Does Exercise Performance Differ Among Male Law Enforcement Officers Based on Their Body Mass Index Category?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Parameters
2.3. Upper Body and Trunk Muscular Endurance
2.3.1. One-Minute Push-Ups and Sit-Ups
2.3.2. Twenty-Meter Multistage Fitness Test (20MSFT)
2.4. Lower Body Power and Peak Power Output
Vertical Jump (VJ) Height
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Overview
2.5.2. G*Power Sensitivity Analysis
2.5.3. Normality and Correlation Analysis
2.5.4. Non-Parametric Tests
2.5.5. Parametric Tests
2.5.6. Multicollinearity
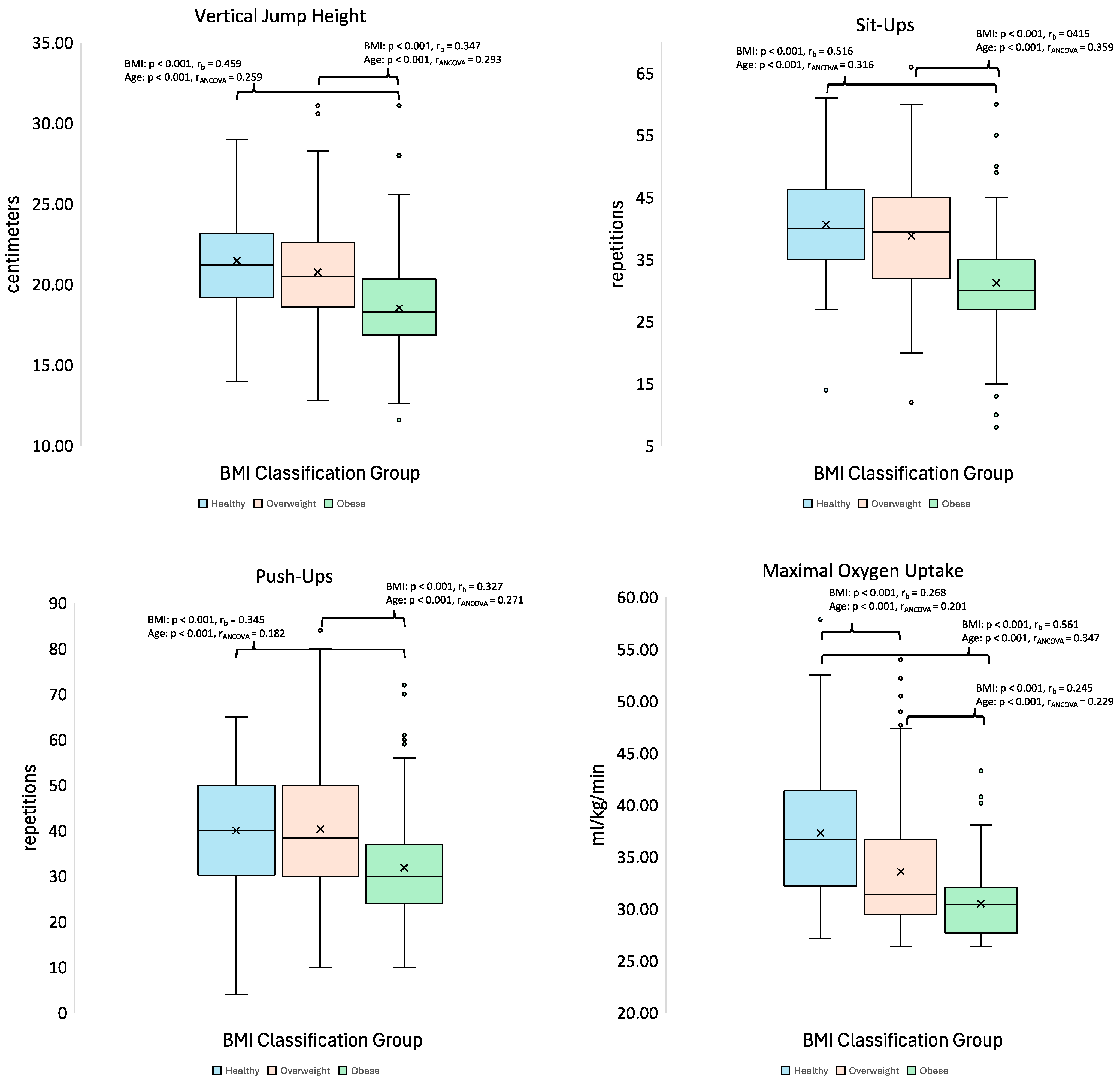
3. Results
3.1. Correlation Analysis
3.2. Demographic Data
3.3. Exercise Performance Measures
3.4. Multicollinearity Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 20MFST | 20 m Multistage Fitness Test |
| ANCOVA | Analysis of Covariance |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CRF | Cardiorespiratory Fitness |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| LEO | Law Enforcement Officer |
| PAPw | Peak Anaerobic Power Output |
| PAT | Physical Ability Test |
| SMM | Skeletal Muscle Mass |
| SWAT | Special Weapons and Tactics |
| TSAC-F | Tactical Strength and Conditioning Facilitator |
| US | United States |
| VJ | Vertical Jump |
| VO2max | Maximal Oxygen Uptake |
References
- Boyce, R.; Jones, G.; Lloyd, C.; Boone, E. A Longitudinal Observation of Police: Body Composition Changes over 12 Years with Gender and Race Comparisons. J. Exerc. Physiol. Online 2008, 11, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kukic, F.; Cvorovic, A.; Dawes, J.J.; Korpanovski, N. Body mass index differences of police cadets and police employees. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference Effects of Applying Physical Activity on Anthropological Status of Children Adolescents and Adults, Belgrade, Serbia, 11–12 December 2017; pp. 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sörensen, L.; Smolander, J.; Louhevaara, V.; Korhonen, O.; Oja, P. Physical activity, fitness and body composition of Finnish police officers: A 15-year follow-up study. Occup. Med. 2000, 50, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dopsaj, M.; Vuković, M. Prevalence of the body mass index (BMI) among the members of the Ministry of Interior of the Republic of Serbia: Pilot study. Bezbednost 2015, 57, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukic, F.; Dopsaj, M. Structural analysis of body composition status in Abu Dhabi police personnel. NBP Nauka Bezbednosti Polic. 2016, 21, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, J.J.; Orr, R.M.; Flores, R.R.; Lockie, R.G.; Kornhauser, C.; Holmes, R. A physical fitness profile of state highway patrol officers by gender and age. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 29, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.Q.; Clasey, J.L.; Yates, J.W.; Koebke, N.C.; Palmer, T.G.; Abel, M.G. Relationship of Physical Fitness Measures vs. Occupational Physical Ability in Campus Law Enforcement Officers. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissett, D.; Bissett, J.; Snell, C. Physical agility tests and fitness standards: Perceptions of law enforcement officers. Police Pract. Res. 2012, 13, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canetti, E.F.D.; Orr, R.M.; Brown, W.; Schram, B.; Lockie, R.G.; Dawes, J.J. The Use of Musculoskeletal Fitness Measures as Indicators of Performance in Police Occupational Tasks. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2024, 17, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, J. Accuracy of Self-Reported Height, Body Mass and Derived Body Mass Index in a Group of Law Enforcement Officers. Nauka Bezb. Polic. 2019, 24, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, J.; Orr, R.; Elder, C.; Rockwell, C. Association between Body Fatness and Measures of Muscular Endurance Among Part-Time Swat Officers. J. Aust. Strength Cond. 2014, 22, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Dawes, J.J.; Kornhauser, C.L.; Crespo, D.; Elder, C.L.; Lindsay, K.G.; Holmes, R.J. Does Body Mass Index Influence the Physiological and Perceptual Demands Associated with Defensive Tactics Training in State Patrol Officers? Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2018, 11, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, J.J.; Lindsay, K.; Bero, J.; Elder, C.; Kornhauser, C.; Holmes, R. Physical Fitness Characteristics of High vs. Low Performers on an Occupationally Specific Physical Agility Test for Patrol Officers. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 2808–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, J.J.; Orr, R.M.; Siekaniec, C.L.; Vanderwoude, A.A.; Pope, R. Associations between anthropometric characteristics and physical performance in male law enforcement officers: A retrospective cohort study. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 28, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čvorović, A.; Kukić, F.; Heinrich, K.M.; Dopsaj, M. Association of waist to height ratio with 2.4 kilometers running time among male police populations. Work 2022, 71, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, M.L.; Gaesser, G.A.; Butcher, J.D.; Després, J.-P.; Dishman, R.K.; Franklin, B.A.; Garber, C.E. ACSM Position Stand: The Recommended Quantity and Quality of Exercise for Developing and Maintaining Cardiorespiratory and Muscular Fitness, and Flexibility in Healthy Adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, R.; Carter, J.; Jebb, S.A.; Bennett, D.; Lewington, S.; Piernas, C. Associations of Skeletal Muscle Mass and Fat Mass With Incident Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study of UK Biobank Participants. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukic, F.; Dopsaj, M.; Dawes, J.; Orr, R.M.; Cvorovic, A. Use of human body morphology as an indication of physical fitness: Implications for police officers. Int. J. Morphol. 2018, 36, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukic, F.; Cvorovic, A.; Dawes, J.; Orr, R.M.; Dopsaj, M. Relations of body voluminosity and indicators of muscularity with physical performance of police employees: Pilot study. Balt. J. Sport Health Sci. 2018, 4, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, E.C.; Porto, L.G.; Nogueira, R.M.; Martins, W.R.; Fonseca, R.M.; Lunardi, C.C.; de Oliveira, R.J. Body Composition is Strongly Associated With Cardiorespiratory Fitness in a Large Brazilian Military Firefighter Cohort: The Brazilian Firefighters Study. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper Institute. Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Fitness Standards in Law Enforcement. Available online: https://www.valorforblue.org/Clearinghouse/697/Frequently-Asked-Questions-Regarding-Fitness-Standards-in-Law-Enforcement (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Orr, R.; Pope, R.; Peterson, S.; Hinton, B.; Stierli, M. Leg Power As an Indicator of Risk of Injury or Illness in Police Recruits. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2016, 13, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomes, C.D.; Sawyer, S.; Orr, R.; Schram, B. Ability of fitness testing to predict injury risk during initial tactical training: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Inj. Prev. 2020, 26, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockie, R.; Dawes, J.J.; Sakura, T.; Schram, B.; Orr, R.M. Relationships Between Physical Fitness Assessment Measures and a Workplace Task-Specific Physical Assessment Among Police Officers: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2023, 37, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.; Maupin, D.; Lockie, R.G.; Dawes, J.J.; Simas, V.; Canetti, E.; Schram, B.; Orr, R. Evaluating the Variability Between 20-m Multistage Fitness Test Estimating Equations in Law Enforcement Recruits. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2024, 38, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockie, R.G.; Dawes, J.J.; Kornhauser, C.L.; Holmes, R.J. Cross-Sectional and Retrospective Cohort Analysis of the Effects of Age on Flexibility, Strength Endurance, Lower-Body Power, and Aerobic Fitness in Law Enforcement Officers. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukic, F.; Orr, R.; Markovic, M.; Dawes, J.; Cvorovic, A.; Koropanovski, N. Factorial and Construct Validity of Sit-Up Test of Different Durations to Assess Muscular Endurance of Police Students. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, L.A.; Lambert, J. A maximal multistage 20-m shuttle run test to predict VO2 max. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1982, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsbottom, R.; Brewer, J.; Williams, C. A progressive shuttle run test to estimate maximal oxygen uptake. Br. J. Sports Med. 1988, 22, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, S.P.; Harackiewicz, D.V.; Harman, E.A.; Frykman, P.N.; Rosenstein, M.T. Cross-validation of three jump power equations. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, B.K.; Dawes, J.J.; Lockie, R.G. Relationships Between Tests of Strength, Power, and Speed and the 75-Yard Pursuit Run. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2022, 36, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using Effect Size-or Why the P Value Is Not Enough. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, J.; Andrade, M.; Gealh, L. Characterization of the physical condition and cardiovascular risk of highway police officers. Rev. Andal. Med. Deporte 2015, 7, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Christophi, C.A.; Farioli, A.; Baur, D.M.; Moffatt, S.; Zollinger, T.W.; Kales, S.N. Association Between Push-up Exercise Capacity and Future Cardiovascular Events Among Active Adult Men. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e188341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, M.; Foshag, P.; Brzęk, A.; Vollenberg, R.; Jehn, U.; Littwitz, H.; Leischik, R. Cardiorespiratory Fitness Is Associated with a Reduced Cardiovascular Risk in Occupational Groups with Different Working Conditions: A Cross-Sectional Study among Police Officers and Office Workers. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, H.; Eler, N. The Relationship between Body Composition and Jumping Performance of Volleyball Players. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 2019, 7, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, M.J.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Leonard, M.; Martaindale, M.H.; Bloomer, R.J.; Pence, J.; Martin, S.E. Risk Factors for Cardiometabolic Disease in Professional Firefighters. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2023, 65, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, M.J.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Leonard, M.; Martaindale, M.H.; Bloomer, R.J.; Pence, J.; Martin, S.E. Firefighters with Higher Cardiorespiratory Fitness Demonstrate Lower Markers of Cardiovascular Disease Risk. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2022, 64, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B. ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription 9th Ed. 2014. J. Can. Chiropr. Assoc. 2014, 58, 328. [Google Scholar]
- Flouris, A.D.; Metsios, G.S.; Famisis, K.; Geladas, N.; Koutedakis, Y. Prediction of VO2max from a new field test based on portable indirect calorimetry. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproule, J.; Kunalan, C.; McNeill, M.; Wright, H. Validity of 20-MST for predicting VO2max of adult Singaporean athletes. Br. J. Sports Med. 1993, 27, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.; Cooper, R.; Aihie Sayer, A.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Cooper, C.; Deary, I.J.; Demakakos, P.; Gallacher, J.; Martin, R.M.; McNeill, G.; et al. Body mass index, muscle strength and physical performance in older adults from eight cohort studies: The HALCyon programme. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Jiang, Y. The Relationship between Body Mass Index and Physical Fitness among Chinese University Students: Results of a Longitudinal Study. Healthcare 2020, 8, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Age | Height | Body Mass | BMI | VJ | Sit−Ups | Push−Ups | VO2max | PAPw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (cm) | −0.019 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Body mass (kg) | 0.197 ** | 0.504 ** | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Body mass Index (kg/m2) | 0.249 ** | 0.017 | 0.861 ** | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Vertical Jump (cm) | −0.442 ** | −0.052 | −0.352 ** | −0.396 ** | − | − | − | − | − |
| Sit−Ups (repetitions) | −0.376 ** | −0.010 | −0.372 ** | −0.446 ** | 0.466 ** | − | − | − | − |
| Push−Ups (repetitions) | −0.344 ** | −0.226 ** | −0.383 ** | −0.328 ** | 0.501 ** | 0.663 ** | − | − | − |
| VO2max (mL/kg/min) | −0.418 ** | 0.037 | −0.427 ** | −0.541 ** | 0.409 ** | 0.580 ** | 0.517 ** | − | − |
| Peak Power Output (watts) # | 0.069 | 0.511 ** | 0.956 ** | 0.807 ** | −0.063 | −0.302 ** | −0.269 ** | −0.200 ** | − |
| Relative Peak Power Output (watts/kg) | −0.317 ** | 0.282 ** | 0.311 ** | 0.209 ** | 0.710 ** | 0.199 ** | 0.197 ** | 0.120 * | 0.590 ** |
