Causal Associations Between Pre-Pregnancy Diabetes Mellitus and Pre-Eclampsia Risk: Insights from a Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Populations
2.3. Genetic Instrument Selection
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Genetic Instruments
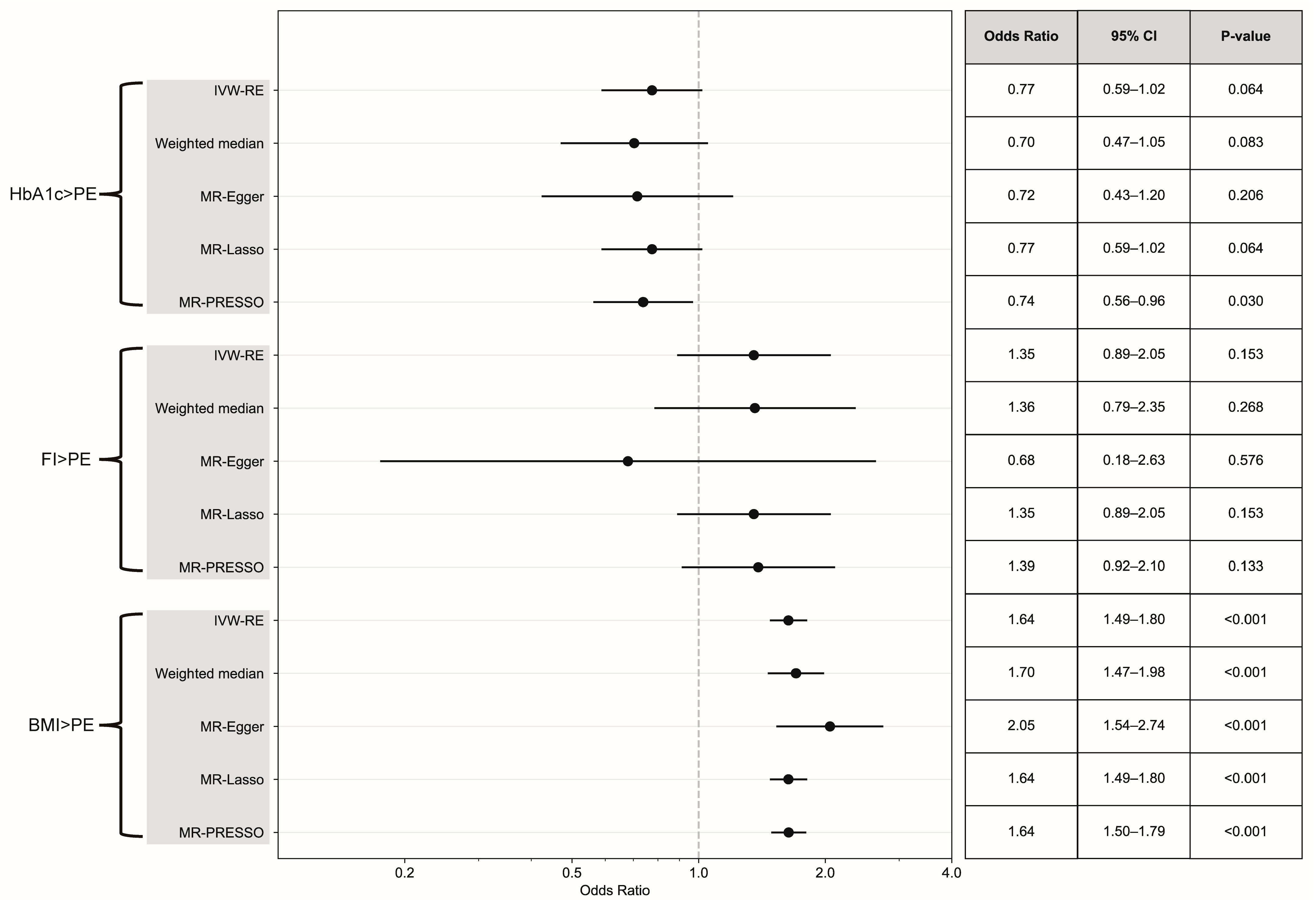
3.2. Causal Association of DM Types with PE
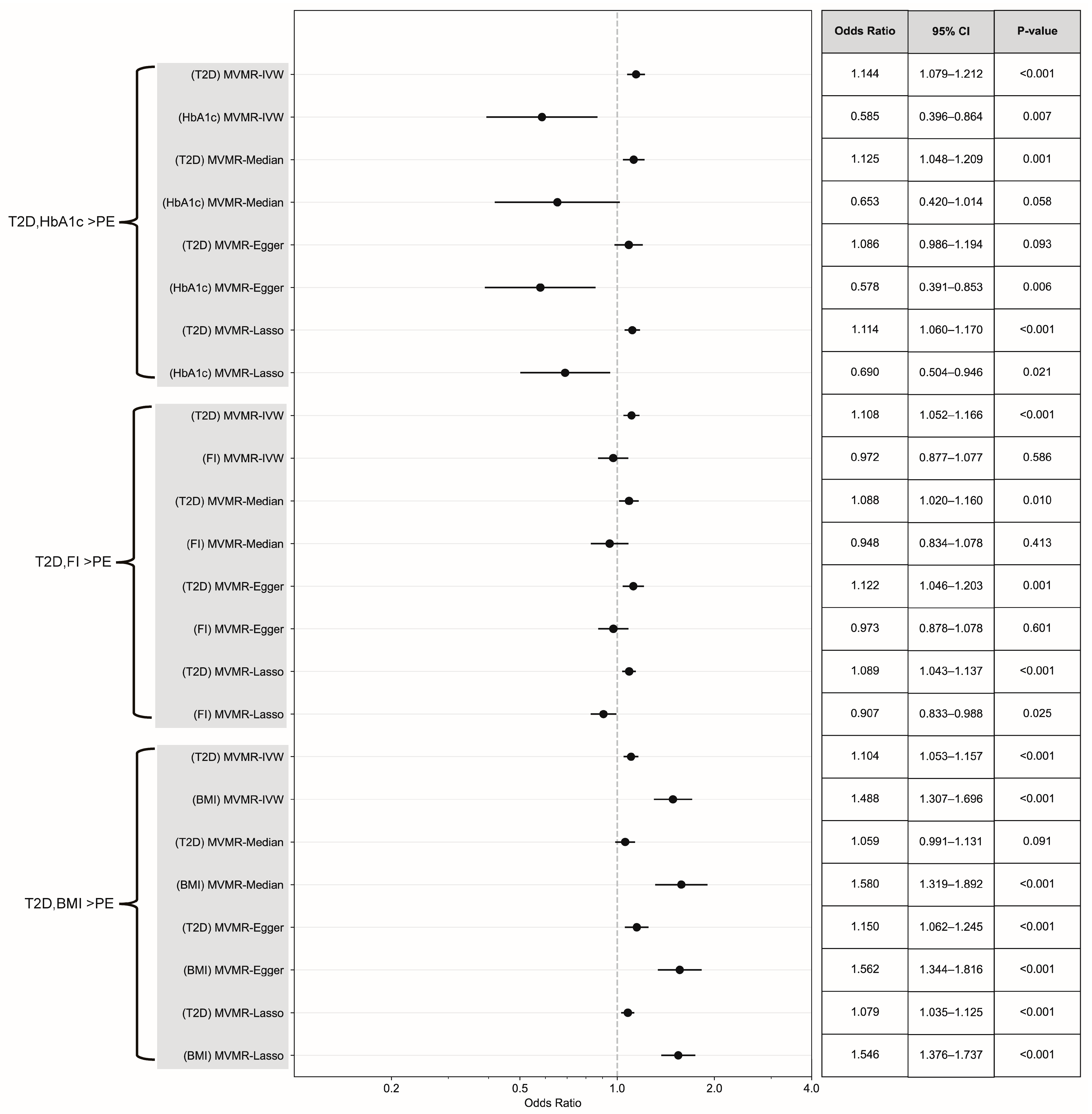
3.3. Causal Effect Assessment via Continuous Exposure and MVMR
3.4. Association Between Diabetes Treatment and PE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| IVs | Instrumental variables |
| IVW-RE | Inverse variance weighted random effects |
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| MVMR | Multivariable Mendelian randomization |
| PE | Pre-eclampsia |
| T1D | Type 1 diabetes |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
References
- Magee, L.A.; Nicolaides, K.H.; von Dadelszen, P. Preeclampsia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.A.; Seely, E.W. Update on Preeclampsia and Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 53, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Baker, P.N.; Granger, J.P.; Davidge, S.T.; Tong, C. Long-Term Impacts of Preeclampsia on the Cardiovascular System of Mother and Offspring. Hypertension 2023, 80, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassi, A.; Sala, A.; Mazzera, I.; Restaino, S.; Vizzielli, G.; Driul, L. Long-term outcomes of patients with preeclampsia, a review of the literature. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2023, 42, 2217448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, E.D.; Gloyn, A.L.; Evans-Molina, C.; Joseph, J.J.; Misra, S.; Pajvani, U.B.; Simcox, J.; Susztak, K.; Drucker, D.J. Diabetes mellitus-Progress and opportunities in the evolving epidemic. Cell 2024, 187, 3789–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.J.; Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.R. Diabetes mellitus, the fastest growing global public health concern: Early detection should be focused. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.H.T.; Mo, J.M.Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, J.V.; Schooling, C.M.; He, B.; Luo, S.; Au Yeung, S.L. A two-sample Mendelian randomization study explores metabolic profiling of different glycemic traits. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattoni, A.; Korbutt, G.; Tomei, A.A.; García, A.J.; Pepper, A.R.; Stabler, C.; Brehm, M.; Papas, K.; Citro, A.; Shirwan, H.; et al. Harnessing cellular therapeutics for type 1 diabetes mellitus: Progress, challenges, and the road ahead. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2025, 21, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xie, Q.; Pan, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Peng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Tong, N. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults: Pathogenesis, prevention and therapy. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2024, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornová, M.; Šimják, P.; Anderlová, K. Preeclampsia and diabetes mellitus. Ceska Gynekol. 2023, 88, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Wambua, S.; Lee, S.I.; Okoth, K.; Wang, Z.; Fayaz, F.F.A.; Eastwood, K.-A.; Nelson-Piercy, C.; Nirantharakumar, K.; Crowe, F.L. Autoimmune diseases and adverse pregnancy outcomes: An umbrella review. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestgaard, M.; Sommer, M.C.; Ringholm, L.; Damm, P.; Mathiesen, E.R. Prediction of preeclampsia in type 1 diabetes in early pregnancy by clinical predictors: A systematic review. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørgaard, S.K.; Vestgaard, M.J.; Jørgensen, I.L.; Ásbjörnsdóttir, B.; Ringholm, L.; McIntyre, H.D.; Damm, P.; Reinhardt Mathiesen, E. Diastolic blood pressure is a potentially modifiable risk factor for preeclampsia in women with pre-existing diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feig, D.S.; Donovan, L.E.; Zinman, B.; Sanchez, J.J.; Asztalos, E.; Ryan, E.A.; Fantus, G.; Hutton, E.; Armson, A.B.; Lipscombe, L.; et al. Metformin in women with type 2 diabetes in pregnancy (MiTy): A multicentre, international, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, I.; Lumpuy-Castillo, J.; Magalhaes, G.; Sánchez-Ferrer, C.F.; Lorenzo, Ó.; Peiró, C. Mechanisms of endothelial activation, hypercoagulation and thrombosis in COVID-19: A link with diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zou, J.; Lin, A.; Chi, J.; Hao, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z. Oxidative Stress, Endothelial Dysfunction, and N-Acetylcysteine in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxid. Redox. Signal 2024, 40, 968–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, Z.; Burianova, A.; Koubova, K.; Mrstik, M.; Jirkovska, M.; Cizkova, K. The interplay of inflammation and placenta in maternal diabetes: Insights into Hofbauer cell expression patterns. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1386528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanirowski, P.J.; Wątroba, M.; Pyzlak, M.; Wejman, J.; Szukiewicz, D. Expression of Placental Lipid Transporters in Pregnancies Complicated by Gestational and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambua, S.; Singh, M.; Okoth, K.; Snell, K.I.E.; Riley, R.D.; Yau, C.; Thangaratinam, S.; Nirantharakumar, K.; Crowe, F.L. Association between pregnancy-related complications and development of type 2 diabetes and hypertension in women: An umbrella review. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dori-Dayan, N.; Cukierman-Yaffe, T.; Zemet, R.; Cohen, O.; Levi, K.; Mazaki-Tovi, S.; Yoeli-Ullman, R. Insulin requirements during pregnancy in women with type 1 diabetes treated with insulin pump. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2024, 40, e3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cashin, A.G.; Lamb, S.E.; Hopewell, S.; Vansteelandt, S.; VanderWeele, T.J.; MacKinnon, D.P.; Mansell, G.; Collins, G.S.; Golub, R.M.; et al. A Guideline for Reporting Mediation Analyses of Randomized Trials and Observational Studies: The AGReMA Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au Yeung, S.L.; Gill, D. Standardizing the reporting of Mendelian randomization studies. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Chen, W.-M.; Burren, O.; Cooper, N.J.; Quinlan, A.R.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Farber, E.; Bonnie, J.K.; Szpak, M.; Schofield, E.; et al. Fine mapping of type 1 diabetes susceptibility loci and evidence for colocalization of causal variants with lymphoid gene enhancers. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, A.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Kemper, K.E.; Zheng, Z.; Yengo, L.; Lloyd-Jones, L.R.; Sidorenko, J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 143 risk variants and putative regulatory mechanisms for type 2 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Spracklen, C.N.; Marenne, G.; Varshney, A.; Corbin, L.J.; Luan, J.; Willems, S.M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Horikoshi, M.; et al. The trans-ancestral genomic architecture of glycemic traits. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 840–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengo, L.; Sidorenko, J.; Kemper, K.E.; Zheng, Z.; Wood, A.R.; Weedon, M.N.; Frayling, T.M.; Hirschhorn, J.; Yang, J.; Visscher, P.M.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for height and body mass index in ∼700000 individuals of European ancestry. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3641–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Spiller, W.; Del Greco, M.F.; Sheehan, N.; Thompson, J.; Minelli, C.; Smith, G.D. Improving the visualization, interpretation and analysis of two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization via the Radial plot and Radial regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, J.M.B.; Wood, A.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Burgess, S. Robust methods in Mendelian randomization via penalization of heterogeneous causal estimates. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, E.; Davey Smith, G.; Windmeijer, F.; Bowden, J. An examination of multivariable Mendelian randomization in the single-sample and two-sample summary data settings. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Fang, H.; Yang, J. A generalized linear mixed model association tool for biobank-scale data. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.C.; Vestgaard, M.; Nørgaard, S.K.; Damm, P.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Ringholm, L. Prediction and prevention of preeclampsia in women with preexisting diabetes: The role of home blood pressure, physical activity, and aspirin. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1166884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, H.R.; Howgate, C.; O’Keefe, J.; Myers, J.; Morgan, M.; Coleman, M.A.; Jolly, M.; Valabhji, J.; Scott, E.M.; Knighton, P.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of pregnant women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes: A 5-year national population-based cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, P.; Ekbom, P.; Damm, P.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Nielsen, B.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B. Signs of maternal vascular dysfunction precede preeclampsia in women with type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2007, 21, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Sowers, J.R. Hypertension in Diabetes: An Update of Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Disease. Hypertension 2021, 78, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, V.; Salzmann, A.; Burgess, S.; Chaturvedi, N. A Guide for Selection of Genetic Instruments in Mendelian Randomization Studies of Type 2 Diabetes and HbA1c: Toward an Integrated Approach. Diabetes 2023, 72, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhuza, M.P.U.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Qi, L.; Chen, D.; Liang, Z. The association between maternal HbA1c and adverse outcomes in gestational diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.L.; Wenger, J.B.; James-Todd, T.; Lamparello, B.M.; Halprin, E.; Serdy, S.; Fan, S.; Horowitz, G.L.; Lim, K.-H.; Rana, S.; et al. The association of circulating angiogenic factors and HbA1c with the risk of preeclampsia in women with preexisting diabetes. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2014, 33, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B.; Hu, L.; Meng, X.; Wu, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, B. Association of higher HbA1c within the normal range with adverse pregnancy outcomes: A cross-sectional study. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, W.R.; McCarthy, C.; Elovitz, M.; Parry, S.; Durnwald, C. Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Nondiabetic Patients with an Elevated Early Pregnancy HbA1c. Am. J. Perinatol. 2022, 29, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, I.M.; Badger, G.J.; McBride, C.A. Prepregnancy physiology and subsequent preterm preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2025, 232, 314.e1–314.