrothermal synthesis of cubic-rhombohedral-In2O3 microspheres with superior acetone sensing performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 613, 156045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullica, D.F.; Lok, C.K.C.; Perkins, H.O.; Young, V. X-ray Photoelectron Final-state Screening in La(OH)3: A multiplet Structural Analysis. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 4039–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunding, M.F.; Hadidi, K.; Diplas, S.; Løvvik, O.M.; Norby, T.E.; Gunnæs, A.E. XPS characterisation of in situ treated lanthanum oxide and hydroxide using tailored charge referencing and peak fitting procedures. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2011, 184, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.; Wu, A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, W.; Sun, L. Enhanced ethanol sensing performance of Au and Cl comodified LaFeO3 nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.; Yang, Y.; Cui, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, W.; Sun, L.; Peng, H.; Deng, X. Effect of synthesis route on electrical and ethanol sensing characteristics for LaFeO3-δ nanoparticles by citric sol-gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 393, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cao, E.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Sun, B.; Yu, Z. La and Fe co-doped walnut-like cubic-rhombohedral-In2O3 for highly sensitive and selective detection of acetone vapor. Mater. Lett. 2023, 336, 133869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelis, B.A.D.; Schiavello, M. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of nonstoichiometric tungsten oxides. J. Solid State Chem. 1977, 21, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Jang, Y.S.; Yang, N.H.; Yuan, L.; Pang, S.J. XPS and XRD study of the electrochromic mechanism of WOx films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 99, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teresa, J.M.D.; Dorr, K.; Muller, K.H.; Schultz, L. Strong influence of the Mn3+ content on the binding energy of the lattice polarons in manganese perovskites. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, R5928–R5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.D.; Cai, Q.; Yang, J.; Kim, M.; Yelon, W.B.; James, W.J.; Shin, Y.W.; Scarfino, B.J.; Anderson, H.U. Coupled electrical and magnetic properties in (La,Sr)FeO3−δ. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 10C314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.; Chu, Z.; Wang, H.; Hao, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y. Effect of film thickness on the electrical and ethanol sensing characteristics of LaFeO3 nanoparticle-based thick film sensors. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 7180–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemufulwi, M.I.; Swart, H.C.; Shingange, K.; Mhlongo, G.H. ZnO/ZnFe2O4 heterostructure for conductometric acetone gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2023, 377, 133027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Gao, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, T. Design of WO3-SnO2 core-shell nanofibers and their enhanced gas sensing performance based on different work function. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 442, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhu, P.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Li, J.; Liang, T.; Xie, T. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation activity via a stable perovskite-type LaFeO3/In2S3 Z-scheme heterostructured photocatalyst: Unobstructed photoexcited charge behavior of Z-scheme photocatalytic system exploration. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 901, 163628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Lázaro, J.P.; López-Urías, F.; Muñoz-Sandoval, E.; Courel-Piedrahita, M.; Carreon-Alvarez, A.; Rodríguez-Betancourtt, V.M.; Zamudio-Torres, I.; Guillén-López, E.S.; Palafox-Corona, A. Evaluation of MgCo2O4 Nanoparticles as a Gas Sensor for the Detection of Acetone in the Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Range. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2022, 19, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-R. Handbook of Bond Dissociation Energies in Organic Compounds; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, V.; Roshan, H.; Mirzaei, A.; Neri, G.; Ayesh, A.I. Nanostructured Metal Oxide-Based Acetone Gas Sensors: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sensing Materials | Synthesis Approach | Temperature (°C) | Concentration (ppm) | Response (Rg/Ra) | τres./rec. (s). | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFO nanocrystalline powders | Sol-gel method | 260 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 62/107 | [4] |
| Biomorphic porous LFO | Sorghum straw biotemplate | 240 | 200 | 12.2 | 9/18 | [5] |
| Yolk-shell LFO microspheres | Hydrothermal method & annealing and etching process | 225 | 100 | 25.5 | 5/25 | [6] |
| LFO porous microspheres | Hydrothermal method | 260 | 100 | 29.0 | 9/17 | [7] |
| LFO nanoparticles | Sol-gel method | 138 | 100 | 16.6 | 37/38 | This work |
| α-Fe2O3/LFO porous nano-octahedron | Solvothermal method & annealing process | 230 | 100 | 21.0 | 1/3 | [8] |
| PANI/LFO nanocomposites | Sol-gel method & compositing process | 120 | 100 | 36.6 | 44/102 | [9] |
| Mesoporous La2O3/LFO composites | Hydrothermal method | 200 | 100 | 42.0 | 9/15 | [10] |
| Hollow α-Fe2O3/LFO nanostructures | Microwave-assisted hydrothermal method | 350 | 100 | 48.3 | 17/2 | [14] |
| 5WO3-LFO nanocomposites | Sol-gel method & compositing process | 132 | 100 | 33.4 | 28/9 | This work |
| 10WO3-LFO nanocomposites | Sol-gel method & compositing process | 138 | 100 | 55.1 | 36/25 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, E.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Sun, B.; Hao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, Z. WO3-LaFeO3 Nanocomposites for Highly Sensitive Detection of Acetone Vapor at Low Operating Temperatures. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11080439
Cao E, Zhang Y, Sun L, Sun B, Hao W, Zhang Y, Nie Z. WO3-LaFeO3 Nanocomposites for Highly Sensitive Detection of Acetone Vapor at Low Operating Temperatures. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(8):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11080439
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Ensi, Yixuan Zhang, Li Sun, Bing Sun, Wentao Hao, Yongjia Zhang, and Zhongquan Nie. 2023. "WO3-LaFeO3 Nanocomposites for Highly Sensitive Detection of Acetone Vapor at Low Operating Temperatures" Chemosensors 11, no. 8: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11080439
APA StyleCao, E., Zhang, Y., Sun, L., Sun, B., Hao, W., Zhang, Y., & Nie, Z. (2023). WO3-LaFeO3 Nanocomposites for Highly Sensitive Detection of Acetone Vapor at Low Operating Temperatures. Chemosensors, 11(8), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11080439







