Differences in Inpatient Total Costs in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Analysis from a Romanian Tertiary Care Center
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
| n | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol consumption | No use | 54 | 60.0% |
| Abuse | 20 | 22.2% | |
| Regular use | 15 | 16.7% | |
| Unknown | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Cause of injury | Fall | 67 | 74.4% |
| Road traffic accident | 21 | 23.3% | |
| Aggression | 2 | 2.2% | |
| Comorbidity burden | >1 | 38 | 42.2% |
| 1 | 28 | 31.1% | |
| 0 | 24 | 26.7% | |
| Discharge location | Home | 84 | 93.3% |
| Other | 5 | 5.6% | |
| Rehabilitation | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Discharge status | Alive | 85 | 94.4% |
| Dead | 5 | 5.6% | |
| Drug use | No | 90 | 100.0% |
| Education | University (13+ years) | 58 | 64.4% |
| High school (9–12 years) | 25 | 27.8% | |
| Primary school (1–4 years) | 3 | 3.3% | |
| No formal education | 2 | 2.2% | |
| Secondary school (5–8 years) | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Unknown | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Employment | Retired | 58 | 64.4% |
| Employed | 22 | 24.4% | |
| Unemployed | 8 | 8.9% | |
| Other | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Unknown | 1 | 1.1% | |
| GCS severity | Mild | 87 | 96.7% |
| Moderate | 3 | 3.3% | |
| Imagery | Yes | 90 | 100.0% |
| Imagery information | CT | 90 | 100.0% |
| Marital status | Married | 47 | 52.2% |
| Widowed | 19 | 21.1% | |
| Single | 18 | 20.0% | |
| Separated | 3 | 3.3% | |
| Unknown | 2 | 2.2% | |
| Living together | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Mechanism of injury | Ground-level fall | 59 | 65.6% |
| Direct impact: head against an object | 12 | 13.3% | |
| Fall from height >1 m (3 ft) | 10 | 11.1% | |
| Acceleration/deceleration | 4 | 4.4% | |
| Direct impact: blow to the head | 3 | 3.3% | |
| Crush | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Missing data | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Modified Marshall score | II | 80 | 88.9% |
| I | 7 | 7.8% | |
| III | 3 | 3.3% | |
| Place of injury | Home | 60 | 66.7% |
| Street | 27 | 30.0% | |
| Other | 2 | 2.2% | |
| Sports facility | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Post traumatic amnesia | No | 71 | 78.9% |
| Yes | 19 | 21.1% | |
| Return to work | Yes | 46 | 51.1% |
| No | 23 | 25.6% | |
| Unknown | 21 | 23.3% | |
| Settlement type | Urban | 61 | 67.8% |
| Rural | 29 | 32.2% | |
| Sex | male | 61 | 67.8% |
| female | 29 | 32.2% | |
| Smoking | No use | 67 | 74.4% |
| Regular use | 21 | 23.3% | |
| Abuse | 2 | 2.2% | |
| Substance use | No use | 90 | 100.0% |
| Type of injury | Closed | 88 | 97.8% |
| Crush | 1 | 1.1% | |
| Penetrating | 1 | 1.1% |
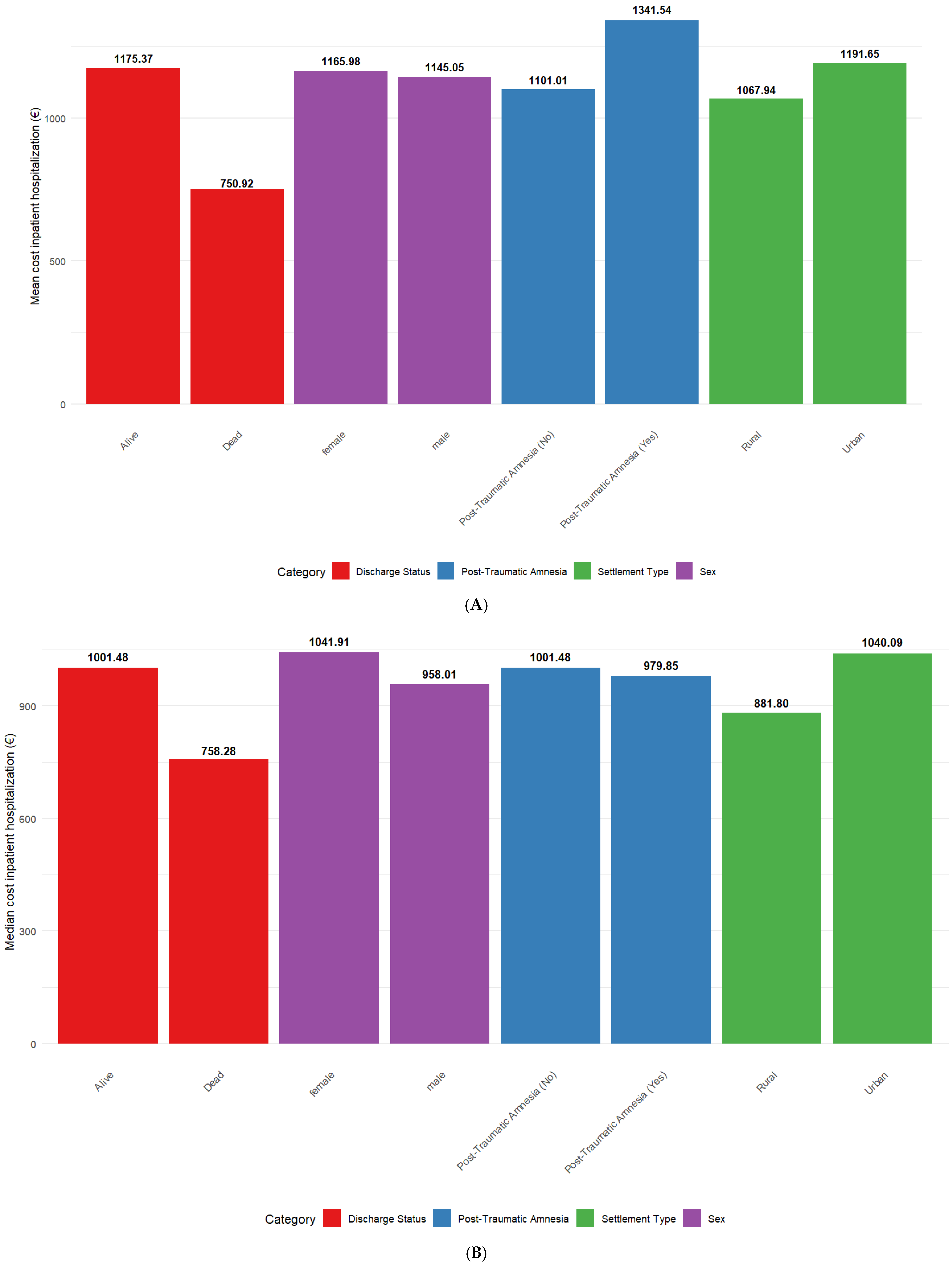

3.2. Wilcoxon Test
3.3. Kruskal–Wallis
3.4. Spearman Correlations
4. Discussion
