Gamified Exercise in Virtual Reality: A Novel Intervention for Enhancing Mental Health and Reducing Suicidal Ideation in Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Type of Research and Study Participants
2.2. Measurement Tool and Test Process
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Steps for Developing the Exercise Protocol
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VR | Virtual Reality |
References
- Chambers, L.W.; Chambers, L.W. Prevalence and Monetary Costs of Dementia in Canada; Alzheimer Society of Canada: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Hendrie, H.C.; Hall, K.S.; Hui, S. The relationships between age, sex, and the incidence of dementia and Alzheimer disease: A meta-analysis. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1998, 55, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorm, A.F.; Jolley, D. The incidence of dementia: A meta-analysis. Neurology 1998, 51, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coxon, J.P.; Goble, D.J.; Leunissen, I.; Van Impe, A.; Wenderoth, N.; Swinnen, S.P. Functional brain activation associated with inhibitory control deficits in older adults. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelazo, P.D.; Craik, F.I.; Booth, L. Executive function across the life span. Acta Psychol. 2004, 115, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, N.S.; Zainuddin, N.A.; Seman, Z.; Khamal, N.R.; Ismail, M.H. Trends of completed suicide rates among Malaysian elderly between 1995 and 2020. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alés, G.; Jiang, T.; Keyes, K.M.; Gradus, J.L. The recent rise of suicide mortality in the United States. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2022, 43, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Declining suicide rates in China (1990–2017): Gender and age specific analyses. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 352, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, T.E., Jr.; Brown, J.S.; Wingate, L.R. The psychology and neurobiology of suicidal behavior. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2005, 56, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- At, B. The measurement of pessimism: The hopelessness scale. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1974, 42, 861–865. [Google Scholar]
- Greydanus, D.E.; Bacopoulou, F.; Tsalamanios, E. Suicide in adolescents: A worldwide preventable tragedy. Keio J. Med. 2009, 58, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceppi, L. Caring for Older Adults: Bio-Psycho-Social Assessment and Well-Being in Nursing Homes. 2024. Available online: https://boa.unimib.it/handle/10281/460362# (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Cooney, G.M.; Dwan, K.; Greig, C.A.; Lawlor, D.A.; Rimer, J.; Waugh, F.R.; McMurdo, M.; Mead, G.E. Exercise for depression. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD004366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuch, F.B.; Vancampfort, D.; Richards, J.; Rosenbaum, S.; Ward, P.B.; Stubbs, B. Exercise as a treatment for depression: A meta-analysis adjusting for publication bias. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 77, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, S.; Mun, W.; Kim, G. Associations between physical activity, mental health, and suicidal behavior in Korean adolescents: Based on data from 18th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey (2022). Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutar, R.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, V. Suicide and prevalence of mental disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of world data on case-control psychological autopsy studies. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 329, 115492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Yuhuai, C.; Jing, Z.; Pengling, L. Effect of air pollution and rural-urban difference on mental health of the elderly in China. Iran. J. Public Health 2015, 44, 1084. [Google Scholar]
- Sadek, J.; Diaz-Piedra, B.; Saleh, L.; MacDonald, L. A narrative review: Suicide and suicidal behaviour in older adults. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1395462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridniya, H.; Sefidgar, A.; Bagheri Ragheb, G.; Saberi, A. The Impact of Gamified Exercise Activities on Increasing Motivation for Participation in Sports Classes: A Case Study of Public Library Staff in Tehran Province. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 26, 259–280. [Google Scholar]
