A Scoping Review of Clinical Studies on Procedures of Ultrasound-Guided Injection to Ensure Hygiene and Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Review Questions
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.3.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Study Screening and Selection
2.5. Data Extraction and Data Charting
2.6. Data Analysis and Presentation of Results
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Studies
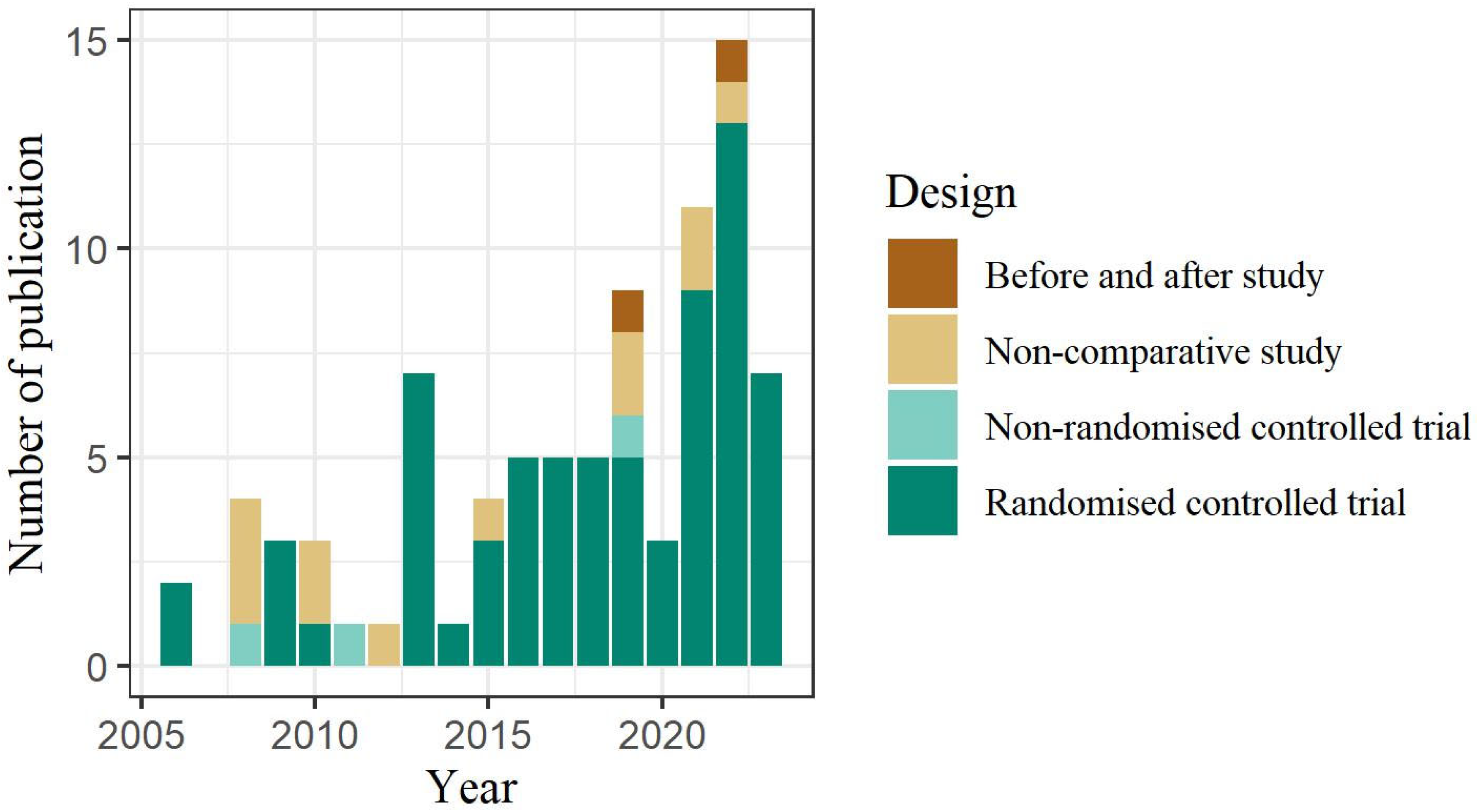
3.2. Characteristics of the Selected Studies
3.3. Procedures for US-Guided Injection in the Literature
3.3.1. Procedures for Maintaining Skin and Probe Hygiene
3.3.2. US Coupling Agent
| Category | Procedure | Materials Used | Frequency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SProbe disinfection | Disinfect the probe | chlorhexidine, solution of didecyldiethylammonium chloride (DDAC) 0.45% a, solution of povidone–iodine, 70% alcohol | 5 (5.81%) | [30,31,32,33], [34] a |
| Not specified or inferred from images | 81 (94.19%) | |||
| Use of probe cover | Affix the sterilized probe cover | sterile barrier/sheath/cover/barrier/wrapping/film, sterilized gloves, sterile surgical drape, sterile transparent field dressing, sterile camera sleeve | 24 (27.91%) | [30,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57] |
| Not affixed with the sterilized probe cover | 9 (10.47%) | [31,32,34,58,59,60,61,62,63] | ||
| Not specified or inferred from images | 53 (61.63%) | |||
| Skin disinfection | Disinfect with alcohol | alcohol swap, alcohol, 70% alcohol, aqueous solution containing ethanol 85% vol, isopropyl alcohol solution, alcohol-based disinfection solution | 10 (11.63%) | [48,58,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71] |
| Disinfect with iodophors | povidone–iodine, a solution of iodopovidone 10%, 10% polyvidone–iodine, betadine, type II mucosal iodine | 18 (20.93%) | [30,34,35,45,46,54,57,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82] b | |
| Disinfect with chlorhexidine | chlorhexidine, chlorhexidine 0.5% solution | 4 (4.65%) | [33,42,50,83] | |
| Disinfect with alcohol and povidone–iodine solution | 70% alcohol and povidone–iodine solution | 2 (2.33%) | [32] | |
| Disinfect with chlorhexidine and alcohol solution | ChloraPrep, chlorhexidine and isopropyl alcohol solution, 2% chlorhexidine gluconate and 70% isopropyl alcohol, chlorhexidine alcohol 0.5% | 4 (4.65%) | [62,84,85,86] | |
| Disinfect with benzalkonium chloride | benzalkonium chloride 0.25% | 1 (1.16%) | [34] c | |
| Disinfect with antiseptic (not specified) | 50 (58.14%) |
| Category | Procedure | Materials Specified | Frequency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application of the US coupling agent to the probe | Apply nonsterile US gel | 6 (6.98%) | [35,48,50,54,57,58] | |
| Apply sterile US gel | sterile gel/sterile ultrasound gel, sterile lubrication packets, sterile lubricant contact gel | 15 (17.44%) | [32,34,37,38,39,42,44,47,52,56,66,83,84,87,88] | |
| Apply povidone–iodine solution | 1 (1.16%) | [30] | ||
| Apply 85% ethanol solution | 1 (1.16%) | [67] | ||
| Not specified or inferred from images | 63 (73.26%) |
3.3.3. Comprehensive Overview of Infection Prevention Procedures
3.3.4. US-Based Methods to Enhance Safety and Accuracy
3.3.5. Gaps Between Reported Practices and Recommended Guidelines
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
4.2. Debates on Hygiene Protocols During US-Guided Procedures
4.3. Limitations of This Study
4.4. Practical Implications for Clinical Decision Making
4.5. Research and Guideline Development Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DDAC | Didecyldiethylammonium chloride |
| US | Ultrasound |
| KISS | Koreanstudies Information Service System |
| KMD | Korean Medicine doctor |
References
