Abstract
In recent years, the use of ion-selective membranes in the sensing and assessment of environmental contaminants has become a critical goal. Using sodium tetraphenylborate (TPB) and phosphotungstic acid (PTA) as ion-pairing agents, two sensitive and selective sensors were manufactured to evaluate the electrochemical response of moxifloxacin hydrochloride (MOX). The optimal electrochemical behavior was attained by fine-tuning all assay parameters. The manufactured membranes’ performance was optimal in a pH range from 1.0 to 5.0 with a linearity between 1 × 10−6 M and 1 × 10−2 M. The MOX–TPB and MOX–PTA membrane electrodes have Nernstian slopes of 59.2 ± 0.60 mV/decade and 58.4 ± 0.50 mV/decade, respectively. The proposed method was used to determine MOX in its pure form as well as real pharmaceutical wastewater effluents. The fabricated electrodes were effectively applied for the sensitive and selective determination of MOX in actual wastewater effluents without the need for any pre-treatment processes.
1. Introduction
Antibiotics are a class of medications that are widely utilized in both human and veterinary medicine. Antibiotics’ broad use may result in their presence in the environment, posing a significant danger to antibiotic resistance. Fluoroquinolones are typically found in surface water and soil because they are discharged intact in urine and so may reach the main hospital sewage. Due to the antibiotic’s harmful effects on human beings when they are present in the surrounding environment, there is no permissible value for their presence in the soil or water [1].
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride (MOX) (Figure 1) is a synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic discovered in 1999 [2,3]. MOX can act on Gram-positive as well as Gram-negative bacteria. It performs its action by preventing bacterial cell reproduction through the inhibition of the microbial DNA gyrase that plays an important role in DNA splitting [4].
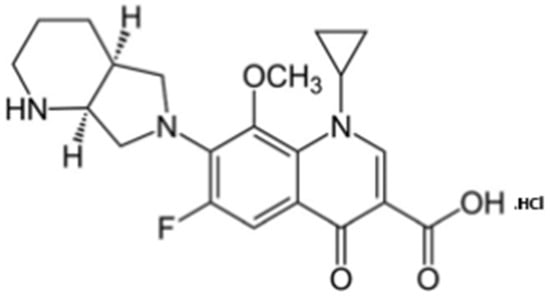
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of moxifloxacin hydrochloride.
Different analytical techniques were applied for the quantification of MOX in dosage form and in biological fluids, including spectroscopy [5,6,7,8], liquid chromatography (LC) coupled to ultraviolet (UV) [9,10,11,12] or fluorescence detectors [13,14], capillary electrophoresis [15,16], and LC coupled to mass spectrometric detectors [17,18]. It is important to note that most of the reported assay techniques include tedious and time-consuming steps, derivatization, and/or sophisticated instruments. Electrochemistry has a significant impact on the analysis of MOX, through the application of oxidative voltammetry in its quantification [19]. Furthermore, a voltametric sensor, prepared using a platinum electrode with a binary layer of poly(1,5-diaminonaphthalene) and platinum nanoparticles, was used for the simultaneous determination of the studied drug and paracetamol [20]. Molecularly imprinted polymer electrodes were applied to MOX quantification in tablets, plasma [21], and spiked urine samples [22]. Poly-vinyl chloride (PVC), carbon paste, and screen-printed membrane sensors were prepared to be applied for the MOX quantification in tablet form [23,24,25] and it was determined using zinc oxide nanorod-modified membranes [26]. On the other hand, potentiometric sensors based on sulfated cyclodextrin-carbon nanofiber were used for MOX quantification in dosage form, urine, and blood serum [27]. Hitherto, there is no published work dealing with the potentiometric determination of MOX in wastewater effluents.
It is critical to detect and monitor the researched medication in wastewater effluents. The presence of these antibiotics in water samples even in small quantities can constitute a great danger to human health, especially in light of growing antibiotic resistance [28].
The environmental analysis of MOX depends mainly on LC coupled to tandem mass spectrometry [29] and, to some extent, on LC with UV [30] or a fluorescence detector [31]. Before using LC, sample preparation and extraction should be performed to exclude the matrix effect and to pre-concentrate the analyte. As a result, a simple and cost-effective analytical method for monitoring the researched drug in environmental water samples is urgently needed. The use of membrane-sensitive electrodes can be considered a smart tool to meet this need.
