Education and Protein Supplementation Improve Nutritional Biomarkers among Hypoalbuminemic Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Quasi-Experimental Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
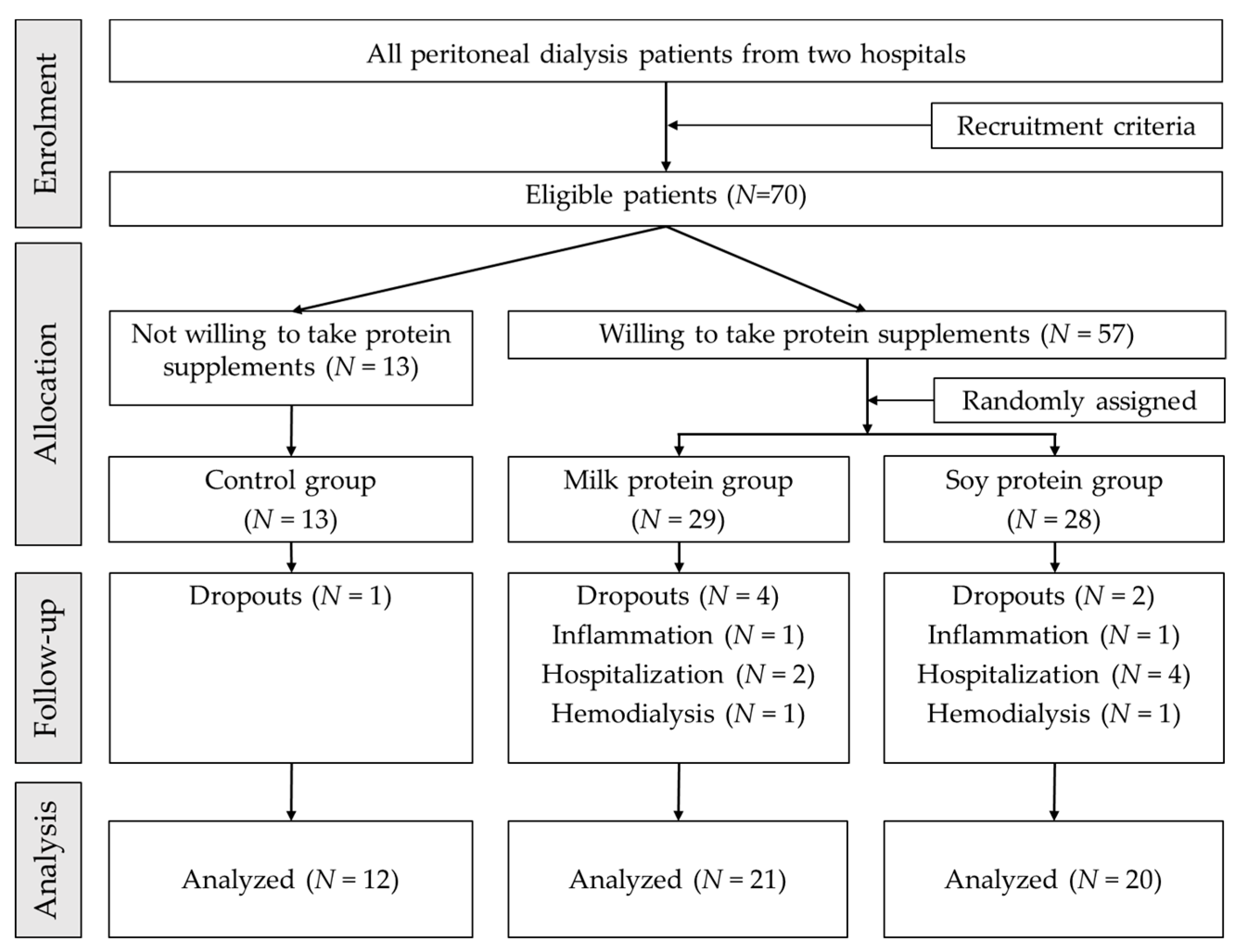
2.1. Study Design, Settings, and Patients
2.2. Interventions
2.3. Dietary Intake Assessment
2.4. Clinical and Biochemical Parameters
2.5. Ethical Approval
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. Effects on Daily Nutrient Intake
3.3. Effects on Biochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.K.; Chow, K.M.; Van de Luijtgaarden, M.W.; Johnson, D.W.; Jager, K.J.; Mehrotra, R.; Naicker, S.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Yu, X.Q.; Lameire, N. Changes in the worldwide epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwong, V.W.K.; Li, P.K.T. Peritoneal dialysis in Asia. Kidney Dis. (Basel) 2015, 1, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.X.; Gao, X.; Inglese, G.; Chuengsaman, P.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Yu, A. A global overview of the impact of peritoneal dialysis first or favored policies: An opinion. Perit. Dial. Int. 2014, 35, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, J.J.; Thomas, F.; Nagy, K.; Arogundade, F.; Avesani, C.M.; Chan, M.; Chmielewski, M.; Cordeiro, A.C.; Espinosa-Cuevas, A.; Fiaccadori, E.; et al. Global Prevalence of Protein-Energy Wasting in Kidney Disease: A Meta-analysis of Contemporary Observational Studies from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp Ikizler, T.; Cano, N.J.; Franch, H.; Fouque, D.; Himmelfarb, J.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kuhlmann, M.K.; Stenvinkel, P.; TerWee, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Prevention and treatment of protein energy wasting in chronic kidney disease patients: A consensus statement by the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windahl, K.; Faxén Irving, G.; Almquist, T.; Lidén, M.K.; van de Luijtgaarden, M.; Chesnaye, N.C.; Voskamp, P.; Stenvinkel, P.; Klinger, M.; Szymczak, M.; et al. Prevalence and Risk of Protein-Energy Wasting Assessed by Subjective Global Assessment in Older Adults with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease: Results From the EQUAL Study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Han, D.S. Nutrition in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leinig, C.E.; Moraes, T.; Ribeiro, S.; Riella, M.C.; Olandoski, M.; Martins, C.; Pecoits-Filho, R. Predictive Value of Malnutrition Markers for Mortality in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2011, 21, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennankore, K.K.; Bargman, J.M. Nutrition and the Kidney: Recommendations for Peritoneal Dialysis. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2013, 20, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodebo, B.T.; Shah, A.; Kopple, J.D. Is it Important to Prevent and Treat Protein-Energy Wasting in Chronic Kidney Disease and Chronic Dialysis Patients? J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahathevan, S.; Se, C.H.; Ng, S.; Khor, B.H.; Chinna, K.; Goh, B.L.; Gafor, H.A.; Bavanandan, S.; Ahmad, G.; Karupaiah, T. Clinical efficacy and feasibility of whey protein isolates supplementation in malnourished peritoneal dialysis patients: A multicenter, parallel, open-label randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 25, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, R. Daily protein intake and survival in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3715–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjiong, H.L.; Zijlstra, F.J.; Rietveld, T.; Wattimena, J.L.; Huijmans, J.G.M.; Swart, G.R.; Fieren, M.W.J.A. Peritoneal protein losses and cytokine generation in automated peritoneal dialysis with combined amino acids and glucose solutions. Mediators. Inflamm. 2007, 2007, 97272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjiong, H.L.; Swart, R.; van den Berg, J.W.; Fieren, M.W. Amino Acid-based peritoneal dialysis solutions for malnutrition: New perspectives. Perit. Dial. Int. 2009, 29, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dukkipati, R.; Kopple, J.D. Causes and prevention of protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney failure. Semin. Nephrol. 2009, 29, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, J.J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Cuppari, L.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kaysen, G.; Mitch, W.E.; Price, S.R.; Wanner, C.; Wang, A.Y.M.; et al. Etiology of the Protein-Energy Wasting Syndrome in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Statement from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM). J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibotto, G.; Sofia, A.; Saffioti, S.; Bonanni, A.; Mannucci, I.; Parodi, E.L.; Cademartori, V.; Verzola, D. Effects of peritoneal dialysis on protein metabolism. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, S25–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Nutrition in Chronic Renal Failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, S1–S140. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, Y.; Qian, Q. Protein Nutrition and Malnutrition in CKD and ESRD. Nutrients 2017, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, S.; Campbell, K.L.; Bogard, J.; Millichamp, A. Nutrition prescription to achieve positive outcomes in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. Nutrients 2014, 6, 416–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Cano, N.J.; Budde, K.; Chazot, C.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Mak, R.H.; Mehrotra, R.; Raj, D.S.; Sehgal, A.R.; Stenvinkel, P.; et al. Diets and enteral supplements for improving outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chrisman, M.; Diaz Rios, L.K. Evaluating MyPlate after 8 Years: A Perspective. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. Eval. 2019, 51, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouque, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.; Cano, N.; Chauveau, P.; Cuppari, L.; Franch, H.; Guarnieri, G.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kaysen, G.; et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Hopewell, S.; Schulz, K.F.; Montori, V.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Devereaux, P.J.; Elbourne, D.; Egger, M.; Altman, D.G. CONSORT 2010 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010, 340, c869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010, 340, c332. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.J.; Seo, A.R.; Kang, E.H.; Kim, S.B.; Park, S.K.; Park, J.S. A cross-sectional study comparing the nutritional status of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis patients in Korea. J. Ren. Nutr. 1999, 9, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Y.; Sanderson, J.; Sea, M.M.; Wang, M.; Lam, C.W.; Li, P.K.; Lui, S.F.; Woo, J. Important factors other than dialysis adequacy associated with inadequate dietary protein and energy intakes in patients receiving maintenance peritoneal dialysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satirapoj, B.; Limwannata, P.; Kleebchaiyaphum, C.; Prapakorn, J.; Yatinan, U.; Chotsriluecha, S.; Supasyndh, O. Nutritional status among peritoneal dialysis patients after oral supplement with ONCE dialyze formula. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2017, 10, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamon, K.M.; Lambert, K. Oral nutritional supplementation in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis: A randomised, crossover pilot study. J. Ren. Care 2018, 44, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, B.; Piccoli, A.; Trio, R.; Laccetti, R.; Nastasi, A.; Paglione, A.; Memoli, A.; Memoli, B. Dietary phosphate restriction in dialysis patients: A new approach for the treatment of hyperphosphataemia. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wei-Jie, Y. Effects of soy protein containing isoflavones in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, K. Does Whey Protein Supplementation Improve the Nutritional Status in Hypoalbuminemic Peritoneal Dialysis Patients? Ther. Apher. Dial. 2017, 21, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.J.; Ma, F.; Wang, Q.Y.; He, S.L. The effects of oral nutritional supplements in patients with maintenance dialysis therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, S.; Ho, S.C. Meta-analysis of the effects of soy protein containing isoflavones on the lipid profile. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.W.; Bush, H.M. Soy protein effects on serum lipoproteins: A quality assessment and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled studies. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2011, 30, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.T.; Chen, J.R.; Yang, C.S.; Peng, S.J.; Ferng, S.H. Effect of soya protein on serum lipid profile and lipoprotein concentrations in patients undergoing hypercholesterolaemic haemodialysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 95, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabibi, H.; Immani, H.; Hedayati, M.; Atabak, S.; Rahmani, L. Effects of soy consumption on serum lipids and apoproteins in peritoneal dialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Perit. Dial. Int. 2010, 30, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Protein Source | Milk Protein Supplement a | Soy Protein Supplement b |
|---|---|---|
| Per package (g) | 44.5 | 48.0 |
| Energy (kcal) | 205.0 | 206.0 |
| Protein (g) | 16.8 | 16.8 |
| Protein (% Energy) | 32.9 | 32.5 |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 18.0 | 19.0 |
| Carbohydrate (% Energy) | 35.1 | 36.9 |
| Fat (g) | 7.3 | 7.0 |
| Fat (% Energy) | 32.0 | 30.6 |
| Saturated Fat (g) | 1.4 | 0.7 |
| Trans Fat (g) | 0 | 0 |
| Ca (mg) | 226.8 | 158.4 |
| PO4 (mg) | 116.6 | 211.6 |
| Ca/PO4 | 1.95 | 0.75 |
| Characteristics | Control Group (n = 12) | Milk Protein Group (n = 21) | Soy Protein Group (n = 20) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, male (%) | 4 (33.3) | 9 (42.9) | 5 (25.0) | 0.482 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.3 ± 6.0 | 23.1 ± 2.6 | 23.4 ± 4.1 | 0.304 |
