Abstract
H2S gas sensors were fabricated using Ag nanowire/hollow polypyrrole nanotube nanocomposite (Ag NW/hollow PPy NT) film for sensing ppb-level H2S gas at room temperature. The morphology, phase composition and crystalline structure of Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites were analyzed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffractometry (XRD) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). TEM and SEM images revealed that Ag NWs were well dispersed in the hollow PPy NT matrix. IR results showed no interaction between Ag NWs and hollow PPy NTs in the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites. The effect of the amount of added Ag NWs on the response of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites to the ppb-level H2S gas was investigated. Comparative gas-sensing results revealed that the introduction of Ag NWs onto hollow PPy NTs was effective in promoting the sensor response to H2S gas. More importantly, the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite had a strong response to ppb-level H2S gas at room temperature.
1. Introduction
H2S is an extremely toxic gas that can seriously injure human health and the environment. The odor of H2S is exceedingly strong and smelly and can be detected at a low level. On a population basis, the average odor detection threshold is about 30 to 50 ppb because human noses are very sensitive to H2S in the air [1]. For odor control, the H2S standard is 30 ppb for a one-hour average, as adopted by the California Air Resources Board (CARB). Moreover, the acceptable limit of H2S is 20~100 ppb according to the Scientific Advisory Board on Toxic Air Pollutants, USA [2]. Therefore, fabricating a strongly responsive H2S gas sensor is important for sensing ppb-level H2S gas. Moreover, fabricating a room-temperature-type gas sensor has attracted much attention because it can potentially be applied to air quality Internet of Things (IoT) products [3]. The most important sensing techniques, such as electrochemical gas sensors [4], quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) sensors [5], optical sensors [6] and metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) gas sensors [7] have been widely used to detect H2S gas.
Many reviews on MOSs [8,9], conducting polymers (CPs) [10,11] and their composite materials [12,13,14] for sensing H2S gas have been published. MOSs have been the most popular used materials for sensing H2S gas because of their outstanding properties such as easy fabrication, small size, low weight, and low cost [2]. However, MOS-based H2S gas sensors exhibit a limited selectivity, lack flexibility and generally are operated at a high temperature (>100 °C) [11]. An alternative to MOSs is the use of CPs for sensing H2S gas because of their advantages such as easy preparation, working at room temperature, good flexibility, and capability for sensing H2S gas at a ppb level [14,15]. Among the currently used CPs, polypyrrole (PPy) has attracted considerable attention because of its easy oxidation, conductive property, water solubility, relatively good environmental stability and the commercial availability of pyrrole monomers [13]. Accordingly, PPy has been studied for sensing H2S at room temperature [16,17,18]. Garg et al. [16] fabricated PPy microwires via template-assisted chemical polymerization for sensing 200 ppm of H2S at room temperature. Nerkar et al. [17] fabricated a flexible H2S gas sensor based on PPy film for sensing H2S ranging from 10 ppm to 100 ppm at room temperature. Hasan et al. [18] fabricated PPy nanofibers via chemical polymerization for sensing 30 ppm of H2S at room temperature.
Generally, the incorporation of noble metals into CPs, such as Pd, Au and Ag, is the most attractive strategy for improving gas-sensing responses of the resulting sensors because of the chemical and electronic sensitization effects of noble metals [19,20]. Ag is commonly used to decorate CPs for improving the gas-sensing performances of CP-based gas sensors, such as their response, thermal stability, conductivity and adsorption performance, because Ag has a low cost, very high electrical conductivity, high efficiency and high reactivity toward O2 adsorption [12,21,22,23,24]. Yang et al. [22] fabricated a NH3 gas sensor that was made of Ag nanoparticle (Ag NP)-decorated PPy nanotubes for sensing NH3 ranging from 10 ppm to 200 ppm at room temperature. Khanna et al. [23] fabricated a H2S gas sensor based on an Ag NP-PPy nanocomposite film for sensing H2S at 250 °C. Hasan et al. [24] fabricated a H2S gas sensor that was made of Ag NP-modified PPy nanotubes for sensing 20 ppm of H2S at room temperature. The sensing performance of CP-based gas sensors are related to their morphology, microstructure and size [25,26]. Therefore, the fabrication of nanoscale-based CPs is an attractive strategy for sensing applications. Among the nanostructured materials, one-dimensional (1D) nanomaterials, such as nanowires, nanorods, nanotubes and nanofibers, have been popularly used as sensing materials because of their outstanding properties including a high surface area, high length-to-diameter ratio and fast charge carrier transportation [27,28,29,30,31]. Additionally, the nanomaterials with hollow structures have attracted much interest for many applications due to their distinct advantages, such as large specific surface areas and short distances for the transport of charge carriers [32]. Accordingly, hollow PPy 1D nanomaterials have been used for solid-phase extraction [33], cancer therapy [34] and electromagnetic pollution management [35] applications. However, no attempt has been made to use hollow PPy 1D-based materials for fabricating a ppb-level H2S gas sensor working at room temperature. In this study, a room-temperature ppb-level H2S gas sensor that was made of a Ag nanowire (Ag NW)/hollow PPy nanotube (PPy NT) nanocomposite was fabricated using chemical oxidation and the polyol process. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis were used to analyze the composition and morphologies of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites. The effect of the added amount of the Ag NWs on the response of the H2S gas sensors made of Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites to ppb-level H2S was studied. Furthermore, the gas-sensing properties of the H2S gas sensor based on Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites at room temperature, including the linearity of the sensing curve, response time, recovery time, repeatability, selectivity, influence of ambient humidity, long-term stability and sensing mechanism, were studied.
