Diversity and Safety of Acupotomy Treatments for Lumbar Spine Disorders in South Korea: A Review of Clinical Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
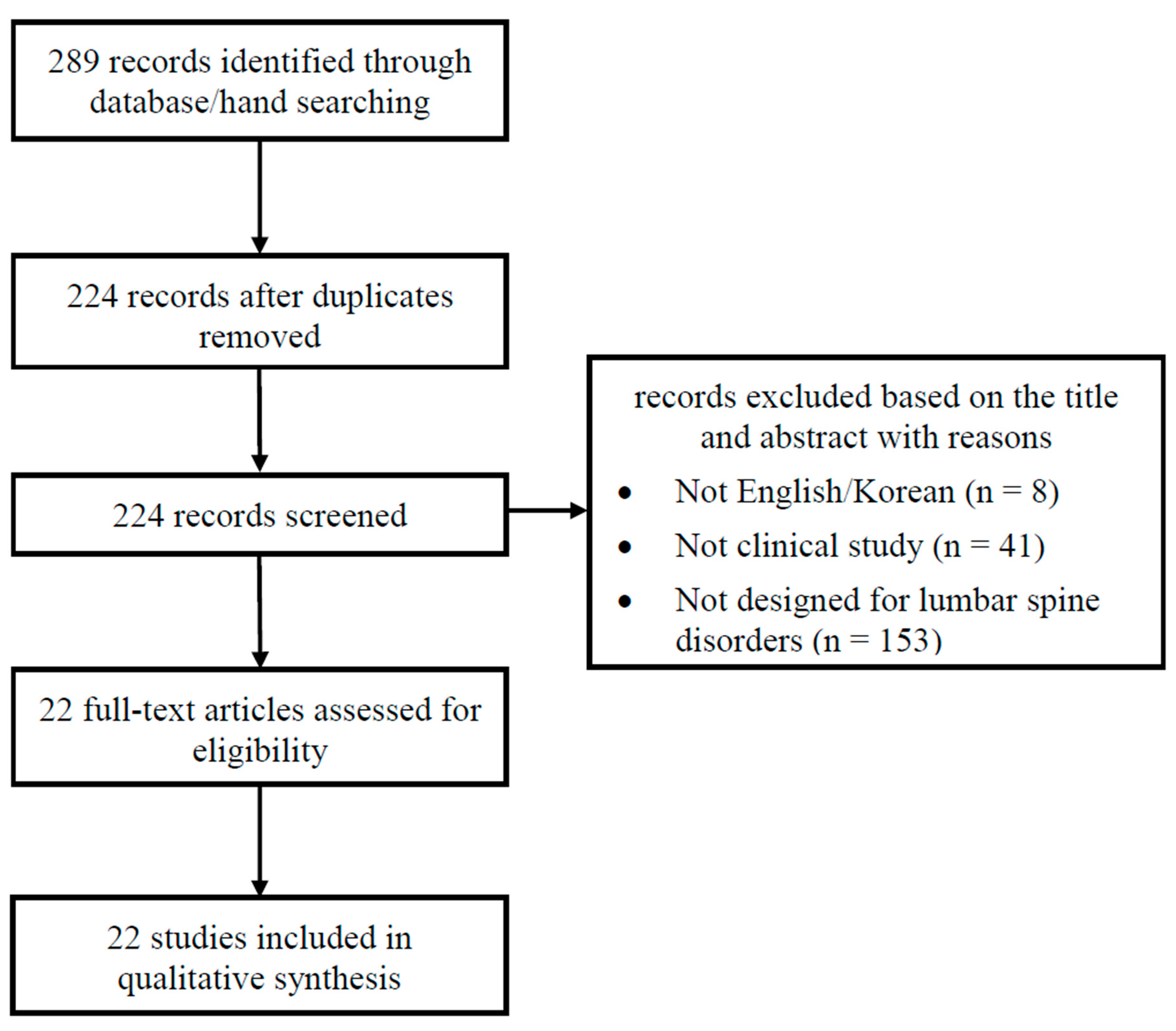
3.1. Results of the Search
3.2. Participants in Included Clinical Trials
3.3. Reporting of Treatment Procedures
3.3.1. Diagnosis
3.3.2. Acupotomy Treatment Procedures
3.4. Reporting Clinical Outcomes, Safety, and Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, H. Summarization of acupotomology system. J. Eng. Sci. 2006, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Quan, W.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, J.; Liu, Z.; Fu, P.; You, S. Clinical evaluation of needle knife in the treatment of cervical spondylosis. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2006, 5, 316–318. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, M.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Yu, S.; Lin, Z. Acupotomy therapy for lumbar disc herniation: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, M.; Fang, T.; Chen, M.; Yan, X. Acupotomy therapy for chronic nonspecific neck pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 6197308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, R.; Chen, Q.; Song, M.; Xue, Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, W. Acupotomy therapy for knee osteoarthritis pain: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 2168283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, C.R.; Choi, T.Y.; Lee, M.S. Intramuscular stimulation therapy for healthcare: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Acupunct. Med. 2012, 30, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabago, D.; Slattengren, A.; Zgierska, A. Prolotherapy in primary care practice. Prim. Care 2010, 37, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.K.; Kim, E.; Yoon, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, H.; Kwon, O.; Jung, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Yang, C.; et al. Acupotomy versus manual acupuncture for the treatment of back and/or leg pain in patients with lumbar disc herniation: A multicenter, randomized, controlled, assessor-blinded clinical trial. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.E.; Lee, I.S.; Chae, Y. Determining the adequate dose of acupuncture for personalised medicine. Acupunct. Med. 2021, 39, 565–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, H.; Altman, D.G.; Hammerschlag, R.; Youping, L.; Taixiang, W.; White, A.; Moher, D. Revised standards for reporting interventions in clinical trials of acupuncture (STRICTA): Extending the CONSORT statement. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2010, 16, ST-1–ST-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.I.