Abstract
Background/Objectives: The prognosis of patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF) is significantly affected by inflammatory state and immune dysregulation. The systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI), which reflects neutrophil, monocyte, and lymphocyte dynamics, has emerged as a potential marker of immune-inflammatory status. However, its role in predicting HBV-ACLF outcomes remains unclear. This research aims to elucidate the prognostic value of SIRI and its dynamic changes combined with disease severity scores in predicting the outcomes of HBV-ACLF. Methods: The study included HBV-ACLF patients enrolled in a multicenter clinical study between July 2019 and April 2024. Based on 90-day outcomes, the participants were categorized into survival and death groups. Clinical data and SIRI values were collected on days 0 (baseline), 3, 7, and 14. Independent prognostic factors were identified using Cox regression and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) analysis. The predictive value of dynamic SIRI changes combined with disease severity scores was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Results: A total of 153 patients with HBV-ACLF were analyzed, including 104 in the survival group and 49 in the death group. SIRI values were significantly lower in the survival group than in the death group across all time points. Multivariate Cox regression analysis identified that an increased ΔSIRI at day 3 (ΔSIRI3), a higher MELD score, and a lower albumin level were independently associated with increased 90-day mortality. The combination of SIRI on day three (SIRI3) and MELD-Na score on day three (MELD-Na3) demonstrated the highest predictive performance, with an AUC of 0.817 (95% CI: 0.750–0.883). Conclusions: The combination of the SIRI and MELD-Na score on day three provides a strong predictive value for the short-term prognosis of HBV-ACLF, highlighting its potential utility in early prognostic evaluation.
1. Introduction
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is characterized by hepatic and/or systemic organ dysfunction with high short-term mortality [1,2]. It involves acute deterioration of liver function against a background of chronic liver disease, often leading to multiple organ failure. In China, hepatitis B virus-related ACLF (HBV-ACLF) is the predominant form of ACLF [3,4,5]. Chronic liver damage caused by hepatitis B virus infection, including fibrosis and cirrhosis, provides the pathological basis for ACLF development. Acute triggers, including the active replication of the hepatitis B virus, alcohol consumption, and infections, can cause extensive necrosis of hepatocytes and rapid deterioration of liver function [5,6]. Therefore, HBV acts not only as the underlying cause of chronic liver disease but also as the trigger for the acute onset of HBV-ACLF [7].
HBV infection can trigger systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), leading to multiple organ failure involving the liver, kidneys, brain, lungs, coagulation abnormalities, and circulatory system [8,9]. In ACLF, systemic inflammation serves as the major driver of organ dysfunction through three main mechanisms: (1) immune-mediated injury, such as neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) that cause oxidative stress and microcirculatory dysfunction; (2) metabolic dysregulation, in which energy resources are diverted to sustain immune activation, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction; (3) interaction with organ-specific pathways, such as proinflammatory cytokines that increase blood–brain barrier permeability and activate microglia, thereby aggravating hepatic encephalopathy [5,6,10]. In addition to liver failure, ACLF frequently affects extrahepatic organs. Hemodynamic changes, including splanchnic vasodilation, decreased systemic vascular resistance, and impaired cardiac output, contribute to tissue hypoperfusion and organ injury. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced nitric oxide signaling contributes to cardiac dysfunction [11], while chemokine-mediated inflammatory responses negatively affect pulmonary function [12]. Renal injury often results from renal vasoconstriction and reduced glomerular filtration [13], while neurological impairment is linked to hyperammonemia and cerebral edema [14]. These organ failures and SIRS establish a vicious cycle: SIRS induces vascular endothelial injury and impairs organ perfusion, while organ failure, particularly of the liver and kidneys, exacerbates inflammation by reducing clearance of cytokine release. This bidirectional interaction accelerates disease progression and worsens prognosis in ACLF patients [15].
In HBV-ACLF, pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are released due to HBV infection, intestinal barrier dysfunction, bacterial translocation, and increased susceptibility to microbial invasion. When PAMPs bind to pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), they trigger innate immune activation, resulting in cell death and tissue damage in both hepatic parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells. Furthermore, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) stimulate the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8, contributing to cytokine storm and SIRS [16,17]. In HBV-ACLF patients, monocytes and macrophages demonstrate reduced HLA-DR expression and metabolic dysfunction, resulting in impaired antigen presentation, phagocytic activity, and oxidative burst [18,19]. Neutrophils display multiple functional defects, including impaired phagocytosis, chemotaxis, degranulation, and NETs formation, thereby increasing susceptibility to infections [20]. Peripheral natural killer (NK) cells are decreased due to enhanced apoptosis and migration, while intrahepatic NK cell accumulation contributes to liver injury [21]. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ), primarily produced by NK and T cells, plays a dual role in antiviral immunity and immunopathology in HBV-ACLF [22]. In CD4+ T cells, the upregulation of B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) via IL-6 and TNF signaling suppresses their activation and cytokine production, correlating with disease severity [23]. The imbalance of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, and IFN-γ and the resulting cytokine storm drive organ dysfunction and disease progression in ACLF [24,25,26].
Liver transplantation is considered one of the most effective treatments for ACLF. Nevertheless, the limited availability of liver donors and high costs have restricted its widespread clinical application. Meanwhile, no effective medical therapies are currently available. Therefore, early evaluation of the short-term prognosis in ACLF patients is crucial for guiding clinical treatment. Although there are several clinical prognostic models for ACLF, such as the Child–Turcotte–Pugh (CTP), model for end-stage liver disease (MELD), the model for end-stage liver disease combined with serum sodium (MELD-Na), and the chronic liver failure combined with organ failure score (CLIF-C OFs), their clinical utility is limited due to complex calculations and the inclusion of multiple variables [27,28,29]. Additionally, most of these models were developed in Western countries, where alcohol-related liver disease is the predominant etiology of ACLF, while, in China, HBV infection is the primary cause. Consequently, there is an urgent need to identify more accessible and reliable prognostic markers for HBV-ACLF patients in China.