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
Pyrrole monomer (Py, 98%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), methyl orange (MO, Acros Organics, Geel, Belgium), ammonium persulfate ((NH4)2S2O8, APS, 98.7%, J.T. Baker, NJ, USA), ethylene glycol (C2H6O2, EG, 99%, J.T. Baker), silver nitrate (AgNO3, 99.5%, Shimakyu’s Pure Chemicals, Osaka, Japan), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP, Mw~40,000, Sigma-Aldrich) and copper (II) chloride dihydrate (CuCl2·2H2O, Shimakyu’s Pure Chemicals) were purchased.
2.2. Fabrication of Hollow PPy NTs
Hollow PPy nanotubes were fabricated via a chemical oxidation method according to the literature [36]. Firstly, 0.98 g of MO was dissolved in 150 mL of deionized water (DIW) under magnetic stirring until completely dissolved. Then, 0.7 g of Py monomer was added into the MO solution at 5 °C for 30 min. Additionally, the as-prepared APS solution (the molar ratio of Py to APS was 1:1) was slowly added into the as-prepared mixture of MO and Py solution, and the as-prepared mixture solution was stirred for 24 h at 5 °C. Finally, the black precipitates were washed using ethanol and DIW to obtain a light-yellow filtrate.
2.3. Fabrication of Ag NWs
Ag NWs were prepared by a polyol process according to the previous reports [37,38]. Firstly, 0.022 mM of PVP and 4 mM of CuCl2 were dissolved in 10 mL of EG and heated at 160 °C under vigorously stirring. Then, 0.2 g of AgNO3 was dissolved in the EG solution in the dark, and heated at 160 °C for 40 min. Finally, the as-prepared Ag nanowires were collected via centrifugation and were washed using acetone and DIW.
2.4. Fabrication of H2S Gas Sensor Based on Ag NW/Hollow PPy NT Nanocomposites
Firstly, Ag NW/hollow PPy NT solutions with eight different weight ratios of Ag NWs to hollow PPy NTs were prepared by adding 0.002 g, 0.01 g, 0.02 g, 0.04 g, 0.06 g, 0.08 g, 0.12 g and 0.16 g of Ag NWs, respectively, into the 10 mL of PPy (0.7 g) as-prepared solution and sonicating (power: 250 W) them for 30 min: they were labeled as P-1 (0.3 wt%), P-2 (1.5 wt%), P-3 (3.0 wt%), P-4 (6.0 wt%), P-5 (9.0 wt%), P-6 (12 wt%), P-7 (18 wt%) and P-8 (25 wt%), respectively. Then, the as-prepared various Ag NW/hollow PPy NT solutions were spin-coated on an alumina substrate with interdigitated Au electrodes (shown as Figure 1a). Finally, the as-prepared devices were dried at 60 °C in air for 2 h. Therefore, H2S gas sensors based on Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite films were obtained (shown as Figure 1b).
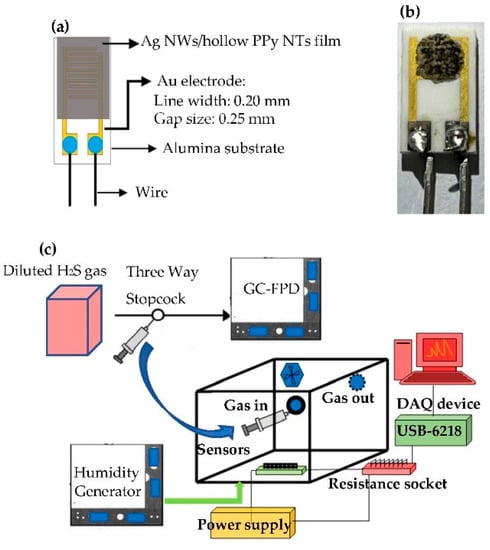
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of H2S gas sensor, (b) optical image of H2S gas sensor (P-7) and (c) measurement system for testing gas sensors.
2.5. Material Characterization and Gas-Sensing Test
The composition and morphologies of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite films were studied via X-ray diffraction (XRD) using Cu-Kα radiation (Lab XRD-6000, Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, Nicolet 380, Thermo Fisher, Scientific, Taipei, Taiwan), scanning electron microscopy (SEM, TM4000Plus, Tokyo, Japan), transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-1400; JEOL, Tokyo, Japan), selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis.
