Abstract
Background and aim: Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs) are innovative drugs based on genes, tissues, or cells that target rare and severe diseases. ATMPs have shown promising clinical outcomes but are associated with high costs, raising questions about cost-effectiveness. Hence, this systematic review aims to analyze the cost-effectiveness and cost-utility profiles of the European Medicines Agency-authorized ATMPs for treating rare diseases. Methods: A systematic review was conducted following PRISMA guidelines. Studies were identified by searching PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and ProQuest scientific databases. Economic evaluations reporting incremental cost-effectiveness/utility ratios (ICERs/ICURs) for ATMPs were included. Costs were standardized to 2023 Euros, and a cost-effectiveness plane was constructed to evaluate the results against willingness-to-pay (WTP) thresholds of EUR 50,000, EUR 100,000, and EUR 150,000 per QALY, as part of a sensitivity analysis. Results: A total of 61 studies met the inclusion criteria. ATMPs for rare blood diseases, such as tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel, were found to be cost-effective in a majority of studies, with incremental QALYs ranging from 1.5 to 10 per patient over lifetime horizon. Tisagenlecleucel demonstrated a positive cost-effectiveness profile in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (58%), while axicabtagene ciloleucel showed a positive profile in the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (85%). Onasemnogene abeparvovec for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) showed uncertain cost-effectiveness results, and voretigene neparvovec for retinal diseases was not cost-effective in 40% of studies, with incremental QALYs around 1.3 and high costs exceeding the WTP threshold set. Conclusions: ATMPs in treating rare diseases show promising economic potential, but cost-effectiveness varies across indications. Policymakers must balance innovation with system sustainability, using refined models and the long-term impact on patient outcomes.
1. Introduction
Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs) were developed as innovative biological products that directly target the cause of the disease and significantly improve health outcomes of patients who face neoplasms, metabolic, blood, cardiovascular, neurologic, retinal, and rare diseases [1]. The Committee for Advanced Therapies (CAT), established by the European Medicines Agency (EMA), has classified ATMPs as gene therapies, somatic-cell therapies, tissue-engineered medicines, and combined ATMPs [2]. In 2008, the Advanced Medicines Regulation was implemented, regulating the development and marketing authorization of ATMPs, providing an immense opportunity to treat rare diseases [3]. The definitions and classification according to Regulation (EC) No 1394/2007 and Directive 2001/83/EC are represented in Supplementary Material Table S1. The centralized authorization process is carried out through the CAT, and is responsible for the scientific evaluation, classification, safety, efficacy, and quality estimate, and the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) provides the final decisions based on submitted opinions [4]. In 2024, 20 ATMPs were already authorized within the European Union market, 16 with orphan designation proposed for rare disease treatment [5]. ATMPs are associated with elevated costs, largely due to their innovative, often one-time administration; especially in the case of ATMPs for ultra-rare diseases, the cost per patient tends to be even higher than for rare diseases. However, it remains unclear whether these prices are justified by clinical outcomes [6]. In this sense, economic evaluations are crucial to ensure that innovative and advanced treatments provide value for money while considering budget constraints [7,8]. However, this can be challenging due to the following methodological issues: limited size and design of trials, uncertain data on long-term effects, uncertain efficacy assessment, limited data on estimating impact on quality of life, and reduced generalizability [7]. Furthermore, to inform healthcare payers, there is a great need for robust economic evidence in ATMP therapies [7]. Despite this, to date, there is a lack in the literature addressing an overview of the real cost-effectiveness profile of ATMPs for rare diseases, considering their sustained therapeutic and clinical outcomes. Hence, using cost-effectiveness principles may assess the health and cost impact of ATMPs, compared to standard treatments, and assist in economic allocation strategies considering budget constraints. Therefore, this study aims to create an overview of the current state of the art regarding the cost-effectiveness and/or cost-utility profiles of ATMPs for rare and ultra-rare diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol, Registration, and Reporting
The protocol for this review was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO, reference CRD42023472088). A systematic review was conducted, and its reporting followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020 statement guidelines) [9].
2.2. Eligibility Criteria, Information Sources, and Search Strategy
The literature search was conducted on 4 October 2024, according to the eligibility criteria detailed in Table 1. During the literature research, the following databases were used: PubMed (MEDLINE), Embase, Web of Science, and ProQuest. The search strategy included a combination of headings and keywords to delineate the target, Patient, Intervention (check Table S2), Comparator, Outcomes, and Study design (PICOS), criteria, utilizing MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) or Emtree terms, as appropriate, and searching within the title and abstract fields detailed in Table S3. We conducted a targeted three-stage search using brand names of ATMPs, their generic names, and pharmacoeconomic terms such as “cost-effectiveness,” “cost–utility,” “ICER,” “ICUR”, “QALY,” and “economic evaluation.” Boolean operators AND/OR were utilized to refine the search parameters. Search strategy and syntax are detailed in the Supplementary Material (Tables S3 and S4).

Table 1.
Eligibility criteria.
2.3. Study Selection, Data Extraction, and Data Synthesis
The literature search and screening process, which was based on the PICOS question, was independently conducted by two researchers (M.S. and M.K.) using a double-blind process. To assess the level of agreement between reviewers during the study selection phase, the Cohen’s kappa coefficient was calculated. All records were independently evaluated by both reviewers, resulting in a substantial agreement (Cohen’s kappa = 0.78), indicating reliable inter-rater consistency. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion or by involving a third reviewer (S.M.). After the duplicate studies were removed, the titles and abstracts of identified studies were reviewed, selecting those suitable for further assessment. Afterward, the full text of the identified studies was reviewed to ensure the completeness of all criteria (Figure 1). The differences that arose during the research were discussed, and the opinion of the other two researchers (E.M. and V.O.) was sought. The following data were extracted from each record identified: country of the paper, year of publication, INN name of the evaluated ATMP, treatment comparator, therapeutic indication (diagnosis) to which medicine was assessed, incremental cost-effectiveness/cost-utility ratio, as well as whether ATMP cost-effective profile (see Table S5). Additionally, methodological aspects of all the economic evaluations included were evaluated by extracting data regarding study design, type of costs considered (direct and indirect), costs’ perspectives, willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of the country considered in the study, and reference year of costs, as well as applied discount rate, the presence of sensitivity analyses, and time horizon of the analysis (see Table S6).
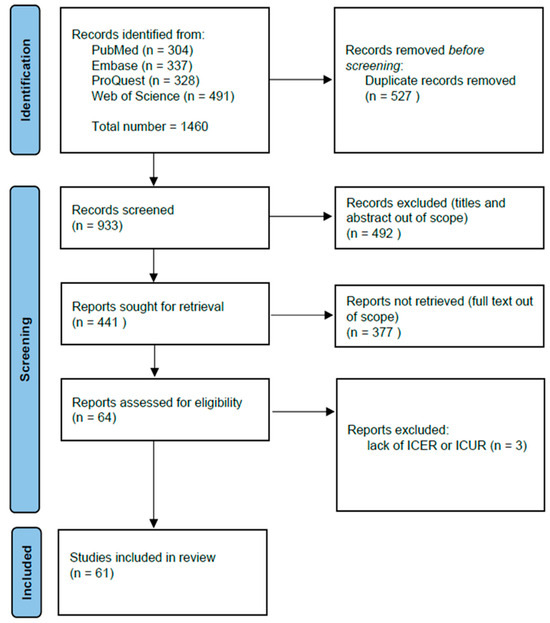
Figure 1.
The PRISMA flow diagram of study selection.
2.4. Quality Assessment
The quality of papers and assessment was evaluated using a checklist proposed by Olry de Labry-Lima et al. [10]. The checklist was compiled using a questionnaire composed by ISPOR to assess the credibility and relevance of economic modeling studies [11,12]. It also incorporates guidelines for conducting a systematic review of economic evaluation [11,12]. Through the use of the checklist, the adequacy of all studies was assessed, including their methodological soundness and conclusions. This evaluation covered several domains of design (eligible population, intervention, and comparator, and adequate study design, appropriate time horizon, and viewpoint study perspective), data analysis (resources, unit costs, relevant outcome, main measure of effect, and sensitivity analysis), interpretation, generalizability, and conflict of interest [10]. A detailed explanation of each domain is shown in Table S7. Compared to the CHEERS checklist, the checklist used in this study also includes reporting information of the following: study population, setting and location, comparators, perspective, time horizon, discount rate, selection, measurement and valuation of outcomes, currency, rationale and description of the model, analytics and assumptions, characterizing uncertainty, characterizing heterogeneity, conflict of interest, and generalizability. In addition, each study was assessed for a wide range of potential biases. These included selection bias, study design bias, measurement bias, data availability bias, extrapolation bias, modeling bias, assumption bias, uncertainty bias, data source bias, omission bias, and misclassification bias. Because many of the included studies were sponsored by pharmaceutical companies, a separate column indicating any potential conflicts of interest was included. This was performed in cases where the company that funded the study had at least one employee listed as an author. To assess the robustness of our primary outcome, we excluded studies with a high or unclear risk of bias. Studies scoring above an arbitrary threshold of 75% were considered to have higher reporting quality [7]. The results are represented as moderate/low (the effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimated effect), moderate (moderately confident in the estimated effect), moderate/high (the effect is likely to be close to the estimated effect), or high (effect lies close to that of the estimated effect estimate).
