Potential Impact of Physical Activity on Measures of Well-Being and Quality of Life in People with Rare Diseases: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
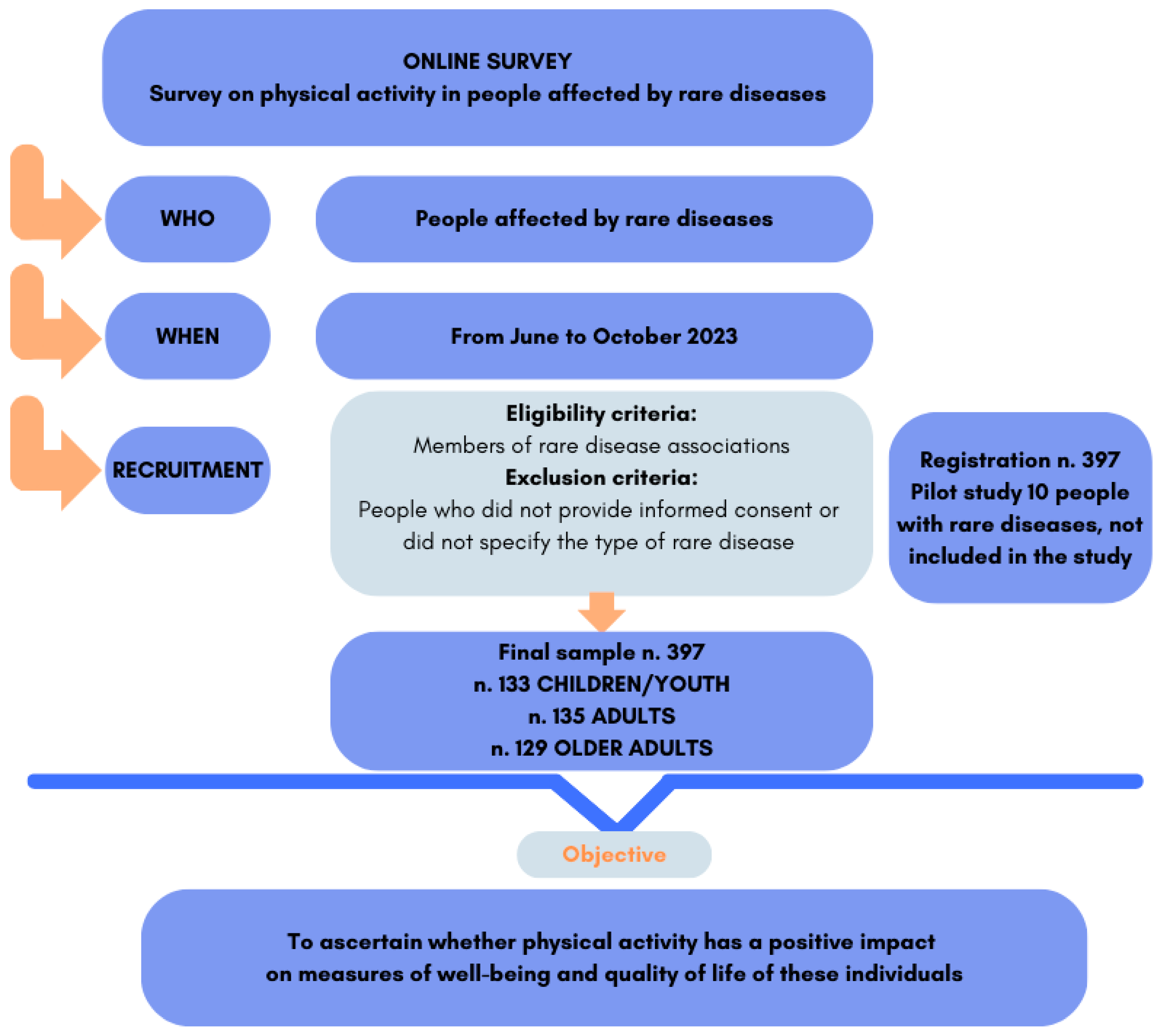
2.1. Design and Sample of the Study
2.2. Procedure for Data Collection
2.3. Instrument for Collecting Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
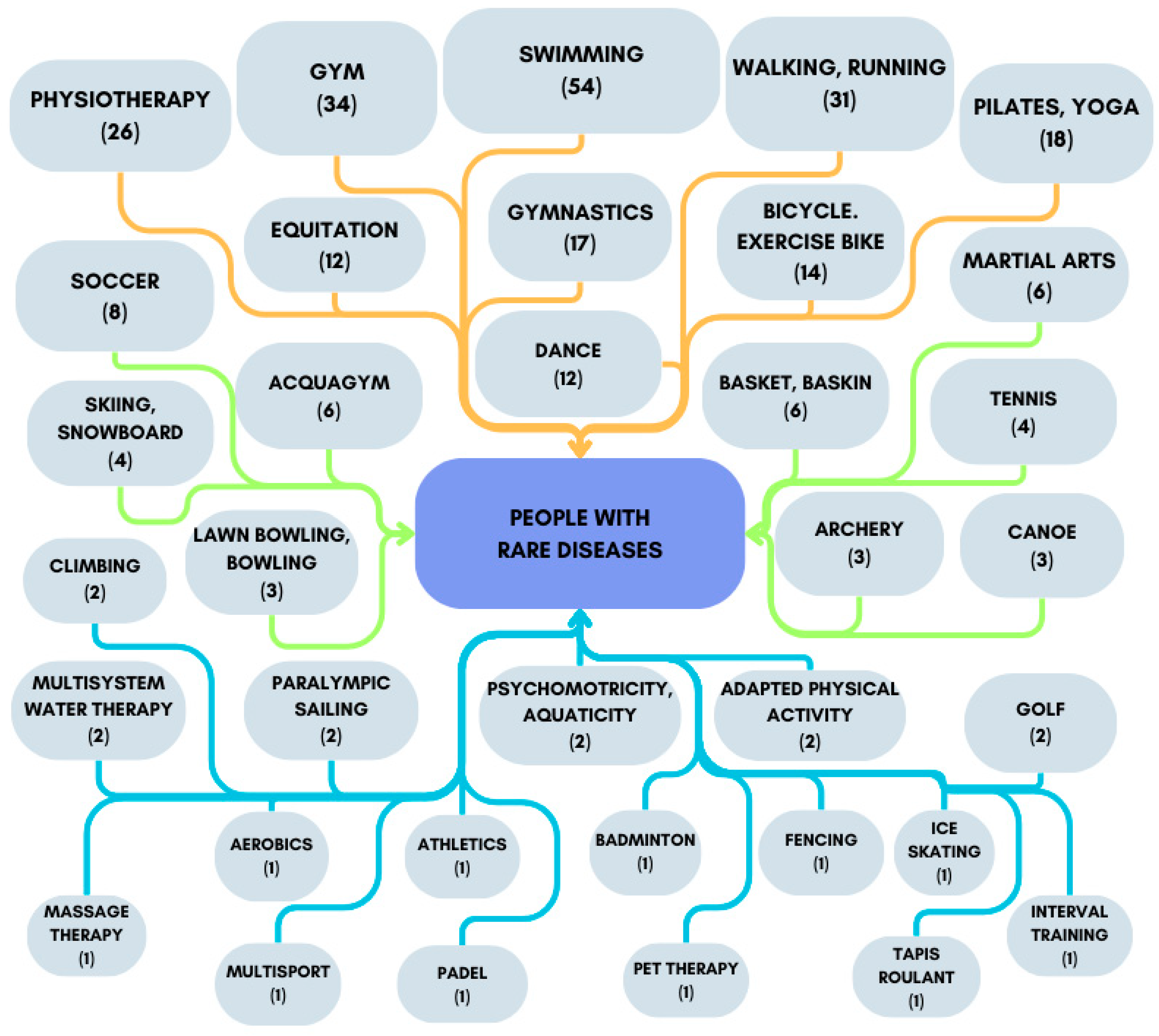
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic and Medical History Characteristics
3.2. The Importance of PA between and within Age Groups
3.3. The Reasons Why PA Is Not Practiced by Age Groups
3.4. The Evaluation of State or Local Support, Suitability of Facilities, and Trained Personnel for PA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ISS Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Malattie Rare. 2021. Available online: https://www.iss.it/malattie-rare (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Wakap, S.N.; Lambert, D.M.; Olry, A.; Rodwell, C.; Gueydan, C.; Lanneau, V.; Murphy, D.; Le Cam, Y.; Rath, A. Estimating cumulative point prevalence of rare diseases: Analysis of the Orphanet database. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nation Resolution. Addressing the Challenges of Persons Living with a Rare Disease and Their Families: Resolution/Adopted by the General Assembly; On Report of the Third Committee, 16 December 2021: 76/132; United Nation Resolution: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.rarediseasesinternational.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Final-UN-Text-UN-Resolution-on-Persons-Living-with-a-Rare-Disease-and-their-Families.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Tukker, A.; Royal, C.D.; Bowman, A.B.; McAllister, K.A. The Impact of Environmental Factors on Monogenic Mendelian Diseases. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 181, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWhorter, N.; Ndugga-Kabuye, M.K.; Puurunen, M.; Ernst, S.L. Complications of the Low Phenylalanine Diet for Patients with Phenylketonuria and the Benefits of Increased Natural Protein. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliberti, S.M.; De Caro, F.; Funk, R.H.W.; Schiavo, L.; Gonnella, J.; Boccia, G.; Capunzo, M. Extreme Longevity: Analysis of the Direct or Indirect Influence of Environmental Factors on Old, Nonagenarians, and Centenarians in Cilento, Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliberti, S.M.; Funk, R.H.W.; Ciaglia, E.; Gonnella, J.; Giudice, A.; Vecchione, C.; Puca, A.A.; Capunzo, M. Old, Nonagenarians, and Centenarians in Cilento, Italy and the Association of Lifespan with the Level of Some Physicochemical Elements in Tap Drinking Water. Nutrients 2023, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliberti, S.M.; Donato, A.; Funk, R.H.W.; Capunzo, M. A Narrative Review Exploring the Similarities between Cilento