The Prevalence of Dysphagia in Individuals Living in Residential Aged Care Facilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Information Sources
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction and Summary Measures
2.4. Quality Appraisal
2.5. Results Synthesis
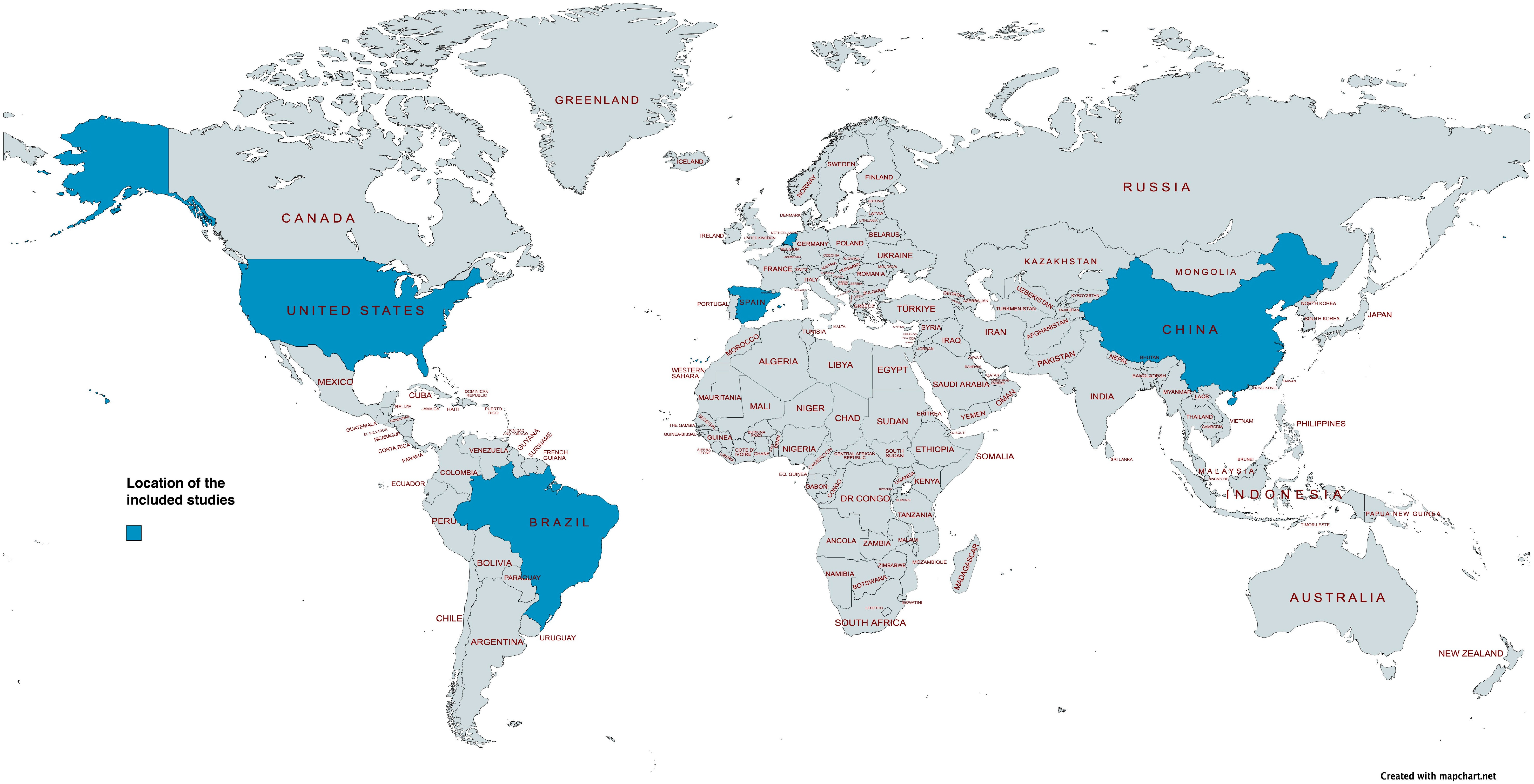
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Assessment Tools Used
3.3. Who Completed the Assessment
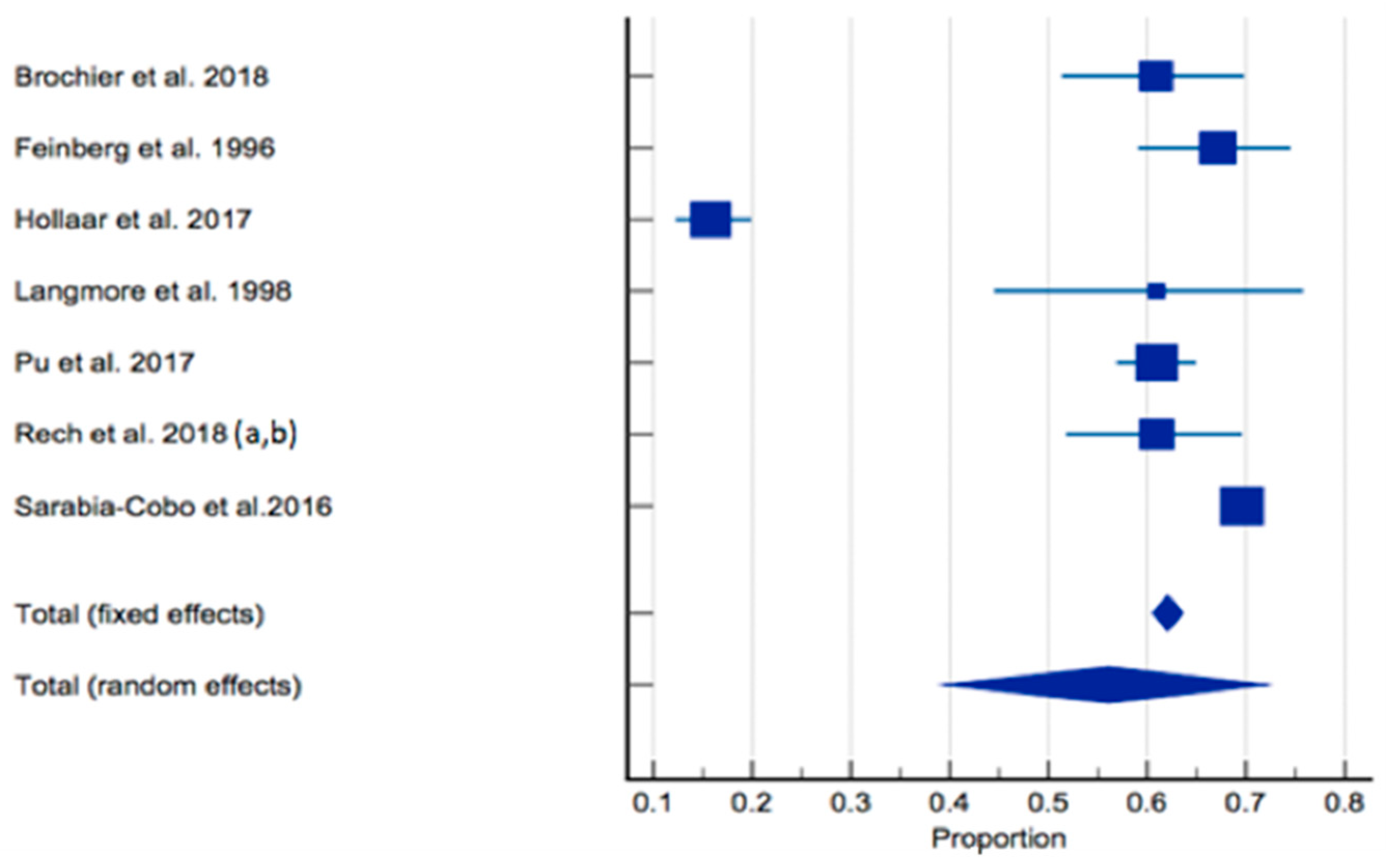
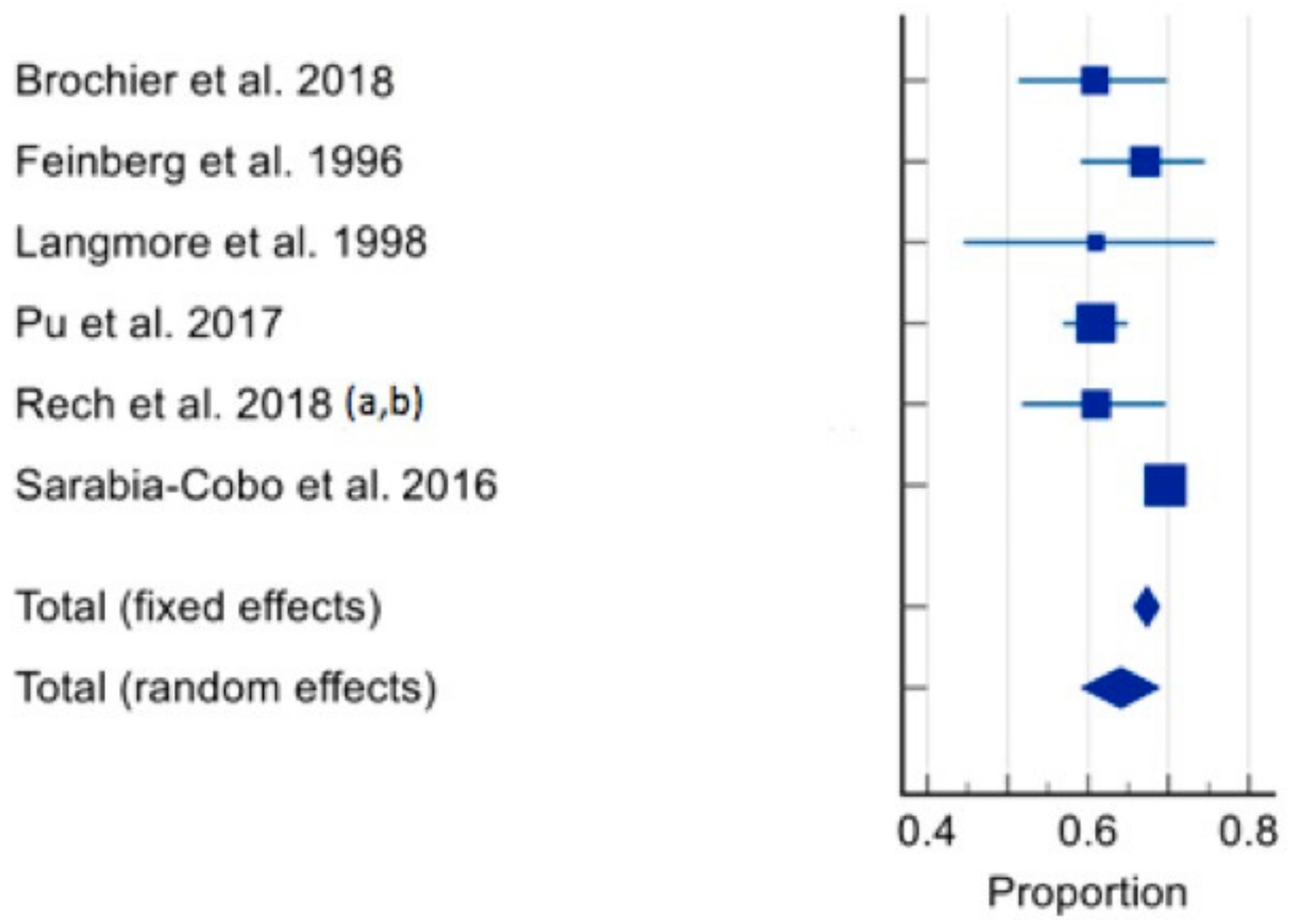
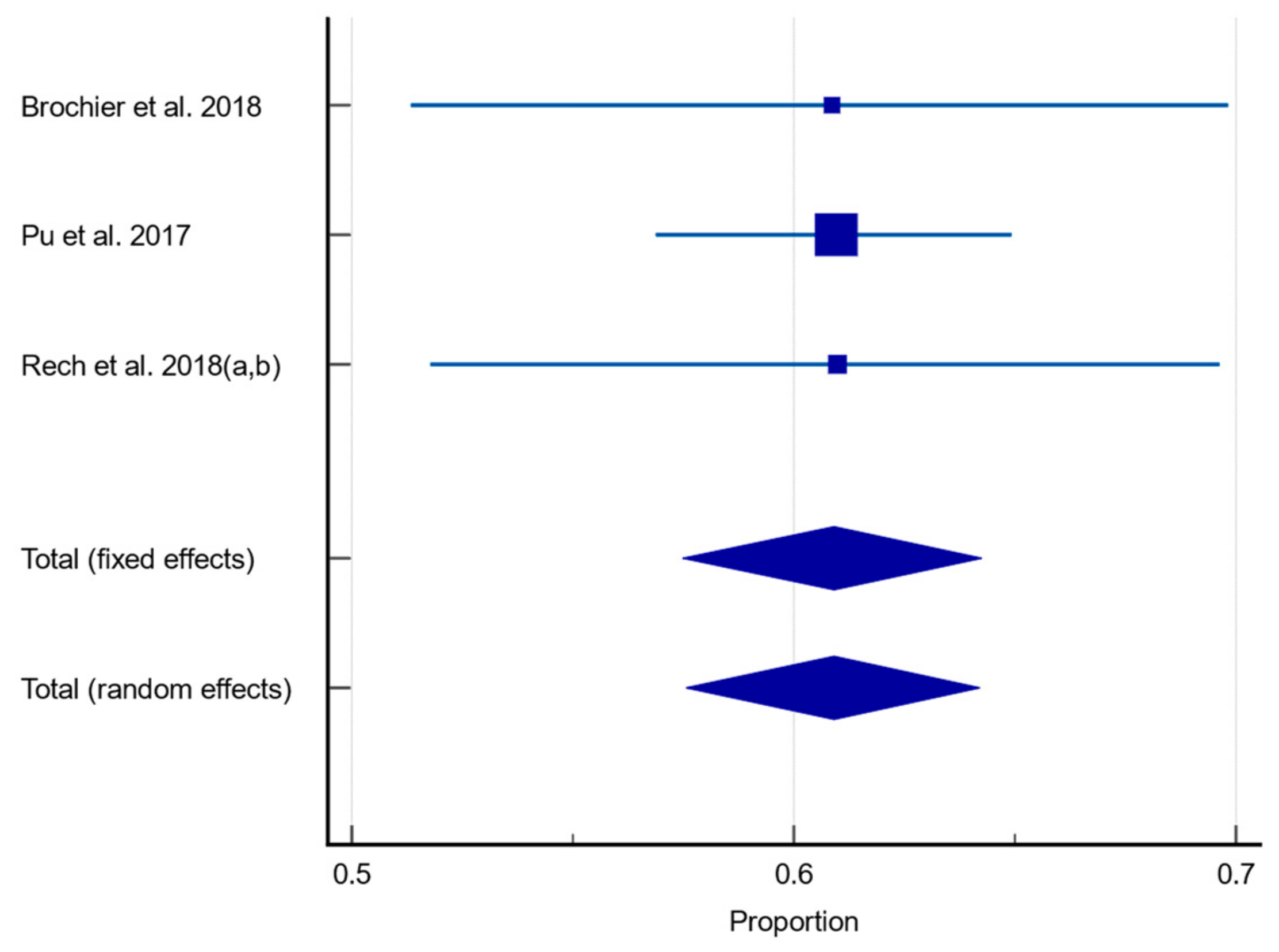
3.4. Prevalence of Dysphagia
3.5. Quality Appraisal
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Department of Economic and Social Affairs: Population Division. World Population Ageing 2020, Highlights: Living Arrangements of Older Persons; United Nations: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ashby, S.; Beech, R. Addressing the Healthcare Needs of an Ageing Population: The Need for an Integrated Solution. Int. J. Collab. Res. Intern. Med. Public Health 2016, 8, 284. [Google Scholar]
- Paolucci, F.; Paolucci, F.; Ergas, H. Providing and financing aged care in Australia. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2011, 4, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weech-Maldonado, R.; Pradhan, R.; Dayama, N.; Lord, J.; Gupta, S. Nursing Home Quality and Financial Performance: Is There a Business Case for Quality? Inq. J. Health Care Organ. Provis. Financ. 2019, 56, 0046958018825191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal Comission into Aged Care Quality and Safety. Final Report: Care, Dignity and Respect: Volume 4B; Australian Government: Canberra, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Care Quality Commission. How CQC Monitors, Inspects and Regulates Adult Social Care Services; The Stationery Office: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care. Improving Food and Nutrition in Aged Care. Available online: https://www.health.gov.au/our-work/improving-food-nutrition-aged-care (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Department of Health and Aged Care. Lifting the Standard of Food and Nutrition in Aged Care. Available online: https://www.health.gov.au/ministers/the-hon-anika-wells-mp/media/lifting-the-standard-of-food-and-nutrition-in-aged-care (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia: Summary of Findings, 2019. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/health/disability/disability-ageing-and-carers-australia-summary-findings/latest-release (accessed on 11 July 2023).
- Eskildsen, M.; Price, T. Nursing home care in the USA. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2009, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, M.L.J.; Caffrey, C.; Melekin, A.; Singh, P. Post-Acute and Long-Term Care Providers and Services Users in the United States, 2017–2018; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office for National Statistics. Life Expectancy in Care Homes, England and Wales: 2021 to 2022. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/birthsdeathsandmarriages/lifeexpectancies/articles/lifeexpectancyincarehomesenglandandwales/2021to2022 (accessed on 11 July 2023).