Quality assessment analysis was conducted by two reviewers (M.S. and M.K.) independently, and any discrepancies were discussed.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) and incremental cost-utility ratio (ICUR) were identified and extracted for each included study to summarize the estimated cost-effectiveness for each ATMP. In studies where the pharmacoeconomic profile is not explicitly stated but expressed in percentages, without explicit information about pharmacoeconomic profile, we considered any profile exceeding 50% to be cost-effective; otherwise, it was classified as negative. Also, for studies that did not explicitly report ICER/ICUR values, these were calculated as the difference in costs between the intervention and the comparator, divided by the difference in their effectiveness, representing the additional cost per additional unit of health benefit (e.g., QALY) gained. All identified ICER/ICUR values were standardized in a single currency (Euro). To ensure comparability, all costs were adjusted for inflation and converted into 2023 Euros using the CCEMG-EPPI cost converter tool (2024 version). CCEMG–EPPI represents a two-stage tool. In the first stage, the original cost is adjusted to 2023 price levels using a gross domestic product deflator index (‘GDPD values’), which is seen as a measure of overall inflation, considering price changes across many different economic sectors. Additionally, in the second stage, the calculator was used to convert the 2023 price–year adjusted cost estimate from the original currency to Euros using conversion rates based on purchasing power parity (PPP) for GDP. This makes currency conversion more accurate, so costs are compared using the same average international standards, which is not based just on exchange rates but rather the actual cost in each country [13]. In cases where the base year was not specified in the study, the year of publication was used.
A qualitative analysis of all ATMPs’ CE profiles identified was represented with a Sankey flow diagram grouping for ATMPs and their approved indications. Finally, given well-documented concerns about a meta-analysis of cost-effectiveness studies (including heterogeneity in resource utilization and pricing across contexts), no meta-analysis was attempted for this study [14,15,16,17].
Cost-effective profiles of ATMPs for rare diseases were compared on a cost-effectiveness plane. Results were plotted in terms of incremental QALYs (x-axis) and incremental costs relative to alternative treatments (y-axis). To set a common threshold for the cost-effectiveness profile definition, which considers substantial differences in willingness to pay (WTP) across global settings, a sensitivity analysis was carried out using three WTP thresholds: EUR 50,000/QALY, EUR 100,000/QALY, and EUR 150,000/QALY. These high thresholds were also set considering the Highly Specialised Technologies (HST) program, established by the British National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE), which recommends higher WTPs for very rare conditions.
All screening and data management tasks were performed using Microsoft Excel, version 2406 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA), while Sankey diagrams were created with the Sankey MATIC tool [18]. The cost-effectiveness plane was generated using the R programming language for statistical computing (R and R Studio, version 4.4.2).
3. Results
3.1. The Literature Search and Screening Results
The search across the four databases queried identified 1460 relevant papers. As shown in Figure 1, n = 527 duplicates were removed, and n = 933 titles and abstracts were screened, yielding n = 441 eligible studies. Additionally, n = 337 papers without full-text availability were removed. During the full-text screening stage, we excluded all publication types that did not meet the eligibility criteria. Reports assessed for eligibility were n = 64, and among these, n = 3 were excluded due to a lack of information on ICER/ICUR or QALY. The final number of studies included in the systematic review was n = 61 (Figure 1).
3.2. Quality Assessment Results
The assessments of the quality of evidence were conducted using the checklist from Olry de Labry-Lima et al. [10], 2023 (Table S7). Studies that scored very low quality (n = 3), due to the lack of the necessary information according to the PICOS, were excluded from the analysis (Figure 1). Overall, among the included studies (n = 61), most economic evaluations (54%, n = 33 studies) showed moderate-to-high certainty of evidence and strength of recommendations. Furthermore, 11% (n = 7) of the studies achieved a high certainty rating, while 33% (n = 20) a moderate rating, and 2% (n = 1) a moderate/low. Regarding the latter, lower scores are surely related to the intrinsic nature of clinical trials of orphan drugs for rare disease treatment due to the small sample sizes, the single-arm design methods, and so on. All these factors can potentially impact overall efficacy in cost-effectiveness estimation. Furthermore, the quality of the evidence itself was affected by the lack of information about the comparator and reference year in the cost-effectiveness analysis; these factors can impact the conclusion. Some of the most frequently identified potential risks of bias are assumption bias (39%), study design bias (31%), and extrapolation bias (37%). In 55% of the analyzed studies, a potential conflict of interest was identified due to at least one author being affiliated with the funding company (Table S8).
3.3. Overall Characteristics of Studies Included in the Review
The global geographical distribution of the n = 61 economic evaluation shows a significant majority of studies carried out in the United States (41%; n = 26) (Figure 2). A minority of studies were conducted in European settings, e.g., Spain (5%; n = 3), Switzerland (3%; n = 2), Netherlands (3%; n = 2), Ireland (3%; n = 2), Germany (3%; n = 2), France (3%; n = 2), Italy (2%; n = 1), and Sweden (2%; n = 1) (Figure 2). Additionally, 93% of the included studies use a lifetime time horizon, and some studies simulate the horizon until the remaining surviving patients reach 100 years of age, which is the assumption of lifetime. All identified studies used discount rates that are consistent with the guidelines of the countries in which the studies were conducted. The highest discount rate, up to 5%, was observed in countries such as Australia and China. All methodological information of the overall included studies was extracted and reported in Tables S5 and S6.
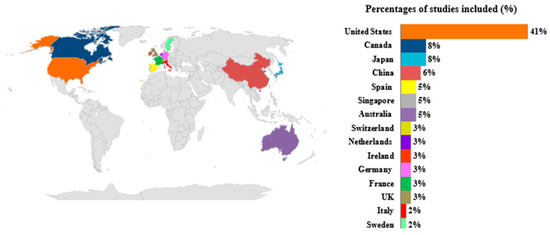
Figure 2.
Global distribution of economic evaluations included in the review.
Overall, the Sankey diagram, shown in Figure 3, illustrates the overall distribution of the pharmacoeconomic profiles of ATMPs and their approved indication(s) detected from the included studies. The width of each flow demonstrates the number of included economic evaluations, and ATMPs are presented in descending order, specifically from axicabtagene ciloleucel (n = 23 studies) [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41] to etranacogene dezaparvovec (n = 1 study) [42]. The second nodes represent the approved indications of ATMP. Moreover, 85% [19,20,22,23,24,25,26,27,29,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38] of the studies assessed axicabtagene ciloleucel as cost-effective compared to alternatives in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) treatment, while 66% (n = 2) assessed a positive cost-effective profile in follicular lymphoma (FL) treatment [40,41]. Also, 58% (n = 7) of included studies demonstrated a positive cost-effective profile of tisagenlecleucel in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) treatments [43,44,45,46,47,48,49], while brexucabtagene autoleucel demonstrated a 100% (n = 5) positive pharmacoeconomic profile in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and ALL treatments [50,51,52,53,54], the same percentage showed etranacogene dezaparvovec in the hemophilia B treatment [42]. Furthermore, 75% (n = 3) of included economic evidence concluded a positive pharmacoeconomic profile of ciltacabtagene autoleucel in multiple myeloma (MM) treatment [55,56,57], while 60% (n = 3) of economic evidence demonstrated voretigene neparvovec as a cost-effective option in RPE65-associated inherited retinal disease (RPE65-IRD treatment) [58,59,60].
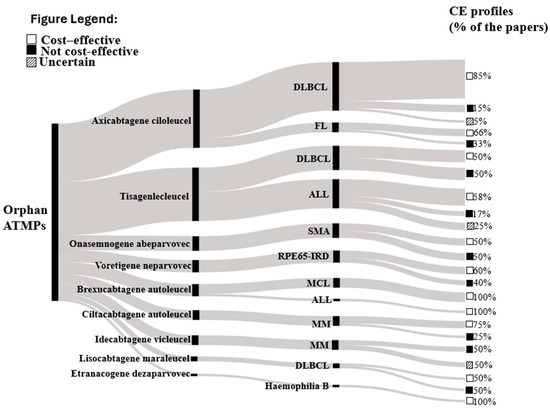
Figure 3.
