Screen-Printed Gold Electrode Functionalized with Deferoxamine for Iron(III) Detection
Abstract
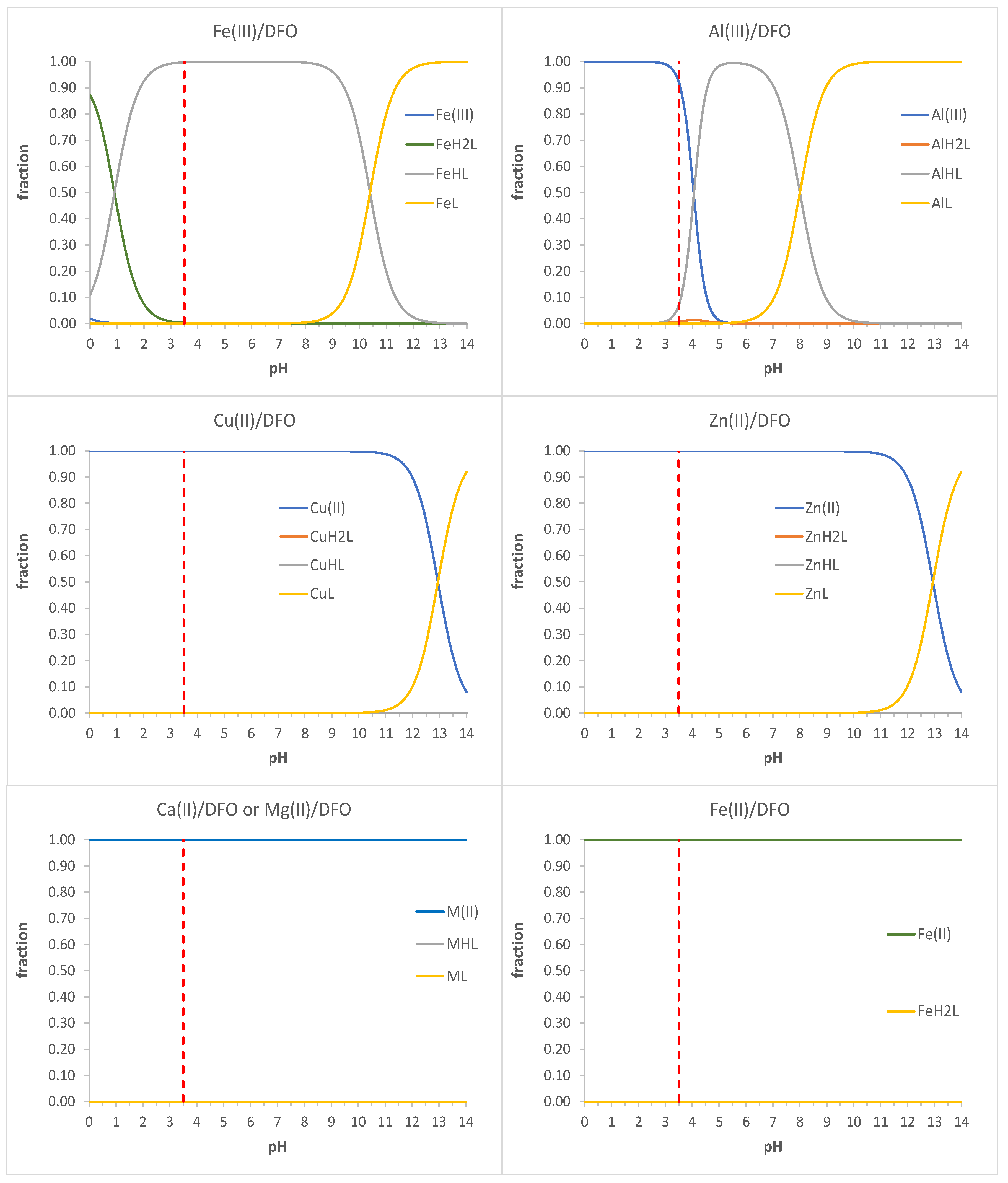
:1. Introduction
- it can only be intramuscularly injected;
- it can cause long term damage to the body;
- it has a high price;
- it is toxic when not bound to iron.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
2.2. Functionalization of the Working Gold Electrode
2.3. Area and Capacitance of the Modified Gold Working Electrode
2.4. Fe(III) Determination by Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV)
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Electrode Functionalization
3.2. Working Gold Electrode Characterization
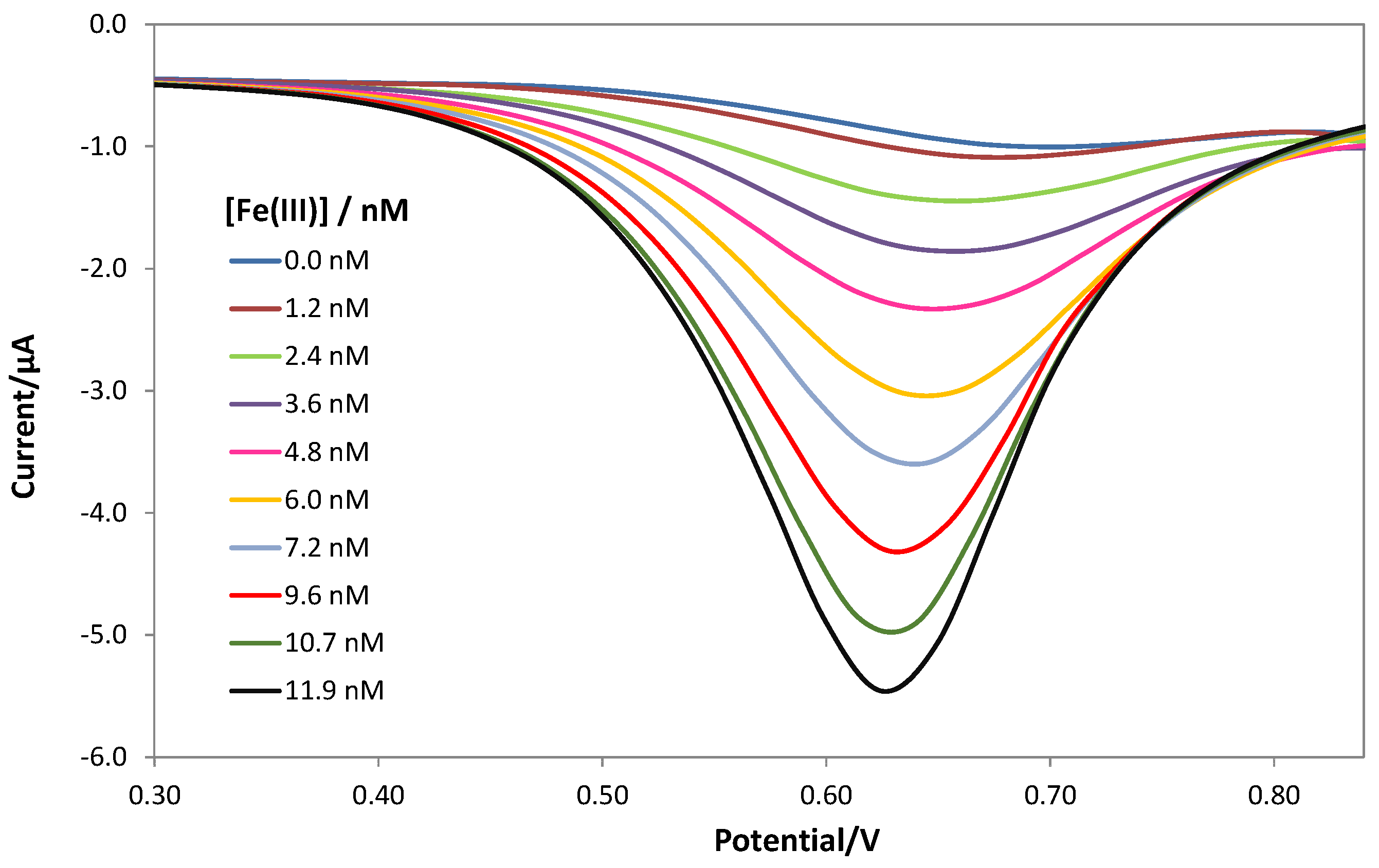
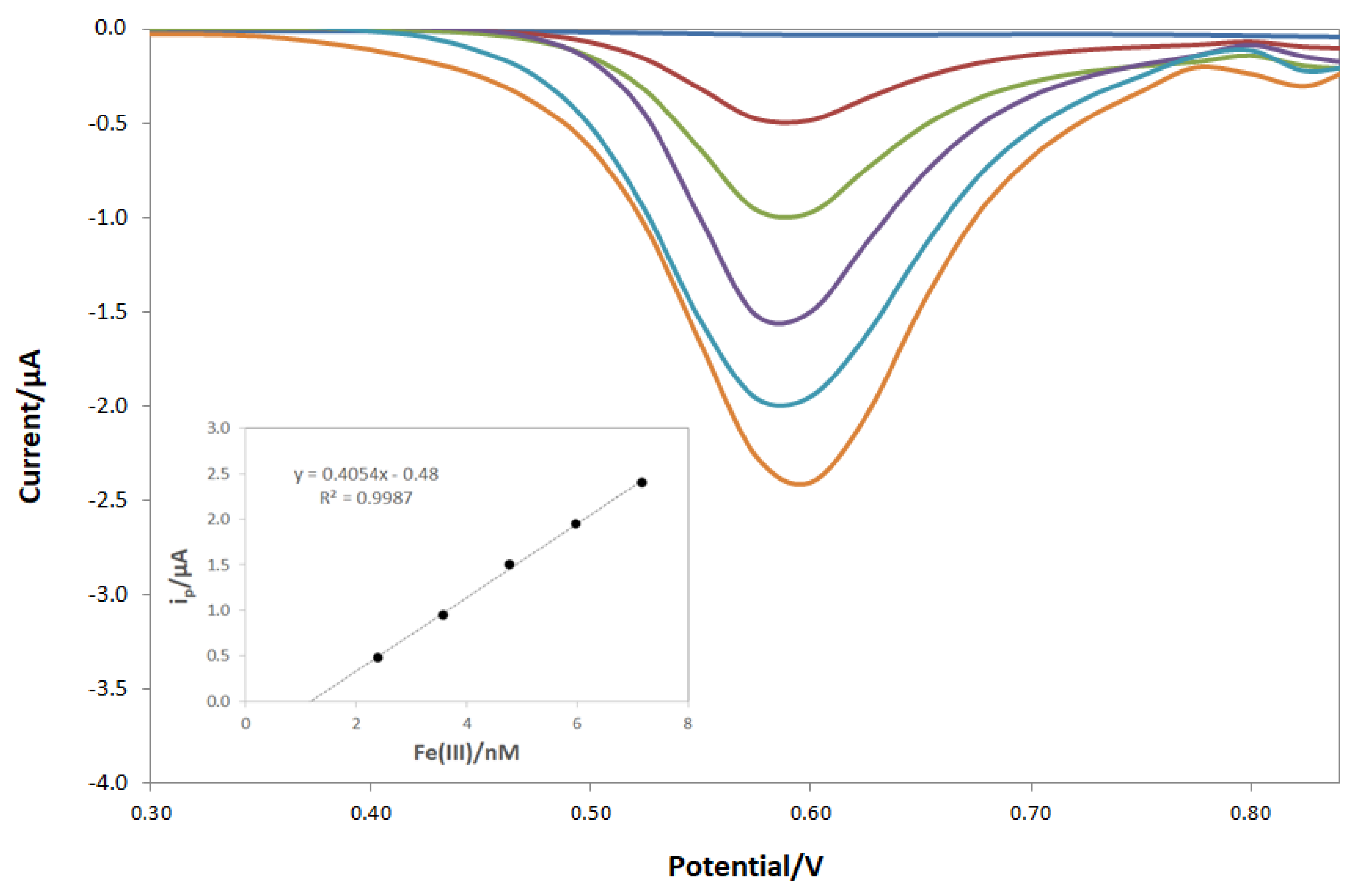
3.3. Fe(III) Determination by DPV Analysis
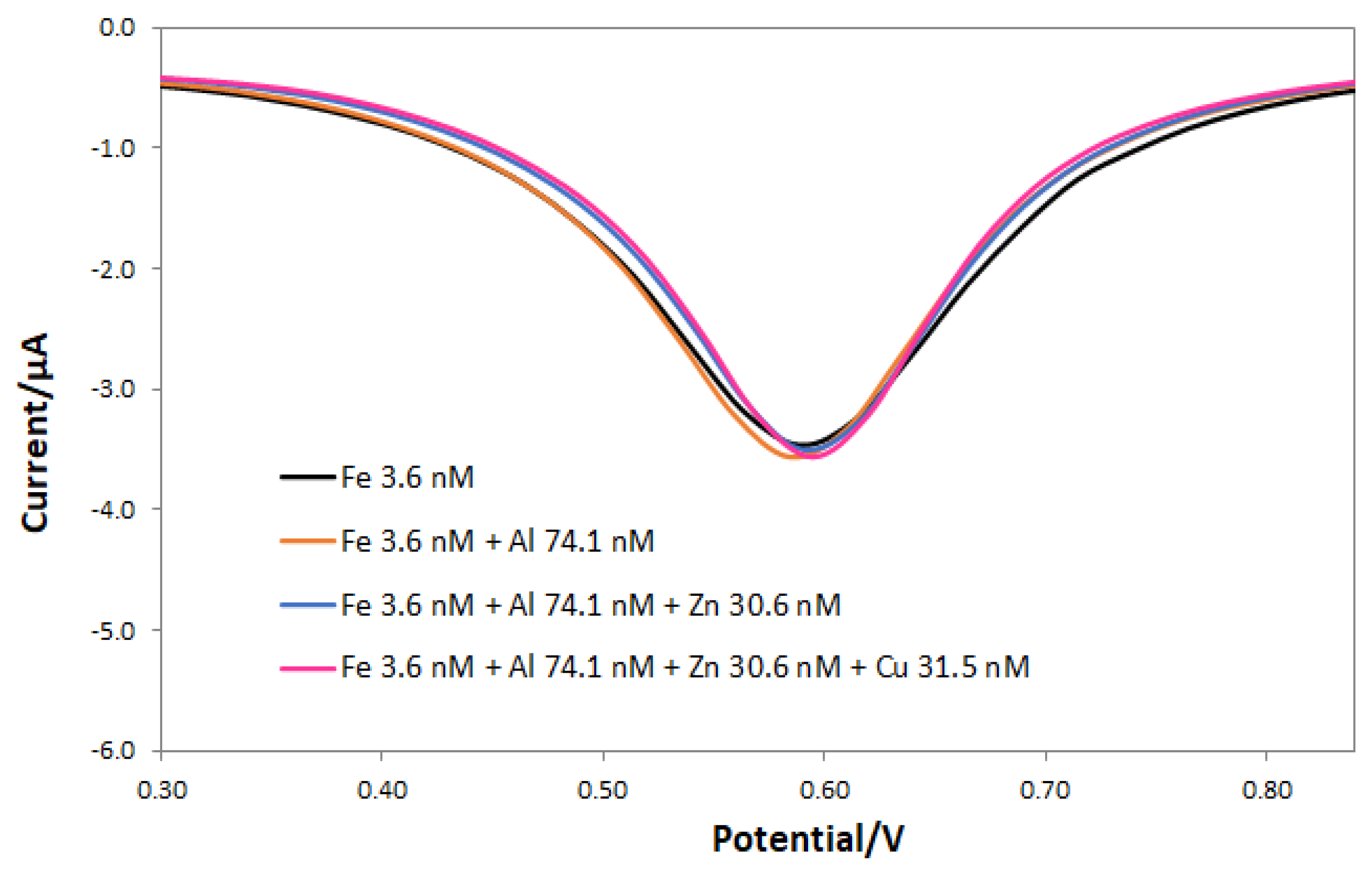
3.4. Interferences
3.5. Fe(III) Determination in a Tap Water Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keberle, H. The Biochemistry of Desferrioxamine and its Relation to Iron Metabolism. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1964, 119, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faa, G.; Crisponi, G. Iron chelating agents in clinical practice. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 184, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, J.; Wray, A.A. Deferoxamine In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557654/ (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- Whitten, C.F.; Gibson, G.W.; Good, M.H.; Goodwin, J.F.; Brough, A.J. Studies in Acute Iron Poisoning. I. Desferrioxamine in the Treatment of Acute Iron Poisoning: Clinical Observations, Experimental Studies, and Theoretical Considerations. Pediatrics 1965, 36, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, N.F. Long-Term Therapy with Deferiprone. Acta Haematol. 