The gas-sensing and electrical properties of the H2S gas sensors made of Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite films were measured at room temperature using a bench system, as shown in Figure 1c. The free volume of the bench chamber was 24 L. Firstly, each gas sensor was connected to a load resistor. A fixed 5 V was supplied to the sensor circuit using a power supply. Then, the voltage of each testing gas sensor at the end of the load resistor was measured using a DAQ device (NI, USB-6218). Finally, the resistance of each testing H2S gas sensor was calculated according to the as-measured voltage. The desired H2S gas concentrations were produced by a two-step dilution process using dry air. First, the 1000 ppm standard H2S gas was diluted to 1 ppm. Then, the 1 ppm H2S was further diluted to the desired H2S gas concentrations. Finally, the required H2S gas concentrations were analyzed by using a gas chromatograph (GC, TRACE 1300, Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with a flame photometric detector (FPD). The relative uncertainty for the preparing H2S gas that ranged from 10 to 1000 ppb was 12%. The required interfering gas concentrations were confirmed by a calibrated gas sensor system (Dräger X-am 5000 with a resolution of 0.1 ppm). The principal apparatus for controlling the generation of humidity was a divided humidity generator, in which the proportion of dry and humid air under a total flow rate was 10 L/min to obtain the required humidity conditions for humidity testing. The model of the two mass flow controllers (Hastings) and flow display power supply used was the Protec PC-540 manufactured by Sierra Instruments Inc. The relative humidity (RH) values were measured using a calibrated hygrometer (Rotronic) with an accuracy of ±0.1% RH. When the bench system obtained the desired RH values, it stopped supplying humidity and then injected the desired H2S gas into the system. All experiments were studied at room temperature (25 ± 1 °C) and 40% RH, except for the testing of the effect of the ambient humidity on the sensor. The sensor response (S) was defined by Equation (1):
where Rair and Rgas are the electrical resistances of the sensor in the air at 40% RH and in the testing gas, respectively.
S = (Rair − Rgas)/Rair (%)
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Ag NW/Hollow PPy NT Nanocomposites
3.1.1. XRD Analysis
Figure 2 presents the XRD spectra of the pristine Ag NWs, pristine hollow PPy NTs and Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite. XRD patterns of pristine Ag NWs had four sharp diffraction peaks at 2θ = 38°, 44°, 64° and 77°, conforming to the (111), (200), (220) and (311) planes of Ag and showing the face-centered cubic (FCC) structure of Ag [39]. XRD patterns of pristine hollow PPy NTs showed a broad peak at 24° because of the scattering from PPy chains at the interplanar spacing and the formation of amorphous PPy [40,41,42]. XRD patterns of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite had the main characteristic peaks of Ag NWs and hollow PPy NTs, revealing the existence of Ag NWs and hollow PPy NTs in the nanocomposites.
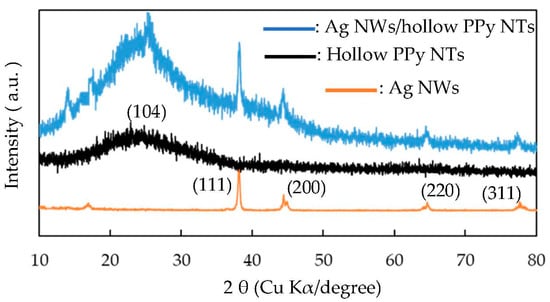
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of Ag NWs, hollow PPy NTs and Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite (P-7).
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis
Figure 3 presents the IR spectra of the pristine hollow PPy NTs and Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite. For IR spectrum of pristine hollow PPy NTs (Figure 3a), the N-H stretching, C=C stretching, C-N stretching, N-H bands and C–H wagging of PPy conformed to 3300, 1600, 1450, 1040 and 790 cm−1 were observed [43,44]. The IR spectrum of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite had the same main characteristic absorption peaks of the pristine hollow PPy NTs, indicating that there was no interaction between the Ag NWs and hollow PPy NTs during the blending process.
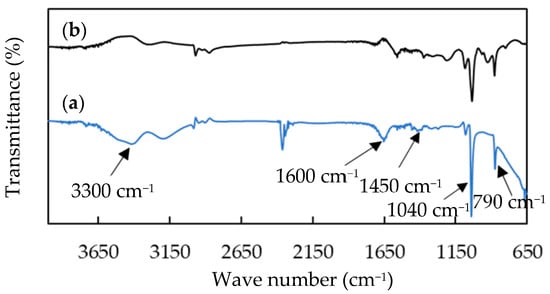
Figure 3.
IR spectra of (a) hollow PPy NTs and (b) Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite (P-7).
