Investigation of the Colorimetric Characteristics of VX in Squaraine-Based Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Synthesis of Squaraine Probe (SP)
2.3. Establishment of Colorimetry
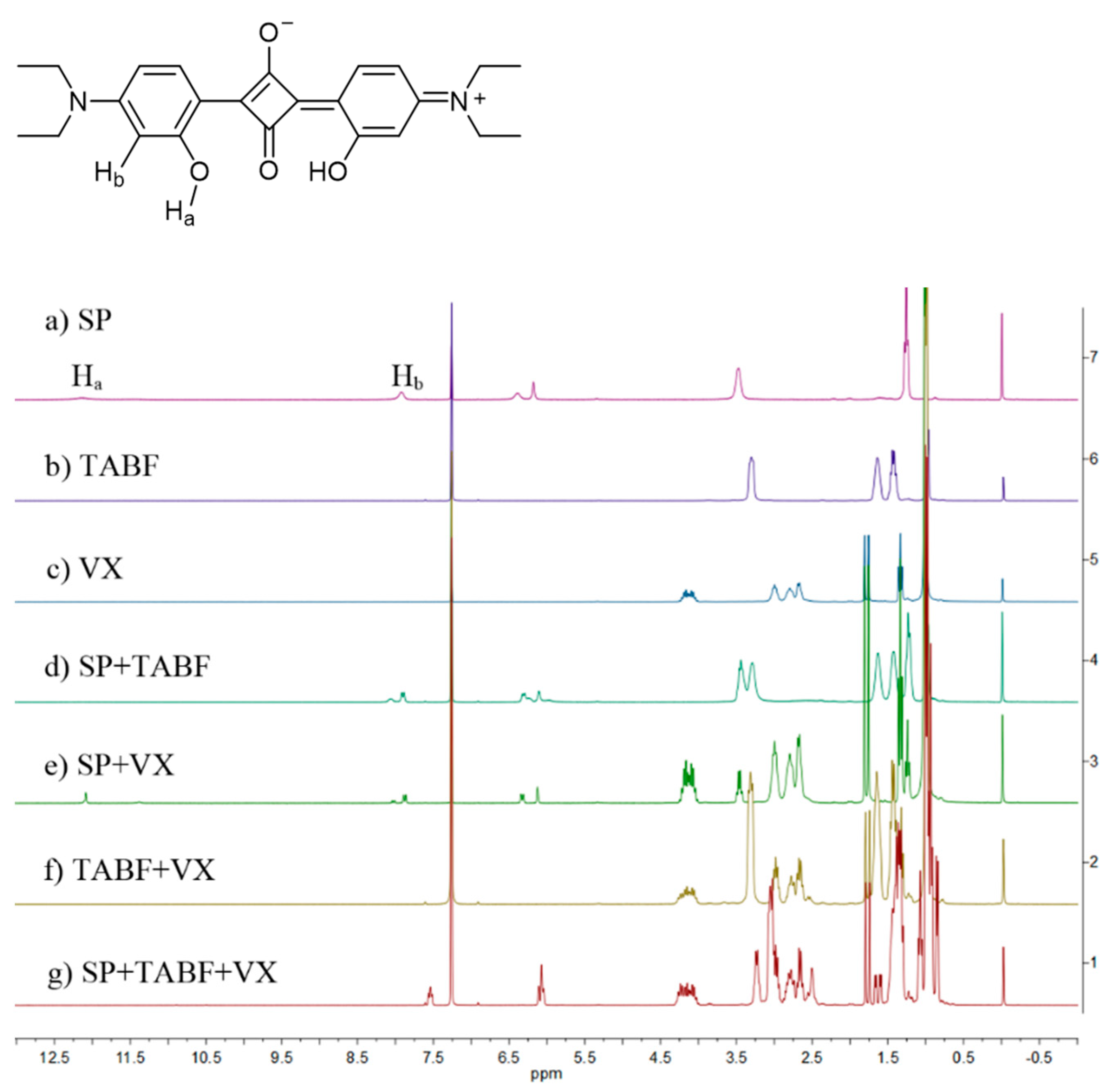
2.4. Detection Mechanism
3. Results
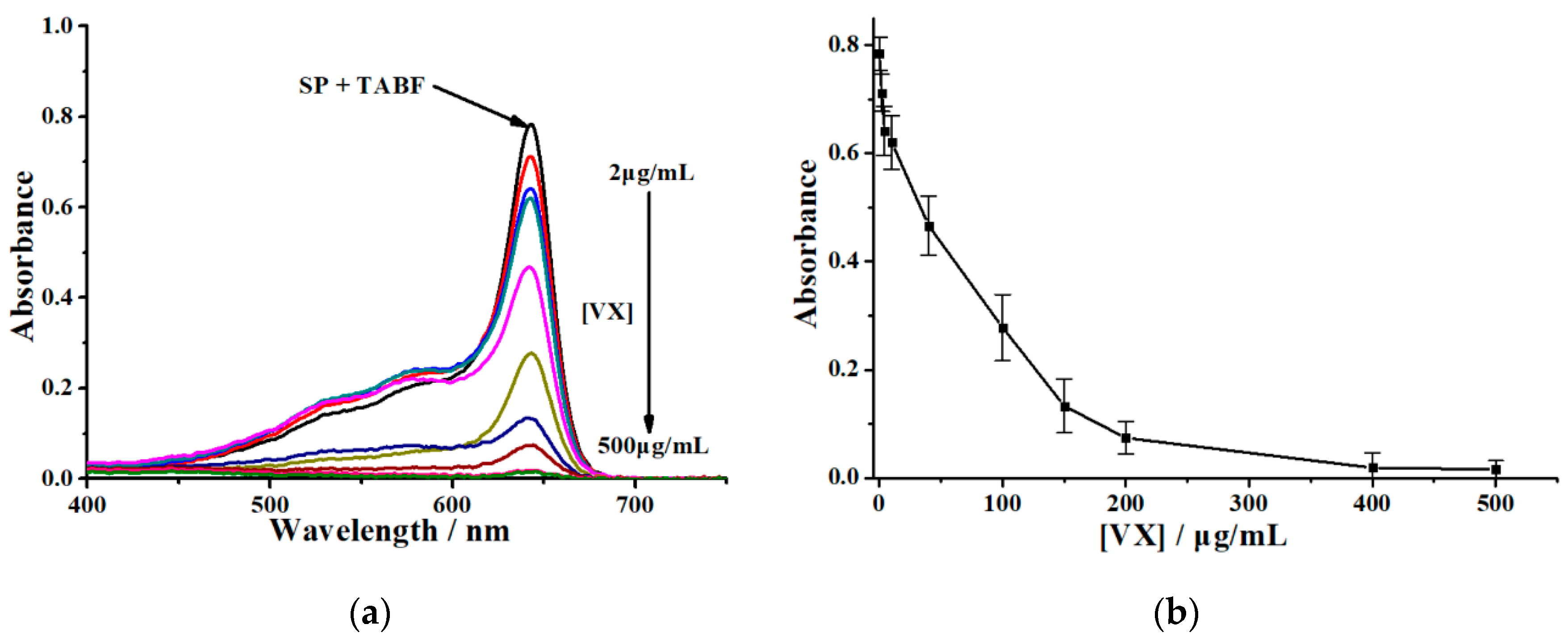
3.1. Colorimetry for VX Detection
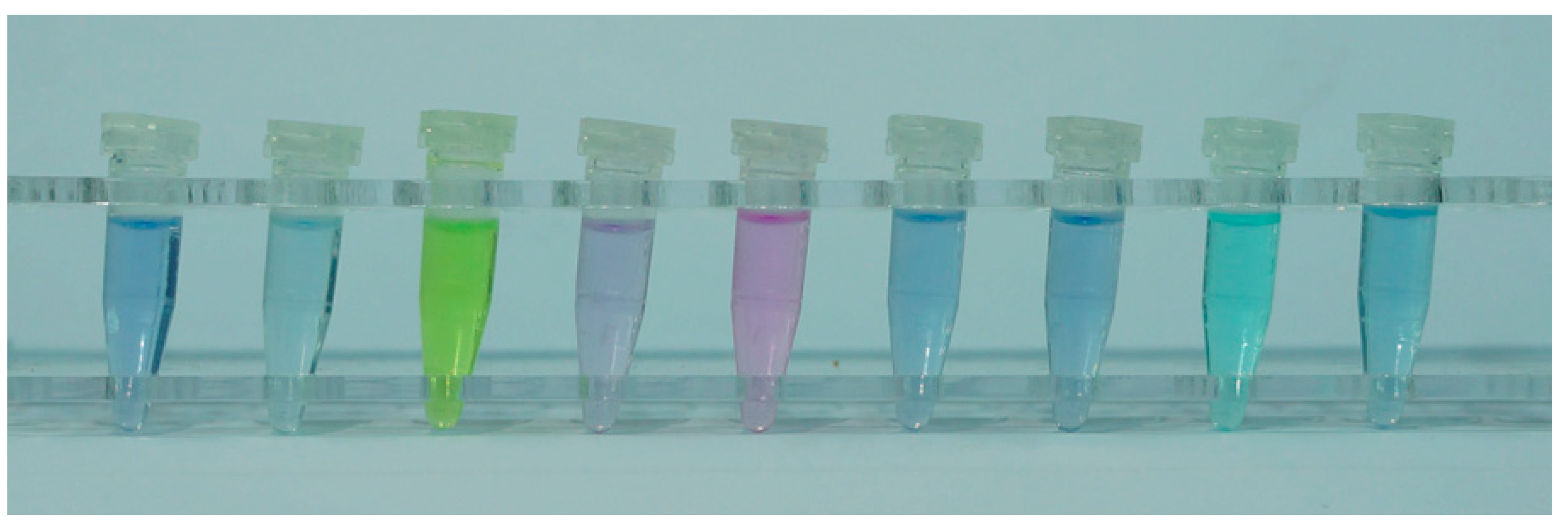
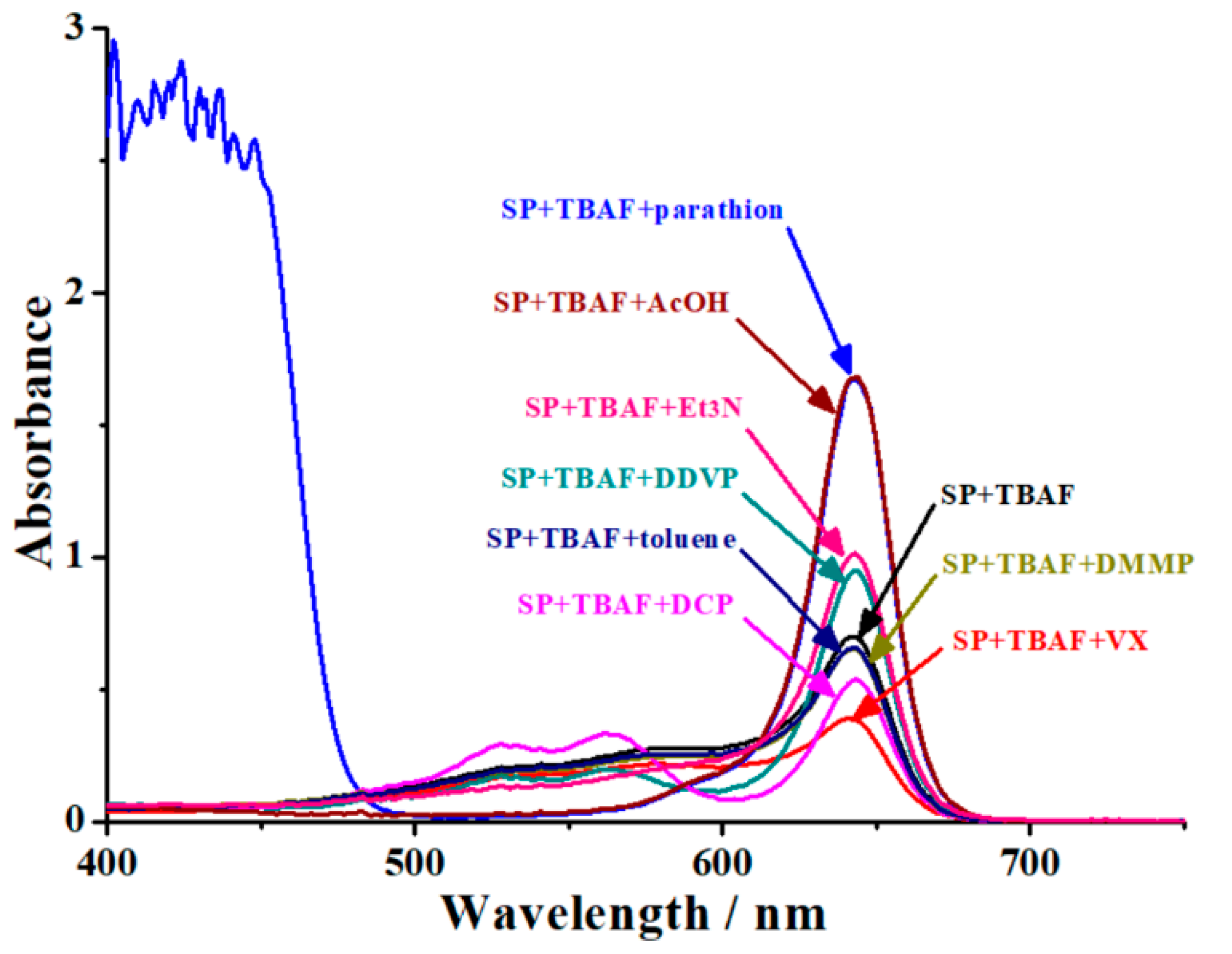
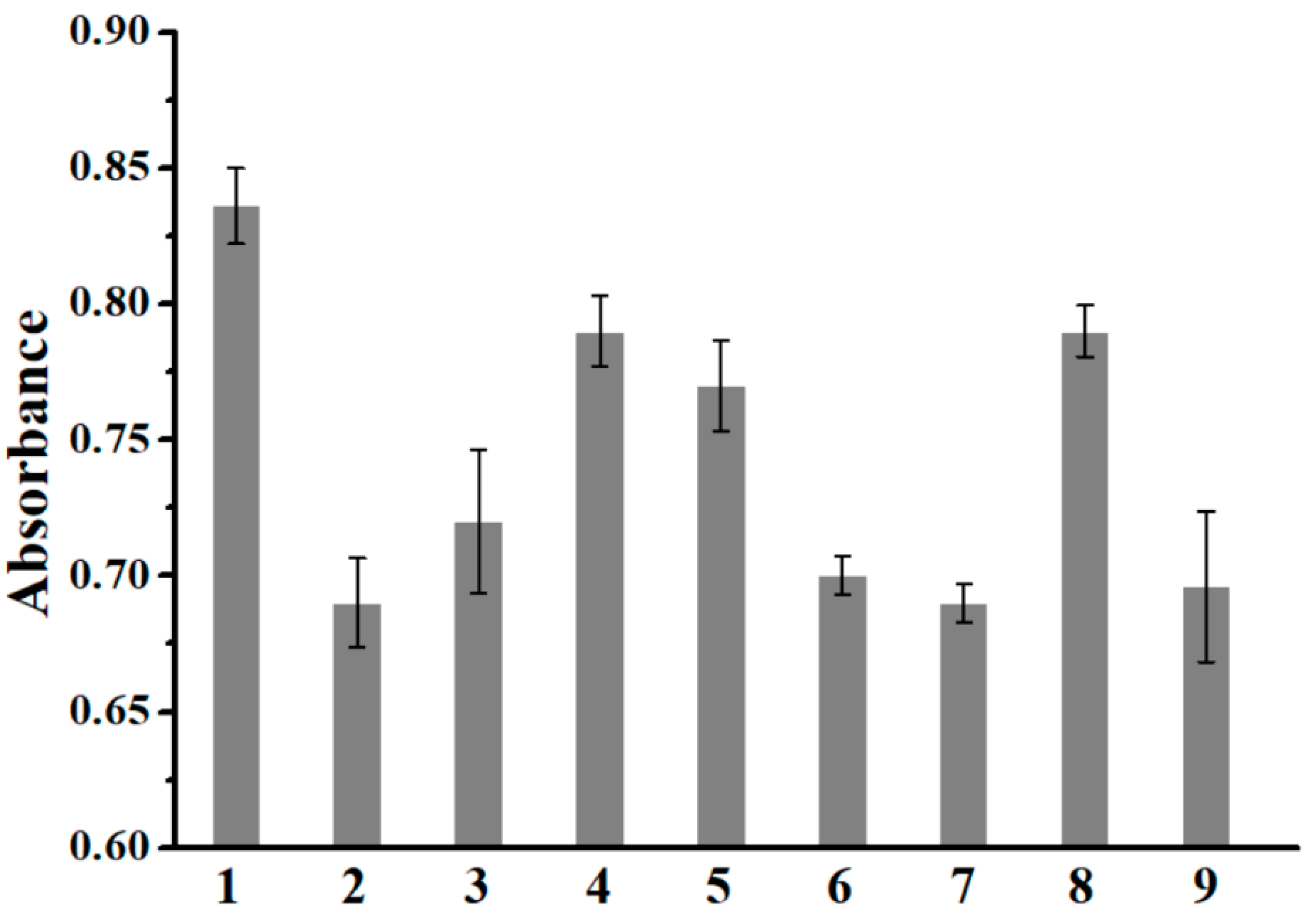
3.2. Selectivity and the Anti-Interference Ability of Colorimetry
3.3. Mechanism for the Colorimetric Detection of VX
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, R.S.; Rao, G.H.; Sharma, G.D.; Singh, S.P. Squaraine-fullerene conjugate for single component organic solar cells. Opt. Mater. 2022, 134, 113230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Delcamp, J.H. Near-infrared unsymmetrical squaraine core-based sensitizers for co-sensitized high-photocurrent dye-sensitized solar cells. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renno, G.; Cardano, F.; Ilieva, V.; Viscardi, G.; Fin, A. Near-Infrared Squaraine Dyes as Bright Fluorescent Probes: A Structure–Activity Photophysical Investigation in Liposomes. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 2022, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khopkar, S.; Shankarling, G. Synthesis, photophysical properties and applications of NIR absorbing unsymmetrical squaraines: A review. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 170, 107645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilina, K.; MacCuaig, W.M.; Laramie, M.; Jeouty, J.N.; McNally, L.R.; Henary, M. Squaraine Dyes: Molecular Design for Different Applications and Remaining Challenges. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 31, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Xu, W.; Guo, Y.; Fu, N. Near-infrared squaraine dye as a selective protein sensor based on self-assembly. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 245, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnarasu, C.; Barbero, N.; Barolo, C.; Visentin, S. Interaction of squaraine dyes with proteins: Looking for more efficient fluorescent turn-on probes. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 184, 108873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Fu, N. Self-assembled nanosensor based on squaraine dye for specific recognition and detection of human serum albumin. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 255, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, Y.; Fan, J.; Wang, R.; Fu, N. A squaraine and Hg2+-based colorimetric and “turn on” fluorescent probe for cysteine. Talanta 2013, 114, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.; Chen, Y.; Fan, J.; Wang, G.; Lin, S. A bifunctional “Turn On” fluorescent probe for trace level Hg2+ and EDTA in aqueous solution via chelator promoted cation induced deaggregation signalling. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 203, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Mei, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, S. Colorimetric and fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive recognition of Cu2+ and Fe3+ based on asymmetric squaraine dye. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 142, 109592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ye, B.; Xia, G.; Wang, H. A multi-responsive squaraine-based “turn on” fluorescent chemosensor for highly sensitive detection of Al3+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ in aqueous media and its biological application. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 249, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, N.; Xu, M.M.; Jiang, C.; Wang, J.; Song, G.; Wang, Y. Turn on fluorescent detection for Cd2+ based on surfactant controlled squaraine aggregation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 208, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolkin, B.; Levi, N.; Karton-Lifshin, N.; Yehezkel, L.; Zafrani, Y.; Columbus, I. Oxidative Detoxification of Sulfur-Containing Chemical Warfare Agents by Electrophilic Iodine. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 13949–13955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, G.; Mikler, J.; Hill, I.; Weatherby, K.; Thiermann, H.; Worek, F. Simultaneous quantification of VX and its toxic metabolite in blood and plasma samples and its application for in vivo and in vitro toxicological studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 2704–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.M.; Vu, A.K.; Mayer, B.P.; Hok, S.; Valdez, C.A.; Alcaraz, A. Part 3: Solid phase extraction of Russian VX and its chemical attribution signatures in food matrices and their detection by GC-MS and LC-MS. Talanta 2018, 186, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.T.; Qualley, A.; Hughes, G.T.; Arroyo, J.W.; Malloy, T.A.; Piatkowski, T.; Russell, M.; Lewis, D.; Rubenstein, H.M. Anchoring the quantification of VX and Russian VX using portable gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and focusing agents. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 468, 116659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M.; Karasova, J.Z.; Kuca, K.; Pikula, J.; Holas, O.; Korabecny, J.; Cabal, J. Colorimetric dipstick for assay of organophosphate pesticides and nerve agents represented by paraoxon, sarin and VX. Talanta 2010, 81, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Kazui, Y.; Miyaguchi, H.; Ohmori, H.; Tanaka, R.; Jin, J. Simple colorimetric screening of the nerve agent VX using gold nanoparticles and a hand-powered extraction device. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 327, 128902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Mantri, Y.; Retout, M.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jorns, A.; Fajtova, P.; Yim, W.; Moore, C.; Xu, M.; et al. A Charge-Switchable Zwitterionic Peptide for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Deng, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; Gong, N.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Teng, X.; Yang, C.; et al. A paper-based assay for the colorimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 variants at single-nucleotide resolution. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Oladoye, P.O.; Olanrewaju, C.A.; Akinsola, G.O. Organophosphorus pesticides: Impacts, detection and removal strategies. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Xu, D.; Wang, G.; Geng, L.; Xu, R.; Wang, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X. Novel colorimetric aptasensor based on MOF-derived materials and its applications for organophosphorus pesticides determination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, H.; Han, X.; He, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K. Colorimetric and fluorescent sensors for detection of nerve agents and organophosphorus pesticides. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 344, 130278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, S.W.; Zhang, B.; Tu, Q.; Wang, J.; Yuan, M.S. Non-biological fluorescent chemosensors for pesticides detection. Talanta 2022, 240, 123200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciano, D.; Columbus, I.; Elias, S.; Goldvaser, M.; Shoshanim, O.; Ashkenazi, N.; Zafrani, Y. Role of the P-F bond in fluoride-promoted aqueous VX hydrolysis: An experimental and theoretical study. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 10042–10049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, S.; Saphier, S.; Columbus, I.; Zafrani, Y. Polysaccharide-Thickened Aqueous Fluoride Solutions for Rapid Destruction of the Nerve Agent VX. Introducing the Opportunity for Extensive Decontamination Scenarios. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Majhi, S.; Sharma, K.; Ali, M.; Sharma, S.; Choudhary, D.; Tripathi, C.S.P.; Guin, D. BSA stabilized copper nanoclusters as a highly sensitive and selective probe for fluorescence sensing of Fe3+ ions. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 787, 139226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Rana, H. Chromogenic and fluorogenic detection and discrimination of nerve agents Tabun and Vx. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16490–16493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qin, M.; You, J.; Liu, K.; Ding, L.; Liu, T.; Kong, J.; Fang, Y. Rapid and colorimetric evaluation of G-series nerve agents and simulants using the squaraine-ethanolamine adducts. Dye. Pigment. 2022, 197, 109870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, B.; Geng, S.; Cao, W.; Guo, L.; Xu, J.; Huang, F.; Chen, L. Investigation of the Colorimetric Characteristics of VX in Squaraine-Based Solutions. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11020137
Du B, Geng S, Cao W, Guo L, Xu J, Huang F, Chen L. Investigation of the Colorimetric Characteristics of VX in Squaraine-Based Solutions. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(2):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11020137
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Bin, Shu Geng, Wei Cao, Lei Guo, Jianjie Xu, Feng Huang, and Lina Chen. 2023. "Investigation of the Colorimetric Characteristics of VX in Squaraine-Based Solutions" Chemosensors 11, no. 2: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11020137
APA StyleDu, B., Geng, S., Cao, W., Guo, L., Xu, J., Huang, F., & Chen, L. (2023). Investigation of the Colorimetric Characteristics of VX in Squaraine-Based Solutions. Chemosensors, 11(2), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11020137





