Abstract
With the rapid scientific and technological changes that occur every day, a new kind of necessity, real-time, rapid, and accurate detection methods, preferably also non- or minimally invasive and non-destructive, has emerged. One such method is laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF), applied in various fields of activity in recent decades, ranging from industry and biochemistry to medicine and even heritage sciences. Fluorescence-based spectroscopic methods have all of the above-mentioned characteristics, and their functionality has been proven in many studies. Yet, they have not known great success as other molecular techniques. This paper is a short synthesis of the role of the laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy technique in heritage sciences, the main applications in this field, along with its advantages and limitations. The article focuses on the most common types of lasers used, the merging of two or more methods into hybrid techniques, the enhancement of the analytical capabilities of LIF and post-processing methods, and also explores some future development possibilities of LIF.
1. Introduction
Generally speaking, fluorescence is the process of light emission by certain molecules or atoms as a consequence of them being stimulated through either physical (light absorbance), mechanical (friction), or chemical means. Of the broad domain of fluorescence spectroscopies, laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) spectroscopy is defined as the spontaneous emissions from atoms or molecules that have been excited by laser radiation. Simply put, when laser radiation interacts with matter, particles may absorb photons and pass onto an excited energy state, from which they must de-excite and return to the ground state, through various mechanisms, one of which is spontaneous fluorescence emission [1]. These processes can be illustrated and easily understood through the Jablonski diagram [2]. The fluorescence emission is a very rapid process, as the time between the excitation and return to the ground state, called lifetime, is about a few nanoseconds [3].
Unlike broadband sources, lasers have the advantage of being highly coherent and directional, bright, almost monochromatic light sources, which allow the very selective excitation of fluorophores [4]. Moreover, these properties reflect in good spectral, temporal, and spatial resolutions [5]. Since its beginnings in the 1970s, this technique has developed into a versatile method of analysis for a wide range of applications, such as industry, biochemistry, biophysics, medicine, environmental protection, and even cultural heritage [6,7,8,9,10,11,12].
LIF offers the user the advantage of being a non-contact and non-invasive analysis technique, which, when operated using the right parameters, does not cause alterations to the target’s surface, thus making it suitable for the heritage sciences field [13,14]. This real-time technique does not require sampling and can be performed in almost any location, due to the technological advances, especially in the spectral instrumentation, which have allowed the miniaturization and portability of LIF systems [15,16].
The LIF technique has been employed in heritage studies for several decades. However, despite its great potential, it has not reached the same level of applicability as other molecular spectroscopy techniques, such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). This is probably related to one of the drawbacks of LIF, which is that the emission bands are relatively broad. Moreover, numerous times the fluorescence bands cannot be attributed unambiguously, as the acquired spectrum can be affected by the overlapping of multiple fluorophores’ signals emitting in the same region. Moreover, for a more complex characterization of the investigated samples, several wavelengths could be required, which implies a high cost. All things considered, for specific applications and in well-defined experimental boundaries, LIF has shown its utility in the heritage science field.
2. Aim
In the past decade, there have been several LIF reviews aimed at describing the state of the art in using LIF spectroscopy in various fields of activity, mostly focused on biochemistry, medicine, and environmental applications. In a 2012 review, Zare talked about LIF’s advantages and some personal experiences in working with LIF for the detection of gas and liquid molecules [17]. Moving forward about a decade, in the past two years, multiple papers have been published, reviewing the applications of fluorescence. Taylor and Lai [18] recently reviewed the application of LIF for designing biochemical sensors, with the potential to be used in numerous fields, including environmental protection and medical imaging and diagnosis. In a similar approach, Dinesan and Kumar [19] conducted a review of LIF applications for gas-phase ion detection, covering how to adapt measurement schemes from condensed- to gas-phase experiments and building quadrupole ion traps and improving the signal-to-noise ratio in such experiments. Zacharioudaki and co-workers [20] talked about various types of LIF, light sources, detector and fluorescence recordings, fluorescent compounds, fluorescence quenching and interferences in fluorescence measurements, and LIF applications in environmental samples, including water, soils, and sediments. Kwaśny and Bombalska [21] have written about the five decades of LIF-use in the medical field, with applications including the detection of endogenous fluorophores and biological tissues, with the aim of improving medical diagnosis for skin diseases, caries, atherosclerosis, cancers, and the guiding of medical procedures, such as photodynamic therapy. In the field of cultural heritage, LIF has been less used as compared to other areas of application. Related to heritage science applications, there is a review of Nevin and partners [22], which was aimed at spectroscopic methods using laser sources for art and archaeology, and discussed the elemental characterization of materials through laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA–ICP–MS), molecular characterization through LIF, LIDAR (light detection and ranging) LIF, laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (LDI-MS), matrix-assisted (MA) LDI–MS, atmospheric pressure (AP) MALDI, and hybrid systems, including at least two spectroscopic techniques, such as LIF-Raman, LIF-LIBS, LIBS-Raman, and Raman-XRF, LIBS-MS.
Seeing how the scientific literature already contains references about LIF theory, the design of LIF set-ups, optical geometries, detection systems, and light sources used, ranging from arc lamps to multiphoton microscopy, designing of molecular probes for detection of non-fluorescence molecules, and that some of them even tackled the commercial availability, or, rather, lack of LIF systems, the objective of the present paper is not to reiterate already known information, but rather to present an up-to-date image of the current state of the art in the application of laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy in the field of heritage sciences.
3. LIF Applications in Heritage Sciences
As noted by Anglos et al. [23], most organic materials observed in art and archaeology and some inorganic ones (mostly minerals) have fluorescence properties, making them suitable for LIF studies. In order to attain a picture of the interest of using LIF in heritage-related studies, a search was conducted throughout several multidisciplinary databases following a combination of key-words: “laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy” and “art”, “archaeology”, “paintings”, “organic binders”, “pigments”, “ceramics”, “graffiti”, “consolidants”, “adhesives”, “glue”, “bacteria”, “fungi”, “icons”, “mortar”, “bricks”, “marble”, “mural painting”, “secco”, and “fresco”, all pertaining to the major classes of materials identifiable through fluorescence spectroscopy or to the major object types. The search was conducted in parallel in the Clarivate WoS database, which indexes high-quality scholarly literature from all over the world, and in the combined libraries of three of the main scientific literature providers: Elsevier, Springer, and Wiley. Of the results returned by the search in the Elsevier, Springer, and Wiley databases (Figure 1a), it can be observed that most LIF studies focus on the study of bacteria (~18%), followed by organic binders (~15%), adhesives (~13%), and pigments (~10.5%). On the other hand, for the search conducted in the WoS database (Figure 1b), most returned results were related to studies of pigments (>25%) and art, in general (~18%), followed by bacteria (~14%). For both search groups, the lowest percentages were returned for graffiti (<0.2%), secco (<0.35%), consolidants (<0.6%), marble (<1.20%), bricks (<1.35%), mural painting (<1.55%), and fresco (<1.70%). While some of the categories appear correlated for both search groups, there is a considerable discrepancy between the percentages returned for other search terms, such as adhesives (from 13 to <1%), paintings (varying between 14 and <3 %), and organic binders (from 15 to <1%).
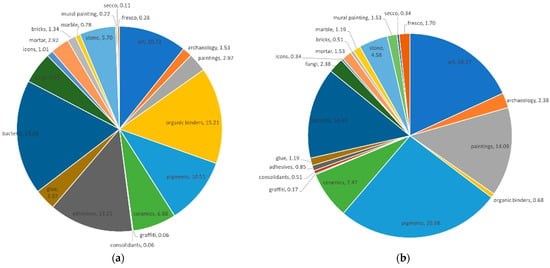
Figure 1.
Graphical representation of the input of the search terms for the (a) Elsevier, Springer and Wiley; (b) WoS databases.
What can be speculated here is that while some subjects have been extensively studied, others have not. Clearly, there has been a greater focus oriented towards the study of organic materials, such as bacteria, since there have already been lots of experiments conducted on this subject coming from the medical field, which had experienced a greater expansion. On the other hand, one of the earliest preoccupations of the heritage scientists was the identification of pigments. This is also evident from the literature cited in the Supplementary Material [11,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90], which lists the main types of lasers used in heritage studies since the early 1990s, along with their characteristics and the type of material(s) studied. On the other hand, new types of materials and art are lacking the thorough investigation that traditional art materials have received. Thus, graffiti and other contemporary painting materials could be a niche that is worth studying.
As previously mentioned, pigments, both organic and inorganic, are amongst the most encountered materials in the studied literature, along with polymers, waxes, resins, adhesives, organic binders, oils, and stones in the form of either laboratory mock-ups or real objects, as can be observed in Table 1, which summarizes some of the fluorophores accounted for in scientific studies and their corresponding excitation/emission wavelengths.

Table 1.
Synthesis of excitation and emission wavelengths of the main fluorophores encountered in the literature.