The systemic inflammatory response has been proposed as one of the mechanisms for ACLF [30]. Infection, cytokine release, and immune dysfunction can trigger or exacerbate a strong inflammatory response, resulting in impaired systemic circulation, organ dysfunction, and poor clinical outcomes [25,31]. Therefore, it is essential to incorporate inflammation-related indicators in the prognostic assessments. The initiation and progression of ACLF are closely associated with systemic inflammation, with neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes serving as key immune effector cells [32,33,34]. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and red cell distribution width (RDW) have been demonstrated to predict the short-term prognosis of ACLF patients [10,35]. Nonetheless, most of the above inflammatory indicators only consist of one or two hematological parameters, which cannot fully reflect the systemic inflammatory and immune status, thereby limiting their prognostic value. The systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) is an innovative index for assessing inflammation derived from these immune cells, reflecting the balance between inflammation and immune status [36,37]. SIRI was initially proposed by Qi et al. to predict the prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in 2016, demonstrating excellent predictive efficacy [36]. Recent studies have demonstrated strong associations between SIRI and prognosis in various cancers and cardiovascular diseases [38,39,40]. However, the prognostic significance of SIRI fluctuations in ACLF remains unclear. This research aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of dynamic changes in SIRI for predicting the outcomes of HBV-ACLF (MELD score 16–32). Furthermore, the use of a multicenter cohort and rigorous statistical methods (LASSO + Cox + ROC) provides a novel and robust approach to early prognostic assessment in HBV-ACLF patients.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This study was designed as a prospective, multicenter clinical study. A total of 153 HBV-ACLF patients meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria were enrolled from seven hospitals in China between July 2019 and April 2024: (1) The Fifth Medical Centre of the General Hospital of the People’s Liberation Army; (2) Beijing Youan Hospital of Capital Medical University; (3) Beijing Ditan Hospital Capital Medical University; (4) Tianjin Third Central Hospital; (5) Shijiazhuang Fifth Hospital; (6) Tongji Hospital of Tongji Medical University; and (7) Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University. This research received approval from the leading ethics committee, the Fifth Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital (2020041D) and was further reviewed and approved by the ethics committees of all participating centers. The study adhered to the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, 1964.
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
All participants, infected with the hepatitis B virus, met the diagnostic criteria for ACLF established by the Asia Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) [41].
The inclusion criteria were as follows:
(1) Individuals aged 18–65;
(2) Clinical diagnosis of HBV-ACLF, as determined by:
- Chronic hepatitis B infection based on persistent HBsAg or HBV-DNA positivity for over 6 months;
- Serum total bilirubin ≥ 5 mg/dL (85 μmol/L);
- INR ≥ 1.5 or PTA < 40%;
- Development of ascitic or hepatic encephalopathy within a month;
- MELD score ranging from 16 to 32.
To ensure diagnostic accuracy and adherence to APASL criteria, all cases were independently reviewed and confirmed by two senior hepatologists prior to inclusion.
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
(1) Co-infection with other hepatotropic viruses;
(2) Presence of acute kidney injury (AKI);
(3) Severe extrahepatic organ dysfunction, including disease of the heart, brain, lungs, kidneys, or other organs diseases, especially uncontrolled bacterial infections such as sepsis or septic shock;
(4) Bone marrow aplasia;
(5) Malignant neoplasms;
(6) Pregnant or lactating women.
In addition, patients with Grade III–IV hepatic encephalopathy were not enrolled, as these cases are widely recognized in international guidelines as indicative of advanced hepatic failure and are frequently associated with a poor short-term prognosis or the need for urgent liver transplantation. To minimize prognostic bias associated with end-stage disease and ensure cohort homogeneity in evaluating outcomes of medically managed HBV-ACLF patients without liver transplantation, only patients with Grade I–II hepatic encephalopathy were included.
2.4. Treatment Protocols
All patients received standardized treatment according to national liver failure guidelines [42]. They received antiviral therapy, improvements in liver function, and general medical treatment. Some went through artificial liver support therapy.
2.5. Sample Size Estimation
Given the exploratory nature of this study and the lack of previously published data on the SIRI value measured on day 3 in patients with HBV-ACLF, a formal a priori sample size calculation was not feasible at the study design stage. Therefore, a post hoc sample size estimation was performed using actual data from our prospective cohort to assess whether the sample size was adequate for detecting clinically meaningful differences. On Day 3, the mean SIRI values in the survival and death groups were 2.28 and 5.34, respectively, with standard deviations of 2.39 and 6.04. The calculated effect size (Cohen’s d) was approximately 0.67, which indicates a moderate to large effect. Accordingly, PASS 15.0 software was used to estimate the required sample size, assuming a significance level (α) of 0.05, a power of 0.80, a two-sided t-test with unequal variances, and a 2:1 group allocation ratio. After accounting for a 20% potential dropout or loss to follow-up, the final estimated sample size was 131 (87 in the survival group and 44 in the death group). The actual cohort exceeded this threshold, ensuring adequate statistical power.
2.6. Data Collection and Clinical Scores
The following data were collected at the time of enrolment: (1) demographic information (age, sex, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, smoking, alcohol consumption); (2) laboratory data: all the participants fasted for 8 to 12 h. The following morning, fasting venous blood samples were obtained and sent to the hospital’s laboratory department within two hours for examination. Parameters included white blood cell count (WBC), neutrophils, monocytes, platelets (PLT), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), γ-glutamate aminotransferase (GGT), total bilirubin, creatinine (Cr), international normalized ratio (INR), albumin (ALB); (3) Complications: ascites, infection, and hepatic encephalopathy. Patients were monitored to calculate the SIRI, CTP [43], MELD [44], MELD-Na [45], and CLIF-C OFs [46] on days 0, 3, 7, and 14 after admission.
The Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI)
The SIRI was introduced as an indicator to assess the inflammatory and immune status of HBV-ACLF patients. It was calculated using the following formula [36] (Figure 1). All parameters in the formula were obtained from routine peripheral blood tests. SIRI values were calculated at baseline (day 0, the day of enrollment), and on days 3, 7, and 14 after admission.
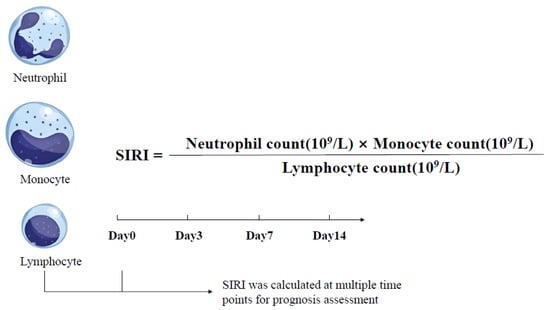
Figure 1.
Formula and time points of systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) in HBV-ACLF patients.
2.7. Follow-Up and Outcomes
Patients were followed for 90 days through telephone or hospital records and were subsequently categorized into death or survival groups based on clinical outcomes. Patients who underwent liver transplantation or were lost to follow-up were excluded from the final analysis.
2.8. Clinical Definitions
Cirrhosis was diagnosed based on liver biopsy, the evidence of hepatic nodules shown in abdominal imaging, a history of clinical decompensation, or endoscopic evaluation revealing esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding [47].
Smoking was defined as the daily consumption of at least one cigarette daily for a minimum duration of six months [48]. Alcohol consumption was defined as over 40 g/day for men or 20 g/day for women for a period reaching five years [49]. Diabetes was defined by random blood glucose levels ≥ 11.1 mmol/L, fasting blood glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol/L on at least two occasions, HbA1c levels ≥ 6.5%, or a prior diagnosis of diabetes with ongoing use of antidiabetic medications [50]. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥ 90 mmHg on at least three separate days, or a previous diagnosis of hypertension with current use of antihypertensive medications [51].
