Exploring the Efficacy of Vessilen® in Treating Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: A Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IC/BPS | Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome |
| NIDDK | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases |
| AUA | American Urological |
| ESSIC | AssociationEuropean Society for the Study of Interstitial Cystitis |
| GAG | Glycosaminoglycan |
| CS | Chondroitin Sulfate |
| HA | Hyaluronic Acid |
| PPS | Pentosan Polysulfate |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| PEA | Palmitoylethanolamide |
| ALIAmides | Autacoid Local Injury Antagonist Amides |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa B |
| CYP | Cyclophosphamide |
| TUR | Transurethral Resection |
| BCG | Bacillus Calmette–Guérin |
| MMC | Mitomycin C |
| EPI | Epirubicin |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| PGI-I | Patient Global Impression of Improvement |
| ICIQ-FLUTS | International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire Female Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms |
| PGI-I | Patient Global Impression of Improvement |
References
- Abrams, P.; Cardozo, L.; Fall, M.; Griffiths, D.; Rosier, P.; Ulmsten, U.; van Kerrebroeck, P.; Victor, A.; Wein, A.; Standardisation Sub-Committee of the International Continence Society. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2002, 21, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillenwater, J.Y.; Wein, A.J. Summary of the National Institute of Arthritis, Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases Workshop on Interstitial Cystitis, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, 28–29 August 1987. J. Urol. 1988, 140, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanno, P.M.; Burks, D.A.; Clemens, J.Q.; Dmochowski, R.R.; Erickson, D.; Fitzgerald, M.P.; Forrest, J.B.; Gordon, B.; Gray, M.; Mayer, R.D.; et al. Interstitial Cystitis Guidelines Panel of the American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. AUA guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Merwe, J.P.; Nordling, J.; Bouchelouche, P.; Bouchelouche, K.; Cervigni, M.; Daha, L.K.; Elneil, S.; Fall, M.; Hohlbrugger, G.; Irwin, P.; et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: An ESSIC proposal. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggaral, N.; Leslie, S.W.; Lotfollahzadeh, S. Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, J.R.; Mokrzycki, M.L.; Jayne, C.J. Differentiating interstitial cystitis from similar conditions commonly seen in gynecologic practice. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2009, 144, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.Q.; Link, C.L.; Eggers, P.W.; Kusek, J.W.; Nyberg, L.M., Jr.; McKinlay, J.B.; BACH Survey Investigators. Prevalence of painful bladder symptoms and effect on quality of life in black, Hispanic, and white men and women. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.H.; Elliott, M.N.; Suttorp, M.; Bogart, L.M.; Stoto, M.A.; Eggers, P.; Nyberg, L.; Clemens, J.Q. Prevalence of Symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Among Adult Females in the United States. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, J.C. Interstitial cystitis: A chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 88, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliebø-Jones, P.; Hjelle, K.M.; Mohn, J.; Gudbrandsdottir, G.; Roth, I.; Chaudhry, A.A.; Bergesen, A.K.; Beisland, C. Management of Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS): A Practical Guide. Adv. Urol. 2022, 2022, 7149467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldenborg, F.; Fall, M.; Enerbäck, L. Proliferation and transepithelial migration of mucosal mast cells in interstitial cystitis. Immunology 1986, 58, 411–416. [Google Scholar]