- Starr, K.N.P.; McDonald, S.R.; Bales, C.W. Nutritional Vulnerability in Older Adults: A Continuum of Concerns. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2015, 4, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fávaro-Moreira, N.C.; Krausch-Hofmann, S.; Matthys, C.; Vereecken, C.; Vanhauwaert, E.; Declercq, A.; Bekkering, G.E.; Duyck, J. Risk Factors for Malnutrition in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of the Literature Based on Longitudinal Data. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2016, 7, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereda, E.; Pedrolli, C.; Klersy, C.; Bonardi, C.; Quarleri, L.; Cappello, S.; Turri, A.; Rondanelli, M.; Caccialanza, R. Nutritional status in older persons according to healthcare setting: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence data using MNA. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarya, S.; Singh, K.; Sabharwal, M. Changes during aging and their association with malnutrition. J. Clin. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 6, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, W.; Hankey, C. Aging, Nutritional Status and Health. Healthcare 2015, 3, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolino, D.; Passarelli, P.C.; De Angelis, P.; Piccirillo, G.B.; D’Addona, A.; Cesari, M. Poor Oral Health as a Determinant of Malnutrition and Sarcopenia. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelig, R.; Goldstein, S.; Touger-Decker, R.; Firestone, E.; Golden, A.; Johnson, Z.; Kaseta, A.; Sackey, J.; Tomesko, J.; Parrott, J.S. Tooth Loss and Nutritional Status in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JDR Clin. Transl. Res. 2022, 7, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilgrim, A.L.; Robinson, S.M.; Sayer, A.A.; Roberts, H.C. An overview of appetite decline in older people. Nurs. Older People 2015, 27, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, W.E.; Haverkort, E.B.; Algra, Y.A.; Mollema, J.; Hollaar, V.R.Y.; Naumann, E.; De Van Der Schueren, M.A.E.; Jerković-Ćosić, K. The association between polypharmacy and malnutrition(risk) in older people: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 49, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytekin Sahin, G.; Caferoglu, Z. The food service quality and its effects on nutritional status in nursing home residents. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 47, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, A. Dysphagia in the elderly: A multidisciplinary approach. J. Datta Meghe Inst. Med. Sci. Univ. 2022, 17, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speech Pathology Association of Australia. Dysphagia Clinical Guidelines Speech Pathology; Association of Australia Victoria: Melbourne, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chilukuri, P.; Odufalu, F.; Hachem, C. Dysphagia. Mo. Med. 2018, 115, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.-Y.; Zhang, P.-P.; Wang, X.-W. Presbyphagia: Dysphagia in the elderly. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejaeger, M.; Liesenborghs, C.; Dejaeger, E. Presbyphagia; InTech: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakheit, A.M.O. Management of neurogenic dysphagia. Postgrad. Med. J. 2001, 77, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziewas, R.; Allescher, H.-D.; Aroyo, I.; Bartolome, G.; Beilenhoff, U.; Bohlender, J.; Breitbach-Snowdon, H.; Fheodoroff, K.; Glahn, J.; Heppner, H.-J.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of neurogenic dysphagia–S1 guideline of the German Society of Neurology. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2021, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shune, S.E.; Karnell, L.H.; Karnell, M.P.; Van Daele, D.J.; Funk, G.F. Association between severity of dysphagia and survival in patients with head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2012, 34, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayer, R.; Sinha, U. Dysphagia in head and neck cancer: A review. Open J. Stomatol. 2013, 03, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Shehri, A.M. Drug-induced dysphagia. Ann. Saudi Med. 2003, 23, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, H. Presbyphagia and sarcopenic dysphagia: Association between aging, sarcopenia, and deglutition disorders. J. Frailty Aging 2014, 3, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfino, J.E.; Gawron, A.J. Achalasia: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2015, 313, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaindlstorfer, A.; Pointner, R. An appraisal of current dysphagia diagnosis and treatment strategies. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 10, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, N.; Hamdy, S. Oropharyngeal dysphagia: Manifestations and diagnosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliaferri, S.; Lauretani, F.; Pelá, G.; Meschi, T.; Maggio, M. The risk of dysphagia is associated with malnutrition and poor functional outcomes in a large population of outpatient older individuals. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2684–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Bryant, L.; Hemsley, B. Dysphagia and Quality of Life, Participation, and Inclusion Experiences and Outcomes for Adults and Children With Dysphagia: A Scoping Review. Perspect. ASHA Spéc. Interes. Groups 2022, 7, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attrill, S.; White, S.; Murray, J.; Hammond, S.; Doeltgen, S. Impact of oropharyngeal dysphagia on healthcare cost and length of stay in hospital: A systematic review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018, 18, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etges, C.L.; Scheeren, B.; Gomes, E.; Barbosa, L.D.R. Screening tools for dysphagia: A systematic review. CoDAS 2014, 26, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estupiñán Artiles, C.; Regan, J.; Donnellan, C. Dysphagia screening in residential care settings: A scoping review. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2021, 114, 103813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-P.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, D.-Z.; Li, T.-T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-W. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Eating Assessment Tool-10 (EAT-10) in Screening Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dysphagia 2023, 38, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.D.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, S.H. The Gugging Swallowing Screen in dysphagia screening for patients with stroke: A systematic review. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2020, 107, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, G.H.; Martino, R. Clinical Evaluation of Patients with Dysphagia: Importance of History Taking and Physical Exam; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pongpipatpaiboon, K.; Inamoto, Y.; Aoyagi, Y.; Shibata, S.; Kagaya, H.; Matsuo, K. Clinical Evaluation of Dysphagia; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 35–98. [Google Scholar]
