Mind the Gap Between Estimated Needs and Current Resources in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
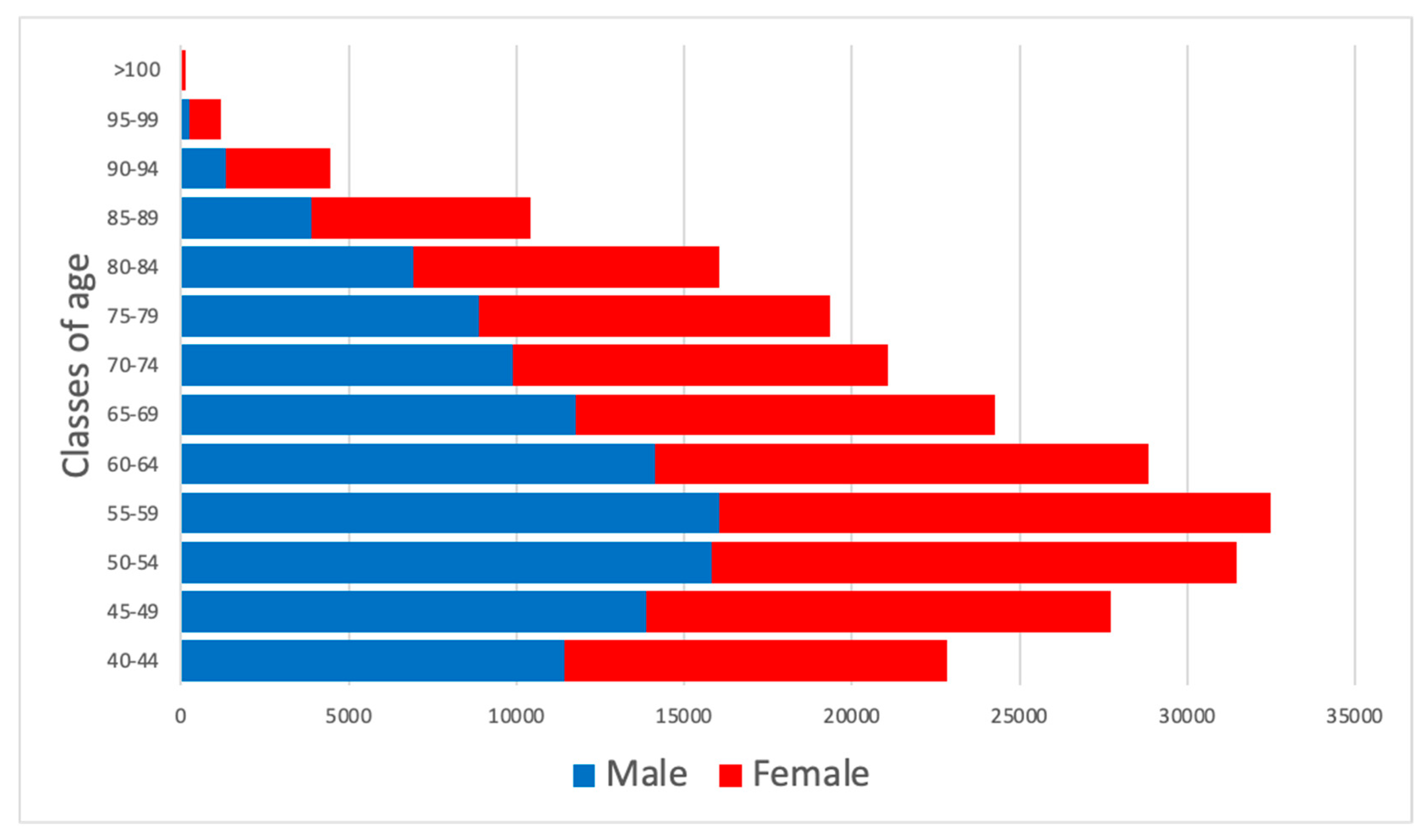
2.1. Inhabitants Determination
2.2. Choice of Epidemiologic Studies to Determine CKD Prevalence
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Operative Procedures for the Estimation of CKD Prevalence According to eGFR and Albuminuria
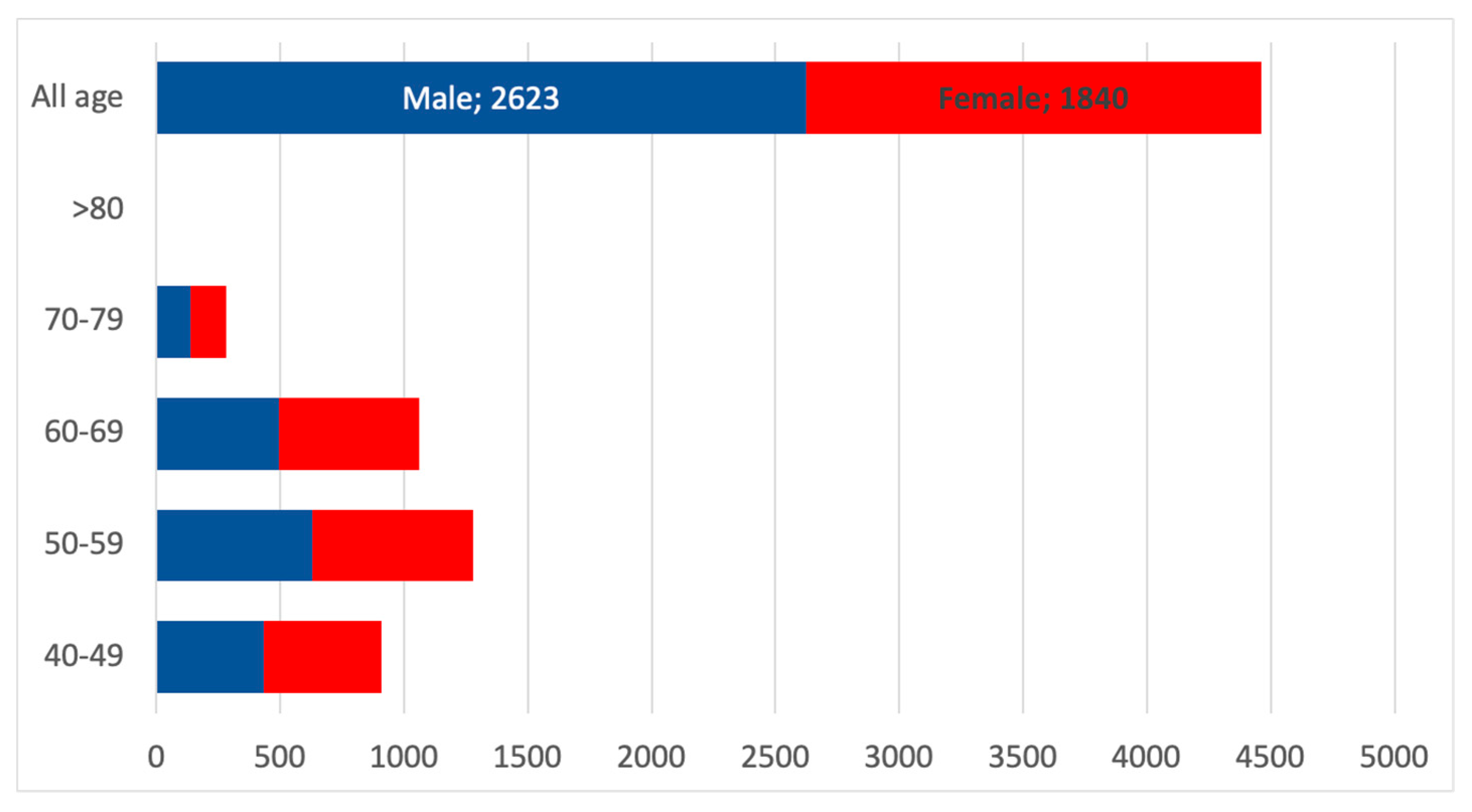
2.4. Estimation of the Number of Nephrologists Controls
- -
- 14 visits per day, five days a week, 48 weeks a year.
- -
- 30 min for each consultation.
- -
- An average period of 3 h per week, related to other management activities related to the outpatient clinic.
