Biologic Therapies and Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients with Asthma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
- PubMed: (((asthma[Title/Abstract]) AND ((pediatric OR children OR adolescents)) AND (biologic therapies[Title/Abstract] OR omalizumab[Title/Abstract] OR mepolizumab[Title/Abstract] OR benralizumab[Title/Abstract] OR dupilumab[Title/Abstract] OR tezepelumab[Title/Abstract])) AND ((quality of life OR HRQoL OR PAQLQ));
- Scopus: TITLE-ABS-KEY(asthma) AND ALL(pediatric OR children OR adolescents) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(biologic therapies OR omalizumab OR mepolizumab OR benralizumab OR dupilumab OR tezepelumab) AND ALL(quality of life OR HRQoL OR PAQLQ);
- Web of science: (((TS=(asthma)) AND ALL=(pediatric OR children OR adolescents)) AND TS=(biologic therapies OR omalizumab OR mepolizumab OR benralizumab OR dupilumab OR tezepelumab)) AND ALL=(quality of life OR HRQoL OR PAQLQ).
2.2. Study Selection Criteria
2.2.1. (P) Population
2.2.2. (I) Intervention
2.2.3. (C) Comparison
2.2.4. (O) Outcomes
2.2.5. (S) Types of Studies
2.3. Data Extraction Process
- Name of the first author and year of publication;
- Countries in which the study was conducted;
- Type of study;
- Number of participants, their age range, and gender;
- Condition (i.e., asthma phenotype);
- Biologic therapy administered to the participants;
- Comparison between groups (e.g., biologic vs. placebo);
- Treatment and follow-up duration;
- QoL instrument and version used;
- Treatment efficacy on asthma control;
- QoL outcomes.
2.4. Study Quality Assessment
3. Results
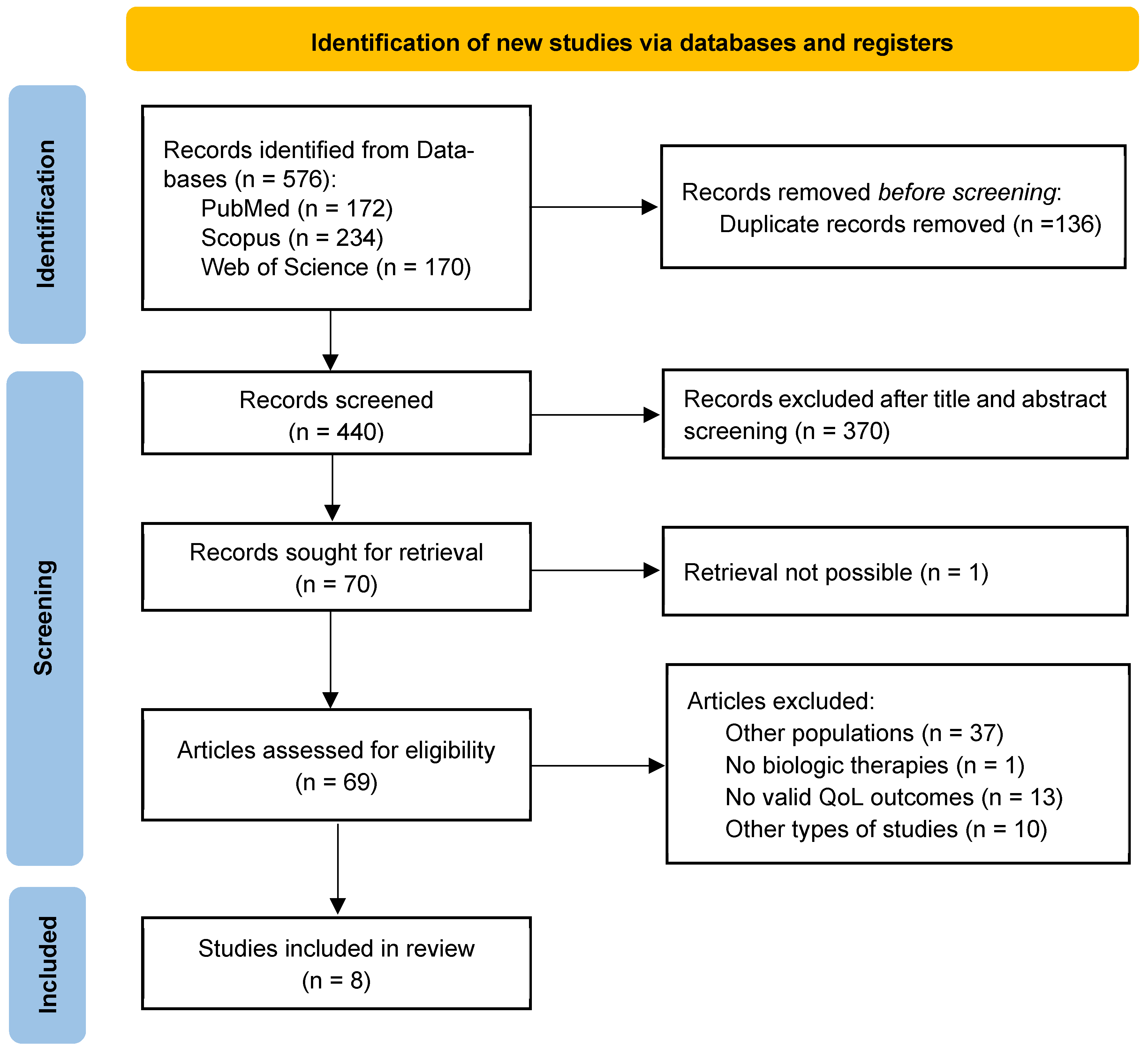
3.1. Literature Identification and Screening
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Efficacy of Biologic Therapies on Asthma Control and HRQoL
3.3.1. Dupilumab and HRQoL
3.3.2. Omalizumab and HRQoL
3.3.3. Mepolizumab and HRQoL
3.4. Studies’ Main Limitations
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanisms Linking Biologic Therapies to HRQoL Improvements
4.2. Parents and Caregivers’ QoL
4.3. Comparative Effectiveness Across Biologic Agents
4.4. Strengths and Limitations of This Review
4.4.1. Strengths
4.4.2. Limitations
4.5. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GINA | Global Initiative for Asthma |
| HRQoL | Health-Related Quality of Life |
| ICS | Inhaled corticosteroids |
| LABA | Long-acting beta-agonists |
| MMAT | Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool |
| PAQLQ | Pediatric Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis |
| QoL | Quality of Life |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| RoB | Risk of Bias |
| SABA | Short-acting beta-agonists |
References
- Dharmage, S.C.; Perret, J.L.; Custovic, A. Epidemiology of Asthma in Children and Adults. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, H.; Oh, J.; Kim, S.; Miligkos, M.; Yon, D.K.; Papadopoulos, N.G. Global Burden of Asthma among Children and Adolescents with Projections to 2050: A Comprehensive Review and Forecasted Modeling Study. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2025, 68, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okobi, O.E.; Okoronkwo, C.A.; Duru, H.; Iyayi, I.R.; Adeakin-Dada, T.O.; Doherty, N.O.; Okobi, O.E.; Okoronkwo, C.A.; Duru, H.O.; Iyayi, I.R.; et al. A Review of the Latest Guidelines for Diagnosing and Managing Asthma in Children in the United States and Canada. Cureus 2024, 16, e68135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, M.; Abu-Hasan, M. Asthma in the Preschool-Age Child. In Kendig & Chernick’s Disorders of the Respiratory Tract in Children, 8th ed.; Saunders: Collingwood, ON, Canada, 2012; pp. 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, S.; Seglani, S.; Challands, J. Perioperative Management of the Child with Asthma. BJA Educ. 2022, 22, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Iniciative for Asthma (GINA). Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention (2024 Update); Global Iniciative for Asthma (GINA): Fontana, WI, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Roberto, G.; Barberi, S.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. What’s New in Pediatric Asthma and Rhinitis Phenotypes and Endotypes? Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 24, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albonasir, D.Z.K.K.; Almasoodi, D.K.N.H.; Aldulaimy, D.A.H.K. A Cross-Sectional Study in Iraq to Evaluate the Quality of Life of Pediatric Patients with Asthma. J. Prev. Diagn. Manag. Hum. Dis. 2023, 3, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Iede, M.; Alfaouri, K.; Manzlgi, D.; Nazzal, L.; Awaisheh, T.; Alsharif, O.; Al-Zayadneh, E. Asthma Control, Its Related Factors, and Impact on Quality of Life among Pediatric Patients at a Tertiary Center in Jordan: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Asthma 2025, 62, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossny, E.; Adachi, Y.; Anastasiou, E.; Badellino, H.; Custovic, A.; El-Owaidy, R.; El-Sayed, Z.A.; Filipovic, I.; Gomez, R.M.; Kalayci, Ö.; et al. Pediatric Asthma Comorbidities: Global Impact and Unmet Needs. World Allergy Organ. J. 2024, 17, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffin, J.M.; Castro, M.; Bacharier, L.B.; Fuhlbrigge, A.L. The Role of Comorbidities in Difficult-to-Control Asthma in Adults and Children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-González, S.; Zabala-Baños, M.d.C.; Astasio-Picado, Á.; Jurado-Palomo, J. Psychological and Sociocultural Determinants in Childhood Asthma Disease: Impact on Quality of Life. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamjamratsri, K.; Suksawat, Y.; Kiewngam, P.; Jotikasthira, W.; Sawatchai, A.; Klangkalya, N.; Kanchongkittiphon, W.; Manuyakorn, W. Longitudinal Study on Peak Expiratory Flow Monitoring and Its Impact on Quality of Life in Childhood Asthma. J. Asthma 2025, 62, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnady, H.G.; Sherif, L.S.; ElGindi, H.D.; Shaaban, F.A.; Abdelmohsen, A.M.; Salah, D.A.; Abdel-Latif, G.A.; Fahmy, R.F. Assessment of Quality of Life of Primary Caregivers of Egyptian Asthmatic Children and Adolescents. Indian J. Community Med. 2020, 45, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElGendi, S.; Mostafa, S.; Walli, M.; Hassan, O.; ElAwady, M.; Omar, D. Assessment of Health-Related Quality of Life in Asthmatic Children and Their Caregivers. Int. J. Med. Sci. Public Health 2017, 6, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Fierstein, J.; Boon, K.; Kanaley, M.; Zavos, P.; Volerman, A.; Vojta, D.; Gupta, R.S. Parental Quality of Life and Self-Efficacy in Pediatric Asthma. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2021, 58, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleath, B.; Carpenter, D.; Davis, S.A.; Garcia, N.; Reuland, D.S.; Tudor, G.; Loughlin, C.E. Adolescent Asthma Management Self-Efficacy and Responsibility: Impact on Asthma Control and Quality-of-Life. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2023, 60, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foronda, C.L.; Kelley, C.N.; Nadeau, C.; Prather, S.L.; Lewis-Pierre, L.; Sarik, D.A.; Muheriwa, S.R. Psychological and Socioeconomic Burdens Faced by Family Caregivers of Children With Asthma: An Integrative Review. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2020, 34, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, H.; Wu, X.; Cui, Y.; Huang, H.; Zheng, S.; Li, H. Caregiver Burden among Parents of School-Age Children with Asthma: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1368519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldirawi, A.; Al-Qudimat, A.R.; Al Rawwad, T.; Alhalaiqa, F.; Alwawi, A.; Jin, Y.; Abuzerr, S.; Hammad, E.; Rjoub, L. Impact of Asthma Control on Quality of Life among Palestinian Children. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabiat, D.H.; Jabery, M.A.A. Health Related Quality of Life in Paediatric Chronic Health Conditions: A Comparative Study among Children and Adolescents in Jordan. Health 2013, 5, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juniper, E.F.; Guyatt, G.H.; Feeny, D.H.; Ferrie, P.J.; Griffith, L.E.; Townsend, M. Measuring Quality of Life in Children with Asthma. Qual. Life Res. Int. J. Qual. Life Asp. Treat. Care Rehabil. 1996, 5, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesse, R.; Borrelli, G.; Mongelli, G.; Mastrorilli, V.; Cardinale, F. Treating Pediatric Asthma According Guidelines. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommanus, S.; Sitcharungsi, R.; Lawpoolsri, S. Effects of an Asthma Education Camp Program on Quality of Life and Asthma Control among Thai Children with Asthma: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maabreh, R.; Alrabab’a, M.H.; Morsy, M.A.; Al-Akash, H.Y.; Rajeh Saifan, A.; Al-Yateem, N. Guideline Implementation for Improved Asthma Management and Treatment Adherence in Children in Jordan. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.M.; Hughes, L.; Ford, W.R. Assessing Inhaler Techniques of Asthma Patients Using Aerosol Inhalation Monitors (AIM): A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulood, K.B.; Khan, M.; Syed Sulaiman, S.A.; Khan, A.H. Assessing the Impact of Health Education Intervention on Asthma Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices: A Cross-Sectional Study in Erbil, Iraq. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, H.; Katchamat, N. Asthma Symptom Self-Monitoring Methods for Children and Adolescents: Present and Future. Children 2025, 12, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, P.; Sundar, S.; Suresh, P.; Vajravelu, L.K.; Aravindhan, V. Interleukin-13 as a Potential Biomarker in the Management of Pediatric Asthma—A Longitudinal Study. Eur. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 23, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnoli, R.; Brambilla, I.; Giovannini, M.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. New Approaches in Childhood Asthma Treatment. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 23, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaverri Repáraz, C.M.; Lacalle Fabo, E.; Erroz Ferrer, M.; Gimeno-Castillo, M.; Castro-Garrido, I.; Ibarzabal-Arregi, M.; González Arza, N.; Viguria, N.; Moreno-Galarraga, L. Tailoring Biologic Therapies for Pediatric Severe Asthma: A Comprehensive Approach. Children 2025, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anda Suárez, P.X.; Romero, U.M.; Méndez, N.G.; Rengel Chalco, M.J.; Vivas Monzón, M.A.; Zavala Gama, C.G. Advancements in Biologic Therapies for Pediatric Asthma: Emerging Therapies and Future Directions. Cureus 2025, 17, e83629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perikleous, E.P.; Steiropoulos, P.; Nena, E.; Paraskakis, E. Biologic Therapies in Pediatric Asthma. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipps, B.E.; Lanier, B.; Milgrom, H.; Deschildre, A.; Hedlin, G.; Szefler, S.J.; Kattan, M.; Kianifard, F.; Ortiz, B.; Haselkorn, T.; et al. Omalizumab in Children with Uncontrolled Allergic Asthma: Review of Clinical Trial and Real-World Experience. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1431–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, V.; Pelaia, C.; Zunno, R.; Pelaia, G. Biologicals Decrease Psychological Distress, Anxiety and Depression in Severe Asthma, despite Covid-19 Pandemic. Respir. Med. 2022, 200, 106916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indolfi, C.; Dinardo, G.; Klain, A.; Contieri, M.; Umano, G.R.; Decimo, A.; Ciprandi, G.; Del Giudice, M.M. Time Effect of Dupilumab to Treat Severe Uncontrolled Asthma in Adolescents: A Pilot Study. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2023, 51, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, C.; Glanville, J.; Briscoe, S.; Featherstone, R.; Littlewood, A.; Metzendorf, M.-I.; Noel-Storr, A.; Paynter, R.; Rader, T.; Thomas, J.; et al. Chapter 4: Searching for and Selecting Studies. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.5 (Updated August 2024); Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: Oxford, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Furuya-Kanamori, L.; Lin, L.; Kostoulas, P.; Clark, J.; Xu, C. Limits in the Search Date for Rapid Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies. Res. Synth. Methods 2023, 14, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methley, A.M.; Campbell, S.; Chew-Graham, C.; McNally, R.; Cheraghi-Sohi, S. PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: A Comparison Study of Specificity and Sensitivity in Three Search Tools for Qualitative Systematic Reviews. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2014, 14, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajvanshi, N.; Kumar, P.; Goyal, J.P. Global Initiative for Asthma Guidelines 2024: An Update. Indian Pediatr. 