- Epis, O.; Bruschi, E. Interventional ultrasound: A critical overview on ultrasound-guided injections and biopsies. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32 (Suppl. 80), S78–S84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.H.; Chen, X.T.; Vangsness, C.T., Jr. Ultrasound-guided knee injections are more accurate than blind injections: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Arthrosc. Sports Med. Rehabil. 2021, 3, e1177–e1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.-R.; Rajasekaran, S.; Ashworth, N. Ultrasound-guided shoulder girdle injections are more accurate and more effective than landmark-guided injections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Yang, C.; Kim, S. The transformation of acupuncture practice using ultrasonography: Expert opinions. JAMS 2024, 17, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Yun, J.M.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, Y.J.; Ko, D.K.; Heo, I.; Shin, W.-C.; Cho, J.-H.; Seo, B.-K.; Ha, I.-H. Survey on the current usage of ultrasound-guided procedures in Korean Medicine clinics and hospitals. Medicine 2024, 103, e37659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, H.; Armstrong, P.; Tansek, R. Emergency department ultrasound probe infection control: Challenges and solutions. Open Access Emerg. Med. 2015, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, T.; Ferguson, J.; Davis, W.; Russo, M.; Argintar, E. Does the use of ultrasound affect contamination of musculoskeletal injections sites? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, J.P.; Fhlatharta, M.N.; Ryan, J.W.; MacMahon, P.J.; Eustace, S.J.; Kavanagh, E.C. Complications in image-guided musculoskeletal injections. Skelet. Radiol. 2021, 50, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Medical Ultrasound Society. Guidelines for the Administration of Ultrasound Guided Musculoskeletal Injections; British Medical Ultrasound Society: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Provincial Infectious Diseases Advisory Committee. Best Practices for Cleaning, Disinfection and Sterilization of Medical Equipment/Devices in All Health Care Settings, 3rd ed.; Public Health Ontario: Marie, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lorentzen, T.; Nolsoe, C.P.; Ewertsen, C.; Nielsen, M.B.; Leen, E.; Havre, R.F.; Gritzmann, N.; Brkljacic, B.; Nurnberg, D.; Kabaalioglu, A.; et al. EFSUMB Guidelines on Interventional Ultrasound (INVUS), Part I. General Aspects (long version). Ultraschall Med. 2015, 36, E1–E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J. Infection prevention for ultrasound practitioners during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin. Ultrasound 2021, 6, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society of Diagnostic Medical Sonography. Guidelines for infection prevention and control in sonography: Reprocessing the ultrasound transducer. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2020, 36, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunstall, T.D. Infection Control in the Sonography Department. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2010, 26, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, J.M.; Hammer, H.B. Ultrasound-guided procedures: Techniques and usefulness in controlling inflammation and disease progression. Rheumatology 2012, 51 (Suppl. 7), vii31–vii35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, R.M.; Furmanek, S.; English, C. Ultrasound probe use and reprocessing: Results from a national survey among U.S. infection preventionists. Am. J. Infect. Control 2018, 46, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sconfienza, L.M.; Viganò, S.; Martini, C.; Aliprandi, A.; Randelli, P.; Serafini, G.; Sardanelli, F. Double-needle ultrasound-guided percutaneous treatment of rotator cuff calcific tendinitis: Tips & tricks. Skelet. Radiol. 2013, 42, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Ahn, J.H.; Ryu, D.S.; Kang, C.H.; Jung, S.M.; Park, M.S.; Shin, D.-R. Ultrasonography for nerve compression syndromes of the upper extremity. Ultrasonography 2015, 34, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, E.W.; Cole, D.; Jacobs, B.; Phillips, S.F. Existing evidence on ultrasound-guided injections in sports medicine. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2018, 6, 2325967118756576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narouze, S.; Peng, P.W. Ultrasound-guided interventional procedures in pain medicine: A review of anatomy, sonoanatomy, and procedures: Part ii: Axial structures. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2010, 35, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, T.; Martiny, H.; Merz, E.; Doffert, J.; Wustner, M.; Lessel, W.; Heynemann, H.; Enzmann, T.; Dudwiesus, H.; Nuernberg, D.; et al. DEGUM Recommendations on Infection Prevention in Ultrasound and Endoscopic Ultrasound. Ultraschall Med. 2018, 39, 284–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Godfrey, C.; McInerney, P.; Soares, C.B.; Khalil, H.; Parker, D. Methodology for JBI scoping reviews. In The Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers Manual 2015; Joanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, Australia, 2015; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Takashima, R.; Yano, R. Is skin disinfection before subcutaneous injection necessary? The reasoning of certified nurses in infection control in Japan. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruyn, G.A.; Schmidt, W.A. How to perform ultrasound-guided injections. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 23, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narouze, S.N. Atlas of Ultrasound-Guided Procedures in Interventional Pain Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Methods for the Development of NICE Public Health Guidance. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/process/pmg4 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Seo, H.-J.; Kim, S.-Y. What is scoping review? JoHTA 2018, 6, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, E.-B. Research trends and clinical applications of neural mobilization in Korea: A scoping review. J. Churna Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2021, 16, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, T.-S.; Moon, J.-H.; Park, C.-Y.; Oh, M.-J.; Choi, Y. The effectiveness of ultrasound-guided essential bee venom pharmacopuncture combined with integrative Korean medical treatment for rib fracture: A case study. J. Korean Med. Rehabil. 2019, 29, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, S.; Taheri, P.; Banimehdi, M.; Taghavi, A. Effectiveness of blind & ultrasound guided corticosteroid injection in impingement syndrome. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2015, 8, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Nomkhondorj, O.; Cho, M.G.; Lee, J.J.; Hwang, J.T.; Hong, M.S. Comparison between anterior and posterior approaches for ultrasound-guided glenohumeral steroid injection in primary adhesive capsulitis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 23, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, R.; Grimaldi, A.; Wajswelner, H.; Hodges, P.; Abbott, J.H.; Bennell, K.; Vicenzino, B. Exercise and load modification versus corticosteroid injection versus ‘wait and see’ for persistent gluteus medius/minimus tendinopathy (the LEAP trial): A protocol for a randomised clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, D.; Corazza, A.; Fabbro, E.; Ferrero, G.; Sabino, G.; Serafini, G.; Silvestri, E.; Sconfienza, L.M. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous injection to treat de Quervain’s disease using three different techniques: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahadi, T.; Asilian, M.; Raissi, G.R.; Khalifeh Soltani, S.; Soleymanzadeh, H.; Sajadi, S. Ultrasound-guided vs. blind coccygeal corticosteroid injections for chronic coccydynia: A randomized, clinical trial. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2022, 10, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahadi, T.; Nik, S.S.; Forogh, B.; Madani, S.P.; Raissi, G.R. Comparison of the effect of ultrasound-guided injection of Botulinum toxin type A and corticosteroid in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 101, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei-Ghazani, A.; Karimi, N.; Forogh, B.; Madani, S.P.; Ebadi, S.; Fadavi, H.R.; Sobhani-Eraghi, A.; Emami Razavi, S.Z.; Raeissadat, S.A.; Eftekharsadat, B. Comparison of ultrasound-guided local ozone (O2–O3) injection vs corticosteroid injection in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: A randomized clinical trial. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei-Ghazani, A.; Najarzadeh, S.; Mansoori, K.; Forogh, B.; Madani, S.P.; Ebadi, S.; Fadavi, H.R.; Eftekharsadat, B. The effects of ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection compared to oxygen–ozone (O2–O3) injection in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2517–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei-Ghazani, A.; Nikbakht, N.; Forogh, B.; Raissi, G.R.; Ahadi, T.; Ebadi, S.; Roomizadeh, P.; Fadavi, H.R.; Raeissadat, S.A.; Eftekharsadat, B. Comparison between effectiveness of ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection above versus below the median nerve in mild to moderate carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 97, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, S.; Karimzad, Y.; Aflakian, N.; Forogh, B.; Mansoori, K.; Babaei-Ghazani, A. Extracorporeal shockwaves therapy versus corticosteroid injection for the treatment of non-calcific rotator cuff tendinopathies: A randomized trial. Curr. Orthop. Pract. 