Biosimilar Insulins and Their Impact on Prices and Utilization of Insulins in Bulgaria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Study
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Utilization and Price Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biosimilars Availability
3.2. Changes in Prices
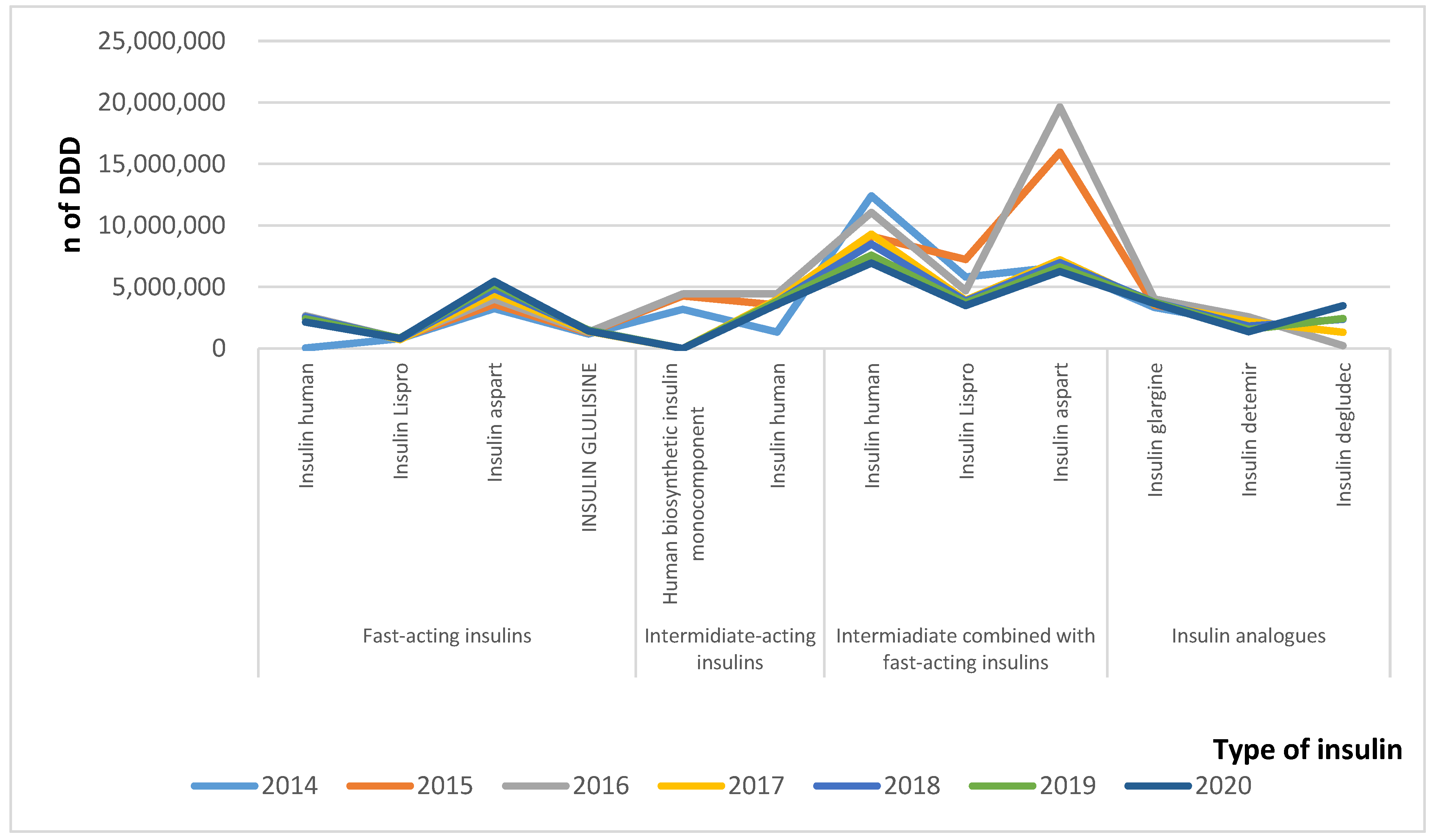
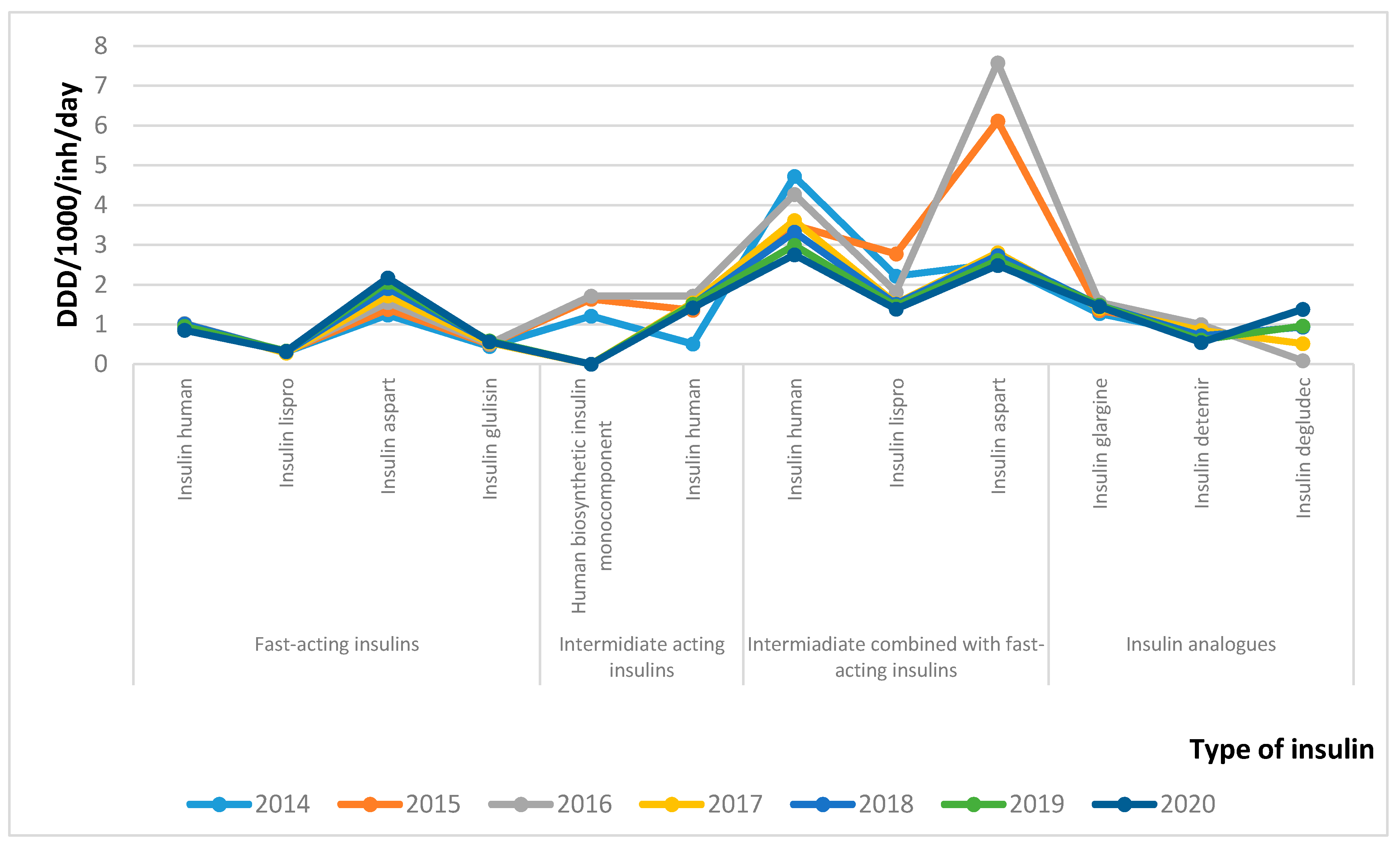
3.3. Changes in Utilization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassali, M.A.; Alrasheedy, A.A.; McLachlan, A.; Nguyen, T.A.; AL-Tamimi, S.K.; Ibrahim, M.I.; Aljadhey, H. The experiences of implementing generic medicine policy in eight countries: A review and recommendations for a successful promotion of generic medicine use. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dylst, P. Analysis of European policy towards generic medicines. GABI J. 2014, 3, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moorkens, E.; Vulto, A.G.; Huys, I.; Dylst, P.; Godman, B.; Keuerleber, S.; Claus, B.; Dimitrova, M.; Petrova, G.; Sović-Brkičić, L.; et al. Policies for biosimilar uptake in Europe: An overview. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rémuzat, C.; Kapuśniak, A.; Caban, A.; Ionescu, D.; Radière, G.; Mendoza, C.; Toumi, M. Supply-side and demand-side policies for biosimilars: An overview in 10 European member states. J. Mark Access Health Policy 2017, 5, 1307315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dylst, P.; Vulto, A.; Simoens, S. Barriers to the uptake of biosimilars and possible solutions: A Belgian case study. Pharmacoeconomics 2014, 3, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre-Ferrandiz, J.; Towse, A.; Berdud, M. Biosimilars: How can payers get long-term savings? Pharmacoeconomics 2016, 34, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoens, S. A review of generic medicine pricing in Europe. Gabi J. 2012, 1, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, C.; Ionescu, D.; Radière, G.; Rémuzat, C.; Lee, D.; Toumi, M. Potential Societal Value of Biosimilars Adoption: The Example of UK. In Proceedings of the ISPOR 18th Annual European Congress, Milan, Italy, 7–11 November 2015; Available online: http://www.ispor.org/research_pdfs/51/pdffiles/PHP279.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- IMS Health. The Impact of Biosimilar Competition. 2015. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/growth/tools-databases/newsroom/cf/itemdetail.cfm?item_type=251&lang=en&item_id=8602 (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Heinemann, L.; Hompesch, M. Biosimilar Insulins: Basic Considerations. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valov, V.; Doneva, M.; Borisova, A.M.; Tankova, T.; Czech, M.; Manova, M.; Savova, A.; Peikova, L.; Petrova, G. Regional differences in diabetic patients’ pharmacotherapy in Bulgaria. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Doneva, M.; Valov, V.; Borisova, A.-M.; Tankova, T.; Savova, A.; Manova, M.; Czech, M.; Petrova, G. Comparative analysis of the cost of insulin treated patients in Bulgaria. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2013, 27, 3748–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harston, A.H. Biosimilar Approvals Stall during COVID-19 Pandemic, but the Pipeline Grows. Biosimilars Law Bulletin. 2020. Available online: https://www.biosimilarsip.com/2020/06/09/biosimilar-approvals-stall-during-covid-19-pandemic-but-the-pipeline-grows/ (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- National Council on Prices and Reimbursement. Positive Drug List, Annex 1. Electronic Register. Available online: Portal.ncpr.bg/registers/pages/register/archive.xhtml (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- National Health Insurance Fund. Register of the Number of Patients and Reimbursed Sum. Available online: https://www.nhif.bg/page/218 (accessed on 18 December 2020).
- National Statistical Institute. Population—Demographic, Migration, and Forecast. Available online: https://www.nsi.bg/node/2920 (accessed on 18 December 2020).
- WHO. Introduction to DDD Indicators. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/atc-ddd-toolkit/indicators (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Davies, M.; Dahl, D.; Heise, T.; Kiljanski, J.; Mathieu, C. Introduction of biosimilar insulins in Europe. Diabet. Med. 2017, 34, 1340–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troien, P.; Newton, M.; Scott, K. The Impact of Biosimilar Competition in Europe December 2020. IQVIA Inc. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/human-use/docs/biosimilar_competition_en.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Heinemann, L. Biosimilar Insulin and Costs: What Can We Expect? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015, 10, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotham, D.; Barber, M.J.; Hill, A. Production costs and potential prices for biosimilars of human insulin and insulin analogues. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e000850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakariqi, L. Trends in prescribing and utilization of antidiabetic drugs in primary health care in Albania during 2004–2014. Int. J. Surg. Med. 2016, 2, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, L.; Lau, E.; Luk, A.; Sobrepena, L.; Tran, Q.K.; Kesavadev, J.; Jia, W.; Yu, W.; Tsang, C.C.