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.I. A Case Report of a lumbar herniated intervertebral disc Patient Treated with Korean Medical Treatments, Mainly Managed by Acupotomy. J. Haehwa Med. 2022, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, E.H.; Kim, S.C.; Lim, N.R.; Na, W.M.; Lim, S.I.; Shin, J.B.; Lee, G.-M. Case study of Oriental Medicine treatment with acupotomy of the herniated lumbar intervertebral disc patient. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2008, 25, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.W.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, G.M. The Comparative Study of Effects between Acupotomy and its Cotreatment with Spine Decompression Therapy on HIVD Patients. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2012, 29, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S.; Park, S.W.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, G.M. The Clinical Effects of acupuncture and Acupotomy Therapy for HIVD. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2010, 27, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, J.; Cho, S. A Case Report of Acupotomy Treatment on the Failed Back Surgery Syndrome. J. Korean Med. Soc. Acupotomology 2023, 7, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Y.Z.; Fan, X.H.; Liang, W.Q.; Wei, X.; Zhao, M.-D.; Huo, Y.-X.B.; Zhang, T.B.; Yin, Y. The effect of ultrasound-guided acupotomy and Juanbi decoction on lumbar disc herniation: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2023, 102, e32622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.C.; Choi, J.; Kim, H. A Case Report of Acupotomy Treatment at Internal Intervertebral Foramen on the Chronic HIVD Patient. J. Korean Med. Soc. Acupotomology 2023, 7, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.I. Clinical effect of acupotomy combined with Korean medicine: A case series of a herniated intervertebral disc. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2016, 9, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.K.; Lee, Y.R.; Cha, H.J.; Sung, K.J.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.I. Intractable Pain Management by Combined Korean Medicine Treatment Including Acupotomy in Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Case Report. Korean J. Acupunct. 2021, 38, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Jo, H.K.; Yoo, H.R.; Seol, I.C. Case Report: Changes in Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Lumbar Disc Herniation Treated with Korean Medicine. J. Intern. Korean Med. 2018, 39, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.M.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.W.; Yeom, S.C.