Depressive Symptoms and Associated Factors Among Middle-Aged and Older Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Gender Differences Based on a Health Ecological Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Process
2.2. Assessment of CKD
2.3. Assessment of Depressive Symptoms
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Characteristics of Study Participants
3.2. Associated Factors of Depressive Symptoms in Chinese Middle-Aged and Older CKD Patients
3.3. Description of the Basic Characteristics of Participants by Gender
3.4. Gender Differences in Depressive Symptoms and Associated Factors Among CKD Patients
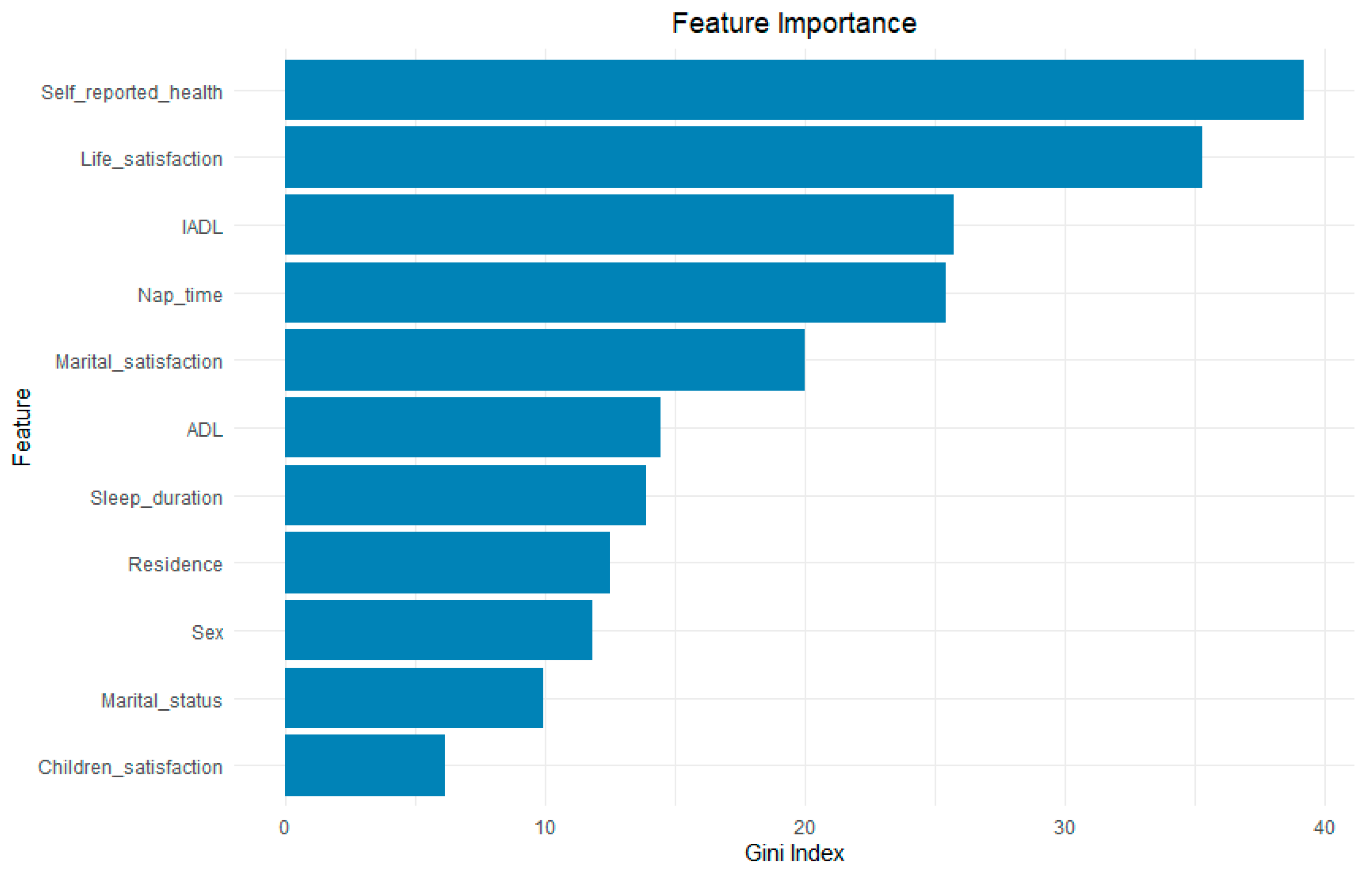
3.5. Results of Random Forest
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, X.; Guo, X.; Ren, Z.; Li, X.; He, M.; Shi, H.; Zha, S.; Qiao, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; et al. The prevalence of depressive symptoms and associated factors in middle-aged and elderly Chinese people. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 293, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Fu, T.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G. Childhood trauma, psychache, and depression among university students: A moderated mediation model. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1414105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, A.; Ghosh, M.; Kar, N.; Basilio, M. Distribution of depressive disorders in the elderly. J. Neurosci. Rural. Pract. 2010, 1, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkotzamanis, V.; Koliopanos, G.; Sanchez-Niubo, A.; Olaya, B.; Caballero, F.F.; Ayuso-Mateos, J.L.; Chatterji, S.; Haro, J.M.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Determinants of verbal fluency trajectories among older adults from the English longitudinal study of aging. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2023, 30, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengpid, S.; Peltzer, K.; Anantanasuwong, D. Prevalence and determinants of incident and persistent depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older adults in thailand: Prospective cohort study. BJPsych Open 2023, 9, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tengku, M.T.; Yunus, R.M.; Hairi, F.; Hairi, N.N.; Choo, W.Y. Social support and depression among community dwelling older adults in asia: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e26667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Ma, C.; Xu, G.; Yin, H.; Xu, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Prevalence of depressive disorders and treatment in China: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiat. 2021, 8, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: An update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2011 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockwell, P.; Fisher, L.A. The global burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2020, 395, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Nie, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, F.F.; et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: Results from the sixth China chronic disease and risk factor surveillance. Jama Intern. Med. 2023, 183, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Global prevalence of chronic kidney disease—A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sharma, S.C.; Chalise, P.; Regmee, J.; Sharma, S. Anxiety and depression among patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing haemodialysis in a tertiary care centre: A descriptive cross-sectional study. JNMA J. Nepal. Med. Assoc. 2022, 60, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.; Vecchio, M.; Craig, J.C.; Tonelli, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Nicolucci, A.; Pellegrini, F.; Saglimbene, V.; Logroscino, G.; Fishbane, S.; et al. Prevalence of depression in chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhi, F.; Abedi, N.; Beyene, J.; Kurdyak, P.; Jassal, S.V. Association between depression and mortality in patients receiving long-term dialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yan, Y.; Qiu, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, R. Association between sedentary behavior and depression in us adults with chronic kidney disease: Nhanes 2007–2018. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Wang, S.; Yan, Y.; Lu, Q.; Pei, J.; Guo, W.; Yang, X.; Li, Y. Association between chronic diseases and depression in the middle-aged and older adult chinese population-a seven-year follow-up study based on charls. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1176669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Huang, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Shang, S. Factors influencing depression in community-dwelling elderly patients with osteoarthritis of the knee in china: A cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, Y.J.; Lee, Y.B. Factors influencing depression among elderly patients in geriatric hospitals. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2013, 25, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of depression incidence and influence factors among middle-aged and elderly diabetic patients in China: Based on charls data. BMC Psychiatry 2024, 24, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.V. Advantages and disadvantages of using artificial neural networks versus logistic regression for predicting medical outcomes. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, X.; Fan, X.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Sun, D. Determinants of life satisfaction in older adults with diabetes in china: A national cross-sectional study. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1585752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Y. Prevalence and predictive risk factors of self-stigmatization in patients with rare diseases: Based on health ecology model. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2023, 69, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, S.; Ge, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, N.; Wang, B.; et al. Classification of high-risk depressed mood groups in cancer patients based on health ecology model. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 347, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Smith, J.P.; Strauss, J.; Yang, G. Cohort profile: The China health and retirement longitudinal study (charls). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchetti, P.; Wolf, L.E.; Segal, M.R.; McCulloch, C.E. Ethics and sample size. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 161, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.; Cao, S.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, R.; Ma, J.; Ran, Q.; Xian, X. An explainable predictive model for anxiety symptoms risk among Chinese older adults with abdominal obesity using a machine learning and shapley additive explanations approach. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1451703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Zou, Y.; Wu, S.K.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.S.; Wang, J.W.; Zhang, L.X.; Zhao, M.H.; Wang, L. Prevalence and associated factors of depressive symptoms among chronic kidney disease patients in China: Results from the Chinese cohort study of chronic kidney disease (c-stride). J. Psychosom. Res. 2020, 128, 109869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.L.; Liang, S.; Zhu, F.L.; Liu, J.Q.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, X.M.; Cai, G.Y. The prevalence of depression and the association between depression and kidney function and health-related quality of life in elderly patients with chronic kidney disease: A multicenter cross-sectional study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Wan, B.; Zhong, J.; Wang, M.; Tang, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Ye, Y.; Liu, X.; Peng, L.; et al. Risk of fall in patients with chronic kidney disease: Results from the China health and retirement longitudinal study (charls). BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.; Artin, K.H.; Oxman, M.N. Screening for depression in the older adult: Criterion validity of the 10-item center for epidemiological studies depression scale (ces-d). Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, H.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Tao, Q. The reliability and validity of the center for epidemiologic studies depression scale (ces-d) for Chinese university students. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, E.M.; Malmgren, J.A.; Carter, W.B.; Patrick, D.L. Screening for depression in well older adults: Evaluation of a short form of the ces-d (center for epidemiologic studies depression scale). Am. J. Prev. Med. 1994, 10, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.; Yin, W. The relationship between depressive symptoms and activity of daily living disability among the elderly: Results from the China health and retirement longitudinal study (charls). Public Health 2021, 198, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Duan, Y.; Guo, F.; Chen, G. Prevalence and related influencing factors of depression symptoms among empty-nest older adults in China. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 91, 104183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, S.; Yan, X.; Pei, L.; Wang, Z. Adverse childhood experiences and trajectories of adl disability among middle-aged and older adults in China: Findings from the charls cohort study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2022, 26, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Lin, H.; Ma, X.; Ma, H.; Lan, Y.; Sun, P.; Yang, J. The regional disparities in liver disease comorbidity among elderly chinese based on a health ecological model: The China health and retirement longitudinal study. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Lin, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z.; Jiang, X. Association between activities of daily living and depressive symptoms among older adults in China: Evidence from the charls. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1249208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Ke, C. Longitudinal follow-up studies on the bidirectional association between adl/iadl disability and multimorbidity: Results from two national sample cohorts of middle-aged and elderly adults. Gerontology 2021, 67, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, P.; He, Y. Effect of chemotherapy on prognosis in patients with primary pancreatic signet ring cell carcinoma: A large real-world study based on machine learning. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e302685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, X.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, K. Association between indoor ventilation frequency and iadl disability among Chinese older adults. Indoor Air 2025, 2025, 7882633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Miranda, A.; Craig, D.W.; Shekhtman, T.; Kmoch, S.; Bleyer, A.; Szelinger, S.; Kato, T.; Kelsoe, J.R. Ntrk1 mutation co-segregating with bipolar disorder and inherited kidney disease in a multiplex family causes defects in neuronal growth and depression-like behavior in mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibotto, G.; Esposito, P.; Picciotto, D.; Verzola, D. Testosterone disorders and male hypogonadism in kidney disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2021, 41, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morssinkhof, M.; van Wylick, D.W.; Priester-Vink, S.; van der Werf, Y.D.; den Heijer, M.; van den Heuvel, O.A.; Broekman, B. Associations between sex hormones, sleep problems and depression: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sovijit, W.N.; Sovijit, W.E.; Pu, S.; Usuda, K.; Inoue, R.; Watanabe, G.; Yamaguchi, H.; Nagaoka, K. Ovarian progesterone suppresses depression and anxiety-like behaviors by increasing the lactobacillus population of gut microbiota in ovariectomized mice. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 168, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daches, S.; Vine, V.; George, C.J.; Kovacs, M. Age related sex differences in maladaptive regulatory responses to sadness: A study of youths at high and low familial risk for depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 294, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; He, D. Self-rated health, socioeconomic status and all-cause mortality in Chinese middle-aged and elderly adults. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Montagni, I.; Matsuzaki, K.; Shimamoto, T.; Cariou, T.; Kawamura, T.; Tzourio, C.; Iwami, T. The association between depressive symptoms and self-rated health among university students: A cross-sectional study in France and Japan. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, S.S.; Muthuppalaniappan, V.; Banerjee, D. Gaps in modern heart failure and chronic kidney disease research. Eur. Cardiol. 2023, 18, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kong, J.; Pan, J.; Huang, K.; Zhou, W.; Diao, X.; Cai, J.; Zheng, J.; Yang, X.; Xie, W.; et al. Kidney damage causally affects the brain cortical structure: A mendelian randomization study. Ebiomedicine 2021, 72, 103592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.H.; Wu, K.; Luo, H.Q.; Cao, P.Y.; Ren, X.H. prevalence of loss of activities of daily living and influencing factors in elderly population in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2016, 37, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, A.; Wellard, S.; Caltabiano, M. The impact of fatigue on daily activity in people with chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Nurs. 2010, 19, 3006–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, N.; Han, Q.; Li, T.; Feng, Z.; He, Q.; Shen, Y. The role of depression and physical activity in the association of between sleep quality, and duration with and health-related quality of life among the elderly: A uk biobank cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.F.; Hsu, P.T.; Yang, K.L. The mediating effect of sleep quality and fatigue between depression and renal function in nondialysis chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.; Han, L.K.; Verhoeven, J.E.; Aberg, K.A.; van den Oord, E.C.; Milaneschi, Y.; Penninx, B.W. An integrative study of five biological clocks in somatic and mental health. Elife 2021, 10, e59479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Di, J.; Zhao, G.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Association of nighttime sleep duration with depressive symptoms and its interaction with regular physical activity among Chinese adolescent girls. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murack, M.; Kadamani, A.K.; Guindon-Riopel, A.; Traynor, O.H.; Iqbal, U.H.; Bronner, S.; Messier, C.; Ismail, N. The effect of probiotic supplementation on sleep, depression-like behaviour, and central glucose and lactate metabolism in male and female pubertal mice exposed to chronic sleep disruption. Psychoneuroendocrino 2024, 168, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocek, J.; Prasko, J.; Genzor, S.; Hodny, F.; Vanek, J.; Pobeha, P.; Belohradova, K.; Ociskova, M. Sleep disturbance and immunological consequences of covid-19. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2023, 17, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Virtanen, S.; Xu, H.; Carrero, J.J.; Chang, Z. Association between incident depression and clinical outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Cheng, Y.C.; Zhang, N.H.; Luo, R.; Guo, K.L.; Ge, S.W.; Xu, G. Effect of marital status on depression and mortality among patients with chronic kidney disease from national health and nutrition examination survey 2005–2014. Kidney Dis. 2021, 7, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, J.K.; Levy, B.; Chen, B.; Fried, T.; Stahl, S.T.; Schulz, R.; Doyle, M.; Kershaw, T. Husbands’ and wives’ physical activity and depressive symptoms: Longitudinal findings from the cardiovascular health study. Ann. Behav. Med. 2015, 49, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, M.R.; Choi, E.J.; Ko, E.; Um, Y.J.; Choi, Y.J. The mediating effect of life satisfaction and the moderated mediating effect of social support on the relationship between depression and suicidal behavior among older adults. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2021, 36, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Felix, M.S.; Paek, S.C.; Lamy, F.R. Social activities and depressive symptoms among elderly based on rural and urban differences in China: A national cross-sectional study. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2024, 17, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, N.H.N.; Thi, K.H.N.; Hue, M.T.; Luong, N.T.; Quoc, T.P.; Duc, D.M.; Thi Thanh Mai, V.; Hong, T.T. Perceived barriers to mental health services among the elderly in the rural of vietnam: A cross sectional survey in 2019. Health Serv. Insights 2021, 14, 1647035789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzaro, D.; Becchetti, C.; Trapani, S.; Lavezzo, B.; Zanetto, A.; D’Arcangelo, F.; Merli, M.; Lapenna, L.; Invernizzi, F.; Taliani, G.; et al. Influence of sex in alcohol-related liver disease: Pre-clinical and clinical settings. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2023, 11, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivielso, J.M.; Carriazo, S.; Martin, M.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Bermudez-López, M.; Ortiz, A. Gender-specific risk factors and outcomes of hyperkalemia in ckd patients: Smoking as a driver of hyperkalemia in men. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, d212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eveleens, M.B.; Chesnaye, N.C.; Schouten, R.; Michels, W.M.; Bos, W.; Szymczak, M.; Krajewska, M.; Evans, M.; Heimburger, O.; Caskey, F.J.; et al. Associations between depressive symptoms and disease progression in older patients with chronic kidney disease: Results of the equal study. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Peng, X.; Gu, Y.; Shang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, L.; Mei, G.; Xiong, C.; Li, H.; et al. Associations between smoking, sex hormone levels and late-onset hypogonadism in men differ depending on age. Aging Albany NY 2021, 13, 5226–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Total (n = 1422) | Male (n = 789) | Female (n = 633) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic factors | |||
| Age, n (%) | |||
| 45–60 | 335 (23.56) | 166 (21.04) | 169 (26.70) |
| >60 | 1087 (76.44) | 623 (78.96) | 464 (73.30) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Non-Han | 118 (8.30) | 59 (7.48) | 59 (9.32) |
| Han | 1304 (91.70) | 730 (92.52) | 574 (90.68) |
| Self-reported Health, n (%) | |||
| Good | 147 (10.34) | 104 (13.18) | 43 (6.79) |
| Fair | 645 (45.36) | 364 (46.13) | 281 (44.39) |
| Poor | 630 (44.30) | 321 (40.68) | 309 (48.82) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | |||
| No | 1250 (87.90) | 681 (86.31) | 569 (89.89) |
| Yes | 172 (12.10) | 108 (13.69) | 64 (10.11) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | |||
| No | 1310 (92.12) | 735 (93.16) | 575 (90.84) |
| Yes | 112 (7.88) | 54 (6.84) | 58 (9.16) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | |||
| No | 894 (62.87) | 501 (63.50) | 393 (62.09) |
| Yes | 528 (37.13) | 288 (36.50) | 240 (37.91) |
| Stroke, n (%) | |||
| No | 1266 (89.03) | 694 (87.96) | 572 (90.36) |
| Yes | 156 (10.97) | 95 (12.04) | 61 (9.64) |
| Depressive Symptoms, n (%) | |||
| No | 706(49.65) | 450(57.03) | 256(40.44) |
| Yes | 716(50.35) | 339(42.97) | 377(59.56) |
| ADLs, n (%) | |||
| No | 1048 (73.70) | 613 (77.69) | 435 (68.72) |
