Parenting When Children Have Lyme Disease: Fear, Frustration, Advocacy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials and Procedure
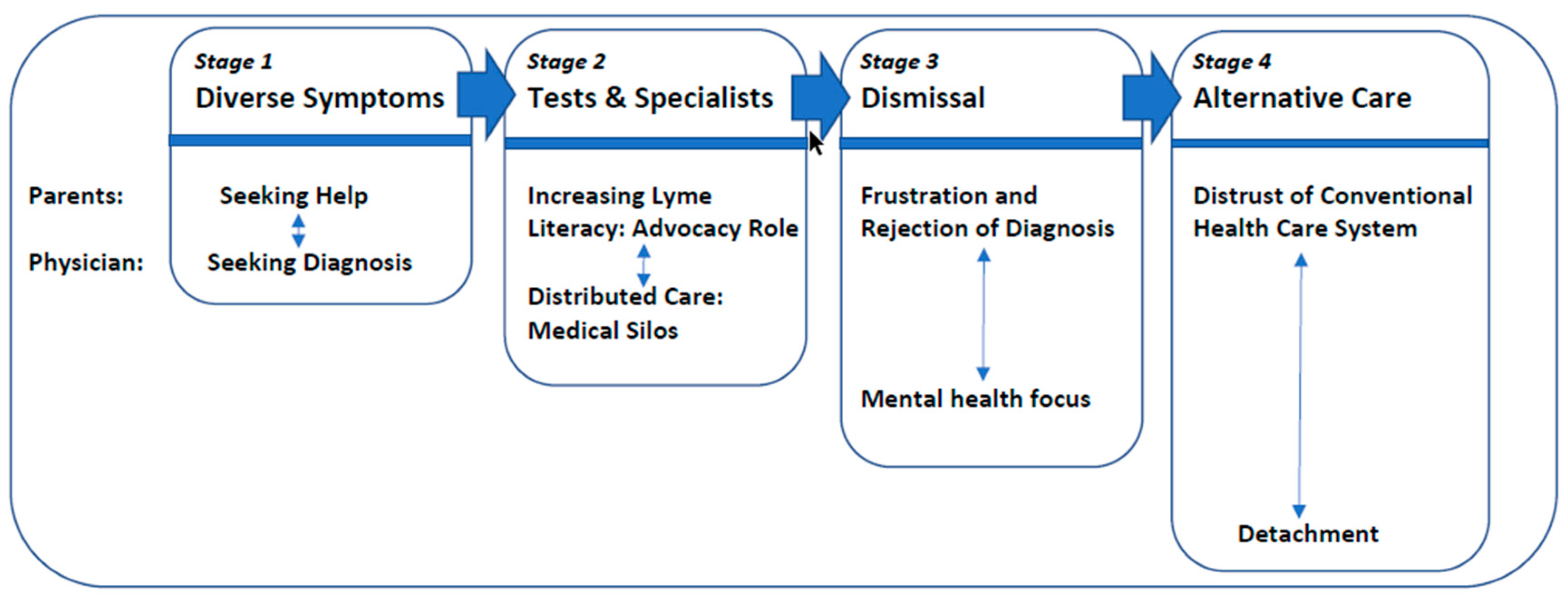
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebi, K.L.; Ogden, N.H.; Semenza, J.C.; Woodward, A. Detecting and attributing health burdens to climate change. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 085004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greig, J.D.; Young, I.; Harding, S.; Mascarenhas, M.; Waddell, L.A. A scoping review of Lyme disease research relevant to public health. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2018, 44, 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- Lieske, D.J.; Lloyd, V.K. Combining public participatory surveillance and occupancy modelling to predict the distributional response of Ixodes scapularis to climate change. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Githeko, A.K.; Lindsay, S.W.; Confalonieri, U.E.; Patz, J.A. Climate change and vector-borne diseases: A regional analysis. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 78, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leighton, P.A.; Koffi, J.K.; Pelcat, Y.; Lindsay, R.; Ogden, N.H. Predicting the speed of tick invasion: An empirical model of range expansion for disease vector Ixodes scapularis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, N.H.; Radojevic, M.; Wu, X.; Duvuuri, V.R.; Leighton, P.A.; Wu, J. Estimated effects of projected climate change on the basic reproductive number of the Lyme disease vector Ixodes scapularis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, V.K.; Hawkins, R.G. Under-Detection of Lyme Disease in Canada. Healthcare 2018, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, S.; Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R.; Burns, S.; Fleming, S.; Badcock, J.; Hanan, S.; Gaulin, C.; Leblanc, M.A.; Russell, C.; et al. Surveillance for Lyme disease in Canada: 2009–2015. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2017, 5, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lyme Disease Charts and Figures: Historical Data. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/stats/graphs.html (accessed on 21 June 2019).