2024, 61, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippendorff, K. Content Analysis: An Introduction to Its Methodology; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-5063-9566-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Q.N.; Fàbregues, S.; Bartlett, G.; Boardman, F.; Cargo, M.; Dagenais, P.; Gagnon, M.-P.; Griffiths, F.; Nicolau, B.; O’Cathain, A.; et al. The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) Version 2018 for Information Professionals and Researchers. Educ. Inf. 2018, 34, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Hinojosa, N.K.; Sánchez-Tec, G.A. Calidad de Vida En Pacientes Con Asma Alérgica Severa En Tratamiento Con Omalizumab. Rev. Alerg. México 2018, 65, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonica, G.W.; Malvezzi, L.; Blasi, F.; Paggiaro, P.; Mantero, M.; Senna, G.; Heffler, E.; Bonavia, M.; Caiaffa, P.; Calabrese, C.; et al. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps Impact in Severe Asthma Patients: Evidences from the Severe Asthma Network Italy (SANI) Registry. Respir. Med. 2020, 166, 105947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnz-Różyk, K.; Lis, J.; Warchoł, M.; Kucharczyk, A. Clinical and Economic Impact of a One-Year Treatment with Omalizumab in Patients with Severe Allergic Asthma within a Drug Programme in Poland. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akenroye, A.; Lassiter, G.; Jackson, J.W.; Keet, C.; Segal, J.; Alexander, G.C.; Hong, H. Comparative Efficacy of Mepolizumab, Benralizumab, and Dupilumab in Eosinophilic Asthma: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 1097–1105.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarraf, H.N.; Masoud, H.H.; Zidan, M.; Wahba, B. Effectiveness and Safety of Omalizumab in Severe, Persistent IgE-Mediated Asthma in Pediatric and Adult Patients: A Real-World Observational Study in Egyptian Population. J. Asthma 2020, 57, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, T.; Odajima, H.; Okamasa, A.; Kawase, M.; Komatsubara, M.; Mayer, B.; Yancey, S.; Ortega, H. Efficacy and Safety of Mepolizumab in Japanese Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pérez, R.; Poza-Guedes, P.; Mederos-Luis, E.; Sánchez-Machín, I. Real-Life Performance of Mepolizumab in T2-High Severe Refractory Asthma with the Overlapping Eosinophilic-Allergic Phenotype. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchnerová, O.R.; Valena, T.; Novosad, J.; Teřl, M. Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Omalizumab in Patients with Uncontrolled Severe Allergic Asthma from the Czech Republic. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2019, 36, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hew, M.; Gillman, A.; Sutherland, M.; Wark, P.; Bowden, J.; Guo, M.; Reddel, H.K.; Jenkins, C.; Marks, G.B.; Thien, F.; et al. Real-life Effectiveness of Omalizumab in Severe Allergic Asthma above the Recommended Dosing Range Criteria. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilò, M.B.; Martini, M.; Antonicelli, L.; Aliani, M.; Carone, M.; Cecchi, L.; De Michele, F.; Polese, G.; Vaghi, A.; Musarra, A.; et al. Severe Asthma: Follow-up after One Year from the Italian Registry on Severe Asthma (IRSA). Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 55, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Corren, J.; Bourdin, A.; Chupp, G.; Israel, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brightling, C.E.; Griffiths, J.M.; Hellqvist, Å.; Bowen, K.; et al. Tezepelumab in Adults and Adolescents with Severe, Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, M.; Yang, W.H.; Hébert, J.; De Takacsy, F.; Stril, J.-L. The Real World Effect of Omalizumab Add on Therapy for Patients with Moderate to Severe Allergic Asthma: The ASTERIX Observational Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, C.; Pohl, W.; Milger, K.; Skowasch, D.; Schulz, C.; Gappa, M.; Koerner-Rettberg, C.; Jandl, M.; Schmidt, O.; Zehetmayer, S.; et al. Characterization of Obesity in Severe Asthma in the German Asthma Net. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 3417–3424.