3.1.3. SEM and TEM Analyses
Figure 4 presents the SEM images of the pristine hollow PPy NTs, pristine Ag NWs and Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites. Figure 4a reveals that the pristine hollow PPy NTs had irregular synapses with a branching structure where the lengths of the tubes were in the range of 3~5 µm. Figure 4a reveals that the pristine Ag NWs had a highly ordered wire structure where their lengths were in the range of 2.5~5.5 µm. Figure 4c–g show the SEM images of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites with varying weight percentages of the added Ag NWs ranging from 0.3 wt% to 25 wt%. As the added amount of Ag NWs was increased, obvious and homogeneously dispersed Ag NWs in the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites were observed. Additionally, the Ag NWs physically contacted the hollow PPy NTs in the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites. However, when the amount of added Ag NWs was upped to 25 wt%, aggregated Ag NWs were observed.
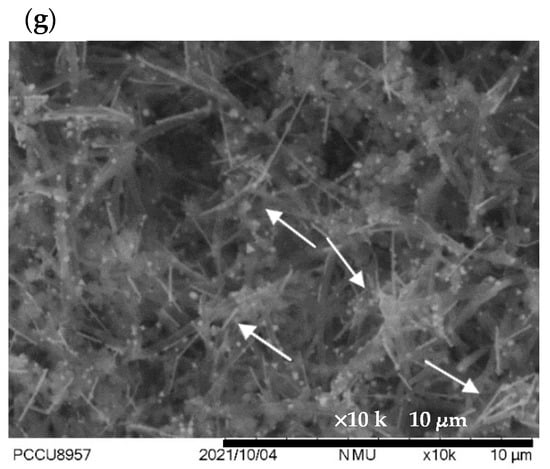
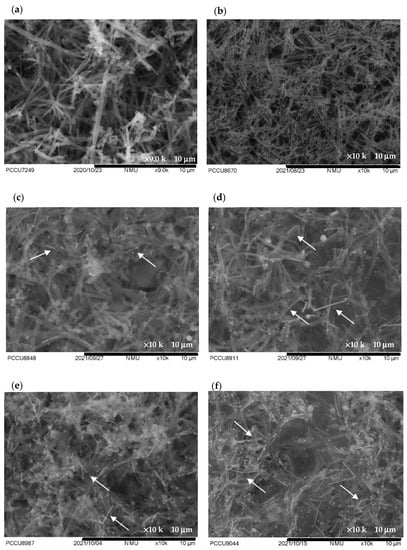

Figure 4.
SEM images of (a) pristine hollow PPy NT film, (b) pristine Ag NW film, (c) P-1 (0.3 wt%) film, (d) P-4 (6.0 wt%) film, (e) P-6 (12 wt%) film, (f) P-7 (18 wt%) film and (g) P-8 (25 wt%) film. (White arrows indicated the Ag NWs).
Figure 5 shows the TEM images of the pristine of PPy NTs and Ag NWs. The low-magnification TEM image of the pristine hollow PPy NTs (Figure 5a) shows that the size and shape of hollow PPy NTs are like the observations from the SEM. The higher-magnification TEM image of the selected area in Figure 5a shows that the PPy NTs had a hollow structure where the wall thickness of the tube and inner diameter of the hollow PPy NTs were about 52 nm and 34 nm, respectively (Figure 5b). The low-magnification TEM image of the pristine Ag NWs (Figure 5c) clearly shows the perfect straightness of the nanowires along the longitudinal axis. The higher-magnification TEM image of the Ag NWs shows that the diameter of the Ag NWs was about 58 nm (Figure 5d). The high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) image of the Ag NWs shows that the fringe spacings of 0.237 nm agree with the (111) crystal plane of FCC Ag (Figure 5e). The SAED pattern (inset in Figure 5e) represents a complex crystalline structure of different facets for the FCC Ag, revealing that each Ag NW was not a single crystal because the pattern contains an interpenetrated set of two individual diffraction patterns and the diffraction spots cannot be assigned to any simple pattern associated with FCC Ag [45]. Elemental analysis (Figure 5f) and EDX elemental mapping (Figure 5g) suggested that the presence of Ag was only in the composition of the Ag NWs. Moreover, the results of Figure 5d,g (as shown with white arrows) indicate the presence of Ag nanoparticles on top of the Ag NWs.
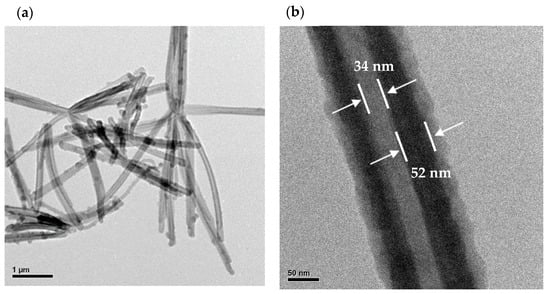
Figure 5.
TEM images of pristine hollow PPy NTs: (a) low-magnification, (b) high-magnification. TEM images of pristine Ag NWs: (c) low-magnification, (d) high-magnification, (e) HRTEM (inset is corresponding SAED pattern), (f) EDX spectrum and (g) EDX elemental map.