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; et al. JADE Collaborative Study Group. Cross-sectional survey of biosimilar insulin utilization in Asia: The Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation Program. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rémuzat, C.; Dorey, J.; Cristeau, O.; Ionescu, D.; Radière, G.; Toumi, M. Key drivers for market penetration of biosimilars in Europe. J. Mark Access Health Policy 2017, 5, 1272308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, B.; Huys, I.; Vulto, A.G.; Simoens, S. Identifying Key Benefits in European Off-Patent Biologics and Biosimilar Markets: It is Not Only About Price! BioDrugs 2020, 34, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type of Insulin | Trade Name of Biosimilar | Trade Name of Originator | Date of Approval by EMA | Available on the National Market |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| insulin glargine | Abasaglar | Lantus | 9 September 2014 | 2 November 2019 |
| insulin glargine | Lusdana | Lantus | 1 April 2017, withdrawn 29 October 2018 | n.a. |
| insulin glargine | Semglee | Lantus | 27 March 2018 | n.a. |
| insulin lispro | Admelog | Humalog | 19 May 2017 | n.a. |
| insulin lispro | Lyumjev | Humalog | 24 March 2020 | 2 October 2020 |
| insulin aspart | Sar-Asp | NovoRapid | June 2020 | n.a. |
| Insulin aspart | Kixelle | NovoRapid | February 2021 | n.a. |
| Type of Insulin | INN | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast-acting insulin | Insulin human | 1.18667 | 1.10853 | 1.10853 | 1.03173 | 1.03173 | 1.03173 | 1.03173 |
| Insulin lispro | 1.89787 | 1.89787 | 1.79987 | 1.89787 | 1.89787 | 1.89787 | 1.89787 | |
| Insulin aspart | 1.84960 | 1.84960 | 1.84960 | 1.84960 | 1.84960 | 1.84960 | 1.84960 | |
| Insulin glulisine | 1.48453 | 1.48187 | 1.45547 | 1.43067 | 1.43067 | 1.40667 | 1.40667 | |
| Intermediate-acting | Insulin human | 1.18667 | 1.10853 | 1.10853 | 1.03173 | 1.03173 | 1.03173 | 1.03173 |
| Intermediate-combined with fast-acting | Insulin human | 1.18667 | 1.10853 | 1.10853 | 1.03173 | 1.03173 | 1.03173 | 1.03173 |
| Insulin lispro | 2.90907 | 2.90907 | 2.90907 | 2.90907 | 2.90907 | 2.90907 | 2.90907 | |
| Insulin aspart | 1.85507 | 1.85507 | 1.85507 | 1.85507 | 1.85507 | 1.85507 | 1.85507 | |
| Insulin analogues | Insulin glargine | 2.77867 | 2.70400 | 2.57107 | 2.24693 | 2.24693 | 2.23840 | 2.22707 |
| Insulin detemir | 3.30000 | 3.26400 | 3.26400 | 3.26400 | 3.26400 | 3.26187 | 3.24173 | |
