A Cost Analysis of Diabetic Hand Infections: A Study Based on Direct, Indirect, and One-Year Follow-Up Costs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
- Hospitalization cost: A triangular distribution (min: TRY 8000; mode: TRY 12,000; max: TRY 18,000).
- Surgical intervention cost: A normal distribution (mean: TRY 6500; SD: TRY 1200).
- Antibiotic therapy duration (days): A uniform distribution (range: 10–21 days).
- Re-infection rate: A beta distribution (α = 3, β = 20), based on recurrence observations.
- Lost workdays: A triangular distribution (min: 7; mode: 14; max: 28 days).
- Using the European Central Bank’s (htpp://www.ecb.europa.eu, accessed on 23 July 2025). annual average foreign exchange rates, a multiplicative factor for converting the cost to the corresponding year’s US dollar value was calculated.
- The cost was then multiplied by the conversion factor to obtain a USD amount.
- According to the US Annual Inflation statistics, this amount was converted to its equivalent in the final quarter of 2022 (https://www.bls.gov/data/inflation_calculator.htm, accessed on 23 July 2025).
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| WBC | White blood cell |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| VAC | Vacuum-assisted closure |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision |
| NHS | National Health Service |
References
- World Health Organization: Diabetes Factsheet No: 312. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Sivanandam, A.; Krishnan, N.; Nunez, D.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic hand infections: An often overlooked complication of diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 3371–3379. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, L.M.; Phillips, T.J. Wound healing and treating wounds: Differential diagnosis and evaluation of chronic wounds. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, J.; Anderson, I.W. Hand infections: An audit of 160 infections treated in an accident and emergency department. J. Hand Surg. Br. 1993, 18, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.; Barlaan, P.I.; Fung, B.K.; Ip, J.W. Hand infection in diabetic patients. Hand Surg. 2011, 16, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.G.; Lutale, J.; Gill, G.V.; Archibald, L.K. Tropical diabetic hand syndrome: Risk factors in an adult diabetes population. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 5, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Chauhan, A.; Sethi, N.T. Tropical diabetic hand syndrome. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2008, 28, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, A.K.; Puhaindran, M.E.; Lim, A.Y.; Looi, K.P. Common bacterial infections of the hand. Singap. Med. J. 2006, 47, 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, M.; Barron, E.; Chadwick, P.; Evans, T.; Kong, W.M.; Rayman, G.; Sutton-Smith, M.; Todd, G.; Young, B.; Jeffcoate, W.J. The cost of diabetic foot ulcers and amputations to the National Health Service in England. Diabet. Med. 2019, 36, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, S.; Periasamy, M.; Bhardwaj, P.; Bharathi, R.R.; Mohan, M.; Sabapathy, S.R. Diabetic Hand Infections: Factors at Presentation Influencing Amputation and Number of Surgical Procedures. Indian J. Plast Surg. 2021, 54, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundlach, B.K.; Sasor, S.E.; Chung, K.C. Hand Infections: Epidemiology and Public Health Burden. Hand Clin. 2020, 36, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, A.; Claxton, K.; Sculpher, M. Decision Modelling for Health Economic Evaluation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, D.P. Estimating the Cost of Illness. Am. J. Public Health 1967, 57, 424–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, Y.; Gurbuz, K. Treatment Outcomes and Clinical Evaluation of Upper Extremity Infections Related to Diabetes. Erciyes Med. J. 2020, 42, 400–405. [Google Scholar]