Easy preparation, rapid response, selectivity, the ability to use turbid analyte solutions, and inexpensive cost are all advantages of ion-selective electrodes (ISEs). Furthermore, their responses are independent of the sensor’s surface area, allowing for electrode downsizing [32,33].
The evaporation of the inner solution in liquid inner contact ISEs causes an osmotic pressure variation and change in the internal solution volume. The transport of water across the membrane occurs due to pressure changes, leading to membrane deterioration [34]. Furthermore, they have the disadvantage of accumulating interfacial charges on the membrane, which causes charge transmission to stop. As a result, noise affects the potential, causing deviation with time, and impairs technique sensitivity [35,36,37]. Solid contact electrodes, which eliminate the use of the inner filling solution and replace it with a solid-state junction among the membrane and the metal electrode, have recently become a popular technique to circumvent the problems of liquid contacting the inner electrodes [38] (Figure 2).
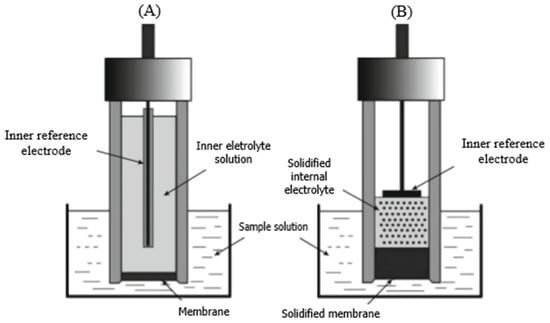
Figure 2.
Diagram for the liquid contact ISE (A) and solid contact ISE (B).
In this work, two solid contact glassy carbon ISEs were made from this perspective. The ISEs for sensor one (MOX-TPB) and sensor two (MOX-PTA) were made with sodium tetraphenylborate and phosphotungstic acid, respectively, as ion pairing agents. A comparison of the working conditions was undertaken to clarify the optimal working parameters. Furthermore, the current study uses the produced membranes in the straightforward, easy, sensitive, and selective quantification of MOX in real wastewater effluents without the need for sample preparation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
A digital mV/pH meter (Model 3510; Jenway, UK) was applied for the potentiometric measurement. It was coupled to an Ag/AgCl type bi-junctional reference electrode. A Jenway (UK) glass electrode was used all over the assay. The solid contact was made with a glassy carbon electrode (3 mm diameter, CH Instruments, Bee Cave, TX, USA).
2.2. Chemicals, Reagents, and Standard Solutions
Bio Vision provided the MOX pure standard (USA). A certificate (CAS # 186826-8) declared that it was 99.98% pure. Prolabo, Paris, France, provided TPB, PTA, HCl, sodium hydroxide, potassium chloride, AgNO3, and THF. Sigma, Darmstadt, Germany, provided the dioctyl phthalate (DOP), nitrophenyl octyl ether (NPOE), and bis(2-ethyl hexyl) sebacate (2-EHS). Fluka Chemie (Taufkirchen) in Germany provided PVC of high molecular weight grade. Aquatron (Glasgow, UK) provided the deionized H2O from their water still.
MOX stock standard solution (1 × 10−2 M) was prepared in deionized water. Working solutions (1 × 10−3 to 1 × 10−8 M) were prepared from the MOX stock standard solution through cautious dilution using the same solvent.
2.3. Sensors’ Fabrication, Calibration, and Optimization
Mixing 190 mg of PVC, 0.4 mL of 2-EHS, and 10 mg of TPB (sensor 1) or PTA (sensor 2) was performed in two separate Petri dishes. Dissolution of the mixtures was performed in 6 mL THF. The THF solution was directly applied to a glassy carbon electrode. The applied solution was allowed to completely evaporate. Conditioning of the prepared membrane was carried out by soaking in 0.01 M MOX stock standard solution for 24 h. The electrodes were stored in the same MOX solution.
