Design and Evaluation of a Competitive Phosphorescent Immunosensor for Aflatoxin M1 Quantification in Milk Samples Using Mn:ZnS Quantum Dots as Antibody Tags
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Solutions and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Synthesis of DHLA Capped Mn-Doped ZnS QDs
2.3.2. Bioconjugation Protocols and Purification
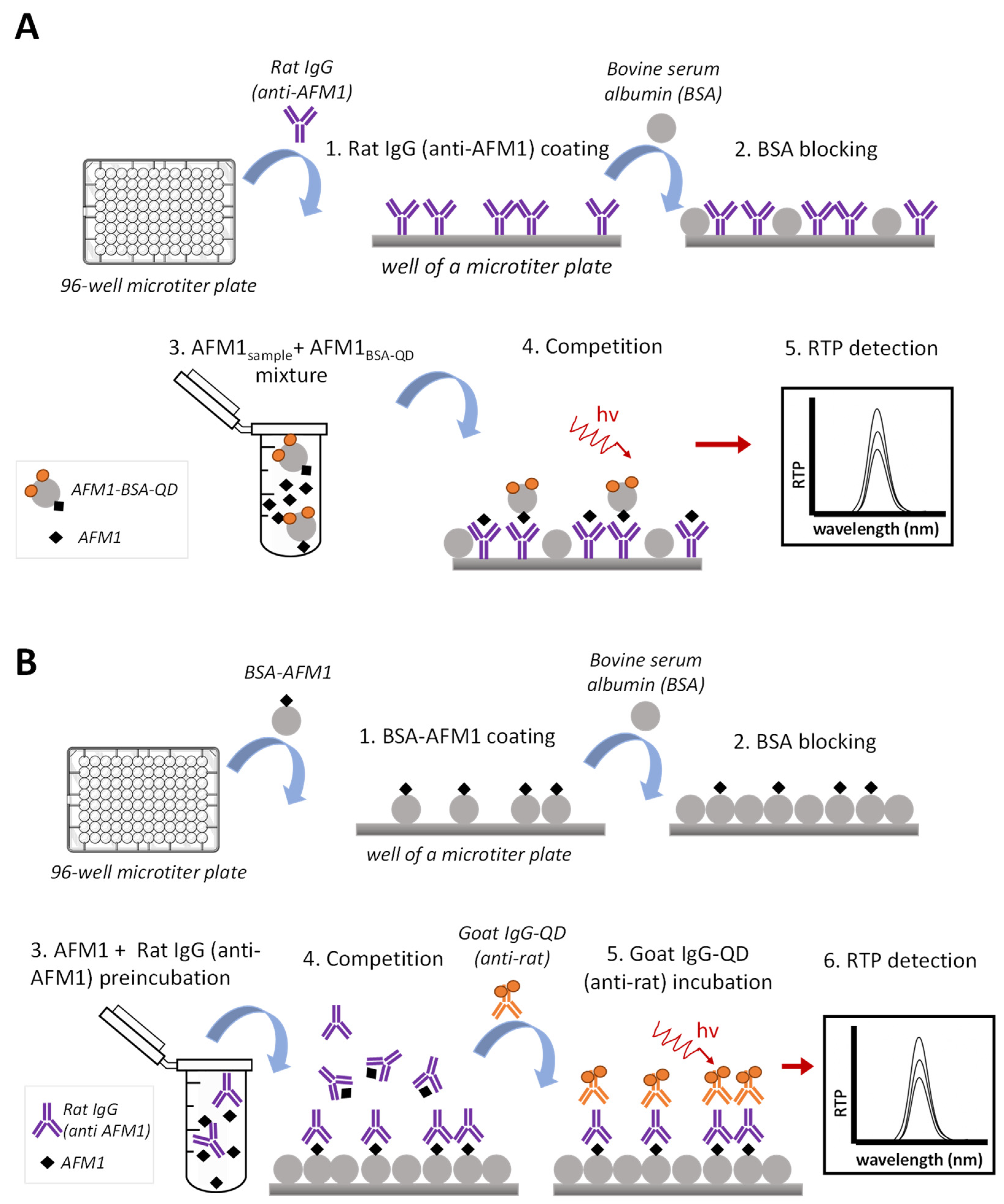