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.E.; Song, D.-S. The study on the effect of acupotomy in lumbar HIVD. J. Acupunct. Res. 2008, 25, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, I.S.; Yuk, D.I.; Song, D.H.; Kim, M.J.; Hong, K.E. Case Study of with Dochim (刀鍼) & Gwanchim (管鍼) Therapy Combined with Korean Medicine Treatment of Herniated Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Patients. J. Korean Acupunct. Moxibustion Soc. 2013, 28, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, Y.I. The effect of acupotomy on lumbar herniated intervertebral disc: Report of a case series. Acupuncture 2015, 32, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, B.M.; Hong, K.E. Four case of HIVD-lumbar spine patient treated with acupotomy. J. Acupunct. Res. 2008, 25, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, H.B.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, E.; Kim, Y.I. Cervical and lumbar herniated nucleus pulposus resorption after acupotomy with integrative Korean medicine treatment: A case series of two patients. J. Acupunct. Res. 2019, 36, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.Y.; Sur, Y.C.; Jang, W.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, K.H.; Shin, G.S.; Han, Y.-S. Study and three Cases Report for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Treatment Using a Combination of Acupotomy and Existing Treatments. Korean J. Orient. Physiol. Pathol. 2012, 26, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Yuk, D.I.; Sung, I.s.; Song, D.H.; Kim, M.J.; Hong, K.E. Clinical study of lumbar spine stenosis treated by using acupotomy combined with oriental medical treatments. J. Pharmacopunct. 2013, 16, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.W.; Choi, B.S.; Oh, M.S. The Effect of Acupotomy on Traumatic Acute Low back pain: Case Report. J. Haehwa Med. 2017, 26, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, Y.J.; Sung, K.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, E.; Kim, Y.I. A patient with ankylosing spondylitis treated with acupotomy and traditional Korean medicine. J. Acupunct. Res. 2019, 36, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.C.; Kim, H.; Jung, S. A Case Report of Acupotomy Treatment on the Acute Myelitis Patient. J. Korean Med. Soc. Acupotomology 2023, 7, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J. Case Report of Abnormal Spinal Curvature Improved by Acupotomy and Combined Korean Medicine Treatment. J. Korean Med. Soc. Soft Tissue 2022, 6, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Ji, Y.S.