The virologic breakthrough was defined as a 10-fold increase in serum HBV DNA from the lowest level during treatment in patients who initially responded well to antiviral treatment and did not change their treatment plan. Naïve antiviral therapy was defined as the absence of prior antiretroviral treatment (ART), while antiviral discontinuation indicates the termination of antiviral therapy and consequent viral rebound [52].
Ascites were diagnosed based on clinical manifestations, diagnostic abdominal puncture, and abdominal imaging [53]. Hepatic encephalopathy was diagnosed using the West Haven criteria [54]. Bacterial infections, including spontaneous peritonitis, pulmonary infection, gastrointestinal infection, and sepsis, were diagnosed according to established consensus guidelines [55].
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed and figures plotted using R version 4.2 and GraphPad Prism version 10.1.2. Normally distributed continuous variables were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), with group comparisons analyzed using the Student’s t-test. Non-normally distributed continuous variables were presented as median (interquartile range (IQR)), and group comparisons were conducted using the Mann–Whitney U test. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages, with group comparisons analyzed using the chi-square or Fisher’s exact test. Transplantation-free survival at 28, 60, and 90 days was analyzed using Kaplan–Meier analysis. Longitudinal changes in SIRI and disease severity scores (MELD, MELD-Na, CTP, and CLIF-C OFs) at days 0, 3, 7, and 14 were analyzed using linear mixed-effects models, with group, time, and the group × time interaction as fixed effects. The Bonferroni correction was applied for post hoc pairwise comparisons. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to identify predictors of 90-day mortality. Variables with p < 0.05 in the univariate analysis were entered into least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression with ten-fold cross-validation to select optimal predictors and address multicollinearity. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was conducted to assess the predictive performance of dynamic changes in SIRI combined with disease severity scores (MELD, MELD-Na, CTP, and CLIF-C OFs) for 90-day mortality. The area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity were calculated to assess discriminative ability. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
A total of 215 patients were screened. Of these patients, 50 met at least one exclusion criterion: 11 did not fulfill the APASL-ACLF criteria, 8 did not meet the MELD score 16–32 range, 7 refused to participate, 6 presented with AKI, 5 did not meet the age range, 5 had malignant tumors, 4 had uncontrolled infection, 2 had hyperthyroidism, 1 had psychiatric disorders, and 1 was complicated with another virus infection. Ultimately, 165 patients were enrolled. During the follow-up, three patients were lost to follow-up and nine underwent liver transplantation. A total of 153 patients were included in the final analysis. Figure 2 displays the flowchart for selecting participants.
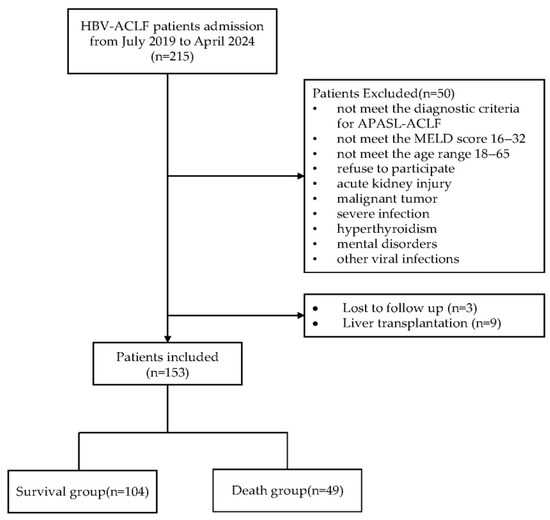
Figure 2.
Flowchart for selecting participants.
The participants were categorized into two distinct groups—those who survived and those who did not—based on their 90-day outcomes. The survival group comprised 104 individuals, including 86 men and 18 women. Conversely, the death group consisted of 49 cases, with 45 men and 4 women. The baseline differences between the two groups in terms of co-morbidities, clinical features, and laboratory parameters were analyzed. Notably, the death group exhibited significantly higher levels of ALP, Cr, INR, total bilirubin, MELD, MELD-Na, CTP, and CLIF-C OFs scores compared to the survival group (p < 0.05, Table 1). SIRI values at days 0, 3, 7, and 14 were significantly higher in the death group than in the survival group, with all comparisons showing statistically significant differences (Table 2). Additionally, patients were stratified into high and low SIRI groups based on the median SIRI0 value (1.944), and comparisons of baseline characteristics between groups are summarized in Supplementary Table S1.

Table 1.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of survival and death groups.

Table 2.
Comparison of SIRI values between survival and death groups at different timepoints.
3.2. Prognostic Outcomes and Dynamic Inflammatory Profiles
Figure 3 presents the Kaplan–Meier (KM) survival curve for the entire group, illustrating transplantation-free survival over time. At 28 days, the transplantation-free survival was 78.43%, with 120 patients surviving and 33 patients dying. At 60 days, the transplantation-free survival was 67.97%, with 104 patients surviving and 49 patients dying. At 90 days, the transplantation-free survival was 67.97%, with 104 patients surviving and 49 patients dying.
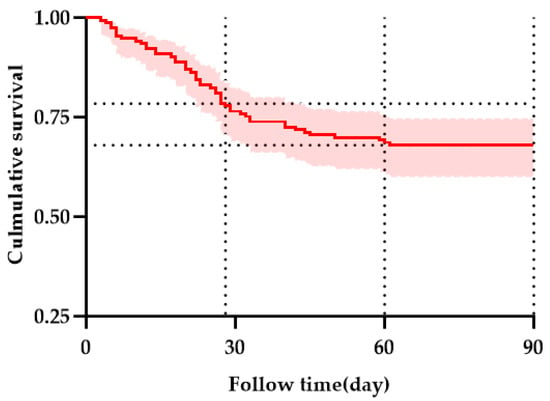
Figure 3.
Kaplan–Meier curves showing the survival of all enrolled patients. Horizontal reference lines indicate TFS at 28 and 60 days. The red line with a shaded area indicating the 95% confidence interval.
Longitudinal changes in SIRI, MELD, MELD-Na, CTP, and CLIF-C OF scores at days 0, 3, 7, and 14 were compared between the survival and death groups using linear mixed-effects models. As shown in Figure 4a–e, SIRI and disease severity scores were significantly higher in the death group (p < 0.05).
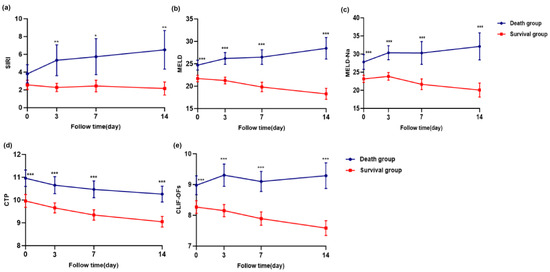
Figure 4.