- Johnson, K.O.; Nelder, M.P.; Russell, C.; Li, Y.; Badiani, T.; Sander, B.; Sider, D.; Patel, S.N. Clinical manifestations of reported Lyme disease cases in Ontario, Canada: 2005–2014. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgermans, L.; Goderis, G.; Vandevoorde, J.; Devroey, D. Relevance of chronic lyme disease to family medicine as a complex multidimensional chronic disease construct: A systematic review. Int. J. Fam. Med. 2014, 138016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Tickborne Diseases of the United States—A Reference Manual for Healthcare Providers, 5th ed.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018.
- Government of Canada. For Health Professionals: Lyme Disease. 2018. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/lyme-disease/health-professionals-lyme-disease.html (accessed on 21 June 2019).
- Glaude, P.D.; Huber, A.M.; Mailman, T.; Ramsey, S.; Lang, B.; Stringer, E. Clinical characteristics, treatment, and outcome of children with Lyme arthritis in Nova Scotia. Paediatr. Child Health 2015, 20, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ogden, N.H.; Arsenault, J.; Hatchette, T.F.; Mechai, S.; Lindsay, L.R. Antibody responses to Borrelia burgdorferi detected by western blot vary geographically in Canada. PLoS ONE 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrouillet, C.; Milord, F.; Lambert, L.; Vibien, A.; Ravel, A. Lyme disease: Knowledge and practices of family practitioners in southern Quebec. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 26, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, S.; Ogden, N.H.; Leighton, P.A.; Adam-Poupart, A.; Milord, F.; Lindsay, L.R.; Barkati, S.; Thivierge, K. Practices of Lyme disease diagnosis and treatment by general practitioners in Quebec, 2008–2015. BMC Fam. Pract. 2017, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, C.R.; Lloyd, V.K.; Gould, O.N. Motivations and experiences of Canadians seeking treatment for Lyme disease outside of the conventional Canadian health-care system. J. Patient Exp. 2017, 5, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, D.; Hewitt, H. A qualitative approach to understanding patients’ diagnosis of Lyme disease. Pub. Health Nurs. 2006, 23, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Vitulano, L.; Lee, R.; Weiss, T.R.; Colson, E.R. Experiences of patients identifying with chronic Lyme disease in the healthcare system: A qualitative study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2014, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebman, A.W.; Aucott, J.N.; Weinstein, E.R.; Bechtold, K.T.; Smith, K.C.; Leonard, L. Living in Limbo: Contested narratives of patients with chronic symptoms following Lyme disease. Qual. Health Res. 2017, 27, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, D.; Bull, R.; Winzenberg, T. The daily patterns of time use for parents of children with complex needs: A systematic review. J. Child Health Care 2012, 16, 26–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.; Glass, N.; Ford, R. Care in the home for seriously ill children with complex needs: A narrative literature review. J. Child Health Care 2014, 19, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, G.; Kuo, D.Z.; AAP Committee on psychosocial aspects of child and family health; AAP Council on children with disabilities. Psychosocial Factors in children and youth with special health care needs and their families. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20183171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciver, D.; Jones, D.; Nicol, M. Parents’ experiences of caring for a child with chronic pain. Qual. Health Res. 2010, 20, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.; Vickers, M.; Wilkes, L.; Barton, B. Financial implications for parents working fulltime and caring for a child with chronic illness. Aust. J. Early Child 2011, 36, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzmann, J.; Peek, N.; Heymans, H.; Maurice-Stam, H.; Grootenhuis, M. Consequences of caring for a child with a chronic disease: Employment and leisure time of parents. J. Child Health Care 2014, 18, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.L.; Kobayashi, D.; Golden, S.L.; Nageswaran, S. Rural and nonrural differences in providing care for children with complex chronic conditions. Clin. Pediatr. 2012, 51, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, G.; Bunce, A.; Johnson, L. How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods 2006, 18, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neergaard, M.A.; Olesen, F.; Andersen, R.S.; Sondergaard, J. Qualitative description—The poor cousin of health research? BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2009, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harborne, A.; Wolpert, M.; Clare, L. Making sense of ADHD: A battle for understanding? Parents’ views of their children being diagnosed with ADHD. Clin. Child. Psychol. Psych. 2004, 9, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, R.B.; Fesler, M.C. Chronic Lyme disease: A working case definition. Am. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 14, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Canada. Lyme Disease in Canada: A Federal Framework. 2017. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/content/dam/phac-aspc/documents/services/publications/diseases-conditions/lyme-disease-canada-federal-framework/lyme-disease-canada-federal-framework-eng.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2019).