and the Already Defined “Blue Zones” in Terms of Environment, Nutrition, and Lifestyle: Can Cilento Be Considered an Undefined “Blue Zone”? Nutrients 2024, 16, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barg, C.J.; Armstrong, B.D.; Hetz, S.P.; Latimer, A.E. Physical disability, stigma, and physical activity in children. Int. J. Disabil. Dev. Educ. 2010, 57, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.J. Benefits and barriers to physical activity for individuals with disabilities: A social-relational model of disability perspective. Disabil. Rehabil. 2013, 35, 2030–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascondo, J.; Martín-López, A.; Iturricastillo, A.; Granados, C.; Garate, I.; Romaratezabala, E.; Martínez-Aldama, I.; Romero, S.; Yanci, J. Analysis of the Barriers and Motives for Practicing Physical Activity and Sport for People with a Disability: Differences According to Gender and Type of Disability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeting, J.; Merom, D.; Astuti, P.A.S.; Antoun, M.; Edwards, K.; Ding, D. Physical activity interventions for adults who are visually impaired: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e34036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitchison, B.; Rushton, A.B.; Martin, P.; Barr, M.; Soundy, A.; Heneghan, N.R. The experiences and perceived health benefits of individuals with a disability participating in sport: A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Disabil. Health J. 2022, 15, 101164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claridge, E.A.; Bloemen, M.A.T.; Rook, R.A.; Obeid, J.; Timmons, B.W.; Takken, T.; Van Den Berg-Emons, R.J.G.; De Groot, J.F.; Gorter, J. Physical activity and sedentary behaviour in children with spina bifida. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, T.J.; McIsaac, T.; Douillette, K.; Gaulton, N.; Hunter, S.; Rhodes, R.E.; Prince, S.A.; Carson, V.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; et al. Sedentary behaviour and health in adults: An overview of systematic reviews. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, S197–S217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin Ginis, K.A.; van der Ploeg, H.P.; Foster, C.; Lai, B.; McBride, C.B.; Ng, K.; Pratt, M.; Shirazipour, C.H.; Smith, B.; Vásquez, P.M.; et al. Participation of people living with disabilities in physical activity: A global perspective. Lancet 2021, 398, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliberti, S.M.; Cavallo, P.; Capunzo, M.; Brongo, S.; Giraldi, L.; Santoro, E.; Boccia, G. Relationship between health, lifestyle, psychosocial factors and academic performance: A cross-sectional study at the University of Salerno. Epidemiol. Biostat. Public Health 2019, 16, e12938-1. [Google Scholar]
