Abstract
Extracellular vesicles are involved in many physiological and pathological activities. They transport miRNAs to recipient cells during their role in intercellular communication, making them emerging biomarkers of many diseases. Interest in exosomal miRNAs has grown after they have shown numerous advantages as biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and evaluation of cancer treatment. This work describes the development of a biosensor for the detection of 21-5p miRNA in human serum using screen-printed carbon electrodes modified with gold nanoparticles fabricated in situ, an innovative approach to avoid the use of more expensive gold substrates that provide better analytical outputs. The several variables involved in the assembly of the biosensor were optimized by univariant mode. Under the best conditions, the biosensor showed a linear response from 0.010 fM to 10 pM, with a limit of detection (LOD) of 4.31 aM. The sensitivity was 0.3718 relative Ω per decade concentration in buffered saline solutions, and the standard deviation of the blank is 2.94 Ω. A linear response was also obtained when human serum samples were tested with miRNA 21-5p. Interference from similar miRNA and miss-match miRNA sequences was evaluated and good selectivity for miRNA 21-5p was observed. Overall, the device proposed is an alternative approach to gold substrates, which typically result in more sensitive systems and lower LODs, which compares favorably to current gold-based biosensors for the targeted miRNA. This design may be further extended to other nucleic acids.
1. Introduction
Exosomes play an important role in many physiological and pathological activities by promoting intercellular communication and adapting cell responses to the external environment [1,2]. In the brain, exosomes secreted by all central nervous system (CNS) cell lineages are referred to as brain-derived exosomes (BDEs) [3]. They are involved in neurological diseases such as abnormal neuronal development, neurodegenerative diseases, epilepsy, mental syndromes, stroke, brain injury, and brain tumors [2], and also play a role in neuronal communication. In cancer, exosomes play a key role in tumor development and proliferation and also in malignant development of cancer through processes such as immunosuppression by inhibiting immune cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis in activated CD8+ T cells, and reducing natural killer cell activity [4]. Therefore, monitoring of specific miRNA could provide better control over health and disease states.
MicroRNAs (or miRNAs) are small, noncoding, single-stranded RNA molecules of 20–22 nucleotides that are expressed in many tissues and cell types and are capable of regulating gene expression and subsequently acting in various physiological and pathological activities [5,6]. These miRNAs control a variety of biological activities such as proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, migration, invasion, metabolism, and stress response [7] and can act as tumor suppressors or/and oncogenes [6]. Certain miRNAs in neurons are known to play important roles in nervous system development and function, such as neuronal differentiation, neuronal patterning, cell identity formation and maintenance, synaptogenesis, and neuronal plasticity [7,8]. In addition, some studies report that miRNAs can act as both neuroregulators and neuroprotectors [9].
Thus, miRNA measurement and quantification may provide a more reliable and less invasive method for early disease diagnosis and prognosis, as well as therapeutic targets for many diseases, including neurological and cancer diseases [7,8]. In this regard, Dai Li et al. pointed out that miRNA 21-5p plays an important role in the pathogenesis of many diseases by regulating autophagy. For example, neuronal extracellular vesicles enriched in miRNA 21-5p are important in suppressing neuronal autophagy and may act as neuroprotectors. In another example, treatment with exosomal miRNA 21-5p after traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a potential therapeutic approach to treat nerve damage. In this context, exosomes derived from neurons modified with specific miRNA may represent a new treatment option for TBI and other neurological diseases [10].
Biosensors are an interesting alternative to conventional methods for the detection of miRNA 21-5p in serum samples because they are rapid, inexpensive, sensitive, and allow easy sample pretreatment. They require small sample volumes and allow point-of-care applications [11]. To date, several research papers have been published on the detection of miRNA 21-5p using electrochemical systems. These are listed in Table 1. The different analytical features are related to the different approaches used to build the biosensor, including different substrates (carbon or gold), different nanomaterials, or the type of measurement (with or without labeling). In addition, the works listed in Table 1 involve different technical approaches, about which it is important to remember that simpler methods are less error-prone, less expensive, and less technically complex.
Importantly, a direct comparison of these methods shows that gold substrates are associated with lower LOD values. However, gold is an expensive substrate to be used in point-of-care systems for global use. To avoid this and ensure good analytical data, only a portion of gold may be employed, which may be used for miRNA binding. To this end, gold nanoparticles could be casted on carbon substrates [12]. Considering that this is an electrochemical technique, these gold nanoparticles could also be assembled in situ in a very simple and quick approach. It is enough to cover the 3-electrode system with a gold salt solution and apply appropriate electrochemical conditions to generate suitable nanoparticles on the surface.
Thus, this work proposes a simple approach for a highly sensitive miRNA assay suitable for point-of-care applications using carbon substrates. Screen-printed carbon electrodes (C-SPEs) are used, which are subsequently modified with in situ synthesized gold nanoparticles and with the complementary sequence of miRNA 21-5p having a thiol terminal and a spacer of adenosines to avoid steric hindrance during hybridization. The different variables are optimized, and the best conditions are used to evaluate the response of the biosensor in human serum.