2023, 34, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, F.; Eftekharsadat, B.; Babaei-Ghazani, A.; Jahanjoo, F.; Zeinali, M. A randomized prospective comparison of ultrasound-guided and landmark-guided steroid injections for carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 34, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, R.A., II; Newberry, M.; Zitek, T.; Farrow, J.; Mechanic, O.J.; Rosselli, M. Ultrasound-guided trigger point injections for the treatment of neck and back pain in the emergency department: A randomized trial. J. Ultrasound Med. 2023, 42, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulabi, D.; Uysal, M.A.; Akça, A.; Colak, I.; Çeçen, G.S.; Gumustas, S. USG-guided injection of corticosteroid for lateral epicondylitis does not improve clinical outcomes: A prospective randomised study. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2017, 137, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, A.K.; Bhattacharya, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mitra, M.; Mandal, M. Ultrasound versus fluoroscopy-guided caudal epidural steroid injection for the treatment of chronic low back pain with radiculopathy: A randomised, controlled clinical trial. Indian J. Anaesth. 2016, 60, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, J.S.; Yi, T.I.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Gu, H.G. The usefulness of ultrasonographyguided injection comparing to blind injection in patients with chronic subdeltoid bursitis. Clin. Pain 2006, 5, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.B.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.W.; Sung, K.W.; Jung, I.; Lee, C. Ultrasound guided shoulder joint injection through rotator cuff interval. Korean J. Pain 2008, 21, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizides, A.; Gruber, H.; Peer, S.; Galiano, K.; Bale, R.; Obernauer, J. Ultrasound guided versus CT-controlled pararadicular injections in the lumbar spine: A prospective randomized clinical trial. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezian, K.; Sobotová, K.; Kuliha, M.; Chang, K.V.; Ceé, J.; Angerová, Y.; Özçakar, L. Ultrasound-guided perineural vs. peritendinous corticosteroid injections in carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 57, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, F.; Babaee, M.; Peydayesh, P.; Esmaily, H.; Raeissadat, S.A. Comparison between the effects of ultrasound guided intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), high molecular weight hyaluronic acid, and their combination in hip osteoarthritis: A randomized clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskins, Z.; Bromley, K.; Lewis, M.; Hughes, G.; Hughes, E.; Hennings, S.; Cherrington, A.; Hall, A.; Holden, M.A.; Stevenson, K.; et al. Clinical effectiveness of one ultrasound guided intra-articular corticosteroid and local anaesthetic injection in addition to advice and education for hip osteoarthritis (HIT trial): Single blind, parallel group, three arm, randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2022, 377, e068446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaikner, M.; Kogl, N.; Gruber, H.; Bale, R.; Ho, W.M.; Skalla-Oberherber, E.; Loizides, A. Ultrasound-guided versus computed tomography-controlled periradicular injections of the first sacral nerve: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Med. Ultrason. 2023, 25, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaghzadeh, A.; Zarei Kurdkandi, H.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Biglari, F.; Jafari Kafiabadi, M. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for chronic lateral ankle instability after modified Broström-Gould surgery: A randomized, single-blinded, prospective controlled trial. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2023, 8, 24730114231168633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepsoparn, M.; Thanphraisan, P.; Tanpowpong, T.; Itthipanichpong, T. Comparison of a platelet-rich plasma injection and a conventional steroid injection for pain relief and functional improvement of partial supraspinatus tears. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2021, 9, 23259671211024937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.; Pandey, P. An ultrasound-guided interfascial injection approach versus an ultrasound-assisted nerve stimulating approach of obturator nerve block: A randomized clinical trial. Cureus 2022, 14, e24037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Lee, S.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Liu, F.W.; Chiou, H.J.; Chan, R.C.; Chou, C.L. Short-term effect of ultrasound-guided low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid injection on clinical outcomes and imaging changes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of the ankle and foot joints. A randomized controlled pilot trial. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Liu, J.; Ma, L.; Cai, Z.; Meng, C.; Qi, S.; Zhou, H. Ultrasound-guided versus fluoroscopy-controlled lumbar transforaminal epidural injections: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Su, D.; Liao, L.; Yang, H.; Fang, H.; Wang, X. Clinical effects and safety of the use of methylene blue for the treatment of lumbar facet joint syndrome. Pain Physician 2022, 25, E15–E26. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, B.F.; Peters, K.S.; Hackett, L.; Murrell, G.A. Ultrasound-Guided Versus Blind Subacromial Corticosteroid Injections for Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkucak, M.; Batmaz, İ.; Kerimoglu, S.; Ayar, A. Comparison of clinical outcomes of ultrasonography-guided and blind local injections in facet syndrome: A 6-week randomized controlled trial. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2020, 33, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lim, K.B.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, K.T. Randomized controlled trial for efficacy of intra-articular injection for adhesive capsulitis: Ultrasonography-guided versus blind technique. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 1997–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misirlioglu, T.O.; Akgun, K.; Palamar, D.; Erden, M.G.; Erbilir, T. Piriformis syndrome: Comparison of the effectiveness of local anesthetic and corticosteroid injections: A double-blinded, randomized controlled study. Pain Physician 2015, 18, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, R.R. Platelet-rich plasma efficacy versus corticosteroid injection treatment for chronic severe plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2014, 35, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.D.; Nam, H.S.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, Y. Treatment effects of ultrasound-guided capsular distension with hyaluronic acid in adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; JGee, S.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Hwang, S.H. Comparison of blind technique and ultrasonography guided technique of subacromial subdeltoid bursa injection. J. Korean Acad. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 34, 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Creuzé, A.; Fok-Cheong, T.; Weir, A.; Bordes, P.; Reboul, G.; Glize, B.; de Seze, M. Novel use of botulinum toxin in long-standing adductor-related groin pain: A case series. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2022, 32, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeberg, O.M.; Bautz-Holter, E.; Tveitå, E.K.; Juel, N.G.; Kvalheim, S.; Brox, J.I. Subacromial ultrasound guided or systemic steroid injection for rotator cuff disease: Randomised double blind study. BMJ 2009, 338, a3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.L.; Lange, J. Surgery versus ultrasound-guided steroid injections for trigger finger disease: Protocol of a randomized controlled trial. Dan. Med. J. 2013, 60, A4633. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Jeon, D.-H.; Kim, B.-J.; Park, J.-W.; Oh, M.-S. The effectiveness of ultrasound-guided Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy at acromioclavicular joint of shoulder in patients with anterior shoulder pain: A retrospective study. J. Orient. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 31, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Oh, T.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Oh, M.S. A comparative study on the pain and treatment satisfaction between Korean medical treatment combined with ultrasound guided Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy in thoracic paravertebral space and non-guided Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy on patients with ribs fracture: A retrospective study. J. Orient. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 29, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, C.W.; Haotian, B.; Lee, G.W.; Noh, K.C. Comparison of extracorporeal shock wave therapy and ultrasound-guided shoulder injection therapy in patients with supraspinatus tendinitis. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Oh, M.S. Comparison of ultrasound guided Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy effect and unguided Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy effect on cervical facet joint of acute cervical pain patient caused by traffic accidents: A retrospective study. J. Orient. Rehabil. Med. 2022, 32, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami Razavi, S.Z.; Azadvari, M.; Fateh, H.R.; Ghahvechi Akbari, M.; Kazemi, S.; Rezaee, E. Short-term efficacy of ultrasonographic guidance for intra-articular corticosteroid injection in hallux rigidus: A single-blind randomized controlled trial. Foot Ankle Int. 2021, 42, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Cao, J.; Li, T.; Zheng, B.; Wang, M.; Zheng, R. Efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided local injections of etanercept into entheses of ankylosing spondylitis patients with refractory Achilles enthesitis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, 642–649. [Google Scholar]
- Karabaş, Ç.; Talay Çaliş, H.; Topaloğlu, U.S.; Karakükçü, Ç. Effects of ultrasound guided leukocyte-rich platelet-rich plasma (LR-PRP) injection in patients with pes anserinus tendinobursitis. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2021, 60, 103048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshmiri, S.; Velayati, M.; Momenzadeh, S. Clinical effectiveness of ultrasound-guided biolaser versus ozone therapy in reducing chronic pain in knee osteoarthritis: A three-month follow-up study. Iran. J. Radiol. 2023, 20, e129700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.-L.; An, K.Y.; Park, S.M.; Bae, B.J. The ultrasound-guided injection of prolotherapy and steroid mixture in patients with adhesive capsulitis. J. Korean Orthop. Soc. Sports Med. 2010, 9, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, Y.-L.; Nam, G.-Y.; Noh, K.-H. Blind and ultrasonography-guided injection therapy for calcific tendinitis of supraspinatus. J. Korean Orthop. Ultrasound Soc. 2008, 1, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, K.Y.; Moon, Y.L. Ultrasound-guided proliferative and local steroid injection for subacromial bursitis. J. Korean Orthop. Ultrasound Soc. 2008, 1, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, K.Y.; Moon, Y.L.; Yang, K.H. Injection therapy for calcific tendinitis of shoulder under the sonographic guidance. J. Korean Orthop. Ultrasound Soc. 2008, 1, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, W.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Chen, C.P.; Chen, M.J.; Yu, T.Y.; Chen, Y.J. Plantar fasciitis treated with local steroid injection: Comparison between sonographic and palpation guidance. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2006, 34, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mao, H.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. Comparative study of ultrasonic-guided betamethasone local injection and extracorporeal shock wave therapy in post-stroke hemiplegic shoulder pain: A randomized clinical trial. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1158500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaut, A.; Planche, L.; Auzanneau, L.; Cormier, G. Management of acromioclavicular joint disease by manual therapy versus corticosteroid injections: The protocol of a non-inferiority study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddy, E.; Ogollah, R.O.; Oppong, R.; Zwierska, I.; Datta, P.; Hall, A.; Hay, E.; Jackson, S.; Jowett, S.; Lewis, M.; et al. Optimising outcomes of exercise and corticosteroid injection in patients with subacromial pain (impingement) syndrome: A factorial randomised trial. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogaboom, N.; Malanga, G.; Cherian, C.; Dyson-Hudson, T. A pilot study to evaluate micro-fragmented adipose tissue injection under ultrasound guidance for the treatment of refractory rotator cuff disease in wheelchair users with spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2021, 44, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgensmeier, K.; Jurgensmeier, D.; Kunz, D.E.; Fuerst, P.G.; Warth, L.C.; Daines, S.B. Intra-articular injections of the hip and knee with triamcinolone vs ketorolac: A randomized controlled trial. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riel, H.; Olesen, J.L.; Jensen, M.B.; Vicenzino, B.; Rathleff, M.S. Heavy-slow resistance training in addition to an ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection for individuals with plantar fasciopathy: A feasibility study. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2019, 5, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obernauer, J.; Galiano, K.; Gruber, H.; Bale, R.; Obwegeser, A.A.; Schatzer, R.; Loizides, A. Ultrasound-guided versus computed tomography-controlled facet joint injections in the middle and lower cervical spine: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Med. Ultrason. 2013, 15, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, P.C.; Dudson, C.; Gregory, K.M.; Singh, H.; Boyd, K.T. Autologous blood injection with dry-needling vs dry-needling alone treatment for chronic plantar fasciitis: A randomized controlled trial. Foot Ankle Int. 2022, 43, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sante, L.; Villani, C.; Santilli, V.; Valeo, M.; Bologna, E.; Imparato, L.; Paoloni, M.; Iagnocco, A. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid vs platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis. Med. Ultrason. 2016, 18, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagara, H.; Nair, H.; Kolli, S.; Thota, G.; Uppal, V. Ultrasound imaging of the spine for central neuraxial blockade: A technical description and evidence update. Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2021, 11, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Hospital Epidemiology and Infection Control. Guidelines for Use and Care of Ultrasound Gel. Available online: https://infectioncontrol.ucsfmedicalcenter.org/policy-section/section-4-ucsf-medical-center-hospital-wide-policies-and-procedures (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- UK Health Securitiy Agency. Good Infection Prevention Practice: Using Ultrasound Gel. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/ultrasound-gel-good-infection-prevention-practice/good-infection-prevention-practice-using-ultrasound-gel#contents (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Darouiche, R.O.; Wall, M.J., Jr.; Itani, K.M.; Otterson, M.F.; Webb, A.L.; Carrick, M.M.; Miller, H.J.; Awad, S.S.; Crosby, C.T.; Mosier, M.C.; et al. Chlorhexidine-alcohol versus povidone-iodine for surgical-site antisepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, D.G.; Ringer, M.; Alvarado, C.J. Prospective randomised trial of povidone-iodine, alcohol, and chlorhexidine for prevention of infection associated with central venous and arterial catheters. Lancet 1991, 338, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koibuchi, H.; Fujii, Y.; Kotani, K.; Konno, K.; Matsunaga, H.; Miyamoto, M.; Taniguchi, N. Degradation of ultrasound probes caused by disinfection with alcohol. J. Med. Ultrason. 2011, 38, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydogan, E.; Kozanhan, B.; Can, S. Comparison of ultrasound images obtained by different disinfection methods used. Medicine 2019, 8, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuzier, R.; Lammens, S.; Becuwe, L.; Bataille, B.; Sleth, J.; Jochum, D.; Boselli, E. The use of ultrasound in France: A point of view from experienced regional anesthesiologists. Acta Anaesthesiol. Belg. 2016, 67, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Caturelli, E.; Giacobbe, A.; Facciorusso, D.; Villani, M.R.; Squillante, M.M.; Siena, D.A.; Cellerino, C.; Andriulli, A. Free-hand technique with ordinary antisepsis in abdominal US-guided fine-needle punctures: Three-year experience. Radiology 1996, 199, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, G.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Lacelli, F.; Silvestri, E.; Aliprandi, A.; Sardanelli, F. Rotator cuff calcific tendonitis: Short-term and 10-year outcomes after two-needle US-guided percutaneous treatment—Nonrandomized controlled trial. Radiology 2009, 252, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sconfienza, L.M.; Bandirali, M.; Serafini, G.; Lacelli, F.; Aliprandi, A.; Di Leo, G.; Sardanelli, F. Rotator cuff calcific tendinitis: Does warm saline solution improve the short-term outcome of double-needle US-guided treatment? Radiology 2012, 262, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.; McCracken, D. US probes: Risk of cross infection and ways to reduce it—Comparison of cleaning methods. Radiology 1999, 213, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, S.; Kellner, W.; Kellner, H. Interventional radiology and the musculoskeletal system. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2004, 18, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, K.-S. Ultrasound-guided intra-articular injections. Korean J. Med. 2015, 89, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