3. Results
3.1. CKD G1
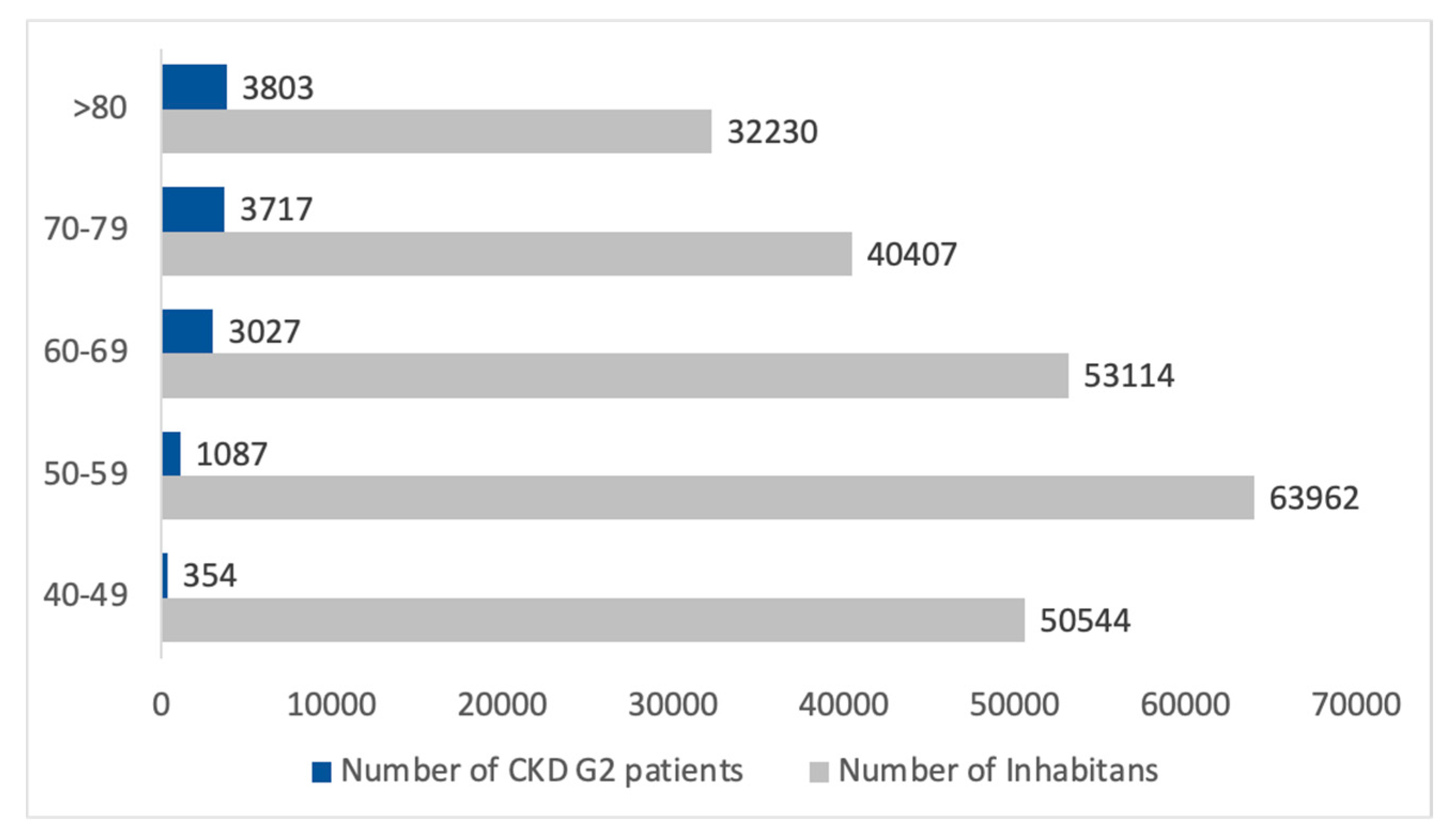
3.2. CKD G2
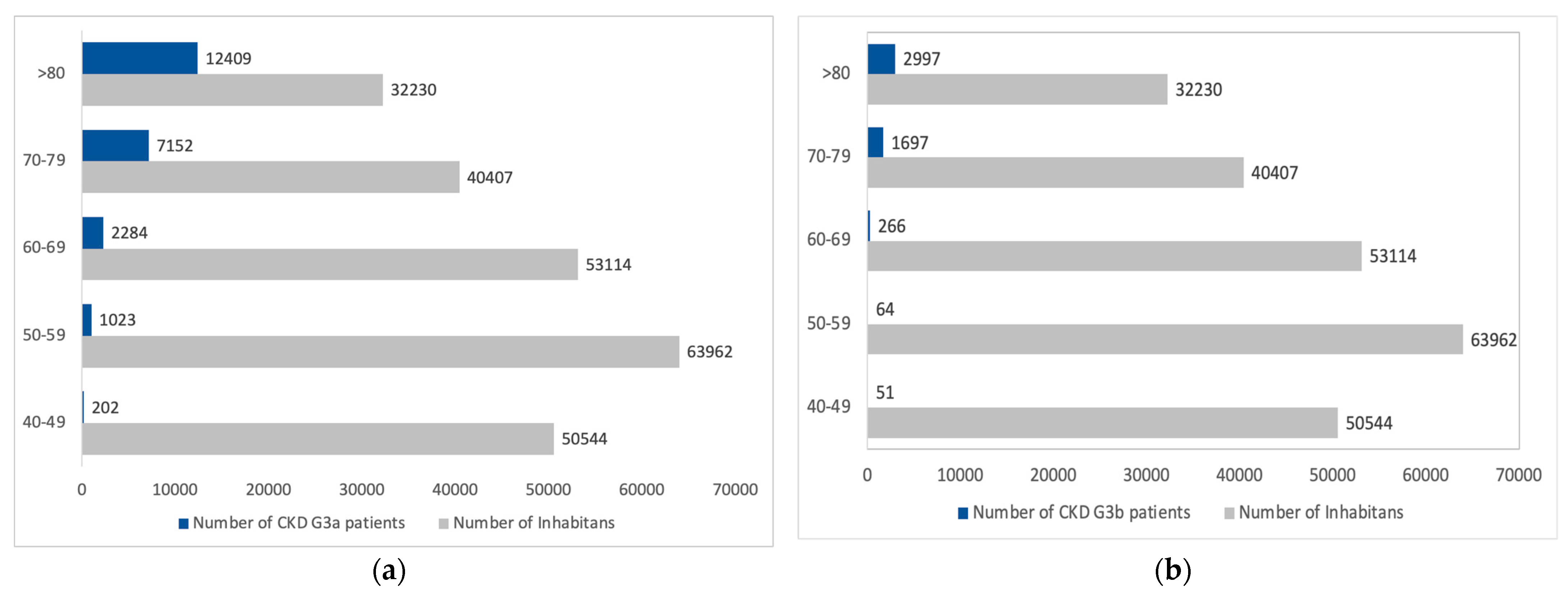
3.3. CKD G3
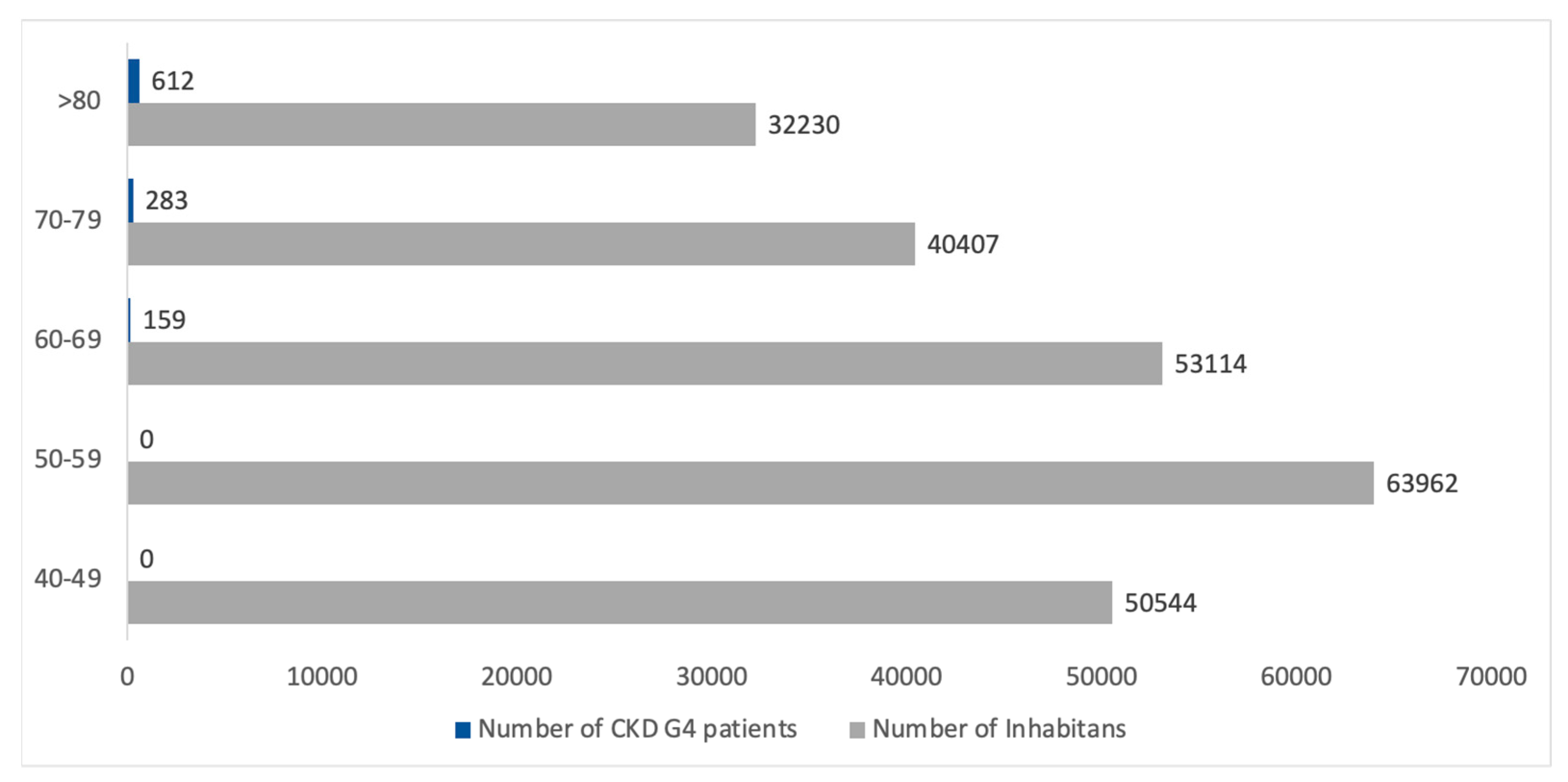
3.4. CKD G4
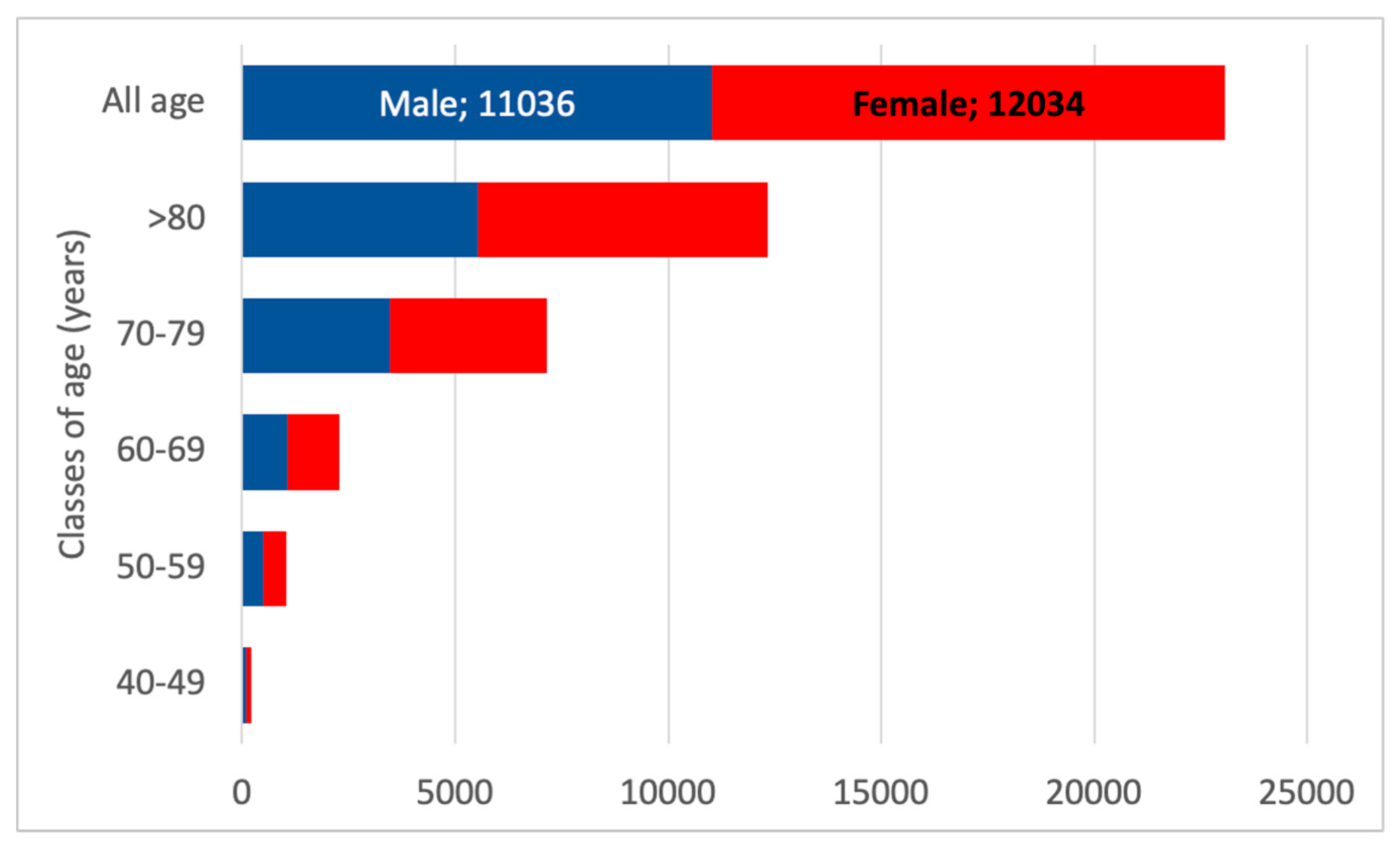
3.5. CKD G5
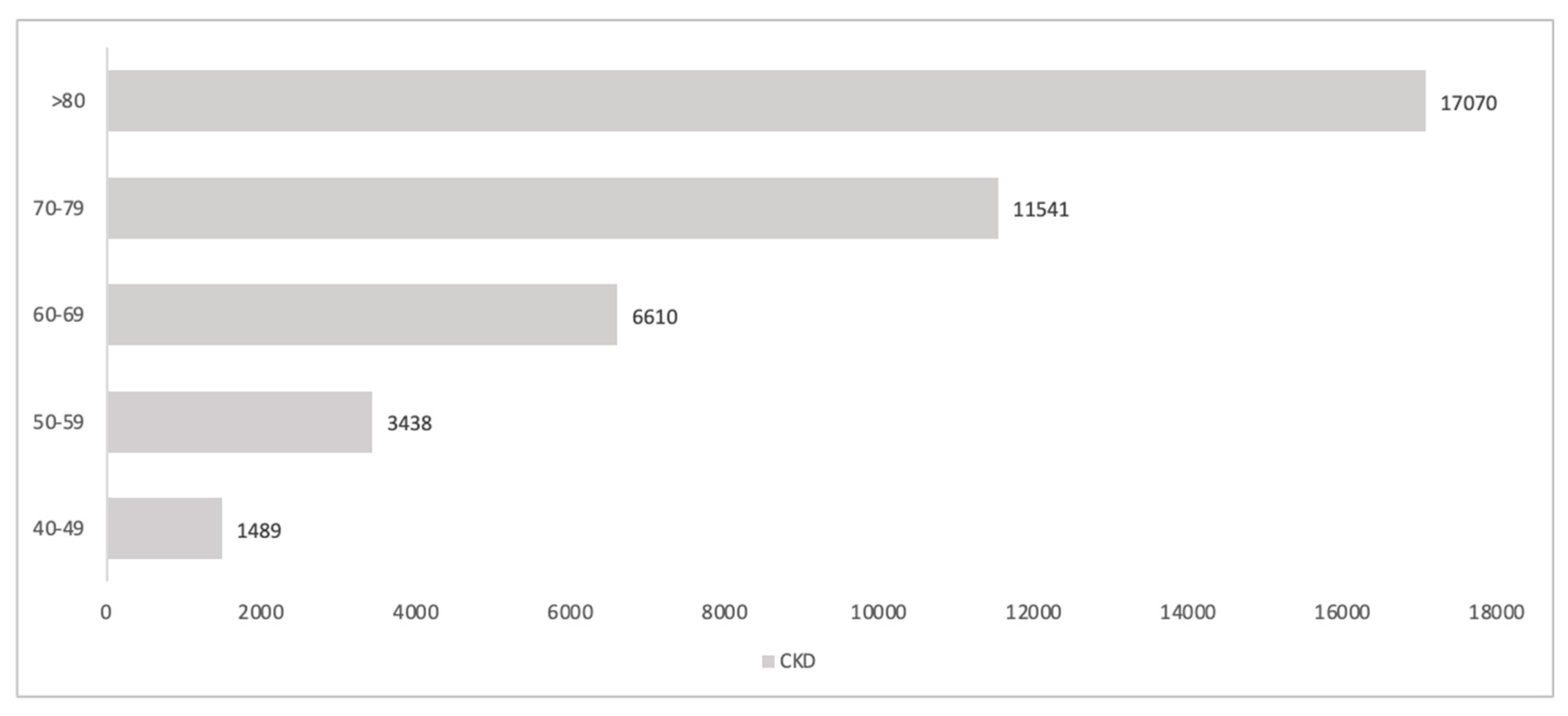
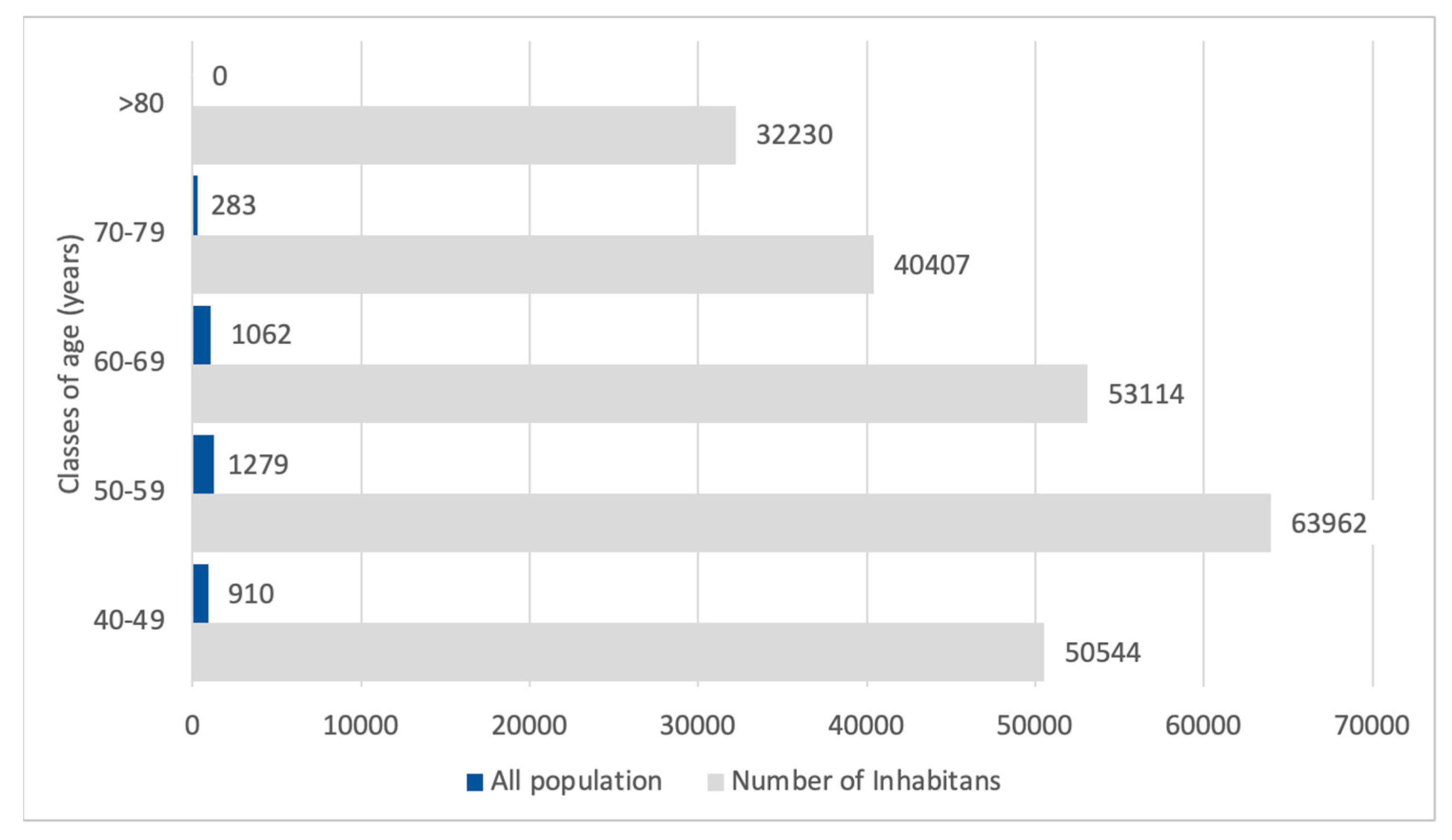
3.6. Projection of the Number of Nephrologist Consultations in the Whole Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| eGFR | estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| INCIPE | Initiative on Nephropathy, of relevance to public health, which is Chronic, possibly in its Initial stages, and carries a Potential risk of major clinical Endpoints |
| CAREHES | Cardiovascular risk in Renal Patients of the Italian Health Examination Survey |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 |
| MRA | Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist |
| GLP-1 RA | Glucagon-like peptide-1 Receptor Agonists |
| ISTAT | Italian Statistics Institute |
| RRT | Renal Replacement Therapy |
| GP | General Practitioner |
References
- Vanholder, R.; Annemans, L.; Brown, E.; Gansevoort, R.; Gout-Zwart, J.J.; Lameire, N.; Morton, R.L.; Oberbauer, R.; Postma, M.J.; Tonelli, M.; et al. Reducing the costs of chronic kidney disease while delivering quality health care: A call to action. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse, R.J.; Milders, J.; Rotmans, J.I.; Caskey, F.J.; Evans, M.; Torino, C.; Szymczak, M.; Drechsler, C.; Wanner, C.; Pippias, M.; et al. Predicting Hospitalization and Related Outcomes in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review, External Validation, and Development Study. Kidney Med. 2025, 7, 101016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2100–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2162–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Velde, M.; Matsushita, K.; Coresh, J.; Astor, B.C.; Woodward, M.; Levey, A.; de Jong, P.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium. Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A collaborative meta-analysis of high-risk population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tungsanga, S.; Fung, W.; Okpechi, I.G.; Ye, F.; Ghimire, A.; Li, P.K.-T.; Shlipak, M.G.; Tummalapalli, S.L.; Arruebo, S.; Caskey, F.J.; et al. Organization and Structures for Detection and Monitoring of CKD Across World Countries and Regions: Observational Data From a Global Survey. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2024, 84, 457–468.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyesubula, R.; Conroy, A.L.; Calice-Silva, V.; Kumar, V.; Onu, U.; Batte, A.; Kaze, F.F.; Fabian, J.; Ulasi, I. Screening for Kidney Disease in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Semin. Nephrol. 2022, 42, 151315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/kidney-disease/php/data-research/index.html (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Available online: https://kidney.ca/KFOC/media/images/PDFs/Facing-the-Facts-2023-HIghlights-from-the-Annual-Statistics-on-Organ-Donation.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Nagai, K.; Asahi, K.; Iseki, K.; Yamagata, K. Estimating the prevalence of definitive chronic kidney disease in the Japanese general population. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2021, 25, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.; Randall, S.; Lee, C.M.Y.; Thomas, E.; Chakera, A.; Chai, K.; Estai, M.; Frith, M.; Hendrie, D.; Boyd, J.; et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in Western Australia, 2010–2020. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e092320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, K.; Stel, V.S.; Gambaro, G.; Hallan, S.; Völzke, H.; Ärnlöv, J.; Kastarinen, M.; Guessous, I.; Vinhas, J.; Stengel, B.; et al. CKD Prevalence Varies across the European General Population. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenssen, T.G.; Bodegård, J.; Sveen, K.A.; Thuresson, M.; Birkeland, K.I. Prevalence, outcomes, costs, and treatments of a contemporary population with chronic kidney disease in Norway: A nationwide observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2025, 26, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, C.; Palacios, B.; Aranda, U.; Capel, M.; Sicras, A.; Sicras, A.; Hormigo, A.; Alcázar, R.; Manito, N.; Botana, M. Costs and healthcare utilisation of patients with chronic kidney disease in Spain. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2021, 21, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, C.; Aranda, U.; Palacios, B.; Capel, M.; Sicras, A.; Sicras, A.; Hormigo, A.; Alcázar, R.; Manito, N.; Botana, M. Epidemiology, clinical profile, management, and two-year risk complications among patients with chronic kidney disease in Spain. Nefrol. Engl. Ed. 2021, 41, 670–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, A.G.; Casserly, L.F.; Cronin, C.J.; Chernenko, T.; Cullen, W.; Hannigan, A.; Saran, R.; Johnson, H.; Browne, G.; Ferguson, J.P. Prevalence and variation of Chronic Kidney Disease in the Irish health system: Initial findings from the National Kidney Disease Surveillance Programme. BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, F.J.; Methven, S.; Boag, D.E.; Spalding, E.M.; Macgregor, M.S. Chronic kidney disease prevalence and secular trends in a UK population: The impact of MDRD and CKD-EPI formulae. QJM Int. J. Med. 2011, 104, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumann, N.; Baumeister, S.E.; Rettig, R.; Lieb, W.; Werner, A.; Döring, A.; Peters, A.; Koenig, W.; Hannemann, A.; Wallaschofski, H.; et al. Regional variation of chronic kidney disease in Germany: Results from two population-based surveys. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2015, 40, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambaro, G.; Yabarek, T.; Graziani, M.S.; Gemelli, A.; Abaterusso, C.; Frigo, A.C.; Marchionna, N.; Citron, L.; Bonfante, L.; Grigoletto, F.; et al. Prevalence of CKD in northeastern Italy: Results of the INCIPE study and comparison with NHANES. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarda, L.; Bozzeda, A.L.; Ricci, P. Epidemiologia della insufficienza renale cronica in una popolazione: I residenti nella provincia di Mantova [Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease in the population of the Mantua district]. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2010, 27 (Suppl. 52), S10-6. [Google Scholar]
- Gorini, A.; Costanzo, A.M.; Egan, C.G.; di Luzio Paparatti, U. Renal status in adult volunteers in central Italy: Results from Family Abbott Renal Disease Monitoring Project (FARM) study. J. Nephrol. 2012, 25, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donfrancesco, C.; Palleschi, S.; Palmieri, L.; Rossi, B.; Noce, C.L.; Pannozzo, F.; Spoto, B.; Tripepi, G.; Zoccali, C.; Giampaoli, S. Estimated glomerular filtration rate, all-cause mortality and cardiovascular diseases incidence in a low risk population: The MATISS study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciao, G.; Berardi, P.; Vecchi, L.; Buoncristiani, E.; Eroli, M.; Levêque, A. Epidemiologia della malattia renale cronica in una popolazione: I residenti nel territorio umbro “eugubino-gualdese” [Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease in a population: Residents in the territory of Umbria “Gubbio—Gualdese”]. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2014, 31, gin/31.3.2. [Google Scholar]
- Marino, C.; Ferraro, P.M.; Bargagli, M.; Cascini, S.; Agabiti, N.; Gambaro, G.; Davoli, M. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the Lazio region, Italy: A classification algorithm based on health information systems. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuano, V.; Lamaida, N.; Borrelli, M.I.; Capuano, E.; Fasolino, A.; Capuano, E.; Sonderegger, M.; Capuano, R.; Citro, V.; Franculli, F. Prevalenza e trend (1998–2008) dell’insufficienza renale cronica in un’area dell’Italia meridionale: I dati del progetto VIP [Chronic kidney disease prevalence and trends (1998–2008) in an area of southern Italy. The data of the VIP project]. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2012, 29, 445–451. [Google Scholar]
- Pani, A.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Masala, M.; Piras, D.; Atzeni, A.; Pilia, M.G.; Ferreli, L.; Balaci, L.; Curreli, N.; Delitala, A.; et al. Prevalence of CKD and its relationship to eGFR-related genetic loci and clinical risk factors in the SardiNIA study cohort. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nicola, L.; Donfrancesco, C.; Minutolo, R.; Lo Noce, C.; Palmieri, L.; De Curtis, A.; Iacoviello, L.; Zoccali, C.; Gesualdo, L.; Conte, G.; et al. Prevalence and cardiovascular risk profile of chronic kidney disease in Italy: Results of the 2008–12 National Health Examination Survey. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015, 30, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, C.; Pagnoni, F.; Cena, T.; Ceriotti, D.; De Ambrosi, D.; De Vito, M.; Faggiano, F. Estimate of the prevalence of subjects with chronic diseases in a province of Northern Italy: A retrospective study based on administrative databases. BMJ Open. 2023, 13, e070820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, K.; Jager, K.J.; Dounousi, E.; Kainz, A.; Nitsch, D.; Ärnlöv, J.; Rothenbacher, D.; Browne, G.; Capuano, V.; Ferraro, P.M.; et al. Methodology used in studies reporting chronic kidney disease prevalence: A systematic literature review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30 (Suppl. S4), iv6–iv16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Ahmed, S.B.; Carrero, J.J.; Foster, B.; Francis, A.; Hall, R.K.; Herrington, W.G.; Hill, G.; Inker, L.A.; Kazancıoğlu, R.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatridi, F.; Carrero, J.J.; Cornec-Le Gall, E.; Kanbay, M.; Luyckx, V.; Shroff, R.; Ferro, C.J. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Children and Adults: A commentary from the European Renal Best Practice (ERBP). Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2025, 40, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Shi, J. Domain-specific physical activity and sedentary behavior in relation to chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional analysis of 24,950 U.S. adults in NHANES 1999–2012. Ren Fail. 2025, 47, 2525460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Li, M.; Fan, Y. Sedentary behavior and risk of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2025, 57, 2917–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, Y.; Baciga, F.; Bulighin, F.; Amicone, M.; Mosconi, G.; Storari, A.; Brugnano, R.; Pozzato, M.; Motta, D.; D’alessandro, C.; et al. Physical activity and exercise in chronic kidney disease: Consensus statements from the Physical Exercise Working Group of the Italian Society of Nephrology. J. Nephrol. 2024, 37, 1735–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimori, J.Y.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Oka, T.; Isaka, Y. Plant-Dominant Low-Protein Diets: A Promising Dietary Strategy for Mitigating Disease Progression in People with Chronic Kidney Disease-A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, F.K.; Zattarin, A.; Cinquini, C.; Toniazzo, S.; Francini Pesenti, F.; Stefanelli, L.F.; Cacciapuoti, M.; Bettin, E.; Calò, L.A.; Spinella, P. Low-Protein Diet in Elderly Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 4 and 5 in Conservative Management: Focus on Sarcopenia Development. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri Khosroshahi, R.; Zare, M.; Zeraattalab-Motlagh, S.; Kiany, F.; Talebi, S.; Mohammadi, H. Effects of a Low-Protein Diet on Kidney Function in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. Rev. 2025, 83, e2127–e2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakino, S.; Hasegawa, K.; Tamaki, M.; Minato, M.; Inagaki, T. Kidney-Gut Axis in Chronic Kidney Disease: Therapeutic Perspectives from Microbiota Modulation and Nutrition. Nutrients 2025, 17, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, F.K.; Stefanelli, L.F.; Zattarin, A.; Lovato Correa Dias, L.; Redi, G.; Khalf, R.; Del Prete, D.; Nalesso, F. Protein Counting as an Educational Strategy to Optimize Low-Protein-Diet Adherence and Satisfaction in Stage 4 and 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, G.; Di Lauro, M.; Cornali, K.; Masci, C.; Vanni, G.; Vita, C.; Noce, A. Sustainability and role of plant-based diets in chronic kidney disease prevention and treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1562409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H.; Yang, T.; Sun, M.; Yang, Z.; Guo, X. Effect of intensive water-salt diet nursing intervention on blood pressure and volume load in patients with chronic renal failure. Ren. Fail. 2025, 47, 2474854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, J.; Rao, J.; Lai, W.; Wei, Q.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhang, J. Joint effects of sodium intake and circadian rhythm of urinary sodium excretion on prognosis of chronic kidney disease: A prospective study. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2025, 16, 20406223251344474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group; Herrington, W.G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Hauske, S.J.; Emberson, J.R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.J.; et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuffield Department of Population Health Renal Studies Group. SGLT Inhibitor Meta-Analysis Cardio-Renal Trialists’ Consortium. Impact of diabetes on the effects of sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors on kidney outcomes: Collaborative meta-analysis of large placebo controlled trials. Lancet 2022, 400, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staplin, N.; Roddick, A.J.; Emberson, J.; Reith, C.; Riding, A.; Wonnacott, A.; Kuverji, A.; Bhandari, S.; Baigent, C.; Haynes, R.; et al. Net effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibition in different patient groups: A meta-analysis of large placebo-controlled randomized trials. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 41, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Dekkers, C.C.J.; Barbour, S.J.; Cattran, D.; Abdul Gafor, A.H.; Greasley, P.J.; Laverman, G.D.; Lim, S.K.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on proteinuria in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease (DIAMOND): A randomised, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, G.; Taylor, A.H.; Fujita, T.; Ohtsu, H.; Lindhardt, M.; Rossing, P.; Boesby, L.; Edwards, N.C.; Ferro, C.J.; Townend, J.N.; et al. Effect of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists on proteinuria and progression of chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, P.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Bakris, G.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Gislum, M.; Gough, S.C.L.; Idorn, T.; Lawson, J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.E.; et al. The rationale, design and baseline data of FLOW, a kidney outcomes trial with once-weekly semaglutide in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, F.K.; Fanton, G.; Zanetti, F.; Carta, M.; Nalesso, F.; Novara, G. Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease: Epidemiological Analysis in a NorthEastern District of Italy Focusing on Access to Nephrological Care. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Coelho, F.; Andrade, L. Smoking and Kidney Disease: Risk Factors, Challenges, and Preventive Strategies. Contrib. Nephrol. 2021, 199, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kang, S.; Joo, Y.S.; Lee, C.; Nam, K.H.; Yun, H.R.; Park, J.T.; Chang, T.I.; Yoo, T.H.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Smoking, Smoking Cessation, and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Results from KNOW-CKD Study. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2021, 23, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.; Lee, S.; Joo, Y.S.; Nam, K.H.; Yun, H.R.; Chang, T.I.; Kang, E.W.; Yoo, T.H.; Han, S.H.; Kang, S.W.; et al. Association of smoking with incident CKD risk in the general population: A community-based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeinzadeh, F.; Shahidi, S.; Seirafian, S.; Rouhani, M.H.; Mortazavi, M.; Maghami-Mehr, A.; Vahdat, S. Association of alcohol consumption with the prevalence and various stages of chronic kidney disease. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2023, 28, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.S.; Koh, H.; Nam, K.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Yun, H.R.; Park, J.T.; Kang, E.W.; Chang, T.I.; et al. Alcohol Consumption and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: Results from the Korean Cohort Study for Outcome in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, B.; Song, N.; Shi, Y.; Fang, Y.; Ding, X. Alcohol consumption and its association with chronic kidney disease: Evidence from a 12-year China health and Nutrition Survey. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, E.C.; Hirst, J.A.; Verbakel, J.Y.; McLellan, J.H.; Hobbs, F.D.R.; Stevens, R.J.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S. Systematic Review and Metaanalysis Comparing the Bias and Accuracy of the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration Equations in Community-Based Populations. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, P.M.; Lombardi, G.; Gambaro, G. Impact of the new, race-free CKD-EPI equation on prevalence and clinical outcomes of CKD in northeastern Italy: The INCIPE study. J. Nephrol. 2022, 35, 1767–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., III; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Inker, L.A.; Coresh, J. GFR estimation: From physiology to public health. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velema, M.S.; de Ronde, W. Elevated plasma creatinine due to creatine ethyl ester use. Neth. J. Med. 2011, 69, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williamson, L.; New, D. How the use of creatine supplements can elevate serum creatinine in the absence of underlying kidney pathology. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, bcr2014204754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolignano, D.; Coppolino, G.; Lacquaniti, A.; Buemi, M. From kidney to cardiovascular diseases: NGAL as a biomarker beyond the confines of nephrology. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 40, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, F.K.; Filippi, I.; Giavarina, D.; Kaushik, M.; Rodighiero, M.P.; Crepaldi, C.; Teixeira, C.; Nadal, A.F.; Rosner, M.H.; Ronco, C. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the early diagnosis of peritonitis: The case of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. Contrib. Nephrol. 2012, 178, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onopiuk, A.; Tokarzewicz, A.; Gorodkiewicz, E. Cystatin C: A kidney function biomarker. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 68, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eeghen, S.A.; Wiepjes, C.M.; T’Sjoen, G.; Nokoff, N.J.; den Heijer, M.; Bjornstad, P.; van Raalte, D.H. Cystatin C-Based eGFR Changes during Gender-Affirming Hormone Therapy in Transgender Individuals. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhuyzen, J. Cystatin C: A promising marker and predictor of impaired renal function. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2006, 36, 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, V.; Martino, F.; Gastaldon, F.; Scalzotto, E.; Caprara, C.; Fortunato, A.; Pinaffo, G.; Marchetti, C.; Fabbi, F.; Giavarina, D.; et al. Copeptin levels and kidney function in ADPKD: Case-control study. Clin. Nephrol. 2016, 86, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, V.; Gastaldon, F.; Caprara, C.; Giuliani, A.; Martino, F.; Ferrari, F.; Ronco, C. Predictors of rapid disease progression in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Minerva Med. 2017, 108, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjune, S.; Oehm, S.; Todorova, P.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Erger, F.; Benzing, T.; Burst, V.; Grundmann, F.; Antczak, P.; et al. Copeptin in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Real-world experiences from a large prospective cohort study. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 2194–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, G.; Cruciat, R.C.; Leucuta, D.C.; Al Srouji, N.; Popa, S.L.; Ismaiel, M.; Dumitrascu, D.I.; Ismaiel, A. Copeptin as a Biomarker in Chronic Kidney Disease-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Selistre, L.; Rech, D.L.; de Souza, V.; Iwaz, J.; Lemoine, S.; Dubourg, L. Diagnostic Performance of Creatinine-Based Equations for Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate in Adults 65 Years and Older. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castel-Branco, M.M.; Lavrador, M.; Cabral, A.C.; Pinheiro, A.; Fernandes, J.; Figueiredo, I.V.; Fernandez-Llimos, F. Discrepancies among equations to estimate the glomerular filtration rate for drug dosing decision making in aged patients: A cross sectional study. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2024, 46, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyzer, J.M.; Hoffmann, J.J.; Ringoir, L.; Nabbe, K.C.; Widdershoven, J.W.; Pop, V.J. Age- and gender-specific brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) reference ranges in primary care. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepaldi, C.; Rosner, M.; Teixeira, C.; Martos, L.B.; Martino, F.K.; Rodighiero, M.P.; Ronco, C. Is brain natriuretic peptide a reliable biomarker of hydration status in all peritoneal dialysis patients? Blood Purif. 2014, 37, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alehagen, U.; Goetze, J.P.; Dahlström, U. Reference intervals and decision limits for B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and its precursor (Nt-proBNP) in the elderly. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2007, 382, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan Manani, S.; Virzì, G.M.; Giuliani, A.; Clementi, A.; Brocca, A.; Dissegna, D.; Martino, F.; d’Amore, E.S.G.; Ronco, C. Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and Kidney Transplantation: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Nephron 2017, 136, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, D.; Luna, B.; Loayza, E.; Taboada, G.; Ramaswami, U. Prevalence of Fabry disease in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2023, 140, 107714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiderscheit, A.K.; Hauer, J.J.; Smith, R.J.H. C3 glomerulopathy: Understanding an ultra-rare complement-mediated renal disease. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2022, 190, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, M.; Gowrishankar, S. Glomerulocystic disease. NDT Plus. 2010, 3, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Caprara, C.; Kinsey, G.R.; Corradi, V.; Xin, W.; Ma, J.Z.; Scalzotto, E.; Martino, F.K.; Okusa, M.D.; Nalesso, F.; Ferrari, F.; et al. The Influence of Hemodialysis on T Regulatory Cells: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Blood Purif. 2016, 42, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.Y.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.P.; Yang, C.W.; Ko, E.J.; Ryu, D.-R.; Kang, S.-W.; Park, J.T.; et al. Outcomes of Remote Patient Monitoring for Automated Peritoneal Dialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nephron 2021, 145, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozali, M.T.; Satibi, S.; Forthwengel, G. The impact of mobile health applications on the outcomes of patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Life 2023, 16, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhu, J.; Xie, J.; Luo, Y.; Dong, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Cheng, A.S. The Impact of Digital Health Interventions on Psychological Health, Self-Efficacy, and Quality of Life in Patients With End-Stage Kidney Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e74414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amici, G.; D’Angela, D.; Lo Cicero, A.; Romanini, D.; Martino, F.K.; Spandonaro, F. Pilot health technology assessment study: Organizational and economic impact of remote monitoring system for home automated peritoneal dialysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, F.K.; Novara, G.; Nalesso, F.; Calò, L.A. Conservative Management in End-Stage Kidney Disease between the Dialysis Myth and Neglected Evidence-Based Medicine. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.K.; Chow, K.M.; Van de Luijtgaarden, M.W.; Johnson, D.W.; Jager, K.J.; Mehrotra, R.; Naicker, S.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Yu, X.Q.; Lameire, N. Changes in the worldwide epidemiology of peritoneal dialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K.; Blake, P.; Cordy, P.; Garg, A.X. Global trends in rates of peritoneal dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.X.; Gao, X.; Inglese, G.; Chuengsaman, P.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Yu, A. A Global Overview of the Impact of Peritoneal Dialysis First or Favored Policies: An Opinion. Perit. Dial. Int. 2015, 35, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.cuore.iss.it/indagini/CuoreData (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/diabete/epidemiologia-italia (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/obesita/epidemiologia-italia (accessed on 2 October 2025).