Longitudinal changes in SIRI and disease severity scores (MELD, MELD-Na, CTP, and CLIF-C OFs) at days 0, 3, 7, and 14 in the survival and death groups of patients with HBV-ACLF. Panels (a) SIRI, (b) MELD, (c) MELD-Na, (d) CTP, (e) CLIF-C OFs. Statistical comparisons were performed using linear mixed-effects models for repeated measures, including group, time, and group × time interaction as fixed effects. Bonferroni correction was applied for post hoc pairwise comparisons. p < 0.05, <0.01 and <0.001 were considered statistically significant and are indicated by one (“*”), two (“**“), and three (“***”) asterisks, respectively.
3.3. Identification of Prognostic Factors via Univariate Analysis and LASSO-Selected Multivariate Cox Regression
Univariate Cox regression analysis identified SIRI0, SIRI3, SIRI7, SIRI14, ΔSIRI3, ΔSIRI7, and ΔSIRI14, along with MELD, CTP, and CLIF-OFs, to be significantly associated with 90-day prognosis in patients with HBV-ACLF (p < 0.05, Table 3). To further identify independent prognostic factors and reduce potential multicollinearity, LASSO regression was applied to variables with p < 0.05 in the univariate Cox analysis. Ten-fold cross-validation was used to select the optimal lambda value (λ = 0.0257), minimizing the mean cross-validated partial likelihood deviance. The coefficient path plot revealed that six variables retained non-zero coefficients at this λ value: SIRI3, SIRI14, ΔSIRI3, MELD, CTP, and ALB (Figure 5). Considering collinearity between baseline and dynamic SIRI values and the clinical relevance, only ΔSIRI on day 3 (ΔSIRI3) was retained for the multivariate Cox regression model. Consequently, ΔSIRI3, MELD, CTP, and ALB were included in the final multivariate model.

Table 3.
Univariate COX analysis of influencing 90-day prognosis in patients with HBV-ACLF.
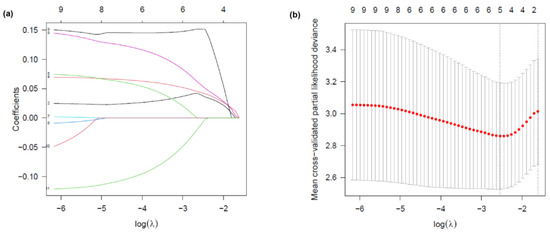
Figure 5.
LASSO regression analysis for variable selection. (a) LASSO coefficient profile plot. Each colored line represents the coefficient trajectory of a candidate variable as a function of log(λ). Variables with non-zero coefficients at the optimal λ were selected for the model. (b) Selection of the tuning parameter (λ) in the LASSO Cox regression model using ten-fold cross-validation. Partial likelihood deviance is plotted against log(λ). Dotted vertical lines indicate the optimal lambda that minimizes the deviance, and the most regularized model within one standard error. Six variables with non-zero coefficients were selected at the optimal λ.
Multivariate Cox regression revealed that increased ΔSIRI at day 3 (ΔSIRI3), a higher MELD score, and lower albumin levels were independently associated with increased 90-day mortality. The CTP score showed no significant association (Table 4).

Table 4.
Multivariate COX regression analysis of selected biomarkers in patients with HBV-ACLF.
3.4. Predictive Value of SIRI Combined with Disease Severity Score for 90-Day Prognosis in HBV-ACLF Patients
The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was generated to evaluate the predictive performance of SIRI combined with various disease severity scores (MELD, MELD-Na, CTP, CLIF-C OFs) for the 90-day prognosis of HBV-ACLF at baseline and day 3, respectively. Among them, the combination of SIRI on day 3 (SIRI3) and MELD-Na on day 3 (MELD-Na3) had the highest AUC, with a sensitivity of 91.84% and a specificity of 62.50%, exceeding that of the baseline combined disease severity score (Figure 6).
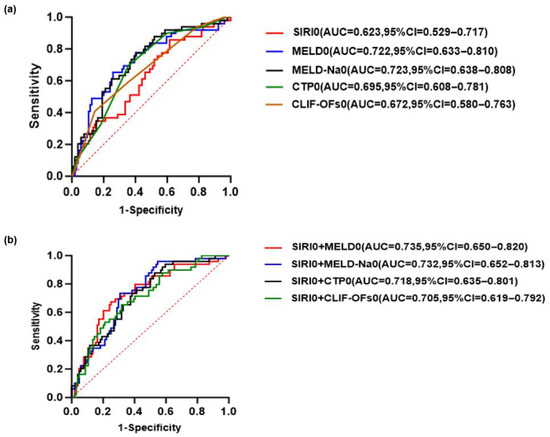
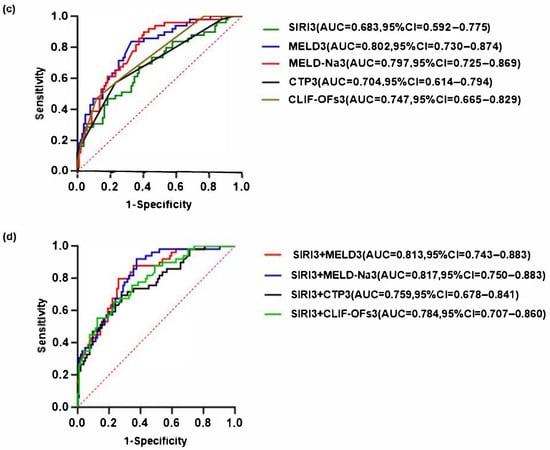
Figure 6.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for predicting the 90-day prognosis of patients with HBV-ACLF (a) SIRI and disease severity scores at baseline predict the prognosis of HBV-ACLF. (b) The predictive value of SIRI combined with various disease severity scores at baseline for the prognosis of HBV-ACLF. (c) SIRI and disease severity score at day 3 predict the prognosis of HBV-ACLF. (d) The predictive value of SIRI combined with various disease severity scores at day 3 for the prognosis of HBV-ACLF. The red dashed diagonal line represents the reference line indicating no discrimination.
4. Discussion
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major global health burden, with approximately one million deaths annually resulting from acute or chronic HBV infection [56]. ACLF is characterized by rapid deterioration and high short-term mortality, with limited effective medical treatment. Therefore, early disease evaluation and prognostic assessment are essential for timely clinical decision making [57]. In this study, we focused on identifying early prognostic indicators in HBV-ACLF patients. To avoid confounding effects on survival outcomes, patients who underwent liver transplants or were lost to follow-up were excluded from prognostic analysis. Liver transplantation, as the most effective treatment for ACLF, may distort the natural course of the disease. Furthermore, because liver transplantation is not randomly assigned, confounding factors including the affordability of liver resources and transplant indications could be relevant.
