Improved Recognition Accuracy of Myrrh Decoction Pieces by Electronic Nose Technology Using GC-MS Analysis and Sensor Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
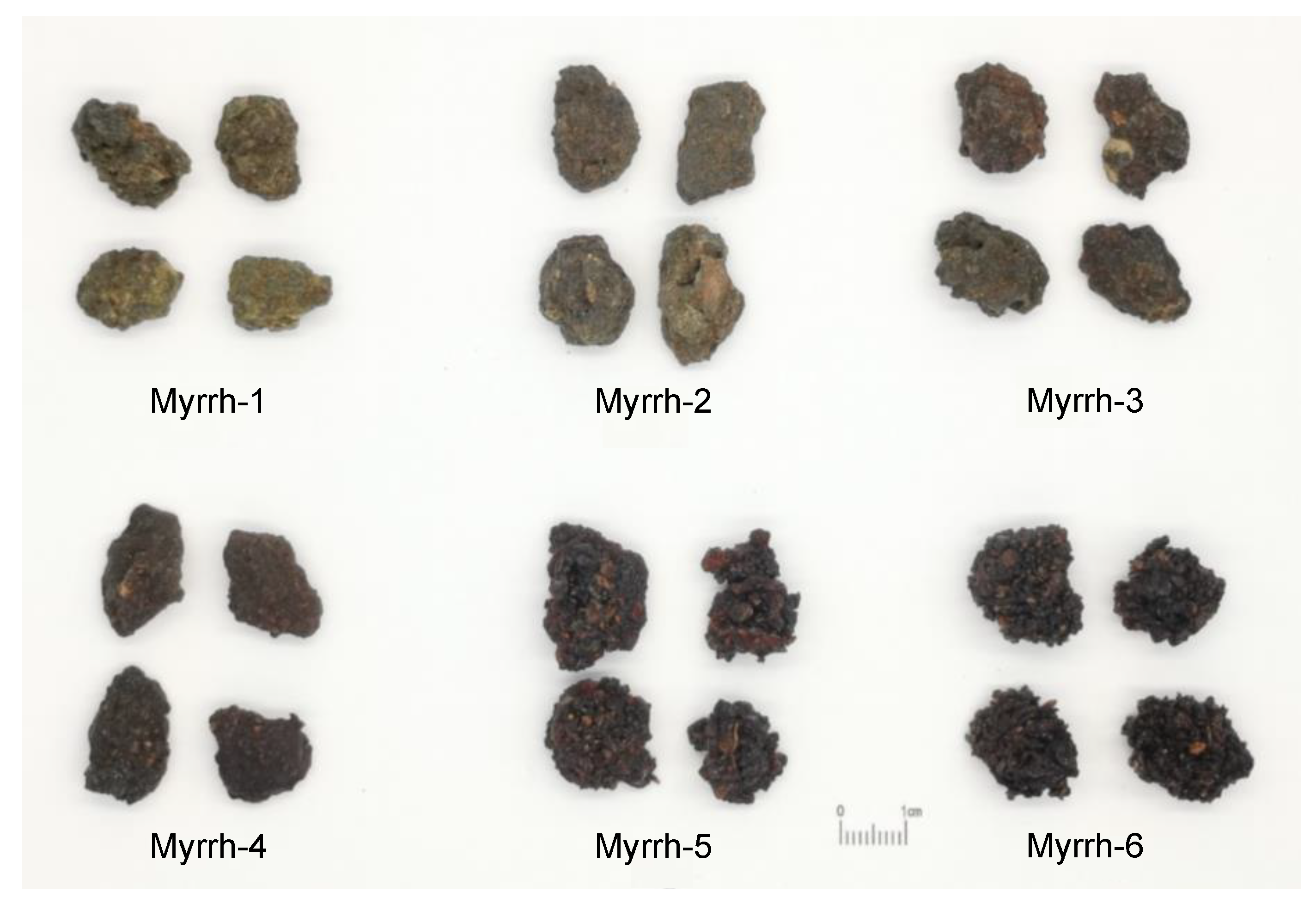
2.1. Preparation of Myrrh
2.2. GC-MS Analysis Procedure
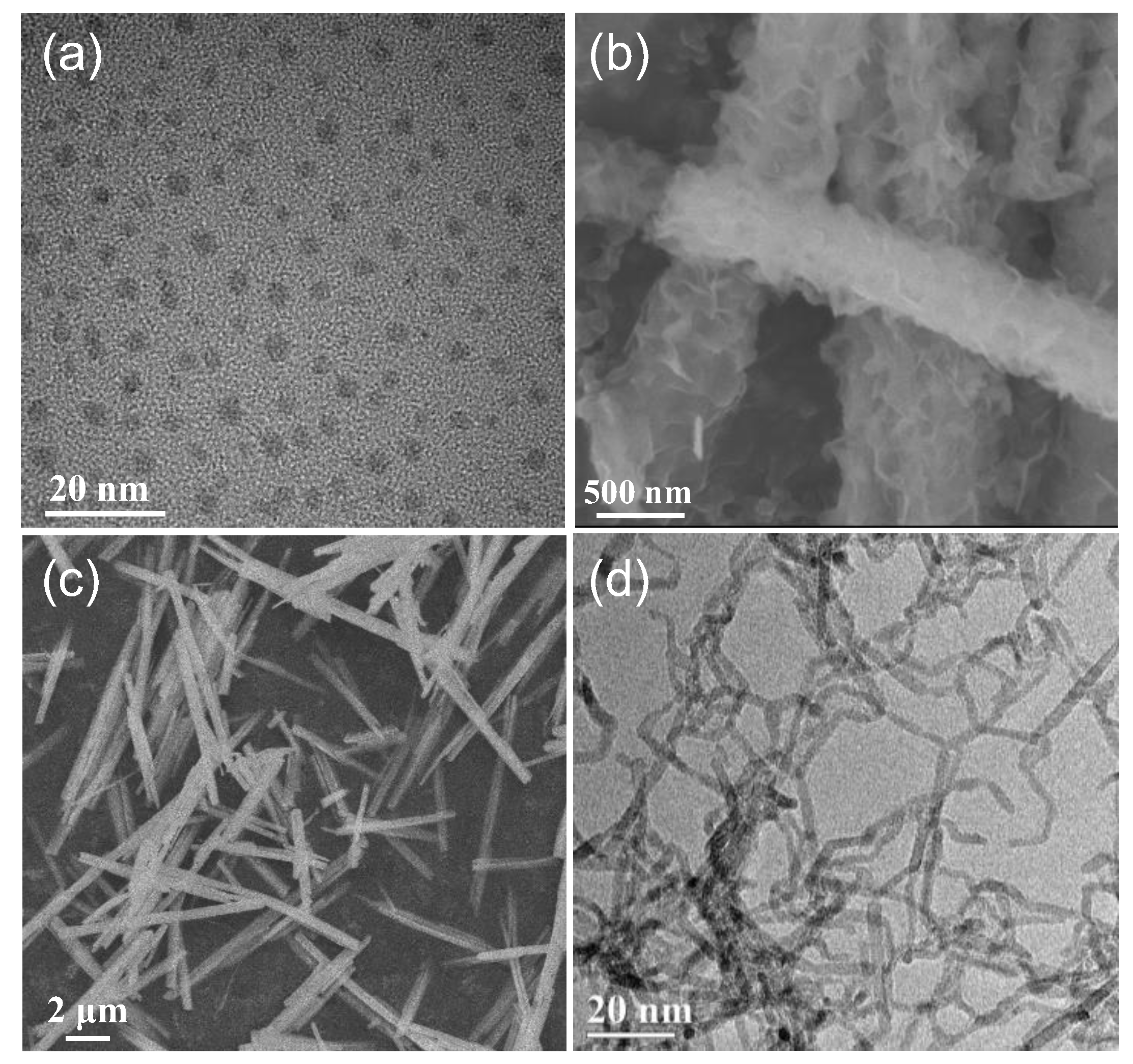
2.3. Sensor Array Fabrication
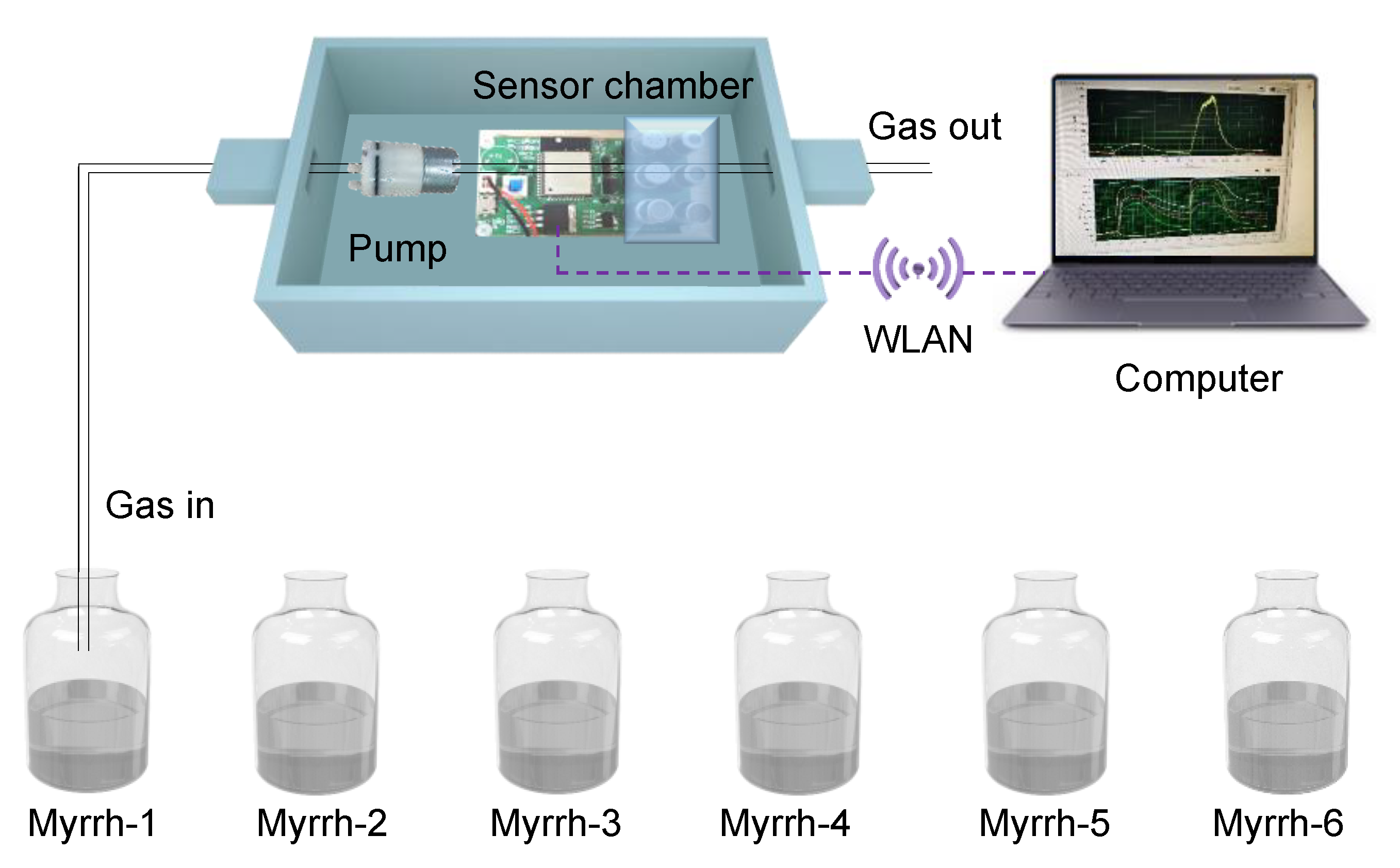
2.4. Electronic Nose Measurement
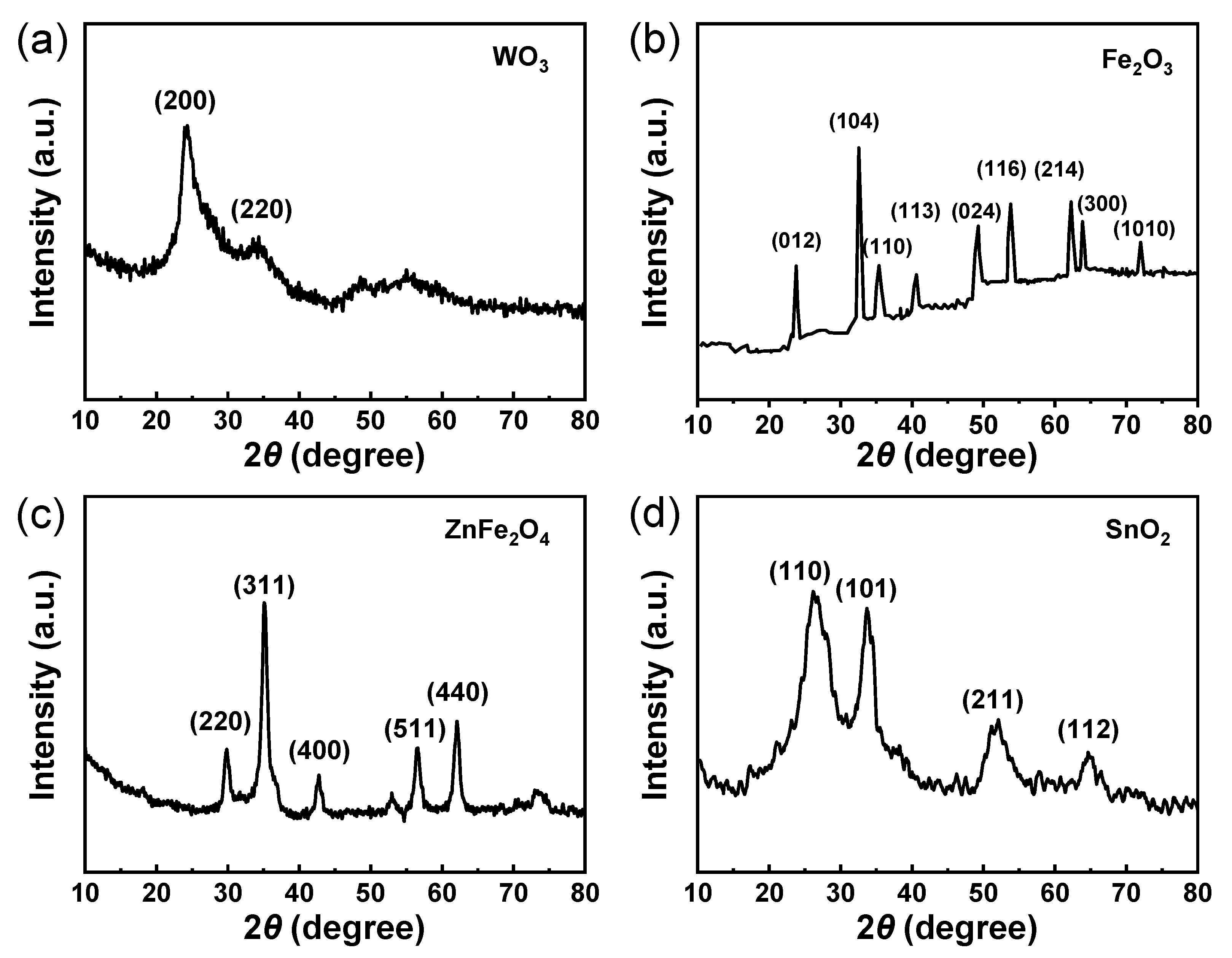
2.5. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
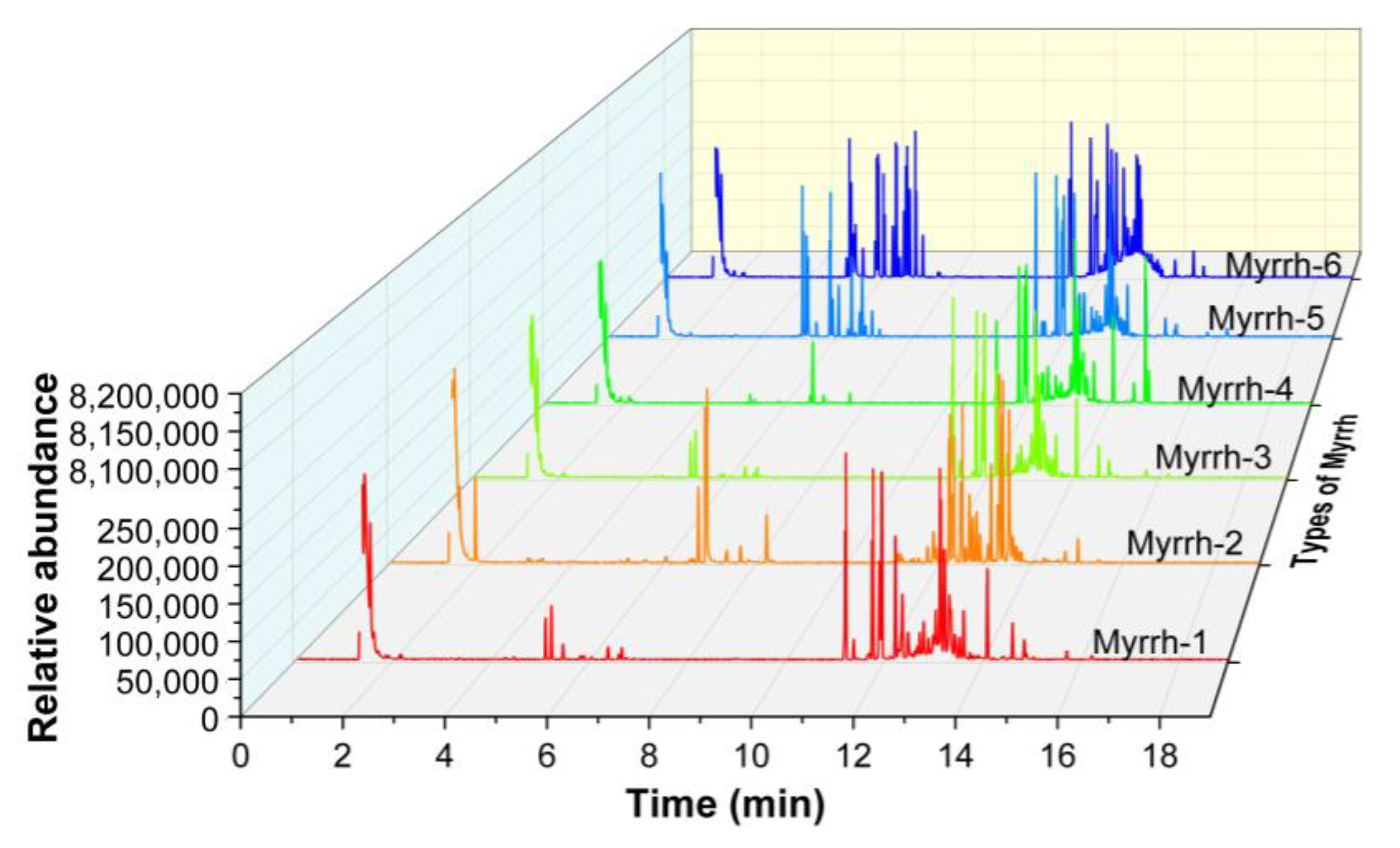
3.1. GC–MS Analysis Results of Myrrh Volatile Gases
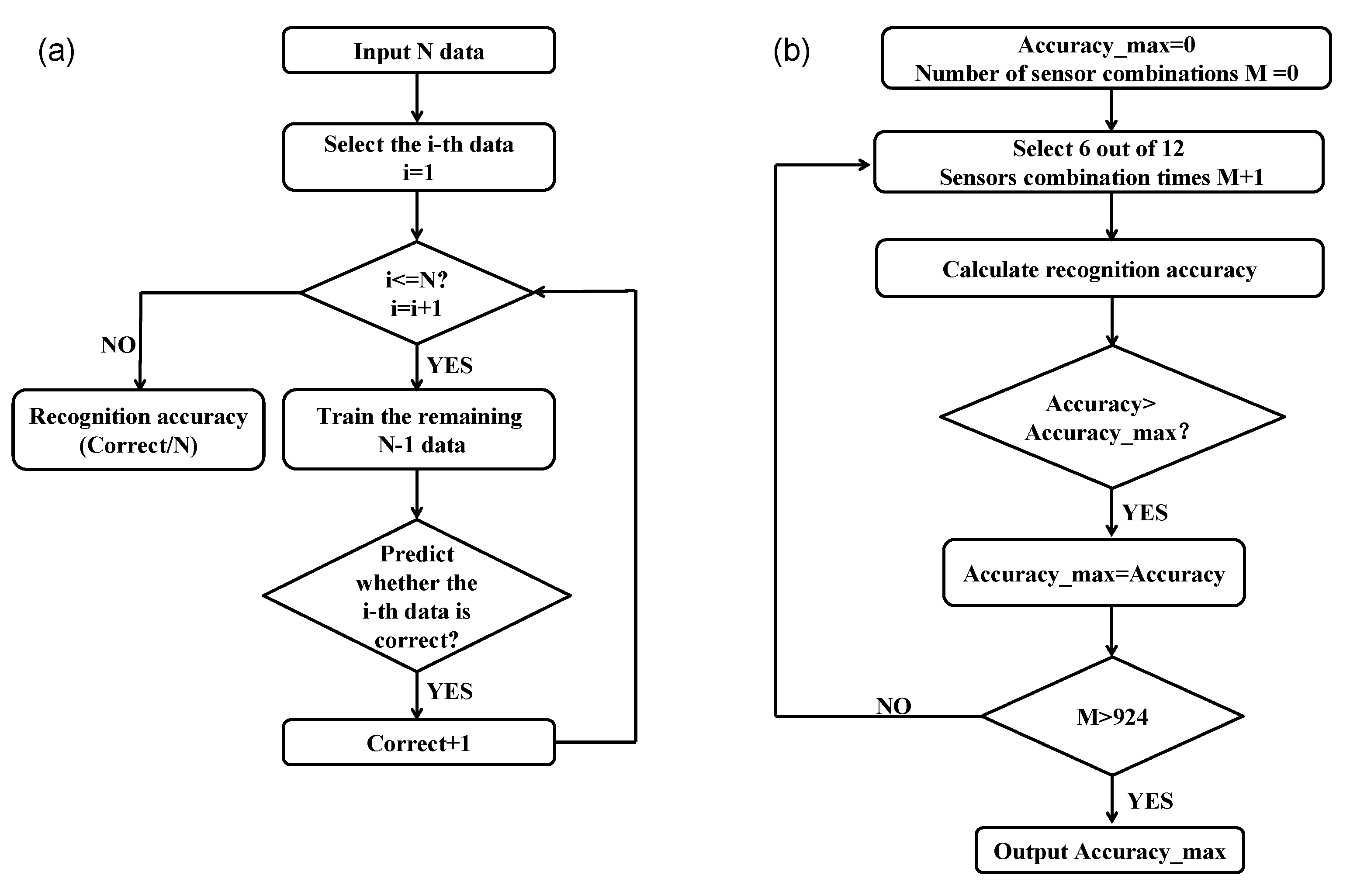
3.2. Sensor Selectionof Gases for Electronic Nose
3.3. Results of Electronic Nose Analysis of Myrrh Volatile Gases
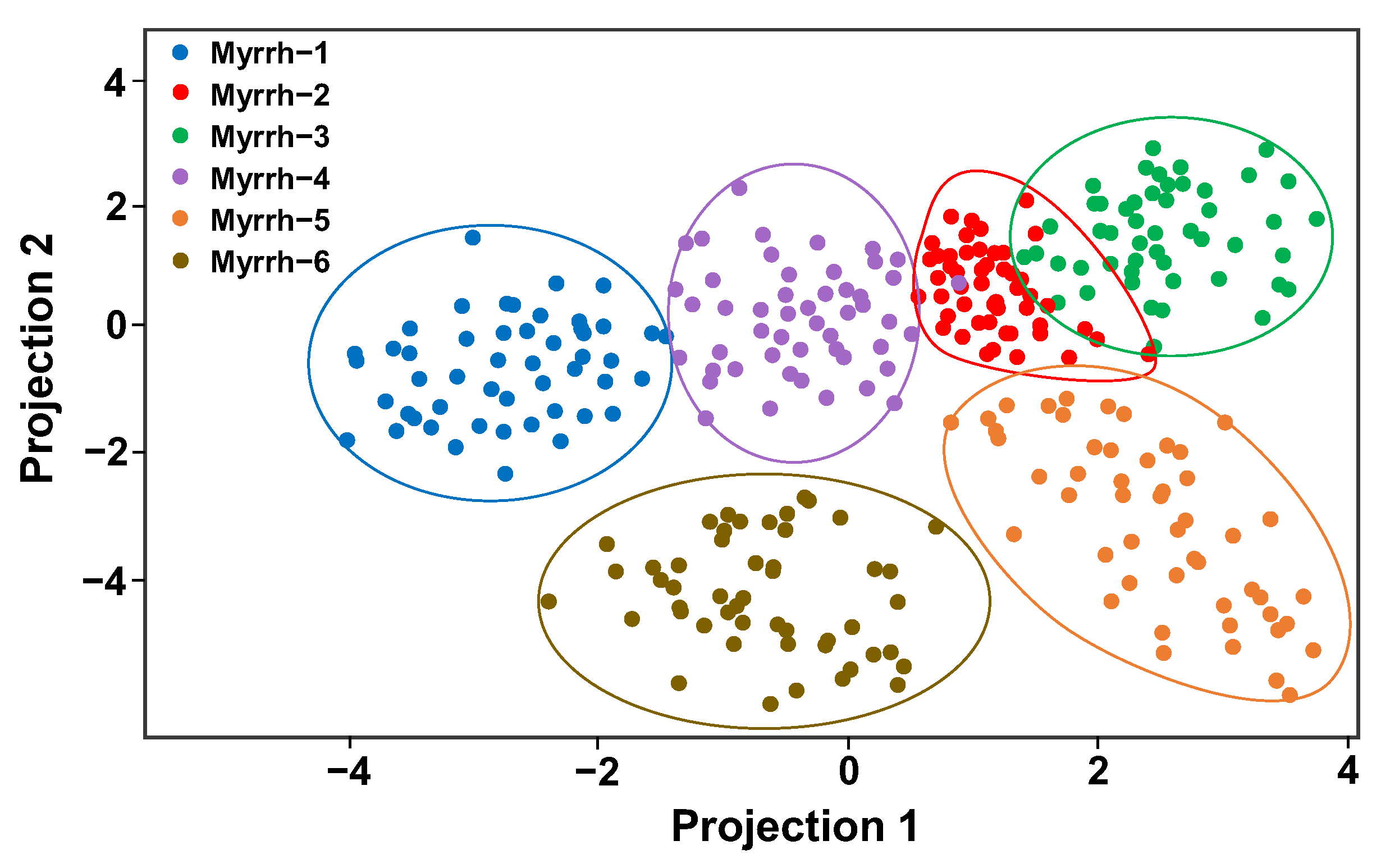
3.4. Classification of Myrrh Samples Using LDA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Qian, D.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Hong, W.; Meng, X.; Tang, H. Z-Guggulsterone Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Targeting the p53/CCNB1/PLK1 Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 2780–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, W.E.; Shehata, T.M.; Mohamed, M.E.; Younis, N.S.; Elsewedy, H.S. Enhancement of Curcumin Anti-Inflammatory Effect via Formulation into Myrrh Oil-Based Nanoemulgel. Polymers 2021, 13, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, R.A.; Loutfy, N.; Hassan, A. Myrrh and trematodoses in Egypt: An overview of safety, efficacy and effectiveness profiles. Parasitol. Int. 2009, 58, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leo, V.; Cagnacci, A.; Cappelli, V.; Biasioli, A.; Leonardi, D.; Seracchioli, R. Role of a natural integrator based on lipoic acid, palmitoiletanolamide and myrrh in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain and endometriosis. Minerva Ginecol. 