| Yes | 374 (26.30) | 176 (22.31) | 198 (31.28) |
| IADLs, n (%) | |||
| No | 963 (67.72) | 583 (73.89) | 380 (60.03) |
| Yes | 459 (32.28) | 206 (26.11) | 253 (39.97) |
| Health behavior factors | |||
| Smoking, n (%) | |||
| No | 1400 (98.45) | 771 (97.72) | 629 (99.37) |
| Yes | 22 (1.55) | 18 (2.28) | 4 (0.63) |
| Drinking, n (%) | |||
| No | 932 (65.54) | 380 (48.16) | 552 (87.20) |
| Yes | 490 (34.46) | 409 (51.84) | 81 (12.80) |
| Nap Time, n (%) | |||
| 0 | 584 (41.07) | 286 (36.25) | 298 (47.08) |
| <30 | 277 (19.48) | 153 (19.39) | 124 (19.59) |
| 30–89 | 353 (24.82) | 215 (27.25) | 138 (21.80) |
| ≥90 | 208 (14.63) | 135 (17.11) | 73 (11.53) |
| Sleep Duration, n (%) | |||
| <7 | 1096 (77.07) | 571 (72.37) | 525 (82.94) |
| 7–9 | 278 (19.55) | 183 (23.19) | 95 (15.01) |
| >9 | 48 (3.38) | 35 (4.44) | 13 (2.05) |
| Activity, n (%) | |||
| Inactive | 635 (44.66) | 352 (44.61) | 283 (44.71) |
| Active | 787 (55.34) | 437 (55.39) | 350 (55.29) |
| Social network factors | |||
| Marital Status, n (%) | |||
| Other | 153 (10.76) | 62 (7.86) | 91 (14.38) |
| Married and Cohabiting | 1269 (89.24) | 727 (92.14) | 542 (85.62) |
| Marital Satisfaction, n (%) | |||
| Dissatisfied | 164 (11.53) | 46 (5.83) | 118 (18.64) |
| Satisfied | 1258 (88.47) | 743 (94.17) | 515 (81.36) |
| Children Satisfaction, n (%) | |||
| Dissatisfied | 81 (5.70) | 47 (5.96) | 34 (5.37) |
| Satisfied | 1341 (94.30) | 742 (94.04) | 599 (94.63) |
| Life Satisfaction, n (%) | |||
| Dissatisfied | 228 (16.03) | 100 (12.67) | 128 (20.22) |
| Satisfied | 1194 (83.97) | 689 (87.33) | 505 (79.78) |
| Living and working conditions factors | |||
| Place of Residence, n (%) | |||
| Urban | 421 (29.61) | 239 (30.29) | 182 (28.75) |
| Rural | 1001 (70.39) | 550 (69.71) | 451 (71.25) |
| Type of Residence, n (%) | |||
| Private Residence | 1382 (97.19) | 765 (96.96) | 617 (97.47) |
| Other | 40 (2.81) | 24 (3.04) | 16 (2.53) |
| Education Level, n (%) | |||
| Illiterate | 226 (15.89) | 64 (8.11) | 162 (25.59) |
| Primary School or Below | 663 (46.62) | 370 (46.89) | 293 (46.29) |
| Above Primary School | 533 (37.48) | 355 (44.99) | 178 (28.12) |
| Social policy factors | |||
| Insurance, n (%) | |||
| No | 26 (1.83) | 11 (1.39) | 15 (2.37) |
| Yes | 1396 (98.17) | 778 (98.61) | 618 (97.63) |
| Pension, n (%) | |||
| No | 1099 (77.29) | 575 (72.88) | 524 (82.78) |
| Yes | 323 (22.71) | 214 (27.12) | 109 (17.22) |
| Variables | OR (95%CI) | p | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic factors | |||
| Gender | 1.405 | ||
| Male | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Female | 1.40 (1.05–1.87) | 0.021 | |
| Age | 1.122 | ||
| 45–60 | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| ≥60 | 0.97 (0.72–1.31) | 0.832 | |
| Ethnicity | 1.024 | ||
| Non-Han | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Han | 1.18 (0.76–1.84) | 0.466 | |
| Self-reported Health | 1.339 | ||
| Good | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Fair | 1.35 (0.87–2.09) | 0.178 | |
| Poor | 3.04 (1.92–4.81) | <0.001 | |
| Hypertension | 1.044 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 0.99 (0.68–1.44) | 0.946 | |
| Diabetes | 1.041 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 0.66 (0.41–1.06) | 0.083 | |
| Dyslipidemia | 1.141 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 1.10 (0.84–1.44) | 0.488 | |
| Stroke | 1.078 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 1.47 (0.97–2.23) | 0.066 | |
| ADLs | 1.396 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 1.48 (1.08–2.05) | 0.016 | |
| IADLs | 1.450 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 1.98 (1.46–2.68) | <0.001 | |
| Health behavior factors | |||
| Smoking | 1.036 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 2.13 (0.76–5.99) | 0.153 | |
| Drinking | 1.284 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 1.00 (0.75–1.34) | 1.000 | |
| Nap Time | 1.121 | ||
| <30 | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| 0 | 0.97 (0.69–1.36) | 0.845 | |