Table 1.
Recent electrochemical biosensors for miRNA 21 detection.
Table 1.
Recent electrochemical biosensors for miRNA 21 detection.
| Technique | Electrode | LOD | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIS | GC | 2.3 fM | 10–70 fM | [13] |
| CV/EIS | Gold | 0.168 fM | 1 fM–10 nM | [14] |
| CV/EIS | Gold | 2.75 fM | 10 fM–10 nM | [15] |
| CV | Gold | 49 aM | 100 aM–1 nM | [16] |
| SWV | Gold | 0.4 fM | 1 fM–200 pM | [17] |
| SWV | Gold | 10 aM | 10 aM–1 nM | [18] |
| SWV | Gold | 7.3 aM | 10 aM–100 fM | [19] |
| DPV | Gold | 1 pM | 1.0 pM–10 nM | [20] |
| DPV | Gold | 0.29 fM | 1 fM to 1 nM | [21] |
| DPV | Gold | 67 aM | 0–100 fM | [22] |
| DPV | Gold | 65 aM | 0.1 fM–1 nM | [23] |
| AMP | GC | 29 fM | 0.096–25 pM | [24] |
| EIS | Carbon | 4.31 aM | 0.01 fM–10 pM | This work |
AMP–amperometry; EIS–Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy; GC-Glassy Carbon; DPV–Differential Pulse Voltammetry; CV–Cyclic Voltammetry; SWV–Square Wave Voltammetry; LOD–Limit of detection.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
All chemicals were of analytical grade and ultrapure Milli-Q water (conductivity < 0.1 µS/cm) was used. Solutions containing miRNA or to be in contact with miRNA had autoclaved laboratory water. All reagents were used without additional purification. Potassium ferricyanide II 3-hydrate (K4[Fe(CN)6]·3H2O), potassium ferricyanide III (K3[Fe(CN)6]), sodium phosphate dibasic dihydrate, and magnesium chloride were purchased from Riedel-deHaen; gold (III) chloride trihydrate, ≥99.9% trace metal base (HAuCl4), sulfuric acid 95–97%, mercaptosuccinic acid (MSA), and DL-dithiothreitol (DTT) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich; phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solutions were made by dissolution of tablets from Amresco; Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris) from Fisher BioReagents and sodium chloride from Panreac; potassium chloride and calcium chloride dihydrate were purchased from Merck; and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) was purchased from BDH.
The oligonucleotide probes were miRNA 21-5p purified by HPLC with the corresponding sequence 5′-UAG CUU AUC AGA CUG AUG UUG A-3′, and anti-miRNA 21-5p (complementary strand modified with thiol end and containing adenine spacer), 5′-Thiol-C6-AAA AAA UCA ACA UCA GUC UGA UAA GCU A-3′ and were obtained from Metabion. The oligonucleotide used for selectivity studies was miRNA 26a-5p (5′-UUC AAG UAA UCC AGG AUA GGC U-3′) and a mismatch sequence from miRNA 21-5p (5′-UAG GUU AUC ACA AUG AUC UUG A-3′). Autoclaved water was used to prepare the solutions.
A 0.05 M solution of H2SO4 was prepared for cleaning the commercial SPEs. The gold nanoparticles were obtained with a solution of 1.0 × 10−4 M HAuCl4, prepared in Milli-Q water. The stock solution of oligonucleotide for anti-miRNA (1.0 mM) was prepared in SSPE buffer containing also 0.02 M EDTA, 2.98 M NaCl, and 0.2 M phosphate buffer (diluted 20-fold, pH 7.4). The stock solution for miRNA 21-5p (1.0 mM) was prepared in Tris-HCl consisting of Tris (0.02 M), NaCl (0.14 M), MgCl2 (0.001 M), KCl (0.005 M), and CaCl2 (0.001 M) with a pH of 7.4. Less concentrated standards with a pH of 7.4 were prepared by appropriate dilution of the previous solution in 0.010 M PBS buffer. Finally, the same buffer solution was used for the immobilization and hybridization buffer. It is important to clarify that PBS buffer was used as obtained by dissolution of Amresco tablets, while phosphate buffer solutions were prepared by dissolution of sodium phosphate dibasic dihydrate.
For the selectivity assay, the solutions of the interfering species were prepared in the same buffer used for the immobilization and hybridization phases. The concentration of miRNA 26-5p stock solution was 1.0 mM, and this was used to prepare the standard solutions tested. Electrochemical properties were performed in a solution of 5.0 × 10−3 M of K3[Fe(CN)6] and 5.0 × 10−3 M K4[Fe(CN)6] redox probe in 0.010 M PBS buffer, pH 7.4.
2.2. Apparatus
Electrochemical measurements were performed using a PalmSens4 potentiostat/galvanostat controlled by PSTrace 5.8 software. Commercial carbon screen-printed electrodes (C-SPEs) were from Metrohm DropSens (DRP-110) and had a three-electrode system, including (a) a carbon counter electrode, (b) a silver reference electrode, and (c) a 4 mm diameter carbon working electrode. The C-SPEs were connected to a switchbox from PalmSens, which allows connection to the potentiostat.