2019, 71, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemenih, M.; Abebe, T.; Olsson, M. Gum and resin resources from some Acacia, Boswellia and Commiphora species and their economic contributions in Liban, south-east Ethiopia. J. Arid Environ. 2003, 55, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, S.R.; Al-Ghadeer, A.R.; Ali, R.; Qamar, W.; Aljarboa, S. Analysis of inorganic and organic constituents of myrrh resin by GC-MS and ICP-MS: An emphasis on medicinal assets. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C. Application of Molecular Methods in the Identification of Ingredients in Chinese Herbal Medicines. Molecules 2018, 23, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Luo, D.; Gholamhosseini, H.; Li, Z.; He, J. Identification of Chinese Herbal Medicines with Electronic Nose Technology: Applications and Challenges. Sensors 2017, 17, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, D.R.; Sarno, R.; Zulaika, E. DWTLSTM for electronic nose signal processing in beef quality monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lei, T.; Zhang, S.; Shao, X.; Xie, C. A novel headspace integrated E-nose and its application in discrimination of Chinese medical herbs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Li, T. Highly sensitive and selective detection of human-derived volatile organic compounds based on odorant binding proteins functionalized silicon nanowire array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Huang, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, T.; Liang, Y. Comparison of the volatile compounds of Atractylodes medicinal plants by headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 570, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zheng, T.; Shi, Y.; Wei, F.; Ma, S.; He, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, X. Analysis of the fingerprint profile of bioactive constituents of traditional Chinese medicinal materials derived from animal bile using the HPLC-ELSD and chemometric methods: An application of a reference scaleplate. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2019, 174, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Wu, M.; Lin, R.; Li, X.; Ding, H.; Han, L.; Yang, W.; Song, X.; Li, W.; Qu, H.; et al. Application and development trends of gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry for traditional Chinese medicine, clinical, food and environmental analysis. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Gao, H.; Ye, M.; Shang, H.; Yao, X.; Yao, Z. Characterization of chemical profile and quantification of representative components of DanLou tablet, a traditional Chinese medicine prescription, by UHPLC-Q/TOF-MS combined with UHPLC-TQ-MS. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2020, 180, 113070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoli, A.; Steffens, C.; Paschoalin, R.T.; Graboski, A.M.; De Mello Brandão, H.; de Carvalho, B.C.; Bellini, J.L.; de Paula Herrmann, P.S. Volatile compounds monitoring as indicative of female cattle fertile period using electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchmenko, T.; Umarkhanov, R.; Lvova, L. E-nose for the monitoring of plastics catalytic degradation through the released Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 322, 128585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, R.S.; Facure, M.H.M.; Mercante, L.A.; Correa, D.S. Electronic nose based on hybrid free-standing nanofibrous mats for meat spoilage monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 353, 131114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xue, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Yu, W.