3.2. Effect of Amount of Added Ag NWs on the Response of Ag NW/Hollow PPy NT Nanocomposite Films to H2S Gas
The response (S) of the H2S gas sensor that was made of pristine hollow PPy NTs was only 0.02, even upon exposure to a high H2S testing concentration of 10 ppm. To improve the response (S) of the H2S gas sensor that was made of pristine hollow PPy NT film for sensing ppb-level H2S gas at room temperature, the film was modified with Ag NWs. Figure 6 plots the effect of the amount of Ag NWs blended to modify the film on the response (S) of the H2S gas sensors, based on the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite films exposing to 500 ppb H2S at room temperature. The response (S) of the H2S gas sensors made of Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite films increased by increasing the concentration of blended Ag NWs up to 18 wt% (P-7). These results were due to the fact that the higher concentration of blended Ag NWs can increase the surface reaction sites and improve the conductivity of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite film (based on the results of SEM, Figure 4c–f) [12,46], promoting the catalytic activity of the sensor. However, when the concentration of blended Ag NWs increased to 25 wt% (P-8), the response (S) decreased because of the decrease in the number of active sites due to the agglomeration of Ag NWs [46]. The response (S) of the H2S gas sensor that was made of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite film (P-7) to 500 ppb H2S exhibited the strongest response (S) (a little over 12%) and best long-term stability at room temperature, and was therefore tested further to evaluate its other gas-sensing properties.
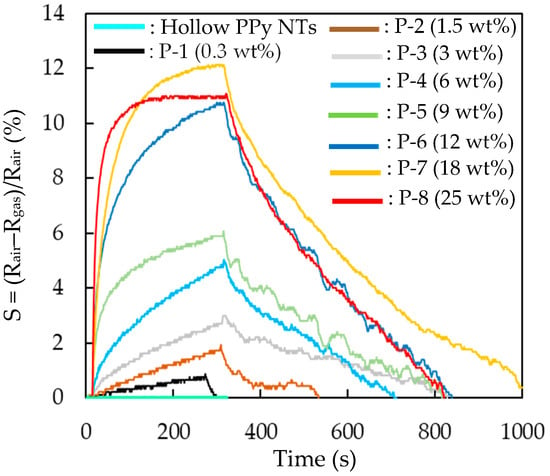
Figure 6.
Effect of the added amount of the Ag NWs in Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites on the response to 500 ppb H2S gas at room temperature and at 40% RH. (Hollow PPy NTs exposed to 10 ppm H2S).
3.3. Gas-Sensing Properties of Ag NW/Hollow PPy NT Nanocomposite Films
Figure 7a plots the dynamic responses (S) of the H2S gas sensor (P-7) toward H2S ranging from 10 to 1000 ppb at the exposure time of 120 s, at room temperature and at 40% RH. It had a response (S) of 1% even to 10 ppb H2S (as shown in inset). Figure 7b presents the response (S) of the H2S gas sensor (P-7) when the H2S gas ranged from 10 to 1000 ppb at room temperature and at 40% RH. The linear fitting curve equation for the H2S gas sensor (P-7) was Y = 0.0308X + 0.6279; R2 = 0.9897. The limit of detection (LOD) that was calculated at the calibration point of 10 ppb by considering a S/N of 3 was 4.5 ppb.
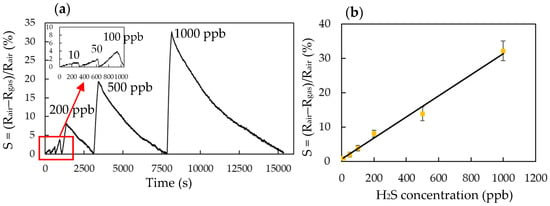
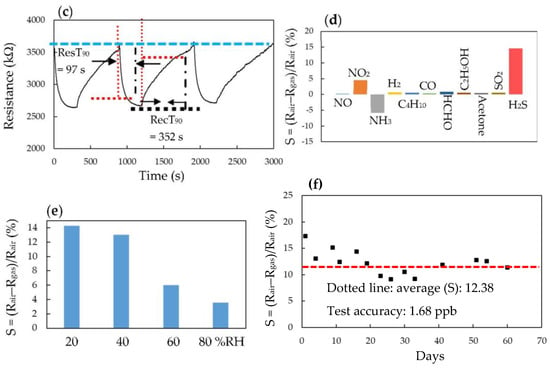
Figure 7.
(a) Response (S) of the H2S sensor (P-7) toward 10~1000 ppb H2S at room temperature, (b) linear fitting curve of the H2S sensor (P-7) with concentration of H2S at the range of 10~1000 ppb, (c) response/recovery and repeatability of the H2S sensor (P-7) to 500 ppb H2S at room temperature, (d) interfering of various gases on 500 ppb H2S (NO: 1 ppm, NO2: 1 ppm, NH3: 5 ppm, H2: 10,000 ppm, C4H10: 100,000 ppm, CO: 20 ppm, HCHO: 10 ppm, C2H5OH: 30 ppm, acetone: 10 ppm and SO2: 1 ppm), (e) effect of ambient humidity on the response of the H2S sensor (P-7) to 500 ppb H2S and (f) long-term stability.