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
The electrochemical methods include cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and square-wave voltammetry (SWV) using a redox probe as 5.0 × 10−3 M of [Fe(CN)6]3− and 5.0 × 10−3 M of [Fe(CN)6]4− in PBS buffer (pH 7.4). The CV method was performed at a sampling rate of 50 mV/s with sampling potentials ranging from −0.3 to +0.7 V. The EIS method was performed with the circuit open through a sinusoidal potential perturbation with 50 data points and an amplitude of 0.01 V, logarithmic in a frequency range of 0.1 to 100,000 Hz (data was collected under Open Circuit Potential). PalmSens 5.5 PSTrace software was used to create a Randle equivalent circuit for EIS data. The EIS data were fitted to a Randles equivalent circuit using PalmSens 5.5 PSTrace and analyzed using Nyquist plots that reflect the mixed kinetic process occurring at the electrode–electrolyte interface, which can be expressed as the real part of the impedance (Z′) or the resistance and its imaginary part (Z″). The Randles circuit includes the components Rs, which is the solution resistance, Rct, which is charge transfer resistance, Cdl which is the double-layer capacitance based on high frequency, and Zw, which is the diffusional resistance element, Warburg impedance (62). Concerning Nyquist plots, the semicircle diameter indicates the electron transfer resistance (Rct) and is essential to know the information between the electrode–electrolyte and the reaction [25]. The diameter of the semicircle in the Nyquist diagram was used to calculate the charge transfer resistance (Rct) (57). The SWV method was used with a frequency of 2 Hz, a step height of 25 mV, and sampling potentials of −0.3 to +0.7 V. The electrochemical tests were performed in triplicate.
To evaluate hybridization, microRNA 21-5p standard solutions ranging from 0.01 fM to 100 pM prepared in PBS buffer (pH = 7.4) were tested by EIS. The LOD was calculated as x + 3σ, where σ is the standard deviation of successive measurements and x is the average value of the blank signals (EIS) [26]. Calibration curves signaled hybridization with target miRNA and were performed for miRNA 21-5p concentrations ranging from 0.01 fM to 100 pM in PBS buffer, pH 7.4, and human blank serum (0.01 fM to 100 pM) from Cormay®. Selectivity was assessed by calibrating the electrodes with miRNA 26a-5p solutions, ranging from 0.01 fM to 10 pM, or finding the response to a single solution of a mismatch miRNA from miRNA 21-5p.
2.4. Development of Electrochemical Biosensor on C-SPE
The biosensor was assembled as shown in Figure 1, following the procedures described in [27] with adaptations. Before modification, the surface of the working electrode of the C-SPE was cleaned by electrochemical treatment with 0.050 M H2SO4 for 5 cycles with CV from −0.1 to +1.5 V and a scan rate of 50 mV/s. The surface was then washed with autoclaved water. Then, the electrodeposition of AuNPs was made by chronoamperometry at −1.5 V for a suitable timing. Next, the anti-miRNA 21-5p with a thiol end was mixed with DTT (0.1 M) solution, heated to 90 °C for 5 min, and incubated on the working electrode with Tris, EDTA, and NaCl solution, pH of 7.4, for 1 h. After washing with autoclaved water, 1 mg/mL MSA solution was cast on the working electrode for 2 h at room temperature to block the nonspecific binding regions. The biosensor was then washed and kept at 4 °C in humid environment until further use.
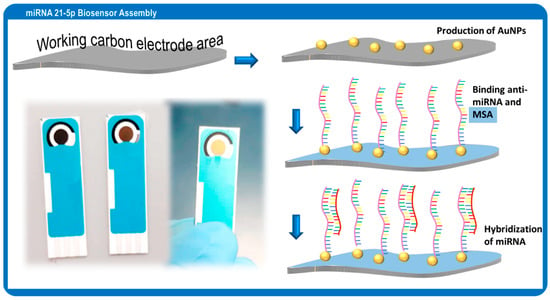
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the assembly of the microRNA 21-5p sensing area on the carbon working electrode and hybridization with the target miRNA.
2.5. Characterization by Atomic Force Microscopy
Morphological analysis of the biosensor was evaluated using atomic force microscopy (AFM) experiments. Measurements were performed in a tapping mode Veeco Metrology Multimode, Nanoscope IVA. The Nanoscope program was used to analyze the AFM images acquired in the tapping mode.
