Arthroscopy for Femoroacetabular Impingement in Athletes Versus Non-Athletes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
- P (Problem): femoroacetabular impingement (FAI);
- I (Intervention): arthroscopy;
- C (Comparison): athletes versus non-athletes;
- O (Outcomes): patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) and complications;
- T (Timings): A minimum follow-up period of 24 months;
- D (Design): clinical study.
2.3. Selection and Data Collection
2.4. Data Items
2.5. Assessment of the Risk of Bias
2.6. Synthesis Method
3. Results
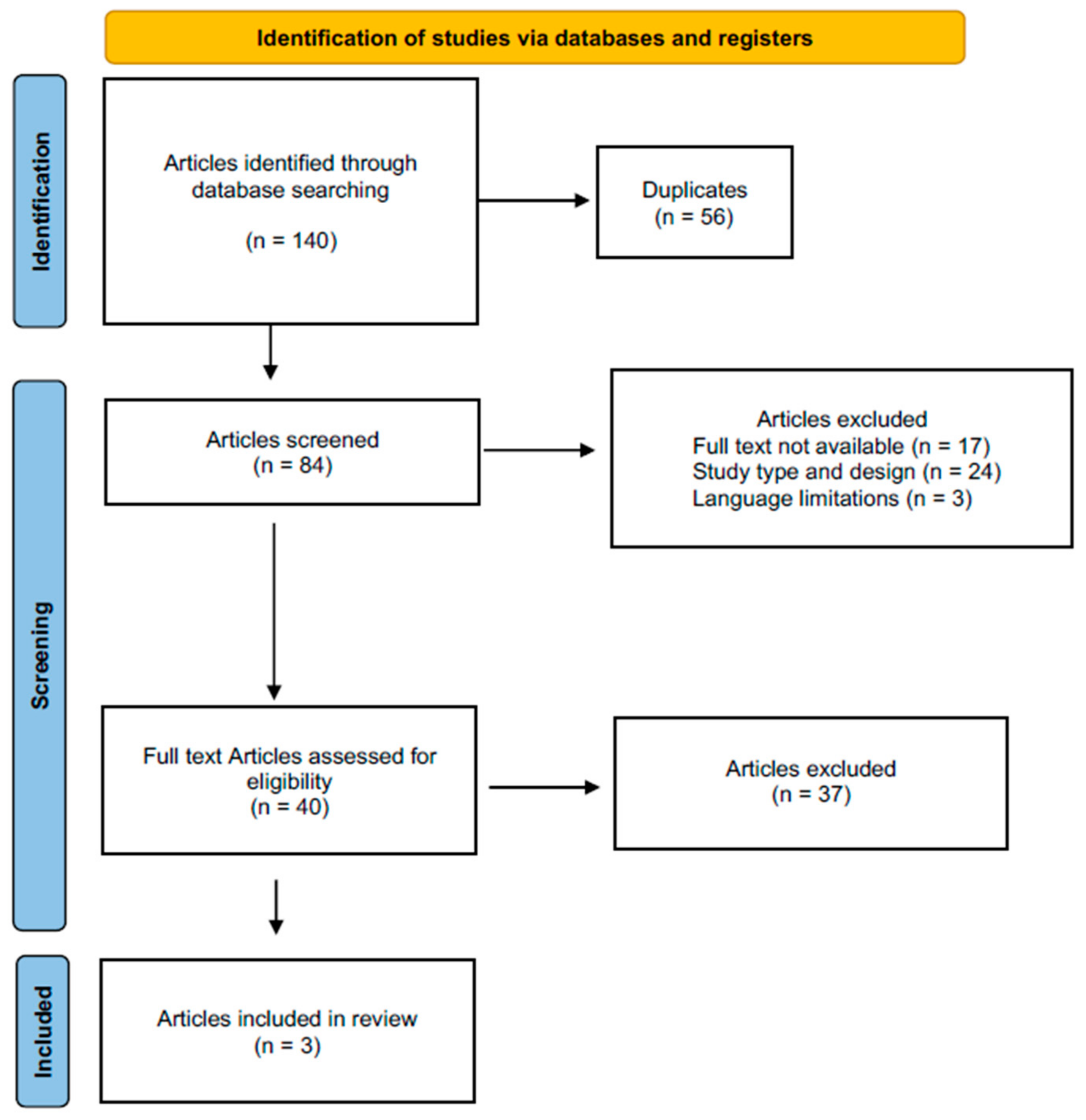
3.1. Study Selection
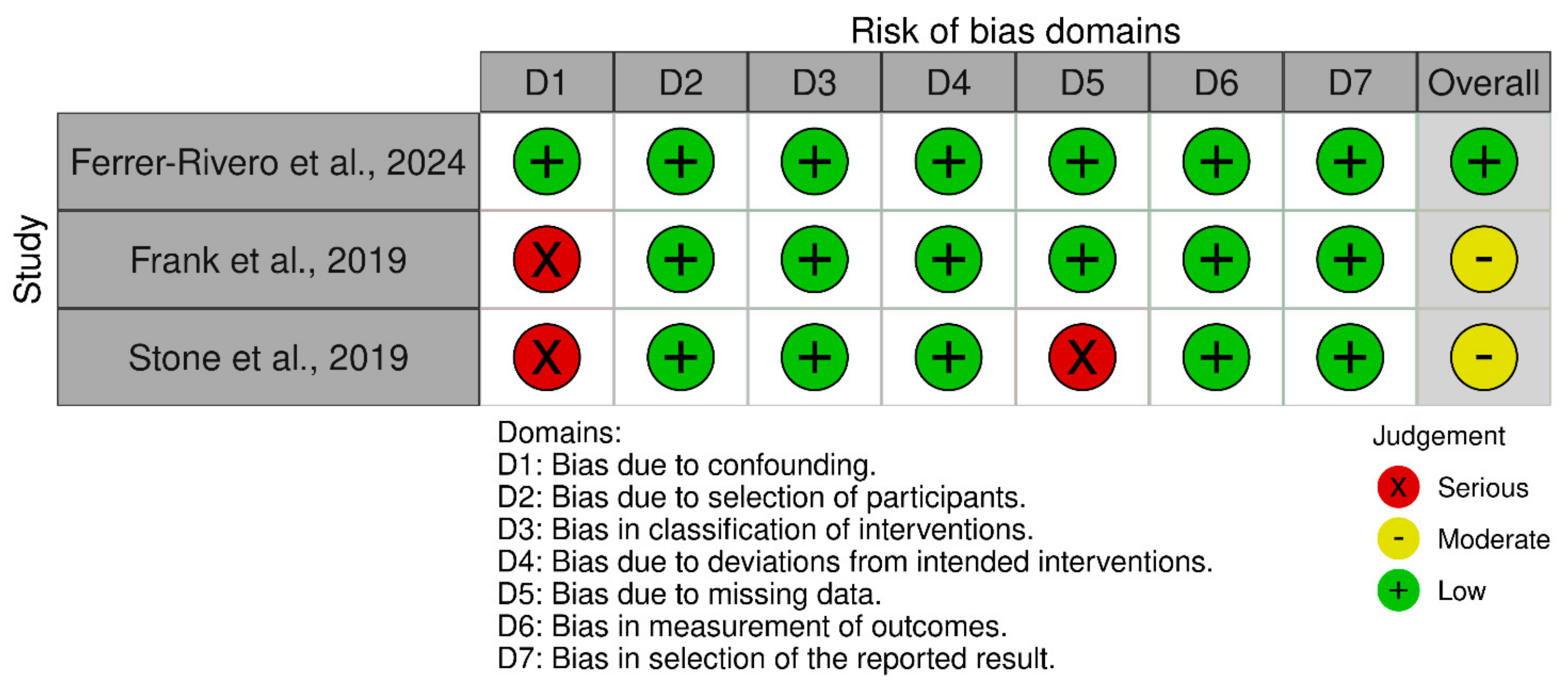
3.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
3.3. Study Characteristics and Results of Individual Studies
3.4. Baseline Comparability
3.5. Synthesis of Results
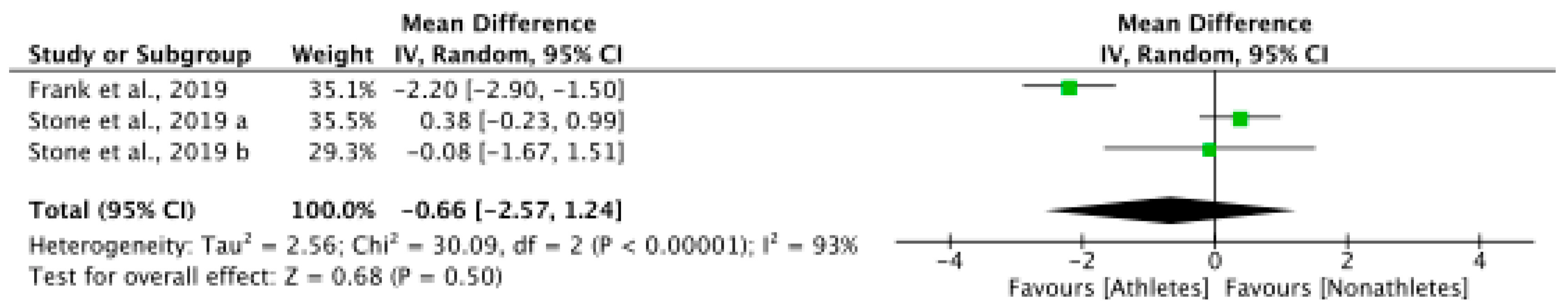
3.6. Meta-Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serong, S.; Schutzbach, M.; Fickert, S.; Niemeyer, P.; Sobau, C.; Spahn, G.; Zinser, W.; Landgraeber, S. Parameters affecting baseline hip function in patients with cam-derived femoroacetabular impingement syndrome: Data analysis from the German Cartilage Registry. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2021, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierannunzii, L. Femoroacetabular impingement: Question-driven review of hip joint pathophysiology from asymptomatic skeletal deformity to end-stage osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2019, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, M.; Kalhor, M.; Leunig, M.; Ganz, R. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: Femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2005, 87, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rego, P.; Beaulé, P.E.; Ayeni, O.R.; Tey, M.; Marin-Peña, O.; Dantas, P.; Wilkin, G.; Grammatopoulos, G.; Mafra, I.; Smit, K.; et al. Femoroacetabular Impingement: What the Surgeon Wants to Know. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2019, 23, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiman, M.P.; Goode, A.P.; Cook, C.E.; Hölmich, P.; Thorborg, K. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for the diagnosis of hip femoroacetabular impingement/labral tear: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, A.; Schenk, P.; Jentzsch, T.; Rahm, S.; Zingg, P.O. FAI morphology increases the risk for osteoarthritis in young people with a minimum follow-up of 25 years. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2021, 141, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Oca, C.; Trivellin, G.; D’Orazio, L.; Sambugaro, E.; Mezzari, S.; Zanetti, G.; Corbo, V.R.; Magnan, B. Hip arthroscopy in osteoarthritis consequent to FAI. Acta Biomed. 2016, 87 (Suppl. S1), 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ao, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y. Postoperative femoral head cartilage injury after hip arthroscopic treatment for femoroacetabular impingement syndrome and labral tear. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2024, 25, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Lindtner, R.A.; Schaller, L.; Schmaranzer, F.; Schmaranzer, E.; Vavron, P.; Endstrasser, F.; Brunner, A. Hip arthroscopy with initial access to the peripheral compartment for femoroacetabular impingement: Midterm results from a large-scale patient cohort. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2024, 25, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatz, M.; Driessen, A.; Eschweiler, J.; Tingart, M.; Migliorini, F. Arthroscopic surgery versus physiotherapy for femoroacetabular impingement: A meta-analysis study. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2020, 30, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Liu, Y.; Catalano, G.; Trivellas, A.; Eschweiler, J.; Tingart, M.; Maffulli, N. Medium-term results of arthroscopic treatment for femoroacetabular impingement. Br. Med. Bull. 2021, 138, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliorini, F.; Maffulli, N. Arthroscopic Management of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 3708–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Zurmuhle, C.A.; Stetzelberger, V.M.; Schwab, J.M.; Steppacher, S.D.; Tannast, M. The New Bern Chondrolabral Classification Is Reliable and Reproducible. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2021, 479, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narvaez, M.V.; Cady, A.; Serrano, B.; Youssefzadeh, K.; Banffy, M. Outside-In Capsulotomy of the Hip for Arthroscopic Pincer Resection. Arthrosc. Tech. 2021, 10, e615–e620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, A.O.; Falotico, G.; Enseki, K.; Cunha, R.A.; Ejnisman, B.; Arliani, G.; Cohen, M. Morphological Changes of the Hip Commonly Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement Are Not Correlated with Rotational Range of Hip Motion in Elite Soccer Athletes. Sports Health 2021, 13, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigg, S.D.; Schroeder, J.D.; Hulsopple, C. Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2020, 19, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, H.; Trane, R.N.; Pomeranz, S.J. Cam and Pincer Type of Femoroacetabular Impingement. J. Surg. Orthop. Adv. 2016, 25, 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Bensler, S.; Dietrich, T.J.; Zubler, V.; Pfirrmann, C.W.A.; Sutter, R. Pincer-type MRI morphology seen in over a third of asymptomatic healthy volunteers without femoroacetabular impingement. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, K.A.; Mojica, E.S.; Lott, A.; Carter, C.; Gonzalez-Lomas, G. Characterization of pincer-type Hip impingement in professional women’s ice hockey players. Phys. Sportsmed. 2023, 51, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clohisy, J.C.; Baca, G.; Beaulé, P.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Larson, C.M.; Millis, M.B.; Podeszwa, D.A.; Schoenecker, P.L.; Sierra, R.J.; Sink, E.L.; et al. Descriptive epidemiology of femoroacetabular impingement: A North American cohort of patients undergoing surgery. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, T.R.; Johnson, B.L.; Morris, W.Z.; Montanez, B.; Serbin, P.A.; Wagner, K.J., 3rd; Wilson, P.L.; Alizai, H.; Ellis, H.B., Jr. Soft Tissue Cam Impingement in Adolescents: MRI Reveals Impingement Lesions Underappreciated on Radiographs. Am. J. Sports Med. 2023, 51, 3749–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.; Yen, Y.M.; Tourn, D.; Smit, K.; Carsen, S. A Unique and Characteristic Cam FAI Morphology in Young Patients with Comorbid Inflammatory Conditions. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2020, 102, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimmick, S.; Stevens, K.J.; Brazier, D.; Anderson, S.E. Femoroacetabular impingement. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 51, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, M.; Yeung, M.; Simunovic, N.; Ayeni, O.R. Does Femoroacetabular Impingement Contribute to the Development of Hip Osteoarthritis? A Systematic Review. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2015, 23, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisciotti, A.; Pogliacomi, F.; Cepparulo, R.; Fiorentino, G.; DI Pietto, F.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Bisciotti, A.; Bisciotti, G.N. Femoroacetabular impingement: Correlation between imaging parameters, sport activity and chondral damage. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriaza, R.; Saavedra-García, M.; Arriaza, A.; Cruz-Cámara, A.; Leyes, M.; Cerezal, L.; Maestro, A. Prevalence of hip femoroacetabular impingement deformities in high-level (La Liga) male professional football players. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne, M.; Ng, K.C.G.; Mantovani, G.; Catelli, D.S. Biomechanics of Femoroacetabular Impingement. In Sports Injuries: Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment and Rehabilitation; Doral, M.N., Karlsson, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Liu, Y.; Eschweiler, J.; Baroncini, A.; Tingart, M.; Maffulli, N. Increased range of motion but otherwise similar clinical outcome of arthroscopy over open osteoplasty for femoroacetabular impingement at midterm follow-up: A systematic review. Surgeon 2022, 20, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Maffulli, N.; Baroncini, A.; Eschweiler, J.; Tingart, M.; Betsch, M. Revision Surgery and Progression to Total Hip Arthroplasty After Surgical Correction of Femoroacetabular Impingement: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Sports Med. 2022, 50, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Maffulli, N.; Knobe, M.; Eschweiler, J.; Tingart, M.; Baroncini, A. Arthroscopic labral repair for femoroacetabular impingement: A systematic review. Surgeon 2022, 20, e225–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Baroncini, A.; Eschweiler, J.; Knobe, M.; Tingart, M.; Maffulli, N. Return to sport after arthroscopic surgery for femoroacetabular impingement. Surgeon 2023, 21, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Maffulli, N.; Bell, A.; Cuozzo, F.; Hildebrand, F.; Weber, C.D. Midterm results after arthroscopic femoral neck osteoplasty combined with labral debridement for cam type femoroacetabular impingement in active adults. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucenti, L.; Maffulli, N.; Bardazzi, T.; Pipino, G.; Pappalardo, G.; Migliorini, F. No Effect of Cigarette Smoking in the Outcome of Arthroscopic Management for Femoroacetabular Impingement: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucenti, L.; Maffulli, N.; Bardazzi, T.; Saggini, R.; Memminger, M.; Simeone, F.; Migliorini, F. Return to Sport Following Arthroscopic Management of Femoroacetabular Impingement: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Cocconi, F.; Bardazzi, T.; Masoni, V.; Gardino, V.; Pipino, G.; Maffulli, N. The ligamentum teres and its role in hip arthroscopy for femoroacetabular impingement: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2024, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhni, E.C.; Ramkumar, P.N.; Cvetanovich, G.; Nho, S.J. Approach to the Patient with Failed Hip Arthroscopy for Labral Tears and Femoroacetabular Impingement. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyl, M.; Walenczak, K.; Domzalski, M.E. Athletes do better after FAI arthroscopic treatment in male population. J. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 26, 2309499018760111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, K.M.; Shah, M.R.; Youm, T. Femoroacetabular impingement—Diagnosis and treatment. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 2010, 68, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.M.; Farooqi, A.S.; Feroe, A.G.; Lee, A.; Cusano, A.; Novais, E.; Wuerz, T.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Parisien, R.L. Open and arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: A review of current concepts. J. Hip Preserv. Surg. 2022, 9, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Tian, K.; Gao, G.; Liu, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Arthroscopic Repair of Acetabular Cartilage Delamination Using Chondral Nail Fixation in Patients With Femoroacetabular Impingement. Arthrosc. Tech. 2024, 13, 102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, L.; Tharakan, S.; Klein, B.; Trasolini, R.G.; Sgaglione, N.A.; Cohn, R.M. Capsular Repair, Labral Repair, and Femoroplasty are Increasingly Performed for the Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome. Arthroscopy 2024, 40, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrum, C.L. Editorial Commentary: Earlier Hip Arthroscopy May Result in Improved Outcomes for Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome in Symptomatic Athletes: No Time Like the Present Could Mean Better Luck Next Year. Arthroscopy 2022, 38, 2192–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, R.F.; Melugin, H.P.; Zhou, J.; LaPrade, M.D.; Bernard, C.; Leland, D.; Levy, B.A.; Krych, A.J. Incidence of Femoroacetabular Impingement and Surgical Management Trends Over Time. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, A.E.; Bedi, A.; Horner, N.S.; de Sa, D.; Simunovic, N.; Philippon, M.J.; Ayeni, O.R. Indications and Outcomes for Microfracture as an Adjunct to Hip Arthroscopy for Treatment of Chondral Defects in Patients with Femoroacetabular Impingement: A Systematic Review. Arthroscopy 2016, 32, 190–200.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, J.W.; Jones, K.S. Hip arthroscopy in athletes: 10-year follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 2140–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, M.J.; Miller, S.T.; Geeslin, A.G. Rehabilitation and Return to Sport After Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement: A Review of the Recent Literature and Discussion of Advanced Rehabilitation Techniques for Athletes. Arthrosc. Sports Med. Rehabil. 2022, 4, e125–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, I.M.; Nwachukwu, B.U.; Beck, E.C.; Jan, K.; Gowd, A.K.; Nho, S.J. Comparing Outcomes of Competitive Athletes Versus Nonathletes Undergoing Hip Arthroscopy for Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenabar, T.; O’Donnell, J. Successful treatment of isolated, partial thickness ligamentum teres (LT) tears with debridement and capsulorrhaphy. Hip Int. 2013, 23, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhart, J.J.; Streit, J.J.; Bedi, A.; Bush-Joseph, C.A.; Nho, S.J.; Salata, M.J. Correlation of pelvic incidence with cam and pincer lesions. Am. J. Sports Med. 2014, 42, 2649–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkara, A.A.; Westermann, R.W.; Rosneck, J.; Lynch, T.S. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Outcomes After Hip Arthroscopy in Femoroacetabular Impingement. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, J.; Logishetty, K.; Davda, K.; Iranpour, F. Cams and pincer impingement are distinct, not mixed: The acetabular pathomorphology of femoroacetabular impingement. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howick, J.; Glasziou, P.; Greenhalgh, T.; Heneghan, C.; Liberati, A.; Moschetti, I.; Phillips, B.; Thornton, H.; Goddard, O.; Hodgkinson, M. The 2011 Oxford CEBM Levels of Evidence. Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. 2011. Available online: https://www.cebm.net/index.aspx?o=5653 (accessed on January 2025).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.; Maffulli, N.; Eschweiler, J.; Schenker, H.; Tingart, M.; Betsch, M. Arthroscopic versus mini-open rotator cuff repair: A meta-analysis. Surgeon 2023, 21, e1–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.L.; Philippon, M.J. Evidence of validity for the hip outcome score in hip arthroscopy. Arthroscopy 2007, 23, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 6.3 (updated February 2022); Cochrane: London, UK, 2022; Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on January 2025).