First, LIF studies in heritage sciences (HSs) focused on the identification of paintings materials—pigments, varnishes, and binders. Myioshi [24] and Borgia [26] both focused on obtaining the characteristic spectra of pigments and resins for oil paintings. Miyoshi employed a nitrogen laser and obtained the characteristic spectra for dammar, mastic, copal, colophony, sandarac, amber, and shellac, while Borgia and Castillejo [28] used KrF lasers to study varnishes and pigments, including hematite, malachite, lead white, titanium white, zinc white, ultramarine ash, cadmium yellow, Naples yellow, orpiment, cadmium red, red lead, vermilion, and carbon. The concern for LIF analysis of natural and synthetic pigments was encountered in the following years, also [97], followed by an increase in studies oriented towards identifying mural painting pigments [68,69,76,77] and contemporary artworks [72] and materials [71]. Moreover, in the case of multiple-layer systems, such is the case of paintings, one must take into account that the registered fluorescence emission might come not just from the top layer, but also from an underlayer. This was demonstrated by Elias et al. [98], who studied fresh and aged model samples and proved that the color of the underlying paint layer influences the emission spectra of varnishes. Although the recent years did not present many LIF studies, of the few that can be observed in the scientific literature, most still focused on the investigation of pigments [85,87]. However, despite the majority of studies focusing on pigment identification, there is no database available online to facilitate the search for specific spectral fingerprints. Such databases can be obtained for FTIR, Raman, XRF, and XRD data [99,100,101,102], but not for LIF data.
The LIDAR applications were also an important part of LIF studies at the beginning of 2000, for the characterization of stone monuments and building façades, and the biological attack on such objects [103]. LIDAR applications have the additional advantage that they can be used regardless of ambient light, from a considerably longer distance away, and can scan larger surfaces. Green alga (Coccomyxa minor and Pleurococcus sp.) and cyanobacterium (Chroococcus sp.), which are typical biodeteriogens of stone monuments, have been characterized with LIDAR, prior to and after the application of biocides on calcareous and dolomitic marble samples and on real historical buildings ([27,29,49,104]), providing functional and taxonomic information for biodeteriogens films [16]. Such microorganisms can contribute to the degradation of stone monuments by inducing physical and chemical alterations, due to the excretion of enzymes, acids, and the formation of secondary substances [27]. Lognoli and collaborators [29] tried to differentiate between cyanobacteria and green alga, based on the potential of remote LIF to highlight the presence phycobilin. The authors based their study on the fact that, even though both green algae and cyanobacteria have a high chlorophyll content, they differ through their phycobilin content. This fluorescent pigment, especially in the form of phycoerythrin and phycocyanin, can be observed in cyanobacteria, but not in green algae. Starting from this, they showed how fluorescence can be useful to differentiate between the two lithophilous photoautotrophic microorganisms, with the final aim of searching for the proper biocide to remove such unwanted biodeteriogens from the surface of stone monuments. Thus, besides the chlorophyll response, with a main emission peak at 670–690 nm, and a second one, as a shoulder, at 730–740 nm, the cyanobacteria also showed two emission maxima at approximately 570 and 660 nm, corresponding to phycocyanin and phycoerythrin, respectively [27].
Different types of natural rocks (Carrara marble, lithotypes of Rosso Veronese, Scaglia, mortars, travertine, and sandstones) were analyzed with LIF lidar so as to determine their specific fingerprints ([32,55,104]) and to aid in future restoration processes. The obtained results were significantly improved through the use of multivariate techniques, which allow for a good classification of not only the biodeteriorated areas, but also the surface soiling patterns [49,103]. A further step was taken by Bruno and colleagues [82], who used LIF scanning to evaluate the efficiency of essential oils applied for the decontamination of cyanobacteria obtained from the Roman catacombs of SS. Marcelino and Pietro in Rome. They reported that lavender and thyme essential oils proved the most efficient, even at low concentrations, for destroying phototrophic biofilms, without inducing alterations on the painted surface.
Another important part of LIF studies concentrated on the determination of the fluorescence fingerprints of organic media in paintings, including casein, egg yolk, and egg white, and animal tissues adhesives ([34,40,58,63,91]). In fact, the fluorescence of organic media has been studied by Nevin and his collaborators for several years, extending the use of LIF towards total emissions ([44,54,61,105]) and time-resolved imaging fluorescence spectroscopy ([42,73,92]), including the effect of light exposure on the binding media [45]. These studies evidenced that the fluorescence response of various binding media comes from the intrinsic fluorophores, mostly proteins, such as collagen, casein, albumin, and other animal skin, milk, and egg proteins, respectively. Their response is dependent on the excitation wavelength and can be used to differentiate between general classes of proteins in art works, especially when it is coupled with the multivariate statistical analysis. Moreover, fluorescence spectroscopy can be useful even for monitoring the molecular changes in protein composition following exposure to intense light [45].
Fluorescence spectroscopy has also been widely used to assess various degradation products for the understanding of changes that appear in materials over time, or those induced by external stress factors, with the goal of preventive conservation, in either natural or artificial aging experiments. Such an example is the case of amino acids and their degradation products, which have been the object of several studies focused on protein-based binding media used in paintings, including proteins found in milk (casein), eggs (ovalbumin, lysozyme), and animal connective tissues (collagen). The fluorescence emissions of these products are mainly related to the presence of the amino acids tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine. In addition to having different excitation and emission wavelengths (280/348 nm, 274/303 nm, and, respectively, 257/282 nm), these amino acids are also characterized by different quantum yields and lifetimes. Of them, tryptophan has the highest quantum yield (0.20), similar to tyrosine (0.14) and much higher than phenylalanine (0.04), which often leads to tryptophan emission covering that of phenylalanine and, partially, that of tyrosine [40]. In these studies, a wide range of excitation wavelengths were used, between 230 and 360 nm. For this broad excitation interval, emission bands were detected between 300 and 450 nm, mainly corresponding to tryptophan and tyrosine degradation products, including kynurenine (290/435 nm), N-formyl kynurenine (360/435 nm), n-acetyl tyrosine ethyl ester (260/301 nm), n-acetyl tryptophan (260/310 nm, 280/355 nm), pentosidine (280/380 nm), and Maillard reaction products (345–350/400–450 nm).
Consolidants used in restoration interventions in the past 50 years, such as vinylic or acrylic resins, were studied by Colao et al. [58], who used two UV wavelengths, 266 and 355 nm, to characterize these materials. The authors included five materials: acrylic resins (Paraloid B 72, Primal AC33), vinylic and polyvinyl resins (Vinavil and Mowilith 50), and soluble nylon (Calaton). The results show that while the 355 nm excitation wavelength did not produce significantly different spectra for the five resins, with only a broad fluorescence emission band centered at 475–485 nm, the 266 nm wavelength was able to obtain different spectral signatures. While the band obtained for the 355 nm excitation was specific for resins, in general, it did not allow for the discrimination of different types of resins. On the other hand, the 266 nm wavelength generated a small variation in the fluorescent response of the resins, with a central peak at 435 nm for soluble nylon, 315 nm for the Primal AC 33, 330 nm for Mowilith 50, 335 nm for Paraloid 72, and 340 nm for Vinyl.
Some challenging materials, such as polymers, were also examined with the aid of laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy. Their versatile properties in conjunction with various enhancers, such as plasticizers, stabilizers, and colorants, led to them being used either alone or in mixtures, for numerous modern art objects. However, their properties are also what makes them prone to degradation [53]. Since polymers have not been used in the creation of art for a very long time, compared to historical materials, there is a lack of understanding regarding their time-degradation characteristic. Toja and co-workers [53] tried to fill in this gap by studying lamps composed of polymer materials, naturally aged for approximately 50 years. The investigation highlighted ongoing molecular deterioration patterns, mainly the active deacetylation and butadiene oxidation of the polyvinyl acetate and acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene polymers, but not for the cellulose acetate.
Given that laser-cleaning technology has evolved in recent decades, and that its use in restoration works has increased, the need for precise and rapid analytical protocols for monitoring the cleaning process has emerged. Moreover, the possibility of the online monitoring and control of restoration interventions can optimize the results of the cleaning process [106]. In order to ensure that no damage is inflicted upon the surface, non-invasive techniques, such as LIF or OCT (optical coherence tomography), have been employed for examining cleaned surfaces. One such case was that of Simileanu and colleagues, who used the 266 harmonics of a Nd:YAG laser to evaluate the stress induced by the laser operated at 1064 nm in the process of cleaning a parchment [107]. They concluded that, operated at the proper parameters, the 1064 nm wavelength did not induce harm to the collagenous substrates. The LIF technique was also used in a study from 2009, for the monitoring of the outcome of laser cleaning [47]. The authors employed a KrF excimer laser emitting at 248 nm, to evaluate the effect of laser cleaning on doped PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate) and Paraloid B72 samples overpainted, in order to assess laser cleaning efficiency on overpainting and its safety for original paintings, and observed this approach to be successful. Moretti et al. [80] used the same 248 nm KrF excimer laser for both cleaning and LIF, but at considerably lower fluences for the latter: for laser cleaning, the fluence was varied between 0.1 and 1.1 J/cm2, while for the LIF evaluation the fluence was 0.005 J/cm2. The authors concluded that LIF was useful for both assessing the cleaned surfaces and to monitor the cleaning process, and that the use of a single laser for both cleaning and evaluating the outcome was a clear benefit.
Materials, such as textiles, have been studied to a lesser extent using LIF methods. For instance, Di Lazzaro et al. [94] conducted a study on the Arquata shroud, one of the few surviving copies of the Shroud of Turin. The authors used strictly non-destructive techniques, namely, imaging topological radar, absolute diffused reflectance, absorption spectroscopy, and laser-induced fluorescence, with the aim of aiding future conservation treatments. They used a 266 nm laser and analyzed 15 5 mm × 5 mm areas on the entire shroud, including stains and inscriptions. Their results indicated that the LIF spectra of all analyzed areas were dominated by the presence of cellulose, and even indicated the areas inside the body impression, areas with an advanced degradation of cellulose fibers. An interesting finding was that the authors were able to timeframe the Arquata shroud. They did this by highlighting the similarity between the LIF spectra of the shroud and 400-year-old naturally aged cellulose. LIF showed the limitations with regard to the identification of the blood-like stains on the shroud, which were compared against the spectra of the most common Renaissance-age red pigments, but did not match. However, along with the other techniques, the authors implied that the author could have mixed the pigment with blood.