- WHO World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD). Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/37108/9241544554.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Vahedi, M.; Rahimzadeh, M. Sample size calculation in medical studies. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2013, 6, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Caspersen, C.J.; Powell, K.F.; Christenson, G.M. Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: Definitions and distinctions for health–related research. Public Health Rep. 1985, 100, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kruk, J. Physical Activity and Health. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2009, 10, 721–728. [Google Scholar]
- Jacinto, M.; Oliveira, R.; Brito, J.P.; Martins, A.D.; Matos, R.; Ferreira, J.P. Prescription and Effects of Strength Training in Individuals with Intellectual Disability-A Systematic Review. Sports 2021, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 9789240015128. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, D.F.; Madans, J.; Anda, R.F.; Kleinman, J.C.; Kahn, H.S.; Byers, T. Recreational physical activity and ten-year weight change in a US national cohort. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1993, 17, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, D.L.; Johannsen, N.M.; Lavie, C.J.; Earnest, C.P.; Church, T.S. The role of exercise and physical activity in weight loss and maintenance. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, J.E.; Blair, S.N.; Jakicic, J.M.; Manore, M.M.; Rankin, J.W.; Smith, B.K.; American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Appropriate physical activity intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saris, W.H.M.; Blair, S.N.; Van Baak, M.A.; Eaton, S.B.; Davies, P.S.W.; Di Pietro, L.; Fogelholm, M.; Rissanen, A.; Schoeller, D.; Swinburn, B.; et al. How much physical activity is enough to prevent unhealthy weight gain? Outcome of the IASO 1st Stock Conference and consensus statement. Obes. Rev. 2003, 4, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO QoL Group. Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment. Psychol. Med. 1998, 28, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogart, K.; Hemmesch, A.; Barnes, E.; Blissenbach, T.; Beisang, A.; Engel, P.; Chloe Barnes Advisory Council on Rare Diseases. Healthcare access, satisfaction, and health-related quality of life among children and adults with rare diseases. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, O.; Amayra, I.; López-Paz, J.F.; Lázaro, E.; Caballero, P.; García, I.; Rodríguez, A.A.; García, M.; Luna, P.M.; Pérez-Núñez, P.; et al. Effects of Teleassistance on the Quality of Life of People with Rare Neuromuscular Diseases According to Their Degree of Disability. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 637413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.; Lambert, C.; Coulthard, L.; Pennington, L.; Kolehmainen, N. Social participation to support good mental health in neurodisability. Child Care Health Dev. 2021, 47, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, Z.I.; Jose, P.E.; Koyanagi, A.; Meilstrup, C.; Nielsen, L.; Madsen, K.R.; Koushede, V. Formal social participation protects physical health through enhanced mental health: A longitudinal mediation analysis using three consecutive waves of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE). Soc. Sci. Med. 2020, 251, 112906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Feng, Z.; Gong, S.; Dong, D. Social activity as mediator between social support and psychological quality of life among people with rare diseases: A national repetitive cross-sectional study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 150, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Cramm, J.M.; Nieboer, A.P. Social participation is an important health behaviour for health and quality of life among chronically ill older Chinese people. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliberti, S.M.; Funk, R.H.W.; Schiavo, L.; Giudice, A.; Ciaglia, E.; Puca, A.A.; Gonnella, J.; Capunzo, M. Clinical Status, Nutritional Behavior, and Lifestyle, and Determinants of Community Well-Being of Patients from the Perspective of Physicians: A Cross-Sectional Study of Young Older Adults, Nonagenarians, and Centenarians in Salerno and Province, Italy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disease Classification ICD-10 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Macrodomain | Block | Disease |
| Neoplasms | Malignant neoplasms | Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer syndrome Epithelioid sarcoma Lymphoplasmacytic leukaemia |
| Benign neoplasms | Lymphangioma | |
| Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | Coagulation defects, purpura, and other haemorrhagic conditions | Glanzmann disease Haemophilia |
| Certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | Di George syndrome Sarcoidosis of lung | |
| Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Metabolic disorders | Phenylketonuria Muscle carnitine palmityltransferase deficiency Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency Homocystinuria Gaucher disease Renal tubulo-interstitial disorders in cystinosis Fabry disease Hunter syndrome Sanfilippo syndrome Acute porphyria Neuropathic heredofamilial amyloidosis Familial partial lipodystrophy |
| Mental and behavioural disorders | Disorders of psychological development | Autism Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein syndrome Rett syndrome |
| Diseases of the nervous system | Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system | Friedreich ataxia (autosomal recessive) Ataxia telangiectasia Hereditary spastic paraplegy Spinal muscular atrophy |
| Polyneuropathies and other disorders of the peripheral nervous system | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy Other polyneuropathy | |