Sankey chart of the CE profile of ATMPs and their specific diagnosis. Footnotes: The Sankey diagram depicts the distribution of cost-effectiveness analyses of ATMPs. Each segment represents a particular ATMP, with the flow’s size indicating the number of analyses deemed cost-effective or not. It also shows the relative frequency of the ATMPs for each therapeutic indication. Abbreviations: DLBCL—Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; ALL—Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia; FL—Follicular lymphoma; SMA—Spinal muscular atrophy; MCL—Mantle cell lymphoma; MM—Multiple myeloma; Cost-effectiveness (CE); RPE 65-IRD: Inherited retinal diseases due to RPE65 variants.
3.4. Cost-Effectiveness Profiles of the Overall Studies
Figure 4 illustrates the results plotted into a cost-effective plane. In more depth, most of the included studies are in the northeast quadrant (positive incremental costs and positive incremental QALY assessing ATMP as the therapeutic choice that gains more health benefits, but also more expenses compared to alternatives) [19,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,38,39,40,41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79]. Studies falling below the threshold of EUR 100,000/QALY consider ATMPs cost-effective compared to the alternative therapies [19,22,24,25,27,29,31,33,34,35,36,38,40,41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,52,53,54,55,62,63,65,67,69,72,73,78,79]. Specifically, studies evaluating the cost-effectiveness of tisagenlecleucel are located below the WTP of EUR 100,000/QALY, making them a viable therapeutic choice, with incremental QALY often over five, but they also have significantly higher incremental costs [43,44,45,46,48,78]. On the contrary, axicabtagene ciloleucel represents a therapeutic option with lower incremental QALY but also notably lower incremental costs [21,22,23,24,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,39,40,41]. Additionally, it is noticeable that studies of this ATMP estimate very similar ICERs, leading to a large concentration at one point. The six studies in the southeast quadrant (negative incremental cost and positive incremental QALY) represent the dominant therapeutic choices, with higher effectiveness but also lower costs [20,37,42,58,75,77]. Also, four studies evaluating the cost-effectiveness of voretigene neparvovec in retinal disease treatment represent therapy outside the WTP of EUR 100,000/QALY, with low incremental QALY but high incremental costs [59,60,66,73]. Despite most references focusing on incremental QALY up to two and low incremental costs, some studies are outliers, and these are most commonly examining the cost-effectiveness of onasemnogene abeparvovec [68,76] and only one study that estimates etranacogene dezaparvovec in hemophilia treatment [42]. Unlike etranacogene dezaparvovec, which represents a dominant outlier, onasemnogene abeparvovec has extreme values in both the dominant square and the northeast quadrant.
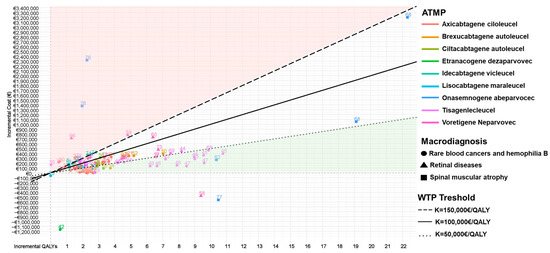
Figure 4.
Cost-effectiveness plane stratified by ATMPs and macro-diagnosis. Notes: northeast quadrant: more effective but more costly; southeast quadrant: dominant = more effective and less costly; northwest quadrant: dominated = less effective and more costly; southwest quadrant: less effective but less costly.
3.5. Cost-Effectiveness Profiles of ATMPs for Rare Blood Cancer and Hemophilia B Treatment
The summary of the results, including the analysis of ATMPs and their therapeutic indication, is provided in this study. Table 2 presents the mean ICER and mean incremental QALY, excluding outliers due to significant variations. Moreover, as shown in Figure 4, the majority of studies examining the pharmacoeconomic profile of axicabtagene ciloleucel are concentrated below the WTP threshold of EUR 100,000/QALY; however, one study is observed in the dominant quadrant. Among n = 20 studies evaluating the cost-effectiveness of axicabtagene ciloleucel in the treatment of DLBCL [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38], 85% (n = 17) of them demonstrated cost-effectiveness compared to the alternatives [19,20,22,23,24,25,26,27,29,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38], considering the mentioned threshold. Also, axicabtagene ciloleucel represented a cost-effective strategy as a second-line DLBCL treatment in n = 5 [23,32,33,34,38] evaluated studies, while the other n = 5 studies also proved its cost-effectiveness in the subsequent treatment lines [20,23,30,32,35]. From the total amount of included studies, seven studies were identified that lie below the EUR 50,000/QALY WTP threshold [29,30,31,32,35,36,38]. Two studies even exceed the highest range in the sensitivity analysis of EUR 150,000 per QALY [21,30]. As shown in Figure 4, axicabtagene ciloleucel presented an unfavorable cost-effectiveness profile in n = 3 evaluated studies [28,30,32], of which Wu et al. [30] concluded in the first, second, and third lines of therapy compared with the alternatives, taking into account the threshold of EUR 29,449/QALY. In addition to its established role in treating DLBCL, axicabtagene ciloleucel has shown promise in the potential treatment of FL [39,40,41], where 66% (n = 2) [40,41] of included studies demonstrated cost-effectiveness compared to alternatives (mosunetuzumab, SoC), considering a threshold of EUR 105,750/QALY. Moreover, Oluwole [40] and Potnis [39] have estimated their cost-effective profile in third-line FL treatment, leading to completely different conclusions in the same settings from the same perspective, but by using different types of models (such as partitioned survival versus the Markov model; differences in assumptions on survival extrapolations, specific utility values, and cost inputs, see Table S6). Also, the median ICER for axicabtagene ciloleucel is EUR 64,540/QALY in DLBCL and EUR 66,829/QALY in FL. As presented in Figure 4, n = 13 [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,65,67,69,72,78,79] studies examining the cost-effectiveness of tisagenlecleucel in treating rare blood cancer diseases are located below the set threshold of EUR 100,000/QALY. Out of the 13 studies mentioned, nine fall within the cost-effectiveness threshold of EUR 50,000/QALY [43,45,46,47,48,49,65,69,79]. Additionally, two studies [23,30] are very close to the quadrant that promotes the dominance of older therapies over the mentioned ATMP. Regarding Table S5, seven economic evaluation studies of tisagenlecleucel [43,44,45,46,47,48,49] demonstrated an affordable pharmacoeconomic profile in treatment compared to the standard of care, clofarabine, and blinatumomab. As shown in Table S5, n = 3 did not estimate a cost-effective profile [65,67,72], considering that Carey [63] conducted his research on a pediatric and younger patient population, with an estimated ICER EUR 71,370/QALY on the WTP threshold of EUR 43,943/QALY. Notably, Wang [49] and Choe [23] estimated tisagenlecleucel is likely to be a cost-effective and lifesaving strategy as the third line for ALL therapy with ICERs EUR 47,222/QALY and EUR 53,545/QALY from Singapore (WTP threshold EUR 105,750/QALY) and EUR 99,012/QALY from US the perspective (WTP threshold EUR 117,318/QALY). The assessment of the cost-effectiveness profile of tisagenlecleucel in DLBCL treatment is still uncertain, with an equal number of studies showing that the therapy is cost-effective (n = 5) [23,48,69,70,79] and that it is not [23,30,61,63,71]. The median ICER for tisagenlecleucel in ALL treatment is EUR 49,081/QALY, while in DLCBL treatment the amount is higher, amounting to EUR 68,098/QALY.

Table 2.
Study Overview and Key Characteristics.
Figure 4 also shows that ciltacabtagene autoleucel for the MM treatment seems to be a cost-effective strategy (n = 3) in studies below the WTP threshold of EUR 100,000/QALY [55,56,57]. On the other side, the CE profile of idecabtagene vicleucel for the same indication seems to be uncertain [55,56,57,74]. For MCL therapeutic indication, brexucabtagene autoleucel is also considered a cost-effective option compared to the alternative therapy, with a range of ICERs varying from EUR 26,140/QALY to EUR 76,656/QALY, while ICUR is slightly higher: EUR 67,720/QALY [50,51,52,53,54]. Also, lisocabtagene maraleucel demonstrated an uncertain pharmacoeconomic profile, with a low number of included studies [30,75].
Regarding the hemophilia B treatments, etranacogene dezaparvovec is approved for this indication and represents a cost-effective alternative in German settings with a WTP of EUR 50,000/QALY. ATMP does not lead to a significantly higher incremental QALY, but it results in savings of EUR 1,200,000, representing a dominant treatment (Figure 4) [42].
Axicabtagene ciloleucel demonstrated an affordable pharmacoeconomic profile in first, second, third, and subsequent lines of treatment for DLBCL, as well as in follicular lymphoma. In contrast, tisagenlecleucel, while showing a favorable pharmacoeconomic profile in DLBCL, did not demonstrate strong cost-effectiveness in FL. Meanwhile, brexucabtagene autoleucel demonstrated a favorable pharmacoeconomic profile in MCL, and ciltacabtagene autoleucel showed similar promise in MM, whereas idecabtagene vicleucel did not exhibit a favorable profile for the same indication.