- Waddell, L.A.; Greig, J.; Lindsay, L.R.; Hinckley, A.F.; Ogden, N.H. A systematic review on the impact of gestational Lyme disease in humans on the fetus and newborn. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, P.; Azar, R.; Luke, A.; Doucet, S.; Montelpare, W.; Nagel, D.; Hyndman, N.; Thompson, K. Falling through the cracks: Barriers to accessing services for children with complex health conditions and their families in New Brunswick. J. N. Brunswick Stud. 2017, 8, 133–158. [Google Scholar]
- Luke, A.; Doucet, S.; Azar, R. Paediatric patient navigation models of care in Canada: An environmental scan. Paediatr. Child. Health 2018, 23, e46–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunst, C.J.; Trivette, M. Empowerment, effective helpgiving practices and family-centered Care. Pediatr. Nurs. 1996, 22, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Demographic Information 1 | Number of Participants (n = 23) | Percentage of Participants |
|---|---|---|
| Gender of letter writer | ||
| Female | 20 | 87% |
| Male | 0 | 0% |
| No answer provided | 3 | 13% |
| Number of parents in household | ||
| One | 3 | 13% |
| Two | 18 | 78% |
| No answer provided | 2 | 9% |
| Number of children in family | ||
| One | 3 | 13% |
| Two | 10 | 43% |
| Three | 4 | 17% |
| Four | 4 | 17% |
| No answer provided | 2 | 9% |
| Children in family with confirmed or suspected Lyme disease | ||
| One | 13 | 56% |
| Two | 5 | 22% |
| Three | 3 | 13% |
| No answer provided | 2 | 9% |
| Province | ||
| Ontario | 11 | 48% |
| Alberta | 4 | 17% |
| British Columbia | 3 | 13% |
| Nova Scotia | 1 | 4% |
| Quebec | 1 | 4% |
| No answer provided | 3 | 13% |
| Area | ||
| Rural | 6 | 26% |
| Urban | 12 | 52% |
| No answer provided | 5 | 22% |
| Type of Symptom | Symptoms Reported |
|---|---|
| Pain | Arthritis/generalized pain/spinal pain |
| Migrating joint pain/swollen and inflamed joints/twisted fingers | |
| Headaches/pressure/sudden pain/brain feels inflamed | |
| Pain in limbs/stabbing pain/restless legs | |
| Pain in stomach/chest/ribs/stomach | |
| Developmental Issues | Delayed growth/delayed puberty |
| Poor in-utero growth | |
| Psychological Symptoms | Attention deficit/hyperactivity |
| Anger/Aggression/Irritability | |
| Altered personality/mood swings | |
| Anxiety/panic attacks | |
| Depression | |
| Hallucinations/paranoia /psychosis | |
| Nightmares | |
| Obsessive compulsive disorder | |
| Tics (blinking/throat clearing/toe walking/vocal tics, movements) | |
| Self-harm | |
| Social phobia/withdrawal | |
| Suicidal thoughts | |
| Neurological & Cognitive Symptoms | Brain fog/confusion/memory loss |
| Cognitive losses or delays (reading/speech/math/writing) | |
| Inflamed cranial nerves | |
| Facial droop/palsy | |
| Fainting | |
| Sensory issues (vision, hearing, taste, smell)/nystagmus | |
| Tingling/numbness/tightness in extremities | |
| Tremors/seizures | |
| Uncontrollable muscle contractions | |
| Vertigo/dizziness/poor balance | |
| Various Physical Symptoms | Anal fissures/rectal bleeding |
| Appetite loss/anorexia | |
| Baker’s cysts | |
| Bed wetting/frequent urination | |
| Blood and mucous in stool | |
| Breaking teeth/deformed fingernails | |
| Cardiac complications | |
| Croup (recurring)/relentless coughing | |
| Diarrhea/colicky/constipation | |
| Dry/red/blistering eyes/bags under eyes | |
| Ear infections | |
| Elevated C-reactive protein levels | |
| Elevated liver enzymes | |
| Fever | |
| Food/alcohol/heat intolerance | |
| Flushed cheeks/red lines on cheeks | |
| Gastric reflux/heartburn /drooling | |
| Herzheimer reaction | |
| High blood pressure | |
| Hormonal issues | |
| Insomnia/sleepwalking | |
| Irregular bloodwork | |
| Jaundice | |
| Low ferritin levels/low white blood cell count | |
| Mouth sores | |
| Nausea/vomiting | |
| Pneumonia | |
| Poor hair growth | |
| Rash:/hives/red, puple bumps/bullseye/ringworm/molluscum contagiosum | |
| Skin sensitivity/eczema /itchiness | |
| Short of breath at rest/shallow breathing /pale | |
| Sinus issues/colds/flu symptoms/phlegm | |
| Soaking sweats | |