| BMI Classification Group | Age (years) | Height (cm) | Body Mass (kg) | Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | N | N | N | ||||||||||||||
| Median (IQR) | Healthy | 102 | 36 (30−41.5) *† | 102 | 180.3 (175.2−183.5) | 102 | 74.8 (70.9−80.7) *†¥§ | 102 | 23.7 (22.8−24.4) *†¥§ | ||||||||
| Overweight | 259 | 39 (33−45) *‡ | 260 | 180.3 (175.2−185.4) | 260 | 88.4 (83.4−92.9) *‡∞¥ | 260 | 27.3 (26.2−28.6) *‡∞¥ | |||||||||
| Obese | 170 | 43 (36−47) ‡† | 170 | 180.3 (175.2−183.5) | 170 | 104.3 (99.2−113.3) ‡†§∞ | 170 | 32.1 (31−33.9) ‡†§∞ | |||||||||
| Total | 531 | 39 (33−46) | 532 | 180.3 (175.2−185.4) | 532 | 90.7 (81.6−101.1) | 532 | 28 (25.4−30.9) | |||||||||
| Mean ± SD | Healthy | 102 | 35.93 | ± | 7.62 | 102 | 180.7 | ± | 7.18 | 102 | 76.1 | ± | 7.72 | 102 | 23.27 | ± | 1.39 |
| Overweight | 259 | 38.88 | ± | 7.07 | 260 | 179.66 | ± | 6.72 | 260 | 88.43 | ± | 8.49 | 260 | 27.35 | ± | 1.46 | |
| Obese | 170 | 40.83 | ± | 7.15 | 170 | 180.33 | ± | 7.31 | 170 | 107.46 | ± | 12.7 | 170 | 32.99 | ± | 2.95 | |
| Total | 531 | 38.94 | ± | 7.39 | 532 | 180.07 | ± | 6.99 | 532 | 92.15 | ± | 15.14 | 532 | 28.37 | ± | 4.06 | |
| BMI Classification Group | Sit−Ups (Repetitions) | Push−Ups (Repetitions) | VO2Max (mL/kg/min) | Vertical Jump (cm) | Absolute PAPw (watts) | Relative PAPw (watts/kg) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||||||||||||||||
| healthy | 102 | 40.69 | ± | 8.14 | 100 | 40.05 | ± | 11.79 | 99 | 37.32 | ± | 6.85 | 90 | 21.47 | ± | 2.95 | 90 | 2706.55 | ± | 399.81 | 90 | 35.4 | ± | 2.6 |
| overweight | 260 | 38.85 | ± | 8.19 | 260 | 40.32 | ± | 13.67 | 253 | 33.58 | ± | 5.89 | 239 | 20.78 | ± | 3.11 | 239 | 3226.18 | ± | 412.45 | 239 | 36.3 | ± | 2.2 |
| obese | 170 | 31.28 | ± | 8.33 | 168 | 31.9 | ± | 11.92 | 116 | 30.52 | ± | 3.43 | 149 | 18.55 | ± | 2.94 | 149 | 3924.09 | ± | 525.28 | 149 | 36.6 | ± | 1.7 |
| Total | 532 | 36.79 | ± | 9.06 | 528 | 37.59 | ± | 13.34 | 482 | 33.56 | ± | 6.01 | 478 | 20.22 | ± | 3.23 | 478 | 3345.89 | ± | 623.74 | 478 | 36.2 | ± | 2.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalez, D.E.; Melrose, D.R.; Kukić, F.; Lockie, R.G.; Orr, R.M.; Dawes, J.J. Does Exercise Performance Differ Among Male Law Enforcement Officers Based on Their Body Mass Index Category? Healthcare 2025, 13, 1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13131584
Gonzalez DE, Melrose DR, Kukić F, Lockie RG, Orr RM, Dawes JJ. Does Exercise Performance Differ Among Male Law Enforcement Officers Based on Their Body Mass Index Category? Healthcare. 2025; 13(13):1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13131584
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalez, Drew E., Don R. Melrose, Filip Kukić, Robert G. Lockie, Robin M. Orr, and J. Jay Dawes. 2025. "Does Exercise Performance Differ Among Male Law Enforcement Officers Based on Their Body Mass Index Category?" Healthcare 13, no. 13: 1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13131584
APA StyleGonzalez, D. E., Melrose, D. R., Kukić, F., Lockie, R. G., Orr, R. M., & Dawes, J. J. (2025). Does Exercise Performance Differ Among Male Law Enforcement Officers Based on Their Body Mass Index Category? Healthcare, 13(13), 1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13131584