Following the conditioning stage, the calibration step was carried out by submerging the manufactured sensors in MOX standard solutions in the concentration range from 1 × 10−2 to 1 × 10−8 M. Deionized water was utilized to wash each membrane between measurements. The standard graphs were prepared. These graphs were then utilized to obtain the unknown MOX concentrations.
Studying and adjusting the parameters affecting the membrane performance resulted in optimal membrane performance. The competency of the electrodes was evaluated in accordance with the IUPAC recommendations [39]. Various plasticizers of different polarities were used to assess the impact of the plasticizer type on the membrane performance. To obtain the best electrode performance, the plasticizers 2-EHS, DOP, and NPOE were tested. The influence of pH on the membranes’ performance was investigated by a MOX standard solution (1 × 10−4 M), and 0.1 M sodium hydroxide or 0.1 M hydrochloric acid were added dropwise. To determine the best pH range for the constructed sensors, a graphical representation of the electrode potential against the solutions’ pH was constructed. For a month, the stability of the measured potential and repeatability of MOX-prepared sensors were monitored. Every day, the potential was measured using MOX standard solutions in the range 1 × 10−2 M–1 × 10−6 M, and the slope (mV/decade) was calculated for each constructed membrane. The calculated slopes were compared to the slopes acquired in the initial calibration. The membranes’ thermal stability was examined in a temperature range of 25–40 °C. By determining the potentiometric selectivity coefficients (PSCs) for the analyzed interferents, the selectivity of the manufactured membranes was effectively tested using the matched potential method (MPM). The PSC is the ratio between the concentration of the studied drug and that of the interferent in a reference solution that results in the same potential change [40].
2.4. Application
Different distilled and tap water samples containing known MOX concentrations were prepared. The pH of the prepared samples was adjusted to be in the range of 1.0–5.0. The fabricated membranes were used to quantify the studied drug concentrations, and the recovery percent was calculated.
Real wastewater samples were collected from a pharmaceutical factory producing MOX tablets. The samples’ pH was adjusted to be in the range of 1.0–5.0. The obtained samples were filtered utilizing nylon membrane filters to remove fine particle debris. Storage of filtered samples was performed in dark glass bottles in a cool place to prevent any degradation of the sample.
The built sensors were used to determine the MOX concentrations in the collected real wastewater samples using the standard curves. A comparison was carried out between the results acquired by applying the suggested method and those obtained by using a reference method [12] after applying solid-phase extraction.
3. Results
3.1. Manufactured Membranes’ Performance Evaluation
Table 1 shows the performance evaluation parameters for the manufactured electrodes. An almost ideal Nernstian behavior was attained between the 1 × 10−6 M and 1 × 10−2 M MOX solutions. Sensor 1 and sensor 2 had slopes of 59.2 ± 0.60 mV/decade and 58.4 ± 0.50 mV/decade, respectively (Table 1). Figure 3 depicts standard plots.

Table 1.
Electrochemical response characteristics of the fabricated electrodes.
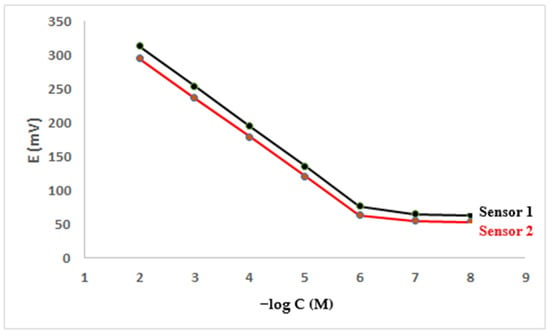
Figure 3.
Profile of the potential (in mV) versus −log concentration (in M) for MOX sensors at pH 3.
The performance of the manufactured membranes was evaluated using IUPAC criteria [39], including different parameters such as response time, optimal pH range, linearity, the effect of plasticizer type, and limit of detection.
The impact of the plasticizer type was investigated by experimenting with three different plasticizers of varying polarity (DOP, NPOE, and 2-EHS). The plasticizer that offered the best results was 2-EHS, whose constructed sensors had slopes that were closer to the optimal Nernstian values. On the other hand, the membranes fabricated using NPOE and DOP showed slopes of 50.20 ± 0.60 mV/decade (n = 3) and 48.70 ± 0.40 mV/decade (n = 3), respectively.