2.6. Analytical Performance of the Biosensor
The binding of miRNA 21-5p to the sensing area was made by incubating several miRNA 21-5p standard solutions of increasing concentrations, prepared in either PBS or 1000-fold diluted human serum (commercially available), for a fixed time. The extension of binding against miRNA concentration was monitored by recording the electrochemical signals of the iron redox probe after incubation of each standard concentration. The analytical performance of the biosensor was obtained in the form of calibration curves by EIS, plotting Rct values against log concentration of miRNA 21-5p. Concentration ranges of linear response and LODs were extracted from these. Selectivity tests were performed in two ways: (a) by evaluating the response of the biosensor designed to miRNA 21-5p to independent solutions of miRNA 26-5p; and (b) by checking the response to a mismatch miRNA from miRNA 21-5p, with a concentration of 0.1 pM.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Carbon Electrode Pre-Treatment
Before constructing the biosensor, the surface of the working electrode was pre-treated by CV with an H2SO4 solution, aiming to ensure the production of reproducible data. This pre-treatment resulted in the oxidation of contaminating materials on the electrode surface (usually ink components or other adsorbed materials), which were subsequently more soluble in water and easily removed from the measurement surface by washing. This procedure improved the reproducibility between different commercial SPEs and their stability under successive incubation with buffer solution [28]. The number of cycles was optimized and set to five cycles as the best condition.
3.2. Electrodeposition of the Gold Nanoparticles
The first step in the construction of the biosensor was the formation of AuNPs on the electrode surface to create binding sites for the thiol-modified complementary miRNA strand [29]. This approach aimed to develop a more cost-effective method to fabricate a gold-based nucleic acid detection system to improve the performance of current nucleic acid biosensor systems, as shown in Table 1. These nanoparticles also exhibit exceptional electrical and catalytic properties [30,31], which can help improve the electrochemical performance of a normal carbon electrode. This is a result of current enhancement due to high conductivity and surface area generated by AuNPs.
This was done by applying a fixed potential to the surface of the electrode containing a gold salt solution, resulting in the formation of AuNPs in situ. Preliminary data indicated that stirring and the use of nitrogen improved the reproducibility of electrodeposited nanoparticles and that longer times resulted in surfaces that reflected as gold, indicating a higher gold content (Figure S1). To this end, various potential values were investigated [32], with −1.5 V providing the most reproducible data.
The time needed to apply the constant potential was considered critical. A shorter time means fewer and smaller particles, while a longer time means more particles but not necessarily a larger surface area because the particles may be clustered. The best time for nanoparticle growth was determined by running a wide range of electrodeposition options from 100 to 1200 s at −1.5 V. Figure S2 shows the different Rct values obtained in this study. The 100 s electrodeposition lowered the Rct values compared to the blank value, confirming the existence of gold at the electrode surface. However, the effect of AuNPs was not too obvious because the Rct value was not too different from the blank value. For increasing times beyond 100 s, the Rct value decreased continuously, confirming the increasing formation of AuNPs in the working electrode region. Considering that the differences in Rct value between 900 and 1200 s were not significant and that higher time points may lead to clustered spots of gold nanoparticles [33,34], 900 s would be the best choice to achieve a larger gold surface area for subsequent binding of thiol-modified complementary miRNA.
Overall, the CV and SWV data agreed with the EIS data. As a reference for the 900 s electrodeposition, the measurements from CV showed a significant decrease in peak-to-peak potential separation, which was also related to increasing currents (~120 to ~151 µA). In SWV, the average peak current after electrodeposition of AuNPs was ~136 µA, which was much higher than the current value obtained after cleaning (80 µA). These results are shown in Figure 2. The absolute data in the EIS showed that the Rct values decreased from ~256 Ω after electrode pre-treatment to ~20 Ω after electrodeposition of AuNPs, which was also a significant change.
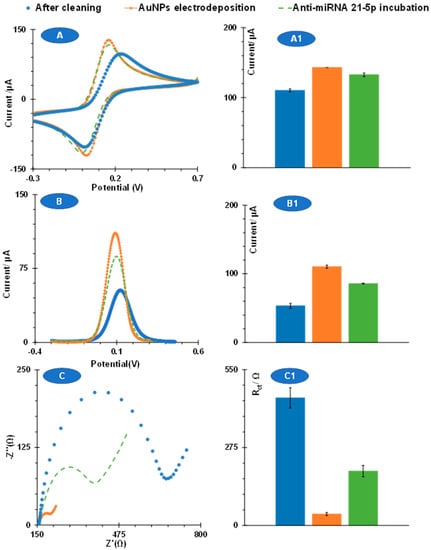
Figure 2.
CV (A), SWV (B), and EIS (C) measurements of the devices at the several stages of the biosensor assembly, including the pre-treatment process, after AuNPs electrodeposition, and after incubation of miRNA21-5p and MSA. Graphics A and B show current peak intensity and C the resistance to charge transfer, all of these represented in the corresponding graphics (1).
Considering the data obtained, it would be logical to choose 900 s. However, the time of electrodeposition may have a major impact on hybridization, which is not necessarily favored by more AuNPs. The complementary sequence also requires hybridization so that the miRNA can reach the complementary sequence without steric hindrance, which also depends on the number of nanoparticles on the surface and how they are formed. Therefore, it was considered that this important variable should be selected by testing the sensitivity of miRNA binding at each time point of electrodeposition.