Another area that has been less studied in the cultural heritage (CH) sector is that of microorganism, such as fungi or viruses, even though there are a few studies that indicate the usefulness of LIF in this field. For instance, Bengtsson et al. [108] used 337 nm radiation coupled with statistical analysis methods to identify eight types of fungi grown on silicone rubber, while Owoicho et al. [109] demonstrated promising results for the application of LIF for virus detection.
4. Laser Types
Although simple in theory, the process of surface stimulation by laser radiation requires a thorough knowledge of the processes that may occur during the interaction of radiation with matter, especially when considering cultural heritage items, for which non-destructivity is very important.
The typical set-up of an LIF experiment involves several key components, as illustrated in Figure 2: the excitation part, including the laser and, potentially, some focusing lens; the collection part, with the spectrograph and maybe some other optical components, such as mirrors; and the processing part, the computer with the necessary software programs. Of these, the choice of the laser source is very important, as it must take into account the features of the investigated samples, such as the chemical nature and thermal sensitivity [22], in order to ensure that the experimental procedure does not induce damage to the investigated object.
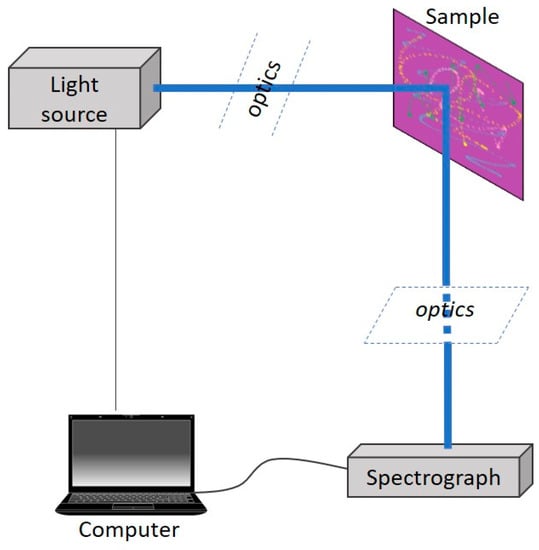
Figure 2.
Typical simplified LIF set-up.
Most studies encountered in the specific literature involve the use of lasers emitting in the UV region (see Figure 3). In only 4% of the studies were visible-domain lasers (442, 532 nm) used. The majority used the 266 and 355 nm wavelengths, followed by the 248 nm wavelength.
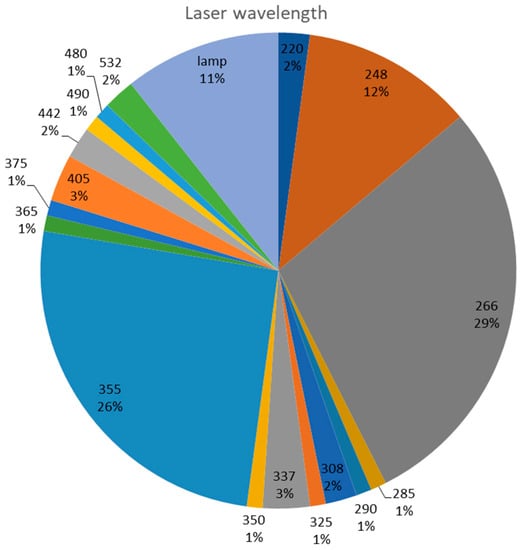
Figure 3.
Graphical representation of the predominance of excitation wavelengths encountered in the scientific literature.
One of the drawbacks when researching LIF scientific literature is that there is a considerable lack of uniformity in reporting important parameters, such as pulse duration, spot size, and repetition rate of laser fluence. This can be observed in the Supplementary Materials, which shows a synthesis of the main laser types and parameters. The supplementary file contains references of LIF, but also broadband emission fluorescence. Figure 4 shows a distribution of the types of excitation light used in fluorescence studies, based on the studied literature presented in the supplementary file. As can be observed, the most common type of laser used in LIF studies is the Nd:YAG laser, which is very versatile, and can be configured so that the user can benefit not only from its fundamental wavelength, but also its harmonics at 532, 355, and 266 nm, and, in some cases, even 213 nm. This broad range of available wavelengths, from UV to NIR, along with the tunability of the laser energy, from hundreds of mJ down to only a few tenths of mJ, make this type of laser suitable not only for LIF, but also for Raman and LIBS applications [110,111]. Within this wide range of energies, the typical energies per pulse revolve a few mJ, so as to avoid the destruction of fragile heritage layers, with fluences below 1 mJ/cm2.
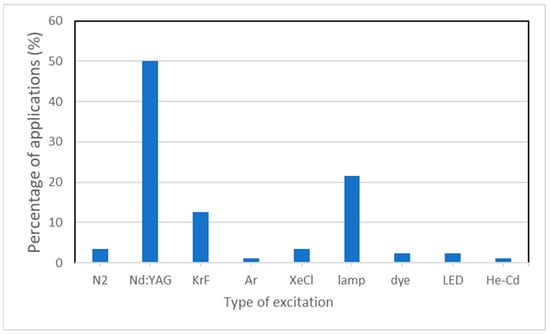
Figure 4.
Type of excitation used in fluorescence studies.
5. From Single to Hybrid Techniques
When performing heritage science investigations, there is often the need to examine an object or material from different perspectives, in order to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of that object. Hence, most studies include at least one other characterization method in addition to LIF. In time, technological advances that have allowed the miniaturization of optics and electronics have also sustained the design and creation of hybrid systems. The combination of two or more spectroscopic techniques can yield a better, more complex analysis of the studied material or object, as complementary information can be obtained. The main key for the components of these combined systems is to be partially compatible, that is, to have some common parts. Since the early 2000s, heritage scientists have sensed the usefulness of hybrid techniques, and multiple prototypes have been created by various research groups. Some of the main advantages of hybrid systems, in addition to, of course, multiple analytical abilities, are the fact that they help reduce the time needed for analysis and sample manipulation, and that they can offer greater accuracy by analyzing the same spot on the object’s surface.
A LIBS-LIF system was tested in the beginning of the 2000s, which made use of fundamental, second and third harmonic frequencies (1064, 532, 355 nm) of a nanosecond pulsed Nd:YAG laser [23,112], with pulse energies ranging from 2 to 20 mJ. However, that system has had limited use, only for pigment analysis, with potential applications in art and archaeology. Other studies from the same period, with the potential to be applied in the heritage sciences, focused on applying LIBS-LIF systems for the detection of metal, obtaining their specific spectral signals [113,114]. However, despite their versatility and simplicity, LIBS-LIF (or LA-LIF, when LIF measurements are performed in the plasma generated by laser ablation [115]), such hybrid systems have not been further developed.
Another possible combination is that of LIF with Raman spectroscopy. In itself, any Raman device can be observed as hybrid, as it can also yield fluorescence [22], along with the Raman signal, although most times this is considered an unwanted effect [116]. Given that the Raman technique employs lasers in the Vis-IR region, and that LIF works best with UV lasers, their combination would yield a complex, complete characterization of the investigated materials. LIF–Raman combinations are possible and there have been some attempts to merge those two techniques in the mid-90s [117,118] for applications in the automotive and aeronautical industries, specifically flame combustion modeling. However, similarly to the LIBS–LIF hybrid, these systems have not known much success and the use of such combined techniques has not been reported in the field of heritage sciences to date.
By far, though, one of the most proficient combinations was that of LIBS with Raman, both of which allow for rapid, online, in situ analysis, without sample preparation [119]. This kind of set-up is the most predominant in the heritage literature, and, as such, there are even reviews on this topic [120]. The combination of these two techniques has even yielded miniaturized set-ups suitable for in situ applications [121]. The two techniques share similar instrumental configurations, but require different specifications in terms of resolution, efficiency, and spectral range [122]. The ease of combining these two techniques comes from the fact that operators can easily switch from LIBS to Raman, just by reducing the laser pulse energy to avoid thermal damage and/or ablation. Although, at first, their potential started to be explored in the frames of planetary missions [123], for the analysis of minerals and rock samples, their operating principle makes them easily adjustable for heritage studies. In fact, mineral and pigment samples are amongst the most studied with the use of hybrid LIBS–Raman systems [119,122,124,125,126]. Numerous studies have focused on demonstrating the potential of this hybrid technique, while some have tried to make a step towards material discrimination and classification.