- Hanno, P.M.; Landis, J.R.; Matthews-Cook, Y.; Kusek, J.; Nyberg, L., Jr. The diagnosis of interstitial cystitis revisited: Lessons learned from the National Institutes of Health Interstitial Cystitis Database study. J. Urol. 1999, 161, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A.C.; Fantozzi, R. The role of histamine in neurogenic inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeker, R.; Enerbäck, L.; Fall, M.; Aldenborg, F. Recruitment, distribution, and phenotypes of mast cells in interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2000, 163, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Kutch, J.J.; Ellingson, B.M.; Martucci, K.T.; Harris, R.E.; Clauw, D.J.; Mackey, S.; Mayer, E.A.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Apkarian, A.V.; et al. Brain white matter changes associated with urological chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Multisite neuroimaging from a MAPP case-control study. Pain 2016, 157, 2782–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tore, F.; Tuncel, N. Mast cells: Target and source of neuropeptides. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 3433–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ens, G.; Garrido, G.L. Role of Cystoscopy and Hydrodistention in the Diagnosis of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 624–628. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, K.M.; Killinger, K.A.; Mounayer, M.H.; Boura, J.A. Are ulcerative and nonulcerative interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome 2 distinct diseases? A study of coexisting conditions. Urology 2011, 78, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L.J.; Landis, J.R.; Erickson, D.R.; Nyberg, L.M. The Interstitial Cystitis Data Base Study: Concepts and preliminary baseline descriptive statistics. Urology 1997, 49 (Suppl. S5A), 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennevik, G.E.; Meijlink, J.M.; Hanno, P.; Nordling, J. The role of glomerulations in bladder pain syndrome: A review. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, S.; Laganà, A.S.; Casarin, J.; Raffaelli, R.; Cromi, A.; Sturla, D.; Franchi, M.; Ghezzi, F. An Update on Treatment Options for Interstitial Cystitis. Prz. Menopausalny 2020, 19, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C. Advances in intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome (BPS)/interstitial cystitis (IC). Low. Urin. Tract Symptoms 2018, 10, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloe, L.; Leon, A.; Levi-Montalcini, R. A proposed autacoid mechanism controlling mastocyte behavior. Agents Actions 1993, 39, C145–C147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, H.M.; Horne, D.J.; Sheather, S. Clinical Applications of Visual Analogue Scales: A Critical Review. Psychol. Med. 1988, 18, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uren, A.D.; Cotterill, N.; Pardoe, M.; Abrams, P. The International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaires (ICIQ): An Update on Status and Direction. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2020, 39, 1889–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offiah, I.; McMahon, S.B.; O’Reilly, B.A. Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Diagnosis and management. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2013, 24, 1243–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanno, P.; Dmochowski, R. Status of international consensus on interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome/painful bladder syndrome: 2008 snapshot. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2009, 28, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanno, P.M. Interstitial cystitis-epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, clinical markers. Rev. Urol. 2002, 4 (Suppl. S1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, W.J.; Ha, U.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.J.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, T.K.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.W. Reduction of oxidative stress may play a role in the anti-inflammatory effect of the novel herbal formulation in a rat model of hydrochloric acid-induced cystitis. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2015, 34, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.Q.; Erikson, D.R.; Varela, N.P.; Lai, H. Diagnosis and treatment of Interstitial cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. J. Urol. 2022, 208, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Hjelle, K.M.; Mohn, J.; Guðbrandsdottir, G.; Roth, I.; Chaudhry, A.A.; Bergesen, A.K.; Beisland, C. Current status of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome (BPS): A narrative review of emerging evidence. Urology 2021, 156, e48–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülpınar, Ö.; Esen, B.; Kayış, A. Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkıdık, M. Assessment of long-term intravesical hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, and combination therapy for patients with bladder pain syndrome. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2019, 72, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Petrosino, S.; Puigdemont, A.; Della Valle, M.F.; Fusco, M.; Verde, R.; Allarà, M.; Aveta, T.; Orlando, P.; Di Marzo, V.A. Adelmidrol increases the endogenous concentrations of palmitoylethanolamide in canine keratinocytes and down-regulates an inflammatory reaction in an in vitro model of contact allergic dermatitis. Vet. J. 2016, 207, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, D.; D’Amico, A.; Cinelli, M.P.; Esposito, G.; Di Marzo, V.; Iuvone, T. Adelmidrol, a palmitoylethanolamide analogue, reduces chronic inflammation in a carrageenin-granuloma model in rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, S.; Brazis, P.; Della Valle, M.F.; Miolo, A.; Puigdemont, A. Inhibitory effect of topical adelmidrol on antigen-induced skin wheal and mast cell behavior in a canine model of allergic dermatitis. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Britti, D.; Morittu, V.M.; Evangelista, M.; Cuzzocrea, S. Adelmidrol, in combination with hyaluronic acid, displays increased anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects against monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Impellizzeri, D.