- Gürbüz, K.; Ekinci, Y. Is the Preoperative Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Level Predictive of the Severity of Diabetic Hand Infection According to Surgical and Clinical Outcomes? Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2021, 129, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozan, F.; Gürbüz, K.; Celik, I.; Dursun, Z.B.; Uzun, E. Evaluation of major and minor lower extremity amputation in diabetic foot patients. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 47, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Chronic Complications of Diabetes. Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabet. Diabetes Care 2024, 47 (Suppl. S1), S157–S179. [Google Scholar]
- Unachukwu, C.; Babatunde, S.; Ihekwaba, A.E. Diabetes; hand and/or foot ulcers: A cross-sectional hospital-based study in Port Harcourt; Nigeria. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 75, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, M.; Manu, C.; Vas, P. The current burden of diabetic foot disease. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 17, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, E.; Adeleye, O.; Gezawa, I.; Okpe, I.; Enamino, M.; Ezeani, I. Burden of diabetic foot ulcer in Nigeria: Current evidence from the multicenter evaluation of diabetic foot ulcer in Nigeria. World J. Diabetes 2019, 10, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.H.; Salata, K.; Hussain, M.A.; Zamzam, A.; de Mestral, C.; Wheatcroft, M.; Harlock, J.; Awartani, D.; Aljabri, B.; Verma, A.; et al. The economic burden of inpatient diabetic foot ulcers in Toronto; Canada. Vascular 2020, 28, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Z.J.; Surendra, N.K.; Saxena, A.; Car, J. Clinical and economic burden of diabetic foot ulcers: A.5-year longitudinal multi-ethnic cohort study from the tropics. Int. Wound J. 2021, 18, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, C.M.; Sugita, T.H.; Rosa, M.Q.M.; Pedrosa, H.C.; Rosa, R.D.S.; Bahia, L.R. Annual Direct Medical Costs of Diabetic Foot Disease in Brazil: A.Cost of Illness Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, J.F.; Fuller, G.W.; Vowden, P. Diabetic foot ulcer management in clinical practice in the UK: Costs and outcomes. Int. Wound J. 2018, 15, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, M.; Rayman, G.; Jeffcoate, W.J. Cost of diabetic foot disease to the National Health Service in England. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatyeva, V.I.; Severens, J.L.; Ramos, I.C.; Galstyan, G.R.; Avxentyeva, M.V. Costs of Hospital Stay in Specialized Diabetic Foot Department in Russia. Value Health Reg. Issues 2015, 7, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Açar, İ.H.; Açar, N.G.; Sayiner, Z.A.; Araz, M.; Akarsu, E. Hospitalisation Cost of Diabetic Patients with Foot Ulcers: A Retrospective Descriptive Analysis from Turkey. Turk. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 25, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrepnek, G.H.; Mills, J.L., Sr.; Armstrong, D.G.A. Diabetic Emergency One Million Feet Long: Disparities and Burdens of Illness among Diabetic Foot Ulcer Cases within Emergency Departments in the United States; 2006–2010. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.B.; Desai, U.; Cummings, A.K.; Birnbaum, H.G.; Skornicki, M.; Parsons, N.B. Burden of diabetic foot ulcers for medicare and private insurers. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.G.; Swerdlow, M.A.; Armstrong, A.A.; Conte, M.S.; Padula, W.V.; Bus, S.A. Five year mortality and direct costs of care for people with diabetic foot complications are comparable to cancer. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2020, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchero, H.; Kangambega, P.; Lin, L.; Mukisi-Mukaza, M.; Brunet-Houdard, S.; Briatte, C.; Retali, G.R.; Rusch, E. Cost of diabetic foot in France; Spain; Italy; Germany and United Kingdom: A systematic review. Ann. Endocrinol. 2018, 79, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksuz, E.; Malhan, S.; Sonmez, B.; Numanoglu Tekin, R. Cost of illness among patients with diabetic foot ulcer in Turkey. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