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, Y.I. The effect of acupotomy on lumbar and cervical spine combined with oriental medical treatment: Report of five cases. J. Acupunct. Res. 2014, 31, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafhoumi, A.; Nabian, M.H.; Mehrpour, S.R. Prolotherapy in musculoskeletal disorders, guideline for orthopedic application. Open J. Regen. Med. 2023, 12, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Kim, S.A.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Leem, J. Using magnetic resonance imaging to measure the depth of acupotomy points in the lumbar spine: A retrospective study. Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 100679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
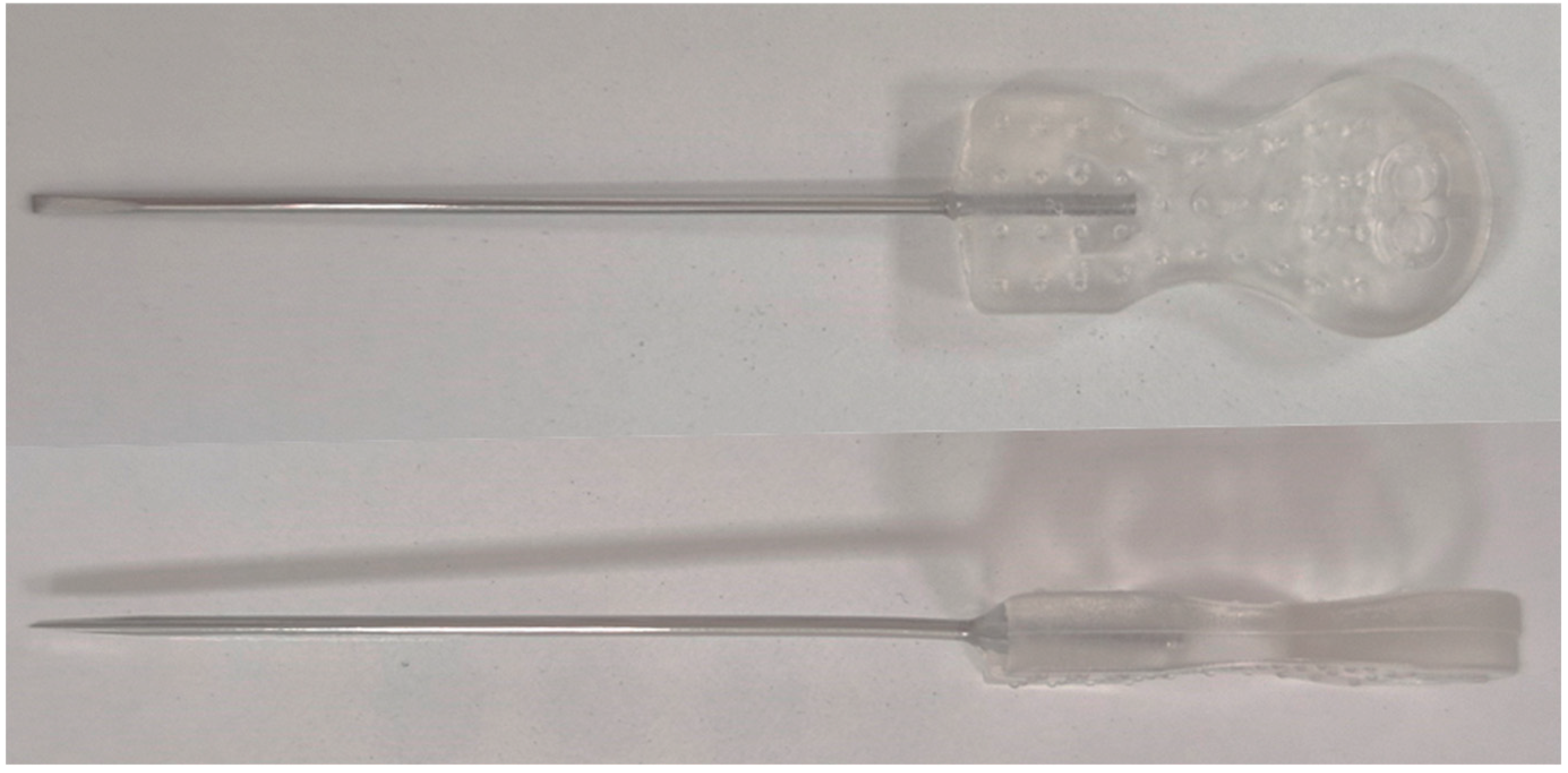
| No. Author (Year)/Type | Diagnosis/Diagnosis | Acupotomy (No., Sex, Age) | Treatment Frequency (Total Session) | Tissue Damage | Sites/No. of Needle/Size of Needle (Length, Diameter, Thickness) (mm) | Anesthesia | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (Intervention, No., Sex, Age) | |||||||
| 1. Lee et al. (2008)/case series [21] | HIVD/ MRI | 3 (M: 1), mean 53 | 1–2/10 d (1–2) | Ligament, proliferated/hardened tissues, tender points of spine, process, muscle fascia, herniated/extruded discs | Sites of tissue damage/5–15/70 × 1.0 × 0.8 | NR | VAS, site of pain, gait performance |
| - | |||||||
| 2. Kwak and Hong (2008)/case series [24] | HIVD/X-ray, MRI | 4 (F: 4), mean 58.25 | (1) | Narrowed intervertebral space | Ligamentum flavum, tender points/NR/70 × 1.0 × 0.8 | NR | VAS, ODI, satisfaction |
| - | |||||||
| 3. Jang et al. (2008)/case report [12] | HIVD/MRI | 1 (F), 48 | 2/w (3) | Degenerative discs | Ashi and tender points at BL23, BL24, BL25, GV3, EX-B2, etc./2–3/NR × NR × 0.8 | Not used | Neurological examination (SLRT, Milgram test, etc.), pain, ODI |
| - | |||||||
| 4. Yun et al. (2010)/RCT [14] | HIVD/CT, MRI | Acupotomy + ACU; 33 (M: 20), 51.21 ± 13.97 | 1/w (1–2) | Proliferated/hardened tissues, tender points, muscle fascia, herniated/extruded discs | Sites of tissue damage/5–15/70 × 1.0 × 0.8 | NR | VAS, ODI, Odom’s degree |
| ACU;30 (M: 16), 50.23 ± 12.34 | |||||||
| 5. Jung et al. (2012)/case series [26] | stenosis/MRI, fluoroscopy (X-ray) | 3 (M: 2), mean 59.33 | (1) | Protruded discs, spinal stenosis | Transverse process, facet joint, lamina of vertebral arch, ligamentum flavum/NR/100 × 1.0 × 0.8 (I-4 type), 80 × NR × 0.5, 80 × NR × 1.0 | Lidocaine | NRS, ODI, Odom’s criteria |
| - | |||||||
| 6. Park et al. (2012)/CCT [13] | HIVD/MRI | Acupotomy + spine decompression; 20 (M: 10), 43.20 ± 11.78 | (1–3) | Proliferated/hardened tissues, herniated/extruded discs, sacroiliac joint, greater sciatic notch, ischial spine, muscle fascia | Sites of tissue damage/5–15/75 × 0.5 × 0.4 | NR | VAS, ODI |