3.6. Cost-Effectiveness Profiles of ATMPs for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type I Treatment
Onasemnogene abeparvovec, representing ATMP approved for serious, rare diseases, such as spinal muscular atrophy type I, demonstrated significant variations in its pharmacoeconomic profile depending on settings (Figure 4). Specifically, n = 2 studies are substantially above the WTP of 100,000/QALY (not cost-effective) [68,76]. In contrast, n = 3 studies are below the threshold of cost-effective, with n = 1 study falling into the dominant quadrant (ICER EUR −53,073/QALY) [77] (see Figure 4). Two studies were identified that fall below the set threshold of EUR 50,000/QALY, both studies identify a similar incremental QALY of approximately 11, while showing a significant difference in incremental cost. They were conducted within the same healthcare setting and used nusinersen as the comparator. The study conducted by Wang et al. is the only one that exceeds the highest defined threshold of EUR 150,000 per QALY, considering both comparators, but the application of the highest discount rate for both cost and effectiveness of as much as 5% may be the reason, which is in line with Australian HTA guidelines [76]. Median ICER of onasemnogene abeparvovec amounts to EUR 94,492/QALY.
Also, a variation in the profiles is observed depending on the comparator. Most studies in which the comparator was nusinersen demonstrate a positive cost-effectiveness profile [62,68,77], while in all studies with BSC or SoC as comparators the profile is negative [62,68,76,77]. The same ATMP, onasemnogene aberparovec, when compared to nusinersen, reported a wide ICER ranging from EUR 25,979/QALY to EUR 55,152/QALY [62,68,76].
In contrast to all other analyzed ATMPs, onasemnogene abeparvovec demonstrated the highest sensitivity to the choice of comparator, discount rate, and time horizon.
3.7. Cost-Effectiveness Profiles of ATMPs for Retinal Diseases with RP E65-Mutation Treatment
Voretigene neparvovec, a novel therapy approved for IRD patients with a rare biallelic RPE65 mutation, was cost-effective compared to the standard of care in n = 3 studies [58,59,60] with a WTP threshold above EUR 100,000/QALY (i.e., EUR 119,944/QALY). Based on the information provided by Uhrmann’s [59] study in a German setting, the ICUR calculated for this ATMP was about EUR 156,853/QALY, with the threshold set at EUR 359,833/QALY. Hence, Uhrmann et al. considered voretigene neparvovec cost-effective versus SoC, despite its high cost [59]. There was a similar case in the United Kingdom. Hence, in this setting, for voretigene neparvovec, higher thresholds, ranging from EUR 124,607/QALY to EUR 373,821/QALY, are accepted as per the use of the ATMP for ultra-orphan conditions [60]. Zimmermann et al. [66] estimated that the incremental cost per QALY calculated for voretigene neparvovec (i.e., EUR 555,631/QALY from the US perspective) was not cost-effective even if considering higher thresholds related to ultra-rare diseases. Additionally, it was observed that only one study falls within the dominant quadrant [58], while as many as two studies [66,69] are positioned under the highest set threshold of EUR 150,000/QALY. Despite significantly higher costs, the highest incremental QALY observed was only around 10. Considering the three ICERs included in this study, the median ICER for voretigene neparvovec in the treatment of retinal diseases due to the RP E65 mutation is EUR 114,003 per QALY.
This ATMP is considered cost-effective only when a higher willingness-to-pay threshold is applied, consistent with ultra-rare disease valuation frameworks, since the condition it treats affects a very small patient population.
4. Discussion
This systematic review comprises the literature that evaluates the cost-effectiveness of ATMPs in rare disease treatment, specifically detecting the three most frequent macro-diagnoses: rare blood cancers (B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia-ALL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-DLBCL, multiple myeloma-MM, mantle cell lymphoma-MCL, follicular lymphoma-FL, and hemophilia B); spinal muscular atrophy type I- SMA; and retinal diseases with RP E65-mutation treatment. Main findings indicate that, while ATMPs approved for these rare diseases generally incur higher costs, they also provide superior QALYs compared to their standard of care or best supportive care, or alternative treatments.
More in-depth, tisagenlecleucel has emerged as a particularly promising option for rare blood disease treatment, such as ALL and DLBCL. Despite the availability of numerous therapeutic alternatives, this ATMP demonstrates significantly higher incremental QALYs, often ranging from 2 to 10 compared to the standard of care (SoC) [23,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,61,63,65,67,69,70,72,78,79]. These substantial health gains justify their elevated incremental costs in most healthcare settings, supporting their cost-effectiveness across diverse economic evaluations [80]. Moreover, these findings suggest that tisagenlecleucel, despite its high upfront costs, may result in long-term savings for healthcare systems by reducing the burden of disease and the need for subsequent interventions. Corroborating our findings, several studies have already evaluated the clinical efficacy of tisagenlecleucel, demonstrating its highly effective outcomes, in terms of short-term and long-term survival for the ALL treatment in both pediatric and adult populations [81,82,83,84,85]. Moreover, in addition to providing a therapeutic alternative that ensures safety and efficacy for patients enrolled in clinical trials, real-world evidence has shown that the results obtained with tisagenlecleucel are closely aligned with those observed in pivotal trials, further reinforcing its efficacy [86]. From a cost perspective, another systematic review by Andrade et al. has also assessed the cost-effectiveness of tisagenlecleucel for ALL treatments in children and young adults [80]. This review also highlighted that, although tisagenlecleucel is significantly more expensive than conventional therapies, it performed favorably on the ICER, remaining below the threshold of $100,000/QALY. This also confirmed that tisagenlecleucel is a more effective strategy than traditional small molecules and biological therapies in terms of life years and QALYs gained, making it a valuable option. A similar case is observed with axicabtagene ciloleucel, which also demonstrates strong cost-effectiveness profiles for the DLBCL treatment. However, its incremental QALY gains are lower than those observed with tisagenlecleucel for ALL and DLBCL. Importantly, therapy remains cost-effective from first- to third-line treatments, with its ICER estimates below the threshold set at EUR 100,000/QALY [20,23,30,32,35], but the cost-effectiveness tends to decline in later treatment lines. This could probably be explained due to reduced efficacy and smaller incremental health benefits in patients with more advanced DLBCL disease. Hence, a Chinese study showed that axicabtagene ciloleucel is not cost-effective as a second-line therapy in their setting (ICER: EUR 35,764/QALY; WTP: EUR 29,450/QALY), but this is not the case from the US perspective (ICER: EUR 111,318/QALY; WTP: EUR 117,318/QALY) [32].
Moreover, a recent systematic review by Thavorn et al. [87] showed similar results even if investigating only chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies for hematologic and solid malignancies. Hence, their cost-effectiveness plane underscores the same conclusions regarding the pharmacoeconomic profile of axicabtagene ciloleucel and tisagenlecleucel, emphasizing that studies evaluating the profile of axicabtagene ciloleucel are more concentrated until incremental QALY 3, while tisagenlecleucel achieves the highest concentration from 8 to 11 incremental QALY. Also, the CE plane clearly shows a positive economic profile of brexucabtagene autoleucel in MCL and ALL treatments, which is consistent with the findings of our study. Compared to the cost-effectiveness plane, our study supports a better cost-effectiveness profile of ciltacabtagene autoleucel in MM treatment, concluding that the new studies have been conducted and have been included in our research.
Regarding hemophilia B treatment with ATMPs, etranacogene dezaparvovec has been evaluated economically in only one study in Germany. This study classified it as cost-effective when compared to the current standard of care, coagulation factor IX (FIX) therapy [42]. The limited number of evaluations can be attributed to the novelty of the therapy and its recent market approval, a necessity of lifelong administration, as emphasized in hemophilia B treatment guidelines [88]. The recent study conducted by Pipe et al. [89] demonstrated a better safety and efficacy profile of etranacogene dezaparvovec compared to FIX therapy, improving the quality of life in patients with hemophilia B.
About the treatment of SMA type I with ATMPs, data from real-world settings exist to support the efficacy of the treatment, but it seems that its high cost may be a limitation in some settings [90]. Specifically, Dean et al., 2021 [77] identified it as a dominant option for SMA type I in patients under two years of age, with ICERs below US thresholds. However, in Australia, onasemnogene abeparvovec was not cost-effective (2 QALYs gained; high ICER), reflecting regional variations in healthcare economics [76]. This variability across healthcare systems underscores the need for tailored approaches to reimbursement policies.
Regarding retinal rare disease, a similar non-homogeneous situation was identified as per the SMA treatment with ATMPs. Hence, economic evaluations identified in this matter included voretigene neparvovec, a novel therapy approved for IRD patients with a rare biallelic RPE65 mutation, demonstrating an important distinction between high incremental costs and low incremental QALYs. Specifically, ICER analyses estimate incremental QALY gains of approximately 1.3 years compared to standard care [91]. While therapy offers clinical benefits, its pharmacoeconomic profile indicates that it is unlikely to represent good value for money relative to alternative treatments under traditional thresholds. This raises significant concerns regarding its economic feasibility in routine clinical practice.