Thus, different calibrations were made for each of the time conditions, from 0.010 fM to 100 pM, and the average/typical results obtained are shown in Figure 3 and Figures S3–S6. In general, it was clear that increasing the deposition time of the gold electrode resulted in more sensitive responses for decreasing concentrations of miRNA. While the 100 s deposition resulted in a random response, the 300 s deposition resulted in a linear response from 0.10 pM up to the higher concentrations tested. The 600 s deposition allowed the inclusion of an additional standard solution in the linear range and showed a linear response down to 0.010 pM. The 900 s allowed a further extension of the linear range to the minimum concentration tested, 0.010 fM, but showed signal saturation at the higher concentration tested, indicating that the upper limit of the linear range is 10 pM. The 1200 s increased the sensitivity of the response but decreased the extent of the linear range, which now ranged from 0.010 fM to 1.0 pM. Therefore, these results support the choice of 900 s for electrodeposition of AuNPs. The data obtained also confirmed that a stable and sensitive sensor response could be expected.
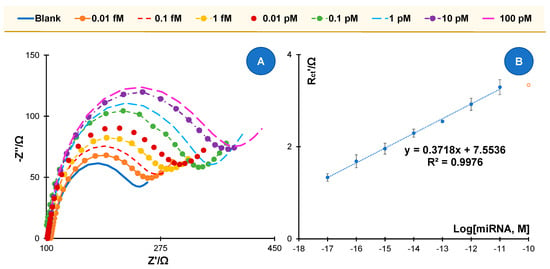
Figure 3.
Calibration of the miRNA 21-5p biosensor in buffer background. (A) Nyquist plots; (B) and the corresponding calibration curve in 5.0 × 10−3 M [Fe(CN)6]3− and 5.0 × 10−3 M [Fe(CN)6]4−, in standard solutions prepared in buffer and using relative Rct data.
3.3. Creating the Sensing Surface
The sensing surface was created by binding the complementary strand of miRNA 21-5p, modified with a thiol (to bind the gold particles), next to a spacer of consecutive adenosines (to improve hybridization by increasing mobility and avoid steric hindrance). This was followed by MSA incubation to fill the empty sites on the gold surface. Figure 2 shows the CV, SWV, and EIS data generated after anti-miRNA and MSA binding as a reference for the data obtained for 900 s. Overall, the changes in electrochemical behavior induced in this step were most evident in the potential shift in the CV and SWV data and in the increased Rct values in the EIS. Moreover, in SWV, the average peak current changed from ~136 µA to ~124 µA after anti-miRNA/MSA immobilization. The most pronounced change was then translated by EIS, in that typical Rct values increased from ~20 Ω to ~72 Ω after anti-miRNA/MSA incubation. This suggests that EIS may be more sensitive than CV and EIS to perform calibration studies. This change was also most pronounced at the different time points of electrodeposition, which also supports the choice of this time point. Overall, these results confirmed the successful modification of the sensor carbon substrate with the sensor element, which also supports the data obtained when testing the different time points of electrodeposition.
3.4. Analytical Performance of the Biosensor in PBS Buffer
The analytical performance of the biosensor was evaluated by calibration curves during EIS measurement. For this purpose, increasing concentrations of miRNA 21-5p were incubated on the surface for 30 min for hybridization, then washed out and replaced by the redox probe ([Fe(CN)6]3− and [Fe(CN)6]4−) to understand the effects of such binding on the electrochemical properties of the working electrode.
The typical calibration plots in the form of Nyquist plots are shown in Figure 3A. In general, the higher the concentration of miRNA 21-5p, the higher the Rct value. To check the reproducibility of the biosensor, three calibration experiments were performed with independent sensors and on different days. Excellent reproducibility is not always achieved, but the variability is mostly due to the commercial SPEs used, which show some variability within a batch. Nevertheless, all biosensors showed a linear range response between 0.01 fM and 10 pM. The average linear plots obtained are shown in Figure 3B, where the error bars reflect the variability of the three independent sensors produced on the same day. Overall, the small variations confirm the overall good reproducibility of the analytical system. The average LOD of these calibrations was 4.31 aM, which is exceptionally low compared to other work using carbon substrates and having detection limits in the fM range. Overall, it can be said that the biosensor has good stability and exceptional detection capabilities.
3.5. Selectivity Test
Selectivity assays were performed by analyzing the feasibility of hybridizing anti-miRNA 21-5p on the sensor surface against another miRNA. The miRNA 26-5p was selected for this purpose. According to some studies, it seems to be oncogenic, being involved in tumorigenesis of various cancers and other biological activities related to non-cancerous human diseases [35,36]. According to other studies, miRNA 26-5p can be used as a therapeutic agent to prevent disease progression by altering various signaling pathways [35]. This study consisted of calibration of the electrode against the competing miRNA and was performed in triplicate. For this purpose, standard solutions of miRNA 26a-5p in increasing concentrations were incubated on the sensing surface for 30 min, washed out, and the subsequent response of the EIS to the iron probe was evaluated. The data obtained is shown in Figure 4. In general, the signals produced by the lowest concentrations were similar to the blank. Only at a concentration of 0.10 pM the competing miRNA was able to change Rct levels to higher values, reaching saturation after incubation of 1 pM solution. These Rct changes were also of small magnitude compared to the normal calibration in PBS. Thus, it can be said that this biosensor is not significantly affected under real conditions by competing miRNAs.