| Diseases of the myoneural junction and muscle | Myasthenia gravis Myotonic dystrophy Nemaline myopathy Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy | |
| Episodic and paroxysmal disorders | Dravet syndrome (severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy) Ondine’s curse | |
| Other disorders of the nervous system | Myalgic encephalomyelitis | |
| Non-classified/non-specified | Cerebral angiopathy due to COL4A1 mutations, motor impairment, hemiparesis, epilepsy | |
| Diseases of the eye and adnexa | Disorders of choroid and retina | Retinitis pigmentosa |
| Diseases of the circulatory system | Diseases of arteries, arterioles and capillaries | Raynaud syndrome |
| Other forms of heart disease | Long QT syndrome Short QT syndrome | |
| Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes not elsewhere classified | Primary lymphoedema | |
| Diseases of the respiratory system | Other respiratory diseases principally affecting the interstitium | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| Diseases of the digestive system | Diseases of the oesophagus, stomach and duodenum | Achalasia of cardia |
| Noninfective enteritis and colitis | Crohn disease Ulcerative colitis | |
| Diseases of liver | Hepatoportal sclerosis | |
| Non-classified/non-specified | Inflammatory bowel disease, short bowel syndrome, stoma carrier | |
| Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue | Atrophic disorders of the skin | Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus |
| Urticaria and erythema | Urticaria due to cold and heat | |
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | Inflammatory polyarthropathies | Still disease |
| Systemic connective tissue disorders | Systemic lupus erythematosus Scleroderma Sjögren disease Behçet disease Antisynthetase syndrome | |
| Spondylopathies | Ankylosing spondylitis | |
| Soft tissue disorders | Fibromyalgia Myositis | |
| Inflammatory polyarthropathies | Psoriatic arthritis | |
| Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities | Congenital malformations and deformations of the musculoskeletal system | Macrodactylia Ehlers-Danlos syndrome |
| Other congenital malformations | Epidermolysis bullosa Ectrodactyly-ectodermal dysplasia- clefting syndrome Neurofibromatosis CHARGE syndrome Alport syndrome Marfan syndrome Sotos syndrome Malan syndrome Prader–Willi syndrome | |
| Characteristics of Respondents (Tot Sample = 397) | Doing PA (Tot Sample = 205) | Not doing PA (Tot Sample = 192) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | |
| Age in groups of year | ||||
| Children/Youth (7–22) | 70 | 34.1 | 53 | 32.8 |
| Adults (23–50) | 78 | 48.1 | 57 | 29.7 |
| Older adults (>50) | 57 | 27.8 | 72 | 37.5 |
| Region | ||||
| Piedmont | 12 | 5.8 | 8 | 4.2 |
| Liguria | 5 | 2.4 | 1 | 0.5 |
| Lombardy | 41 | 20 | 33 | 17.2 |