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Sandler, L.; Muñoz, K.; Hsu, K.; Ecker, J.L.; Thadhani, R. First trimester insulin resistance and subsequent preeclampsia: A prospective study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; An, W.; Lin, L. The Association of Prepregnancy Body Mass Index with Pregnancy Outcomes in Chinese Women. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 8946971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, L.M.; Ness, R.B.; Markovic, N.; Roberts, J.M. The risk of preeclampsia rises with increasing prepregnancy body mass index. Ann. Epidemiol. 2005, 15, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorolajal, J.; Jenabi, E. The association between body mass index and preeclampsia: A meta-analysis. J. Matern Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2016, 29, 3670–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, M.J.; Pérez, M.P.; Aquieri, A.; Nosetto, D.; Pronotti, M.V.; Mazzei, M.; Kudrle, C.; Avaca, H. The Role of Obesity in the Development of Preeclampsia. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2024, 26, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Gill, D.; Glymour, M.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Kutalik, Z.; Holmes, M.V.; Minelli, C.; et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: Update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudball, M.J.; Bowden, J.; Hughes, R.A.; Ly, A.; Munafò, M.R.; Tilling, K.; Zhao, Q.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian randomisation with coarsened exposures. Genet. Epidemiol. 2021, 45, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Bi, Y.; Gao, L.; Yu, S.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Hua, R. Causal Associations Between Pre-Pregnancy Diabetes Mellitus and Pre-Eclampsia Risk: Insights from a Mendelian Randomization Study. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13091085
Ying X, Wu Q, Li X, Bi Y, Gao L, Yu S, Xu X, Li X, Wang Y, Hua R. Causal Associations Between Pre-Pregnancy Diabetes Mellitus and Pre-Eclampsia Risk: Insights from a Mendelian Randomization Study. Healthcare. 2025; 13(9):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13091085
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Xiang, Quanfeng Wu, Xiaohan Li, Yan Bi, Li Gao, Shushu Yu, Xiaona Xu, Xiaotian Li, Yanlin Wang, and Renyi Hua. 2025. "Causal Associations Between Pre-Pregnancy Diabetes Mellitus and Pre-Eclampsia Risk: Insights from a Mendelian Randomization Study" Healthcare 13, no. 9: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13091085
APA StyleYing, X., Wu, Q., Li, X., Bi, Y., Gao, L., Yu, S., Xu, X., Li, X., Wang, Y., & Hua, R. (2025). Causal Associations Between Pre-Pregnancy Diabetes Mellitus and Pre-Eclampsia Risk: Insights from a Mendelian Randomization Study. Healthcare, 13(9), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13091085