The limit of detection was attained at the intersection point of the two extrapolated linear segments of the standard curve [39]. Excellent sensitivity was demonstrated by detection limits as low as 0.24 µg/mL (Table 1).
The pH of the medium influenced the operation of the manufactured sensors. The best electrochemical response was found to be in the pH range from 1.0 to 5.0. (Figure 4).
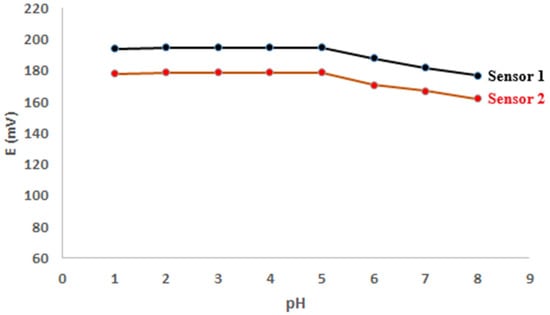
Figure 4.
pH effect on the potential response of MOX membrane sensors.
The sensors’ lifetime was explored by establishing calibration plots and by assessing their properties daily. The lifetimes for both sensors were determined to be 21 days when no changes in potentials (less than ±3 mV) were observed and calibration features were considered (Figure 5). The response time is an important parameter in the membrane performance evaluation, as it reflects the time needed for the manufactured electrode to give a constant reading (±1 mV) after a 10-fold rise in the sample concentration [39]. The constructed sensors’ response time was discovered to be 15 s.
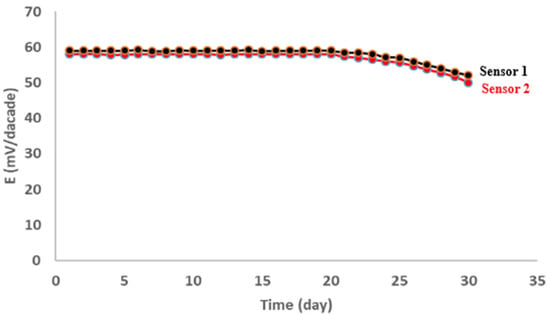
Figure 5.
Stability of the MOX membrane sensors.
The standard curves were plotted in a temperature range from 25 °C to 40 °C to study the effect of the temperature variation on the manufactured membranes. The calibration plots showed no significant changes, demonstrating that the manufactured electrodes have exceptional temperature stability. The results regarding the thermal stability of the fabricated sensors at three temperature levels are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Profile of the potential versus –log concentration for the fabricated sensors at three temperatures (25 °C, 30 °C, and 40 °C).
The manufactured membranes were used to test the method’s accuracy by analyzing various MOX concentrations. The capacity of the analytical assay to bear minute alterations in the working circumstance was tested for method robustness. In addition, the ruggedness of the procedure was assessed to determine its reproducibility. These parameters are summarized in Table 1. Selectivity of the manufactured sensors can be seen to be a deciding parameter in the employment of manufactured sensors because it highlights their applicability in analyzing a real specimen. The electrode selectivity was investigated by measuring its ability to show optimal performance even when different interferents are present in the measured sample. This can be attained by calculating the potentiometric selectivity coefficient (PSC) for each interferent [40]. Interferents were a variety of ions found in real wastewater effluents as well as structurally similar fluoroquinolones (norfloxacin hydrochloride, ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, and levofloxacin hydrochloride). The calculated PSCs are shown in Table 3. They were on the order of 10−3 or less, indicating that the sensors had exceptional selectivity.

Table 3.
Potentiometric selectivity coefficients of the proposed MOX selective sensors by the matched potential method.
3.2. Assay of Water Samples Loaded with MOX
The manufactured electrodes were effectively used to measure MOX in water samples (distilled and tap) loaded with known concentrations of the drug of interest (10−3 M, 10−4 M, and 10−5 M). Table 4 shows the results, which indicate that the approach is highly accurate.

Table 4.
Determination of MOX in spiked water samples using the fabricated membrane sensors.