| Trentino-Alto Adige | 2 | 0.9 | - | - |
| Veneto | 21 | 10.2 | 17 | 8.8 |
| Friuli-Venezia Giulia | 10 | 4.8 | - | - |
| Emilia-Romagna | 12 | 5.8 | 16 | 8.3 |
| Tuscany | 23 | 11.2 | 15 | 7.8 |
| Umbria | 3 | 1.5 | - | - |
| Marche | - | - | 4 | 0.2 |
| Lazio | 33 | 16.1 | 27 | 14.1 |
| Abruzzo | 8 | 3.9 | 6 | 0.3 |
| Molise | 1 | 0.5 | - | - |
| Campania | 12 | 5.8 | 35 | 18.2 |
| Apulia | 11 | 5.3 | 7 | 3.6 |
| Basilicata | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.1 |
| Sicily | 1 | 0.5 | 7 | 3.6 |
| Sardinia | 7 | 3.4 | 8 | 4.2 |
| Disease Macrodomains (WHO ICD-10 classification) | ||||
| Neoplasms (CD) | 8 | 3.9 | 2 | 0.1 |
| Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases (E) | 11 | 5.3 | 15 | 7.8 |
| Diseases of the digestive system (K) | 5 | 2.4 | 8 | 4.2 |
| Diseases of the eye and adnexa (H) | - | - | 2 | 0.1 |
| Mental and behavioural disorder (F) | 13 | 6.3 | 13 | 6.8 |
| Diseases of the circulatory system (I) | 5 | 2.4 | 7 | 3.6 |
| Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities (Q) | 33 | 16.1 | 22 | 11.4 |
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue (M) | 23 | 11.2 | 22 | 11.4 |
| Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (L) | 23 | 11.2 | 18 | 9.3 |
| Diseases of the respiratory system (J) | 4 | 1.9 | 2 | 0.1 |
| Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism (D) | 15 | 7.3 | 12 | 6.2 |
| Diseases of the nervous system (G) | 63 | 30.7 | 65 | 33.8 |
| What are the Motivations behind Engaging in PA? | Children/Youth | Adults | Older Adults | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No % | Enough% | Very% | No% | Enough% | Very% | No% | Enough% | Very% | ||
| Improvement of disease problems | 27.1 | 50 | 22.9 | 23.1 | 43.6 | 33.3 | 24.6 | 49.1 | 26.3 | 0.475 |
| To control weight | 57.1 | 38.6 | 4.3 | 28.2 | 50 | 21.8 | 28.1 | 59.6 | 12.3 | <0.001 |
| To engage in social interaction with the goal of meeting friends or make new acquaintances | 28.5 | 58.6 | 12.9 | 51.3 | 35.9 | 12.8 | 43.8 | 52.7 | 3.5 | 0.046 |
| To enhance the physical condition | 14.3 | 61.4 | 24.3 | 5.1 | 48.7 | 46.2 | 3.5 | 63.2 | 33.3 | 0.005 |
| To enhance mental well-being | 11.4 | 61.4 | 27.2 | 11.5 | 46.2 | 42.3 | 1.8 | 61.4 | 36.8 | 0.159 |
| To surmount obstacles | 21.4 | 51.4 | 27.2 | 32.1 | 50 | 17.9 | 33.4 | 45.6 | 21 | 0.189 |
| To enhance one’s quality of life | 24.3 | 64.3 | 11.4 | 16.7 | 55.1 | 28.2 | 14 | 64.9 | 21.1 | 0.046 |
| It was recommended by the attending physician | 45.7 | 45.7 | 8.6 | 38.5 | 44.9 | 16.6 | 31.6 | 52.6 | 15.8 | 0.180 |
| Variable | IRR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1. Years of PA (Sample size = 203) Log likelihood = −779.1, x2 = 107.43 (12 df), p < 0.001 | |||
| Age in groups of years | |||
| Children/Youth | 1 a | ||
| Adults | 0.75 | 0.68–0.83 | <0.001 |
| Older adults | 0.67 | 0.59–0.75 | <0.001 |
| Disease Macrocategories | |||
| CD | 1 a | ||
