Effectiveness of a Case Management Intervention Combined with Physical Exercise Compared to Physical Exercise Alone in Older People with High Risk of Falls: A Protocol Study of a Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
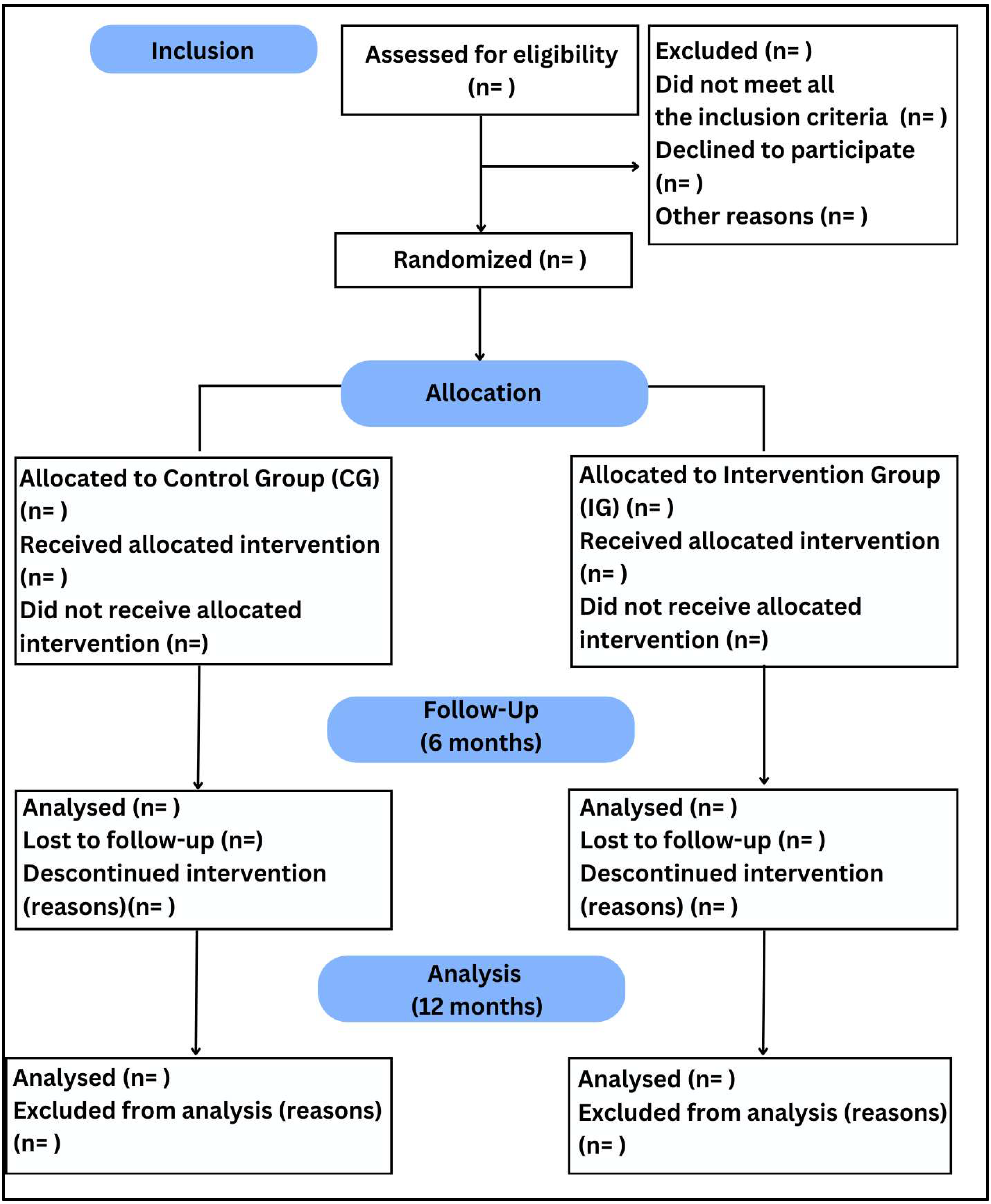
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trial Design
2.2. Study Setting
2.3. Recruitment and Participants
2.4. Interventions
2.4.1. Control Group
2.4.2. Intervention Group
2.5. Outcome Measures
2.6. Primary Outcome Measures
2.7. Secondary Outcome Measures
2.8. Randomization and Blinding
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAGIC | Multidisciplinary and Assistance Program of Falls Management in Faller Older People |
| UFSCar | Federal University of São Carlos |
| ReBEC | Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials |
| DRSs | Regional Health Departments |
| SUS | Unified Health System |
| IBGE | Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics |
| ICMC-USP | Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science of the University of São Paulo |
| MCID | Minimal Clinically Important Difference |
| GCRS | Global Change Rating Scale |
| SAPS | Short Assessment of Patient Satisfaction |
| IG | Intervention Group |
| CG | Control Group |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| fNRis | Functional Near-infrared Spectroscopy |
References
- Li, Y.; Hou, L.; Zhao, H.; Xie, R.; Yi, Y.; Ding, X. Risk factors for falls among community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2023, 9, 1019094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, I.; Adebusoye, B.; Chattopadhyay, K. Health Consequences of Falls among Older Adults in India: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Geriatrics 2023, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Odasso, M.; van der Velde, N.; Martin, F.C.; Petrovic, M.; Tan, M.P.; Ryg, J.; Aguilar-Navarro, S.; Alexander, N.B.; Becker, C.; Blain, H.; et al. World guidelines for falls prevention and management for older adults: A global initiative. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerter, D.G.; Braga, B.F.; Santos, C.D.P.; Silva Junior, D.D.N.; Brito, E.W.G.; Lyra, C.D.O.; Moura, L.K.B.; Barbosa, I. A pessoa idosa na Atenção Primária à Saúde: Um estudo bibliométrico da produção científica internacional. Rev. Bras. Med. Fam. 2021, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candanedo, M.J.B.L.; Gramani-Say, K.; Gerassi, R.C.; Janducci, A.L.; Florido, J.V.B.; Alberto, S.N.; Rossi, P.G.; Ansai, J.H. Effects of case management based on preventing falls in older people: A systematic review. Worldviews Ev. Based Nurs. 2023, 20, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sossai, M.I.; Pantoni, C.B.F.; Gramani-Say, K.; de Melo, M.L.; Maciel, L.T.; Lord, S.R.; Ansai, J.H. A case management strategy to reduce falls in older people with a history of falls: A randomized controlled trial. Geriatr. Nurs. 2024, 59, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, D.B.; Gazarian, P.; Alexander, N.; Araujo, K.; Baker, D.; Bean, J.F.; Boult, C.; Charpentier, P.; Duncan, P.; Latham, N.; et al. The Strategies to Reduce Injuries and Develop Confidence in Elders Intervention: Falls Risk Factor Assessment and Management, Patient Engagement, and Nurse Co-management. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 2733–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, S.N.; Ansai, J.H.; Janducci, A.L.; Florido, J.V.B.; Novaes, A.D.C.; Caetano, M.J.D.; Rossi, P.G.; Tavares, L.R.C.; Lord, S.R.; Gramani-Say, K. A Case Management Program at Home to Reduce Fall Risk in Older Adults (the MAGIC Study): Protocol for a Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2022, 11, e34796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janducci, A.L.; Gramani-Say, K.; da Silva, L.C.; Florido, J.V.B.; Novaes, A.D.C.; Porcatti, L.R.; Ansai, J.H. Treatment fidelity and satisfaction with an intervention based on case management for older people with falls history: Randomized clinical trial. Geriatr. Nurs. 2023, 52, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florido, J.V.B.; Caetano, M.J.D.; Janducci, A.L.; Sossai, M.I.; Dias, A.L.O.; Gramani-Say, K.; Ansai, J.H. Effects of a case management-based intervention on non-motor risk factors for falls in older people with history of falls: A randomised clinical trial. Psychogeriatrics 2024, 24, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). 