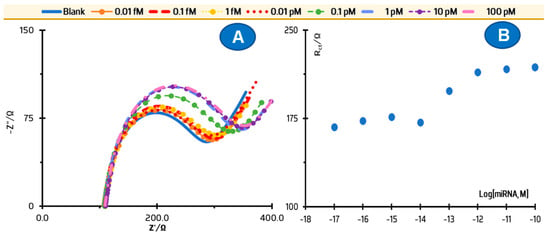
Figure 4.
Response of the microRNA 21-5p biosensor against microRNA 26-5p standard solutions. (A) Nyquist plots; (B) and the corresponding calibration curve.
In another approach, the response of the biosensor was tested against a mismatch sequence that changed from the original miRNA 21-5p sequence in four random nucleotides. The test was made by incubating a concentration of 0.1 pM, which is an intermedium concentration level when considering the calibration curve in the buffer. The results obtained are shown in Figure 5. In general, it is clear that the signal generated by the mismatch sequence is very small when compared to the signal generated by the target sequence, of the same concentration.
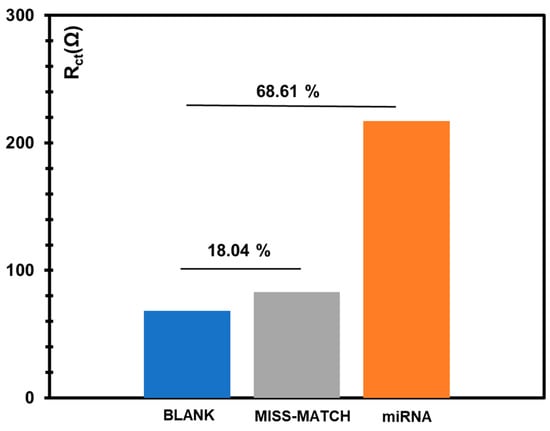
Figure 5.
Response of the microRNA 21-5p biosensor against a mismatched miRNA sequence (miRNA concentrations of 0.1 pM).
3.6. Analytical Performance in Serum Samples
After calibration, the application of the miRNA biosensor was tested in serum samples as shown in Figure 6. Human serum diluted 1000-fold in PBS served as the blank solution, and this solution was used to prepare the standard solutions. Analytical performance was derived from calibrations performed with these solutions and under conditions similar to those used for calibrations in PBS. The typical data obtained in this study are shown in Figure 5. In general, the results obtained showed good analytical characteristics, with a similar slope to that obtained in PBS. The linear response extended over a wide range of concentrations, between 0.01 fM and 10 pM, in similar behavior to that presented in buffered solutions. The device was not tested for concentrations below 0.01 fM as the difference between the blank and the first standard solution is similar to the difference between 0.01 fM and 0.1 fM. This suggests that a lower concentration than 0.01 fM shall lead to a signal that is like the blank. Overall, these results support the possibility of using this biosensor for the analysis of miRNA in human serum samples. The concentrations to which the biosensor responds are sufficient to support 1000-fold serum dilution.
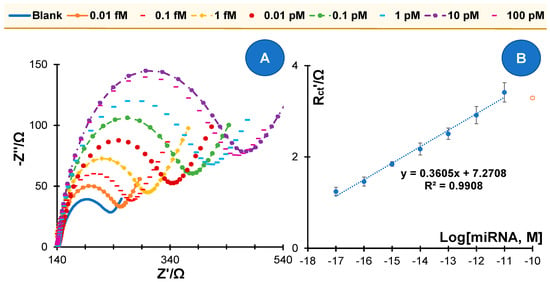
Figure 6.
Calibration of the miRNA 21-5p biosensor in serum background. (A) Nyquist plots; (B) and the corresponding calibration curve in 5.0 × 10−3 M [Fe(CN)6]3− and 5.0 × 10−3 M [Fe(CN)6]4−, in standard solutions prepared in a 1000-fold diluted human serum and using relative Rct data.
3.7. Morphological Characterization of the Biosensor
The morphological changes of the carbon electrode of the SPEs were followed by AFM. Figure S7 shows AFM images of the surfaces at different stages of the electrode assembly. These images were acquired for electrodes prepared with 900 s gold deposition (Figure S7A), after the addition of anti-miRNA, 21-5p/MSA binding (Figure S7B) and including miRNA 21-5p hybridization (Figure S7C). In general, major differences can be seen in the 2D images, with the AuNP deposition step appearing to make the biggest difference. Subsequently, the immobilization of anti-miRNA 21-5p on the AuNP surface showed a difference in roughness (457 nm), indicating that the immobilization of anti-miRNA has a lower roughness when compared with AuNP. Hybridization between the miRNA and the complementary sequence (Figure S7C) showed a significant change in electrode surface area, also resulting in a decreasing roughness (65.4 nm). Since stable double-stranded oligonucleotides with a negative charge on the outer surface may be evenly distributed over the entire surface and all have the same length, the formation of an apparently flatter surface is plausible; the strong negative outer surface of each double strand would help repel each other and create the image of a homogeneous surface [25].
