Influence of Electrotherapy with Task-Oriented Training on Spasticity, Hand Function, Upper Limb Function, and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Subacute Stroke: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design and Ethics
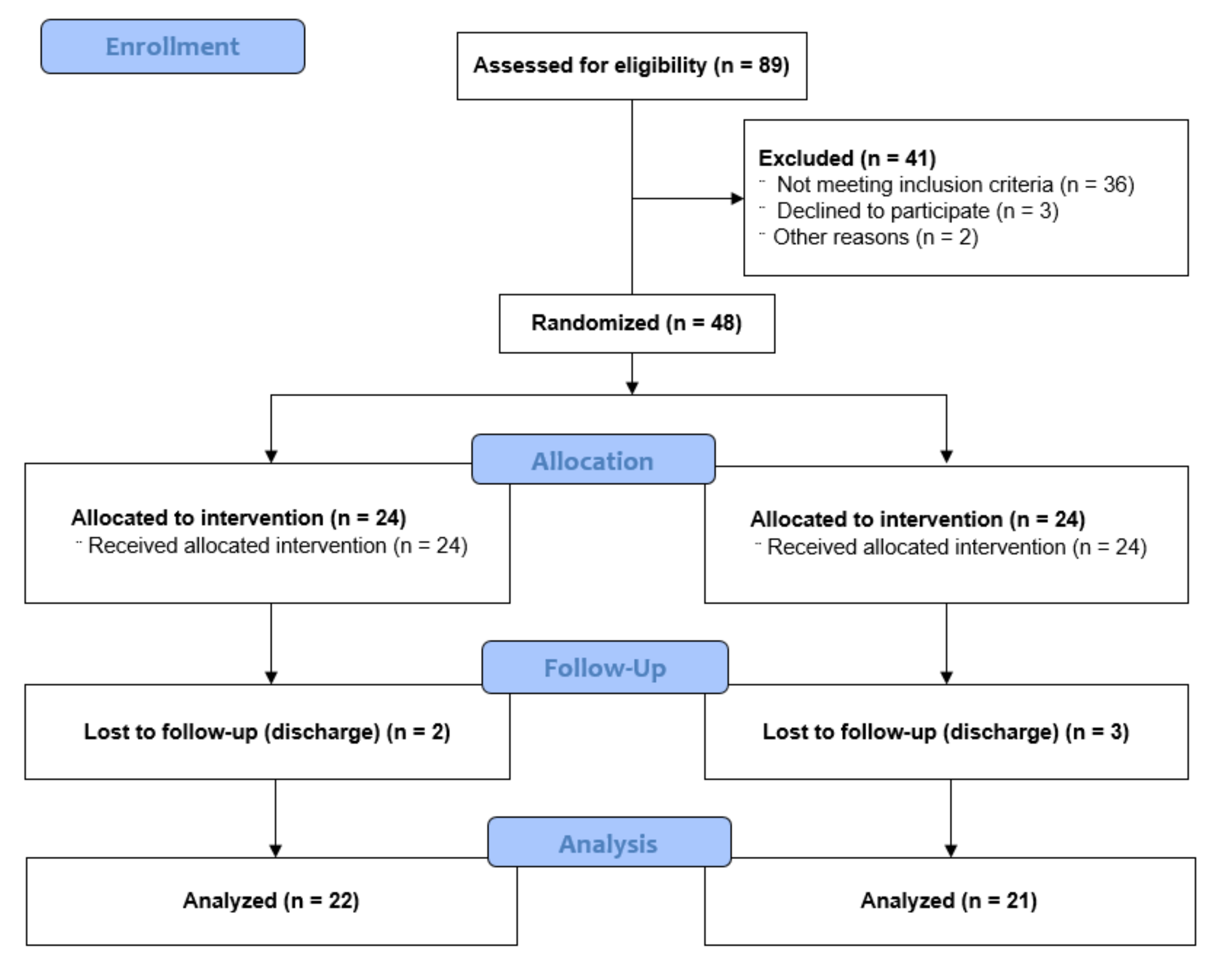
2.2. Participants and Sample Size
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
2.4. Intervention
2.5. Assessments
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Changes in Spasticity
3.3. Changes in Hand Function
3.4. Changes in Upper Limb Function
3.5. Changes in Activities of Daily Living
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rathore, S.S.; Hinn, A.R.; Cooper, L.S.; Tyroler, H.A.; Rosamond, W.D. Characterization of incident stroke signs and symptoms. Stroke 2002, 33, 2718–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakkel, G.; Kollen, B.J.; Wagenaar, R.C. Long term effects of intensity of upper and lower limb training after stroke: A randomised trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, M.Y.; Harris, J.E.; Eng, J.J. A community-based upper-extremity group exercise program improves motor function and performance of functional activities in chronic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-Y.; In, T.-S.; Cho, K.-H.; Song, C.-H. A single trial of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) improves spasticity and balance in patients with chronic stroke. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2013, 229, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.F.; Hui-Chan, C.W. Relief of hemiparetic spasticity by TENS is associated with improvement in reflex and voluntary motor functions. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1992, 85, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipchase, L.S.; Schabrun, S.M.; Hodges, P.W. Peripheral electrical stimulation to induce cortical plasticity: A systematic review of stimulus parameters. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinazzi, M.; Zarattini, S.; Valeriani, M.; Romito, S.; Farina, S.; Moretto, G.; Abbruzzese, G. Long-lasting modulation of human motor cortex following prolonged transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) of forearm muscles: Evidence of reciprocal inhibition and facilitation. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 161, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekeolu, Y.B.; Adak, B.; Göksoy, T. Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) on Barthel Activities of Daily Living (ADL) index score following stroke. Clin. Rehabil. 1998, 12, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuno, K.; Kawaguchi, S.; Kitabeppu, S.; Kitaura, M.; Tokuhisa, K.; Morimoto, S.; Shomoto, K. Effects of peripheral sensory nerve stimulation plus task-oriented training on upper extremity function in patients with subacute stroke: A pilot randomized crossover trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2012, 26, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Jung, J.; In, T.; Kim, T.; Cho, H.-Y. The influence of task-related training combined with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on paretic upper limb muscle activation in patients with chronic stroke. NeuroRehabilitation 2017, 40, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Shin, W. How to do random allocation (randomization). Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakel, B.; Cooper, N.; Adams, H.J.; Messer, B.R.; Law, L.A.F.; Dannen, D.R.; Walsh, D.M. A new transient sham TENS device allows for investigator blinding while delivering a true placebo treatment. J. Pain 2010, 11, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wu, Y.; Li, X. Test-retest reliability and inter-rater reliability of the Modified Tardieu Scale and the Modified Ashworth Scale in hemiplegic patients with stroke. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 50, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jebsen, R.H.; Taylor, N.; Trieschmann, R.B.; Trotter, M.J.; Howard, L.A. An objective and standardized test of hand function. Am. J. Phys. Med. 1969, 50, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, I.