- Deterding, S.; Sicart, M.; Nacke, L.; O’Hara, K.; Dixon, D. Gamification. using game-design elements in non-gaming contexts. In Proceedings of the CHI’11 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–12 May 2011; pp. 2425–2428. [Google Scholar]
- Rüth, M.; Kaspar, K. Educational and social exergaming: A perspective on physical, social, and educational benefits and pitfalls of exergaming at home during the COVID-19 pandemic and afterwards. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 644036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corregidor-Sánchez, A.I.; Polonio-López, B.; Martin-Conty, J.L.; Rodríguez-Hernández, M.; Mordillo-Mateos, L.; Schez-Sobrino, S.; Criado-Álvarez, J.J. Exergames to prevent the secondary functional deterioration of older adults during hospitalization and isolation periods during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, S.A.; Sprague, B.N.; Stephan, A.T.; Doyle, C.E.; Tian, J.; Phillips, C.B.; Ross, L.A. Feasibility and enjoyment of exercise video games in older adults. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 751289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, P.; Fuschillo, S.; Papa, A.; Di Minno, M.N.D.; Maniscalco, M. Exergaming as a Supportive Tool for Home-Based Rehabilitation in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era; Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.: New Rochelle, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 9, pp. 311–313. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal, J.A.; Babyak, M.A.; Doraiswamy, P.M.; Watkins, L.; Hoffman, B.M.; Barbour, K.A.; Herman, S.; Craighead, W.E.; Brosse, A.L.; Waugh, R. Exercise and pharmacotherapy in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Psychosom. Med. 2007, 69, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swacha, J. State of research on gamification in education: A bibliometric survey. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, J.; Hopper, L.; Farrelly, A.M.; Lombard-Vance, R.; Bamidis, P.D.; Konstantinidis, E.I. A scoping review of augmented/virtual reality health and wellbeing interventions for older adults: Redefining immersive virtual reality. Front. Virtual Real. 2021, 2, 655338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo-Prieto, P.; Cancela, J.M.; Rodríguez-Fuentes, G. Immersive virtual reality as physical therapy in older adults: Present or future (systematic review). Virtual Real. 2021, 25, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahabi, M.; Abdul Razak, A.M. Adaptive virtual reality-based training: A systematic literature review and framework. Virtual Real. 2020, 24, 725–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Parreño, J.; Méndez-Ibáñez, E.; Alonso-Arroyo, A. The use of gamification in education: A bibliometric and text mining analysis. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2016, 32, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Sánchez, M.A.; Palos-Sánchez, P.R.; Folgado-Fernández, J.A. Systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis on virtual reality and education. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 155–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Konge, L.; Artino Jr, A.R. The positivism paradigm of research. Acad. Med. 2020, 95, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhou, J.; Bigambo, F.M.; Yan, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, H. The trend of suicide and self-harm in the Chinese population from 2018 to 2022 based on ambulance medical emergency cases: A retrospective study. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1494841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, N.O.; Freeman, H.R.; Jones, J.A.; Luczak, T.; Carruth, D.; Knight, A.C.; Chander, H. Virtual reality induced symptoms and effects: Concerns, causes, assessment & mitigation. Virtual Worlds 2022, 1, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Son, W. Cybersickness and its severity arising from virtual reality content: A comprehensive study. Sensors 2022, 22, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, K.W.; Nakamura, Y.; Lange, K.M. Sport and exercise as medicine in the prevention and treatment of depression. Front. Sports Act. Living 2023, 5, 1136314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladi, E.; Esfahani, M.; Azimkhani, A.; Asan, S. The effect of physical activity and selected games in leisure time on the feeling of loneliness, self-efficacy, and life expectancy of elderly women. Akdeniz Spor Bilim. Derg. 2023, 6, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mize, M.C. Social Connections and Suicide Desire Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Innov. Aging 2023, 7, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Fang, S.; Norwood, W.C.; Guan, L. Effect of Elderly People’s Perceived Value on their Adherence to Outdoor Exercise: The Intermediary Role of Motivation for Active Social Adaptation. INQUIRY J. Health Care Organ. Provis. Financ. 