| Acupotomy; 20 (M: 11), 46.10 ± 11.06 | |||||||
| 7. Sung et al. (2013)/CCT [22] | HIVD/CT, MRI | Acupotomy + Gwanchim; 80 (M: 40), mean 47.37 | (1) | NR | EX-B2, joint capsule of facet joint/NR/75 × 1.0 × NR | Lidocaine + prilocaine | NRS |
| ACU;23 (M: 10), mean 40.82 | |||||||
| 8. Yuk et al. (2013)/clinical trial [27] | stenosis/MRI, X-ray | 437 (M: 172), 65 ± 10 | 1/d (1–3) | NR | Facet joint, erector spinae, intertransverse ligament, ligamentum flavum/NR/75 × 1.0 × NR | Lidocaine + prilocaine | NRS, ODI, global assessment |
| - | |||||||
| 9. Kim et al. (2014)/case series [32] | Various */NA/CT, MRI | 5 (M: 4), mean 55.8 | 1/3–7 d (1–2) | Bulging/herniated discs, annular tears, spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis | Transverse process, BL24, BL25, BL26/NR/75 × 1.2 × NR | NR | NRS, ODI, NDI, ROM |
| - | |||||||
| 10. Kim et al. (2015a)/case series [23] | HIVD/CT, MRI | 7 (M: 5), mean 44.4 | 1/3–5d (1–3) | Herniated discs, spinal stenosis | Adherent sites, tender points/NR/75 × 1.2 × NR | NR | NRS, ODI, ROM |
| - | |||||||
| 11. Kim et al. (2015b)/case series [18] | HIVD/CT, MRI | 5 (NR), mean 47.2 | 3/2w (3) | Extruded/protruded/degenerative diffuse/bulging discs, annular tear | 20–30 mm away from the spinous process, tender points in inner core muscles/3/75 × 1.2 × NR | Lidocaine | NRS, ROM, SLRT, ODI, SF-36 |
| - | |||||||
| 12. Choi et al. (2017)/case series [28] | Fracture and sprain/CT, X-ray | 3 (M: 1), 56.67 | 1/2d (1–2) | Fracture, sprain | Adherent sites, tender points on the erector spinae/NR/50 × NR × 0.5 | NR | NRS, ROM, RMDQ, EQ-5D, satisfaction with the treatment |
| - | |||||||
| 13. Park et al. (2018)/case report [20] | HIVD/MRI | 1 (F), 46 | 1, 2, 5/w (127) | Bulging/diffuse/extruded disk, annular tear, compression of thecal sac | Acupoints on GV meridian, facet joints/NR/50 × NR × 0.5 | NR | NRS, MRI |
| - | |||||||
| 14. Lee et al. (2019)/case report [25] | HIVD/MRI | 1 (M), 48 | 2–3/w (3, 7) | Bulging/extruded/diffuse/protruded discs | GV3, BL23, BL24, BL25, adhesion sites, tender points on the erector spinae/NR/60 × NR × 1.2 | NR | NRS, ROM, MRI |
| - | |||||||
| 15. Kim et al. (2019)/case report [29] | Ankylosing spondylitis/X-ray | 1 (M), 40 | 3/w (9) | Narrowing disc space | Hard nodules of GB20, GB21, EX-HN1, BL10, BL21, BL22, BL23, BL24, BL25, BL26/NR/80 × NR × 0.75 | Lidocaine | NRS, BASFI, ROM, BASDAI, M/K-HAQ |
| - | |||||||
| 16. Choi et al. (2021)/case report [19] | HIVD/MRI | 1 (F), 57 | 5/w (39) | Extruded/herniated discs | BL21, BL22, BL23, BL24, BL25, BL26/NR/NR | NR | NRS, ROM, ODI, EQ-5D, physical examination (SLRT, Milgram test), MRI |
| - | |||||||