| Insulin degludec | 0 | 0 | 5.40640 | 4.58907 | 3.93280 | 3.71253 | 3.35573 |
| Type of Insulin | INN | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 (6 Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast-acting insulins | Insulin human | 2,712,974 | 2,746,003 | 2,743,330 | 2,634,612 | 2,659,802 | 2,485,864 | 1,110,865 |
| Insulin lispro | 1,439,959 | 1,505,685 | 1,551,176 | 1,385,607 | 1,513,013 | 1,610,551 | 772,072 | |
| Insulin aspart | 6,012,484 | 6,661,873 | 7,431,574 | 8,198,453 | 8,994,654 | 9,667,668 | 5,059,650 | |
| Insulin glulisine | 1,721,718 | 1,887,274 | 1,903,362 | 1,996,637 | 2,113,265 | 2,085,594 | 1,003,911 | |
| Intermiddiate-acting | Human biosynthetic insulin mono-component | 3,525,661 | 4,729,230 | 4,573,895 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Insulin human | 1,474,536 | 3,929,373 | 4,573,895 | 4,086,315 | 3,939,394 | 3,949,838 | 0 | |
| Intermiadiate- combined with fast-acting | Insulin human | 13,756,838 | 10,111,514 | 11,419,348 | 9,591,356 | 8,756,552 | 7,829,981 | 1,846,691 |
| Insulin lispro | 10,471,092 | 13,028,771 | 13,666,035 | 11,410,897 | 11,212,032 | 10,772,541 | ||
| Insulin aspart | 12,292,976 | 29,521,937 | 36,423,518 | 13,373,571 | 12,939,875 | 12,280,771 | 3,584,212 | |
| Insulin analogues | Insulin glargine | 8,598,188 | 9,046,884 | 9,050,478 | 8,130,955 | 8,437,987 | 8,392,459 | 5,084,172 |
| Insulin detemir | 6,432,483 | 7,715,453 | 8,420,110 | 7,134,602 | 5,953,854 | 5,052,526 | 5,811,209 | |
| Insulin degludec | 1,066,595 | 5,218,684 | 8,823,325 | 8,177,562 | 0 | |||
| Total | 68,438,910 | 90,883,997 | 102,823,316 | 73,161,688 | 75,343,753 | 72,305,354 | 4,070,907 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tachkov, K.; Mitkova, Z.; Milushewa, P.; Petrova, G. Biosimilar Insulins and Their Impact on Prices and Utilization of Insulins in Bulgaria. Healthcare 2021, 9, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9060697
Tachkov K, Mitkova Z, Milushewa P, Petrova G. Biosimilar Insulins and Their Impact on Prices and Utilization of Insulins in Bulgaria. Healthcare. 2021; 9(6):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9060697
Chicago/Turabian StyleTachkov, Konstantin, Zornitsa Mitkova, Petya Milushewa, and Guenka Petrova. 2021. "Biosimilar Insulins and Their Impact on Prices and Utilization of Insulins in Bulgaria" Healthcare 9, no. 6: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9060697
APA StyleTachkov, K., Mitkova, Z., Milushewa, P., & Petrova, G. (2021). Biosimilar Insulins and Their Impact on Prices and Utilization of Insulins in Bulgaria. Healthcare, 9(6), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9060697







