Colectomy among Fee-for-Service Medicare Enrollees Coded as DRG 330: A Potential Platform to Allow Consumer Cost Transparency?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data
2.2. Study Cohort
2.3. Statistical Analysis
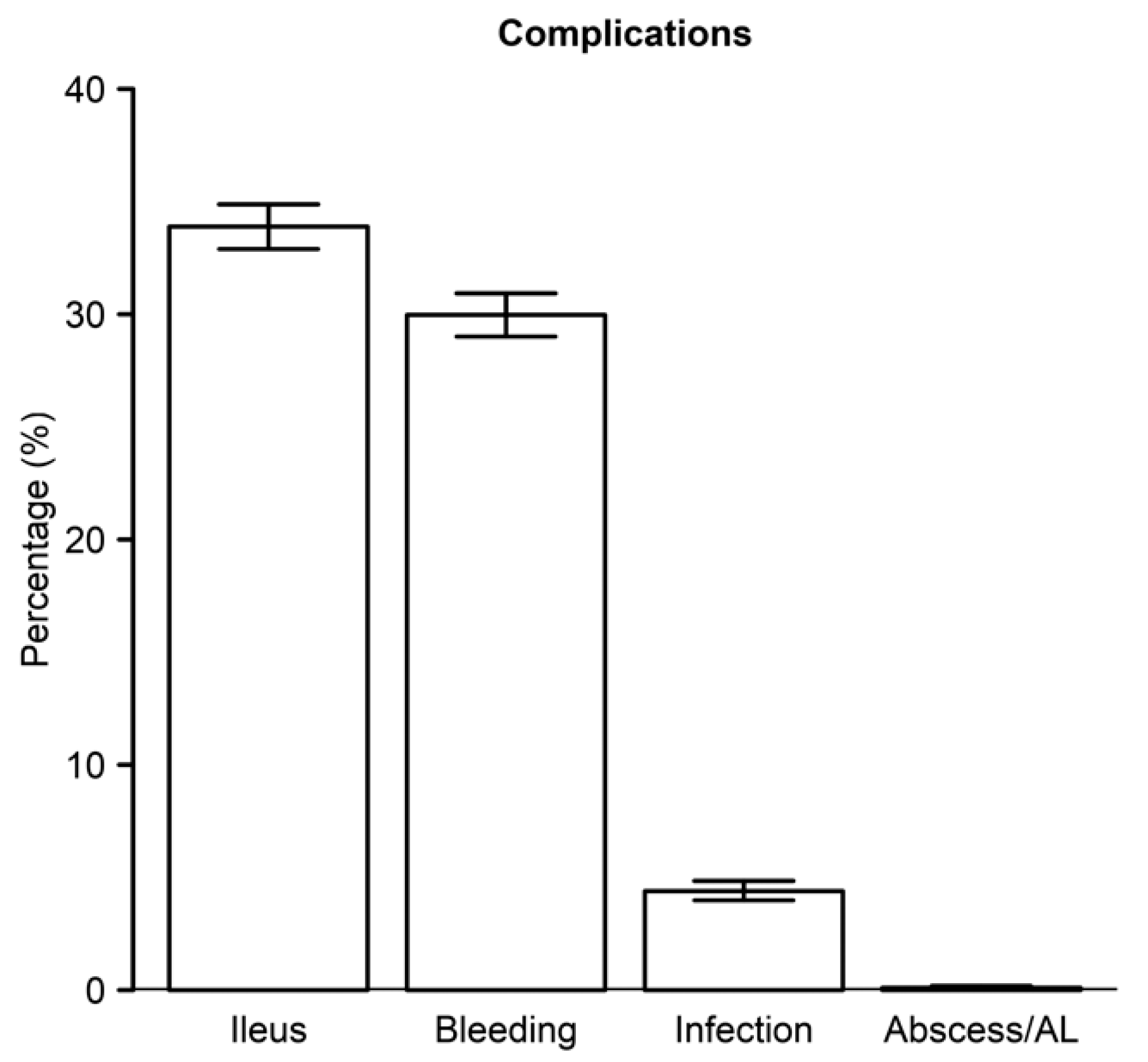
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Hospital Characteristics, Discharge Destination, and Inpatient Mortality
3.3. Colectomies per Provider per Year and Index Hospital Length of Stay (LOS), Charges and Payments
3.4. Comorbidities and Complications Post-Admission
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, B.D.; Sieloff, E.; Mehta, H.B.; Senagore, A.J. Did we prioritize quality improvement in general surgery: Time for a focus on outcomes and enhanced recovery care plans? Am. J. Surg. 2019, 217, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailovic, N.; Kocic, S.; Jakovljevic, M. Review of diagnosis-related group-based financing of hospital care. Health Serv. Res. Manag. Epidemiol. 2016, 3, 2333392816647892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, B.D.; Mehta, H.B.; Sieloff, E.; Shan, Y.; Senagore, A.J. DRG migration: A novel measure of inefficient surgical care in a value based world. Am. J. Surg. 2018, 215, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenda, T.R.; Krell, R.W.; Dimick, J.B. Reliability of hospital cost profiles in inpatient surgery. Surgery 2016, 159, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.B.; Berian, J.R.; Chen, S.; Cohen, M.E.; Bilimoria, K.Y.; Hall, B.L.; Ko, C.Y. Postoperative complications and hospital payment: Implications for achieving value. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2017, 224, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradarelli, J.C.; Healy, M.A.; Osborne, N.H.; Ghaferi, A.A.; Dimick, J.B.; Nathan, H. Variation in medicare expenditures for treating perioperative complications: The cost of rescue. JAMA Surg. 2016, 151, e163340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zogg, C.K.; Najjar, P.; Diaz, A.J.; Zogg, D.L.; Tsai, T.C.; Rose, J.A., Jr.; Scott, J.W.; Gani, F.; Alshaikh, H.; Canner, J.K.; et al. Rethinking priorities: Cost of complications after elective colectomy. Ann. Surg. 2016, 264, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, C.P.; Zutshi, M.; Senagore, A.J.; Remzi, F.H.; Hammel, J.; Fazio, V.W. Prospective, randomized, controlled trial between a pathway of controlled rehabilitation with early ambulation and diet and traditional postoperative care after laparotomy and intestinal resection. Dis. Colon Rectum 2003, 46, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.; Yin, Y.S.; McCandless, L.; Wang, S.; Englesbe, M.; Machado-Aranda, D. Taking control of your surgery: Impact of a prehabilitation program on major abdominal surgery. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2019, 228, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeds, I.L.; Canner, J.K.; Gani, F.; Meyers, P.M.; Haut, E.R.; Efron, J.E.; Johnston, F.M. Increased healthcare utilization for medical comorbidities prior to surgery improves postoperative outcomes. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, N.E.; Feldman, L.; Scott, S.; Zavorsky, G.; Kim, D.J.; Charlebois, P.; Stein, B.; Carli, F. Impact of preoperative change in physical function on postoperative recovery: Argument supporting prehabilitation for colorectal surgery. Surgery 2011, 150, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskins, I.N.; Baginsky, M.; Amdur, R.L.; Agarwal, S. Preoperative hypoalbuminemia is associated with worse outcomes in colon cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorge, C.M.; Kennedy, G.D.; Carchman, E.H. Preoperative blood transfusion is a predictor of worse short-term postoperative outcomes after colectomy. Surgery 2017, 161, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frasson, M.; Flor-Lorente, B.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Granero-Castro, P.; Hervas, D.; Alvarez Rico, M.A.; Brao, M.J.; Sanchez Gonzalez, J.M.; Garcia-Granero, E.; Group, A.S. Risk factors for anastomotic leak after colon resection for cancer: Multivariate analysis and nomogram from a multicentric, prospective, national study with 3193 patients. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawson, E.H.; Hall, B.L.; Louie, R.; Zingmond, D.S.; Ko, C.Y. Identification of modifiable factors for reducing readmission after colectomy: A national analysis. Surgery 2014, 155, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Absence of Surgical Complications (N) | % | Surgical Complications (N) | % | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 76.1 ± 7.5 | - | 77.0 ± 7.5 | - | <0.0001 |
| Sex | |||||
| Men | 1557 | 36 | 3253 | 37 | 0.19 |
| Women | 2767 | 64 | 5495 | 63 | |
| Race | |||||
| White | 3776 | 87 | 7603 | 87 | 0.37 |
| Black | 345 | 8 | 762 | 9 | |
| Hispanic | 63 | 1 | 108 | 1 | |
| Other | 140 | 3 | 275 | 3 | |
| Procedure Type | |||||
| Open | 1833 | 42 | 4034 | 46 | <0.0001 |
| Laparoscopic | 1250 | 29 | 2245 | 26 | |
| Hospital Type | |||||
| Rural | 544 | 13 | 1048 | 12 | 0.33 |
| Urban | 3780 | 87 | 7699 | 88 | |
| Colectomies Per Provider Per Year | 6.1 ± 4.8 | -- | 6.0 ± 4.6 | -- | <0.0001 |
| Length of Stay | 6.7 ± 3.9 | -- | 9.1 ± 5.4 | <0.0001 | |
| Total Charges ($) | 59,058.0 ± 40,437.7 | -- | 76,378.30 ± 54,348.30 | -- | <0.0001 |
| Payments ($) | 11,452.60 ± 7803.10 | -- | 12,169.30 ± 8681.10 | <0.0001 | |
| Discharge Destination | |||||
| Home | 2538 | 59 | 4206 | 48 | 0.0005 |
| Home Health Services | 943 | 22 | 2107 | 24 | |
| SNF | 636 | 15 | 1806 | 21 | |
| Other | 207 | 5 | 629 | 7 | |
| Inpatient Mortality | |||||
| No | 4305 | 99.6 | 8664 | 99.0 | 0.001 |
| Yes | 19 | 0.4 | 84 | 1.0 | |
| Elixhauser Comorbidity Description | Absence of Surgical Complications (N) | % | Surgical Complications (N) | % | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congestive Heart Failure | 351 | 8 | 729 | 8 | 0.69 |