The heterogeneity in the cost-effectiveness profiles of ATMPs for ultra-rare retinal diseases and SMA treatments, compared to the positive cost-effectiveness profiles of ATMPs for rare blood diseases, can be attributed to the small sample sizes related to these rare conditions. Also, a study by Khoa Ho stated that onasemnogene abeparvovec and voretigene neparvove had an additional challenge because they did not know the final price of this therapy, so they used assumed values to examine the cost-effectiveness of this therapy at different price levels [92]. NICE guidelines allow the discount rate for cost as well as an effectiveness of 1.5% for therapies that restore patients to near full or full health, acknowledging their transformative potential, as is the case with voretigene neparvovec and onasemnogene abeparvovec [7]. Due to their highly specific characteristics, these medicines are included in NICE’s ‘Highly Specialised Technologies’ program [93,94].
In comparison with the study by Thavorn et al., the highest incremental QALY observed for the treatment of ATMPs targeting hematological and solid malignancies is approximately seven. In contrast, Figure 4 shows that, in the evaluation of rare and ultra-rare diseases, the incremental QALY gain for onasemnogene abeparvovec reaches a high value of 22, an outlier that reflects long-term, exceptional benefit to the patient, despite the high cost. Among the 61 studies included in the analysis of treatments for rare diseases, 25 reported incremental QALY gains ranging from 5 to 22. The mean incremental QALY of the included studies is four, which is significantly higher compared to other drugs with an orphan designation [95], and is also higher than the incremental QALY in chronic conditions [96]. Some of the outliers identified in this cost-effectiveness analysis can be explained by a combination of methodological factor such as the following: (i) exceptionally high treatment costs, particularly for certain gene therapies such as voretigene neparvovec and onasemnogene abeparvovec, were associated with relatively modest QALY gains, resulting in unfavorable ICERs; (ii) also, low incremental health benefits were sometimes driven by conservative modeling assumptions, including the use of short time horizons or restrictive utility estimates; and methodological factors (iii) due to heterogeneity in the economic models such as differences in discount rates, WTP thresholds, or structural approaches (e.g., Markov models vs. partitioned survival models).
Given the uniqueness of this study, it is important to locate it in terms of the existing literature. Previous research by Olry de Labry-Lima et al. aimed to identify and provide a critical review of ATMP economic analysis [10]. On the other side, Thavorn et al. focused on the cost-effectiveness of chimeric antigen receptor T-cells for oncology patients’ treatment [87], while Khao Ho et al. conducted a systematic review that summarizes cost-effectiveness evidence of potential curative gene therapies and identified their challenges [92]. Furthermore, in 2020, Lloyd et al. published a systematic review on the cost-effectiveness evidence of all authorized ATMPs [7]. The strengths of our study lie in its comprehensive overview of the pharmacoeconomic profiles of ATMPs for treating rare and ultra-rare diseases, as well as in the sensitivity analysis conducted using three thresholds representing different healthcare system contexts, to support policymakers in making decisions.
This study has several limitations. This systematic review exclusively evaluates the economic profiles of EMA-approved ATMPs, and the included studies were sourced globally, to obtain a global framework across diverse economic settings and perspectives. Hence, most studies originated from high-income countries, reflecting the limited accessibility of these therapies in low- and middle-income countries. We recognize that limiting the study to open-access articles may lead to selection bias due to the potential exclusion of relevant papers. Gray literature, reports, and review articles were defined as exclusion criteria, which could cause an incomplete overview. To obtain complete and accurate conclusions on the assessment of the quality of evidence, due to potentially insufficient methodological information, the included study types are more suitable for evaluation using the mentioned checklist. This limitation was accounted for with the risk of bias assessment, where studies with these conditions received lower scores. Although the quality of evidence was assessed using a validated checklist and a double-blind methodology, some degree of subjectivity may have influenced the final estimations. One of the limitations lies in the significant number of studies with limited generalizability, thereby reducing the applicability of the results in general clinical practice. This could be explained by the nature of rare and ultra-rare diseases [19,24,39,49,50,70,76,77]. The quality of effectiveness evidence was low in some cases, but this was caused by the inherent limitations of clinical trials in the field of rare diseases, such as small sample sizes and single-arm study designs. Finally, when studies reported economic profiles of ATMPs over multiple time horizons, the longest horizon was selected to ensure the most robust results. Despite these efforts, uncertainties could remain, particularly regarding the outcomes and economic sustainability of these advanced therapies. It is necessary to consider social, health, and economic differences between countries, which are impossible to adjust and could potentially affect the results. Most of the included studies apply a health system perspective during evaluation, while in the case of orphan ATMP therapies, pricing decisions should include a broader societal perspective, considering the significant impact of these therapies not only on patients but also on their families, caregivers, and society [6]. These findings support the economic value of several ATMPs despite their high acquisition costs, particularly when long-term health gains are accounted for. In particular, the unique characteristics of ATMPs, such as their high upfront costs and often one-time administration, coupled with their potential for long-term, transformative benefits, necessitate robust and adaptable policy approaches. In fact, the findings of this study highlight that, despite the significant acquisition costs of ATMPs, their economic value is frequently supported by substantial gains in QALYs, particularly when considering long-term health impacts. This underscores the critical need for evidence-informed policy strategies to ensure timely and equitable access to these innovative therapies.
Given the innovative nature, high costs, and uncertainty in long-term effectiveness, policymakers must carefully balance innovation with system sustainability. To address these complexities, Managed Entry Agreements (MEAs) and Value-Based Pricing models should be prioritized. These approaches are crucial for mitigating financial uncertainty and aligning costs with actual clinical outcomes [97,98]. It is particularly pertinent to recognize that for ultra-rare diseases, the cost per patient tends to be even higher, and traditional WTP thresholds may be insufficient [99,100]. This often necessitates higher thresholds, or additionally dedicated programs such as those implemented by the British National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) for Highly Specialised Technologies (HST) [93,94].
Furthermore, while most included studies adopt a healthcare system perspective, pricing decisions for orphan ATMP therapies should incorporate a broader societal perspective [101,102]. This involves considering the substantial impact these therapies have not only on patients but also on their families, caregivers, and society.
Therefore, there is an unmet need to develop more evidence to inform resource allocation and pricing negotiations. This approach will ensure that the real-world value of these high-cost therapies is considered. This ideal approach will ensure that the high-cost therapies will remain accessible to the patients who stand to benefit most from them [103]. Hence, in this scenario, adaptive reimbursement frameworks can evolve as more real-world evidence becomes available, potentially incorporating performance-based agreements that link payment to long-term patient outcomes, sharing financial risk between payers and manufacturers.
5. Conclusions
The systematic review presents a narrative synthesis of the overall economic profile of EMA-authorized ATMPs in rare disease treatment. The findings emphasize notable differences across therapeutic areas. Specifically, ATMPs for rare blood diseases, such as tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel, generally showed positive cost-effectiveness profiles, with substantial health gains justifying their elevated costs in most healthcare settings. Similarly, etranacogene dezaparvovec represents a promising innovation for hemophilia B, offering a cost-effective alternative to lifelong coagulation factor IX therapy, though the evidence remains limited due to its recent approval. Ciltacabtagene autoleucel demonstrated a more favorable cost-effectiveness profile compared to idacabtagene vicleucel for the same indication. In contrast, the cost-effectiveness of ATMPs for spinal muscular atrophy (onasemnogene abeparvovec) and inherited retinal diseases (voretigene neparvovec) is less consistent, largely influenced by variations in healthcare contexts, WTP thresholds, and the unique characteristics of these rare conditions.
The findings underscore the need for a more distinct approach to assessment of cost-effectiveness, particularly in rare disease contexts where small sample sizes and limited evidence often make it difficult to assess long-term benefits, which could lead to unforeseen costs for policymakers. Policymakers must carefully weigh the costs and benefits of these therapies, considering both the economic constraints of healthcare systems and the real-world impact on patient outcomes.