At baseline, the proportion of virological breakthroughs in the death group was significantly higher than that in the survival group. Although not statistically significant, the percentage of HBeAg-positive patients in the death group were higher than those in the survival group. Interruption of or reduction in nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs), or drug resistance, may lead to viral rebound and subsequent virological or biochemical breakthroughs, leading to massive hepatocyte necrosis and ACLF development [58]. In addition, HBV-DNA quantification reflects that the level of viral replication, when excessive, may provoke uncontrolled immune-mediated damage, as is consistent with previous studies [59,60]. These findings highlight the dual role of HBV in ACLF. In some patients, HBV infection leads to sustained viral replication and progressive liver dysfunction. In others, HBV serves as an acute precipitating factor, through virological breakthrough or interruption of antiviral treatment.
Systemic inflammation is a hallmark of ACLF and is strongly correlated with disease severity and poor prognosis [61,62]. Many studies have demonstrated that peripheral blood cell counts and derived ratios can serve as indicators of inflammation and immune function of liver failure [10,63]. As important immune cells, neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes play critical roles in the progression of ACLF [64,65]. When ACLF occurs, a significant number of hepatocytes undergo necrosis, releasing DAMPs, which trigger the immune and systemic inflammatory responses [33,66]. Monocytes and neutrophils exhibit chemotactic, phagocytic, and bactericidal roles, and elevated levels reflect enhanced responsiveness to inflammation [67]. Moreover, excessive immune activation impairs lymphocyte production and cell death, leading to a decrease in lymphocyte count, representing immune imbalance and reduced surveillance [68,69,70].
Qi et al. characterized the SIRI value as a novel marker of inflammation [36]. Compared with single inflammatory markers, SIRI integrates monocyte, neutrophil, and lymphocyte count, providing a simple, readily available index that more comprehensively reflects the inflammatory and immune status. It has demonstrated prognostic value in malignancies such as hepatocellular, colorectal, and gallbladder carcinomas [71,72], as well as in cardiovascular conditions such as hypertension and heart failure [73,74]. In decompensated cirrhosis patients, elevated SIRI has been associated with poorer short-term survival [75], and a recent study of 149 HBV-ACLF patients reported that higher SIRI was correlated with more severe liver injury [76]. However, the prognostic significance of dynamic changes in SIRI during ACLF progression has not yet been explored.
This study investigated the influence of dynamic changes in SIRI on HBV-ACLF prognostic value. Longitudinal data on SIRI and disease severity scores (MELD, MELD-Na, CTP, CLIF-OFs) were analyzed using linear mixed-effects models for repeated measures, which allowed for a robust evaluation of within-subject changes over time while accounting for inter-individual variability. We observed dynamic SIRI value shifts in ACLF progression, with the survival group patients exhibiting lower SIRI levels than the death group on days 0, 3, 7, and 14. A similar trend was observed for disease severity scores. Multivariate Cox regression analysis confirmed that the change in SIRI from baseline to day 3 (ΔSIRI3) was an independent predictor of 90-day mortality. This underscores the critical importance of early inflammatory trajectory in ACLF prognosis. The 72-h window appears to represent a pivotal phase in disease evolution, during which immune dysregulation may either stabilize or worsen. A rising ΔSIRI3 may indicate a suboptimal therapeutic response or the progression of occult infections, warranting closer monitoring and potential escalation of care.
While ΔSIRI3 was identified as an independent prognostic factor in multivariate Cox regression, absolute SIRI values on day 3 (SIRI3) were used in ROC analysis and predictive modeling due to their greater clinical feasibility and interpretability. Importantly, the combination of SIRI3 with MELD-Na3 significantly enhanced prognostic accuracy (AUC = 0.817), supporting dynamic multi-parameter assessment during the early phase of hospitalization. The high sensitivity (91.84%) ensures most high-risk patients are identified, while moderate specificity (62.50%) reflects the multifactorial complexity of ACLF. The complementary use of both dynamic change (ΔSIRI3) and absolute value (SIRI3) enables a more practical assessment of prognosis, supporting both statistical robustness and applicability in HBV-ACLF management. This balance supports its potential utility as a screening tool to prioritize intensive monitoring or early therapeutic interventions.
In contrast, ΔSIRI7 and ΔSIRI14 were not independently predictive, possibly due to treatment-related modulation of inflammation after day 3, reduced statistical power from early mortality, or stabilization of immune responses beyond the acute phase. Furthermore, in the Cox regression, proportion of HBeAg positive results were not statistically significant, while ΔSIRI3 values remained independently associated with 90-day mortality, considering that, although HBeAg status are critical indicators of viral activity, their prognostic value in HBV-ACLF remains complicated. This suggests that systemic inflammatory markers were more predictive of 90-day mortality than virological markers. This is consistent with previous findings suggesting that host immunological and inflammatory responses, rather than viral replication alone, drive disease progression in ACLF [30,77]. While age did not reach statistical significance in association with prognosis in this cohort (p = 0.083), a marginal trend was observed. We acknowledge that the pre-specified age range (18–65 years) is a notable limitation, particularly given the established clinical importance of age in HBV-ACLF progression and its potential complex interactions with systemic inflammation. This age restriction may limit the generalizability of our findings, especially to older patients. To address this limitation and better elucidate the prognostic role of SIRI across the age spectrum, future studies should incorporate age-stratified analyses.
It is worth noting that baseline bacterial infections, although clinically controlled, were more common in the death group. Bacterial infections can induce systemic inflammatory responses and affect peripheral immune cell populations, which may in turn influence composite inflammatory indices such as SIRI. However, unlike other indices (e.g., SII) that are significantly impacted by concurrent reductions in platelet and lymphocyte counts, SIRI combines neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes, which may provide a more stable reflection of systemic inflammation in such conditions. This suggests that SIRI may retain prognostic validity even in the presence of low-grade infection.
In addition, the 90-day transplantation-free survival rate observed in this study was 68%, consistent with prior research indicating that ACLF patients enrolled based on APASL criteria had 90-day survival rates between 60% and 70% [78,79,80]. The diagnostic criteria of APASL emphasize liver and coagulation failure, in contrast to the EASL-ACLF criteria, which concentrate on systemic organ failure. ACLF induced by viruses is marked by significant hepatocyte necrosis, systemic inflammatory response, and subsequent complications such as secondary infections, and renal injury, ultimately resulting in poor prognosis [81,82].