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, X.; Yu, G.; Wan, H.; et al. A miniaturized electronic nose with artificial neural network for anti-interference detection of mixed indoor hazardous gases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Maout, P.; Wojkiewicz, J.; Redon, N.; Lahuec, C.; Seguin, F.; Dupont, L.; Mikhaylov, S.; Noskov, Y.; Ogurtsov, N.; Pud, A. Polyaniline nanocomposites based sensor array for breath ammonia analysis. Portable e-nose approach to non-invasive diagnosis of chronic kidney disease. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 274, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; Song, B.; Yuan, K.; Xiao, H.; Cao, Y.; Cao, Q. Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) Derivatives as Promising Chemiresistive Gas Sensing Materials: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, K.; Wang, C.; Zhu, L.; Cao, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, D.W. Fabrication of a Micro-Electromechanical System-Based Acetone Gas Sensor Using CeO2 Nanodot-Decorated WO3 Nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 14095–14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Liu, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, D.W.; Lu, H. Recent progress on flexible room-temperature gas sensors based on metal oxide semiconductor. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Yang, G.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Sun, Y. Analysis of Volatile Components of Auricularia auricula from Different Origins by GC-MS Combined with Electronic Nose. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 8858093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, T.; Eom, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jang, H.W. Chemoresistive materials for electronic nose: Progress, perspectives, and challenges. InfoMat 2019, 1, 289–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ren, Z.; Lee, C. Toward Healthcare Diagnoses by Machine-Learning-Enabled Volatile Organic Compound Identification. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cho, M.; Li, Y.; He, T.; Ahn, J.; Park, J.; Ren, T.; Lee, C.; Park, I. Machine learning-enabled textile-based graphene gas sensing with energy harvesting-assisted IoT application. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, T. An overview: Facet-dependent metal oxide semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 277, 604–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Akbar, S.A.; Morris, P.A. Nanoscale metal oxide-based heterojunctions for gas sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, P.G.; Izu, N.; Shirahata, N.; Masuda, Y. SnO2 Nanosheets for Selective Alkene Gas Sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, T.; Liu, K.; Tan, X.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Q. Oxygen vacancy-rich WO3-x/rGO composite supported Pd catalyst for efficient selective hydrogenation of nitroaromatics. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 932, 167577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Wen, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, C.; Long, C. Mesoporous poorly crystalline α-Fe2O3 with abundant oxygen vacancies and acid sites for ozone decomposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Teng, M.; Yang, R.; Lin, F.; Fu, Y.; Lin, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhong, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; et al. Sb-doped WO3 based QCM humidity sensor with self-recovery ability for real-time monitoring of respiration and wound. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 361, 131691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Huang, X. Ultra-thin nanosheets-assembled hollowed-out hierarchical α-Fe2O3 nanorods: Synthesis via an interface reaction route and its superior gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tan, J.; Dun, M.; Huang, X. Porous ZnFe2O4 nanorods with net-worked nanostructure for highly sensor response and fast response acetone gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, X. SnO2 Quantum Dots and Quantum Wires: Controllable Synthesis, Self-Assembled 2D Architectures, and Gas-Sensing Properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12527–12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y. Gas sensing mechanisms of metal oxide semiconductors: A focus review. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 22664–22684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N.; Shimanoe, K. New perspectives of gas sensor technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerz, A.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Current state of knowledge on the metal oxide based gas sensing mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Yadav, B.K. Electronic nose for detection of food adulteration: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramifar, A.; Karami, H.; Lvova, L.; Kolouri, A.; Łazuka, E.; Piłat-Rożek, M.; Łagód, G.; Ramos, J.; Lozano, J.; Kaveh, M.; et al. Environmental Engineering Applications