Moreover, there is a pressing need for continued research to refine economic models, address data gaps, and develop strategies for reducing the costs of these therapies, ensuring that they are accessible to the patients who would benefit the most.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the following address: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/healthcare13151894/s1, Table S1: Overview of ATMP Types and Their Regulatory Definitions; Table S2. Summary of all EMA-authorized ATMPs with orphan designation.; Table S3. Search Strategy; Table S4. Search Syntaxes; Table S5. Characteristics of included studies; Table S6 Key features of economic methods for the overall included studies; Table S7. Assessment of risk of bias and quality of evidence; Table S8. Quality appraisal of individual included studies according to the checklist.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.O.; methodology, E.M. and V.O.; software, S.M.; formal analysis, M.S., M.K. and S.M.; investigation, M.S., M.K. and S.M.; data curation, M.S., M.K. and S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S., M.K. and S.M.; writing—review and editing, E.M. and V.O.; supervision, V.O.; funding acquisition, V.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Pharma Rare Project (Progettazione e realizzazione di una struttura di health system governance per il patients journey dei pazienti con malattie rare (acronimo progetto)), Campania Region, [Grant code: E63C25000210002] and Task 9.4.3 Spoke 9—(From target to therapy: pharmacology, safety and regulatory competence center), National Center for Gene Therapy and Drugs based on RNA Technology funded by the European Union—NextGenerationEU [Grant code: E63C22000940007].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design and conduct of the study collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
References
- Seoane-Vazquez, E.; Shukla, V.; Rodriguez-Monguio, R. Innovation and competition in advanced therapy medicinal products. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriaud, M.; Kohli, E. RNA-based drugs and regulation: Toward a necessary evolution of the definitions issued from the European union legislation. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1012497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, A.M.; Mariz, S.; Stoyanova-Beninska, V.; Celis, P.; Vamvakas, S.; Larsson, K.; Sepodes, B. Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products for Rare Diseases: State of Play of Incentives Supporting Development in Europe. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Lopez, C.; Agustí, A.; Obach, M.; Vallano, A. Regulatory Framework for Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products in Europe and United States. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicine Agency. CAT Quarterly Highlights and Approved ATMPs. 2024. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/committee-report/cat-quarterly-highlights-approved-atmps-november-2024_en.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Gonçalves, E. Value-based pricing for advanced therapy medicinal products: Emerging affordability solutions. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2022, 23, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Williams, H.; Hughes, D.A. A systematic review of economic evaluations of advanced therapy medicinal products. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 2428–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, B.; Hampson, G.; Michaels, J.; Towse, A.; von der Schulenburg, J.-M.G.; Wong, O. Advanced therapy medicinal products and health technology assessment principles and practices for value-based and sustainable healthcare. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2019, 20, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Labry-Lima, A.O.; Ponce-Polo, A.; García-Mochón, L.; Ortega-Ortega, M.; Pérez-Troncoso, D.; Epstein, D. Challenges for Economic Evaluations of Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products: A Systematic Review. Value Health 2022, 26, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, J.J.; Eddy, D.M.; Kan, H.; Kaltz, C.; Patel, B.; Eldessouki, R.; Briggs, A.H. Questionnaire to Assess Relevance and Credibility of Modeling Studies for Informing Health Care Decision Making: An ISPOR-AMCP-NPC Good Practice Task Force Report. Value Health 2014, 17, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnen, B.; Van Mastrigt, G.; Redekop, W.; Majoie, H.; De Kinderen, R.; Evers, S. How to prepare a systematic review of economic evaluations for informing evidence-based healthcare decisions: Data extraction, risk of bias, and transferability (part 3/3). Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2016, 16, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEMG–EPPI Centre Cost Converter. v.1.7. Available online: https://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/costconversion/default.aspx (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Gomersall, J.S.; Jadotte, Y.T.; Xue, Y.; Lockwood, S.; Riddle, D.; Preda, A. Conducting systematic reviews of economic evaluations. Int. J. Evid.-Based Health 2015, 13, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, G.E.; Elvidge, J. Challenges in synthesising cost-effectiveness estimates. Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R. Systematic reviews of economic evaluations: Utility or futility? Health Econ. 2010, 19, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 5.1.0. 2011. Available online: http://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/ (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- SankeyMATIC. Available online: https://sankeymatic.com/ (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Roth, J.A.; Sullivan, S.D.; Lin, V.W.; Bansal, A.; Purdum, A.G.; Navale, L.; Cheng, P.; Ramsey, S.D. Cost-effectiveness of axicabtagene ciloleucel for adult patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma in the United States. J. Med. Econ. 2018, 21, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Oluwole, O.O.; Diakite, I.; Botteman, M.F.; Snider, J.T.; Locke, F.L. Cost effectiveness of axicabtagene ciloleucel versus tisagenlecleucel for adult patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma after two or more lines of systemic therapy in the United States. J. Med. Econ. 2021, 24, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittington, M.D.; McQueen, R.B.; Ollendorf, D.A.; Kumar, V.M.; Chapman, R.H.; Tice, J.A.; Pearson, S.D.; Campbell, J.D. Long-term Survival and Cost-effectiveness Associated With Axicabtagene Ciloleucel vs. Chemotherapy for Treatment of B-Cell Lymphoma. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e190035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwole, O.O.; Liu, R.; Diakite, I.; Feng, C.; Patel, A.; Nourhussein, I.; Snider, J.T.; Locke, F.L. Cost-effectiveness of axicabtagene ciloleucel versus lisocabtagene maraleucel for adult patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma after two or more lines of systemic therapy in the US. J. Med. Econ. 2022, 25, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.H.; Abdel-Azim, H.; Padula, W.V.; Abou-El-Enein, M. Cost-effectiveness of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel and Tisagenlecleucel as Second-line or Later Therapy in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2245956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyner, A.K.C.; Snider, J.T.; Wade, S.W.; Wang, S.-T.; Buessing, M.G.; Johnson, S.; Gergis, U. Cost-Effectiveness of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B Cell Lymphoma: No Impact of Site of Care. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 3560–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, C.; Vicente, C.; Ball, G. The Cost Effectiveness of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel Versus Best Supportive Care in the Treatment of Adult Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma (LBCL) After Two or More Lines of Systemic Therapy in Canada. PharmacoEconomics 2022, 40, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, S.K.; Saumoy, M.; Schneider, Y.; Serrao, S.; Solaimani, P.; Budde, L.E.; Mei, M.G.; Popplewell, L.L.; Siddiqi, T.; Zain, J.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of second-line axicabtagene ciloleucel in relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140, 2024–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, M.-A.; Kuruvilla, J.; Snider, J.T.; Vadgama, S.; Blissett, R.; El-Moustaid, F.; Smith, N.J.; Patel, A.R.; Johnston, P.B. The Cost-Effectiveness of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel as Second-Line Therapy in Patients with Large B-Cell Lymphoma in the United States: An Economic Evaluation of the ZUMA-7 Trial. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2022, 28, 750.e1–750.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zheng, B.; Cai, H.; Yang, T.; Hong, Y.; Liu, M.; Hu, J. Cost-effectiveness analysis of axicabtagene ciloleucel vs. salvage chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory adult diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in China. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 6113–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos-Oreiro, M.; Heras, A.d.L.; Presa, M.; Casado, M.A.; Pardo, C.; Martín-Escudero, V.; Sureda, A. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel vs. Tisagenlecleucel for the Management of Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in Spain. Cancers 2022, 14, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Keramat, S.A.; Balasooriya, N.N.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Comans, T.; Dong, H. Value for Money of CAR-T Cell Therapy for Patients with Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma in China: Evidence from a Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2023, 21, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftager, A.S.L.; Danø, A.; Eklund, O.; Vadgama, S.; Kanje, V.H.; Munk, E. Axicabtagene ciloleucel compared to standard of care in Swedish patients with large B-cell lymphoma: A cost-effectiveness analysis of the ZUMA-7 trial. J. Med. Econ. 2023, 26, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Lei, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, H.; Zheng, B.; Yang, T.; Liu, M.; Hu, J. Cost-effectiveness analysis of axicabtagene ciloleucel as a second-line treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in China and the United States. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2023, 14, 20406207231168215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwole, O.O.; Patel, A.R.; Vadgama, S.; Smith, N.J.; Blissett, R.; Feng, C.; Dickinson, M.; Johnston, P.B.; Perales, M.