2022. Available online: https://censo2022.ibge.gov.br/panorama/ (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Peduzzi, P.; Concato, J.; Kemper, E.; Holford, T.R.; Feinstein, A.R. A simulation study of the number of events per variable in logistic regression analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buto, M.S.; Fiogbé, E.; Vassimon-Barroso, V.; Rossi, P.G.; Farche, A.C.; Carnavale, B.F.; Takahashi, A.C. Pre-Frail Multicomponent Training Intervention project for complexity of biological signals, functional capacity and cognition improvement in pre-frail older adults: A blinded randomized controlled study protocol. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chodzko-Zajko, W.J.; Proctor, D.N.; Fiatarone Singh, M.A.; Minson, C.T.; Nigg, C.R.; Salem, G.J.; Skinner, J.S. Exercise and Physical Activity for Older Adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1510–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Step Safely: Strategies for Preventing and Managing Falls across the Life-Course; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg International Work Group on the Prevention of Falls by the Elderly. The prevention of falls in later life. Dan. Med. Bull. 1987, 34, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, F.B.D.; Botelho, K.K.P.; Bezerra, A.R.; Azevedo, D.I.D.O.; Santos-Couto-Paz, C.C.D.; Fachin-Martins, E. Cross-cultural adaptation to Brazilian Portuguese of the Michigan neuropathy screening instrument: MNSI-Brazil. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2016, 74, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.R.; Trelha, C.S. Translation, cultural adaptation and evaluation of the psychometric properties of the Falls Risk Awareness Questionnaire (FRAQ): FRAQ-Brazil. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2013, 17, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddy, E.; Muller, S.; Thomas, E. Defining disabling foot pain in older adults: Further examination of the Manchester Foot Pain and Disability Index. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, P.J.; Patterson, C.; Wearing, S.; Baglioni, T. Development and validation of a questionnaire designed to measure foot-health status. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 1998, 88, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.A.; Caramelli, P. Brazilian adaptation of the Addenbrooke’s cognitive examination-revised (ACE-R). Dement. Neuropsychol. 2007, 1, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitrini, R.; Caramelli, P.; Herrera, E.; Porto, C.S.; Charchat-Fichman, H.; Carthery, M.T.; Lima, E.P. Performance of illiterate and literate nondemented elderly subjects in two tests of long-term memory. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2004, 10, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, E.; Sherman, E.M.S.; Spreen, O. A compendium of neuropsychological tests: Administration, norms, and commentary. American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ansai, J.H.; Andrade, L.P.; Rossi, P.G.; Takahashi, A.C.; Vale, F.A.; Rebelatto, J.R. Gait, dual task and history of falls in elderly with preserved cognition, mild cognitive impairment, and mild Alzheimer’s disease. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2017, 21, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Morais, D.; Maximiano-Barreto, M.A.; Luchesi, B.M.; Muniz, M.; Chagas, M.H.N. Development and validation of a face database for the recognition of facial expressions of basic emotions in the Brazilian population. Psicol. Reflex. Crit. 2024, 37, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelo, M.S.; Coelho-Filho, J.M.; Carvalho, A.F.; Lima, J.W.; Noleto, J.C.; Ribeiro, K.G.; Siqueira-Neto, J.I. Validity of the Brazilian version of the Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) among primary care patients. Inter. Psychogeriatr. 