Giakoumaki and associates [116] used a Nd:YAG laser emitting at 532 nm, whose energy was varied between 0.01–0.1 mJ/pulse, corresponding to a fluence below the ablation threshold of 0.03–0.3 J/cm2 for the Raman experiment and 2–4 mJ, corresponding to a fluence between 6 and 12 J/cm2 for the LIBS experiment, in the attempt to characterize powder pigments. Similar parameters were used for the study of three types of samples: fresco, terracotta, and bronze (nanosecond Q-switched Nd:YAG laser emitting at 532 nm, 8 ns pulse duration, variable pulse energy between 0.005 and 115 mJ, 220 Hz repetition rate) in a study by Osticioli and co-workers [127]. They observed that LIBS and Raman spectroscopy had a high correlation in terms of identifying fresco components, and that this combination could yield important information in regard to the manufacturing technique used for the terracotta samples. However, they also highlighted the limitations of this combination, given that no clear Raman signal could be obtained for the metal sample, due to the formation of degradation products. Overall, they concluded that LIBS–Raman hybrid set-ups are highly versatile in terms of the real-time identification of the chemical composition of different materials, with clear spectral responses.
Han and partners [128] tried to highlight the features of calcium minerals, calcite, aragonite, gypsum, and anhydrite by using a hybrid LIBS–Raman set-up consisting of a nanosecond Nd:YAG laser operating at 532 nm, different optical paths, and detector systems for collecting the Raman and LIBS signals. Sharma and colleagues also focused on minerals, including carbonates, sulphates, and silicates, in their study [129]. However, even this type of combination is not suitable for all purposes. For instance, in addition to the limitations indicated in [127], Nevin and Osticioli were not been able to differentiate between natural and synthetic ultramarine by simply using the LIBS–Raman technique. However, they obtained satisfactory results when they combined the data obtained from the LIBS–Raman technique with principal component analysis [126].
In the last 10 years, researchers have extended this combination of LIBS and Raman by also adding LIF. The combination of these three techniques can provide lots of advantages: LIBS can produce real-time, accurate, qualitative, and quantitative information about the elemental composition of solid, liquid, and even gas samples, and it has a low detection limit. Thus, hybrid LIBS–LIF–Raman systems have been reported in several studies [78,129,130,131,132,133,134]. Although the scheme of a triple combination of instruments into one might seem complicated, the similarity between these three techniques actually allows it to be simplified. A typical LIBS–LIF–Raman set-up can contain just one laser, such as a common Nd:YAG laser, which is capable of generating up to five harmonics (1064, 532, 355, 266, 213), with variable pulse energies from around a hundred mJ for the LIBS experiments, down to a few mJ for the LIF experiments and few hundreds of µJ for Raman. The necessary optics would only involve some mirrors and lenses, a polarizer, high-density and notch filters, a beam-splitting crystal, plus an acquisition system, which comprises a monochromator with different diffraction gratings, a detector, and a computer. These three techniques can be merged into a single, small set-up [48], which could be useful not only for laboratory experiments, but also for field campaigns, as such sealed lasers are water- and dust-resistant.
6. Enhancing LIF Analytical Capacity
For some of the molecular characterization techniques applied in heritage science studies, such as Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy or Raman spectroscopy, there is a plethora of freely available, high-quality information useful for the identification of a diverse range of specific compounds, including minerals, but not limited to, pigments or additives [135,136,137,138,139]. The same, however, cannot be said about laser-induced fluorescence spectra, as such types of resources are not available. This may be, at least partially, due to the fact that compound identification is not always straightforward in LIF; numerous fluorophores have overlapping emission domains, which makes it difficult to identify compounds. Therefore, in cases when fluorophores identification is not a simple process, several authors have tried to obtain new ways to improve this process in the fluorescence spectra and resolve the overlapping broadband emissions coming from different fluorophores.
As mentioned by Dooley et al. [140], collecting both fluorescence and reflectance spectra on the same spot and applying a Kubelka–Munk correction function can enhance the fluorescence results by mitigating the quenching effect that may sometimes occur.
Another possible approach to enhancing the analytical capabilities of LIF is to use time-resolved measurements. Time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence (TR-LIF) differs from conventional fluorescence intensity measurements by the fact that the emission detection occurs after the excitation has occurred, while for the fluorescence intensity measurements, excitation and emission occur at the same time. TR-LIF has been chosen by multiple authors because it offers information beyond the possibilities of standard fluorescence intensity measurements, that is, it can provide information about the excited state dynamics and fluorophores, and can overcome the shortcomings of conventional fluorescence intensity measurements [72,73]. Although not all investigated materials showed a usable signal, by selecting proper TR-LIF delay times and gate windows, Marinelli and collaborators [72,73] were able to obtain the specific signals of several natural and synthetic binders and some commercial paints.
7. Data Post-Processing
Another way to improve LIF results is to apply post-processing chemometric methods, which help reduce the dimensionality of big datasets and obtain hidden patterns within mixed signals. Chemometric methods are being routinely employed at present in the post-processing of spectroscopic data, such as XRF, Raman, and FTIR, enhancing the usefulness of these methods [141,142]. Some of the chemometrics encountered in LIF studies are principal component analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis (CA). The theory behind PCA and CA has been detailed in many studies [143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151]. Briefly, PCA is an unsupervised classification method and one of the most-used chemometric approaches in the heritage sciences. Its main purpose is dimension reduction and to compute a new coordinate system, based on the entry data, in which the coordinates are known as principal components (PCs). PCA aims to explain as much as possible of the dataset’s variability with as few PCs as possible [152]. Although the principal components do not have a direct physical correspondence, they reflect the variable inputs, consisting of the main fluorescence bands, as identified in the spectra. Cluster analysis is also an unsupervised classification method. It aims to arrange the dataset into clusters based on similarity, although the created clusters may not necessarily have the same size and shape. Several approaches to CA have been proposed in the literature, such as partitioning methods, hierarchical methods, fuzzy clustering methods, or model-based clustering [152]. At present, there are several software options available on the market, which allow the user to easily apply such statistical methods, without having the need to create complicated mathematical models.
In an early experiment performed by Lognoli and associates [29], in which PCA was applied on lidar fluorescence data, the authors did not observe any significant improvement in applying this statistical method, for the discrimination of green algae and cyanobacteria, nor for the evaluation of biocide action on biodeteriogens. The study showed similar minimal-detection values by direct examination and after PCA processing. In a successive study by the same author and his colleagues [31], PCA was applied on lidar fluorescence data to create thematic maps, highlighting vulnerable areas on the surface of the cathedral and baptistry of Parma, in Italy. PCA was also applied by Raimondi and colleagues [43] in order to analyze the different spectral shapes and to identify the separate contributions of bacterial (Bacillus sp.1, Bacillus sp.2, Pseudomonas sp.1, Pseudomonas sp.2) and fungal (Aureobasidium pullulans, Verticillium sp.) strains. The authors also used hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) and compared the results with those from the PCA, noticing that both PCA and CA results were consistent with each other, and were able to distinguish between bacteria and fungi, separating the contribution of the culture medium from that of the fungal or bacterial strain. Moreover, they managed to differentiate not only between genera, but even between strains, thus opening new perspectives for the accurate detection and differentiation of heterotrophic biodeteriogens.
Given the interference of binders on the analytical determination of organic pigments, together with the already complicated process of identifying overlapping fluorescence signals, Romani and co-workers tried to enhance the differential determination of individual fluorophores in mixtures of organic pigments in binders. To this aim, they applied several multivariate analysis methods to the fluorescence spectra: PCA, MCR (multi-curve resolution), and SAM (spectral angle mapper) [67]. PCA was used to identify the dominant spectral features in the fluorescence spectra of different concentrations of phthalocyanine and azo pigments, the MCR method was used to determine and apply constraints in order to reduce and eliminate the ambiguity associated with a dataset, that is, to retrieve real contributions from different spectral components in a mixture, and the SAM projection algorithm was applied on the fluorescence images acquired, in order to characterize the surface of the samples. The results showed that PCA was useful in discriminating the phthalocyanines’ fluorescence, with characteristic bands at 420 and 650 nm, and also that of azo compounds, which showed a specific emission rate at 520 nm. At the same time, the authors noticed that the addition of acrylic binders resulted in a bathochromic shift of these bands, for which PCA and MRA have helped isolate individual components. The space distribution of the organic pigments in color strips was assessed with the SAM algorithm. When moving forward, from laboratory samples to real, contemporary artwork, the authors observed that MCR was best suited to identify pure compounds.
CA and PCA were applied to lidar fluorescence data, so as to classify the biological patina and soiling patterns on limestone and marble surfaces from the façade of the Coliseum, in Rome, Italy [49].
Multivariate analysis has proven useful for the classification of different classes of binders, and also for the differentiation between fresh and aged binding media [62]. The results of this study could have implications in authentication studies.
Although, especially for pigments of the same family, which are characterized by the same spectral shape, the difference between them could be as subtle as simply a variation in their fluorescence intensity values [83,153], several authors have reached the conclusion that it is best to normalize the spectra used for statistical analysis, so as to reduce the influence of intensity variations [65]. The study conducted by Mounier and colleagues showed that PCA was able to classify the pigments used in 13–16th century illuminated manuscripts based on their fluorescence response. Similarly, PCA, along with the spectral angle mapper (SAM) had proven useful for discriminating between the very similar spectra of microbial communities developed on tufa obtained from the Roman catacombs [154].
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
Regarding the use of laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy in the heritage sciences, numerous details can be retrieved from the scientific literature regarding the experimental set-ups of the various LIF or LIF-including hybrids. Not a lot of information, however, can be gathered about the specific parameters of the lasers included in those studies, not even about the manufacturer. There are a few groups that have dedicated their time to the design and development of LIF ensembles, but which have been patented and used in-house, and have not been commercialized.