| 30–89 | 0.81 (0.56–1.17) | 0.264 | |
| ≥90 | 0.57 (0.37–0.87) | 0.010 | |
| Sleep Duration | 1.083 | ||
| 7–9 | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| <7 | 1.37 (1.01–1.88) | 0.048 | |
| >9 | 1.11 (0.54–2.25) | 0.782 | |
| Activity | 1.092 | ||
| Inactive | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Active | 1.03 (0.80–1.33) | 0.803 | |
| Social network factors | |||
| Marital Satisfaction | 1.274 | ||
| Dissatisfied | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Satisfied | 0.33 (0.20–0.56) | <0.001 | |
| Children Satisfaction | 1.164 | ||
| Dissatisfied | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Satisfied | 0.39 (0.19–0.77) | 0.007 | |
| Life Satisfaction | 1.253 | ||
| Dissatisfied | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Satisfied | 0.22 (0.14–0.35) | <0.001 | |
| Marital Status | 1.056 | ||
| Other | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Married and Cohabiting | 0.46 (0.30–0.70) | <0.001 | |
| Living and working conditions factors | |||
| Place of Residence | 1.459 | ||
| Urban | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Rural | 1.83 (1.32–2.54) | <0.001 | |
| Type of Residence | 1.047 | ||
| Private Residence | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Other | 0.73 (0.33–1.58) | 0.420 | |
| Education Level | 1.379 | ||
| Illiterate | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Primary School or Below | 1.01 (0.69–1.47) | 0.951 | |
| Above Primary School | 0.89 (0.59–1.35) | 0.578 | |
| Social policy factors | |||
| Insurance | 1.021 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 0.77 (0.29–2.03) | 0.590 | |
| Pension | 1.555 | ||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | ||
| Yes | 0.87 (0.61–1.25) | 0.458 | |
| Variables | Male | Female | Coefficient (B) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | OR (95%CI) | VIF | p | OR (95%CI) | VIF | ||
| Demographic factors | |||||||
| Age | 1.123 | 1.182 | |||||
| 45–60 | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| >60 | 0.457 | 1.17 (0.77–1.79) | 0.230 | 0.75 (0.47–1.20) | −0.400 | ||
| Ethnicity | 1.043 | 1.046 | |||||
| Non-Han | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Han | 0.844 | 0.94 (0.51–1.75) | 0.274 | 1.44 (0.75–2.75) | 0.450 | ||
| Self-reported Health | 1.350 | 1.382 | |||||
| Good | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Fair | 0.135 | 1.53 (0.88–2.67) | 0.636 | 1.20 (0.57–2.54) | −0.102 | ||
| Poor | <0.001 | 3.31 (1.85–5.94) | 0.007 | 2.97 (1.35–6.53) | −0.042 | ||
| Hypertension | 1.057 | 1.079 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | 0.531 | 0.86 (0.53–1.39) | 0.333 | 1.38 (0.72–2.65) | 0.535 | ||
| Diabetes | 1.039 | 1.088 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | 0.101 | 0.56 (0.28–1.12) | 0.300 | 0.70 (0.35–1.38) | 0.419 | ||
| Dyslipidemia | 1.210 | 1.119 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | 0.406 | 0.85 (0.59–1.24) | 0.061 | 1.49 (0.98–2.27) | 0.475 | ||
| Stroke | 1.094 | 1.110 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | 0.343 | 1.28 (0.77–2.16) | 0.070 | 2.02 (0.94–4.34) | 0.400 | ||
| ADLs | 1.364 | 1.428 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | 0.020 | 1.68 (1.09–2.61) | 0.359 | 1.26 (0.77–2.05) | −0.403 * | ||
| IADLs | 1.395 | 1.506 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | <0.001 | 2.39 (1.58–3.62) | 0.051 | 1.58 (1.00–2.50) | −0.454 | ||
| Health behavior factors | |||||||
| Smoking | 1.046 | 1.034 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | 0.039 | 3.32 (1.06–10.33) | 0.543 | 0.40 (0.02–7.69) | −2.066 * | ||
| Drinking | 1.091 | 1.074 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | 0.878 | 1.03 (0.73–1.44) | 0.990 | 1.00 (0.55–1.85) | −0.064 | ||
| Nap Time | 1.137 | 1.179 | |||||
| <30 | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| 0 | 0.689 | 0.91 (0.57–1.45) | 0.958 | 0.99 (0.58–1.67) | −0.071 | ||
| 30–89 | 0.309 | 0.78 (0.48–1.27) | 0.488 | 0.81 (0.44–1.49) | −0.053 | ||