1996, 95, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brittenham, G.M. Development of Iron-Chelating Agents for Clinical Use. Blood 1992, 80, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivieri, N.; Freedman, M.; Koren, G.; Hermann, C.; Bentur, Y.; Chung, D.; Klein, J.; Louis, P.S.; Templeton, D.; McClelland, R. Comparison of oral iron chelator L1 and desferrioxamine in iron-loaded patients. Lancet 1990, 336, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Obando, D.; Schipanski, L.G.; Groebler, L.K.; Witting, P.K.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Richardson, D.R.; Codd, R. Conjugates of Desferrioxamine B (DFOB) with Derivatives of Adamantane or with Orally Available Chelators as Potential Agents for Treating Iron Overload. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lin, T.M.; Chanana, S.; Xiong, M.P. Nanogel−DFO conjugates as a model to investigate pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and iron chelation in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, B.; Wen, W.; Zhou, C.; Tian, L.; Ramakrishna, S. Deferoxamine immobilized poly(D,L−lactide) membrane via polydopamine adhesive coating: The influence on mouse embryoosteoblast precursor cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, R.; Emma, G.; Milanese, C.; Dacarro, G.; Taglietti, A.; Nurchi, V.M.; Alberti, G. Novel DFO−SAM on mesoporous silica for iron sensing. Part I. Synthesis optimization and characterization of the material. Analyst 2014, 139, 3932–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alberti, G.; Emma, G.; Colleoni, R.; Pesavento, M.; Nurchi, V.M.; Biesuz, R. Novel DFO−functionalized mesoporous silica for iron sensing. Part 2. Experimental detection of free iron concentration (pFe) in urine samples. Analyst 2014, 139, 3940–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alberti, G.; Quattrini, F.; Colleoni, R.; Nurchi, V.M.; Biesuz, R. Deferoxamine−paper for iron(III) and vanadium(V) sensing. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehuda, Z.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Immobilization of Fe Chelators on Sepharose Gel and Its Effect on Their Chemical Properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5996–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, G.; Zanoni, C.; Magnaghi, L.R.; Santos, M.A.; Nurchi, V.M.; Biesuz, R. DFO@EVOH and 3,4-HP@EVOH: Towards New Polymeric Sorbents for Iron(III). Chemosensors 2020, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlaczyk, M.; Schroeder, G. Deferoxamine-Modified Hybrid Materials for Direct Chelation of Fe(III) Ions from Aqueous Solutions and Indication of the Competitiveness of In Vitro Complexing toward a Biological System. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 15168–15181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.-L.; Moniotte, N.; Nivarlet, N.; Tian, G.; Desmet, J. Design and synthesis of fluorescence-based siderophore sensor molecules for FeIII ion determination. Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 2199–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinetto, P.; Taglietti, A.; Pasotti, L.; Pallavicini, P.; Dacarro, G.; Giulotto, E.; Grandi, M.S. SERS Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Functionalized with A Desferrioxamine B Derived Ligand for Fe(III) Binding and Sensing. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 82, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Alberti, G.; Pesavento, M.; D’Agostino, G.; Quattrini, F.; Biesuz, R.; Zeni, L. A Simple Small Size and Low Cost Sensor Based on Surface Plasmon Resonance for Selective Detection of Fe(III). Sensors 2014, 14, 4657–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norocel, L.; Gutt, G. Development and performance testing of an electrochemical sensor for determination of iron ions in wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2019, 25, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shervedani, R.K.; Akrami, Z. Gold-deferrioxamine nanometric interface for selective recognition of Fe(III) using square wave voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy methods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shervedani, R.K.; Garavand, S.; Samiei Foroushani, M.; Yaghoobi, F. Electrochemical determination of Ga(III) through formation of Ga(III)-deferrioxamine B nanostructures on the glassy carbon electrode surface. Talanta 2016, 149, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, W.P.; Heng, L.Y.; Nathan, S. Highly Sensitive Aluminium(III) Ion Sensor Based on a Self-assembled Monolayer on a Gold Nanoparticles Modified Screen-printed Carbon Electrode. Anal. Sci. 2015, 31, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulman, A. Formation and Structure of Self-Assembled Monolayers. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 1533–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirsky, V.M. New electroanalytical applications of self-assembled monolayers. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.A.; Abd-Elaal, A.A.; Mohamed, G.G. Screen printed ion selective electrodes based on self-assembled thiol surfactant-gold-nanoparticles for determination of Cu (II) in different water samples. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.C.; Batistuti, M.R.; Junior, B.B.; Mulato, M. Aptasensor based on screen-printed electrode for breast cancer detection in undiluted human serum. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 137, 107586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochana, J.; Starzec, K.; Wieczorek, M.; Knihnicki, P.; Góra, M.; Rokicińska, A.; Kuśtrowski, P. Study on self-assembled monolayer of functionalized thiol on gold electrode forming capacitive sensor for chromium (VI) determination. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2019, 23, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koç, Y.; Moralı, U.; Erol, S.; Avci, H. Electrochemical investigation of gold based screen printed electrodes: An application for a seafood toxin detection. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, W.; McDonagh, P.; Doran, J.; McCrudden, D. Covalent Immobilisation of a Nanoporous Platinum Film onto a Gold Screen-Printed Electrode for Highly Stable and Selective Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimafonte, M.; Fulgione, A.; Gaglione, R.; Papaianni, M.; Capparelli, R.; Arciello, A.; Bolletti Censi, S.; Borriello, G.; Velotta, R.; Della Ventura, B. Screen Printed Based Impedimetric Immunosensor for Rapid Detection of Escherichia coli in Drinking Water. Sensors 2020, 20, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Paniagua, M.; Palenzuela-Batista, S.; Manzanares-Palenzuela, C.L.; López-Ruiz, B. Electrochemical genosensor for Klotho detection based on aliphatic and aromatic thiols self-assembled monolayers. Talanta 2020, 212, 120735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevik, E. High sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen by using ferrocene cored asymmetric PAMAM dendrimer interface screen printed electrodes. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etorki, A.M.; Awin, L.A.; El-Rais, M.; Elhabbat, M.S.; Shaban, I.S. Application of gold nanoparticles with 1, 6-Hexanedithiol modified screen-printed carbon electrode as a sensor for determination of arsenic in environmental samples. Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białobrzeska, W.; Firganek, D.; Czerkies, M.; Lipniacki, T.; Skwarecka, M.; Dziąbowska, K.; Cebula, Z.; Malinowska, N.; Bigus, D.; Bięga, E.; et al. Electrochemical Immunosensors Based on Screen-Printed Gold and Glassy Carbon Electrodes: Comparison of Performance for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Detection. Biosensors 2020, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuddusi, K. Modification of screen-printed gold electrode with 1,4-dithiothreitol: Application to sensitive voltammetric determination of Sudan II. Food Qual. Saf. 2021, 5, fyaa039. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, T.A.; Gonçalves, M.V.; Franco, D.L.; Reis, A.B.; Martins, H.R.; Ferreira, L.F. Label-free electrochemical impedance immunosensor based on modified screen-printed gold electrodes for the diagnosis of canine visceral leishmaniasis. Talanta 2019, 195, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burak, D.; Emregul, E.; Emregul, K.C. Copper–Zinc Alloy Nanoparticle Based Enzyme-Free Superoxide Radical Sensing on a Screen-Printed Electrode. Talanta 2015, 134, 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Pesavento, M.; Merli, D.; Biesuz, R.; Alberti, G.; Marchetti, S.; Milanese, C. A MIP-based low-cost electrochemical sensor for 2-furaldehyde detection in beverages. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1142, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemometric Agile Tool (CAT). Available online: http://www.gruppochemiometria.it/index.php/software/19-download-the-rbased-chemometric-software (accessed on 9 July 2021).