-S.; Han, T.-R. New scoring system for jebsen hand function test. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2007, 31, 623–629. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, S.; Kondo, T.; Suzukamo, Y.; Michimata, A.; Izumi, S.I. Reliability and validity of the Manual Function Test in patients with stroke. Am. J. Phys. Med. 2009, 88, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Park, B.-K.; Shin, H.-S.; Kang, Y.-K.; Pyun, S.-B.; Paik, N.-J.; Han, T.-R. Development of the Korean version of Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI): Multi-center study for subjects with stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2007, 31, 283–297. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, A.; Veluswamy, S.K.; Hombali, A.; Mullick, A.; Manikandan, N.; Solomon, J.M. Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on spasticity in adults with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 751–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, C.G.T.; Rakel, B.A.; Blodgett, N.P.; DeSantana, J.M.; Amendola, A.; Zimmerman, M.B.; Walsh, D.M.; Sluka, K.A. Effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on pain, pain sensitivity, and function in people with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Phys. Ther. 2012, 92, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, H.; Crone, C.; Christenhuis, D.; Petersen, N.T.; Nielsen, J.B. Modulation of presynaptic inhibition and disynaptic reciprocal Ia inhibition during voluntary movement in spasticity. Brain 2001, 124, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, S.-C.; Yoon, Y.-W.; Kim, J. High-frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation alleviates spasticity after spinal contusion by inhibiting activated microglia in rats. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, H.; Uchida, K.; Nakajima, H.; Guerrero, A.R.; Watanabe, S.; Takeura, N.; Baba, H. Early transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation reduces hyperalgesia and decreases activation of spinal glial cells in mice with neuropathic pain. Pain 2014, 155, 1888–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mima, T.; Oga, T.; Rothwell, J.; Satow, T.; Yamamoto, J.I.; Toma, K.; Nagamine, T. Short-term high-frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation decreases human motor cortex excitability. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 355, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, A.; Urban, M.I.; Sluka, K.A. Blockade of opioid receptors in rostral ventral medulla prevents antihyperalgesia produced by transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 298, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Kwakkel, G.; Kollen, B.; Lindeman, E. Understanding the pattern of functional recovery after stroke: Facts and theories. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2004, 22, 281–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kwakkel, G.; Kollen, B.; Twisk, J. Impact of time on improvement of outcome after stroke. Stroke 2006, 37, 2348–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.D.; Cacho, E.W.A.; Borges, G. Post-stroke motor and functional evaluations: A clinical correlation using Fugl-Meyer assessment scale, Berg balance scale and Barthel index. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2006, 64, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Sheu, C.F.; Hsueh, I.P.; Wang, C.H. Trunk control as an early predictor of comprehensive activities of daily living function in stroke patients. Stroke 2002, 33, 2626–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghwiri, A.A. Reliability and validity of the Arabic Dynamic Gait Index in people poststroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2014, 21, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, J.; Mehrholz, J. Robotic-assisted training after stroke: RATULS advances science. Lancet 2019, 394, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, M.T. Mirror therapy for motor function of the upper extremity in patients with stroke: A meta-analysis. J. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 50, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafsteinsdóttir, T.B.; Algra, A.; Kappelle, L.J.; Grypdonck, M.H.F. Neurodevelopmental treatment after stroke: A comparative study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Foley, N.; Pereira, S.; Salter, K.; Fernandez, M.M.; Speechley, M.; Sequeira, K.; Miller, T.; Teasell, R. Treatment with botulinum toxin improves upper-extremity function post stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekbib, D.B.; Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Fang, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, J.; Roe, A.W.; Xu, D. Virtual reality therapy for upper limb rehabilitation in patients with stroke: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Brain Inj. 2020, 34, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| TENS (n = 22) | Placebo-TENS (n = 21) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (female/male) | 13/9 | 10/11 | 0.451 |
| Age (years) a | 61.23 ± 7.24 | 61.62 ± 8.32 | 0.870 |
| Etiology (infarction/hemorrhage) | 18/4 | 18/3 | 0.729 |
| Lesion location (frontal/parietal/temporal/occipital/thalamus/basal ganglia/internal capsule/mixed lesion) | 2/3/2/0/ 3/5/3/4 | 1/4/1/1/ 4/3/4/3 | 0.910 |
| Lesion side (right/left) | 15/7 | 15/6 | 0.817 |
| MMSE a | 27.09 ± 2.16 | 27.67 ± 2.08 | 0.379 |
| Onset period (days) a | 59.41 ± 16.77 | 57.95 ± 15.33 | 0.768 |
| TENS (n = 22) | Placebo-TENS (n = 21) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAS | −0.55 ± 0.67 | −0.24 ± 0.54 | Time | <0.001 * |
| Group | 0.103 | |||
| T × G | 0.106 | |||
| JTHFT | 14.82 ± 7.54 | 10.67 ± 8.02 | Time | <0.001 * |
| Group | 0.174 | |||
| T × G | 0.088 | |||
| MFT | 5.59 ± 4.22 | 2.29 ± 2.51 | Time | <0.001 * |
| Group | 0.101 | |||
| T × G | 0.003 * | |||
| MBI | 18.96 ± 11.80 | 13.86 ± 8.57 | Time | <0.001 * |
| Group | 0.301 | |||
| T × G | 0.114 |
| TENS (n = 22) | Placebo-TENS (n = 21) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | p-Value | Pre | Post | p-Value | |
| MAS | 1.23 ± 0.53 | 0.68 ± 0.57 | 0.003 * | 1.29 ± 0.46 | 1.05 ± 0.50 | 0.059 |
| JTHFT | 26.32 ± 8.48 | 41.14 ± 8.79 | <0.001 * | 24.71 ± 9.74 | 35.38 ± 11.03 | <0.001 * |
| MFT | 13.27 ± 3.47 | 18.86 ± 3.83 | <0.001 * | 13.38 ± 3.03 | 15.67 ± 3.55 | 0.001 * |
| MBI | 52.50 ± 11.01 | 71.46 ± 12.95 | <0.001 * | 51.43 ± 12.30 | 65.29 ± 13.49 | <0.001 * |
| MBI | ||
|---|---|---|
| r | p-Value | |
| MAS | −0.087 | 0.578 |
| JTHFT | 0.167 | 0.284 |
| MFT | 0.341 | 0.025 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, J.-H.; Cho, H.-Y.; Hahm, S.-C. Influence of Electrotherapy with Task-Oriented Training on Spasticity, Hand Function, Upper Limb Function, and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Subacute Stroke: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Healthcare 2021, 9, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9080987
Moon J-H, Cho H-Y, Hahm S-C. Influence of Electrotherapy with Task-Oriented Training on Spasticity, Hand Function, Upper Limb Function, and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Subacute Stroke: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Healthcare. 2021; 9(8):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9080987
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Jong-Hoon, Hwi-Young Cho, and Suk-Chan Hahm. 2021. "Influence of Electrotherapy with Task-Oriented Training on Spasticity, Hand Function, Upper Limb Function, and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Subacute Stroke: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Controlled Trial" Healthcare 9, no. 8: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9080987
APA StyleMoon, J.-H., Cho, H.-Y., & Hahm, S.-C. (2021). Influence of Electrotherapy with Task-Oriented Training on Spasticity, Hand Function, Upper Limb Function, and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Subacute Stroke: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Healthcare, 9(8), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9080987