| 17. Cho et al. (2022)/case report [11] | HIVD/MRI | 1 (F), 44 | 5/w (17) | Extruded/herniated discs | BL21, BL22, BL23, BL24, BL25, BL26, etc./NR/80 × NR × 0.75 | NR | NRS, ROM, ODI, EQ-5D, physical examination (SLRT, Milgram test), MRI |
| - | |||||||
| 18. Wang et al. (2023)/RCT [16] | HIVD/MRI, ultrasonography | Acupotomy + herbal medicine; 30 (M: 14), 48.8 ± 7.48 | 1/w (3) | Herniated discs | Medial articular process, below base of transverse process, GB30/NR/80 × NR × 1.2, 80 × NR × 1.0 | Lidocaine | VAS, JOA, ODI, low back outcome scale |
| Herbal medicine; 30 (M: 17), 49.6 ± 5.84 | |||||||
| 19. Woo and Cho (2023)/case report [15] | HIVD + FBSS/NR | 1 (F), 64 | NR (6) | NR | Tender points (vertebral and gluteal regions), lumbar vertebrae/NR/60 × NR × 0.5 | NR | NRS, ROM, tenderness response |
| - | |||||||
| 20. Sun et al. (2023a)/case report [30] | Acute myelitis/MRI | 1 (F), 63 | 3/w (12) | Abnormal high signal intensity at distal spinal cord, conus medullaris | Lumbar vertebrae, BL31, BL32, gluteus maximus, quadriceps femoris/NR/50 × NR × 0.6 | NR | Total sensory score of ASIA |
| - | |||||||
| 21. Sun et al. (2023b)/case report [17] | HIVD/MRI | 1 (M), 70 | 1~2/w (20) | Extruded/protruded discs | Internal intervertebral foramen/NR/50 × NR × 0.6 | NR | NRS, ODI, ROM, SLRT, MRI |
| - | |||||||
| 22. Choi (2023)/case report [31] | Abnormal spinal curvature/X-ray | 1 (F), 36 | 1/w (10) | NR | Tender points/NR/40 × NR × 0.4 | NR | VAS, Cobb’s angle (cervical, thoracic, lumbar) |
| - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, Y.; Son, E.; Lee, S.; Chae, Y.; Yoon, S.-H.; Leem, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, I.-S. Diversity and Safety of Acupotomy Treatments for Lumbar Spine Disorders in South Korea: A Review of Clinical Studies. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13101141
Bae Y, Son E, Lee S, Chae Y, Yoon S-H, Leem J, Lee S, Lee I-S. Diversity and Safety of Acupotomy Treatments for Lumbar Spine Disorders in South Korea: A Review of Clinical Studies. Healthcare. 2025; 13(10):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13101141
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Yubin, Euijin Son, Sooyoon Lee, Younbyoung Chae, Sang-Hoon Yoon, Jungtae Leem, Seunghoon Lee, and In-Seon Lee. 2025. "Diversity and Safety of Acupotomy Treatments for Lumbar Spine Disorders in South Korea: A Review of Clinical Studies" Healthcare 13, no. 10: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13101141
APA StyleBae, Y., Son, E., Lee, S., Chae, Y., Yoon, S.-H., Leem, J., Lee, S., & Lee, I.-S. (2025). Diversity and Safety of Acupotomy Treatments for Lumbar Spine Disorders in South Korea: A Review of Clinical Studies. Healthcare, 13(10), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13101141