-A. An updated cost-effectiveness analysis of axicabtagene ciloleucel in second-line large B-cell lymphoma patients in the United States. J. Med. Econ. 2024, 27, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sancho, A.M.; Presa, M.; Pardo, C.; Martín-Escudero, V.; Oyagüez, I.; Ortiz-Maldonado, V. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel vs. Standard of Care in Second-Line Treatment for Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma in Spain. Cancers 2024, 16, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwole, O.O.; Ray, M.D.; Davies, N.; Bradford, R.; Jones, C.; Patel, A.R.; Locke, F.L. Cost-effectiveness of axicabtagene ciloleucel versus tisagenlecleucel for the treatment of 3L + relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma in the United States: Incorporating longer survival results. J. Med. Econ. 2024, 27, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, M.; Castaigne, J.-G.; Zang, A.; Patel, A.; Hancock, E.; Brighton, N.; Bachy, E. A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel versus Tisagenlecleucel in the Treatment of Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Based on a Real-World French Registry. Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 4282–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsué, S.; Makita, S.; Asou, H.; Matsuda, H.; Yamaura, R.; Taylor, T.D. Cost–effectiveness analysis 3L of axicabtagene ciloleucel vs tisagenlecleucel and lisocabtagene maraleucel in Japan. Futur. Oncol. 2024, 20, 1333–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsué, S.; Makita, S.; Asou, H.; Matsuda, H.; Yamaura, R. Cost-utility analysis of second-line axicabtagene ciloleucel versus standard of care in Japan based on the ZUMA-7 trial. Futur. Oncol. 2024, 20, 2279–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potnis, K.C.; Di, M.; Isufi, I.; Gowda, L.; Seropian, S.E.; Foss, F.M.; Forman, H.P.; Huntington, S.F. Cost-effectiveness of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in adults with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwole, O.O.; Ray, M.D.; Zur, R.M.; Ferrufino, C.P.; Doble, B.; Patel, A.R.; Bilir, S.P. Cost-effectiveness of treating relapsed or refractory 3L+ follicular lymphoma with axicabtagene ciloleucel vs. mosunetuzumab in the United States. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1393939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwole, O.O.; Ray, M.D.; Rosettie, K.L.; Ball, G.; Jacob, J.; Bilir, S.P.; Patel, A.R.; Jacobson, C.A. Cost-Effectiveness of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for Adult Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma in the United States. Value Health 2024, 27, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, N.; Fuchs, H.; Galactionova, K.; Hermans, C.; Pletscher, M.; Schwenkglenks, M. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Etranacogene Dezaparvovec Versus Extended Half-Life Prophylaxis for Moderate-to-Severe Haemophilia B in Germany. PharmacoEconomics Open 2024, 8, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, M.D.; McQueen, R.B.; Ollendorf, D.A.; Kumar, V.M.; Chapman, R.H.; Tice, J.A.; Pearson, S.D.; Campbell, J.D. Long-term Survival and Value of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Pediatric Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Leukemia. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, R.R.; Gloude, N.J.; Schiff, D.; Murphy, J.D. Cost-Effectiveness of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy in Pediatric Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 111, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, F.W.; van Dongen-Leunis, A.; Arons, A.M.M.; Ladestein, J.R.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M.; Groot, C.A.U. Cost-effectiveness of Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-Cell therapy in pediatric relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A societal view. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 105, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santasusana, J.-M.R.; Saldaña, A.d.A.; García-Muñoz, N.; Gostkorzewicz, J.; Llinàs, D.M.; de Heredia, C.D. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Tisagenlecleucel in the Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia in Children and Young Adults in Spain. Clin. Outcomes Res. 2020, 12, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakase, S.; Teshima, T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Q.; Watanabe, Y.; Yang, H.; Qi, C.Z.; Chai, X.; Xie, Y.; Wu, E.Q.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Tisagenlecleucel for the Treatment of Pediatric and Young Adult Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Japan. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2021, 27, 241.e1–241.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Yaghoubi, M.; Seitz, P.; Javanbakht, M.; Brock, E. Cost-Effectiveness of Tisagenlecleucel in Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (pALL) and Adult Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) in Switzerland. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 3427–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Wang, Y.-H.; Li, S.C.T.; Gkitzia, C.; Lim, S.T.; Koh, L.P.; Lim, F.L.W.I.; Hwang, W.Y.K. Cost-effectiveness and budget impact analyses of tisagenlecleucel in adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma from Singapore’s private insurance payer’s perspective. J. Med. Econ. 2021, 24, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, G.; Lemieux, C.; Cameron, D.; Seftel, M.D. Cost-Effectiveness of Brexucabtagene Autoleucel versus Best Supportive Care for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma Following Treatment with a Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Canada. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2021–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersohn, S.; Salles, G.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Wade, S.W.; Simons, C.L.; Bennison, C.; Siddiqi, R.; Peng, W.; Kloos, I.; et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of KTE-X19 CAR T therapy versus real-world standard of care in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma post BTKi in England. J. Med. Econ. 2022, 25, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.; Visco, C. Cost-Effectiveness of brexucabtagene autoleucel for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2023, 64, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.D.; Smith, N.J.; Feng, C.; Jeyakumar, S.; Castaigne, J.-G.; Faghmous, I.; Masouleh, B.K.; Malone, D.C.; Bishop, M.R. Cost-Effectiveness of KTE-X19 for Adults with Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the United States. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 3678–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, C.L.; Malone, D.; Wang, M.; Maglinte, G.A.; Inocencio, T.; Wade, S.W.; Bennison, C.; Shah, B. Cost-effectiveness for KTE-X19 CAR T therapy for adult patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma in the United States. J. Med. Econ. 2021, 24, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ding, S.; Mingming, Z.; Yuping, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Dong, H. Cost effectiveness analysis of CAR-T cell therapy for patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma in China. J. Med. Econ. 2023, 26, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapinos, K.A.; Hu, E.; Trivedi, J.; Geethakumari, P.R.; Kansagra, A. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of CAR T-Cell Therapies vs Antibody Drug Conjugates for Patients with Advanced Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Control 2023, 30, 10732748221142945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, C.; Minakata, D.; Yokoyama, D.; Furuki, S.; Noguchi, A.; Koyama, S.; Oyama, T.; Murahashi, R.; Nakashima, H.; Ikeda, T.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Anti-BCMA Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2024, 30, 118.e1–118.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; Buessing, M.; O’cOnnell, T.; Pitluck, S.; Ciulla, T.A. Cost-effectiveness of Voretigene Neparvovec-rzyl vs Standard Care for RPE65-Mediated Inherited Retinal Disease. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019, 137, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrmann, M.F.; Lorenz, B.; Gissel, C. Cost Effectiveness of Voretigene Neparvovec for RPE65-Mediated Inherited Retinal Degeneration in Germany. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viriato, D.; Bennett, N.; Sidhu, R.; Hancock, E.; Lomax, H.; Trueman, D.; MacLaren, R.E. An Economic Evaluation of Voretigene Neparvovec for the Treatment of Biallelic RPE65-Mediated Inherited Retinal Dystrophies in the UK. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masucci, L.; Tian, F.; Tully, S.; Feng, Z.; McFarlane, T.; Chan, K.K.W.; Wong, W.W.L. CAR T-cell Therapy for Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma in Canada: A Cost-Utility Analysis. Med. Decis. Mak. 2024, 44, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, D.C.; Dean, R.; Arjunji, R.; Jensen, I.; Cyr, P.; Miller, B.; Maru, B.; Sproule, D.M.; Feltner, D.E.; Dabbous, O. Cost-effectiveness analysis of using onasemnogene abeparvocec (AVXS-101) in spinal muscular atrophy type 1 patients. J. Mark. Access Health Policy 2019, 7, 1601484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, N.; Leahy, J.; Trela-Larsen, L.; Mc Cullagh, L.; Barry, M. Cost-utility and value of information analysis of tisagenlecleucel for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the Irish healthcare setting. J. Mark. Access Health Policy 2023, 11, 2166375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, N.; Leahy, J.; Trela-Larsen, L.; McCullagh, L.; Barry, M. Tisagenlecleucel for relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the Irish healthcare setting: Cost-effectiveness and value of information analysis. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 2022, 38, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gye, A.; Lourenco, R.D.A.; Goodall, S. Different Models, Same Results: Considerations When Choosing Between Approaches to Model Cost Effectiveness of Chimeric-Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy Versus Standard of Care. PharmacoEconomics 2024, 42, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Lubinga, S.J.; Banken, R.; Rind, D.; Cramer, G.; Synnott, P.G.; Chapman, R.H.; Khan, S.; Carlson, J. Cost Utility of Voretigene Neparvovec for Biallelic RPE65-Mediated Inherited Retinal Disease. Value Health 2019, 22, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gye, A.; Lourenco, R.A.; Goodall, S. Discrete Event Simulation to Incorporate Infusion Wait-Time When Assessing Cost-Effectiveness of a Chimeric-Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. Value Health 2024, 27, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekhoff, T.F.; Sweegers, C.C.; Krijkamp, E.M.; Mantel-Teeuwisse, A.K.; Leufkens, H.G.; Goettsch, W.G.; Vreman, R.A. Early Cost-Effectiveness of Onasemnogene Abeparvovec-xioi (Zolgensma) and Nusinersen (Spinraza) Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy I in The Netherlands With Relapse Scenarios. Value Health 2021, 24, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Wang, Y.