While LIF could be an alternative for (micro-)destructive techniques, it may also prove to be a good alternative for other techniques that are considered to be non-destructive, such as Raman spectroscopy. For instance, in cases when the Raman signal is obscured by a high-fluorescent background, LIF could be a viable option to identify the composition of the investigated material. However, one of the main drawbacks of LIF is the overlapping of the specific emissions of various fluorophores, which makes it difficult to identify individual fingerprints, especially from similar compounds of classes of materials. Therefore, a legitimate question would be that, in addition to the experiments performed to date, is there still a future for LIF in heritage science studies? The answer to this question would most probably be a positive one, given that the efficiency of LIF is greatly enhanced when coupled with multivariate data analysis methods. Moreover, hybrid techniques that incorporate LIF are continuously being developed and tested in both laboratory studies and field experiments, thus proving an ongoing interest in non-invasive, real-time investigation methods and set-ups.
Of the studied references, one can observed that the domain of the analytical investigation of historical documents and textiles has not received much attention; therefore, this might be a direction that could be extended further in the future. Moreover, the field of biocontamination and new methods of biocleaning would probably be of interest in the near-future, along with improved multivariate statistical methods to decompose and analyze similar fluorescence-emission signals.
Moreover, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, there are no published studies on the use of LIF for the traceability of rocks, pigments, or archaeological findings; therefore, this might also be a direction worth exploring in the future.
Future prospects may also include the expansion of nonlinear optical spectroscopy (multiphoton excitation fluorescence spectroscopy and second and third harmonics generation) domains, which may provide information on multiple levels—about the composition, structure, and morphology of the analyzed materials, with the use of rapid-response lasers.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors11020100/s1, Table S1: Synthesis of the types of lasers used in laser-induced fluorescence studies in the field of cultural heritage.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.G.; literature search and data analysis, L.G. and I.M.C.; writing—original draft preparation, L.G.; writing—review and editing, L.G. and I.M.C.; funding acquisition, I.M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitization, CCCDI—UEFISCDI, project number PN-III-P2-2.1-PED-2021-3576, within PNCDI III, and through the Core Program within the National Research Development and Innovation Plan 2022-2027, conducted with the support of MCID, project no. PN 23 05.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are contained within the article or supplementary material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Telle, H.H.; Gonzalez Urena, A.; Donovan, R.J. Laser-induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy. In Laser Chemistry: Spectroscopy, Dynamics and Applications; Chichester: West Sussex, UK, 2007; pp. 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Jablonski, A. Über den Mechanisms des Photolumineszenz von Farbstoffphosphoren. Z. Phys. 1935, 94, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, L.; Nevin, A.; Nodari, L.; Comelli, D.; Alberti, R.; Gironda, M.; Mosca, S.; Zendri, E.; Piccolo, M.; Izzo, F.C. In-situ technical study of modern paintings part 1: The evolution of artistic materials and painting techniques in ten paintings from 1889 to 1940 by Alessandro Milesi (1856–1945). Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, T.C. Laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF). In Laser Spectroscopy for Sensing: Fundamentals, Techniques and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Borisova, E.G.; Angelova, L.P.; Pavlova, E.P. Endogenous and Exogenous Fluorescence Skin Cancer Diagnostics for Clinical Applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghervase, L.; Carstea, E.; Borisova, E.; Forsea, A. Bringing Light into the Diagnosis of Skin Disorders-Short Review on Laser Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Optical Coherence Tomography in Dermatology. Curr. Med Imaging Former. Curr. Med Imaging Rev. 2014, 10, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbarini, V.; Rossi, R.; Ciparisse, J.F.; Carestia, M.; Gaudio, P.; Malizia, A.; Divizia, A.; De Filippis, P.; Anselmi, M.; Palombi, L.; et al. Laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) as a smart method for fast environmental virological analyses: Validation on Picornaviruses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüttinger, S.; Spille, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Schlüter, M. Laser-Induced Fluorescence in Multiphase Systems. ChemBioEng Rev. 2018, 5, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönlund, R.; Hällström, J.; Johansson, A.; Palombi, L.; Lognoli, D.; Raimondi, V.; Cecchi, G.; Barup, K.; Conti, C.; Brandt, O.; et al. Laser-Induced Fluorescence for Assessment of Cultural Heritage. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Laser Radar Conference, Nara, Japan, 24–28 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Spizzichino, V.; Angelini, F.; Caneve, L.; Colao, F.; Corrias, R.; Ruggiero, L. In Situ study of modern synthetic materials and pigments in contemporary paintings by laser-induced fluorescence scanning. Stud. Conserv. 2015, 60, S178–S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghervase, L.; Carstea, E.M.; Pavelescu, G.; Savastru, D. Laser induced fluorescence efficiency in water quality assessment. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2010, 62, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Fotakis, C.; Anglos, D.; Zafiropulos, V.; Georgiou, S.; Tornari, V. Lasers in the Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Principles and Applications; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Caso, M.F.; Caneve, L.; Spizzichino, V. Intercalibration of Hyperspectral and Multispectral Systems for Laser Induced Fluorescence Imaging. 2019. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12079/54661 (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Angheluta, L.; Striber, J.; Radvan, R.; Simileanu, M. Automated optoelectronic device for qualitative analysis of the artwork surfaces using the LIF technique. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2008, 60, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, J.M.; Utkin, A.B. Application of laser-induced fluorescence in functional studies of photosynthetic biofilms. Processes 2018, 6, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, R.N. My life with lIF: A personal account of developing laser-induced fluorescence. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.T.; Lai, E.P.C. Current state of laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy for designing biochemical sensors. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesan, H.; Kumar, S.S. Laser-Induced Fluorescence (LIF) Spectroscopy of Trapped Molecular Ions in the Gas Phase. Appl. Spectrosc. 2022, 76, 1393–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharioudaki, D.-E.; Fitilis, I.; Kotti, M. Review of Fluorescence Spectroscopy in Environmental Quality Applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwaśny, M.; Bombalska, A. Applications of Laser-Induced Fluorescence in Medicine. Sensors 2022, 22, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, A.; Spoto, G.; Anglos, D. Laser spectroscopies for elemental and molecular analysis in art and archaeology. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2012, 106, 339–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglos, D.; Balas, C.; Fotakis, C. Laser spectroscopic and optical imaging techniques in chemical and structural diagnostics of painted artwork. Am. Lab. 1999, 31, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, T. Fluorescence from resins for oil painting under N2 laser excitation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 29, 1727–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglos, D.; Couris, S.; Mavromanolakis, A.; Zergioti, I.; Solomidou, M.; Liu, W.; Papazoglou, T.; Zafiropulos, V.; Fotakis, C.; Doulgeridis, M.; et al. Artwork diagnostics laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and laser induced fluorescence (LIF) spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks: LACONA I Proceedings, Heraklion, Greece, 4–6 October 1995; Mayer: Vienna, Austria, 1997; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Borgia, I.; Fantoni, R.; Flamini, C.; Di Palma, T.M.; Guidoni, A.G.; Mele, A. Luminescence from pigments and resins for oil paintings induced by laser excitation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 127–129, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, G.; Pantani, L.; Raimondi, V.; Tomaselli, L.; Lamenti, G.; Tiano, P.; Chiari, R. Fluorescence lidar technique for the remote sensing of stone monuments. J. Cult. Heritage 2000, 1, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillejo, M.; Martín, M.; Oujja, M.; Silva, D.; Torres, R.; Domingo, C.; Garcia-Ramos, J.; Sanchez-Cortes, S. Spectroscopic analysis of pigments and binding media of polychromes by the combination of optical laser-based and vibrational techniques. Appl. Spectrosc. 2001, 55, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lognoli, D.; Lamenti, G.; Pantani, L.; Tirelli, D.; Tiano, P.; Tomaselli, L. Detection and characterization of biodeteriogens on stone cultural heritage by fluorescence lidar. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 1780–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colao, F.; Fiorani, L.; Fantoni, R.; Palucci, A.; Striber, J. Diagnostics of stone samples by laser induced fluorescence. In Proceedings of the SPIE 5581: ROMOPTO 2003: Seventh Conference on Optics, Constantat, Romania, 8–11 September 2003; Volume 5581, pp. 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Lognoli, D.; Cecchi, G.; Mochi, I.; Pantani, L.; Raimondi, V.; Chiari, R.; Johansson, T.; Weibring, P.; Edner, H.; Svanberg, S. Fluorescence lidar imaging of the cathedral and baptistery of Parma. Appl. Phys. B Laser Opt. 2002, 76, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantani, L.; Cecchi, G.; Lognoli, D.; Mochi, I.; Raimondi, V.; Tirelli, D.; Trambusti, M.; Valmori, G.; Weibring, P.K.A.; Edner, H.; et al. Lithotypes characterization with a fluorescence lidar imaging system using a multi-wavelength excitation source. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring, GIS Applications, and Geology II, Barcelona, Spain, 9–11 September 2003; pp. 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, D.; D’Andrea, C.; Valentini, G.; Cubeddu, R.; Colombo, C.; Toniolo, L. Fluorescence lifetime imaging and spectroscopy as tools for nondestructive analysis of works of art. Appl. Optics 2004, 43, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, A.; Cather, S.; Anglos, D.; Fotakis, C. Laser-induced fluorescence analysis of protein-binding media, in the conservation of artworks. In Proceedings of the Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks: LACONA VI Proceedings, Vienna, Austria, 21–25 September 2005; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozlee, B.J.; Misra, A.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Ingram, M. Remote Raman and fluorescence studies of mineral samples. Spectroc. Acta Pt. A-Molec. Biomolec. Spectr. 2005, 61, 2342–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristipini, P.; Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Fiorani, L.; Palucci, A. Compact scanning lidar fluorosensor for cultural heritage diagnostics. In Advanced Laser Technologies; Laser Technology Co., Ltd.: Hong Kong, 2004; pp. 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Fiorani, L.; Palucci, A.; Gomoiu, I. Compact scanning lidar fluorosensor for investigations of biodegradation on ancient painted surfaces. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2005, 7, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar]