4. Conclusions
A low-cost, sensitive, and selective biosensor was developed for the determination of miRNA 21-5p using AuNPs directly generated on C-SPEs. The analytical performance of the device raised great expectations, considering that the substrate of the electrode is carbon and that the use of gold nanoparticles is a simple solution for generating very sensitive measurements of miRNA 21-5p. The use of AuNPs was also a great advantage, as they increase the surface area and the quality of the obtained electrochemical signal. In principle, the biosensor produced is expected to cost <€10 per unit in materials and reagents.
Having achieved the optimal conditions for the construction of the biosensor, it can be said that the device fabricated here was simple in terms of materials and number of modification steps and fast in terms of response while showing exceptional analytical properties. Analytically, the biosensor was able to detect very low concentrations of miRNA 21-5p in both buffer and diluted human blood. It is important to note that there were no studies made on long-term stability. So far, the results in serum samples provide promising data that require further studies with real samples with elevated concentrations of miRNA 21-5p.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors10050189/s1, Figure S1: Pictures (left) of the carbon screen-printed electrodes highlighting the effect of time on the electrodeposition of gold on working electrodes and SEM analysis of one of the conditions tested (not the optimum condition selected)., Figure S2: (A)—Electrodeposition time curves at AuNPs modified C-SPE; (B)—Charge transfer resistance after electrodeposition, Figure S3: (A)—EIS changes corresponding to the different miRNA 21-5p concentrations; (B)—Charge transfer resistance of each concentration (100s AuNPs electrodeposition), Figure S4: (A)—EIS changes corresponding to the different miRNA 21-5p concentrations; (B)—Charge transfer resistance of each concentration (300s AuNPs electrodeposition), Figure S5: (A)—EIS changes corresponding to the different miRNA 21-5p concentrations; (B)—Charge transfer resistance of each concentration (600s AuNPs electrodeposition), Figure S6: (A)—EIS changes corresponding to the different miRNA 21-5p concentrations; (B)—Charge transfer resistance of each concentration (1200s AuNPs electrodeposition), Figure S7: AFM scans of AuNPs electrodeposition in 3D (left) and 2D (right) views of the different stages. (A)—900s AuNPs electrodeposition (B)—900s AuNPs electrodeposition/anti-miRNA 21-5p (C)—900s AuNPs electrodeposition/anti-miRNA 21-5p/miRNA 21-5p.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R.C. and M.G.F.S.; Data curation, A.R.C., I.S.P.S. and V.M.S.; Formal analysis, A.R.C. and V.M.S.; Funding acquisition, M.G.F.S.; Investigation, A.R.C., I.S.P.S. and V.M.S.; Methodology, A.R.C. and V.M.S.; Project administration, M.G.F.S.; Resources, M.G.F.S.; Supervision, A.R.C. and M.G.F.S.; Validation, A.R.C. and V.M.S.; Visualization, A.R.C., I.S.P.S. and V.M.S.; Writing—original draft, A.R.C. and V.M.S.; Writing—review and editing, A.R.C. and M.G.F.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge funding from the European Commission through the project MindGAP (FET-Open/H2020/GA829040). A.R.C. acknowledges Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia her PhD grant (SFRH/BD/130107/2017).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or supplementary material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, W.; Bai, X.; Zhang, A.; Huang, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J. Role of Exosomes in Central Nervous System Diseases. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Hareendran, S.; Loh, Y.P. Function of exosomes in neurological disorders and brain tumors. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucl. Acids 2021, 2, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xu, Y.; Deng, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; Yu, P.; Qu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Han, Y.; Qin, C. Brain Derived Exosomes Are a Double-Edged Sword in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalian, S.H.; Ramezani, M.; Jalalian, S.A.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. Exosomes, new biomarkers in early cancer detection. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 571, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Tandon, M.; Alevizos, I.; Illei, G.G. The majority of microRNAs detectable in serum and saliva is concentrated in exosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—MicroRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, R.; Wang, J.; Qin, Z.; Xue, L. Circulating microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers: The advantage and disadvantage. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viswambharan, V.; Thanseem, I.; Vasu, M.M.; Poovathinal, S.A.; Anitha, A. MiRNAs as biomarkers of neurodegenerative disorders. Biomark. Med. 2017, 11, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, I.; Patil, K.S.; Alves, G.; Larsen, J.P.; Møller, S.G. MicroRNAs as neuroregulators, biomarkers and therapeutic agents in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Huang, S.; Zhu, J.; Hu, T.; Han, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, F.; Lei, P. Exosomes from miR-21-5p-increased neurons play a role in neuroprotection by suppressing rab11a-mediated neuronal autophagy in vitro after traumatic brain injury. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1871–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, F.R.R.; Fonseca, L.P. Trends in DNA biosensors. Talanta 2008, 77, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazaca, L.C.; Imamura, A.H.; Gomes, N.O.; Almeida, M.B.; Scheidt, D.T.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Oliveira, O.N.; Janegitz, B.C.; Machado, S.A.S.; Carrilho, E. Electrochemical immunosensors using electrodeposited gold nanostructures for detecting the S proteins from SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Wang, L.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Liao, Y.; Chen, T.