- Speyer, R.; Cordier, R.; Farneti, D.; Nascimento, W.; Pilz, W.; Verin, E.; Walshe, M.; Woisard, V. White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders: Screening and Non-instrumental Assessment for Dysphagia in Adults. Dysphagia 2022, 37, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci Maccarini, A.; Filippini, A.; Padovani, D.; Limarzi, M.; Loffredo, M.; Casolino, D. Clinical non-instrumental evaluation of dysphagia. Acta Otorhino Laryngol. Ital. 2007, 27, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Birchall, O.; Bennett, M.; Lawson, N.; Cotton, S.M.; Vogel, A.P. Instrumental swallowing assessment in adults in residential aged care homes: Practice patterns and opportunities. Australas. J. Ageing 2023, 42, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, E.; O’Reilly, M.; Strange, E.; Franklin, S.; Isenring, E. How much do residential aged care staff members know about the nutritional needs of residents? Int. J. Older People Nurs. 2014, 9, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Aquila, G.; Peladic, N.J.; Nunziata, V.; Fedecostante, M.; Salvi, F.; Carrieri, B.; Liperoti, R.; Carfì, A.; Eusebi, P.; Onder, G.; et al. Prevalence and management of dysphagia in nursing home residents in Europe and Israel: The SHELTER Project. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, M.; Wirth, R.; Schindler, K.; Sieber, C.C.; Hiesmayr, M.; Volkert, D. Dysphagia in Nursing Homes—Results From the NutritionDay Project. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 141–147.e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgaard, D.; Westergren, A.; Skrubbeltrang, C.; Smithard, D. Interventions for Nursing Home Residents with Dysphagia—A Scoping Review. Geriatrics 2021, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueshima, J.; Momosaki, R.; Shimizu, A.; Motokawa, K.; Sonoi, M.; Shirai, Y.; Uno, C.; Kokura, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Nishiyama, A.; et al. Nutritional Assessment in Adult Patients with Dysphagia: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, M.; Yamashita, Y. Oral Health and Swallowing Problems. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2013, 1, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Izumi, M.; Furuta, M.; Takeshita, T.; Shibata, Y.; Kageyama, S.; Ganaha, S.; Yamashita, Y. Posterior teeth occlusion and dysphagia risk in older nursing home residents: A cross-sectional observational study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2017, 44, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivelsrud, M.C.; Hartelius, L.; Bergström, L.; Løvstad, M.; Speyer, R. Prevalence of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Adults in Different Healthcare Settings: A Systematic Review and Meta-analyses. Dysphagia 2022, 38, 76–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2022, 38, 76–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handu, D.P.R.D.N.; Moloney, L.M.S.R.D.N.; Wolfram, T.M.S.R.D.N.; Ziegler, P.P.R.D.N.; Acosta, A.; Steiber, A.P.R.D.N. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Methodology for Conducting Systematic Reviews for the Evidence Analysis Library. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochier, C.W.; Hugo, F.N.; Rech, R.S.; Baumgarten, A.; Hilgert, J.B. Influence of dental factors on oropharyngeal dysphagia among recipients of long-term care. Gerodontology 2018, 35, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollaar, V.R.Y.; van der Putten, G.-J.; van der Maarel-Wierink, C.D.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; de Swart, B.J.M.; de Baat, C.; Creugers, N.H.J. Nursing home-acquired pneumonia, dysphagia and associated diseases in nursing home residents: A retrospective, cross-sectional study. Geriatr. Nurs. 2017, 38, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, D.; Murry, T.; Wong, M.C.M.; Yiu, E.M.L.; Chan, K.M.K. Indicators of dysphagia in aged care facilities. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 2416–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, R.S.; Baumgarten, A.; Colvara, B.C.; Brochier, C.W.; Goulart, B.N.G.; Hugo, F.N.; Hilgert, J.B. Association between oropharyngeal dysphagia, oral functionality, and oral sensorimotor alteration. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, R.S.; Hugo, F.N.; Baumgarten, A.; Santos, K.W.; Goulart, B.N.G.; Hilgert, J.B. Development of a simplified dysphagia assessment by dentists in older persons. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2018, 46, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, M.J.; Knebl, J.; Tully, J. Prandial aspiration and pneumonia in an elderly population followed over 3 years. Dysphagia 1996, 11, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmore, S.E.; Terpenning, M.S.; Schork, A.; Chen, Y.; Murray, J.T.; Lopatin, D.; Loesche, W.J. Predictors of aspiration pneumonia: How important is dysphagia? Dysphagia 1998, 13, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabia-Cobo, C.M.; Pérez, V.; de Lorena, P.; Domínguez, E.; Hermosilla, C.; Nuñez, M.J.; Vigueiro, M.; Rodríguez, L. The incidence and prognostic implications of dysphagia in elderly patients institutionalized: A multicenter study in Spain. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2016, 30, e6–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MapChart. World Map-Simple: Create a Custom Map. Available online: https://www.mapchart.net/world.html (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, F.; Han, X.; Yang, Q.; Lin, T.; Zhou, H.; Tang, M.; Zhou, J.; Shi, H.; et al. Prevalence of Dysphagia in China: An Epidemiological Survey of 5943 Participants. Dysphagia 2021, 36, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Logemann, J.A. Patient Self-Perceptions of Swallowing Difficulties as Compared to Expert Ratings of Videofluorographic Studies. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2008, 60, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, N.; Patterson, J. Dysphagia: Implications for older people. Rev. Clin. Gerontol. 2014, 24, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-H.; Golub, J.S.; Hapner, E.R.; Johns, M.M. Prevalence of Perceived Dysphagia and Quality-of-Life Impairment in a Geriatric Population. Dysphagia 2009, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namasivayam-Macdonald, A.M.; Steele, C.M.; Keller, H.H. Perception Versus Performance of Swallow Function in Residents of Long-Term Care. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2019, 28, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Kent, B.; Cui, Y. Interventions to prevent aspiration in older adults with dysphagia living in nursing homes: A scoping review. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederman, M.S.; Cilloniz, C. Aspiration pneumonia. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2022, 35, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umay, E.; Eyigor, S.; Bahat, G.; Halil, M.; Giray, E.; Unsal, P.; Unlu, Z.; Tikiz, C.; Vural, M.; Cincin, A.T.; et al. Best Practice Recommendations for Geriatric Dysphagia Management with 5 Ws and 1H. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2022, 26, 94–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engh, M.C.N.; Speyer, R. Management of Dysphagia in Nursing Homes: A National Survey. Dysphagia 2022, 37, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pownall, S.; Barnett, E.; Skilbeck, J.; Jimenez-Aranda, A.; Fowler-Davis, S. The Development of a Digital Dysphagia Guide with Care Homes: Co-Production and Evaluation of a Nutrition Support Tool. Geriatrics 2019, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiss, C.J.P.R.D.; Goldberg, L.P.; Dzarnoski, M.P.R.D. Registered Dietitians and Speech-Language Pathologists: An Important Partnership in Dysphagia Management. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 1290–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, R. Nutrition Issues in Dysphagia: Identification, Management, and the Role of the Dietitian. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 1999, 14, S47–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Government Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission. Clinical Governance in Aged Care. Available online: https://www.agedcarequality.gov.au/sites/default/files/media/Fact_sheet_2_Clinical_governance_and_the_Aged_Care_Quality_Standards.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Doan, T.-N.; Ho, W.-C.; Wang, L.-H.; Chang, F.-C.; Nhu, N.T.; Chou, L.-W. Prevalence and Methods for Assessment of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchall, O.; Bennett, M.; Lawson, N.; Cotton, S.M.; Vogel, A.P. The Role of Instrumental Swallowing Assessment in Adults in Residential Aged Care Homes: A National Modified Delphi Survey Examining Beliefs and Practices. Dysphagia 2022, 37, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Kim, J.-S.; Jang, I.; Kim, H. Factors related to dysphagia-specific quality of life in aged patients with neurologic disorders: A cross-sectional study. Geriatr. Nurs. 2022, 43, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, A.; Gonçalves, R.; Rodrigues, I.T. Dysphagia in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2022, 16, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drancourt, N.; El Osta, N.; Decerle, N.; Hennequin, M. Relationship between Oral Health Status and Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Older People: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janto, M.; Iurcov, R.; Daina, C.M.; Neculoiu, D.C.; Venter, A.C.; Badau, D.; Cotovanu, A.; Negrau, M.; Suteu, C.L.; Sabau, M.; et al. Oral Health among Elderly, Impact on Life Quality, Access of Elderly Patients to Oral Health Services and Methods to Improve Oral Health: A Narrative Review. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farpour, S.; Smithard, D.; Farpour, H.R. Dysphagia and Oral Health in Older People. OBM Geriatr. 2020, 4, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenring, E.A.P.A.; Banks, M.P.A.; Ferguson, M.P.R.D.A.; Bauer, J.D.P.A. Beyond Malnutrition Screening: Appropriate Methods to Guide Nutrition Care for Aged Care Residents. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namasivayam, A.M.; Steele, C.M. Malnutrition and Dysphagia in Long-Term Care: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 34, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanař, V.; Hödl, M.; Lohrmann, C.; Amir, Y.; Eglseer, D. Dysphagia and factors associated with malnutrition risk: A 5-year multicentre study. J. Adv. Nurs. 2019, 75, 3566–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajati, F.; Ahmadi, N.; Naghibzadeh, Z.A.-S.; Kazeminia, M. The global prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in different populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author, Year, Country | Study Type | Sample Size (n) | Age (Years) | Gender (% Male) | Prevalence of Dysphagia (n, %) | Tool for Dysphagia Assessment | Professional Who Conducted Dysphagia Assessment | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brochier et al., 2018, Brazil [59] | Prospective cross-sectional | 115 (3 long term care residences) | ≥60 Age range: 60–70 (19.1%) 71–80 (36.6%) ≥81 (44.3%) | 33% M | 70/115 (60.9%) In nervous system diseases: Not reported. In Dementia: Not reported. In Malnutrition: Not reported. In poor dentition: Not reported. | CSE | SLP | Higher xerostomia associated with oropharyngeal dysphagia (p < 0.001). Population able to provide informed consent. |
| Feinberg et al., 1996, USA [64] | Prospective cohort | 152 (Single long-term care facility) | Mean age: 86 Age range: 78–96 | 36.8% M | 102/152 (67%) Oropharyngeal dysphagia: 81/102 (79%) Oesophageal dysphagia: 19/102 (18.6%) In nervous system diseases: Not reported. In dementia: Not reported. In malnutrition: Not reported. In poor dentition: Not reported. | VFSSCSE | CSE—SLP VFSS—Unclear, likely SLP | VFSS completed by 52/152 had 0% history of noted dysphagia (i.e., silent aspiration apparent). Method for gaining consent not reported. |
| Hollaar et al., 2017 The Netherlands [60] | Retrospective cross-sectional | 373 (3 nursing homes) | ≥65 Mean age with dysphagia: 82.2 ± 9.1 Mean age without dysphagia: 83.5 ± 7.8 | 30.3% M | 59/373 (16%) In nervous system diseases: 18/59 (31%) In dementia: Not reported. In malnutrition: Not reported. In poor dentition: Not reported. | Data obtained from medical records. Original diagnostic tool: CSE upon admission, CSE after a cerebrovascular accident or in case of a history of cerebrovascular accident at the time of admission, CSE after reported clinical symptoms of or complaints about swallowing problems or previously registered signs and symptoms in the electronic medical file before admission. | SLP | Number of diagnostic methods completed by SLP unclear. Where dysphagia diagnosis was unclear, the SLP and elderly care physician were consulted for additional information. Method for gaining consent not reported. |
| Langmore et al., 1998, USA [65] | Prospective cohort | 41 (Single nursing home care centre) | ≥60 | 100% M | 25/41 (61.6%) In nervous system diseases: Not reported. In dementia: Not reported. In malnutrition: Not reported. In poor dentition: Not reported. | CSE, VFSS, Scintigraphy examinations (~50% of subjects); Modified FEES (~50% of subjects). | Unclear—likely SLP | 81% of subjects with aspiration pneumonia had oropharyngeal dysphagia. Population able to provide informed consent. |