- Grönlund, R.; Hällström, J.; Johansson, A.; Barup, K.; Svanberg, S. Remote multicolor excitation laser-induced fluorescence imaging. Laser Chem. 2006, 57934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Fiorani, L.; Palucci, A. Application of a scanning hyperspectral lidar fluorosensor to fresco diagnostincs during the CULTURE 2000 campaign in Bucovina. Rev. Monum. Istor. 2006, 1–2, LXXV. [Google Scholar]
- Nevin, A.; Cather, S.; Anglos, D.; Fotakis, C. Analysis of protein-based binding media found in paintings using laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 573–574, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komar, K.; Sliwinski, G. Non-Destructive Observation of the Laser Treatment Effect on Historical Paper via the Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectra. In Proceedings of the Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks: LACONA VI Proceedings, Vienna, Austria, 21–25 September 2005; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, A.; Comelli, D.; Valentini, G.; Anglos, D.; Burnstock, A.; Cather, S.; Cubeddu, R. Time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging of proteinaceous binders used in paintings. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, V.; Palombi, L.; Cecchi, G.; Lognoli, D.; Trambusti, M.; Gomoiu, I. Remote detection of laser-induced autofluorescence on pure cultures of fungal and bacterial strains and their analysis with multivariate techniques. Opt. Commun. 2007, 273, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osticioli, I.; Nevin, A.; Anglos, D.; Burnstock, A.; Cather, S.; Becucci, M.; Fotakis, C.; Castellucci, E. Micro-Raman and fluorescence spectroscopy for the assessment of the effects of the exposure to light on films of egg white and egg yolk. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2008, 39, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, A.; Anglos, D.; Cather, S.; Burnstock, A. The influence of visible light and inorganic pigments on fluorescence excitation emission spectra of egg-, casein- and collagen-based painting media. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2008, 92, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claro, A.; Melo, M.J.; Schäfer, S.; de Melo, J.S.S.; Pina, F.; Berg, K.J.V.D.; Burnstock, A. The use of microspectrofluorimetry for the characterization of lake pigments. Talanta 2008, 74, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimis, A.; Vounisiou, P.; Tserevelakis, G.J.; Melessanaki, K.; Pouli, P.; Filippidis, G.; Beltsios, C.; Georgiou, S.; Fotakis, C. In-depth assessment of modifications induced during the laser cleaning of modern paintings. In Proceedings of the Proc. SPIE 7391, O3A: Optics for Arts, Architecture, and Archaeology II, Munich, Germany, 14–18 June 2009; p. 73910U. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osticioli, I.; Mendes, N.F.C.; Nevin, A.; Zoppi, A.; Lofrumento, C.; Becucci, M.; Castellucci, E.M. A new compact instrument for Raman, laser-induced breakdown, and laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy of works of art and their constituent materials. Rev. Sci. Instruments 2009, 80, 76109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hällström, J.; Barup, K.; Grönlund, R.; Johansson, A.; Svanberg, S.; Palombi, L.; Lognoli, D.; Raimondi, V.; Cecchi, G.; Conti, C. Documentation of soiled and biodeteriorated facades: A case study on the Coliseum, Rome, using hyperspectral imaging fluorescence lidars. J. Cult. Heritage 2009, 10, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persia, F.; Caneve, L.; Conti, P.; Bosco, C.; Grimaldi, F. Study of aging effects on treated marbles by colorimetry and laser induced fluorescence. In Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on “Science and Technology for the Safeguyard of Cultural Heritage in the Mediterranean Basin”, Cairo, Egypt, 6–8 December 2009; Volume 1, pp. 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Raimondi, V.; Cecchi, G.; Lognoli, D.; Palombi, L.; Grönlund, R.; Johansson, A.; Svanberg, S.; Barup, K.; Hällström, J. The fluorescence lidar technique for the remote sensing of photoautotrophic biodeteriogens in the outdoor cultural heritage: A decade of in situ experiments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, A.; Comelli, D.; Osticioli, I.; Toniolo, L.; Valentini, G.; Cubeddu, R. Assessment of the ageing of triterpenoid paint varnishes using fluorescence, Raman and FTIR spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2139–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toja, F.; Nevin, A.; Comelli, D.; Levi, M.; Cubeddu, R.; Toniolo, L. Fluorescence and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy for the analysis of iconic Italian design lamps made of polymeric materials. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, D.; Nevin, A.; Brambilla, A.; Osticioli, I.; Valentini, G.; Toniolo, L.; Fratelli, M.; Cubeddu, R. On the discovery of an unusual luminescent pigment in Van Gogh’s painting ‘les bretonnes et le pardon de pont Aven. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2012, 106, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancristofaro, C.; D’Amato, R.; Caneve, L.; Pilloni, L.; Rinaldi, A.; Persia, F. Performance of nanocomposites for conservation of artistic stones. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1603, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlesi, S. Optical Spectroscopies: Application to the Study of Paint Models. Ph. D. Thesis, Universita degli Studi Firenze, Florence, Italy, 2012. Available online: https://flore.unifi.it/retrieve/handle/2158/1043901/138014/PhD_Thesis_SerenaCarlesi.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Oujja, M.; Vázquez-Calvo, C.; Sanz, M.; De Buergo, M.A.; Fort, R.; Castillejo, M. Laser-induced fluorescence and FT-Raman spectroscopy for characterizing patinas on stone substrates. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Caneve, L.; Fiorani, L.; Dell’Erba, R.; Fassina, V. Diagnostica superficiale non invasiva mediante fluorescenza indotta da laser (LIF) sulle pitture murali di Giusto de’ Menabuoi nel Battistero di Padova. In Da Guariento a Giusto de’Menabuoi: Studi, Ricerche e Restauri; Antiga: Crocetta del Montello (Treviso), Italy, 2012; pp. 85–99. [Google Scholar]
- Raimondi, V.; Cucci, C.; Cuzman, O.; Fornacelli, C.; Galeotti, M.; Gomoiu, I.; Lognoli, D.; Mohanu, D.; Palombi, L.; Picollo, M.; et al. Study of the effects of low-fluence laser irradiation on wall paintings: Test measurements on fresco model samples. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 284, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneve, L.; Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Fiorani, L. Scanning lidar fluorosensor for remote diagnostic of surfaces. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A-Accel. Spectrom. Dect. Assoc. Equ 2013, 720, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oujja, M.; Sanz, M.; Rebollar, E.; Marco, J.; Domingo, C.; Pouli, P.; Kogou, S.; Fotakis, C.; Castillejo, M. Wavelength and pulse duration effects on laser induced changes on raw pigments used in paintings. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 102, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, M.R.; Orecchio, S.; Gennaro, G. Microanalytical method for studying paintings by use of fluorescence spectroscopy combined with principal component analysis. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantoni, R.; Caneve, L.; Colao, F.; Fiorani, L.; Palucci, A.; Dell’Erba, R.; Fassina, V. Laser-induced fluorescence study of medieval frescoes by Giusto de’ Menabuoi. J. Cult. Heritage 2013, 14, S59–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, V.; Karatodorov, S.; Yankov, G.; Zahariev, P.; Tsvekova, E. Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy–a Contemporary Approach to Cultural Heritage. Adv. Bulg. Sci. 2013, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mounier, A.; Le Bourdon, G.; Aupetit, C.; Belin, C.; Servant, L.; Lazare, S.; Lefrais, Y.; Daniel, F. Hyperspectral imaging, spectrofluorimetry, FORS and XRF for the non-invasive study of medieval miniatures materials. Heritage Sci. 2014, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, A.; Cesaratto, A.; Bellei, S.; D’Andrea, C.; Toniolo, L.; Valentini, G.; Comelli, D. Time-resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy and imaging: New approaches to the analysis of cultural heritage and its degradation. Sensors 2014, 14, 6338–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, M.; Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Guiso, M.; Santarelli, M.L. Hyperspectral Fluorescence for Organic Pigment Characterization in Contemporary Artwork. J. Appl. Laser Spectrosc. 2014, 1, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Raimondi, V.; Andreotti, A.; Colombini, M.P.; Cucci, C.; Cuzman, O.; Galeotti, M.; Lognoli, D.; Palombi, L.; Picollo, M.; Tiano, P. Test measurements on a secco white-lead containing model samples to assess the effects of exposure to low-fluence UV laser radiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 337, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, R.; Ortiz, P.; Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Gómez-Morón, M.; Vázquez, M. Laser spectroscopy and imaging applications for the study of cultural heritage murals. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounier, A.; Lazare, S.; Le Bourdon, G.; Aupetit, A.; Servant, L.; Daniel, F. LEDμSF: A new portable device for fragile artworks analyses. Application on medieval pigments. Microchem. J. 2016, 126, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneve, L.; Colao, F.; Del Franco, M.; Palucci, A.; Pistilli, M.; Spizzichino, V. Multispectral imaging system based on laser-induced fluorescence for security applications. In Proceedings of the Proc. SPIE 9995, Optics and Photonics for Counterterrorism, Crime Fighting, and Defence XII, Edinburgh, UK, 26–29 September 2016; p. 999509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, M.; Pasqualucci, A.; Romani, M.; Verona-Rinati, G. Time resolved laser induced fluorescence for characterization of binders in contemporary artworks. J. Cult. Heritage 2017, 23, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, M.; Marinelli, M.; Pasqualucci, A.; Verona-Rinati, G. A preliminary study of contemporary binders by Time Resolved Laser Induced Fluorescence (TR-LIF) spectroscopy: Characterization of the painting Nascita Della Forma by Nato Frascà. In Proceedings of the Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks: LACONA XI Proceedings, Kraków, Poland, 20–23 September 2016; Nicolaus Copernicus University Press: Toruń, Poland, 2017; pp. 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oujja, M.; Psilodimitrakopoulos, S.; Carrasco, E.; Sanz, M.; Philippidis, A.; Selimis, A.; Pouli, P.; Filippidis, G.; Castillejo, M. Nonlinear imaging microscopy for assessing structural and photochemical modifications upon laser removal of dammar varnish on photosensitive substrates. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 22836–22843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronti, L.; Felici, A.C.; Ménager, M.; Vieillescazes, C.; Piacentini, M. Spectral Behavior of White Pigment Mixtures Using Reflectance, Spectral Behavior of White Pigment Mixtures Using Reflectance, Ultraviolet-Fluorescence Spectroscopy, and Multispectral Imaging. Appl Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaviva, S.; Fantoni, R.; Colao, F.; Puiu, A.; Bisconti, F.; Nicolai, V.F.; Romani, M.; Cascioli, S.; Bellagamba, S. LIF/Raman/XRF non-invasive microanalysis of frescoes from St. Alexander catacombs in Rome. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 201, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Hernández, A.; Oujja, M.; Sanz, M.; Carrasco, E.; Detalle, V.; Castillejo, M. Analysis of heritage stones and model wall paintings by pulsed laser excitation of Raman, laser-induced fluorescence and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signals with a hybrid system. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvilay, D.; Bai, X.; Wilkie-Chancellier, N.; Texier, A.; Martinez, L.; Serfaty, S.; Detalle, V. Laser-induced emission, fluorescence and Raman hybrid setup: A versatile instrument to analyze materials from cultural heritage. Spectrochim. Acta-Part B At. Spectrosc. 2018, 140, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzi, L.; Andreotti, A.; Bressan, M.; Colombini, M.P.; Corti, C.; Cuzman, O.; D’Alessandro, N.; Liberatore, L.; Palombi, L.; Raimondi, V.; et al. An interdisciplinary approach to a knowledge-based restoration: The dark alteration on Matera Cathedral (Italy). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, P.; Iwanicka, M.; Melessanaki, K.; Dimitroulaki, E.; Kokkinaki, O.; Daugherty, M.; Sylwestrzak, M.; Pouli, P.; Targowski, P.; Berg, K.J.V.D.; et al. Laser cleaning of paintings: In situ optimization of operative parameters through non-invasive assessment by optical coherence tomography (OCT), reflection FT-IR spectroscopy and laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF). Heritage Sci. 2019, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneve, L.; Guarneri, M.; Lai, A.; Spizzichino, V.; Ceccarelli, S.; Mazzei, B. Non-destructive laser based techniques for biodegradation analysis in cultural heritage. NDT E Int. 2019, 104, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, L.; Rugnini, L.; Spizzichino, V.; Caneve, L.; Canini, A.; Ellwood, N.T.W. Biodeterioration of Roman hypogea: The case study of the Catacombs of SS. Marcellino and Pietro (Rome, Italy). Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, M.; Almaviva, S.; Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Marinelli, M.; Pasqualucci, A.; Puiu, A.; Verona-Rinati, G. Raman and Time-Gated-Lif Spectroscopy for the Identification of Painting Materials. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2019, 86, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fovo, A.D.; Oujja, M.; Sanz, M.; Martínez-Hernández, A.; Cañamares, M.V.; Castillejo, M.; Fontana, R. Multianalytical non-invasive characterization of phthalocyanine acrylic paints through spectroscopic and non-linear optical techniques. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 208, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Morón, M.A.; Ortiz, R.; Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Luna, J.B.; Ortiz, P. Laser-Induced Fluorescence mapping of pigments in a secco painted murals. Ge-Conservacion 2020, 17, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Morón, M.A.; Ortiz, R.; Colao, F.; Fantoni, R.; Gómez-Villa, J.L.; Becerra, J.; Ortiz, P. Monitoring the Restoration of a Seventeenth-Century Wooden Artwork Using Laser-Induced Fluorescence and Digital Image Analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 2021, 75, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, S.; Guarneri, M.; Romani, M.; Giacopini, L.; Francucci, M.; Ciaffi, M.; De Collibus, M.F.; Puiu, A.; Verona-Rinati, G.; Colao, F.; et al. Are the blue daemons really blue? Multidisciplinary study for the colours characterization of the mural paintings inside the Blue Daemons Etruscan tomb. J. Cult. Heritage 2020, 47, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oujja, M.; Agua, F.; Sanz, M.; Morales-Martin, D.; García-Heras, M.; Villegas, M.; Castillejo, M. Multiphoton Excitation Fluorescence Microscopy and Spectroscopic Multianalytical Approach for Characterization of Historical Glass Grisailles. Talanta 2021, 230, 122314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caso, M.F.; Caneve, L.; Spizzichino, V. Improvement of ENEA laser-induced fluorescence prototypes: An intercalibration between a hyperspectral and a multispectral scanning system. Acta IMEKO 2021, 10, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, T.; Martínez-Weinbaum, M.; Aparicio, M.; Maestro-Guijarro, L.; Castillejo, M.; Oujja, M. Spectroscopic and Microscopic Characterization of Flashed Glasses from Stained Glass Windows. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglos, D.; Georgiou, S.; Fotakis, C. Lasers in the analysis of cultural heritage materials. J. Nano Res. 2009, 8, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, A.; Echard, J.-P.; Thoury, M.; Comelli, D.; Valentini, G.; Cubeddu, R. Excitation emission and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy of selected varnishes used in historical musical instruments. Talanta 2009, 80, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, L.; Riedo, C.; Baraldi, C.; Nevin, A.; Gamberini, M.C.; D’Andrea, C.; Chiantore, O.; Goidanich, S.; Toniolo, L. Characterization of fresh and aged natural ingredients used in historical ointments by molecular spectroscopic techniques: IR, Raman and fluorescence. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lazzaro, P.; Guarneri, M.; Murra, D.; Spizzichino, V.; Danielis, A.; Mencattini, A.; Piraccini, V.; Missori, M. Noninvasive analyses of low-contrast images on ancient textiles: The case of the Shroud of Arquata. J. Cult. Heritage 2016, 17, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, L.J.; Shin, K.-S.K.; Zink, J.I. Photoluminescence spectroscopy of natural resins and organic binding media of paintings. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 1991, 30, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persia, F.; Caneve, L.; Colao, F.; D’Amato, R.; Giancristofaro, C.; Ricci, G.; Pilloni, L.; Rinaldi, A. Performance of nanocomposites for conservation of artistic stones. In Proceedings of the 12th International Congress on the Deterioration and Conservation of Stone, New York, NY, USA, 22–26 October 2012; pp. 66–77. [Google Scholar]
- Osticioli, I.; Mendes, N.; Nevin, A.; Gil, F.P.; Becucci, M.; Castellucci, E. Analysis of natural and artificial ultramarine blue pigments using laser induced breakdown and pulsed Raman spectroscopy, statistical analysis and light microscopy. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 73, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.; Magnain, C.; Barthou, C.; Nevin, A.; Comelli, D.; Valentini, G. UV-fluorescence spectroscopy for identification of varnishes in works of art: Influence of the underlayer on the emission spectrum. In Proceedings of the Proc. SPIE 7391, O3A: Optics for Arts, Architecture, and Archaeology II, Munich, Germany, 14–18 June 2009; p. 739104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, K.; Pérez, M.; Rodríguez-Laso, M.D.; Madariaga, J.M. FTIR spectra database of inorganic art materials. Analytical Chemistry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, A. FORS Spectral Database of Historical Pigments in Different Binders. E-Conserv. J. 2014, 2, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, K.; Alonso, M.P.; Rodríguez-Laso, M.D.; Fernández, L.A.; Madariaga, J.M. On-line FT-Raman and dispersive Raman spectra database of artists’ materials (e-VISART database). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortea, I.M.; Chiroșca, A.; Angheluță, L.M.; Serițan, G. INFRA-ART: An Open Access Spectral Library of Art-Related Materials as a Digital Support Tool for Cultural Heritage Science. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2023, 16, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Weibring, P.; Edner, H.; Svanberg, S. Versatile mobile lidar system for environmental monitoring. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 3583–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönlund, R.; Svanberg, S.; Hällström, J.; Barup, K.; Cecchi, G.; Raimondi, V.; Lognoli, D.; Palombi, L. Laser-induced fluorescence imaging for studies of cultural heritage. In O3A: Optics for Arts, Architecture, and Archaeology; Society of Photo Optical: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; p. 66180P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, A.; Anglos, D. Assisted interpretation of laser-induced fluorescence spectra of egg-based binding media using total emission fluorescence spectroscopy. Laser Chem. 2006, 2006, 82823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotakis, C.; Kautek, W.; Castillejo, M. Lasers in the Preservation of Cultural Heritage. Laser Chem. 2006, 2006, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simileanu, M.; Avgerinidou, G.; Angheluta, L.; Radvan, R.; Striber, J.; Miu, L. Laser cleaning of XVIIIth, C. parchment with polychrome inscriptions. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Commun. 2009, 2, 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson, M.; Wallström, S.; Sjöholm, M.; Grönlund, R.; Anderson, B.; Larsson, A.; Karlsson, S.; Kröll, S.; Svanberg, S. Fungus covered insulator materials studied with laser-induced fluorescence and principal component analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 2005, 59, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoicho, O.; Olwal, C.O.; Quaye, O. Potential of laser-induced fluorescence-light detection and ranging for future stand-off virus surveillance. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simileanu, M. Libs quantitative analyses of bronze objects for cultural heritage applications. Rom. Reports Phys. 2016, 68, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Burgio, L.; Clark, R.J. Library of FT-Raman spectra of pigments, minerals, pigment media and varnishes, and supplement to existing library of Raman spectra of pigments with visible excitation. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2001, 57, 1491–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anglos, D. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in art and archaeology. Appl. Spectrosc. 2001, 55, 186A–205A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telle, H.; Beddows, D.; Morris, G.; Samek, O. Sensitive and selective spectrochemical analysis of metallic samples: The combination of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta-Part B At. Spectrosc. 2001, 56, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbk-Kortenbruck, F.; Noll, R.; Wintjens, P.; Falk, H.; Becker, C. Analysis of heavy metals in soils using laser-induced breakdown spectrometry combined with laser-induced fluorescence. Spectrochim. Acta-Part B At. Spectrosc. 2001, 56, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.W.; Omenetto, N. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), part II: Review of instrumental and methodological approaches to material analysis and applications to different fields. Appl. Spectrosc. 2012, 66, 347–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumaki, A.; Osticioli, I.; Anglos, D. Spectroscopic analysis using a hybrid LIBS-Raman system. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2006, 83, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, A.R.; Dibble, R.W.; Barlow, R.S. The structure of turbulent nonpremixed flames revealed by Raman-Rayleigh-Lif measurements. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1996, 22, 307–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.S.A.; Bilger, R.W.; Carter, C.D.; Barlow, R.S.; Chen, J.Y. A Comparison of CMC and PDF Modelling Predictions with Experimental Nitric Oxide Lif/Raman Measurements in a Turbulent H2 Jet Flame. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1995, 105, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehse, M.; Mory, D.; Florek, S.; Weritz, F.; Gornushkin, I.; Panne, U. A combined laser-induced breakdown and Raman spectroscopy Echelle system for elemental and molecular microanalysis. Spectrochim. Acta-Part B At. Spectrosc. 2009, 64, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Niu, G.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Duan, Y. Combined laser-induced breakdown with Raman spectroscopy: Historical technology development and recent applications. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2013, 48, 487–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Lin, Q.; Ding, Y.; Tian, D.; Duan, Y. Integrated instrumentation for combined laser-induced breakdown and Raman spectroscopy. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2019, 47, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shameem, K.M.M.; Dhanada, V.S.; Unnikrishnan, V.K.; George, S.D.; Kartha, V.B.; Santhosh, C. A hyphenated echelle LIBS-Raman system for multi-purpose applications. Rev. Sci. Instruments 2018, 89, 073108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courrèges-Lacoste, G.B.; Ahlers, B.; Pérez, F.R. Combined Raman spectrometer/laser-induced breakdown spectrometer for the next ESA mission to Mars. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 68, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Wang, S.; Guo, G.; Tian, Y.; Duan, Y. Novel laser induced breakdown spectroscopy–Raman instrumentation using a single pulsed laser and an echelle spectrometer. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shameem, K.M.; Dhanada, V.; Harikrishnan, S.; George, S.D.; Kartha, V.; Santhosh, C.; Unnikrishnan, V. Echelle LIBS-Raman system: A versatile tool for mineralogical and archaeological applications. Talanta 2020, 208, 120482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevin, A.; Osticioli, I. Statistical analysis of laser-based spectroscopic data elucidates painting materials. SPIE Newsroom 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osticioli, I.; Mendes, N.F.C.; Porcinai, S.; Cagnini, A.; Castellucci, E. Spectroscopic analysis of works of art using a single LIBS pulsed Raman setup. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kim, D.; Choi, S.; Yoh, J.J. A novel classification of polymorphs using combined LIBS and Raman spectroscopy. Curr. Opt. Photonics 2017, 1, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Misra, A.K.; Lucey, P.G.; Lentz, R.C. A combined remote Raman and LIBS instrument for characterizing minerals with 532 nm laser excitation. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 73, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvilay, D. Evaluation of LIBS LIF Raman Spectroscopies to Analyze Materials from Cultural Heritage. Ph. D. Thesis, L’université De Cergy Pontoise, Paris, France, 2016. Available online: http://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:52015148 (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Bai, X.; Oujja, M.; Sanz, M.; Lopez, M.; Dandolo, C.L.K.; Castillejo, M.; Detalle, V. Integrating LIBS LIF Raman into a single multi-spectroscopic mobile device for in situ cultural heritage analysis. In Proceedings of the SPIE 11058, Optics for Arts, Architecture, and Archaeology VII, Munich, Germany, 24–26 June 2019; p. 1105818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detalle, V.; Bai, X.; Bourguignon, E.; Menu, M.; Pallot-Frossard, I. LIBS-LIF-Raman: A new tool for the future E-RIHS. In Proceedings of the Proc. SPIE 10331, Optics for Arts, Architecture, and Archaeology VI, Munich, Germany, 28–29 June 2017; p. 103310N. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasda, P.; Acosta-Maeda, T.; Lucey, P.; Misra, A.; Sharma, S.; Taylor, G. A Compact Laser Induced Breakdown, Raman, and Fluorescence Spectroscopy Instrument for Mars Exploration. In Proceedings of the 45th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 17–21 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanada, V.S.; George, S.D.; Kartha, V.B.; Chidangil, S.; Unnikrishnan, V.K. Hybrid LIBS-Raman-LIF systems for multi-modal spectroscopic applications: A topical review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2021, 56, 463–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, R.T. RRUFF Project. 2006. Available online: https://rruff.info (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Bell, I.M.; Clarck, R.J.H.; Gibbs, P.J. Raman Spectroscopic Library of Natural and Synthetic Pigments. 1998. Available online: http://www.chem.ucl.ac.uk/resources/raman (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Buzgar, N.; Apopei, A.I.; Buzatu, A. Romanian Database of Raman Spectroscopy. 2014. Available online: http://rdrs.uaic.ro (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Rossman, G. Mineral Spectroscopy Server. 2010. Available online: http://minerals.gps.caltech.edu (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Cortea, I.M. INFRA-ART Spectral Library. 2022. Available online: https://infraart.inoe.ro (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Dooley, K.A.; Chieli, A.; Romani, A.; Legrand, S.; Miliani, C.; Janssens, K.; Delaney, J.K. Molecular Fluorescence Imaging Spectroscopy for Mapping Low Concentrations of Red Lake Pigments: Van Gogh’s Painting The Olive Orchard. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 6046–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, G.; Scatigno, C.; Armetta, F.; Saladino, M.L.; Ciaramitaro, V.; Nardo, V.M.; Ponterio, R.C. Chemometric tools to point out benchmarks and chromophores in pigments through spectroscopic data analyses. Molecules 2022, 27, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortea, I.M.; Ghervase, L.; Rădvan, R.; Serițan, G. Assessment of Easily Accessible Spectroscopic Techniques Coupled with Multivariate Analysis for the Qualitative Characterization and Differentiation of Earth Pigments of Various Provenance. Minerals 2022, 12, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal Component Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.I. A tutorial on Principal Components Analysis Introduction; University of Otago: Dunedin, Otago, New Zealand, 2002; Available online: http://www.cs.otago.ac.nz/cosc453/student_tutorials/principal_components.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Drennan, R.D. Principal Components Analysis. In Statistics for Archaeologists. Interdisciplinary Contributions to Archaeology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bro, R.; Smilde, A.K. Principal component analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drennan, R.D. Cluster Analysis. In Statistics for Archaeologists. Interdisciplinary Contributions to Archaeology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.S.; Landau, S.; Leese, M.; Stahl, D. Cluster Analysis, 5th ed.; Wiley: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cutillo, L. Parametric and multivariate methods. In Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scitovski, R.; Sabo, K.; Martínez-Álvarez, F.; Ungar, Š. Cluster Analysis and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Varmuza, K.; Filzmoser, P. Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis in Chemometrics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pelagotti, A.; Pezzati, L.; Bevilacqua, N.; Vascotto, V.; Reillon, V.; Daffara, C. A study of UV fluorescence emission of painting materials. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Non-Destructive Investigations and Microanalysis for the Diagnostics and Conservation of the Cultural and Environmental Heritage, Lecce, Italy, 15–19 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Caneve, L.; Colao, F.; Spizzichino, V. Analysis of Biofilms from Roman Catacombs by Laser Induced Fluorescence and Multivariate Analysis. In Proceedings of the CMA4CH 2010, Mediterraneum Meeting, Application of Multivariate Analysis and Chemometry to Cultural Heritage and Environment, Taormina, Sicily, Italy, 26–29 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).