Various liver function severity scores, including MELD, MELD-Na, CTP, and CLIF-OFs, can effectively identify the severity of ACLF and predict prognosis [83,84,85]. However, due to the multifactorial etiology of ACLF, using a single indicator to evaluate prognosis has certain limitations. A study reported that the MELD score exhibits limited sensitivity and specificity for ACLF diagnosis and does not incorporate inflammation-related indicators [86]. Our research revealed ROC analyses indicating that the prognostic predictive accuracy for ACLF patients can be improved by combining SIRI3 with the disease severity score. Notably, the exclusion of MELD > 32 and Grade III-IV HE patients is consistent with the natural history of high-risk ACLF. The international guidelines explicitly indicate that these patients should be prioritized for transplant evaluation above simply receiving pharmaceutical therapies [41,87]. In guiding treatment, particularly for HBV-ACLF, the change in SIRI values can be monitored dynamically. When the SIRI value continues to rise during the treatment process, integrated with the MELD-Na score, the treatment strategy can be adjusted over time, incorporating artificial liver support, antiviral medications, or liver transplantation to inform clinical management to improve short-term prognosis.
This study has several limitations. First, the relatively small sample size may limit generalizability and introduce bias. Although post hoc power analysis based on observed data yielded a moderate-to-large effect size (Cohen’s d ≈ 0.67), and the sample size exceeded the estimated requirement, future studies should incorporate more rigorous sample size estimation methods during study design and include larger, independent cohorts to validate these results. Second, SIRI may be affected by treatment protocols. Although all patients received standardized supportive care, individual therapeutic variations were not explicitly analyzed. Future studies should incorporate stratified analysis based on treatment regimens to determine whether SIRI remains a robust prognostic marker across different interventions. Third, the changes in additional inflammatory markers, including CRP and PCT, were not evaluated during the treatment. Fourth, limiting the cohort to ages of 18–65 years minimizes confounding from prevalent age-related comorbidities and polypharmacy, enhancing internal validity for the SIRI-prognosis association. However, this severely restricts generalizability and direct applicability to elderly patients (>65 years), a crucial real-world HBV-ACLF population. Future studies must prioritize including older patients to validate the prognostic utility of SIRI and explore age-specific thresholds. Fifth, our conclusions are applicable only to ACLF patients with MELD 16–32. Since we excluded patients with MELD scores > 32 and those with grade III–IV hepatic encephalopathy, the prognostic value of SIRI in high-risk populations (e.g., MELD > 32 or Grade III-IV HE) requires further validation in future studies. Sixth, given the study design, we did not continually collect long-term follow-up data over 90 days. Future prospective studies are necessary to assess the prognostic significance of SIRI in long-term follow-up. Seventh, some variables with high missing rates, such as HBV DNA, were excluded from the study, and missing data were acknowledged as an additional limitation. Lastly, although patients with uncontrolled infections were excluded, those with controlled infections were included to reflect real-world clinical practice. Since bacterial infections may affect SIRI, future studies with larger cohorts should adjust for infection status in prognostic modeling.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study highlights the prognostic significance of the systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) measured on day 3 in HBV-ACLF patients (MELD 16–32). As an easily obtainable and clinically applicable biomarker, SIRI on day 3 notably enhances the predictive accuracy when combined with the MELD-Na score. Therefore, dynamic monitoring of SIRI, especially on the third day, has important clinical guiding value for evaluating the efficacy of existing treatments and deciding whether additional interventions are needed to alleviate liver failure.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/healthcare13172199/s1, Table S1: Comparison of baseline clinical characteristics between high and low SIRI groups in HBV-ACLF patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Y., H.S. and J.H.; data curation, J.Y., J.C. (Jing Chen), X.L., J.T. and C.L.; formal analysis, J.Y., J.C. (Jing Chen) and J.H.; funding acquisition, J.H.; investigation, H.S., Y.C., T.H., T.C., Q.W., P.G., J.C. (Jinjun Chen) and J.H.; methodology, J.C. (Jing Chen), H.S., Y.C., T.H., T.C., X.L., Q.W., P.G., J.C. (Jinjun Chen) and J.H.; project administration, H.S. and J.H.; resources, Y.C., T.H., T.C., Q.W., P.G., J.C. (Jinjun Chen) and J.H.; software, J.Y. and J.H.; supervision, J.H.; validation, J.Y., J.C. (Jing Chen), C.L. and J.H.; visualization, J.Y., J.C. (Jing Chen) and J.H.; writing—original draft, J.Y.; writing—review and editing, H.S. and J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research, China (NO.2020-1-5031) and the National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Diseases (NCRC-ID202106).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Fifth Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital (protocol code: 2020041D and date of approval: 18 May 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this article.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the participants and investigators of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SIRI | systemic inflammation response index |
| HBV-ACLF | hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| CTP | Child–Turcotte–Pugh |
| MELD | model for end-stage liver disease |
| MELD-Na | model for end-stage liver disease combined with serum sodium |
| CLIF-C OFs | chronic liver failure combined with organ failure score |
| APASL | the Asia Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| WBC | white blood cell count |
| PLT | platelets |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate transaminase |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| GGT | γ glutamate aminotransferase |
| Cr | total bilirubin, creatinine |
| INR | international normalized ratio |
| ALB | albumin |
| SD | standard deviation |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic curves |
| MT | mechanical thrombectomy |
| OS | overall survival |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| TFS | transplantation-free survival |
References
- Mezzano, G.; Juanola, A.; Cardenas, A.; Mezey, E.; Hamilton, J.P.; Pose, E.; Graupera, I.; Ginès, P.; Solà, E.; Hernaez, R. Global burden of disease: Acute-on-chronic liver failure, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2022, 71, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngu, N.L.Y.; Flanagan, E.; Bell, S.; Le, S.T. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Controversies and consensus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Rong, Y.M.; Lu, C.Z.; Li, H. Role of nutritional status and nutritional support in outcome of hepatitis B virus-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 4288–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yan, H.; et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure precipitated by hepatic injury is distinct from that precipitated by extrahepatic insults. Hepatology 2015, 62, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guicciardi, M.E.; Malhi, H.; Mott, J.L.; Gores, G.J. Apoptosis and necrosis in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 977–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; O’Leary, J.G.; Lai, J.C.; Wong, F.; Long, M.D.; Wong, R.J.; Kamath, P.S. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure Clinical Guidelines. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 225–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahmoradi, E.; Mohammadi, R.; Kheirandish Zarandi, P.; Alavian, S.M.; Heiat, M. The CD8+ T cell exhaustion mechanisms in chronic hepatitis B infection and immunotherapeutic strategies: A systematic review. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, X. A Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI)-Based Nomogram for Predicting the Recurrence of Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Radiofrequency Ablation. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; He, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L. The value of NLR versus MLR in the short-term prognostic assessment of HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, A.; Ceolotto, G.; Gola, E.; Sticca, A.; Bova, S.; Morando, F.; Piano, S.; Fasolato, S.; Rosi, S.; Gatta, A.; et al. Positive cardiac inotropic effect of albumin infusion in rodents with cirrhosis and ascites: Molecular mechanisms. Hepatology 2013, 57, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Roisin, R.; Krowka, M.J. Hepatopulmonary syndrome—A liver-induced lung vascular disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Gines, P.; Pavesi, M.; Angeli, P.; Cordoba, J.; Durand, F.; Gustot, T.; Saliba, F.; Domenicali, M.; et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1426–1437.