| Cardiac Arrhythmia | 780 | 18 | 1738 | 20 | 0.012 |
| Valvular Disease | 273 | 6 | 669 | 8 | 0.006 |
| Pulmonary Circulation Disorders | 76 | 2 | 206 | 2 | 0.029 |
| Peripheral Vascular Disorders | 385 | 9 | 813 | 9 | 0.48 |
| Hypertension Uncomplicated | 2576 | 60 | 5288 | 60 | 0.34 |
| Hypertension Complicated | 341 | 8 | 977 | 11 | <0.0001 |
| Paralysis | 13 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0.35 |
| Other Neurological Disorders | 110 | 3 | 237 | 3 | 0.60 |
| Chronic Pulmonary Disease | 778 | 18 | 1788 | 20 | 0.001 |
| Diabetes Uncomplicated | 887 | 21 | 1811 | 21 | 0.82 |
| Diabetes Complicated | 101 | 2 | 229 | 3 | 0.34 |
| Hypothyroidism | 730 | 17 | 1545 | 18 | 0.28 |
| Renal Failure | 345 | 8 | 977 | 11 | <0.0001 |
| Liver Disease | 122 | 3 | 269 | 3 | 0.45 |
| Peptic Ulcer Disease excluding bleeding | 37 | 1 | 87 | 1 | 0.50 |
| Lymphoma | 59 | 1 | 83 | 1 | 0.039 |
| Metastatic Cancer | 1102 | 25 | 1414 | 16 | <0.0001 |
| Solid Tumor without Metastasis | 2070 | 48 | 3803 | 43 | <0.0001 |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis/collagen | 151 | 3 | 325 | 4 | 0.55 |
| Coagulopathy | 82 | 2 | 170 | 2 | 0.89 |
| Obesity | 475 | 11 | 895 | 10 | 0.19 |
| Weight Loss | 322 | 7 | 737 | 8 | 0.06 |
| Fluid and Electrolyte Disorders | 638 | 15 | 1353 | 15 | 0.29 |
| Blood Loss Anemia | 174 | 4 | 378 | 4 | 0.46 |
| Deficiency Anemia | 203 | 5 | 460 | 5 | 0.18 |
| Alcohol Abuse | 14 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 0.31 |
| Drug Abuse | 4 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 1 |
| Psychoses | 38 | 1 | 59 | 1 | 0.23 |
| Depression | 384 | 9 | 903 | 10 | 0.010 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hughes, B.D.; Sommerhalder, C.; Sieloff, E.M.; Williams, K.E.; Tyler, D.S.; Senagore, A.J. Colectomy among Fee-for-Service Medicare Enrollees Coded as DRG 330: A Potential Platform to Allow Consumer Cost Transparency? Healthcare 2020, 8, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040529
Hughes BD, Sommerhalder C, Sieloff EM, Williams KE, Tyler DS, Senagore AJ. Colectomy among Fee-for-Service Medicare Enrollees Coded as DRG 330: A Potential Platform to Allow Consumer Cost Transparency? Healthcare. 2020; 8(4):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040529
Chicago/Turabian StyleHughes, Byron D., Christian Sommerhalder, E Martin Sieloff, Kari E. Williams, Douglas S. Tyler, and Anthony J. Senagore. 2020. "Colectomy among Fee-for-Service Medicare Enrollees Coded as DRG 330: A Potential Platform to Allow Consumer Cost Transparency?" Healthcare 8, no. 4: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040529
APA StyleHughes, B. D., Sommerhalder, C., Sieloff, E. M., Williams, K. E., Tyler, D. S., & Senagore, A. J. (2020). Colectomy among Fee-for-Service Medicare Enrollees Coded as DRG 330: A Potential Platform to Allow Consumer Cost Transparency? Healthcare, 8(4), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040529