Figure 7c plots the real-time resistance of the H2S gas sensor (P-7) to 500 ppb H2S over time at room temperature and at 40% RH. The response time (ResT90) and recovery (RecT90) time were defined as the time taken for the resistance of the sensor to change by 90% of its maximum change after exposing to H2S gas for 300 s, following being switched on and off, respectively. The ResT90/RecT90 of the H2S gas sensor (P-7) was 97/352 s. The sensor also had good reversibility and repeatability.
Figure 7d shows the interfering effects of NO, NO2, H2, NH3, C4H10, CO, HCHO, C2H5OH, CH3COCH3 and SO2 gases on the H2S gas sensor (P-7) at room temperature and at 40% RH. The testing was carried out with the binary mixtures of H2S and a single interfering gas. These interfering gases may be considered as having unobvious interference effects with 500 ppb H2S. Additionally, the H2S gas sensor (P-7) could be suitable for H2S in the H2 purity analysis, as the presence of H2S at trace levels strongly reduces the performance of fuel cell vehicles because the H2 cross-interference is very low. However, the 1 ppm NO2 and 5 ppm NH3 had an obvious interfering effect on the H2S gas sensor (P-7) with H2S at 10 ppb.
Figure 7e shows the effect of the ambient humidity on the response of the H2S gas sensor (P-7) to 500 ppb H2S at room temperature. When the desired ambient humidity was obtained using a divided humidity generator, the 500 ppb H2S was injected into the chamber. The response (S) of the H2S gas sensor (P-7) decreased when the ambient humidity increased because the physisorbed water occupied the active sites of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite film. Thus, a compensation system is needed for calibrating the humidity influence if the H2S gas sensor (P-7) is under a high ambient humidity environment.
Figure 7f shows the results of the long-term stability of the H2S gas sensor (P-7) at testing concentrations of 500 ppb H2S at room temperature and at 40% RH. The mean response (S) of the H2S gas sensor (P-7) to 500 ppb for 60 days was 12.28. The test accuracy of the stability was calculated as the mean absolute error (formula was , where Xi and X are the response value at the testing points and average response value of the H2S gas sensor (P-7), respectively) for 60 days. The test accuracy was 1.68 ppb. The response deviation for 60 days that was calculated as the relative standard deviation (RSD) was 18%.
Table 1 shows the H2S gas-sensing performance of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite (P-7) was compared with that of other previously reported H2S sensors based on conducting polymers and their composites [15,16,17,21,23,24,47]. The morphology of PPy affected the gas-sensing performance. Most of the gas sensors made of PPy-based materials responded to ppm-level H2S gas, but the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite film in this work showed a strong gas response to ppb-level H2S gas and the lowest LOD (4.5 ppb) at room temperature. The response of the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite film was higher than that of Ag NPs/PPy NTs [24], which may be due to the Ag NWs having a high surface area (active sites) and the hollow PPy NTs having fast charge carrier transportation [27,28,29]. Therefore, the H2S gas sensor based on the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite film has a high commercial application value in sensing ppb-level H2S at room temperature, except for the H2S gas sensor that was made of the Au nanoparticle/polyaniline (Au NP/PANI) nanocomposite material. Additionally, the response of the H2S gas-sensing Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite may be further enhanced by use of a Au–Ag bimetal and under UV irradiation at room temperature [48].

Table 1.
Comparison of the performance of the H2S gas sensor developed herein with others from the literature based on conducting polymers and their composites.
3.4. Electrical Property and Gas-Sensing Mechanism
Duc et al. [11], Garg et al. [16], Nerkar et al. [17] and Kriván et al. [49] proposed the H2S gas-sensing mechanism of pristine PPy film via redox reaction, which is the transfer of the protons from H2S to the PPy film. Therefore, based on the above vision, a model (shown as Figure 8) was used to describe the resistance of the H2S gas sensor based on the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite film that was herein reduced upon exposure to H2S gas. When the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite was exposed to H2S, the H2S molecules adsorbed on the Ag NW surface rather than on hollow PPy NTs, because Ag is less electronegative than C; the adsorption of H2S led to a possible dissociation of H2S to form AgS and H+; a charge (H+) transfer occurred from the Ag NWs into the hollow PPy NTs, forming Ag NW/hollow PPy NTsH+●H2S. The released protons entered the hollow PPy NTs, increasing the concentration of charge carriers and leading to an increase in the conductivity of the H2S gas sensor based on the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite film.
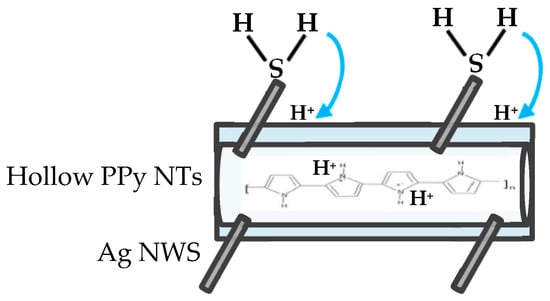
Figure 8.