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasi, S.; Cafarotti, A.; Galletta, F.; Panetta, V.; Riccardi, C.; Calandrelli, V.; Fierro, V.; Dahdah, L.; Artesani, M.C.; Valluzzi, R.L.; et al. Omalizumab Reduces Anaphylactic Reactions and Allows Food Introduction in Food-allergic in Children with Severe Asthma: An Observational Study. Allergy 2025, 80, 1074–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghea, E.C.; Balgradean, M.; Pavelescu, C.; Cirstoveanu, C.G.; Toma, C.L.; Ionescu, M.D.; Bumbacea, R.S. Clinical Experience with Anti-IgE Monoclonal Antibody (Omalizumab) in Pediatric Severe Allergic Asthma—A Romanian Perspective. Children 2021, 8, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, T.B.; Luskin, A.T.; Busse, W.; Zeiger, R.S.; Trzaskoma, B.; Yang, M.; Griffin, N.M.; Chipps, B.E. Omalizumab Effectiveness by Biomarker Status in Patients with Asthma: Evidence From PROSPERO, A Prospective Real-World Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 156–164.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, K.R.; Albers, F.C.; Chipps, B.; Muñoz, X.; Devouassoux, G.; Bergna, M.; Galkin, D.; Azmi, J.; Mouneimne, D.; Price, R.G.; et al. The Clinical Benefit of Mepolizumab Replacing Omalizumab in Uncontrolled Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Allergy 2019, 74, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Therapeutic Efficacy of Omalizumab in Children with Moderate-to-Severe Allergic Asthma Combined with Chronic Sinusitis. Front. Allergy 2023, 4, 1236798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti Randazzese, S.; Lugarà, C.; Galletta, F.; Pioggia, G.; Crisafulli, G.; Caminiti, L.; Gangemi, S.; Ruggeri, P.; Manti, S. Efficacy of Omalizumab after Discontinuation: A Retrospective Single-Center Observational Study in Children with Severe Asthma. Front. Allergy 2025, 6, 1529624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numata, T.; Araya, J.; Miyagawa, H.; Okuda, K.; Takekoshi, D.; Hashimoto, M.; Minagawa, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Hara, H.; Kuwano, K. Real-World Effectiveness of Dupilumab for Patients with Severe Asthma: A Retrospective Study. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, H.; Hahn, B.; Bogart, M.; Bell, C.F.; Bancroft, T.; Chastek, B.; Llanos, J.-P. Impact of Mepolizumab on Exacerbations in Severe Asthma: Results from a U.S. Insurance Claims Data Base. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2020, 41, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitrez, P.M.; De Souza, R.G.; Roncada, C.; Heinzmann-Filho, J.P.; Santos, G.; Pinto, L.A.; Jones, M.H.; Stein, R.T. Impact of Omalizumab in Children from a Middle-income Country with Severe Therapy-resistant Asthma: A Real-life Study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, P.M.; Hinze, C.A.; Campbell, V.; Konwert, S.; Welte, T.; Drick, N.; Kayser, M.Z.; Suhling, H.; Fuge, J. Relationship Between the Response to Antibody Therapy and Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety Disorders in Patients with Severe Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2023, 16, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.P.; Grunwell, J.; Shih, J.; Stephenson, S.; Fitzpatrick, A.M. Exploring the Utility of Noninvasive Type 2 Inflammatory Markers for Prediction of Severe Asthma Exacerbations in Children and Adolescents. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2624–2633.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiß, J.O.; Schmidt, A.; Lindemann, H.; Rudloff, S.; Staatz, A.; Strohner, P.; Becher, G.; Nährlich, L.; Zimmer, K.P. Monitoring of Omalizumab Therapy in Children and Adolescents. Allergol. Sel. 2018, 2, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergienko, D.; Tkachuk, A.; Vyazovaya, I.; Shaboyants, N.; Kirilochev, O. Experience of Long-Term Omalizumab Treatment for Pediatric Asthma in Astrakhan Region. Arch. Euromedica 2020, 10, 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- Haktanir Abul, M.; Naja, A.S.; Fitzpatrick, A.; Phipatanakul, W.; Fleming, L. Evaluation and Management of Severe Asthma in Children. In Severe Asthma; Chung, K.F., Israel, E., Gibson, P.G., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; ISBN 978-1-84984-103-0. [Google Scholar]