| Swollen glands/thyroid/hypothalamus issues/lymph nodes | |
| Weakness/can’t stand or walk/bedridden/ exhaustion | |
| Weight gain/loss |
| Healthcare professionals & sites consulted a | Allergist |
| Clinical and metabolic genetics consultant | |
| Counselor/therapist | |
| Dermatologist | |
| Developmental pediatrician | |
| Ear, nose, and throat specialist | |
| Family doctor | |
| Gastroenterologist | |
| Hospital resident | |
| Immunologist | |
| Infection disease specialist | |
| Local emergency staff | |
| “Lyme literate” US doctor | |
| Lyme specialist | |
| Lymphatic massage drainage therapist | |
| Naturopath (Lyme literate and non) | |
| Neurologist | |
| Neurosurgeon | |
| Nurse practitioner | |
| Obstetrician/gynecologist | |
| Ophthalmologist | |
| Pediatric care teaching hospital | |
| Pediatric gastroenterologist | |
| Pharmacist | |
| Podiatrist | |
| Psychiatric ward/psychiatrist | |
| Rehabilitation hospital | |
| Rheumatologist | |
| Sleep clinic | |
| Social worker | |
| Urologist | |
| Treatments prescribed and attempted | Acyclovir |
| Adrenal fatigue pills | |
| Allergy medication | |
| Antibiotics (oral and IV) b | |
| Anti-malaria drugs (Malarone) | |
| Anti-parasitic drugs | |
| Chinese acupuncture | |
| Chiropractic therapy | |
| Chronic complex disease program | |
| Cognitive behavioral therapy | |
| Cortisone | |
| Counselling | |
| CPAP machine | |
| Diet: sugar free, gluten free, yeast free, vegan, vegan keto, FODMAP | |
| Dietary supplements and vitamins (oral & IV) c | |
| Essential oils/herbals/tinctures | |
| Exercise | |
| Eye patch | |
| Hydrocortisone cream | |
| Intravenous immunoglobin treatment | |
| Journaling | |
| Laser treatment | |
| Pain relievers d | |
| Topical cream/ointment | |
| Psychiatric medications e | |
| Physiotherapy | |
| PICC line | |
| Pool therapy | |
| Rife machine therapy | |
| Traditional Chinese medicine | |
| Tube feeding | |
| Diagnostic tests conducted | Bloodwork f |
| Cardiac workup | |
| CT scan | |
| Electromyography | |
| Genetic testing | |
| Immunology tests | |
| Lumbar puncture | |
| Lyme screening test g | |
| Mono tests | |
| MRI scan | |
| Muscle biopsy | |
| Nasal swabs | |
| Neurological testing | |
| Nerve conduction studies | |
| Endoscopies for throat/liver/pancreas | |
| Sleep-deprived EEG | |
| Specialized T-cell test | |
| Stool and urine sample tests | |
| Viral test | |
| X-ray |
| ADD/ADHD | Malnutrition |
|---|---|
| Anorexia | Mental disorder |
| Anxiety | Mosquito bite |
| Attention seeking | Multiple sclerosis |
| Celiac | Oversleeping |
| Chronic blepharitis/conjunctivitis | Pain amplification syndrome |
| Chronic constipation | PANDAS |
| Chronic fatigue syndrome | Patellofemoral syndrome |
| Conversion disorder | Pediatric migraines |
| Cryptosporidium | Polycystic ovary syndrome |
| Daycare syndrome | Post-concussion syndrome |
| Depression | Psychogenic causes |
| Double jointedness | Psychosomatic symptoms |
| Fybromyalgia | Stomach virus |
| Food sensitivities | Teething |
| Growth spurts/pains | Tourette’s syndrome |
| H1N1 | Unexplained medical illness |
| Infectious mononucleosis | Virus |
| Irritable bowel syndrome |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaudet, E.M.; Gould, O.N.; Lloyd, V. Parenting When Children Have Lyme Disease: Fear, Frustration, Advocacy. Healthcare 2019, 7, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7030095
Gaudet EM, Gould ON, Lloyd V. Parenting When Children Have Lyme Disease: Fear, Frustration, Advocacy. Healthcare. 2019; 7(3):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7030095
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaudet, Emilie M., Odette N. Gould, and Vett Lloyd. 2019. "Parenting When Children Have Lyme Disease: Fear, Frustration, Advocacy" Healthcare 7, no. 3: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7030095
APA StyleGaudet, E. M., Gould, O. N., & Lloyd, V. (2019). Parenting When Children Have Lyme Disease: Fear, Frustration, Advocacy. Healthcare, 7(3), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7030095