Schematic drawing to show the H2S gas-sensing mechanism of Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite film.
4. Conclusions
Room-temperature ppb-level H2S gas sensors made of Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite films were fabricated using a simple strategy. Based on the results of SEM and TEM analyses, the Ag NWs were uniformly decorated onto the hollow PPy NT surface to form the Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposite. The addition of Ag NWs enhanced the response of the H2S gas sensors made of Ag NW/hollow PPy NT nanocomposites toward ppb-level H2S at room temperature owing to the unique catalytic and electronic characteristics of Ag NWs. The H2S gas sensor (P-7) exhibited the highest calibration sensitivity (slope = 0.0308) and good linearity (R2 = 0.9897) between 10 and 1000 ppb, the lowest LOD (4.5 ppb), fast ResT90/RecT90 times (97/352 s), good repeatability and long-term stability (at least 60 days) when working at room temperature.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.-G.S.; methodology, P.-G.S.; investigation, P.-G.S. and X.-C.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.-G.S.; writing—review and editing, P.-G.S.; supervision, P.-G.S.; project administration, P.-G.S.; funding acquisition, P.-G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, grant no. MOST 110-2113-M-034-002.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xue, X.; Xing, L.; Chen, Y.; Shi, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Synthesis and H2S sensing properties of CuO-SnO2 core/shell PN-junction nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2008, 112, 12157–12160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gong, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dou, X. Sensitivity, selectivity, and fast detection of ppb-level H2S gas boosted by ZnO-CuO mesocrystal. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, P.G.; Zheng, Y.L. Room-temperature ppb-level SO2 gas sensors based on RGO/WO3 and MWCNTs/WO3 nanocomposites. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; He, M.; Yu, H.; Li, D. An H2S sensor based on electrochemistry for chicken coops. Sensors 2016, 16, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes, M.; Nogueira, P.; Oliveira, J. Quantification of CO2, SO2, NH3, and H2S with a single coated piezoelectric quartz crystal. Sens. Actuators B 2000, 68, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsari, A.; Sarraf, M.J. Design of a hydrogen sulfide gas sensor based on a photonic crystal cavity using graphene. Superlattice Microstruct. 2020, 138, 106362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraj, A.; Rehman, A.; Belhaouari, S.B.; Saoud, K.M.; Bermak, A. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) sensor: A concept of physical versus virtual sensing. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 2516813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Resistance-based H2S gas sensors using metal oxide nanostructures: A review of recent advances. J. Haz. Mater. 2018, 357, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.I.M.; Awwad, F.; Greish, Y.E.; Mahmoud, S.T. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas sensor: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 2394–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.C.; Ang, B.C.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A.; Baharuddin, A.A.; Wong, Y.H. Review-conducting polymers as chemiresistive gas sensing materials: A review. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, C.; Boukhenane, M.L.; Wojkiewicz, J.L.; Redon, N. Hydrogen sulfide detection by sensors based on conductive polymers: A review. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, G.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, M.; Kuo, C.C.; Wang, S.D. Conducting polymer-inorganic nanocomposite-based gas sensors: A review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2020, 21, 768–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, A.; Han, Y.; Li, T. Sensors based on conductive polymers and their composites: A review. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farea, M.A.; Mohammed, H.Y.; Shirsat, S.M.; Sayyad, P.W.; Ingle, N.N.; Al-Gahouari, T.; Mahadik, M.M.; Bodkhe, G.A.; Shirsat, M.D. Hazardous gases sensors based on conducting polymer composites: Review. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 776, 138703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsat, M.D.; Bangar, M.A.; Deshusses, M.A.; Myung, N.V.; Mulchandani, A. Polyaniline nanowires-gold nanoparticles hybrid network based chemiresistive hydrogen sulfide sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 083502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, R.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, D.; Chakarvarti, S.K. Polypyrrole microwires as toxic gas sensors for ammonia and hydrogen sulphide. J. Sensor. Instrum. 2015, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerkar, D.M.; Jaware, S.E.; Padhye, G.G. Fabrication of a novel flexible room temperature hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas sensor based on polypyrrole films. Indian J. Sci. Res. 2016, 5, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.I.; Bakr, N.A.; Ibrahim, I.M. Morphological, magnetic, optical, surface potential, and H2S gas sensing behavior of polypyrrole nanofibers. J. Electron. Mat. 2021, 50, 2716–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Bang, J.H.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Effect of noble metals on hydrogen sensing properties of metal oxide-based gas sensors. J. Sens. Sci. Technol. 2020, 29, 365–368. [Google Scholar]