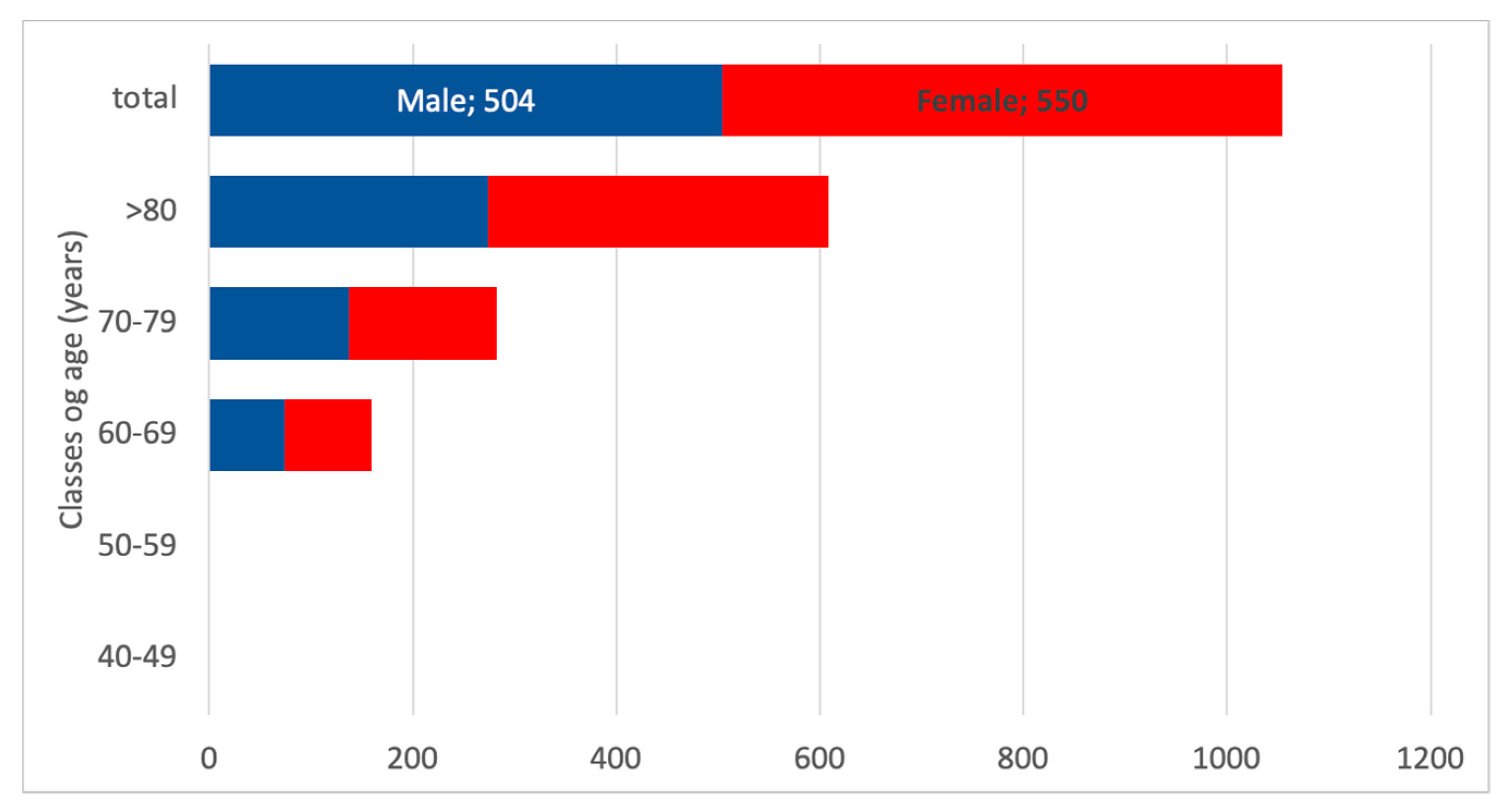
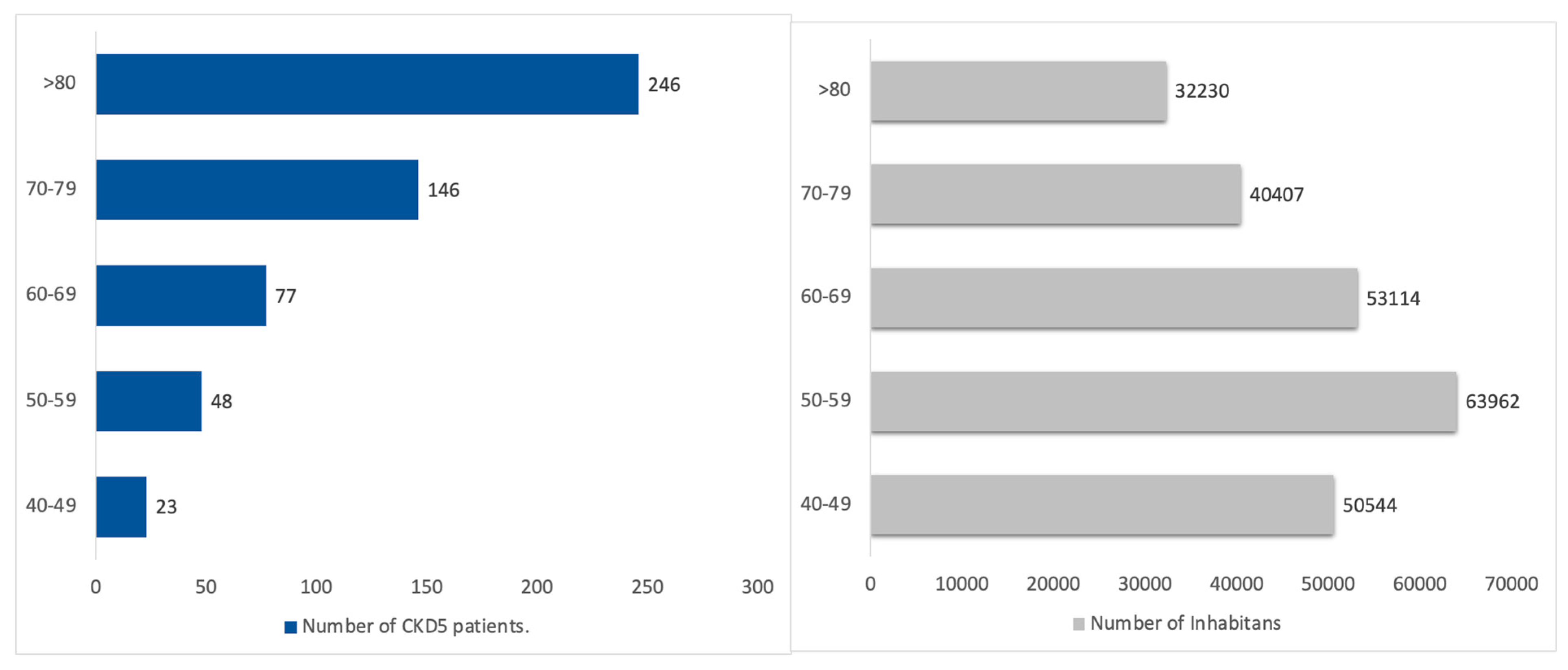
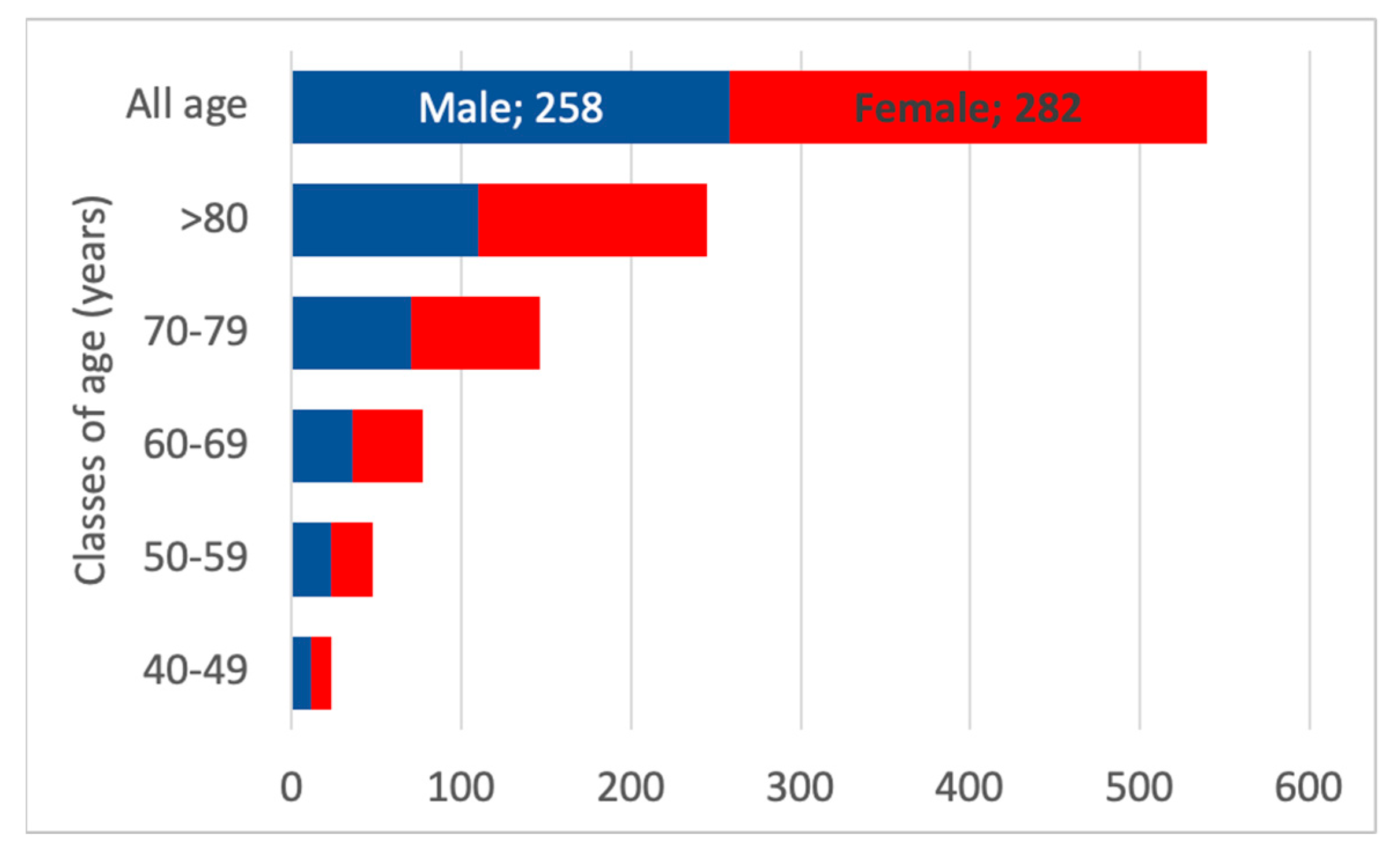
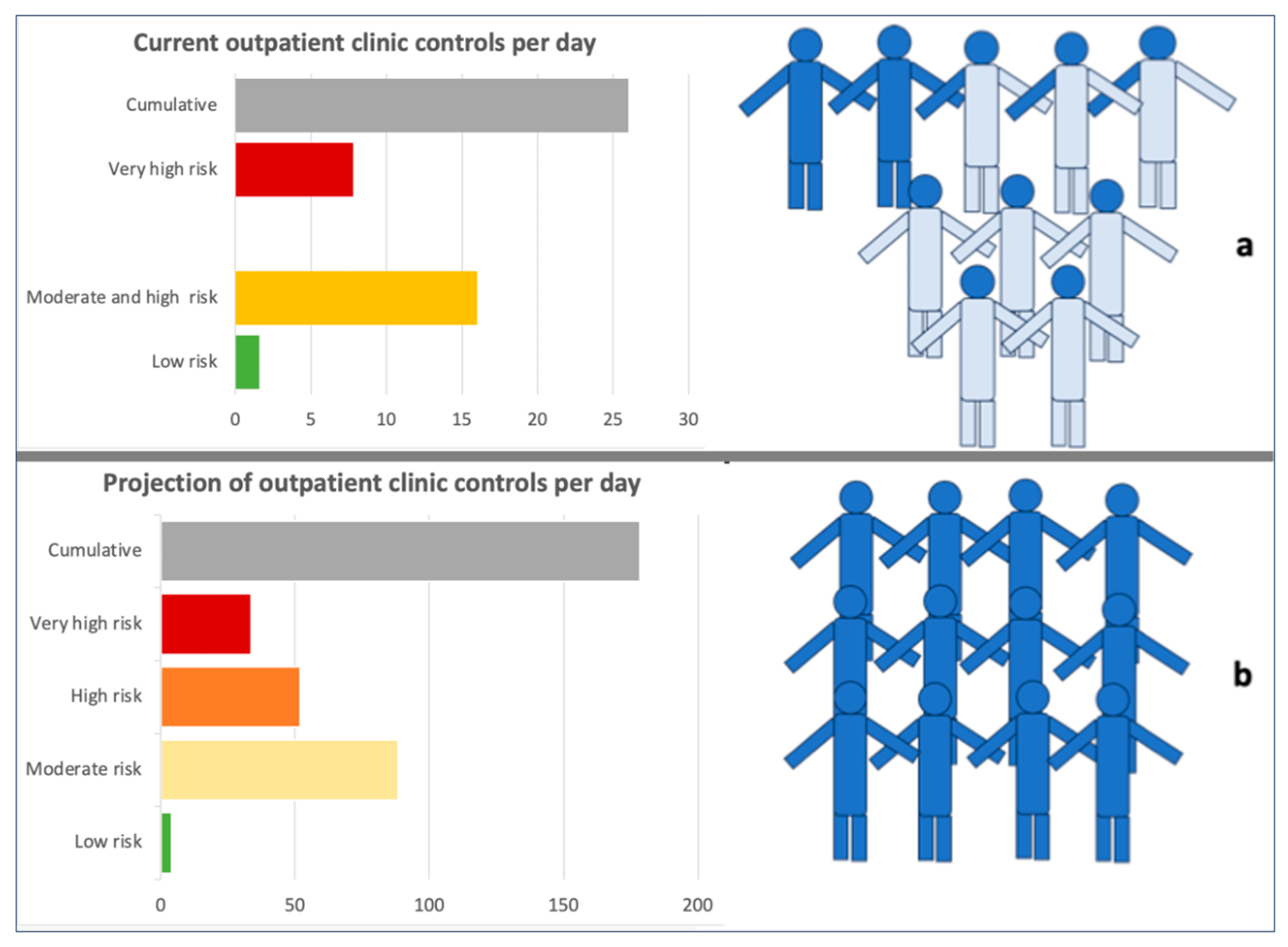
| CKD 1 | CKD2 | CKD 3a | CKD3b | CKD 4 | CKD 1 to 4 Stages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 1.7% | 4.3% | 5.1% | 1.3% | 0.3% | 12.7% |
| Men | 1.7% | 5.0% | 4.8% | 1.4% | 0.3% | 13.2% |
| Female | 1.6% | 3.7% | 5.4% | 1.3% | 0.2% | 12.2% |
| 40–49 years | 1.8% | 0.7% | 0.3% | 0.1% | 0.0% | 2.9% |
| 50–59 years | 2.0% | 1.7% | 1.5% | 0.1% | 0.0% | 5.3% |
| 60–69 years | 2.0% | 5.7% | 3.8% | 0.5% | 0.3% | 12.3% |
| 70–89 years | 0.7% | 9.2% | 13.5% | 4.2% | 0.7% | 28.2% |
| >80 years | 0.0% | 11.8% | 29.2% | 9.3% | 1.9% | 52.2% |
| G1 * | G2 * | G3 * | G4 * | G5 ** | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 1.7 | 4.3 | 5.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | ||||||||||
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | |
| % | 0.088 | 0.790 | 0.122 | 0.063 | 0.799 | 0.138 | 0.794 | 0.149 | 0.057 | 0.517 | 0.172 | 0.431 | 0.2 | ||
| Age | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| 40–49 years | 4.2% |
| 50–59 years | 8.7% |
| 60–69 years | 13.9% |
| 70–79 years | 26.4% |
| 80–89 years | 34.9% |
| >90 years | 9.4% |
| G1 | G2 | G3a | G3b | G4 | G5 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | |
| Number of controls | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | +4 | +4 | ||