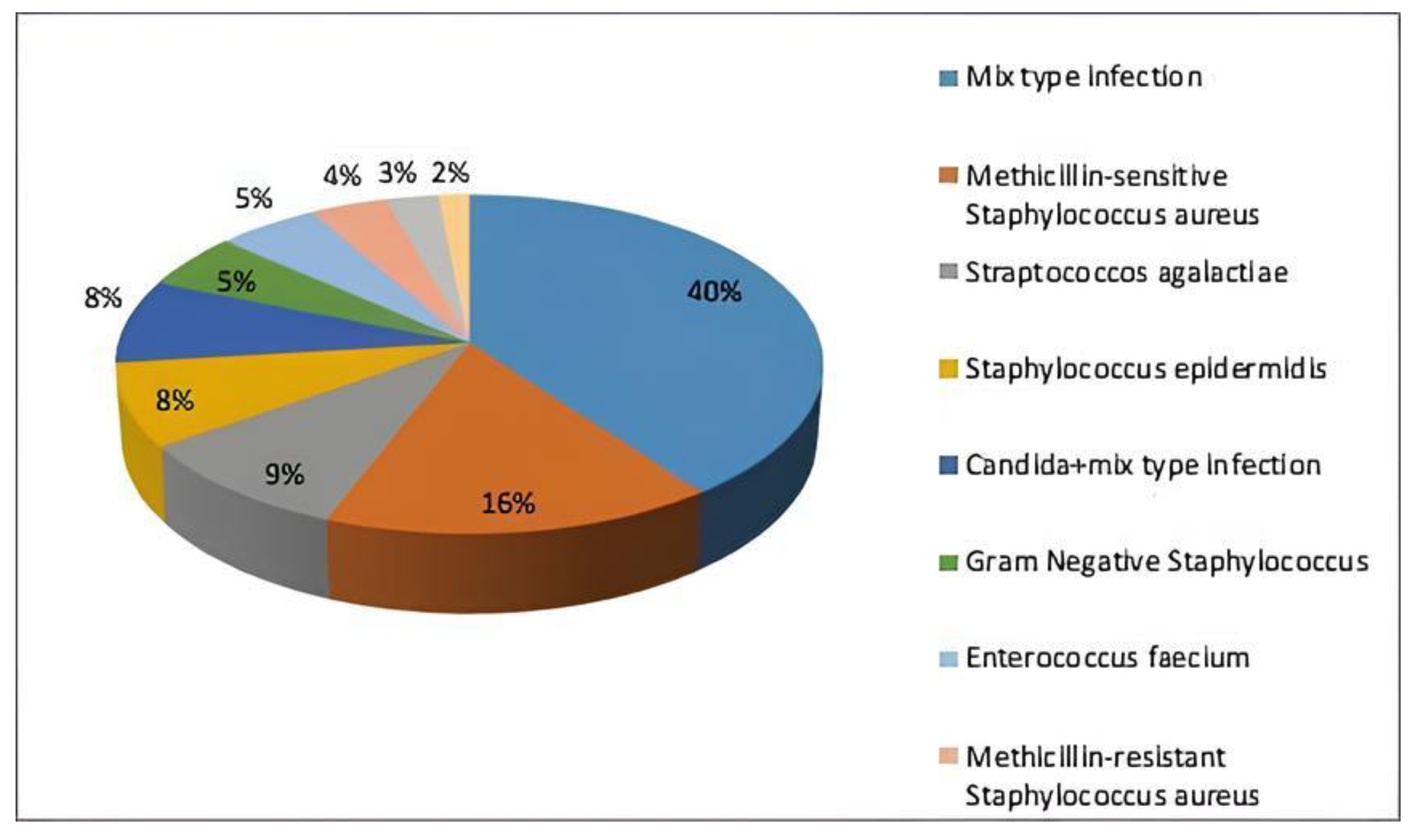
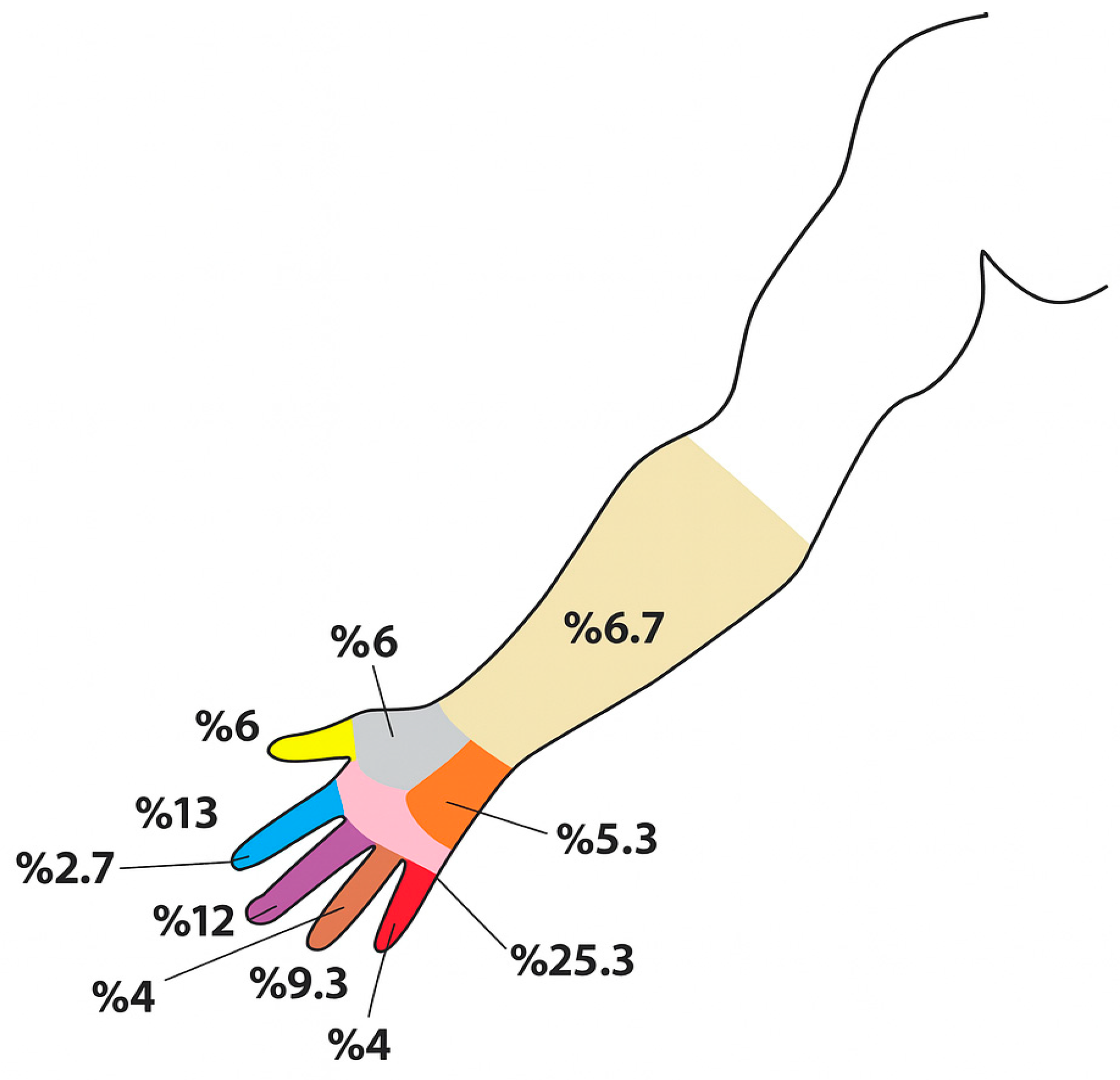
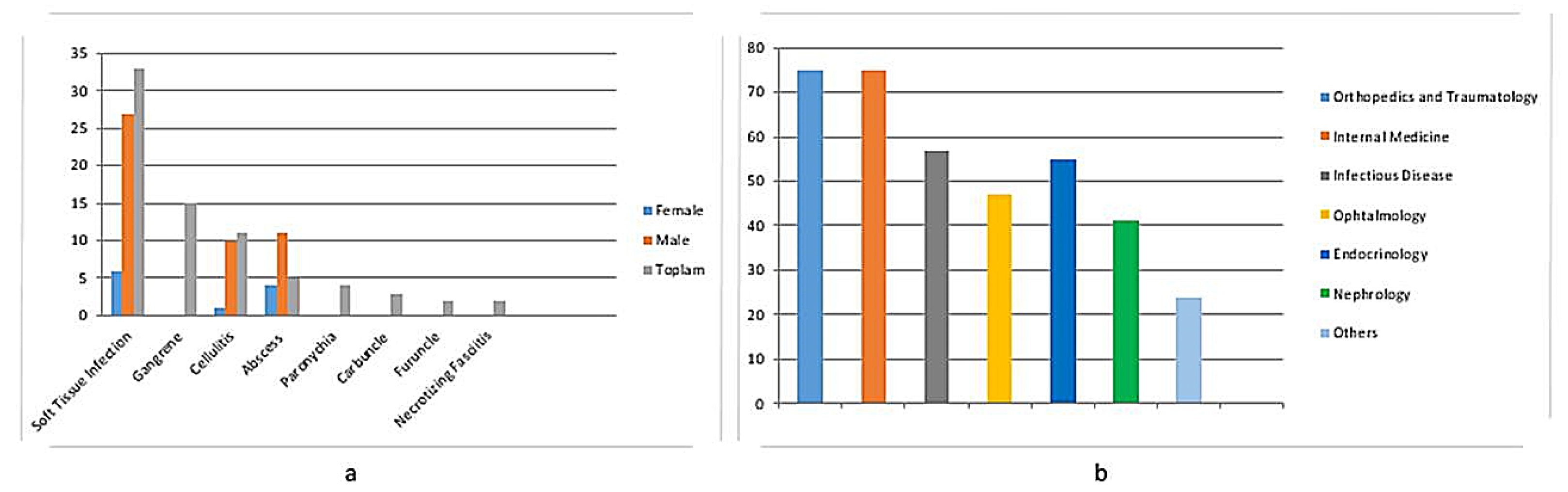
| Parameters | ± SD/Average (Min–Max) |
|---|---|
| Age | 57.01 ± 11.09/62 (28–68) |
| Pre-infection HbA1C (mmol/mol) | 8.20 ± 1.33/8.10 (6−12) |
| Follow-up period (months) | 19.13 ± 10.48/17 (1−44) |
| Blood sugar level at the diagnosis (mg/dL) | 335.81 ± 88.14/324.0 (216.0−365.0) |
| At diagnosis HgA1C value (mmol/mol) | 8.27 ± 1.15/8.30 (6−13) |
| Sedimentation rate at the diagnosis (mm/h) | 33.75 ± 10.16/34.00 (16–65) |
| CRP at the diagnosis (mg/L) | 49.83 ± 15.72/50.00 (25–102) |
| WBC at the diagnosis (#/mcL) | 11,440.80 ± 3151.65/11,440.00 (2400–19,820) |
| Period of hospitalization (days) | 22.68 ± 13.89/22.00 (0–65) |
| Parameters | ± SD/Average (Min–Max) |
|---|---|
| Drug cost Ψ (US dollar) | 5542.426 ± 3519.60/4473.00 (1006.00–19,873.00) |
| Length of stay in the clinic (days) | 19.36 ± 10.45/21 (0–48) |
| The clinic stay cost γ (US dollar) | 6222.64 ± 4377.76/5534.00 (0–18,473.00) |
| Length of stay in the ICU (days) | 3.31 ± 6.80/0 (0–30) |
| The ICU stay cost ∂ (US dollar) | 2256.09 ± 388.44/1842.5 (0–18,567.00) |
| of outpatient clinic visits | 22.29 ± 11.01/20 (7–59) |
| Outpatient clinic visit cost ϕ (US dollar) | 5162.41 ± 3838.55/4382.00 (384.00–15,635.00) |
| Subtotal without surgical treatment | 6228.20 ± 4570.48/4982.00 (498.00–21,116.00) |
| Surgical treatment cost (US dollar) | 3607.33 ± 5290.70/521.00 (21.00–19,407.00) |
| of Days to report incapacity for work (days) | 7.85 ± 21.69/0 (0–102) |
| Incapacity for work cost (US dollar) | 745.53 ± 203.32/0 (0–1002.00) |
| Total cost including whole treatment process (US dollar) | 24,602.22 ± 5257.1523/21,155.00 (3166.00–68,975.00) |
| # of Outpatient Clinic Visits | Types of Surgical Interventions | # | ± SD Average (Min–Max) |
| Drainage | 24 | 18.91 ± 11.13 17.00 (7.00–59.00) | |
| Drainage + VAC | 4 | 18.75 ± 2.98 18.00 (16.00–23.00) | |
| Open Amputation + VAC | 5 | 27.80 ± 11.94 16.50 (10.00–41.00) | |
| Ray Amputation | 18 | 22.83 ± 11.28 20.50 (12.00–58.00) | |