Study Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Rahbi, A.; Al Mahrouqi, O.; Al Ibrahim, H.; Al Saidi, M.; Abid Shah, Y.; Al-Saadi, T. Cost Associated with Geriatric Traumatic Brain Injury in Developing Countries: An Observational Study. World Neurosurg. 2024, 181, e990–e1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.Y.; Lee, A.Y.W. Traumatic Brain Injuries: Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.L.; Theadom, A.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Bannick, M.S.; Montjoy-Venning, W.; Lucchesi, L.R.; Abbasi, N.; Abdulkader, R.; Abraha, H.N.; Adsuar, J.C.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury, 1990–2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 56–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchetti, N.; Taccone, F.S.; Citerio, G.; Pepe, P.E.; Le Roux, P.D.; Oddo, M.; Polderman, K.H.; Stevens, R.D.; Barsan, W.; Maas, A.I.; et al. Neuroprotection in Acute Brain Injury: An up-to-Date Review. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Adelson, P.D.; Andelic, N.; Bell, M.J.; Belli, A.; Bragge, P.; Brazinova, A.; Büki, A.; Chesnut, R.M.; et al. Traumatic Brain Injury: Integrated Approaches to Improve Prevention, Clinical Care, and Research. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 987–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, Z.L.R.; Van Der Vlegel, M.; Van Dijck, J.T.J.M.; Pisică, D.; Van Leeuwen, N.; Lingsma, H.F.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Haagsma, J.A.; Majdan, M.; Polinder, S.; et al. Intramural Healthcare Consumption and Costs After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Collaborative European NeuroTrauma Effectiveness Research in Traumatic Brain Injury (CENTER-TBI) Study. J. Neurotrauma 2023, 40, 2126–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, T.Y.S.; Ng, J.X.; Jayne, C.H.Z.; Ragupathi, T.; Teo, C.K.A.; Yeo, T.T. Changing Demographic Profiles of Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury: An Aging Concern. Front. Surg. 2019, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Gao, X.; Yang, X. The Incidence of Brain Trauma Caused by Road Injuries: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Injury 2023, 54, 110984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Manley, G.T.; Abrams, M.; Åkerlund, C.; Andelic, N.; Aries, M.; Bashford, T.; Bell, M.J.; Bodien, Y.G.; et al. Traumatic Brain Injury: Progress and Challenges in Prevention, Clinical Care, and Research. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 1004–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozes, F.; Delpierre, C.; Costa, N. Mapping the Costs and Socioeconomic Characteristics Involved in Traumatic Brain Injuries: A Scoping Review. J. Rehabil. Med. 2024, 56, 18311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.F.; DePadilla, L.; Xu, L. Costs of Nonfatal Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States, 2016. Med. Care 2021, 59, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijck, J.T.J.M.; Mostert, C.Q.B.; Greeven, A.P.A.; Kompanje, E.J.O.; Peul, W.C.; De Ruiter, G.C.W.; Polinder, S. Functional Outcome, in-Hospital Healthcare Consumption and in-Hospital Costs for Hospitalised Traumatic Brain Injury Patients: A Dutch Prospective Multicentre Study. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, D.; Mohamed Ibrahim, M.I.B.; Boncz, I. What Are the Challenges in Conducting Cost-of-Illness Studies? Value Health Reg. Issues 2014, 4, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Byford, S. Economic Note: Cost of Illness Studies. BMJ 2000, 320, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C. Cost-of-Illness Studies: Concepts, Scopes, and Methods. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2014, 20, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazinova, A.; Rehorcikova, V.; Taylor, M.S.; Buckova, V.; Majdan, M.; Psota, M.; Peeters, W.; Feigin, V.; Theadom, A.; Holkovic, L.; et al. Epidemiology of Traumatic Brain Injury in Europe: A Living Systematic Review. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 1411–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponsford, J.L.; Spitz, G.; Cromarty, F.; Gifford, D.; Attwood, D. Costs of Care after Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, A.A.; Wunderlich, C.A.; Puvanachandra, P.; Gururaj, G.; Kobusingye, O.C. The Impact of Traumatic Brain Injuries: A Global Perspective. NeuroRehabilitation 2007, 22, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Anderson, D.B.; Chen, L.; Feng, S.; Zhou, H. Global, Regional and National Burden of Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e075049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.; Ro, Y.S.; Jeong, J.; Ryu, H.H.; Shin, S.D. Alcohol Intake before Injury and Functional and Survival Outcomes after Traumatic Brain Injury: Pan-Asian Trauma Outcomes Study (PATOS). Medicine 2023, 102, e34560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spille, D.C.; Kuroczik, D.; Görlich, D.; Varghese, J.; Schwake, M.; Stummer, W.; Holling, M. Which Risk Factors Significantly Influence the Outcome of Traumatic Brain Injured Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder? Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2024, 50, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, J.D. Substance Abuse as a Mediating Factor in Outcome from Traumatic Brain Injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1995, 76, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andelic, N.; Jerstad, T.; Sigurdardottir, S.; Schanke, A.-K.; Sandvik, L.; Roe, C. Effects of Acute Substance Use and Pre-Injury Substance Abuse on Traumatic Brain Injury Severity in Adults Admitted to a Trauma Centre. J. Trauma Manag. Outcomes 2010, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumowski, J.F.; Chiaravalloti, N.; Krch, D.; Paxton, J.; DeLuca, J. Education Attenuates the Negative Impact of Traumatic Brain Injury on Cognitive Status. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 2562–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, V.; Fort, E.; Beaudoin-Gobert, M.; Ndiaye, A.; Fischer, C.; Bergeret, A.; Charbotel, B.; Luauté, J. Indicators of Long-Term Return to Work after Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Cohort Study. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Lasprilla, J.C.; Ketchum, J.M.; Dezfulian, T.; Kreutzer, J.S.; O’neil-Pirozzi, T.M.; Hammond, F.; Jha, A. Predictors of Marital Stability 2 Years Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Brain Inj. 2008, 22, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, F.M.; Sevigny, M.; Backhaus, S.; Neumann, D.; Corrigan, J.D.; Charles, S.; Gazett, H. Marital Stability Over 10 Years Following Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2021, 36, E199–E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytter, H.M.; Hjorthøj, C.; Graff, H.J.; Eplov, L.F.; Nordentoft, M.; Benros, M.E.; Erlangsen, A.; Madsen, T. Traumatic Brain Injury and Long-Term Associations with Work, Divorce and Academic Achievement. Prev. Med. 2024, 185, 108062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.K.; Upadhyayula, P.S.; Avalos, L.N.; Cage, T.A. Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Rural-Urban Disparities and Considerations. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Park, J.-E.; Kim, S.-H.; Lim, Y.-C.; You, N.-K.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Choi, H.-Y.; Cho, J.-M. Outcomes of Ultra-Early Decompressive Craniectomy after Severe Traumatic Brain Injury-Treatment Outcomes after Severe TBI. Korean J. Neurotrauma 2014, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, B.; Thomas, S.; Ahrensberg, J.M.; Weaver, R.; Fowler, A.; Bestwick, J.; Harris, T.; Pearse, R. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Return to Work after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norup, A.; Kruse, M.; Soendergaard, P.L.; Rasmussen, K.W.; Biering-Sørensen, F. Socioeconomic Consequences of Traumatic Brain Injury: A Danish Nationwide Register-Based Study. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 2694–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, E.C. European Central Bank. Available online: https://www.ecb.europa.eu/home/html/index.en.html (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Kuckartz, U.; Rädiker, S.; Ebert, T.; Schehl, J. Statistik: Eine Verständliche Einführung; VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2013; ISBN 978-3-531-19889-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Ugiliweneza, B.; Meyer, K.; Lad, S.P.; Boakye, M. Trend and Geographic Analysis for Traumatic Brain Injury Mortality and Cost Based on MarketScan Database. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantonio, A. Sex, Gender, and Traumatic Brain Injury: A Commentary. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, R.C.; Dams-O’Connor, K.; Morrissey, M.R.; Manley, G.T. Geriatric Traumatic Brain Injury: Epidemiology, Outcomes, Knowledge Gaps, and Future Directions. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardif, P.-A.; Moore, L.; Boutin, A.; Dufresne, P.; Omar, M.; Bourgeois, G.; Bonaventure, P.L.; Kuimi, B.L.B.; Turgeon, A.F. Hospital Length of Stay Following Admission for Traumatic Brain Injury in a Canadian Integrated Trauma System: A Retrospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Injury 2017, 48, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.A.; Mallow, P.J.; Vassar, M.; Rizzo, J.A.; Pandya, B.J.; Kruzikas, D.T. Traumatic Brain Injury: Patient Characteristics, Hospital Costs and Trends Over Time. J. Health Econ. Outcomes Res. 2014, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, V.; Hurst, M.; Petersen, T.; Liu, J.; Mollayeva, T.; Colantonio, A.; Sutton, M.; Escobar, M.D. A Population-Based Sex-Stratified Study to Understand How Health Status Preceding Traumatic Brain Injury Affects Direct Medical Cost. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, J.; Sarmiento, K.; Waltzman, D.; Xu, L. Traumatic Brain Injury–Related Hospitalizations and Deaths in Urban and Rural Counties—2017. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2022, 79, 288–296.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matney, C.; Bowman, K.; Berwick, D.; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine. Understanding Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. In Traumatic Brain Injury: A Roadmap for Accelerating Progress; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijck, J.T.J.M.; Dijkman, M.D.; Ophuis, R.H.; De Ruiter, G.C.W.; Peul, W.C.; Polinder, S. In-Hospital Costs after Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Quality Assessment. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, I.; Wood, R.L.; Phillips, C.; Macey, S. The Costs of Traumatic Brain Injury: A Literature Review. Clin. Outcomes Res. 2013, 281, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, L.J.; Thompson, D.; Millham, F.H.; Cowell, L.; Snyder, P.J.; Lenderking, W.R.; Weinstein, M.C. Outcomes and Costs of Acute Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2002, 53, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, L.M.; Ni, Q.; Härtl, R.; Ghajar, J. Impact of Falls on Early Mortality from Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Trauma Manag. Outcomes 2009, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, H.J.; McCormick, W.C.; Kagan, S.H. Traumatic Brain Injury in Older Adults: Epidemiology, Outcomes, and Future Implications. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2006, 54, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.; Cho, G.C.; Lee, J.H.; Park, E.J.; Lee, D.H. Characteristics of Fall-related Head Injury versus Non-head Injury in the Older Adults. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontebasso, A.M.; Figueira, S.; Thavorn, K.; Glen, P.; Lampron, J.; Matar, M. Financial Implications of Trauma Patients at a Canadian Level 1 Trauma Center: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Trauma Surg. Acute Care Open 2020, 5, e000568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umo, I.; James, K.; Didilemu, F.; Sinen, B.; Borchem, I.; Inaido, D.; Ikasa, R. The Direct Medical Cost of Trauma Aetiologies and Injuries in a Resource Limited Setting of Papua New Guinea: A Prospective Cost of Illness Study. Lancet Reg. Health—West. Pac. 2022, 20, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deynse, H.; Van Belleghem, G.; Lauwaert, D.; Moens, M.; Pien, K.; Devos, S.; Hubloue, I.; Putman, K. The Incremental Cost of Traumatic Brain Injury during the First Year after a Road Traffic Accident. Brain Inj. 2019, 33, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.K.; Krishnan, N.; Chyall, L.; Haddad, A.F.; Vega, P.; Caldwell, D.J.; Umbach, G.; Tantry, E.; Tarapore, P.E.; Huang, M.C.; et al. Predictors of Extreme Hospital Length of Stay After Traumatic Brain Injury. World Neurosurg. 2022, 167, e998–e1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.V.; Loo, G.T.; Richardson, L.D.; Legome, E. Patient Factors Associated With Prolonged Length of Stay After Traumatic Brain Injury. Cureus 2024, 16, e59989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodhit, A.; Patel, P.; Daneshvar, Y.; Peters, K.; Stead, L. How Much Does a Traumatic Brain Injury Cost? (P5.337). Neurology 2014, 82, P5-337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitz, G.; McKenzie, D.; Attwood, D.; Ponsford, J.L. Cost Prediction Following Traumatic Brain Injury: Model Development and Validation. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 87, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dismuke-Greer, C.E.; Almeida, E.J.; Silva, M.A.; Dams-O’Connor, K.; Rocek, G.; Phillips, L.M.; Del Negro, A.; Walker, W.C.; Nakase-Richardson, R. Effect of Post-Traumatic Amnesia Duration on Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) First Year Hospital Costs: A Veterans Affairs Traumatic Brain Injury Model Systems Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 104, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, D.; Trevena-Peters, J.; McKay, A.; Ponsford, J. Economic Evaluation of Activities of Daily Living Retraining During Posttraumatic Amnesia for Inpatient Rehabilitation Following Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevena-Peters, J.; McKay, A.; Spitz, G.; Suda, R.; Renison, B.; Ponsford, J. Efficacy of Activities of Daily Living Retraining During Posttraumatic Amnesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Sung, H.