| E | 0.78 | 0.62–0.97 | 0.031 |
| K | 0.80 | 0.58–1.09 | 0.169 |
| H | - | - | - |
| F | 0.65 | 0.51–081 | <0.001 |
| I | 0.91 | 0.69–1.19 | 0.523 |
| Q | 0.72 | 0.59–0.87 | 0.001 |
| M | 0.85 | 0.69–1.04 | 0.121 |
| L | 0.76 | 0.62–0.93 | 0.008 |
| J | 0.49 | 0.32–0.74 | 0.001 |
| D | 0.76 | 0.32–0.74 | 0.016 |
| G | 0.67 | 0.56–0.81 | <0.001 |
| Model 2. Disease Macrocategories (Sample size = 203) Log likelihood = −491.8, x2 = 19.55 (8 df), p = 0.012 | |||
| Age in groups of years | |||
| Children/Youth | 1 a | ||
| Adults | 0.91 | 0.77–1.07 | 0.267 |
| Older adults | 0.88 | 0.74–1.04 | 0.146 |
| Weekly hours of PA | |||
| One hour | 1 a | ||
| Two or two and a half hours weekly | 0.91 | 0.73–1.14 | 0.447 |
| Three hours weekly | 0.87 | 0.69–1.09 | 0.237 |
| Four hours weekly | 1.01 | 0.80–1.28 | 0.911 |
| Five hours weekly | 0.87 | 0.65–1.15 | 0.334 |
| Six hours weekly | 0.58 | 0.41–0.84 | 0.004 |
| >Of seven hours weekly | 0.73 | 0.54–1.00 | 0.056 |
| Model 3. Weekly hours of PA (Sample size = 205) Log likelihood = −392.7 x2 = 5.44 (1 df), p = 0.019 | |||
| Quality of Life | 0.84 | 0.73–0.97 | 0.020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aliberti, S.M.; Sacco, A.M.; Belviso, I.; Romano, V.; Di Martino, A.; Russo, E.; Collet, S.; Ciancaleoni Bartoli, I.; Tuzi, M.; Capunzo, M.; et al. Potential Impact of Physical Activity on Measures of Well-Being and Quality of Life in People with Rare Diseases: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Italy. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12181822
Aliberti SM, Sacco AM, Belviso I, Romano V, Di Martino A, Russo E, Collet S, Ciancaleoni Bartoli I, Tuzi M, Capunzo M, et al. Potential Impact of Physical Activity on Measures of Well-Being and Quality of Life in People with Rare Diseases: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Italy. Healthcare. 2024; 12(18):1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12181822
Chicago/Turabian StyleAliberti, Silvana Mirella, Anna Maria Sacco, Immacolata Belviso, Veronica Romano, Aldo Di Martino, Ettore Russo, Stefania Collet, Ilaria Ciancaleoni Bartoli, Manuel Tuzi, Mario Capunzo, and et al. 2024. "Potential Impact of Physical Activity on Measures of Well-Being and Quality of Life in People with Rare Diseases: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Italy" Healthcare 12, no. 18: 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12181822
APA StyleAliberti, S. M., Sacco, A. M., Belviso, I., Romano, V., Di Martino, A., Russo, E., Collet, S., Ciancaleoni Bartoli, I., Tuzi, M., Capunzo, M., Donato, A., Castaldo, C., Di Meglio, F., & Nurzynska, D. (2024). Potential Impact of Physical Activity on Measures of Well-Being and Quality of Life in People with Rare Diseases: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Italy. Healthcare, 12(18), 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12181822