2.3.3. Phosphorescent Immunoassay Formats Assayed
3. Results and Discussion
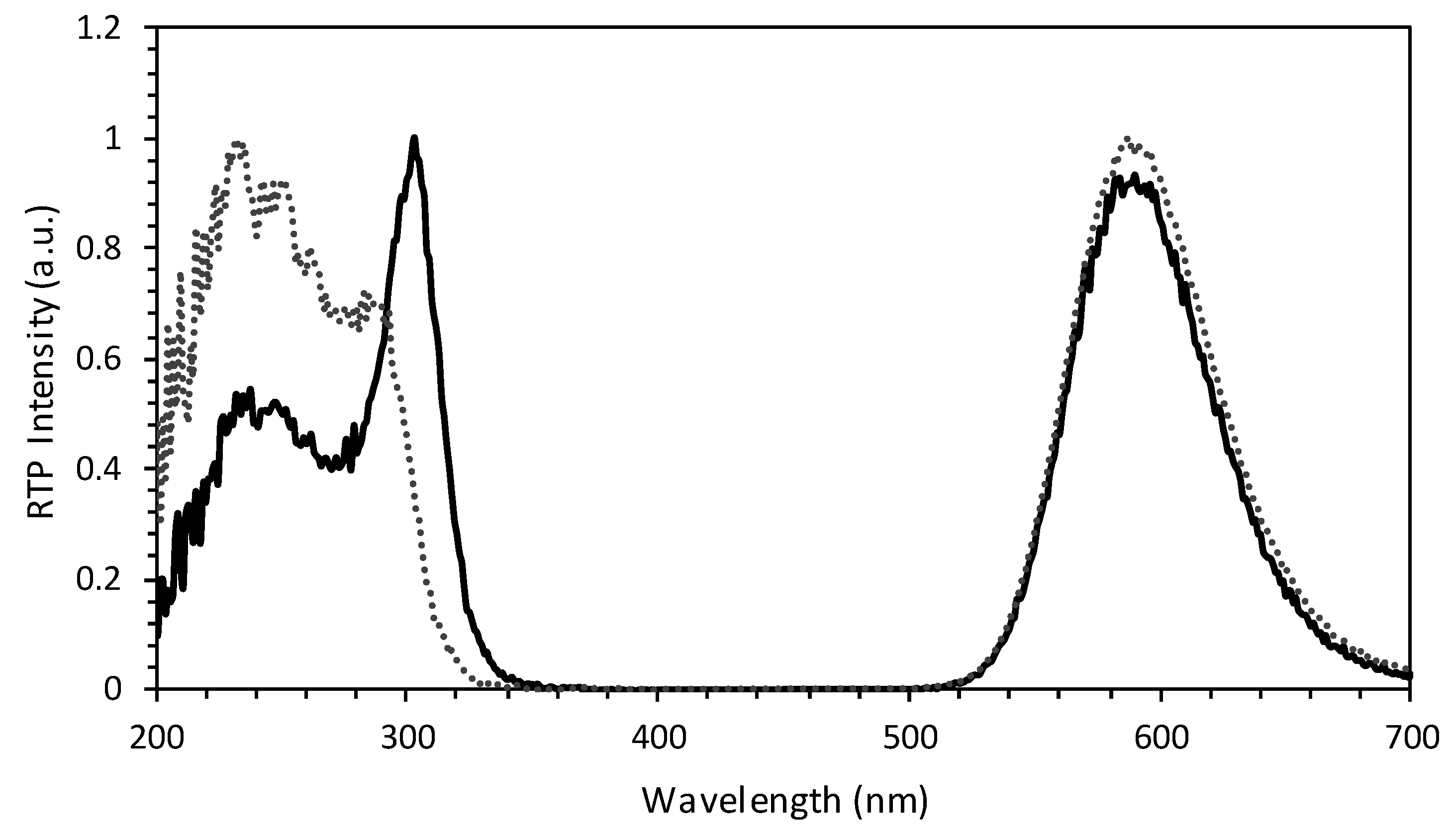
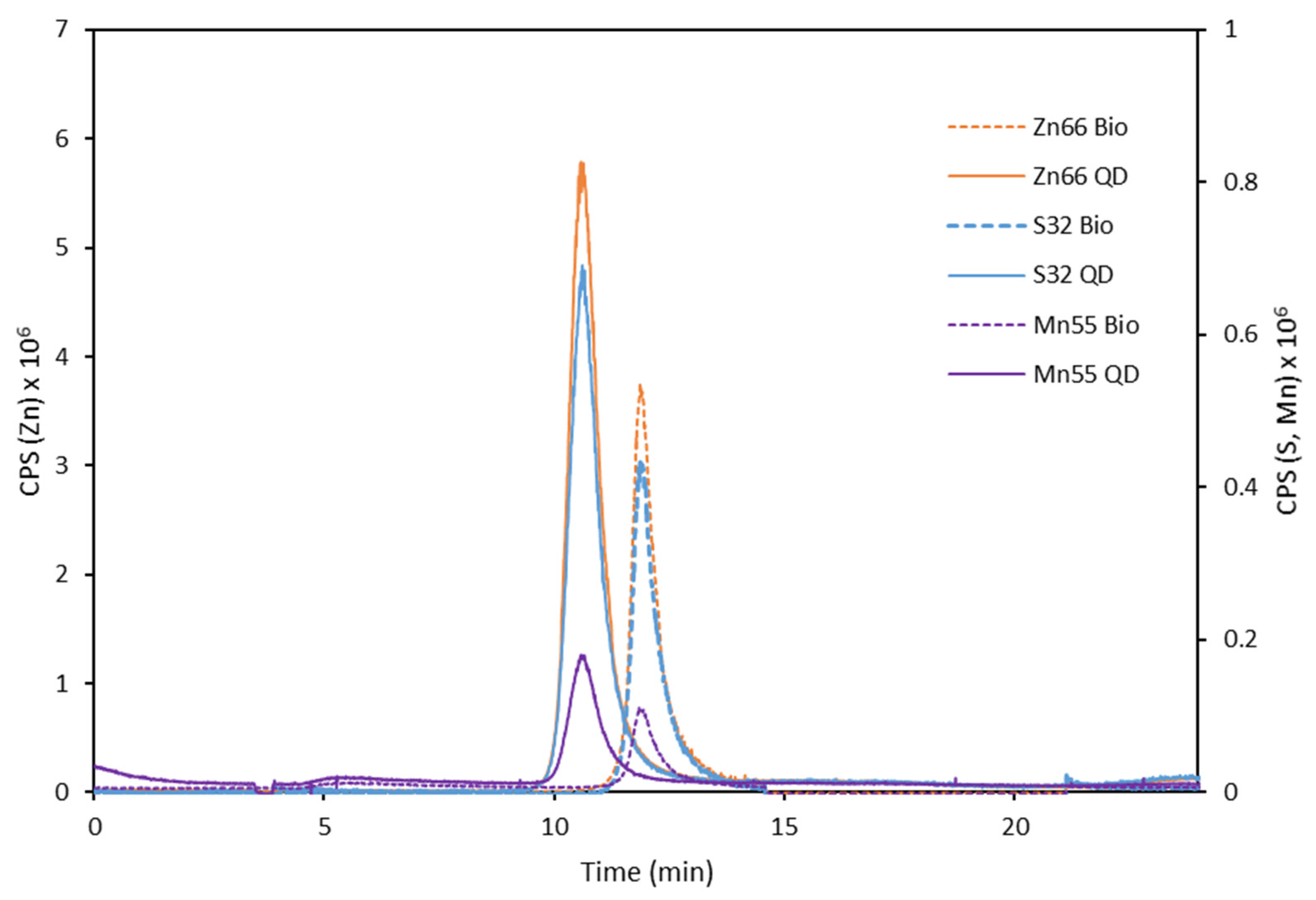
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Antibody-QDs Bioconjugates
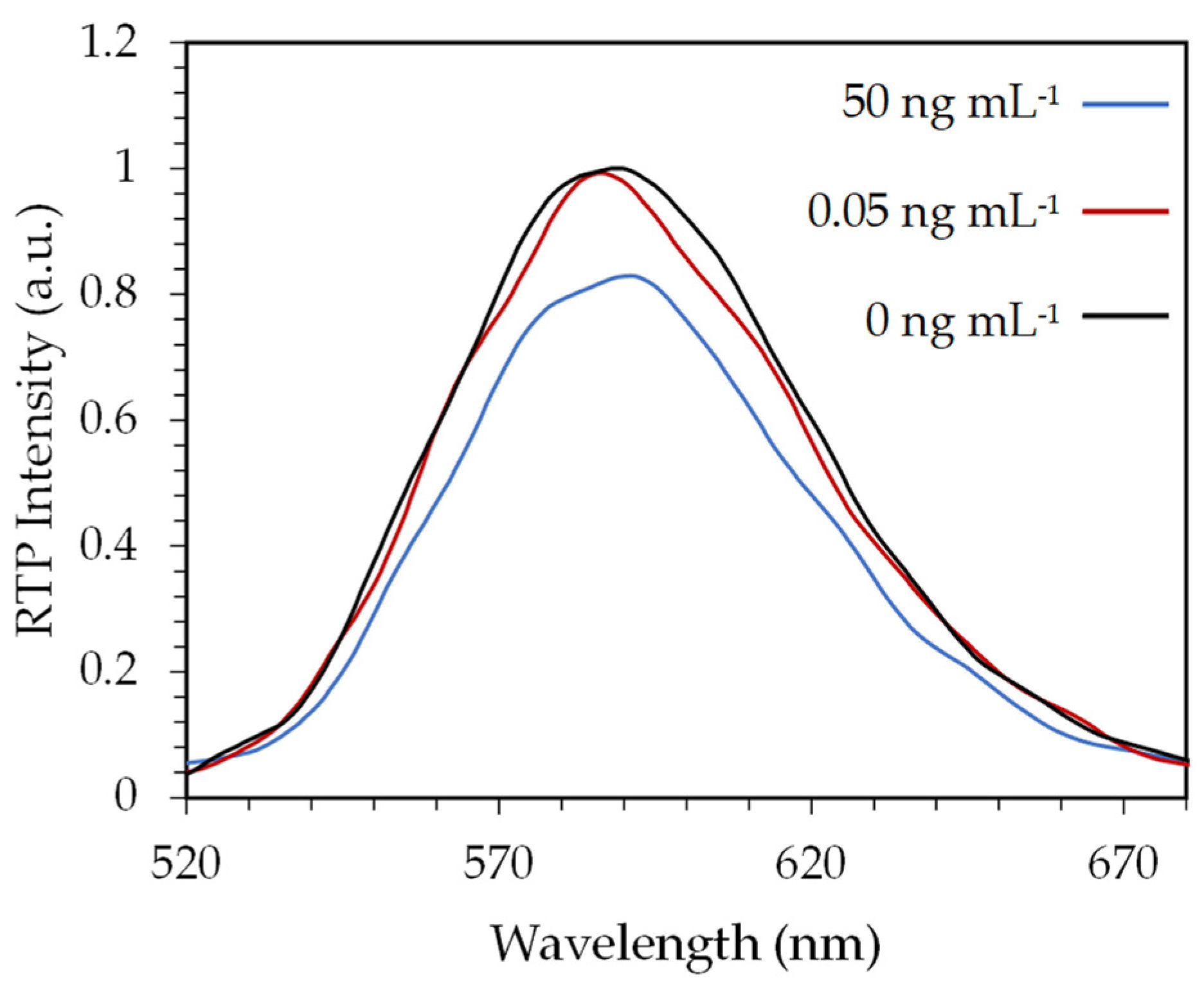
3.2. Evaluation of an Indirect Immunoassay Format for AFM1 Quantification
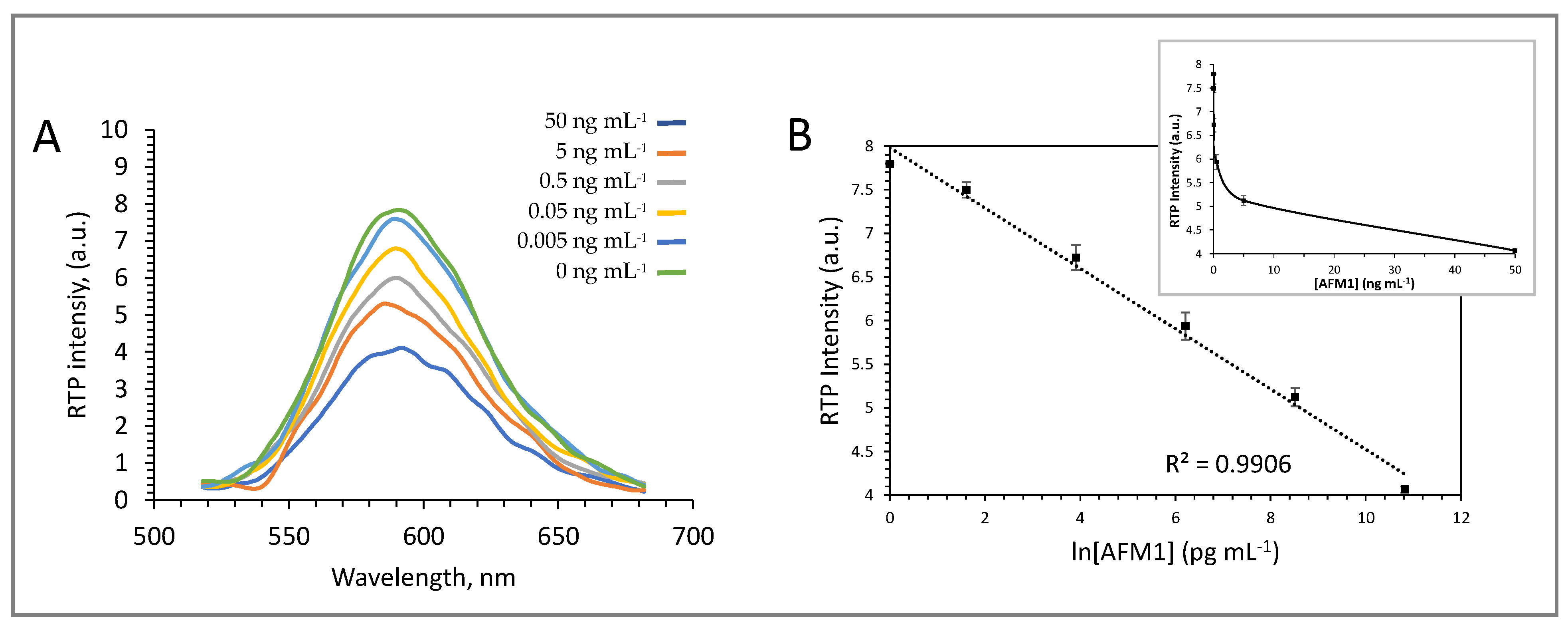
3.3. Evaluation of a Direct Immunoassay Format for AFM1 Quantification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Regulation (EU) No. 165/2010. Off. J. EU 2010, L50, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Min, L.; Fink-Gremmels, J.; Li, D.; Tong, X.; Tang, J.; Nan, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, G. An overview of aflatoxin B1 biotransformation and aflatoxin M1 secretion in lactating dairy cows. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha Turna, N.; Wu, F. Aflatoxin M1 in milk: A global occurrence, intake, & exposure assessment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Hruska, Z.; Diana Di Mavungu, J. Developments in detection and determination of aflatoxins. World Mycotoxin J. 2015, 8, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Kazeminia, M.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Jalali, R.; Mohammadi, M. Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Worldwide from 1988 to 2020: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 8862738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA US. Action Levels for Poisonous or Deleterious Substances in Human Food and Animal Feed; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2000.