| Types of PD | ||||
| CAPD (%) | 5 (41.7) | 5 (23.8) | 12 (60) | 0.063 |
| APD (%) | 7 (58.3) | 16 (76.2) | 8 (40) | 0.063 |
| Medical history | ||||
| Diabetes (%) | 5 (41.7) | 4 (19.0) | 6 (30) | 0.373 |
| Hypertension (%) | 9 (75.0) | 10 (47.6) | 10 (50.0) | 0.273 |
| CVD (%) | 4 (33.3) | 4 (19.0) | 6 (30.0) | 0.602 |
| CVA (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.0) | 0.431 |
| PAOD (%) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.8) | 2 (10.0) | 0.483 |
| Urea clearance test | ||||
| Total Kt/Vurea | 2.19 ± 0.30 | 2.11 ± 0.35 | 2.14 ± 0.41 | 0.459 |
| Peritoneal Kt/Vurea | 1.87 ± 0.45 | 1.83 ± 0.53 | 1.90 ± 0.51 | 0.599 |
| Residual kidney Kt/Vurea | 0.32 ± 0.34 | 0.28 ± 0.36 | 0.24 ± 0.31 | 0.735 |
| RRF (urine volume > 100 mL/day) (%) | 7 (58.3) | 11 (52.4) | 10 (50.0) | 0.900 |
| nPCR (g/kg) | 0.94 ± 0.19 | 1.09 ± 0.22 | 1.02 ± 0.21 | 0.163 |
| Nutrients | Control Group (n = 12) | Milk Protein Group (n = 21) | Soy Protein Group (n = 20) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calorie (kcal/kg) | |||
| Baseline | 26.8 ± 8.3 | 28.6 ± 6.7 | 27.8 ± 8.4 |
| Month 3 | 26.1 ± 7.5 | 30.0 ± 6.2 | 28.1 ± 6.2 |
| Protein (g/kg) | |||
| Baseline | 0.89 ± 0.26 | 1.10 ± 0.43 | 1.02 ± 0.32 |
| Month 3 | 0.97 ± 0.31 * | 1.33 ± 0.57 a,† | 1.16 ± 0.32 a,*,† |
| Protein (%) | |||
| Baseline | 13.5 ± 2.9 | 15.1 ± 3.5 | 14.8 ± 3.5 |
| Month 3 | 14.9 ± 2.5 a | 17.7 ± 5.7 a | 16.6 ± 3.4 a |
| Fat (g) | |||
| Baseline | 49.2 ± 12.7 | 52.9 ± 15.6 | 53.2 ± 24.6 |
| Month 3 | 51.3 ± 13.8 | 60.0 ± 18.7 a | 55.1 ± 15.7 |
| Fat (%) | |||
| Baseline | 28.6 ± 5.4 | 29.3 ± 5.5 | 29.1 ± 5.3 |
| Month 3 | 30.4 ± 6.3 a | 31.4 ± 5.3 | 31.0 ± 7.6 |
| CHO (g) | |||
| Baseline | 226.4 ± 31.8 | 233.0 ± 59.7 | 225.1 ± 71.3 |
| Month 3 | 213.7 ± 37.8 | 221.4 ± 66.5 | 217.1 ± 66.6 |
| CHO (%) | |||
| Baseline | 60.0 ± 6.0 | 57.7 ± 7.4 | 57.9 ± 7.4 |
| Month 3 | 56.8 ± 6.1 | 52.4 ± 8.3 a | 54.0 ± 9.1 |
| Dietary Ca (mg) | |||
| Baseline | 260.2 ± 123.7 | 329.6 ± 141.7 | 317.4 ± 143.1 |
| Month 3 | 262.4 ± 134.6 * | 487.2 ± 147.3 a | 343.3 ± 97.5 * |
| Dietary PO4 (mg) | |||
| Baseline | 602.7 ± 104.9 | 717.5 ± 219.8 | 693.2 ± 273.8 |
| Month 3 | 635.8 ± 185.6 | 928.3 ± 346.4 a,* | 810.0 ± 215.3 a,* |
| Biochemical | Control Group (n = 12) | Milk Protein Group (n = 21) | Soy Protein Group (n = 20) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional biomarkers | |||
| BUN (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 56.0 ± 10.0 | 65.0 ± 17.0 | 66.0 ± 18.0 |
| Month 1 | 62.0 ± 16.0 * | 86.0 ± 23.0 † | 78.0 ± 22.0 *,† |
| Month 2 | 59.0 ± 16.0 * | 86.0 ± 21.0 † | 78.0 ± 16.0 † |
| Month 3 | 61.0 ± 16.0 * | 81.0 ± 21.0 a,c,† | 79.0 ± 17.0 a,† |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 9.6 ± 2.5 | 11.0 ± 3.5 | 10.4 ± 2.7 |
| Month 1 | 10.3 ± 2.9 | 11.7 ± 4.1 | 10.6 ± 3.0 |
| Month 2 | 10.4 ± 2.7 | 11.6 ± 3.6 | 10.3 ± 2.7 |
| Month 3 | 10.4 ± 2.8 a | 11.2 ± 3.9 | 10.8 ± 3.3 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 0.3 |
| Month 1 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 0.4 |
| Month 2 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 3.3 ± 0.4 |
| Month 3 | 3.4 ± 0.3 a | 3.4 ± 0.3 a,b | 3.3 ± 0.4 a,b |