of Electronic Nose Systems Based on MOX Gas Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Natale, C.; Macagnano, A.; Martinelli, E.; Paolesse, R.; Proietti, E.; D’Amico, A. The evaluation of quality of post-harvest oranges and apples by means of an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 78, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; Macagnano, A.; Paolesse, R.; Mantini, A.; Tarizzo, E.; D’Amico, A.; Sinesio, F.; Bucarelli, F.M.; Moneta, E.; Quaglia, G.B. Electronic nose and sensorial analysis: Comparison of performances in selected cases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 50, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, S.; Minaei, S.; Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti, M. Application of electronic nose systems for assessing quality of medicinal and aromatic plant products: A review. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Guan, X.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. Discrimination between Alternative Herbal Medicines from Different Categories with the Electronic Nose. Sensors 2018, 18, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dayyeni, W.S.; Al-Yousif, S.; Taher, M.M.; Al-Faouri, A.W.; Tahir, N.M.; Jaber, M.M.; Ghabban, F.; Najm, I.A.; Alfadli, I.M.; Ameerbakhsh, O.Z.; et al. A Review on Electronic Nose: Coherent Taxonomy, Classification, Motivations, Challenges, Recommendations and Datasets. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 88535–88551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Sensor | Target Gas | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | TGS2611 | Methane | Figaro |
| S2 | MP-4 | Methane, Natural gas | Winson |
| S3 | MP-7 | CO | Winson |
| S4 | Fe2O3 | Ethanol, Ethylene, Propylene | Self-made |