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernan, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savovic, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Rivero, J.; Chahla, J.; Lizano-Diez, X.; Andriola, V.; López-Zabala, I.; Soler-Cano, A.; Tey-Pons, M. Hip arthroscopy is an effective treatment for high-level female athletes. J. Isakos 2024, 9, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.M.; Kunze, K.N.; Beck, E.C.; Neal, W.H.; Bush-Joseph, C.A.; Nho, S.J. Do Female Athletes Return to Sports After Hip Preservation Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome?: A Comparative Analysis. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2019, 7, 2325967119831758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.V.; Beck, E.C.; Malloy, P.; Chahla, J.; Nwachukwu, B.U.; Neal, W.H.; Nho, S.J. Preoperative Predictors of Achieving Clinically Significant Athletic Functional Status After Hip Arthroscopy for Femoroacetabular Impingement at Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up. Arthroscopy 2019, 35, 3049–3056.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author and Year | Journal | Design | Follow-Up (Months) | Group | Patients (n) | Mean Age | Mean BMI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrer-Rivero et al., 2024 [59] | J ISAKOS | Retrospective | 32.4 | Athletes | 11 | 32.0 | 21.7 |
| Non-Athletes | 22 | 32.0 | 21.7 | ||||
| Frank et al., 2019 [60] | Orthop J Sports Med | Retrospective | 31.2 | Athletes | 97 | 36.0 | 23.8 |
| Non-Athletes | 97 | 37.8 | 27.4 | ||||
| Stone et al., 2019 [61] | Arthroscopy | Retrospective | 24.0 | Non-Athletes | 464 | 31.6 | 24.6 |
| Non-Athletes | 60 | 31.6 | 24.6 | ||||
| Athletes | 47 | 31.6 | 24.6 | ||||
| Athletes | 10 | 31.6 | 24.6 |
| Endpoint | Athletes (n = 165) | Non-Athletes (n = 643) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean follow-up (months) | 28.8 ± 3.5 | 25.4 ± 2.9 | 0.99 |
| Mean age | 35.6 ± 1.2 | 32.7 ± 2.3 | 0.4 |
| Mean-BMI | 23.6 ± 0.6 | 25.1 ± 1.1 | 0.2 |
| Women (%) | 100% (108 of 108) | 95% (556 of 583) | 0.7 |
| VAS (mean) | 6.8 ± 1.8 | 6.7 ± 2.0 | 0.8 |
| HOS-ADL (mean) | 66.9 ± 16.6 | 55.3 ± 18.6 | 0.3 |
| HOS-SSS (mean) | 43.2 ± 20.3 | 42.1 ± 22.8 | 0.5 |
| Endpoint | Athletes (n = 165) | Non-Athletes (n = 643) | MD | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS | 1.5 ± 1.9 | 2.1 ± 2.4 | −0.5 | 0.7 |
| HOS-ADL | 91.6 ± 9.9 | 74.6 ± 24.0 | 17.0 | 0.5 |
| HOS-SSS | 82.5 ± 20.4 | 73.2 ± 27.6 | 9.3 | 0.4 |
| Endpoint | Athletes (n = 165) | Non-Athletes (n = 643) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reoperation | 3.1% (3 of 97) | 2.1% (2 of 97) | 0.7 |
| Progression to THA | 0% (0 of 97) | 1.0% (1 of 97) | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Migliorini, F.; Maffulli, N.; Bardazzi, T.; Ramasubramanian, S.; Jeyaraman, N.; Jeyaraman, M. Arthroscopy for Femoroacetabular Impingement in Athletes Versus Non-Athletes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare 2025, 13, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13050470
Migliorini F, Maffulli N, Bardazzi T, Ramasubramanian S, Jeyaraman N, Jeyaraman M. Arthroscopy for Femoroacetabular Impingement in Athletes Versus Non-Athletes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare. 2025; 13(5):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13050470
Chicago/Turabian StyleMigliorini, Filippo, Nicola Maffulli, Tommaso Bardazzi, Swaminathan Ramasubramanian, Naveen Jeyaraman, and Madhan Jeyaraman. 2025. "Arthroscopy for Femoroacetabular Impingement in Athletes Versus Non-Athletes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Healthcare 13, no. 5: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13050470
APA StyleMigliorini, F., Maffulli, N., Bardazzi, T., Ramasubramanian, S., Jeyaraman, N., & Jeyaraman, M. (2025). Arthroscopy for Femoroacetabular Impingement in Athletes Versus Non-Athletes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare, 13(5), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13050470