-Y.; Calfee, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Yao, T.; Max, W. Smoking-Attributable Health Care Expenditures for US Adults With Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2413869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, T.C.; Abadjian, L.; Kincaid, A.; Bilovsky-Muniz, T.; Boreta, L.; Gauger, G.E. The Influence of Chronic Cigarette Smoking on Neurocognitive Recovery after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockhill, C.M.; Jaffe, K.; Zhou, C.; Fan, M.-Y.; Katon, W.; Fann, J.R. Health Care Costs Associated with Traumatic Brain Injury and Psychiatric Illness in Adults. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, L.S.; Doonan, M. Value and Cost Savings From Access to Multi-Disciplinary Rehabilitation Services After Severe Acquired Brain Injury. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 753447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner-Stokes, L.; Dzingina, M.; Shavelle, R.; Bill, A.; Williams, H.; Sephton, K. Estimated Life-Time Savings in the Cost of Ongoing Care Following Specialist Rehabilitation for Severe Traumatic Brain Injury in the United Kingdom. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2019, 34, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkin, C.; Phillips, J.; Radford, K. What Is a ‘Return to Work’ Following Traumatic Brain Injury? Analysis of Work Outcomes 12 Months Post TBI. Brain Inj. 2020, 34, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vadan, I.-M.; Grad, D.; Strilciuc, S.; Stan, A.; Vacaras, V.; Verisezan Rosu, O.; Stefanescu, E.; Livint-Popa, L.; Blesneag, A.V.; Muresanu, D.F. Differences in Inpatient Total Costs in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Analysis from a Romanian Tertiary Care Center. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192466
Vadan I-M, Grad D, Strilciuc S, Stan A, Vacaras V, Verisezan Rosu O, Stefanescu E, Livint-Popa L, Blesneag AV, Muresanu DF. Differences in Inpatient Total Costs in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Analysis from a Romanian Tertiary Care Center. Healthcare. 2025; 13(19):2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192466
Chicago/Turabian StyleVadan, Iulia-Maria, Diana Grad, Stefan Strilciuc, Adina Stan, Vitalie Vacaras, Olivia Verisezan Rosu, Emanuel Stefanescu, Livia Livint-Popa, Alina Vasilica Blesneag, and Dafin F. Muresanu. 2025. "Differences in Inpatient Total Costs in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Analysis from a Romanian Tertiary Care Center" Healthcare 13, no. 19: 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192466
APA StyleVadan, I.-M., Grad, D., Strilciuc, S., Stan, A., Vacaras, V., Verisezan Rosu, O., Stefanescu, E., Livint-Popa, L., Blesneag, A. V., & Muresanu, D. F. (2025). Differences in Inpatient Total Costs in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Analysis from a Romanian Tertiary Care Center. Healthcare, 13(19), 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13192466