2024, 61, 00469580241254539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.; Wilund, K.; Solai, K.; Tamayo, D.; Fast, D.; Venkatesan, P.; Lash, J.P.; Lora, C.M.; Martinez, L.; Alemañy, G.M. Positive psychological intervention delivered using virtual reality in patients on hemodialysis with comorbid depression: Protocol and design for the joviality randomized controlled trial. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2023, 12, e45100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liang, H.-N.; Baghaei, N.; Ma, X.; Yu, K.; Meng, X.; Wen, S. Effects of an immersive virtual reality exergame on university students’ anxiety, depression, and perceived stress: Pilot feasibility and usability study. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e29330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, M.H.; Sidi, H.; Siew Koon, C.; Che Roos, N.A.; Sharip, S.; Abdul Samad, F.D.; Wan Xi, O.; Das, S.; Mohamed Saini, S. Virtual reality (VR) technology for treatment of mental health problems during COVID-19: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloy, K.M.; Milling, L.S. The effectiveness of virtual reality distraction for pain reduction: A systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2010, 30, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishkind, M.C.; Norr, A.M.; Katz, A.C.; Reger, G.M. Review of virtual reality treatment in psychiatry: Evidence versus current diffusion and use. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.A.; Grimmer, K.A.; Sparnon, A.L.; McRae, S.E.; Thomas, B.H. The efficacy of playing a virtual reality game in modulating pain for children with acute burn injuries: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatr. 2005, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, J.R.S.; Velosa, V.H.S.; Abreu, L.T.N.; Jardim, R.L.; Santos, J.A.V.; Peres, B.; Campos, P.F. Virtual reality exposure treatment in phobias: A systematic review. Psychiatr. Q. 2021, 92, 1685–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Zambotti, M.; Yuksel, D.; Kiss, O.; Barresi, G.; Arra, N.; Volpe, L.; King, C.; Baker, F.C. A virtual reality-based mind–body approach to downregulate psychophysiological arousal in adolescent insomnia. Digit. Health 2022, 8, 20552076221107887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.A.; Brodie, M.A.; Mitri, G.; van Schooten, K.; Lovell, N.; Lord, S.R.; Okubo, Y. Virtual Obstacle-Avoidance Training Using Daily-Life Obstacles with Physical Feedback in Older People: A Cross-Over Trial. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=5104022 (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- KS, N. Key in socially driven game dynamics, open the doors of agility—An empirical study on gamification and employee agility. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2023, 42, 1659–1685. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, D.; Rosebrock, L.; Waite, F.; Loe, B.S.; Kabir, T.; Petit, A.; Dudley, R.; Chapman, K.; Morrison, A.; O’Regan, E. Virtual reality (VR) therapy for patients with psychosis: Satisfaction and side effects. Psychol. Med. 2023, 53, 4373–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goumopoulos, C.; Drakakis, E.; Gklavakis, D. Feasibility and acceptance of augmented and virtual reality exergames to train motor and cognitive skills of elderly. Computers 2023, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisso, E.; Signorelli, M.S.; Milazzo, M.; Maglia, M.; Polosa, R.; Aguglia, E.; Caponnetto, P. Immersive virtual reality applications in schizophrenia spectrum therapy: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Choi, D.-H.; Lai, B.; Lu, Z.; Tian, H. Metaverse-based virtual reality experience and endurance performance in sports economy: Mediating role of mental health and performance anxiety. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 991489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E.; Vantaraki, F.; Skoulidi, C.; Anastassopoulos, P.; Vantarakis, A. Promoting physical and mental health among children and adolescents via gamification—A conceptual systematic review. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Mateos, C.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Pérez-López, I.J. The “STAR WARS: The First Jedi” Program—Effects of Gamification on Psychological Well-Being of College Students. Games Health J. 2024, 13, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Shi, H.; Shen, M.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, Y.; Yu, T.; Lian, X.; Yu, T.; Yang, X. The effects of mHealth-based gamification interventions on participation in physical activity: Systematic review. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2022, 10, e27794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaidou, I.; Aristeidis, L.; Lambrinos, L. A gamified app for supporting undergraduate students’ mental health: A feasibility and usability study. Digit. Health 2022, 8, 20552076221109059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Vázquez, D.; Navarro-López, V.; Cano-de-la-Cuerda, R.; Palacios-Ceña, D.; Espada, M.; Bores-García, D.; Delfa-de-la-Morena, J.M.; Romero-Parra, N. Influence of virtual reality and gamification combined with practice teaching style in physical education on motor skills and students’ perceived effort: A mixed-method intervention study. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Lee, S.; Choi, S. A systematic review of research on speech-recognition chatbots for language learning: Implications for future directions in the era of large language models. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2024, 32, 4613–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z.; He, J. Effects of game-based digital interventions for mental disorders: A meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 362, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingili, N.; Oyelere, S.S.; Nyström, M.B.; Anyshchenko, L. A systematic review on the efficacy of virtual reality and gamification interventions for managing anxiety and depression. Front. Digit. Health 2023, 5, 1239435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikroo, M.H. Investigating the Impact of Virtual Reality and Gamification on Improving Physical Activities in Children. 2020. Available online: https://assets-eu.researchsquare.com/files/rs-38390/v1/16dee1f2-5571-4615-91f5-065741edd7ad.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2025). [CrossRef]
| Type | Frequency | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 72 | %100 |
| Female | 0 | %0 | |
| Age | 52–57 years | 14 | %19.4 |
| 58–63 years | 28 | %38.8 | |
| Over 63 years | 30 | %41.6 |
| Statistic | df | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 0.118 | 200 | 0.103 |
| Experiment group | 0.121 | 200 | 0.089 |
| Pre Test | Post Test | Average Difference Between Pre-Test and Post-Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
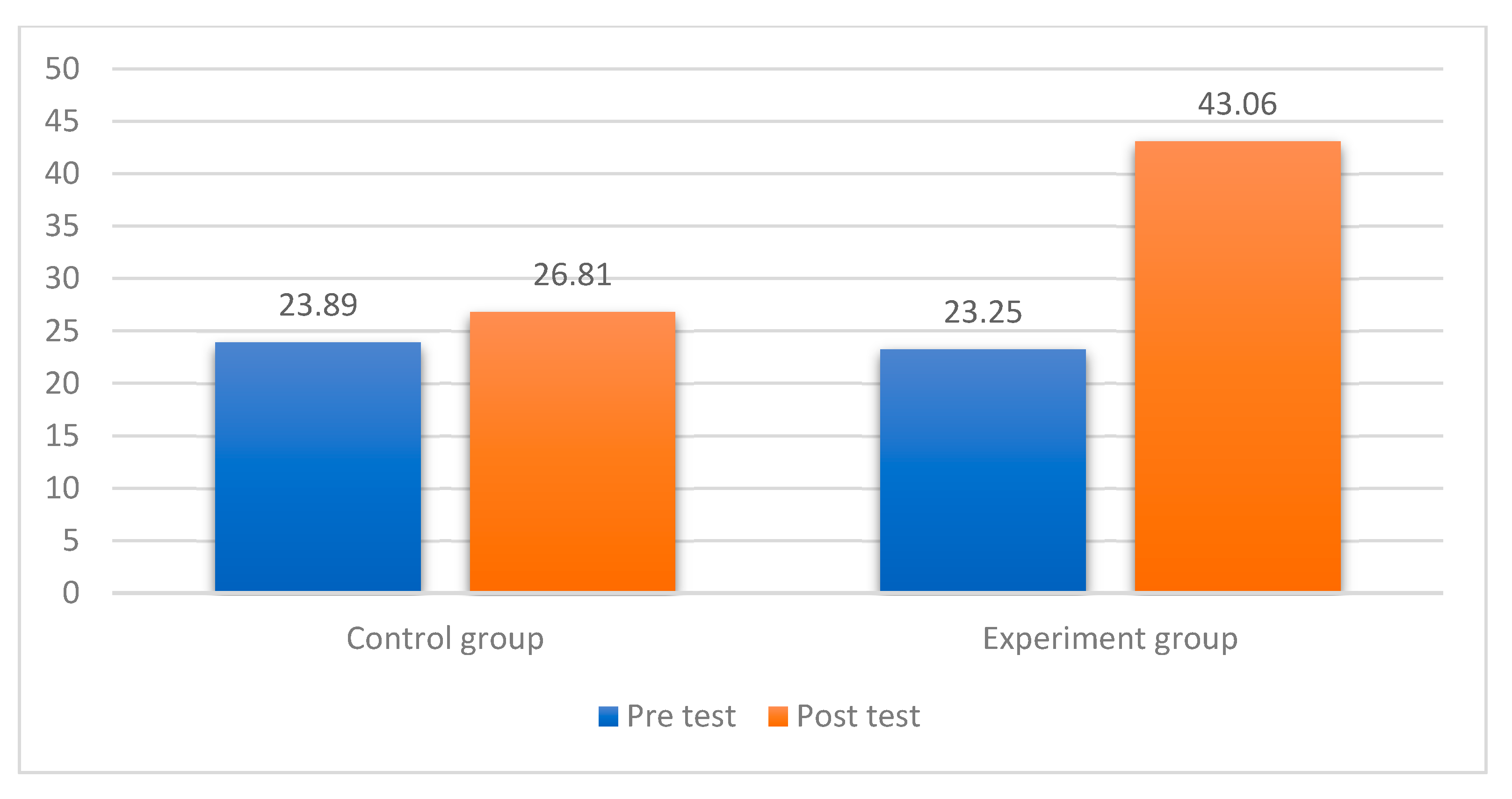
| Control group | 23.89 | 1.97 | 26.81 | 2.41 | 2.92 |
| Experiment group | 23.25 | 2.50 | 43.06 | 3.53 | 19.81 |
| F | Sig. | T | df | Sig. (2-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.255 | 0.001 | −26.693 | 70 | 0.001 |
| −26.693 | 58.219 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Faridniya, H.; Ebrahimi, Z.; Zhao, Z. Gamified Exercise in Virtual Reality: A Novel Intervention for Enhancing Mental Health and Reducing Suicidal Ideation in Older Adults. Healthcare 2025, 13, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080859
Dong Y, Faridniya H, Ebrahimi Z, Zhao Z. Gamified Exercise in Virtual Reality: A Novel Intervention for Enhancing Mental Health and Reducing Suicidal Ideation in Older Adults. Healthcare. 2025; 13(8):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080859
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yujie, Hossein Faridniya, Zinat Ebrahimi, and Zijian Zhao. 2025. "Gamified Exercise in Virtual Reality: A Novel Intervention for Enhancing Mental Health and Reducing Suicidal Ideation in Older Adults" Healthcare 13, no. 8: 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080859
APA StyleDong, Y., Faridniya, H., Ebrahimi, Z., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Gamified Exercise in Virtual Reality: A Novel Intervention for Enhancing Mental Health and Reducing Suicidal Ideation in Older Adults. Healthcare, 13(8), 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080859