- Douglass, E.F., Jr.; Driscoll, P.F.; Liu, D.; Burnham, N.A.; Lambert, C.R.; McGimpsey, W.G. Effect of electrode roughness on the capacitive behavior of self-assembled monolayers. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 7670–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Raya, D.; Madueño, R.; Sevilla, J.M.; Blázquez, M.; Pineda, T. Electrochemical characterization of a 1,8-octanedithiol self-assembled monolayer (ODT-SAM) on a Au (1 1 1) single crystal electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 8026–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.D.; Huynh, T.M.; Nguyen, T.S.V.; Le, D.N.; Baptist, R.; Doan, T.C.D.; Dang, C.M. Nafion/platinum modified electrode-on-chip for the electrochemical detection of trace iron in natural water. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 873, 114396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.D.; Doan, T.C.D.; Huynh, T.M.; Dang, D.M.T.; Dang, C.M. Thermally reduced graphene/nafion modified platinum disk electrode for trace level electrochemical detection of iron. Microchem. J. 2021, 169, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.D.; Nguyen, T.S.V.; Huynh, T.M.; Baptist, R.; Doan, T.C.D.; Dang, C.M. Voltammetric determination of iron (III) using sputtered platinum thin film. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 320, 134607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Pan, D.; Hu, X.; Han, H.; Li, F. Titanium carbide nanoparticles/ion-exchange polymer-based sensor for catalytic stripping determination of trace iron in coastal waters. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 219, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Pan, D.; Pan, F.; Hu, X.; Zhu, R. A functional micro-needle sensor for voltammetric determination of iron in coastal waters. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 128883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Han, H.; Pan, D.; Zhang, H.; Su, Z. Voltammetric determination of total dissolved iron in coastal waters using a glassy carbon electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide, Methylene Blue and gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Pan, D.; Hu, X.; Han, H.; Lin, M.; Wang, C. An electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide/gold nanoparticles modified electrode for determination of iron in coastal waters. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, D.; Remelli, M. Deferoxamine B: A Natural, Excellent and Versatile Metal Chelator. Molecules 2021, 26, 3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