3.3. Assay of MOX in Real Wastewater
The fabricated sensors were used to carry out a careful analysis of several samples obtained from wastewater effluent of a pharmaceutical factory without any preprocessing. The absence of sample pre-treatment is a strong point in favor of the suggested analytical approach. The results obtained were compared to those obtained using a reference assay [12]. The results are declared in Table 5.

Table 5.
Determination of MOX in real wastewater samples from pharmaceutical industrial plant.
4. Discussion
The detection and assessment of environmental pollutants have become critical in recent years. Rather than other analytical techniques, potentiometric electrodes are utilized as an easy-to-use, low-cost alternative that has the merits of excellent sensitivity, no sample preprocessing, and ease of downsizing [41].
The art of this work is demonstrated by the solid-contact potentiometric determination of MOX, depending on the use of TPB and PTA as ion-pairing agents in a PVC matrix. The measured potential depends mainly on the ion exchange across the fabricated membranes, which is proportional to the MOX concentration in the measured solution.
Published papers [23,24,25,26,27] applying different strategies for the potentiometric determination of the studied drug were introduced. They have comparable linearity, accuracy, and sensitivity with the proposed method, but all of them determine the amount of MOX in either tablets or biological fluids.
Two membrane-sensitive electrodes were developed in this study to be used for the sensitive and selective measurement of MOX in actual wastewater effluents without the need for any sample preprocessing.
The membrane performance was adjusted to its optimal state. The plasticizer type was optimized, where 2-EHS was the best one. This is because MOX and 2-EHS have similar polarities. This match allowed for the most efficient exchange of ions through the sensitive membranes.
The detection limits of the manufactured membranes reflect the outstanding sensitivity that matches the purpose of their application. Furthermore, they demonstrated rapid response times across a wide concentration range. These are the most important elements in the successful sensing and assessment of MOX in real samples using the fabricated sensors.
Over a pH range from 1.0 to 5.0, the manufactured membranes demonstrated a consistent response. At pH levels greater than five, the calibration curves showed a significant deviation from linearity. Non-Nernestian slopes were found at higher pH values due to the lower MOX ionization caused by the drug’s decreased solubility.
The selectivity of the suggested method is a crucial parameter that should be thoroughly adjusted to be confident in its applicability, even if different interferents are present in real samples. The selectivity depends mainly on the stereo-specificity and lipophilicity of the two competing species in the sample solution side and the receptor of the ion exchanger [42]. The membrane components, the solvent employed, and the plasticizer-to-PVC-matrix ratio all influence sensor selectivity [43]. Interfacial ion-exchange kinetics are improved by lipophilic ionic sites. TPB and PTA are ionic sites added in membranes used to quantify cations to obtain superior selectivity and sensitivity [44]. During the preconditioning step, TPB or PTA are combined with the quaternary nitrogen of MOX until an equilibrium state is attained and the electrode becomes suitable to sense the studied drug ion. For carrier-based ISEs, polyvinylchloride remains the typical regular matrix. Membrane sensors require plasticizers, which are made up of a supporting background composed of around 66% of membrane solvent and 33% PVC [45]. The presence of such a plasticizer amount allows for quick ion mobility and optimal physical properties for the membrane [46].
5. Conclusions
The uniqueness of our study stems from the lack of previous research on the potentiometric measurement of MOX in real wastewater effluents. The lack of a sample preprocessing regimen confirms the simplicity of the method with respect to the other analytical methodologies used for the MOX analysis. In addition, as compared to LC-MS/MS and UPLC, the suggested approach is cost-effective since it has a reduced cost per sample.
The fabricated sensors have comparable electrochemical performances. They work effectively in wide concentrations and pH ranges. Both membranes are successfully applied for the sensitive and reliable determination of MOX in real wastewater effluents. Sensor 1 is more suitable, since it exhibits a Nernstian slope closer to the ideal Nernstian behavior than does sensor 2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A.A.-G., H.H.A. and A.A.A.; data curation, S.A.A.-G. and A.A.A.; formal analysis, S.A.A.-G.; investigation, S.A.A.-G. and A.A.A.; methodology, S.A.A.-G. and H.H.A.; resources, S.A.A.-G., H.H.A. and A.A.A.; software, S.A.A.-G. and A.A.A.; supervision, S.A.A.-G.; validation, S.A.A.-G.; visualization, S.A.A.-G. and H.H.A.; writing—original draft, S.A.A.-G.; writing—review and editing, S.A.A.-G., H.H.A. and A.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The current work was supported by Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/29), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia (to Hany H. Arab).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest in this manuscript.