| Total protein (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 6.5 ± 0.6 | 6.7 ± 0.6 | 6.4 ± 0.7 |
| Month 1 | 6.6 ± 0.7 | 6.9 ± 0.6 | 6.5 ± 0.8 |
| Month 2 | 6.6 ± 0.7 | 6.9 ± 0.6 | 6.5 ± 0.8 |
| Month 3 | 6.8 ± 0.7 a,b,c | 7.0 ± 0.7 a | 6.7 ± 0.7 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 9.6 ± 0.9 | 10.0 ± 1.4 | 9.7 ± 1.1 |
| Month 1 | 9.7 ± 1.3 | 10.0 ± 1.6 | 9.9 ± 1.2 |
| Month 2 | 9.8 ± 1.5 | 10.0 ± 1.4 | 9.6 ± 1.5 |
| Month 3 | 9.8 ± 1.5 | 10.3 ± 1.4 | 9.8 ± 1.2 |
| Other biochemical parameters | |||
| Serum Ca (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 2.5 ± 0.3 |
| Month 1 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.2 |
| Month 2 | 2.2 ± 0.2 * | 2.4 ± 0.2 *,† | 2.5 ± 0.3 † |
| Month 3 | 2.3 ± 0.1 * | 2.4 ± 0.2 *,† | 2.5 ± 0.2 † |
| Serum PO4 (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 4.2 ± 1.2 | 5.1 ± 1.3 | 5.0 ± 1.7 |
| Month 1 | 4.6 ± 0.9 | 5.3 ± 1.5 | 5.3 ± 1.4 |
| Month 2 | 4.8 ± 0.9 | 5.2 ± 1.3 | 5.1 ± 1.4 |
| Month 3 | 5.3 ± 1.4 a | 5.5 ± 1.8 | 5.2 ± 1.3 |
| Serum Na (mEq/L) | |||
| Baseline | 132.0 ± 4.0 | 134.0 ± 4.0 | 134.0 ± 4.3 |
| Month 1 | 133.0 ± 3.0 | 133.0 ± 5.0 | 134.0 ± 4.4 |
| Month 2 | 133.0 ± 4.0 | 133.0 ± 4.0 | 132.0 ± 4.0 |
| Month 3 | 133.0 ± 3.0 | 132.0 ± 4.0 *,† | 132.0 ± 3.2 *,† |
| Serum K (mEq/L) | |||
| Baseline | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 3.7 ± 0.6 |
| Month 1 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 3.6 ± 0.5 | 3.7 ± 0.7 |
| Month 2 | 3.6 ± 1.0 | 3.5 ± 0.5* | 3.6 ± 0.8 |
| Month 3 | 3.7 ± 0.9 | 3.7 ± 0.5 a | 3.8 ± 0.7 |
| TC (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 181.0 ± 47.0 | 174.0 ± 41.0 | 172.0 ± 32.0 |
| Month 3 | 180.0 ± 40.0 | 174.0 ± 43.0 | 181.0 ± 42.0 |
| TG (mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 235.0 ± 311.0 | 142.0 ± 96.0 | 124.0 ± 65.0 |
| Month 3 | 235.0 ± 291.0 | 125.0 ± 73.0 | 117.0 ± 57.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duong, T.V.; Tsao, C.-A.; Yang, E.; Peng, C.-H.; Hou, Y.-C.; Su, Y.-C.; Chang, J.-T.; Yang, S.-H. Education and Protein Supplementation Improve Nutritional Biomarkers among Hypoalbuminemic Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Quasi-Experimental Design. Healthcare 2019, 7, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7040135
Duong TV, Tsao C-A, Yang E, Peng C-H, Hou Y-C, Su Y-C, Chang J-T, Yang S-H. Education and Protein Supplementation Improve Nutritional Biomarkers among Hypoalbuminemic Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Quasi-Experimental Design. Healthcare. 2019; 7(4):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7040135
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuong, Tuyen Van, Chang-An Tsao, Evelyn Yang, Ching-Hsiu Peng, Yi-Cheng Hou, Yan-Chen Su, Jui-Ting Chang, and Shwu-Huey Yang. 2019. "Education and Protein Supplementation Improve Nutritional Biomarkers among Hypoalbuminemic Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Quasi-Experimental Design" Healthcare 7, no. 4: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7040135
APA StyleDuong, T. V., Tsao, C.-A., Yang, E., Peng, C.-H., Hou, Y.-C., Su, Y.-C., Chang, J.-T., & Yang, S.-H. (2019). Education and Protein Supplementation Improve Nutritional Biomarkers among Hypoalbuminemic Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Quasi-Experimental Design. Healthcare, 7(4), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7040135