2010, 22, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiny, C.; Silva, A.C.D.O.; Nardi, A.E.; Pachana, N.A. Tradução e adaptação transcultural da versão brasileira do Inventário de Ansiedade Geriátrica (GAI). Arch. Clin. Psychiatr. 2011, 38, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargos, F.F.; Dias, R.C.; Dias, J.; Freire, M.T. Adaptação transcultural e avaliação das propriedades psicométricas da Falls Efficacy Scale-International em idosos brasileiros (FES-I-BRASIL). Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2010, 14, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.C.; Samson, M.M.; Verhaar, H.J. Vitamin D deficiency, muscle function, and falls in elderly people. AJCN 2002, 75, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, K.M.; Voth, J.; Munce, S.E.; Straus, S.E.; Jaglal, S.B. Chronic disease and falls in community-dwelling Canadians over 65 years old: A population-based study exploring associations with number and pattern of chronic conditions. BMC Geriatr. 2014, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherbourne, C.D.; Stewart, A.L. The MOS social support survey. Soc. Sci. Med. 1991, 32, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T.; Wilson, A. Polypharmacy and falls in the elderly: A literature review. Nurs. Mid. Stud. 2013, 2, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, D.; Levi, M.; Kurtz, I.; Shany, S.; Zvili, I.; Mualleme, E.; Melzer, I. Nutritional status in relation to balance and falls in the elderly: A preliminary look at serum folate. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 54, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, A.; Hoang, P.T.S.B.; Sharmin, S.; Reijnierse, E.M.; van Wezel, R.J.; Meskers, C.G.; Maier, A.B. Orthostatic hypotension and falls in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntonti, P.; Mitsi, C.; Chatzimichael, E.; Panagiotopoulou, E.K.; Bakirtzis, M.; Konstantinidis, A.; Labiris, G. A systematic review of reading tests. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 16, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, H.C.; Huang, Y.Y. Sensitivity and specificity of hearing tests for screening hearing loss in older adults. J. Otol. 2023, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, B.J.; Higginbotham, N. reliability of the home falls and accidents screening tool (home fast) for identifying older people at increased risk of falls. Disabil. Rehabil. 2002, 24, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, R.L.; Júnior, J.S.V. Confiabilidade da versão brasileira da escala de atividades instrumentais da vida diária. Rev. Bras. Promoção Saúde 2008, 21, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.L.; Ferreira, L.N.; Pereira, L.N. Contribuição para a validação da versão em português do EQ-5D. Acta Médica Port. 2013, 26, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, A.; Hoggart, B. Pain: A review of three commonly used pain rating scales. J. Clin. Nurs. 2005, 14, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, T.S.D.; Gambaro, R.C.; Santos, F.C. Mensuração da dor em idosos: Avaliação das propriedades psicométricas da versão em português do Geriatric Pain Measure. Rev. Dor 2015, 16, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Fried, L.P. Frailty in Older Adults: Evidence for a Phenotype. J. Gerontol. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.M. Versão Brasileira da Short Physical Performance Battery—SPPB: Adaptação Cultural e Estudo da Confiabilidade. Master’s Thesis, Faculdade de Educação, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Zamboni, M. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, R.M. Confiabilidade Intraexaminador da Medida de Força Muscular Isométrica da Musculatura Inversora e Eversora do Tornozelo Utilizando o Dinamômetro Manual em Voluntários Saudáveis. Master’s Thesis, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, Universidade de Campinas, Campinas, Brazil, 2001; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Calixtre, L.B.; Oliveira, A.B.; Alburquerque-Sendín, F.; Armijo-Olivo, S. What is the minimal important difference of pain intensity, mandibular function, and headache impact in patients with temporomandibular disorders? Clinical significance analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2020, 46, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friscia, L.A.; Morgan, M.T.; Sparto, P.J.; Furman, J.M.; Whitney, S.L. Responsiveness of Self-Report Measures in Individuals With Vertigo, Dizziness, and Unsteadiness. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankner, R.; Drory, Y.; Geulayov, G.; Ziv, A.; Novikov, I.; Zlotnick, A.Y.; Moshkovitz, Y.; Elami, A.; Schwammenthal, E.; Goldbourt, U. A controlled intervention to increase participation in cardiac rehabilitation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2015, 22, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawthorne, G.; Sansoni, J.; Hayes, L.; Marosszeky, N.; Sansoni, E. Measuring patient satisfaction with health care treatment using the Short Assessment of Patient Satisfaction measure delivered superior and robust satisfaction estimates. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Rohrer, J.; Borders, T.; Farrell, T. Patient Satisfaction, Self-Rated Health Status, and Health Confidence: An Assessment of the Utility of Single-Item Questions. Am. J. Med. Qual. 2007, 22, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitorio, R.; Stuart, S.; Mancini, M. Executive Control of Walking in People With Parkinson’s Disease With Freezing of Gait. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2020, 34, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, L. Análise de Conteúdo; Edições 70 Ltd.: Lisboa, Portugal, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Picorelli, A.M.A.; Pereira, L.S.M.; Pereira, D.S.; Felício, D.; Sherrington, C. Adherence to exercise programs for older people is influenced by program characteristics and personal factors: A systematic review. J. Physiother. 2014, 60, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, R.K.; Goldberg, S.E.; Van Der Wardt, V.; Burgon, C.; Di Lorito, C.; Godfrey, M.; Dunlop, M.; Logan, P.; Masud, T.; Gladman, J.; et al. A randomised controlled trial of an exercise intervention promoting activity, independence and stability in older adults with mild cognitive impairment and early dementia (PrAISED)—A Protocol. Trials 2019, 20, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkan, R.; Pumper, B.; Smyth, N.; Wirkkala, H.; Ciol, M.A.; Shumway-Cook, A. Exercise adherence following physical therapy intervention in older adults with impaired balance. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardley, L.; Beyer, N.; Hauer, K.; McKee, K.; Ballinger, C.; Todd, C. Recommendations for promoting the engagement of older people in activities to prevent falls. Qual. Saf. Health Care 2007, 16, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simek, E.M.; McPhate, L.; Haines, T.P. Adherence to and efficacy of home exercise programs to prevent falls: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of exercise program characteristics. Prev. Med. 2012, 55, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; Merchant, R.A.; Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D.; Aprahamian, I.; Arai, H.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M.; Bernabei, R.; Cadore, E.L.; Cesari, M.; et al. International Exercise Recommendations in Older Adults (ICFSR): Expert Consensus Guidelines. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2021, 25, 824–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soril, L.J.J.; Leggett, L.E.; Lorenzetti, D.L.; Noseworthy, T.W.; Clement, F.M. Reducing Frequent Visits to the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review of Interventions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, M.C.; Kushel, M.; Ko, M.J.; Penko, J.; Bindman, A.B. The Effectiveness of Emergency Department Visit Reduction Programs: A Systematic Review. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2016, 68, 467–483.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Risk Factor | Assessment |