References
- Seifrtová, M.; Aufartová, J.; Vytlačilová, J.; Pena, A.; Solich, P.; Nováková, L. Determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in wastewater using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry and fluorescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2094–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweetman, S.C. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference, 36th ed.; The pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 302–340. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, M.J. The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, 14th ed.; Merck Research Laboratories, Division of Merck and Co. Inc.: Kenilworth, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 1125–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Drlica, K.; Zhao, X. DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV, and the 4-quinolones. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1997, 61, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Motwani, S.K.; Chopra, S.; Ahmad, F.J.; Khar, R.K. Validated spectrophotometric methods for the estimation of moxifloxacin in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations. Spectrochim. Acta A 2007, 68, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbashir, A.A.; Ebraheem, S.A.; Elwagee, A.H.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. New spectrophotometric methods for the determination of moxifloxacin in pharmaceutical formulations. Acta Chim. Slov. 2013, 60, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamruzzaman, M.; Alam, A.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ragupathy, D.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, S.R.; Kim, S.H. Spectrofluorimetric study of the interaction between europium (III) and moxifloxacin in micellar solution and its analytical application. Spectrochim. Acta A 2012, 86, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghannam, S.M. Atomic absorption spectroscopic, conductometric and colorimetric methods for determination of some fluoroquinolone antibacterials using ammonium reineckate. Spectrochim. Acta A 2008, 69, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Li, D.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Lu, J. High-performance liquid chromatography assay with ultraviolet detection for moxifloxacin: Validation and application to a pharmacokinetic study in Chinese volunteers. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 3437–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, T.; Breilh, D.; Ducint, D.; Dubrez, J.; Jougon, J.; Velly, J.F.; Saux, M.C. Determination of moxifloxacin (BAY 12–8039) in plasma and lung tissue by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection using a fully automated extraction method with a new polymeric cartridge. J. Chromatogr. B 2000, 742, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.L.; Paim, C.S.; Steppe, M.; Schapoval, E.E. Biological assay and liquid chromatographic method for analysis of moxifloxacin in tablets. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelaziz, A.A.; Elbanna, T.E.; Gamaleldeen, N.M. Validated microbiological and HPLC methods for the determination of moxifloxacin in pharmaceutical preparations and human plasma. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.K.; Sudha, V.; Srinivasan, R.; Ramachandran, G. Simple and rapid liquid chromatography method for determination of moxifloxacin in saliva. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 3663–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudah, A. Pharmacokinetics and tissue residues of moxifloxacin in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2009, 50, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, L.A.; Hall, R. Enantiomeric purity assay of moxifloxacin hydrochloride by capillary electrophoresis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 38, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, J.G.; Stass, H.; Heinig, R.; Blaschke, G. Capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence: A routine method to determine moxifloxacin in human body fluids in very small sample volumes. J. Chromatogr. B 1998, 716, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, B.; Ramesh, M.; Borkar, R.M.; Padiya, R.; Banerjee, S.K.; Srinivas, R. Development and validation of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometric method for simultaneous determination of moxifloxacin and ketorolac in rat plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranger, A.D.; Alffenaar, J.W.; Wessels, A.M.; Greijdanus, B.; Uges, D.R. Determination of moxifloxacin in human plasma, plasma ultrafiltrate, and cerebrospinal fluid by a rapid and simple liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2010, 34, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erk, N. Voltammetric behavior and determination of moxifloxacin in pharmaceutical products and human plasma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, W.A.; Beltagi, A.M.; Hathoot, A.A.; Abdel Azzem, M. A Sensitive Voltammetric Sensor for Improved Simultaneous Determination of Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride and Paracetamol. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 167509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Long, N.; Liu, L.; Zhai, H.; Zhu, M. Electrochemical Determination of Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 5069–5076. [Google Scholar]