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J. A ratiometric electrochemical DNA biosensor for detection of exosomal MicroRNA. Talanta 2020, 207, 120298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, M.; Chen, G.; Mao, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, J. An electrochemical biosensor based on DNA “nano-bridge” for amplified detection of exosomal microRNAs. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3474–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.; Yu, L.; Zhao, S.; Chang, K.; Chen, M. Strand displacement-triggered G-quadruplex/rolling circle amplification strategy for the ultra-sensitive electrochemical sensing of exosomal microRNAs. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lu, H.; Shi, R.; Peng, X.X.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, B.; Wan, Q.Q.; Sun, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, G.J. Synergy of Peptide-Nucleic Acid and Spherical Nucleic Acid Enabled Quantitative and Specific Detection of Tumor Exosomal MicroRNA. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13198–13205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Ma, J.; Cao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Yi, Y.; Li, J. Enzyme-free electrochemical biosensor based on double signal amplification strategy for the ultra-sensitive detection of exosomal microRNAs in biological samples. Talanta 2020, 219, 121242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavallaie, R.; McCarroll, J.; Le Grand, M.; Ariotti, N.; Schuhmann, W.; Bakker, E.; Tilley, R.D.; Hibbert, D.B.; Kavallaris, M.; Gooding, J.J. Nucleic acid hybridization on an electrically reconfigurable network of gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles enables microRNA detection in blood. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Tang, Y. Dumbbell Hybridization Chain Reaction Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of Exosomal miRNA. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12026–12032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kseniia, B.; Umer, M.; Islam, M.N.; Gopalan, V.; Lam, A.K.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. An amplification-free electrochemical detection of exosomal miRNA-21 in serum samples. Analyst 2018, 143, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, M.; Wu, H.; Shen, B.; Liu, P.; Ding, S. Electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive exosomal miRNA analysis by cascade primer exchange reaction and MOF@Pt@MOF nanozyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 168, 112554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.L.; Hou, M.F.; Xia, Y.K.; He, W.H.; Yan, A.; Weng, Y.P.; Zeng, L.P.; Chen, J.H. A ratiometric electrochemical biosensor for the exosomal microRNAs detection based on bipedal DNA walkers propelled by locked nucleic acid modified toehold mediate strand displacement reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Li, X.; Cui, D.; Yan, Y. Enzyme-Free Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Localized DNA Cascade Displacement Reaction and Versatile DNA Nanosheets for Ultrasensitive Detection of Exosomal MicroRNA. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 45648–45656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouari, M.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Raouafi, N. Amperometric Biosensing of miRNA-21 in Serum and Cancer Cells at Nanostructured Platforms Using Anti-DNA-RNA Hybrid Antibodies. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8923–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Yoo, J.S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for better electrochemical measurements. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harvey, D. Modern Analytic Chemistry. In Modern Analytical Chemistry; Kane, K., Ed.; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 797. ISBN 0-07-237547-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, A.R.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Fernandes, R.; Sales, M.G.F. Novel and simple electrochemical biosensor monitoring attomolar levels of miRNA-155 in breast cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá, A.C.; Barbosa, S.C.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Wilson, D.; Shimizu, F.M.; Raposo, M.; Oliveira, O.N. Flexible carbon electrodes for electrochemical detection of bisphenol-a, hydroquinone and catechol in water samples. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, C.; Somoza, Á. MicroRNA sensors based on gold nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1807–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.T.S.G.; Souto, D.E.P.; Barragan, J.T.C.; Giarola, J.D.F.; de Moraes, A.C.M.; Kubota, L.T. Electrochemical Biosensors in Point-of-Care Devices: Recent Advances and Future Trends. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 778–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.; Ghica, M.E.; Brett, C.M.A. Gold nanoparticle decorated multiwalled carbon nanotube modified electrodes for the electrochemical determination of theophylline. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5634–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldan, I.; Dobrovetska, O.; Sus, L.; Makota, O.; Pereviznyk, O.; Kuntyi, O.; Reshetnyak, O. Electrochemical synthesis and properties of gold nanomaterials. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2018, 22, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, M.; Mohamed, N. Catalytic application of gold nanoparticles electrodeposited by fast scan cyclic voltammetry to glycerol electrooxidation in alkaline electrolyte. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 4676–4689. [Google Scholar]
- El-Deab, M.S.; Sotomura, T.; Ohsaka, T. Morphological Selection of Gold Nanoparticles Electrodeposited on Various Substrates. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, C730–C737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapolnik, P.; Zapolnik, B. MicroRNA-26a-5p: Multiple functions, multiple possibilities—A mini-review. J. Pre-Clin. Clin. Res. 2020, 14, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wang, H.; Ding, M.; Yang, M.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Chen, L. MicroRNA-26a-5p inhibits proliferation, invasion and metastasis by repressing the expression of Wnt5a in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 6605–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).