- Wood, J.E.; Gill, B.D.; Indyk, H.E.; Rhemrev, R.; Pazdanska, M.; Wood, J. Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Liquid Milk, Cheese and Selected Milk Proteins by Automated Online Immunoaffinity Cleanup with Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. J. AOAC Int. 2021, 104, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Taherimaslak, Z. Determination of aflatoxin M1 in liquid milk using high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection and magnetic solid phase extraction. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 33497–33506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, P.D.; da Silva, J.L.G.; Caldas, E.D. Simultaneous analysis of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2, M1 and ochratoxin A in breast milk by high-performance liquid chromatography/fluorescence after liquid-liquid extraction with low temperature purification (LLE-LTP). J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1304, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jartín, J.M.; Rodríguez-Cañás, I.; Alfonso, A.; Sainz, M.J.; Vieytes, M.R.; Gomes, A.; Ramos, I.; Botana, L.M. Multianalyte method for the determination of regulated, emerging and modified mycotoxins in milk: QuEChERS extraction followed by UHPLC–MS/MS analysis. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognanno, M.; La Fauci, L.; Ritieni, A.; Tafuri, A.; De Lorenzo, A.; Micari, P.; Di Renzo, L.; Ciappellano, S.; Sarullo, V.; Galvano, F. Survey of the occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 in ovine milk by HPLC and its confirmation by MS. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, J.J.; Cong, J.M.; Cai, Z.X.; Zhang, J.S.; Wang, J.L.; Ren, Y.P. Optimization for quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe extraction of mycotoxins and veterinary drugs by response surface methodology for application to egg and milk. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1532, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloglazova, N.V.; Shmelin, P.S.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; De Saeger, S. Liposomes loaded with quantum dots for ultrasensitive on-site determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk products Rapid Detection in Food and Feed. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7795–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gan, N.; Zhou, J.; Xiong, P.; Hu, F.; Cao, Y.; Li, T.; Jiang, Q. An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescent immunoassay for aflatoxin M1 in milk, based on extraction by magnetic graphene and detection by antibody-labeled CdTe quantum dots-carbon nanotubes nanocomposite. Toxins 2013, 5, 865–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, K.K.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Quantum bead-based fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay for ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin M 1 in pasteurized milk, yogurt, and milk powder. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3985–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-González, M.; de la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Fernandez-Argüelles, M.T.; García Alonso, F.J.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M. Quantum Dot Bioconjugates for Diagnostic Applications. Top. Curr. Chem. 2020, 378, 133–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, N.; Spillmann, C.M.; Russ Algar, W.; Pons, T.; Stewart, M.H.; Oh, E.; Susumu, K.; Díaz, S.A.; Delehanty, J.B.; Medintz, I.L. Energy transfer with semiconductor quantum dot bioconjugates: A versatile platform for biosensing, energy harvesting, and other developing applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 536–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo-Gonzalez, E.; Roces, L.; Garcia-Granda, S.; Fernandez-Arguelles, M.T.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M.; Sanz-Medel, A. Influence of Mn2+ concentration on Mn2+-doped ZnS quantum dot synthesis: Evaluation of the structural and photoluminescent properties. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9156–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yan, X.P. Doped quantum dots for chemo/biosensing and bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5489–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cortes, M.; Sotelo González, E.; Fernández-Argüelles, M.T.; Encinar, J.R.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Sanz-Medel, A. Capping of Mn-Doped ZnS Quantum Dots with DHLA for Their Stabilization in Aqueous Media: Determination of the Nanoparticle Number Concentration and Surface Ligand Density. Langmuir 2017, 33, 6333–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmykov, O.; Coulon, J.; Lalevée, J.; Alem, H.; Medjahdi, G.; Schneider, R. Aqueous synthesis of highly luminescent glutathione-capped Mn2+-doped ZnS quantum dots. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 44, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Ma, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Fan, J. Simple and greener synthesis of highly photoluminescence Mn2+-doped ZnS quantum dots and its surface passivation mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 316, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cortés, M.; Fernández-Argüelles, M.T.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Sanz-Medel, A. Sensitive prostate specific antigen quantification using dihydrolipoic acid surface-functionalized phosphorescent quantum dots. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 987, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, G. Facile and sensitive detection of protamine by enhanced room-temperature phosphorescence of Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, W.; Wang, F.; Wei, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Dong, W.; Shuang, S.; Choi, M.M.F. Doped zinc sulfide quantum dots based phosphorescence turn-off/on probe for detecting histidine in biological fluid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 856, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, R.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, J. Manganese-doped ZnS quantum dots as a phosphorescent probe for use in the bi-enzymatic determination of organophosphorus pesticides. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Kang, C.; Xu, S.; Tang, Y. Selective room temperature phosphorescence sensing of target protein using Mn-doped ZnS QDs-embedded molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Limit of detection (LOD) (ng mL−1) | 0.002 |
| Limit of quantification (LOQ) (ng mL−1) | 0.004 |
| Coefficient of variation, CV (%) n = 5 | 6 |
| Linear range (ng mL−1) | LOQ–50 |
| CV = standard deviation/mean (n = 5) | |
| Sample | AFM1 Concentration (pg mL−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added | Experimental | |||
| Skimmed milk | 5 | 4.08 | 81 | 3 |
| Skimmed milk | 500 | 453 | 90 | 14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forcada, S.; Sánchez-Visedo, A.; Melendreras, C.; Menéndez-Miranda, M.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Royo, L.J.; Soldado, A. Design and Evaluation of a Competitive Phosphorescent Immunosensor for Aflatoxin M1 Quantification in Milk Samples Using Mn:ZnS Quantum Dots as Antibody Tags. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020041
Forcada S, Sánchez-Visedo A, Melendreras C, Menéndez-Miranda M, Costa-Fernández JM, Royo LJ, Soldado A. Design and Evaluation of a Competitive Phosphorescent Immunosensor for Aflatoxin M1 Quantification in Milk Samples Using Mn:ZnS Quantum Dots as Antibody Tags. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleForcada, Sergio, Adrián Sánchez-Visedo, Candela Melendreras, Mario Menéndez-Miranda, José M. Costa-Fernández, Luis J. Royo, and Ana Soldado. 2022. "Design and Evaluation of a Competitive Phosphorescent Immunosensor for Aflatoxin M1 Quantification in Milk Samples Using Mn:ZnS Quantum Dots as Antibody Tags" Chemosensors 10, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020041
APA StyleForcada, S., Sánchez-Visedo, A., Melendreras, C., Menéndez-Miranda, M., Costa-Fernández, J. M., Royo, L. J., & Soldado, A. (2022). Design and Evaluation of a Competitive Phosphorescent Immunosensor for Aflatoxin M1 Quantification in Milk Samples Using Mn:ZnS Quantum Dots as Antibody Tags. Chemosensors, 10(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10020041