-H.; Ong, M.J.C.; Gkitzia, C.; Soh, S.Y.; Hwang, W.Y.K. Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Impact Analyses of Tisagenlecleucel in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia from the Singapore Healthcare System Perspective. Clin. Outcomes Res. 2022, 14, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.Z.; Bollu, V.; Yang, H.; Dalal, A.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Tisagenlecleucel for the Treatment of Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in the United States. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 1300–1319.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cher, B.P.; Gan, K.Y.; Aziz, M.I.A.; Lin, L.; Hwang, W.Y.K.; Poon, L.M.; Ng, K. Cost utility analysis of tisagenlecleucel vs salvage chemotherapy in the treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma from Singapore’s healthcare system perspective. J. Med. Econ. 2020, 23, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gye, A.; Goodall, S.; Lourenco, R.D.A. Cost-effectiveness Analysis of Tisagenlecleucel Versus Blinatumomab in Children and Young Adults with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Partitioned Survival Model to Assess the Impact of an Outcome-Based Payment Arrangement. PharmacoEconomics 2023, 41, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadhuri, A.; Dröschel, D.; Guldimann, M.; Jetschgo, C.; Banhazi, J.; Schwenkglenks, M.; Sutherland, C.S. Cost-effectiveness of voretigene neparvovec in the treatment of patients with inherited retinal disease with RPE65 mutation in Switzerland. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2022, 22, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampampa, K.; Zhang, W.; Venkatachalam, M.; Cotte, F.-E.; Dhanda, D. Cost-effectiveness of idecabtagene vicleucel compared with conventional care in triple-class exposed relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients in Canada and France. J. Med. Econ. 2023, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Liu, F.F.; Deger, K.A.; Franco-Villalobos, C.; Proskorovsky, I.; Keating, S.J.; Sorensen, S. Cost-Effectiveness of Lisocabtagene Maraleucel Versus Axicabtagene Ciloleucel and Tisagenlecleucel in the Third-Line or Later Treatment Setting for Relapsed or Refractory Large B-cell Lymphoma in the United States. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 2355–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Scuffham, P.; Byrnes, J.; Downes, M. Cost-effectiveness analysis of gene-based therapies for patients with spinal muscular atrophy type I in Australia. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.; Jensen, I.; Cyr, P.; Miller, B.; Maru, B.; Sproule, D.M.; Feltner, D.E.; Wiesner, T.; Malone, D.C.; Bischof, M.; et al. An updated cost-utility model for onasemnogene abeparvovec (Zolgensma®) in spinal muscular atrophy type 1 patients and comparison with evaluation by the Institute for Clinical and Effectiveness Review (ICER). J. Mark. Access Health Policy 2021, 9, 1889841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furzer, J.; Gupta, S.; Nathan, P.C.; Schechter, T.; Pole, J.D.; Krueger, J.; Pechlivanoglou, P. Cost-effectiveness of Tisagenlecleucel vs Standard Care in High-risk Relapsed Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Canada. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakase, S.; Teshima, T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Q.; Fujita, T.; Yang, H.; Chai, X.; Qi, C.Z.; Liu, Q.; Wu, E.Q.; et al. Cost Effectiveness Analysis of Tisagenlecleucel for the Treatment of Adult Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma in Japan. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2021, 27, 506.e1–506.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.M.; Teixeira, V.R.; Pogue, R.; Figueiredo, A.C.M.G.; Carvalho, J.L. A systematic review on the cost-effectiveness assessment of tisagenlecleucel for refractory or relapsing B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (R/R B-ALL) treatment in children and young adults. Cytotherapy 2023, 25, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leahy, A.B.; Elgarten, C.W.; Grupp, S.A.; Maude, S.L.; Teachey, D.T. Tisagenlecleucel for the treatment of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2018, 18, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espuelas, M.O.; Burridge, S.; Kirkwood, A.A.; Bonney, D.; Watts, K.; Shenton, G.; Jalowiec, K.A.; O’rEilly, M.A.; Roddie, C.; Castleton, A.; et al. Intention-to-treat outcomes utilising a stringent event definition in children and young people treated with tisagenlecleucel for r/r ALL through a national access scheme. Blood Cancer J. 2024, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, J.E.; Grupp, S.A.; Pulsipher, M.A.; Dietz, A.C.; Rives, S.; Myers, G.D.; August, K.J.; Verneris, M.R.; Buechner, J.; Laetsch, T.W.; et al. Pooled safety analysis of tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.J.S.; Grupp, S.A.; DiNofia, A.M. Tisagenlecleucel for treatment of children and young adults with relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e29123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, M.C.; Hu, Z.-H.; Curran, K.; Laetsch, T.; Locke, F.; Rouce, R.; Pulsipher, M.A.; Phillips, C.L.; Keating, A.; Frigault, M.J.; et al. Real-world evidence of tisagenlecleucel for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5414–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavorn, K.; Thompson, E.R.; Kumar, S.; Heiskanen, A.; Agarwal, A.; Atkins, H.; Shorr, R.; Hawrysh, T.; Chan, K.K.-W.; Presseau, J.; et al. Economic Evaluations of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapies for Hematologic and Solid Malignancies: A Systematic Review. Value Health 2024, 27, 1149–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, D.P.; Matino, D.; Astermark, J.; Dolan, G.; D’oIron, R.; Hermans, C.; Jiménez-Yuste, V.; Linares, A.; Matsushita, T.; McRae, S.; et al. International consensus recommendations on the management of people with haemophilia B. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2022, 13, 20406207221085202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipe, S.W.; Leebeek, F.W.; Recht, M.; Key, N.S.; Castaman, G.; Miesbach, W.; Lattimore, S.; Peerlinck, K.; Van der Valk, P.; Coppens, M.; et al. Gene Therapy with Etranacogene Dezaparvovec for Hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, H.A. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec: A Review in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. CNS Drugs 2022, 36, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrelli, F.M.; Merra, A.; Pellegrini, G. Surgery Versus ATMPs: An Example From Ophthalmology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.K.; Borle, K.; Dragojlovic, N.; Dhillon, M.; Kitchin, V.; Kopac, N.; Ross, C.; Lynd, L.D. Economic Evidence on Potentially Curative Gene Therapy Products: A Systematic Literature Review. PharmacoEconomics 2021, 39, 995–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, C.; Bullement, A.; Packman, D.; Long, L.; Robinson, S.; Nikram, E.; Hatswell, A.J.; Melendez-Torres, G.J.; Crathorne, L. Voretigene Neparvovec for Treating Inherited Retinal Dystrophies Caused by RPE65 Gene Mutations: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Highly Specialised Technology Appraisal. PharmacoEconomics 2020, 38, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplin, M.; Bresnahan, R.; Fleeman, N.; Mahon, J.; Houten, R.; Beale, S.; Boland, A.; Dundar, Y.; Marsden, A.; Munot, P. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec for Treating Pre-symptomatic Spinal Muscular Atrophy: An External Assessment Group Perspective of the Partial Review of NICE Highly Specialised Technology Evaluation 15. PharmacoEconomics Open 2023, 7, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.D.; Silver, M.C.; Berklein, F.C.; Cohen, J.T.; Neumann, P.J. Orphan Drugs Offer Larger Health Gains but Less Favorable Cost-effectiveness than Non-orphan Drugs. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 2629–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisløff, T.; Hagen, G.; Hamidi, V.; Movik, E.; Klemp, M.; Olsen, J.A. Estimating QALY Gains in Applied Studies: A Review of Cost-Utility Analyses Published in 2010. PharmacoEconomics 2014, 32, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jommi, C.; Bertolani, A.; Armeni, P.; Costa, F.; Otto, M. Pharmaceutical pricing and managed entry agreements: An exploratory study on future perspectives in Europe. Health Policy Technol. 2023, 12, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskineh, C.; Nasser, S.C. Managed Entry Agreements for Pharmaceutical Products in Middle East and North African Countries: Payer and Manufacturer Experience and Outlook. Value Health Reg. Issues 2018, 16, 33–38, Erratum in Value Health Reg. Issues 2020, 23, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennini, F.S.; Cicchetti, A.; Sciattella, P.; Rumi, F.; Zanuzzi, M.; Carletto, A.; Sammarco, A.; Romano, F.; Russo, P. Determinants of the Financial Impact of Orphan Drugs in Italy: Differences Between Expected and Observed Pharmaceutical Expenditure. Drugs Real World Outcomes 2025, 12, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, M.J.; Noone, D.; Rozenbaum, M.H.; Carter, J.A.; Botteman, M.F.; Fenwick, E.; Garrison, L.P. Assessing the value of orphan drugs using conventional cost-effectiveness analysis: Is it fit for purpose? Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, C.J. Societal Perspectives and Real-World Cost-Effectiveness: Expanding the Scope of Health Economics Inquiry. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 30, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sittimart, M.; Rattanavipapong, W.; Mirelman, A.J.; Hung, T.M.; Dabak, S.; Downey, L.E.; Jit, M.; Teerawattananon, Y.; Turner, H.C. An overview of the perspectives used in health economic evaluations. Cost Eff. Resour. Alloc. 2024, 22, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkova, Z.; Manev, I.; Tachkov, K.; Boyadzhieva, V.; Stoilov, N.; Doneva, M.; Petrova, G. How Managed Entry Agreements Influence the Patients’ Affordability to Biological Medicines—Bulgarian Example. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).