| Fasciotomy + VAC | 7 | 21.71 ± 8.57 22.00 (10.00–35.00) | |
| Fasciotomy + Ray Amputation | 10 | 21.90 ± 9.42 19.50 (10.00–41.00) | |
| Amputation + Flap Reconstruction | 6 | 33.50 ± 13.32 31.50 (16.00–54.00) | |
| Fasciotomy + VAC + Flap Reconstruction | 1 | 21.00 | |
| K-W | 10.728, p = 0.151 | ||
| Cost of Outpatient Clinic Visits (US Dollars) | Types of Surgical Interventions | # | ± SD Average (Min–Max) |
| Drainage | 24 | 3256.45 ± 3250.38 2273.00 (384.00–12,584.00) | |
| Drainage + VAC | 4 | 6489.00 ± 4541.81 7611.50 (498.00–10,235.00) | |
| Open Amputation + VAC | 5 | 5434.20 ± 4095.99 4872.00 (1804.00–12,390.00) | |
| Ray Amputation | 18 | 529.33 ± 229.38 457.50 (192.00–1584.00) | |
| Fasciotomy + VAC | 7 | 6289.71 ± 5044.81 4409.00 (2009.00–15,635.00) | |
| Fasciotomy + Ray Amputation + VAC | 10 | 4065.30 ± 2394.61 4434.50 (845.00–8943.00) | |
| Amputation + Flap Reconstruction | 6 | 1010.00 ± 504.76 1291.00 (387.00–1034.00) | |
| Fasciotomy + Flap Reconstruction | 1 | 1329.00 ± 204.06 1953.00 (237.00–1034.00) | |
| K-W | 21.162, p = 0.004 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuşcu, B.; Gürbüz, K. A Cost Analysis of Diabetic Hand Infections: A Study Based on Direct, Indirect, and One-Year Follow-Up Costs. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151826
Kuşcu B, Gürbüz K. A Cost Analysis of Diabetic Hand Infections: A Study Based on Direct, Indirect, and One-Year Follow-Up Costs. Healthcare. 2025; 13(15):1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151826
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuşcu, Burak, and Kaan Gürbüz. 2025. "A Cost Analysis of Diabetic Hand Infections: A Study Based on Direct, Indirect, and One-Year Follow-Up Costs" Healthcare 13, no. 15: 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151826
APA StyleKuşcu, B., & Gürbüz, K. (2025). A Cost Analysis of Diabetic Hand Infections: A Study Based on Direct, Indirect, and One-Year Follow-Up Costs. Healthcare, 13(15), 1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151826