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Adelmidrol, a palmitoylethanolamide analogue, as a new pharmacological treatment for the management of inflammatory bowel disease. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostardo, E.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cervigni, M.; Porrud, D.; Sommariva, M.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; et al. Adelmidrol + sodium hyaluronate in IC/BPS or conditions associated with chronic urothelial inflammation. A translational study. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 134, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canepa, G.; Campodonico, F.; Tamagno, S.; La Camera, A.; Introini, C. Adelmidrol + hyaluronic acid in the treatment of symptoms associated with intravesical anticancer therapy in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. An observational retrospective investigation. Pelviperineology 2023, 42, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Population Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 58.4 (16.4) |
| Multiparous (%) | 22 (84.6%) |
| Smoking (%) | 1 (3.8%) |
| Previous pelvic surgery (%) | 11 (42.3%) |
| Increased urinary frequency (%) | 14 (56%) |
| Urgency (%) | 8 (32%) |
| Pelvic pressure/discomfort (%) | 4 (16%) |
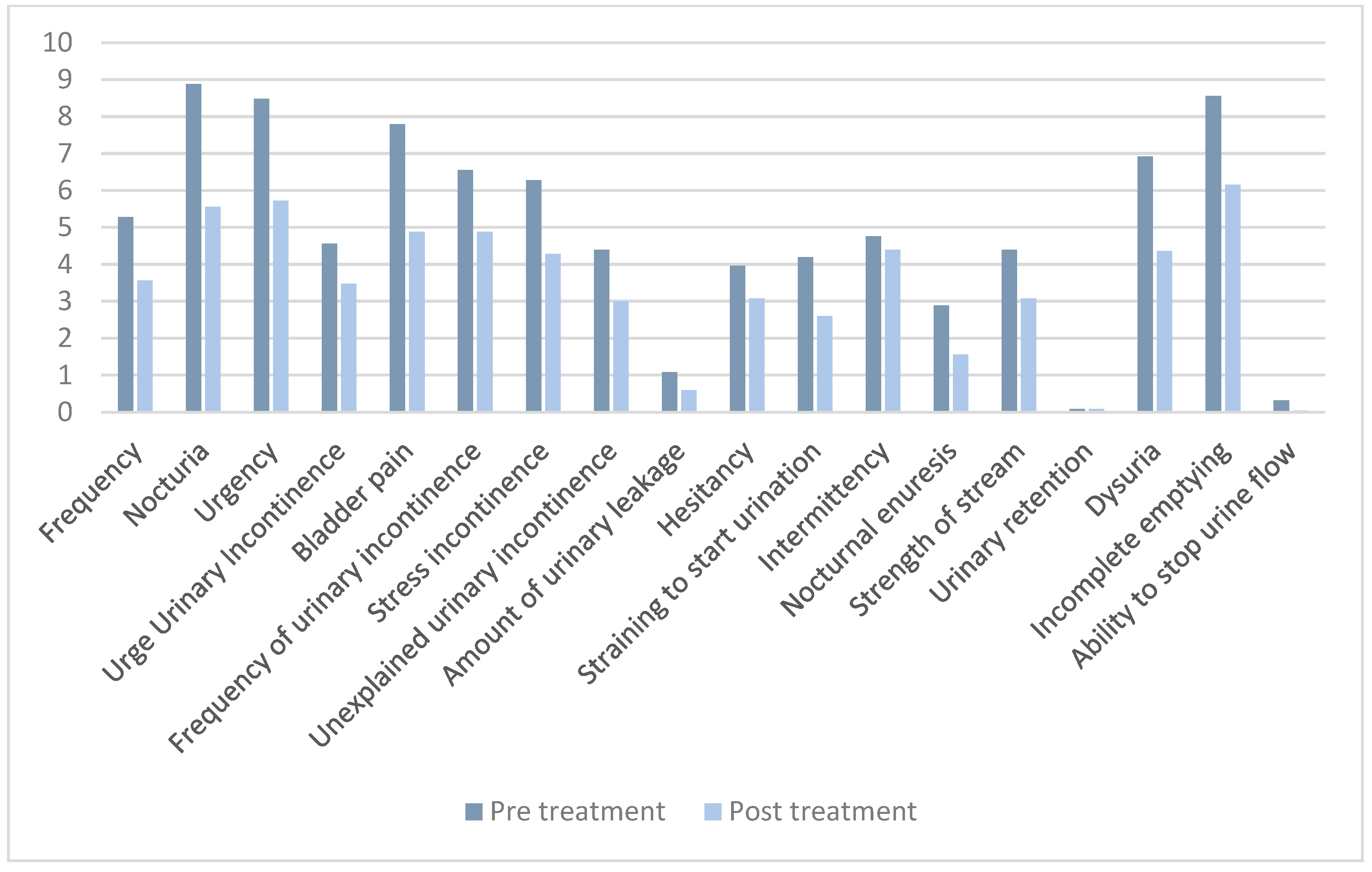
| Questionnaire | Pre-Treatment Score | Post-Treatment Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total ICIQ-FLUTS | 89.3 (41.1) | 61.3 (42.5) | 0.021 |
| 5.3 (5.1) | 3.6 (4.3) | 0.009 |
| 8.9 (4.5) | 5.6(4.8) | <0.001 |
| 8.5 (4.0) | 5.7 (3.9) | <0.001 |
| 4.6 (5.1) | 3.5 (4.2) | 0.061 |
| 7.8 (4.5) | 4.9 (4.0) | <0.001 |
| 6.6 (5.7) | 4.9 (5.2) | 0.022 |
| 6.3 (4.8) | 4.3 (4.3) | 0.006 |
| 4.4 (5.0) | 3.0 (4.4) | 0.007 |
| 1.1 (1.1) | 0.6 (0.6) | 0.006 |
| 4.0 (4.2) | 3.1(4.0) | 0.013 |
| 4.2 (4.8) | 2.6 (3.8) | 0.007 |
| 4.8 (4.5) | 4.4 (4.5) | 0.269 |
| 2.8 (4.4) | 1.6 (3.1) | 0.027 |
| 4.4 (4.1) | 3.1 (3.9) | 0.021 |
| 0.1 (0.4) | 0.1 (0.4) | 0.500 |
| 6.9 (4.8) | 4.4 (4.1) | 0.002 |
| 8.6 (4.6) | 6.2 (4.2) | <0.001 |
| 0.3 (0.6) | 0.04 (0.2) | 0.008 |
| VAS | 4.4 (1.5) | 2.6 (1.8) | <0.001 |
| PGI-I | N/A | 2.8 | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palucci, M.; Barba, M.; Cola, A.; Frigerio, M. Exploring the Efficacy of Vessilen® in Treating Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: A Prospective Study. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13111340
Palucci M, Barba M, Cola A, Frigerio M. Exploring the Efficacy of Vessilen® in Treating Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: A Prospective Study. Healthcare. 2025; 13(11):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13111340
Chicago/Turabian StylePalucci, Mariachiara, Marta Barba, Alice Cola, and Matteo Frigerio. 2025. "Exploring the Efficacy of Vessilen® in Treating Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: A Prospective Study" Healthcare 13, no. 11: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13111340
APA StylePalucci, M., Barba, M., Cola, A., & Frigerio, M. (2025). Exploring the Efficacy of Vessilen® in Treating Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: A Prospective Study. Healthcare, 13(11), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13111340