- Hammam, M.A.; Wagdy, H.A.; El Nashar, R.M. Moxifloxacin hydrochloride electrochemical detection based on newly designed molecularly imprinted polymer. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 275, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefnawy, M.M.; Homoda, A.M.; Abounassif, M.A.; Alanazi, A.M.; Al-Majed, A.; Mostafa, G.A. Potentiometric determination of moxifloxacin in some pharmaceutical formulation using PVC membrane sensors. Chem Cent. J. 2014, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Sindhu, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, A. Determination of AVELOX (Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride) Tablets in Dosage Forms Modified with Potentiometer Sensors: A Comparative Analysis. 2021. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3902688 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Moamed, G.G.; Frag, E.Y.; El-dien, F.A.; Saad, M. Comparative Study of Different Modified Potentiometric Sensors for Determination of Moxifloxacin HCl in Dosage Forms. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2015, 6, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idress, M.O.; Elbashir, A.A.; Nur, O. Potentiometric determination of moxifloxacin by ZnO nanorods modified ion selective electrode. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2017, 8, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhari, N.S.; Gholave, J.V.; Patil, S.S.; Patil, V.R.; Upadhyay, S.S. Enantioselective high performance new solid contact ion-selective electrode potentiometric sensor based on sulphated γ-cyclodextrin-carbon nanofiber composite for determination of multichiral drug moxifloxacin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 882, 114981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladhani, S.; Gransden, W. Increasing antibiotic resistance among urinary tract isolates. Arch. Dis. Child. 2003, 88, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Blaney, L. Systematic optimization of an SPE with HPLC-FLD method for fluoroquinolone detection in wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, F.; Salem, H.; Riad, S.; Elbalkiny, H. Determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in industrial wastewater by high-pressure liquid chromatography and thin-layer chromatography-densitometric methods. J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2014, 27, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Lor, E.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernández, F. Multi-class determination of around 50 pharmaceuticals, including 26 antibiotics, in environmental and wastewater samples by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2264–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stradiotto, N.R.; Yamanaka, H.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Electrochemical Sensors: A Powerful Tool in Analytical Chemistry. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003, 14, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Gawad, S.A.; Arab, H.H. Potentiometric Sensors for the Selective Determination of Benzodiazepine Drug Residues in Real Wastewater Effluents. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, E.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Quality control criteria for solid-contact, solvent polymeric membrane ion-selective electrodes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattrall, R.; Freiser, H. Coated wire ion-selective electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1971, 43, 1905–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Qin, Y. Electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3965–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salem, A.A.; Barsoum, B.N.; Izake, E.L. Potentiometric determination of diazepam, bromazepam, and clonazepam using solid contact ion-selective electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 498, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Pretsch, E. Potentiometric sensors for trace-level analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindner, E.; Umezawa, Y. Performance evaluation criteria for preparation and measurement of macro-and microfabricated ion-selective electrodes (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 80, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Mehtab, S.; Jain, A.K. Selective electrochemical sensor for copper (II) ion based on chelating ionophores. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2006, 575, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kosasy, A.M.; Shehata, M.A.; Hassan, N.Y.; Fayed, A.S.; El-Zeany, B.A. Membrane electrodes for the determination of glutathione. Talanta 2005, 66, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghani, N.T.; Rizk, M.S.; El-Nashar, R.M. Salbutamol plastic membrane electrodes based on individual and mixed ion-exchangers of salbutamolium phosphotungstate and phosphomolybdate. Analyst 2000, 125, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangrong, Y.E.; Yaqin, C.; Yuan, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.I.Y. Salicylate Ion-Selective Electrode Based on New Tetranuclear Copper Complexes of O-Vannlin-methionine as Neutral Carriers. Anal. Sci. 2007, 23, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Schaller, U.; Bakker, E.; Spichiger, U.E.; Pretsch, E. Ionic additives for ion-selective electrodes based on electrically charged carriers. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, G.J.; Thomas, J.D.R. Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Matrix Membrane Ion-Selective Electrodes. In Ion-Selective Electrodes in Analytical Chemistry; Modern Analytical Chemistry; Freiser, H., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.A.; Kusy, R.P. The molecular, physical and mechanical properties of highly plasticized poly(vinyl chloride) membranes. Polymer 1993, 34, 5106–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).