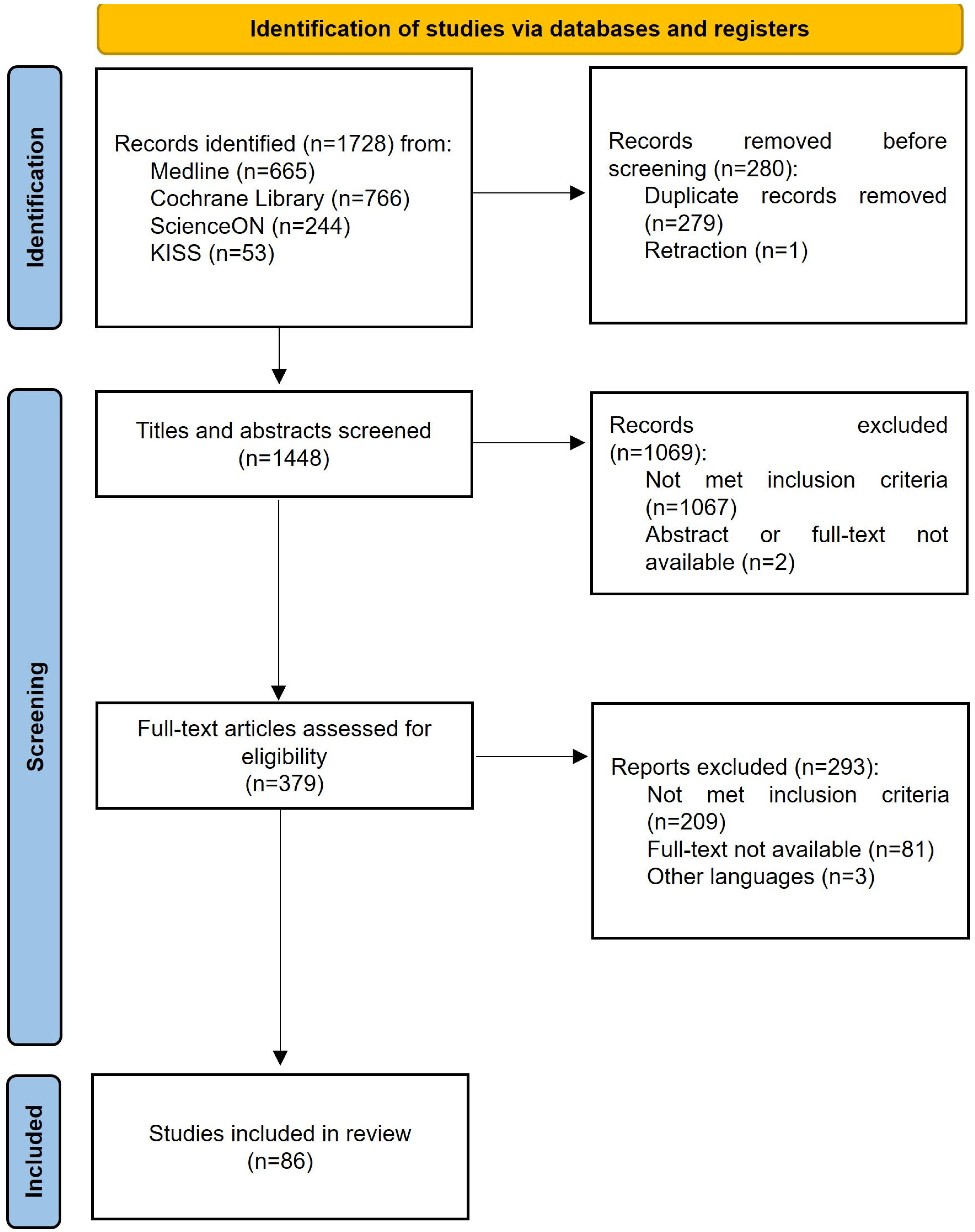
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Study design | Clinical study | Review, meta-analysis, response to letter |
| Participants | Human (no limitations) | Non-human (cadavers, animals) |
| Target site | Musculoskeletal interventions:
| Non-musculoskeletal sites:
|
| Intervention |
|
|
| Procedure description | Must include:
| Excluded if lacking:
|
| Control | No limitation | |
| Outcome | No limitation | |
| Category | Procedure | Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before the injection | |||
| Informed consent | Explain the procedure and precautions and obtain consent | 10 (11.63%) | |
| Allergic reaction test | Test for allergic reactions prior to the procedure | 1 (1.16%) | |
| Probe disinfection | Disinfect the probe | 5 (5.81%) | |
| Use of probe cover | Affix the sterilized probe cover | 24 (27.91%) | |
| Omit affixing the sterilized probe cover | 9 (10.47%) | ||
| Application of the US coupling agent to the probe | Apply nonsterile ultrasound gel | 6 (6.98%) | |
| Apply sterile ultrasound gel | 15 (17.44%) | ||
| Apply povidone–iodine solution | 1 (1.16%) | ||
| Apply 85% ethanol solution | 1 (1.16%) | ||
| Putting on sterile gloves | Wear sterile gloves | 5 (5.81%) | |
| Draping the treatment area | Cover the treatment area with disinfectant cloths/drapes | 14 (16.28%) | |
| Preliminary US scan | Perform a preliminary US scan | 17 (19.77%) | |
| Local anesthesia | Locally anesthetize the area to be treated | 24 (27.91%) | |
| During the injection | |||
| Skin disinfection | Disinfect with alcohol | 10 (11.63%) | |
| Disinfect with iodophors | 18 (20.93%) | ||
| Disinfect with chlorhexidine | 4 (4.65%) | ||
| Disinfect with alcohol and povidone–iodine solution | 2 (2.33%) | ||
| Disinfect with chlorhexidine and alcohol solution | 4 (4.65%) | ||
| Disinfect with benzalkonium chloride | 1 (1.16%) | ||
| Disinfect with antiseptic (not specified) | 50 (58.14%) | ||
| Regurging | Regurge the syringe | 1 (1.16%) | |
| After the injection | |||
| Post-procedure care | Re-disinfect the injection site | 12 (13.95%) | |
| Apply compression hemostasis to the procedure site | 3 (3.49%) | ||
| Apply a bandage to the injection site | 13 (15.12%) | ||
| Post-procedure monitoring | Allow the patient to rest and monitor for any side effects | 13 (15.12%) | |
| Post-procedure instructions for patients | Instruct the patient to prevent contamination or contact with water | 3 (3.49%) | |
| Instruct the patient to promptly report any side effects | 7 (8.14%) | ||
| Instruct the patient to avoid excessive movement and pressure on the treated area | 22 (25.58%) | ||
| Instruct the patient to apply ice pack in case of pain or discomfort | 12 (13.95%) | ||
| Instruct the patient to take medication in case of pain or discomfort | 14 (16.28%) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kweon, Y.; Jeong, G.; Kim, S.; Yang, C.; Cho, E.; Leem, J. A Scoping Review of Clinical Studies on Procedures of Ultrasound-Guided Injection to Ensure Hygiene and Safety. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13101165
Kweon Y, Jeong G, Kim S, Yang C, Cho E, Leem J. A Scoping Review of Clinical Studies on Procedures of Ultrasound-Guided Injection to Ensure Hygiene and Safety. Healthcare. 2025; 13(10):1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13101165
Chicago/Turabian StyleKweon, Yujin, Goeun Jeong, Sungha Kim, Changsop Yang, Eunbyul Cho, and Jungtae Leem. 2025. "A Scoping Review of Clinical Studies on Procedures of Ultrasound-Guided Injection to Ensure Hygiene and Safety" Healthcare 13, no. 10: 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13101165
APA StyleKweon, Y., Jeong, G., Kim, S., Yang, C., Cho, E., & Leem, J. (2025). A Scoping Review of Clinical Studies on Procedures of Ultrasound-Guided Injection to Ensure Hygiene and Safety. Healthcare, 13(10), 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13101165