| ≥90 | 0.076 | 0.61 (0.35–1.05) | 0.039 | 0.47 (0.23–0.96) | −0.390 | ||
| Sleep Duration | 1.099 | 1.154 | |||||
| 7–9 | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| <7 | 0.296 | 1.24 (0.83–1.86) | 0.144 | 1.49 (0.87–2.55) | −0.154 | ||
| >9 | 0.361 | 1.50 (0.63–3.57) | 0.415 | 0.57 (0.15–2.21) | −1.328 | ||
| Activity | 1.125 | 1.079 | |||||
| Inactive | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Active | 0.831 | 0.96 (0.69–1.35) | 0.370 | 1.20 (0.81–1.79) | 0.211 | ||
| Social network factors | |||||||
| Marital Status | 1.076 | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.055 | ||||
| Other | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Married and Cohabiting | 0.039 | 0.53 (0.29–0.97) | 0.003 | 0.39 (0.21–0.73) | −0.211 | ||
| Marital Satisfaction | 1.172 | 1.335 | |||||
| Dissatisfied | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Satisfied | 0.007 | 0.29 (0.12–0.71) | <0.001 | 0.31 (0.16–0.61) | 0.149 | ||
| Children Satisfaction | 1.143 | 1.243 | |||||
| Dissatisfied | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Satisfied | 0.066 | 0.48 (0.22–1.05) | 0.092 | 0.24 (0.05–1.26) | −0.575 | ||
| Life Satisfaction | 1.268 | 1.274 | |||||
| Dissatisfied | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Satisfied | <0.001 | 0.25 (0.14–0.46) | <0.001 | 0.20 (0.10–0.40) | −0.272 | ||
| Living and working conditions factors | |||||||
| Place of Residence | 1.438 | 1.596 | |||||
| Urban | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Rural | 0.047 | 1.55 (1.01–2.38) | 0.002 | 2.34 (1.38–3.97) | 0.217 | ||
| Type of Residence | 1.080 | 1.067 | |||||
| Private Residence | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Other | 0.757 | 1.17 (0.43–3.20) | 0.130 | 0.37 (0.10–1.34) | −1.173 | ||
| Education Level | 1.282 | 1.431 | |||||
| Illiterate | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Primary School or Below | 0.533 | 1.22 (0.65–2.28) | 0.523 | 0.85 (0.51–1.41) | −0.126 | ||
| Above Primary School | 0.454 | 1.28 (0.67–2.46) | 0.088 | 0.59 (0.33–1.08) | −0.394 | ||
| Social policy factors | |||||||
| Insurance | 1.024 | 1.034 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | 0.375 | 0.54 (0.14–2.10) | 0.907 | 0.92 (0.24–3.55) | 0.626 | ||
| Pension | 1.509 | 1.654 | |||||
| No | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | |||||
| Yes | 0.201 | 0.74 (0.47–1.17) | 0.676 | 1.14 (0.61–2.15) | 0.202 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Mou, Y.; Lan, Y.; Sharma, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. Depressive Symptoms and Associated Factors Among Middle-Aged and Older Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Gender Differences Based on a Health Ecological Model. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13161951
Zhang Y, Huang Y, Zhang W, Shi Y, Mou Y, Lan Y, Sharma M, Zhang L, Zhao Y. Depressive Symptoms and Associated Factors Among Middle-Aged and Older Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Gender Differences Based on a Health Ecological Model. Healthcare. 2025; 13(16):1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13161951
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Yingqi Huang, Wenhui Zhang, Ya Shi, Youtao Mou, Yuanyuan Lan, Manoj Sharma, Lei Zhang, and Yong Zhao. 2025. "Depressive Symptoms and Associated Factors Among Middle-Aged and Older Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Gender Differences Based on a Health Ecological Model" Healthcare 13, no. 16: 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13161951
APA StyleZhang, Y., Huang, Y., Zhang, W., Shi, Y., Mou, Y., Lan, Y., Sharma, M., Zhang, L., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Depressive Symptoms and Associated Factors Among Middle-Aged and Older Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Gender Differences Based on a Health Ecological Model. Healthcare, 13(16), 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13161951