| S5 | TGS2610 | Propane, Butane | Figaro |
| S6 | TGS2620 | Ethanol, VOC | Figaro |
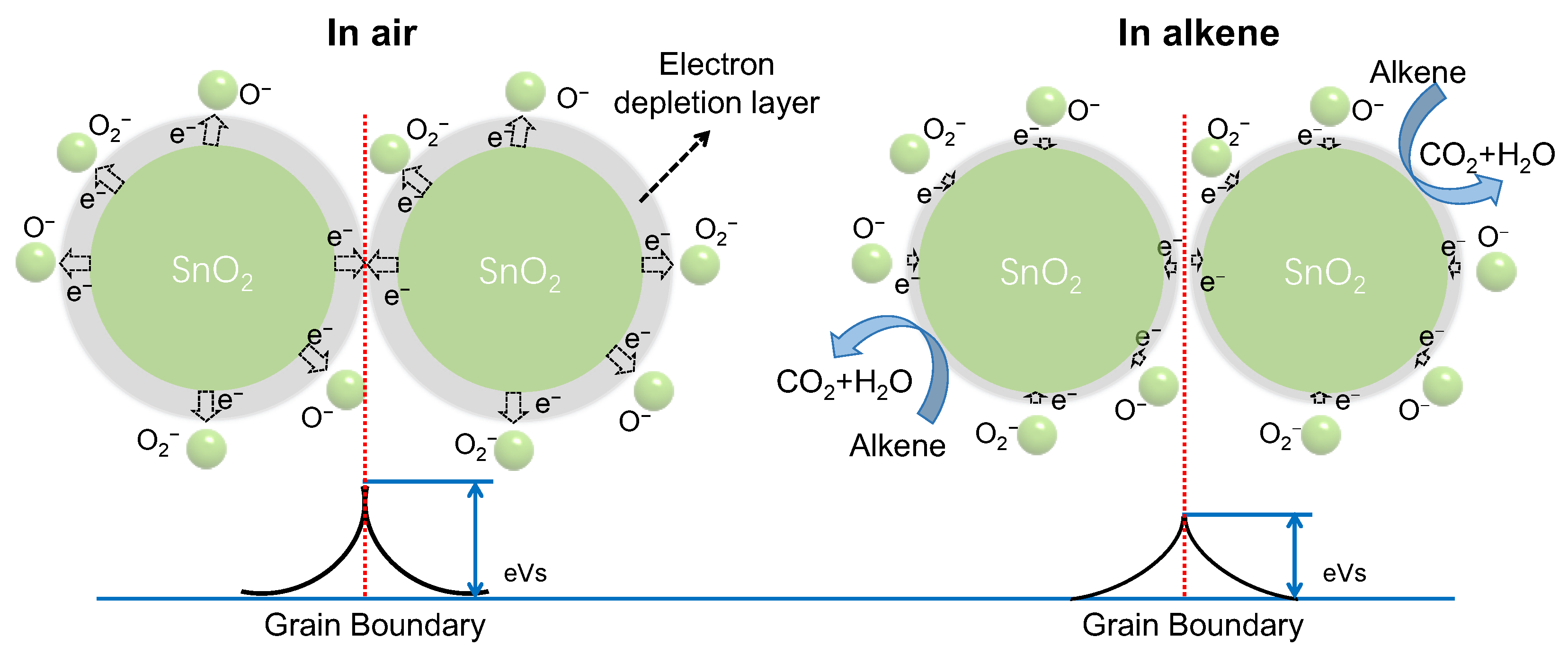
| S7 | SnO2 | Ethylene, Propylene, Alkene, VOC | Self-made |
| S8 | MP-5 | Liquefied gas, Natural gas | Winson |
| S9 | ZnFe2O4 | Ethanol, Formaldehyde, Acetone | Self-made |
| S10 | WSP2110 | Toluene, Formaldehyde, benzene | Winson |
| S11 | TGS2618 | Propane, Butane | Figaro |
| S12 | WO3 | Ethanol, Ethylene, Propylene, Formaldehyde | Self-made |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, G.; He, T.; Xie, X.; Qin, J.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, E. Improved Recognition Accuracy of Myrrh Decoction Pieces by Electronic Nose Technology Using GC-MS Analysis and Sensor Selection. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11070396
Zhou G, He T, Xie X, Qin J, Wei W, Zhang Y, Hao E. Improved Recognition Accuracy of Myrrh Decoction Pieces by Electronic Nose Technology Using GC-MS Analysis and Sensor Selection. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(7):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11070396
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Gailian, Ting He, Xueting Xie, Jianfeng Qin, Wei Wei, Yujing Zhang, and Erwei Hao. 2023. "Improved Recognition Accuracy of Myrrh Decoction Pieces by Electronic Nose Technology Using GC-MS Analysis and Sensor Selection" Chemosensors 11, no. 7: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11070396
APA StyleZhou, G., He, T., Xie, X., Qin, J., Wei, W., Zhang, Y., & Hao, E. (2023). Improved Recognition Accuracy of Myrrh Decoction Pieces by Electronic Nose Technology Using GC-MS Analysis and Sensor Selection. Chemosensors, 11(7), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11070396