- Burg, G.T.; Covar, R.; Oland, A.A.; Guilbert, T.W. The Tempest: Difficult to Control Asthma in Adolescence. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Maspero, J.F.; Rabe, K.F.; Papi, A.; Wenzel, S.E.; Ford, L.B.; Pavord, I.D.; Zhang, B.; Staudinger, H.; Pirozzi, G.; et al. Liberty Asthma QUEST: Phase 3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Study to Evaluate Dupilumab Efficacy/Safety in Patients with Uncontrolled, Moderate-to-Severe Asthma. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.; Lipworth, B.J. Impact of Biologic Therapy on the Small Airways Asthma Phenotype. Lung 2022, 200, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, G.; Tenero, L.; Piazza, M.; Piacentini, G. Severe Pediatric Asthma Therapy: Dupilumab. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 963610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Nici, L.; Sood, S.; ZuWallack, R.; Castro, M. Nonpharmacologic Therapy for Severe Persistent Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Dixey, P.; Bhavsar, P.; Raby, K.; Kermani, N.; Chadeau-Hyam, M.; Adcock, I.M.; Song, W.-J.; Kwon, H.-S.; Lee, S.-W.; et al. Precision Medicine Intervention in Severe Asthma (PRISM) Study: Molecular Phenotyping of Patients with Severe Asthma and Response to Biologics. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00485–02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, E.; Ten Have, L.; Ten Brinke, A.; De Jong, K. Effect of Biologic Therapy on Total Body Composition in Severe Asthma. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2023, 20, 1825–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yancey, S.W.; Ortega, H.G.; Keene, O.N.; Bradford, E.S. Efficacy of Add-on Mepolizumab in Adolescents with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitlin, P.L. Asthma Inflammatory Subtypes and New Biologic Therapies. Rev. Mex. Anestesiol. 2019, 42, 287–293. [Google Scholar]
- Fiocchi, A.G.; Phipatanakul, W.; Zeiger, R.S.; Durrani, S.R.; Cole, J.; Msihid, J.; Gall, R.; Jacob-Nara, J.A.; Deniz, Y.; Rowe, P.J.; et al. Dupilumab Leads to Better-Controlled Asthma and Quality of Life in Children: The VOYAGE Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 62, 2300558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, M.; Vom Hove, M.; Bertsche, A.; Lipek, T.; Kiess, W.; Bertsche, T.; Prenzel, F.; Neininger, M.P. Medication-Related Perceptions of Children and Adolescents with Severe Asthma and Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Non-Interventional Exploratory Study. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2025, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.M.; Pijnenburg, M.W.; Deschildre, A.; De Mir-Messa, I.; Adalen, S.; Amat, F.; Antonino, L.; Biermé, P.; Bravo-Lopez, M.; Carlsen, K.C.L.; et al. Severe Paediatric Asthma Collaborative in Europe: Real-World Data on Children on Biologics. ERJ Open Res. 2025, 11, 00709–02024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, M.; Zhu, A.; Li, J. Four-Week IgE/Baseline IgE Ratio Combined with Tryptase Predicts Clinical Outcome in Omalizumab-Treated Children with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma. Open Med. 2025, 20, 20251176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odajima, H.; Ebisawa, M.; Nagakura, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Akasawa, A.; Ito, K.; Doi, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Katsunuma, T.; Kurihara, K.; et al. Omalizumab in Japanese Children with Severe Allergic Asthma Uncontrolled with Standard Therapy. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Zhi, L.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Hao, G.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; et al. Real-World Safety and Effectiveness of Omalizumab in Moderate to Severe Allergic Asthma Patients in China: A Post-Authorization Study. J. Asthma Allergy 2023, 16, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztafińska, A.; Jerzyńska, J.; Stelmach, W.; Woicka-Kolejwa, K.; Stelmach, I. Quality of Life in Asthmatic Children and Their Caregivers after Two-Year Treatment with Omalizumab, a Real-Life Study. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2017, 5, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztafińska, A.; Gwardys, M.; Podlecka, D.; Mospinek, E.; Stelmach, I. Effectiveness of Omalizumab in Children and Adolescentswith Uncontrolled Allergic Asthma: A Case Seriesfrom Poland. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2021, 38, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, R.A.; Sorkness, C.A.; Kosinski, M.; Schatz, M.; Li, J.T.; Marcus, P.; Murray, J.J.; Pendergraft, T.B. Development of the Asthma Control Test: A Survey for Assessing Asthma Control. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juniper, E.F.; Guyatt, G.H.; Cox, F.M.; Ferrie, P.J.; King, D.R. Development and Validation of the Mini Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 14, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Hirayama, K.; Matsui, E.; Teramoto, T.; Kaneko, H.; Fukao, T.; Orii, K.; Kawamoto, M.; Funato, M.; Ohnishi, H.; et al. [QOL questionnaire for pediatric patients with bronchial asthma and their parents or caregivers. Preparation and evaluation of the short form version 2008 (Gifu)]. Arerugi Allergy 2008, 57, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, D.; Di Filippo, P.; Attanasi, M.; Lizzi, M.; Di Pillo, S.; Chiarelli, F. Biologic Therapy and Severe Asthma in Children. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Jiménez, F.; Pavón-Romero, G.F.; Velásquez-Rodríguez, J.M.; López-Garza, M.I.; Lazarini-Ruiz, J.F.; Gutiérrez-Quiroz, K.V.; Teran, L.M. Biologic Therapies for Asthma and Allergic Disease: Past, Present, and Future. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacharier, L.B.; Maspero, J.F.; Katelaris, C.H.; Fiocchi, A.G.; Gagnon, R.; de Mir, I.; Jain, N.; Sher, L.D.; Mao, X.; Liu, D.; et al. Dupilumab in Children with Uncontrolled Moderate-to-Severe Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Morgan, W.J.; Gergen, P.J.; Mitchell, H.E.; Gern, J.E.; Liu, A.H.; Gruchalla, R.S.; Kattan, M.; Teach, S.J.; Pongracic, J.A.; et al. Randomized Trial of Omalizumab (Anti-IgE) for Asthma in Inner-City Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannini, L.J. Treat to Target Approach for Asthma. J. Asthma 2020, 57, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, E.A.; Moeller, A. Evidence-Based European Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Asthma in Children Aged 5–16 Years. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Authors (Year) | Countries Involved | Study Design | Population | Intervention | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Participants | Age (Years) | Condition | Biologic | Duration | Follow-Up | |||
| Fiocchi et al. (2023) [80] | Multinational | RCT (phase 3) | 350 | 6–11 | Moderate-to-severe type 2 asthma | Dupilumab | 52 weeks | After 24 and 52 weeks |
| Herzig et al. (2025) [81] | Germany | Non-interventional, cross-sectional, explorative, monocentric | 36 | 6–16 | Severe asthma (with or without atopic dermatitis) | Dupilumab | Duration of treatment not specified | No follow-up |
| Liu et al. (2025) [82] | Europe | Cross-sectional observational | 250 | 6–17 | Severe asthma | Omalizumab Mepolizumab Dupilumab | Duration of treatment not specified | No follow-up |
| Lu et al. (2025) [83] | China | Prospective cohort, single-arm trial | 43 | 6–14 | Moderate to severe asthma | Omalizumab | 16 weeks | Every 4 weeks |
| Odajima et al. (2015) [84] | Japan | Prospective clinical, open-label | 38 | 6–15 | Severe allergic asthma | Omalizumab | 24 weeks | 16 weeks |
| Su et al. (2023) [85] | China | Retrospective observational cohort | 316 * | 6–18 | Moderate to severe allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Duration of treatment not specified | 24 weeks |
| Sztafińska et al. (2017) [86] | Poland | Prospective cohort | 19 | 6–15 | Severe allergic asthma | Omalizumab | Duration of treatment not specified | 104 weeks |
| Sztafińska et al. (2021) [87] | Poland | Prospective case series | 17 | 8–16 | Uncontrolled allergic asthma | Omalizumab | 1–3 year | Up to 4, 5 years |
| MMAT Category | Study | Methodological Quality Criteria | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 * | S2 * | Q1 * | Q2 * | Q3 * | Q4 * | Q5 * | ||
| Quantitative RCT | Fiocchi et al. (2023) [80] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Quantitative non-randomized | Herzig et al. (2025) [81] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Cannot tell | Yes |
| Liu et al. (2025) [82] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Lu et al. (2025) [83] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Cannot tell | Yes | |