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordoba, J.; Ventura-Cots, M.; Simón-Talero, M.; Amorós, À.; Pavesi, M.; Vilstrup, H.; Angeli, P.; Domenicali, M.; Ginés, P.; Bernardi, M.; et al. Characteristics, risk factors, and mortality of cirrhotic patients hospitalized for hepatic encephalopathy with and without acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L. Role of Immune Dysfunction in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Prognosis. Discov. Med. 2021, 31, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, R.; Liu, X.Z.; Xu, J.C. The Immune Pathogenesis of Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure and the Danger Hypothesis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 935160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccherini, G.; Weiss, E.; Moreau, R. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Definitions, pathophysiology and principles of treatment. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, K.; Sun, X.; Tian, G.; Zhi, Y.; Fan, Z.; Lv, G. The Mechanisms of Systemic Inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure and Application Prospect of Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 5091275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, D.; Kumar, D.; Jagdish, R.K.; Nautiyal, N.; Hidam, A.; Kumari, R.; Sehgal, R.; Trehanpati, N.; Baweja, S.; Kumar, G.; et al. Bioenergetic Failure Drives Functional Exhaustion of Monocytes in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 856587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiuza, C.; Salcedo, M.; Clemente, G.; Tellado, J.M. In vivo neutrophil dysfunction in cirrhotic patients with advanced liver disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.J.; Yang, N.; Mu, X.; Tang, L.; Wang, S.S.; Zhou, C.B.; Yuan, J.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Yu, Y.Y.; Li, J.; et al. Reduction of natural killer cells is associated with poor outcomes in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatol. Int. 2022, 16, 1398–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, A.; Trehanpati, N.; Garg, V.; Kumar, C.; Garg, H.; Sharma, B.C.; Sarin, S.K. Altered frequencies of dendritic cells and IFN-gamma-secreting T cells with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) therapy in acute-on- chronic liver failure. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Yang, F.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Qiu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, S.; Zeng, D.; et al. BTLA contributes to acute-on-chronic liver failure infection and mortality through CD4(+) T-cell exhaustion. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clària, J.; Stauber, R.E.; Coenraad, M.J.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Pavesi, M.; Amorós, À.; Titos, E.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Oettl, K.; et al. Systemic inflammation in decompensated cirrhosis: Characterization and role in acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Ji, Y.; Liu, T.; Bai, J.; Wang, H.; Yao, R.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Shows T-Cell Exhaustion Landscape in the Peripheral Blood of Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Gut Liver 2024, 18, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, M.A.; Kuo, Y.F.; Asrani, S.; Wong, R.J.; Ahmed, A.; Kwo, P.; Terrault, N.; Kamath, P.S.; Jalan, R.; Singal, A.K. Validating a novel score based on interaction between ACLF grade and MELD score to predict waitlist mortality. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, A.; Dirchwolf, M.; Freeman, R.B. From Child-Pugh to MELD score and beyond: Taking a walk down memory lane. Ann. Hepatol. 2022, 27, 100535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, J.; Shao, L.; Xin, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, D.; Jiang, J.; Sun, S.; Jin, L.; et al. Development of diagnostic criteria and a prognostic score for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Gut 2018, 67, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, V.; Angeli, P.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Clària, J.; Trebicka, J.; Fernández, J.; Gustot, T.; Caraceni, P.; Bernardi, M. The systemic inflammation hypothesis: Towards a new paradigm of acute decompensation and multiorgan failure in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, A.; Patel, V.C.; Adelmeijer, J.; Azarian, S.; Hernandez Tejero, M.; Calvo, A.; Fernández, J.; Bernal, W.; Lisman, T. Mixed Fibrinolytic Phenotypes in Decompensated Cirrhosis and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure with Hypofibrinolysis in Those with Complications and Poor Survival. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R. The Pathogenesis of ACLF: The Inflammatory Response and Immune Function. Semin. Liver Dis. 2016, 36, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, E.; Woollard, K.J.; McPhail, M.J.W.; Antoniades, C.G.; Possamai, L.A. The Role of Monocytes and Macrophages in Acute and Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawiah, M.; Hayat Khan, A.; Abu Farha, R.; Usman, A.; Bitar, A.N. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, monocyte-lymphocyte ratio, and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in stroke-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2023, 39, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Guo, N.; Pan, Q.; Wang, Y. RDW, NLR and RLR in predicting liver failure and prognosis in patients with hepatitis E virus infection. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 63, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Zhuang, L.; Shen, Y.; Geng, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Meng, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z. A novel systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) for predicting the survival of patients with pancreatic cancer after chemotherapy. Cancer 2016, 122, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Xie, H.; Yan, P. Prognostic value of the systemic inflammation response index in human malignancy: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e23486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Hu, W.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Jin, B.; Xu, H.; Du, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lu, X.; et al. High Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) Indicates Poor Outcome in Gallbladder Cancer Patients with Surgical Resection: A Single Institution Experience in China. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 52, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.C.; An, T.Z.; Li, J.X.; Pang, P.F. Systemic Inflammation Response Index is a Prognostic Risk Factor in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing TACE. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2021, 14, 2589–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ni, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Chen, P.; Xing, D. Systemic Inflammation Response Index Is a Promising Prognostic Marker in Elderly Patients with Heart Failure: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 871031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, S.K.; Choudhury, A.; Sharma, M.K.; Maiwall, R.; Al Mahtab, M.; Rahman, S.; Saigal, S.; Saraf, N.; Soin, A.S.; Devarbhavi, H.; et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific association for the study of the liver (APASL): An update. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 353–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure (2018 edition). J. Clin. Hepatol. 2019, 35, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, R.N.; Murray-Lyon, I.M.; Dawson, J.L.; Pietroni, M.C.; Williams, R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br. J. Surg. 1973, 60, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, P.S.; Kim, W.R. The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology 2007, 45, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Sedki, M.; Kwong, A.; Kesselman, A.; Kolli, K.P.; Morelli, G.; Spengler, E.; Said, A.; Lai, J.; Desai, A.; et al. Portal Hypertensive Gastropathy and MELD-Na Score Predict Recurrent Gastrointestinal Bleeding After TIPSS: An ALTA Group Study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 61, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalan, R.; Saliba, F.; Pavesi, M.; Amoros, A.; Moreau, R.; Ginès, P.; Levesque, E.; Durand, F.; Angeli, P.; Caraceni, P.; et al. Development and validation of a prognostic score to predict mortality in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Baumgartner, K.; Bositis, C. Cirrhosis: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 100, 759–770. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Controlling and Monitoring the Tobacco Epidemic; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997; Volume 190. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.M.; Fan, J.G.; National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Fatty Liver Disease Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for alcoholic liver disease: A 2018 update. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2018, 26, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Diabetes Society. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of diabetes mellitus in China (2024 edition). Chin. J. Diabetes 2025, 17, 116–139. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.G. Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension (2024 revision). J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2025, 22, 1–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.P.; Wong, F.; Gines, P.; Bernardi, M.; Ochs, A.; Salerno, F.; Angeli, P.; Porayko, M.; Moreau, R.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; et al. The management of ascites in cirrhosis: Report on the consensus conference of the International Ascites Club. Hepatology 2003, 38, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, K.R.; Bajaj, J.S. Covert and Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy: Diagnosis and Management. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 2048–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, G.; Singh, N. The Evolving Challenge of Infections in Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1150–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, A.; Bian, J.; Huang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Sang, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, X.; et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107295–107302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zheng, M.H.; Yang, Y.; Wei, W.; Yang, Q.; Hu, A.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yan, H. Increased delayed mortality in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure who have prior decompensation. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lu, M. Small Molecule Inhibitors of Hepatitis B Virus Nucleocapsid Assembly: A New Approach to Treat Chronic HBV Infection. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gong, G.; Mao, D.; Gong, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, X.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; et al. Nomogram prediction of individual prognosis of patients with acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, W.J.; Sheen, I.S.; Liaw, Y.F. Hepatitis B virus DNA level predicts hepatic decompensation in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, A.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, B.C.; Maiwall, R.; Pamecha, V.; Moreau, R.; Chawla, Y.K.; Duseja, A.; Mahtab, M.; Rahman, S.; et al. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome in acute-on-chronic liver failure: Relevance of ‘golden window’: A prospective study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelmann, C.; Zhang, I.W.; Clària, J. Mechanisms of immunity in acutely decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e15644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, W.; Chen, L.; Gu, J.; Wu, H.; Xu, H.; Gan, J. Utility of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival. Open Life Sci. 2023, 18, 20220644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; EnQiang, C.; Yao, D.L.; LiBo, Y.; Hong, L.; Lang, B.; Ping, F.; Hong, T. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts short term mortality in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure treated with an artificial liver support system. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Liu, T.; Zhao, Q.; Ji, Y.; Bai, J.; Wang, H.; Yao, R.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J. Genetic landscape and immune mechanism of monocytes associated with the progression of acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatol. Int. 2023, 17, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Merwe, S.; Chokshi, S.; Bernsmeier, C.; Albillos, A. The multifactorial mechanisms of bacterial infection in decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75 (Suppl. S1), S82–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, K.; Han, T.; Jiang, H. Evaluation of prognostic values of inflammation-based makers in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Medicine 2018, 97, e13324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, M.; Tröbs, R.B. The lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio may distinguish complicated from non-complicated pediatric appendicitis: A retrospective study and literature review. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2022, 63, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twu, Y.C.; Gold, M.R.; Teh, H.S. TNFR1 delivers pro-survival signals that are required for limiting TNFR2-dependent activation-induced cell death (AICD) in CD8+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotto-Vasquez, G.; Villacorta-Ampuero, A.K.; Ulloque-Badaracco, J.R.; Hernandez-Bustamante, E.A.; Alarcón-Braga, E.A.; Herrera-Añazco, P.; Benites-Zapata, V.A.; Hernandez, A.V. Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio and Clinical Outcomes in Cholangiocarcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavriilidis, P.; Pawlik, T.M. Inflammatory indicators such as systemic immune inflammation index (SIII), systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic factors of curative hepatic resections for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2024, 13, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Xiang, M.; Tang, J.; Xiong, G.; Zhang, K.; Xia, T.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Chai, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Evaluation of peripheral blood inflammation indexes as prognostic markers for colorectal cancer metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, X. A nomogram based on systemic inflammation markers can predict adverse outcomes in patients with heart failure. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2022, 42, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Dong, S.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, A. Inflammation index SIRI is associated with increased all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among patients with hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1066219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Ju, H.; Wang, G.; He, C.; Wang, W. Association of Systemic Inflammation Response Index with Short-Term All-Cause Mortality in Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis Patients. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 8985–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Wu, L.; Tian, Y.; Luo, X.; Ding, X. Values of the systemic inflammation response index in predicting short-term prognosis of patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Chin. J. Pract. Intern. Med. 2023, 43, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, X.; Jiang, J.; Yang, L.; Xin, J.; Shi, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, K.; Hassan, H.M.; et al. PBMC transcriptomics identifies immune-metabolism disorder during the development of HBV-ACLF. Gut 2022, 71, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.; Kumar, A.; Garg, V.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, B.C.; Sarin, S.K. Clinical profile and predictors of mortality in patients of acute-on-chronic liver failure. Dig. Liver Dis. 2012, 44, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, V.; Garg, H.; Khan, A.; Trehanpati, N.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, B.C.; Sakhuja, P.; Sarin, S.K. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilizes CD34(+) cells and improves survival of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 505–512.e501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Wan, Z.; Fang, H.; Chen, J.; Mu, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Su, H.; et al. Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Accelerates the Recovery of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure by Promoting M2-Like Transition of Monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 885829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duseja, A.; Singh, S.P. Toward a Better Definition of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2017, 7, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.; Gao, B.; Papp, M.; Bañares, R.; Kamath, P.S. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: A distinct clinical syndrome. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75 (Suppl. S1), S27–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Zhuo, T. Construction of a novel prognostic scoring model for HBV-ACLF liver failure based on dynamic data. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalan, R.; Pavesi, M.; Saliba, F.; Amorós, A.; Fernandez, J.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Sawhney, R.; Mookerjee, R.; Caraceni, P.; Moreau, R.; et al. The CLIF Consortium Acute Decompensation score (CLIF-C ADs) for prognosis of hospitalised cirrhotic patients without acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Tang, L.L.; Li, L.; Ju, B. Early prediction of acute-on-chronic liver failure development in patients with diverse chronic liver diseases. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; You, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, J.J.; Zhu, Y.Y. Modified model for end-stage liver disease improves short-term prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 7303–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, A.; Jindal, A.; Maiwall, R.; Sharma, M.K.; Sharma, B.C.; Pamecha, V.; Mahtab, M.; Rahman, S.; Chawla, Y.K.; Taneja, S.; et al. Liver failure determines the outcome in patients of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF): Comparison of APASL ACLF research consortium (AARC) and CLIF-SOFA models. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).