| Pu et al., 2017, China [61] | Prospective cross-sectional | 584 (22 long term care facilities) | ≥ 60 Mean age: 84.5 ± 7.9 Mean age with dysphagia: 85 Mean age without dysphagia: 83.6 Age range: 56–105 Median age: 85 | Not reported. | 356/584 (61.1%) In nervous system diseases: Not reported. In dementia: Not reported. In malnutrition: Not reported. In poor dentition: Not reported. | CSE | SLP and trained research assistants including SLP students | Risk of dysphagia for total sample higher in those with pneumonia (OR 3.578 95% CI: 1.568–8.168, p = 0.002). Population able to provide informed consent. |
| Rech et al., 2018 [62] (a) and Rech et al., 2018 [63] (b), Brazil | Prospective cross-sectional | 123 (exact number of long-term care facilities not reported, located in 3 separate towns) | ≥60 years Mean age: 73.5 ± 8.9 | 34.1% M | CSE: 75/123 (61%) EAT-10 tool: 25/123 (20.3%) DenSAT tool: 65/123 (52.8%) In nervous system diseases: Not reported. In dementia: Not reported. In malnutrition: Not reported. In those with partially functional dentition: 14/75 (18.7%). In those with Nonfunctional dentition: 55/75 (73.3%). | CSE, EAT-10 screening questionnaire; DenSAT assessment tool: Developed by 3 × SLP and conducted by dentists. Questionnaire—Subjective dysphagia. Oral motor and functionality assessment; Swallow assessment. | CSE—SLP DenSAT—Dentist | Dysphagia in those with ≥4 oral sensory motor alterations: 54/75 (72%). Only 27.6% reported difficulty swallowing (i.e., silent aspiration apparent). 47.3% of individuals with dysphagia also had a BMI <24.9 (underweight). Population able to provide informed consent. |
| Sarabia-Cobo et al., 2016, Spain [66] | Prospective cohort | 2384 (12 nursing homes) | Mean age: 88.7 ± 6.8 Mean age with dysphagia: 89.4 ± 6.3 Age range: 69–101 | 26.6% | 1659/2384 (69.6%) In nervous system diseases: Not reported. In dementia: 1135/1659 (68.4%) In malnutrition: Not reported. In poor dentition: Not reported. | Data obtained from medical records. Original diagnostic tool: CSE. | Doctor | Positive correlation between the presence of neurological disease and dysphagia (rho = 0.56, p = 0.00), cognitive impairment and dysphagia (rho = 0.61, p = 0.01) and dysphagia and functional capacity (r = 0.65, p = 0.00). Method for gaining consent not reported. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roberts, H.; Lambert, K.; Walton, K. The Prevalence of Dysphagia in Individuals Living in Residential Aged Care Facilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare 2024, 12, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12060649
Roberts H, Lambert K, Walton K. The Prevalence of Dysphagia in Individuals Living in Residential Aged Care Facilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare. 2024; 12(6):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12060649
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoberts, Hollie, Kelly Lambert, and Karen Walton. 2024. "The Prevalence of Dysphagia in Individuals Living in Residential Aged Care Facilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Healthcare 12, no. 6: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12060649
APA StyleRoberts, H., Lambert, K., & Walton, K. (2024). The Prevalence of Dysphagia in Individuals Living in Residential Aged Care Facilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare, 12(6), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12060649