| A1 | A2 | A3 | Cumulative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 359 (359) | 3228 (3228) | 497 (993) | 4084 (4581) |
| G2 | 646 (646) | 8257 (8257) | 1428 (2856) | 10,331 (11,759) |
| G3a | 9730 (9730) | 1830 (3661) | 693 (407) | 12,253 (15,469) |
| G3b | 2480 (4960) | 467 (1400) | 177 (530) | 3123 (6890) |
| G4 | 372 (1117) | 124 (1242) | 1310 (4138) | 807 (2132) |
| G5 no RRT | 340 (1360) | |||
| G1-5 no RRT | 30,939 (42,790) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martino, F.K.; Nalesso, F. Mind the Gap Between Estimated Needs and Current Resources in Chronic Kidney Disease. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222826
Martino FK, Nalesso F. Mind the Gap Between Estimated Needs and Current Resources in Chronic Kidney Disease. Healthcare. 2025; 13(22):2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222826
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartino, Francesca K., and Federico Nalesso. 2025. "Mind the Gap Between Estimated Needs and Current Resources in Chronic Kidney Disease" Healthcare 13, no. 22: 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222826
APA StyleMartino, F. K., & Nalesso, F. (2025). Mind the Gap Between Estimated Needs and Current Resources in Chronic Kidney Disease. Healthcare, 13(22), 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222826