| Odajima et al. (2015) [84] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | |
| Su et al. (2023) [85] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Cannot tell | Yes | |
| Sztafińska et al. (2017) [86] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | |
| Quantitative descriptive | Sztafińska et al. (2021) [87] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Study | Biologic | Asthma Control | HRQoL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiocchi et al. (2023) [80] | Dupilumab | Significant longitudinal improvements in patients with type 2 phenotype. | Significant improvement in pediatric asthma-related QoL in dupilumab treated patients compared to placebo |
| Herzig et al. (2025) [81] | Dupilumab | Significant patient-reported improvements in disease management. | Dupilumab users presented better QoL scores |
| Liu et al. (2025) [82] | Omalizumab Mepolizumab Dupilumab | Most patients obtained good symptom control, but still experienced asthma. | No significant differences found between biologic therapy groups |
| Lu et al. (2025) [83] | Omalizumab | Patients’ asthma control scores improved after 1 week of treatment; reduced ICS and LABA use; reduced frequency of acute asthma exacerbations. | Significant improvements in asthma-related QoL scores after treatment |
| Odajima et al. (2015) [84] | Omalizumab | Significant improvements in total asthma symptoms, daily activity and nocturnal sleep scores; significant reduction in asthma exacerbation and hospitalization; some patients still experienced at least one adverse event during treatment. | Significant asthma-related QoL improvements between baseline and week 24 of treatment |
| Su et al. (2023) [85] | Omalizumab | Treatment improved lung function and asthma control; only a minority of patients reported adverse events and serious adverse events. | Significant improvements in asthma-related QoL in all domains and overall scores |
| Sztafińska et al. (2017) [86] | Omalizumab | Treatment was associated with reduction in ICS use | Significant improvements in asthma-related QoL scores |
| Sztafińska et al. (2021) [87] | Omalizumab | Improvements in asthma control, reduction in ICS and oral corticosteroids use, and decreased exacerbations | Significant increase in asthma-related QoL scores |
| Instrument | Studies | Instrument Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Items | Domains/Components | Scoring | Score Range | ||
| PAQLQ/ PAQLQ(S) */ PAQLQ(S)-IA * [22] | Fiocchi et al. (2023) [80] Herzig et al. (2025) [81] Liu et al. (2025) [82] Lu et al. (2025) [83] Su et al. (2023) [85] Sztafińska et al. (2017) [86] | 23 | Symptoms Activity limitation Emotional function | 1 to 7 (Higher score = better QoL) | 23–161 |
| miniAQLQ [89] | Sztafińska et al. (2021) [87] | 15 | Symptoms Environmental stimuli Emotional function Activity limitation | 1 to 7 (Higher score = better QoL) | 15–105 |
| QoL short form version 2008 (Gifu) [90] | Odajima et al. (2015) [84] | 10 | Physical domain (asthma attack; instability of symptoms; exercise load) Emotional domain (emotional burden; proper acceptance of asthma) | 1 to 5 (1 = Severe impairment; 5 = No impairment) | 10–50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaz, B.L.; Marrinhas, D.; Pereira, A. Biologic Therapies and Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients with Asthma: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222824
Vaz BL, Marrinhas D, Pereira A. Biologic Therapies and Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients with Asthma: A Systematic Review. Healthcare. 2025; 13(22):2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222824
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaz, Beatriz Luzio, Daniel Marrinhas, and Anabela Pereira. 2025. "Biologic Therapies and Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients with Asthma: A Systematic Review" Healthcare 13, no. 22: 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222824
APA StyleVaz, B. L., Marrinhas, D., & Pereira, A. (2025). Biologic Therapies and Quality of Life in Pediatric Patients with Asthma: A Systematic Review. Healthcare, 13(22), 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13222824