- Navale, S.; Shahbaz, M.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Effect of Ag addition on the gas-sensing properties of nanostructured resistive-based gas sensors: An overview. Sensors 2021, 21, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, A.; Joshi, N.; Singh, A.; Salmi, Z.; Jha, P.; Decorse, P.; Lau-Truong, S.; Mahmoud, R.; Chehimi, M.M.; Aswal, D.K.; et al. H2S sensing using in situ photo-polymerized polyaniline–silver nanocomposite films on flexible substrates. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, L.; Yan, F. Polypyrrole/silver composite nanotubes for gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B. 2010, 145, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kate, K.H.; Damkale, S.R.; Khanna, P.K.; Jain, G.H. Nano-silver mediated polymerization of pyrrole: Synthesis and gas sensing properties of polypyrrole (PPy)/Ag nanocomposite. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 7863–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.I.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Bakr, N.A. The sensitivity of polypyrrole nanotube/(Ag nanoparticle, Ag-NiO nanocomposite) against H2S toxic gas at low temperature. Sens. Transducers 2020, 243, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kumar, V.; Bonyani, M.; Majhi, S.M.; Bang, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, K.H. Conducting polymer nanofibers based sensors for organic and inorganic gaseous compounds. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 14, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Egashira, M. Basic aspects and challenges of semiconductor gas sensors. MRS Bull. 1999, 24, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, M.; Dinan, B.; Akbar, S.A.; Haseeb, A. Gas sensors based on one dimensional nanostructured metal oxides: A review. Sensors 2012, 12, 7207–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Yan, W. One-dimensional nanomaterials in resistive gas Sensor: From material design to application. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, T. Recent progress of nanostructured sensing materials from 0D to 3D: Overview of structure–property-application relationship for gas sensors. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2100515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cancilla, J.C.; Torrecilla, J.S.; Haick, H. Artificial sensing intelligence with silicon nanowires for ultraselective detection in the gas phase. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalev, G. The electrostatically formed nanowire: A novel platform for gas-sensing applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Du, K. Chemiresistive gas sensors based on hollow heterojunction: A review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2002122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Deng, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Kang, X.; Gu, Z. Polypyrrole hollow fiber for solid phase extraction. Analyst 2012, 137, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xiang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, K.; Yang, B. Hollow polypyrrole nanospindles for highly effective cancer therapy. ChemPlusChem 2018, 83, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wu, F.; Xie, A.; Duan, L.; Yang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Sun, M.; Xiong, Z. Hollow polypyrrole nanofiber-based self-assembled aerogel: Large-scale fabrication and outstanding performance in electromagnetic pollution management. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 7604–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, L.; Zhao, Y.; Song, G.; An, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Zhai, S.; Li, Z. Construction of core-shell PPy@MoS2 with nanotube-like heterostructures for electromagnetic wave absorption: Assembly and enhanced mechanism. Compos. Part A 2020, 136, 105965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Yang, W.; No, J.S. Polyurethane sponges decorated with reduced graphene oxide and silver nanowires for highly stretchable gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 265, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; An, X.; Xiong, S.; Jiang, X.; Yu, A. Enhanced gas sensing performance based on the fabrication of polycrystalline Ag@TiO2 core-shell nanowires. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 286, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Kimura, K. Superlattice formation from polydisperse Ag nanoparticles by a vapor-diffusion method. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5662–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, N.S.; Murray, K.S.; Fleming, R.J. Physical properties of polypyrrole films containing trisoxalatometallate anions and prepared from aqueous solution. Synth. Met. 1997, 87, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.Y.; Li, Y.F. Great improvement of polypyrrole films prepared electrochemically from aqueous solutions by adding nonaphenol polyethyleneoxy (10) ether. Polymer 1997, 38, 3997–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougule, M.A.; Pawara, S.G.; Godse, P.R.; Mulika, R.N.; Sen, S.; Patila, V.B. Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole (PPy) thin films. Soft Nanosci. Lett. 2011, 1, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, N.V.; Gadre, A.P.; Bambole, V.A. Investigation of electropolymerized polypyrrole composite film: Characterization and application to gas sensor. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kan, J.; Jiang, T.; Pang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xue, H. Facile synthesis of polypyrrole nanotubes and their supercapacitive application. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 9320–9334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Silver nanowires—Unique templates for functional nanostructures. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1626–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Kwon, O.S.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.S.; You, S.; Jang, J. One-pot synthesis of silver nanoparticles decorated poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanotubes for chemical sensor application. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.L.; Zhang, K.W.; Sun, J.H.; Zhang, D.F.; Luo, R.X.; Li, D.Q.; Liu, C.C. Polythiophene-WO3 hybrid architectures for low-temperature H2S detection. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 197, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.G.; Yu, J.H. Enhanced NO2 gas-sensing properties of Au-Ag bimetal decorated MWCNTs/WO3 composite sensor under UV-LED irradiation. Sens. Actuators A 2020, 303, 111718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriván, E.; Visy, C.; Dobay, R.; Harsányi, G.; Berkesi, O. Irregular response of the polypyrrole films to H2S. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).