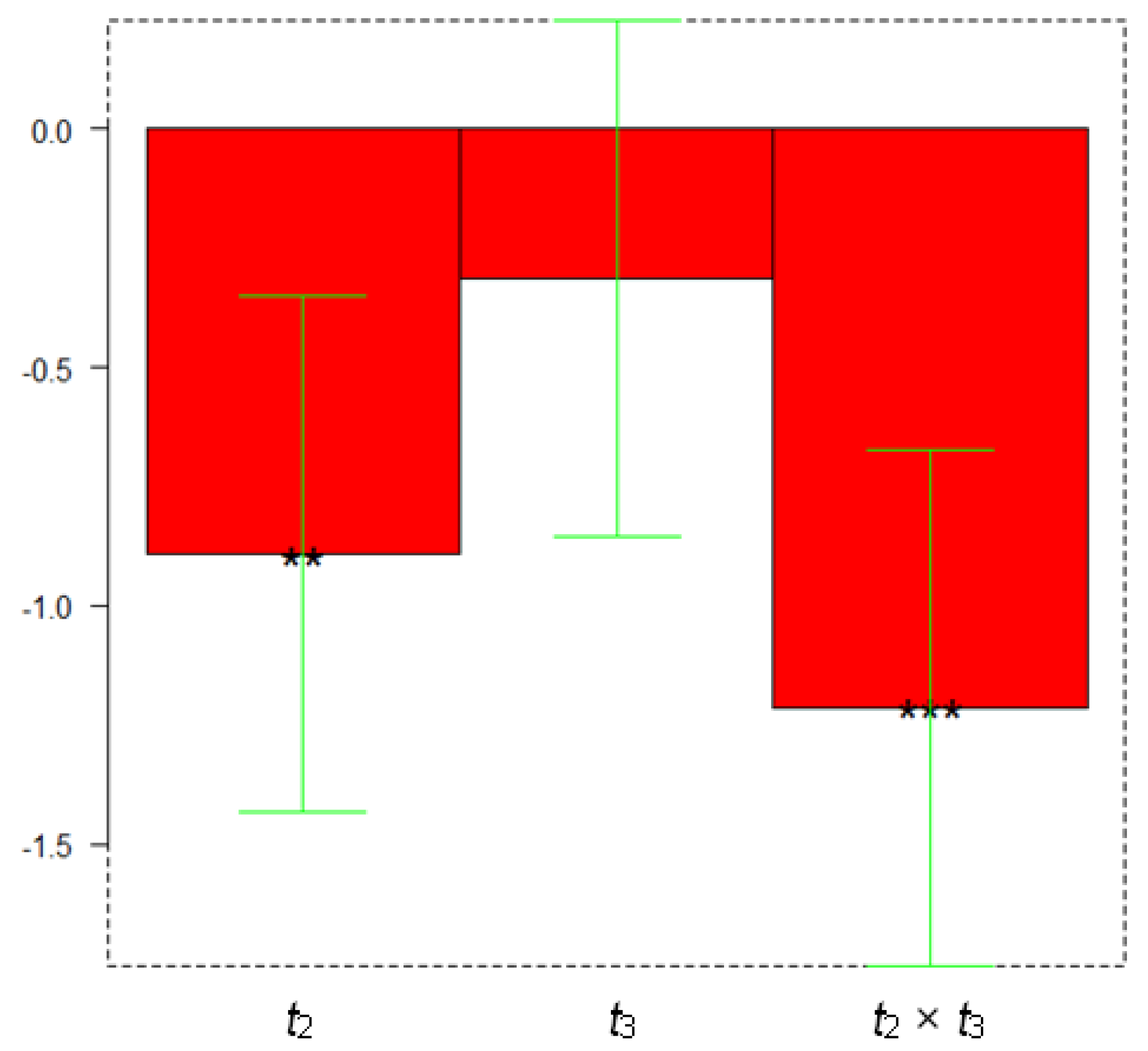



| Parameter | Minimum Level (−) | Maximum Level (+) |
|---|---|---|
| Time second step (t2 min) | 90 | 180 |
| Time third step (t3 min) | 60 | 120 |
| Methods a | Electrodes b | Linear Range/ µg/L | LOD /µg/L | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWV | Nanostructured Pt/nafion | 1–250 | 0.31 | [43] |
| SWV | Pt disck/thermally reduced graphene/nafion | 1–200 | 0.08 | [44] |
| SWV | Thin-film Pt | 300–5000 | 90 | [45] |
| DPV | GCE nano titanium carbide/nafion | 4–3920 | 0.4 | [46] |
| DPV | Micro niddle electrode Au-nanoclustes/PEDOT-PSSc c | 0.55–279 | 0.17 | [47] |
| DPV | GCE/reduced graphene oxide/Methylene Blue/AuNPs | 16.7–5585 | 0.84 | [48] |
| DPV | GCE/reduced graphene oxide/5-Br-PADAP d/AuNPs | 1.7–168 | 0.20 | [49] |
| DPV | Au screen-printed | 0.07–0.7 | 0.03 | This work |
| Cation | Na(I) | K(I) | Ca(II) | Mg(II) | Zn(II) | Al(III) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | 12 | 1.3 | 42 | 8.5 | 0.035 | 0.025 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alberti, G.; Zanoni, C.; Rovertoni, S.; Magnaghi, L.R.; Biesuz, R. Screen-Printed Gold Electrode Functionalized with Deferoxamine for Iron(III) Detection. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10060214
Alberti G, Zanoni C, Rovertoni S, Magnaghi LR, Biesuz R. Screen-Printed Gold Electrode Functionalized with Deferoxamine for Iron(III) Detection. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(6):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10060214
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlberti, Giancarla, Camilla Zanoni, Sara Rovertoni, Lisa Rita Magnaghi, and Raffaela Biesuz. 2022. "Screen-Printed Gold Electrode Functionalized with Deferoxamine for Iron(III) Detection" Chemosensors 10, no. 6: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10060214
APA StyleAlberti, G., Zanoni, C., Rovertoni, S., Magnaghi, L. R., & Biesuz, R. (2022). Screen-Printed Gold Electrode Functionalized with Deferoxamine for Iron(III) Detection. Chemosensors, 10(6), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10060214