|---|---|
| History of falls [16,17,18] | Number of falls, consequences, circumstances Falls risk score |
| Feet changes and footwear [19,20] | Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument Manchester Index Footwear questionnaire |
| Cognitive changes [21,22,23,24,25] | Addenbrooke Cognitive Examination (total score, Mini-Mental State Examination, domains scores, Clock Drawing test, fluency verbal test) Brief Cognitive Screening Battery Digit Span Dual task test (Timed up and Go test associated with fluency task, fNIRS) Memory complaint Social Cognition |
| Depression and anxiety [26,27] | Geriatric Depression Scale Geriatric Anxiety Inventory |
| Fear of falling [28] | Falls Efficacy Scale—International |
| Vitamin D deficiency [29] | Blood test |
| Acute or chronic conditions (osteoporosis, urinary incontinence, cardiovascular disease, dizziness or cerebellar dysfunctions and others) [30] | Presence of morbidities Cardiac frequency Blood pressure |
| Living alone and other social issues [31] | If they live alone WHODAS 2.0 Social Support Survey |
| Use of medications [32] | Dose, frequency, and time of each medication, use of psychotropic drugs |
| Nutritional deficiency [33] | Body mass index Nutritional condition Blood test (calcium, B12 vitamin, K2 vitamin) Mini Nutritional Assessment |
| Postural hypotension [34] | Symptoms Drop in blood pressure after changing position |
| Vision and hearing changes [35,36] | Use of bifocal or multifocal glasses Jaeger Eye Chart Difficulty of hearing or people think you have poor hearing Whisper test |
| Home safety [37] | Home Fast |
| Use of walking devices and functional activities [38,39] | Use of walking devices Lawton & Brody scale EuroQol-5D Fall to the floor and get up test |
| Pain [40,41,42] | Brief Pain Inventory Geriatrics Pain Measure |
| Muscle strength, mobility, gait, and postural balance [43,44,45] | Timed Up and Go test (simple and dual task) Frailty Assessment Short Physical Performance Battery (balance, gait speed, sit-to-stand test) Sarcopenia Assessment Ankle mobility |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morais, D.; Gramani-Say, K.; Melo, M.L.d.; Dias, A.L.O.; Vassimon-Barroso, V.; Ponciano, J.R.; Godoi-Jacomassi, D.; Ansai, J.H. Effectiveness of a Case Management Intervention Combined with Physical Exercise Compared to Physical Exercise Alone in Older People with High Risk of Falls: A Protocol Study of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151814
Morais D, Gramani-Say K, Melo MLd, Dias ALO, Vassimon-Barroso V, Ponciano JR, Godoi-Jacomassi D, Ansai JH. Effectiveness of a Case Management Intervention Combined with Physical Exercise Compared to Physical Exercise Alone in Older People with High Risk of Falls: A Protocol Study of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Healthcare. 2025; 13(15):1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151814
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorais, Daiene, Karina Gramani-Say, Mariana Luiz de Melo, Ana Laura Oliveira Dias, Verena Vassimon-Barroso, Jean Roberto Ponciano, Daniela Godoi-Jacomassi, and Juliana Hotta Ansai. 2025. "Effectiveness of a Case Management Intervention Combined with Physical Exercise Compared to Physical Exercise Alone in Older People with High Risk of Falls: A Protocol Study of a Randomized Clinical Trial" Healthcare 13, no. 15: 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151814
APA StyleMorais, D., Gramani-Say, K., Melo, M. L. d., Dias, A. L. O., Vassimon-Barroso, V., Ponciano, J. R., Godoi-Jacomassi, D., & Ansai, J. H. (2025). Effectiveness of a Case Management Intervention Combined with Physical Exercise Compared to Physical Exercise Alone in Older People with High Risk of Falls: A Protocol Study of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Healthcare, 13(15), 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151814







