Structured Routine Use of Styletubation for Oro-Tracheal Intubation in Obese Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgeries—A Case Series Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arterburn, D.E.; Telem, D.A.; Kushner, R.F.; Courcoulas, A.P. Benefits and risks of bariatric surgery in adults: A review. JAMA 2020, 324, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunnaike, B.O.; Jones, S.B.; Jones, D.B.; Provost, D.; Whitten, C.W. Anesthetic considerations for bariatric surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 95, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, K.H.; Helm, M.; Lak, K.; Higgins, R.M.; Gould, J.C.; Kindel, T.L. The risk of post-operative complications in super-super obesity compared to super obesity in accredited bariatric surgery centers. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2964–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulier, J.P.; Dillemans, B. Anaesthetic factors affecting outcome after bariatric surgery, a retrospective levelled regression analysis. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinari, G.; Foletto, M.; Nagliati, C.; Navarra, G.; Borrelli, V.; Bruni, V.; Fantola, G.; Moroni, R.; Tritapepe, L.; Monzani, R.; et al. Enhanced recovery after bariatric surgery: An Italian consensus statement. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 7171–7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyni-Boureima, R.; Zhang, Z.; Antoine, M.M.L.K.; Antoine-Frank, C.D. A review on the anesthetic management of obese patients undergoing surgery. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Lingle, B.D.; Brothers, J.C.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Morris, A.G.; Greeson, E.M.; Cornett, E.M. The patient with obesity and super-super obesity: Perioperative anesthetic considerations. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2022, 16, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.; Wong, D.T. Airway management and oxygenation in obese patients. Can. J. Anaesth. 2013, 60, 929–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, E. Airway management of the morbidly obese patient. J. Perioper. Pract. 2016, 26, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.S.; Lemmens, H.J.; Brodsky, J.B.; Brock-Utne, J.G.; Levitan, R.M. Laryngoscopy and morbid obesity: A comparison of the “sniff” and “ramped” positions. Obes. Surg. 2004, 14, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.L.; Kunselman, A.R.; Schuler, H.G.; DesHarnais, S. Laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation in the head-elevated position in obese patients: A randomized, controlled, equivalence trial. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 107, 1912–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jang, E.A.; Hong, M.; Bae, H.B.; Kim, J. Ramped versus sniffing position in the videolaryngoscopy-guided tracheal intubation of morbidly obese patients: A prospective randomized study. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2023, 76, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, M.S. Airway management and morbid obesity. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 27, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thota, B.; Jan, K.M.; Oh, M.W.; Moon, T.S. Airway management in patients with obesity. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2022, 16, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neligan, P.J.; Porter, S.; Max, B.; Malhotra, G.; Greenblatt, E.P.; Ochroch, E.A. Obstructive sleep apnea is not a risk factor for difficult intubation in morbidly obese patients. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 109, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvin, P.; Lavaut, E.; Dupont, H.; Lefevre, P.; Demetriou, M.; Dumoulin, J.L.; Desmonts, J.M. Difficult tracheal intubation is more common in obese than in lean patients. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 97, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.H.; Ahn, H.J.; Lee, C.J.; Shin, B.S.; Ko, J.S.; Choi, S.J.; Ryu, S.A. Neck circumference to thyromental distance ratio: A new predictor of difficult intubation in obese patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2011, 106, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, A.; Molinari, N.; Pouzeratte, Y.; Verzilli, D.; Chanques, G.; Jung, B.; Futier, E.; Perrigault, P.F.; Colson, P.; Capdevila, X.; et al. Difficult intubation in obese patients: Incidence, risk factors, and complications in the operating theatre and in intensive care units. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, S.; Huang, S. The association of body mass index with difficult tracheal intubation management by direct laryngoscopy: A meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saasouh, W.; Laffey, K.; Turan, A.; Avitsian, R.; Zura, A.; You, J.; Zimmerman, N.M.; Szarpak, L.; Sessler, D.I.; Ruetzler, K. Degree of obesity is not associated with more than one intubation attempt: A large centre experience. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, T.S.; Fox, P.E.; Somasundaram, A.; Minhajuddin, A.; Gonzales, M.X.; Pak, T.J.; Ogunnaike, B. The influence of morbid obesity on difficult intubation and difficult mask ventilation. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, J.B.; Lemmens, H.J.; Brock-Utne, J.G.; Vierra, M.; Saidman, L.J. Morbid obesity and tracheal intubation. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riad, W.; Vaez, M.N.; Raveendran, R.; Tam, A.D.; Quereshy, F.A.; Chung, F.; Wong, D.T. Neck circumference as a predictor of difficult intubation and difficult mask ventilation in morbidly obese patients: A prospective observational study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2016, 33, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdilek, A.; Beyoglu, C.A.; Erbabacan, Ş.E.; Ekici, B.; Altındaş, F.; Vehid, S.; Köksal, G.M. Correlation of neck circumference with difficult mask ventilation and difficult laryngoscopy in morbidly obese patients: An observational study. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 2860–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrel, J.; Blanc, C.; Frascarolo, P.; Magnusson, L. Videolaryngoscopy improves intubation condition in morbidly obese patients. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2007, 24, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, R.; Galway, U.; You, J.; Kurz, A.; Sessler, D.I.; Doyle, D.J. A randomized comparison between the Pentax AWS video laryngoscope and the Macintosh laryngoscope in morbidly obese patients. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, D., Jr.; Filho, S.M.; Batista, S.; do Nascimento, P., Jr. Comparison of Macintosh and Airtraq™ laryngoscopes in obese patients placed in the ramped position. Anaesthesia 2012, 67, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.H.; Rovsing, L.; Olsen, K.S. GlideScope videolaryngoscope vs. Macintosh direct laryngoscope for intubation of morbidly obese patients: A randomized trial. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2011, 55, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshijima, H.; Denawa, Y.; Tominaga, A.; Nakamura, C.; Shiga, T.; Nagasaka, H. Videolaryngoscope versus Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in adults with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 2018, 44, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrin, T.; Szarpak, L.; Katipoglu, B.; Mishyna, N.; Kockan, B.S.; Ruetzler, K.; Schläpfer, M. Video-assisted versus macintosh direct laryngoscopy for intubation of obese patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Disaster Emerg. Med. J. 2022, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.R.; Jagannathan, N. Should videolaryngoscopy be the standard of care for routine tracheal intubation in obese adults? J. Clin. Anesth. 2018, 45, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.B.; Luk, H.-N. Sheet Barrier and Intubating Stylet. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 1058–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, H.N.; Luk, H.N.; Qu, Z.J.; Shikani, A. A paradigm shift of airway management: The role of video-assisted intubating stylet technique [Internet]. In Advances in Tracheal Intubation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, H.N.; Qu, J.Z.; Shikani, A. Styletubation: The paradigmatic role of video-assisted intubating stylet technique for routine tracheal intubation. Asian J. Anesthesiol. 2023, 61, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, H.N.; Qu, J.Z. Styletubation versus laryngoscopy: A new paradigm for routine tracheal intubation. Surgeries 2024, 5, 135–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikani, A.H. New “seeing” stylet-scope and method for the management of the difficult airway. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 1999, 120, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zundert, A.A.; Pieters, B.M. Combined technique using videolaryngoscopy and Bonfils for a difficult airway intubation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 108, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kelly, F.E.; Cook, T.M. Seeing is believing: Getting the best out of videolaryngoscopy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 117 (Suppl. 1), i9–i13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathory, I.; Granges, J.C.; Frascarolo, P.; Magnusson, L. Evaluation of the Video Intubation Unit in morbid obese patients. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2010, 54, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prekker, M.E.; Driver, B.E.; Trent, S.A.; Resnick-Ault, D.; Seitz, K.P.; Russell, D.W.; Gaillard, J.P.; Latimer, A.J.; Ghamande, S.A.; Gibbs, K.W.; et al. DEVICE investigators and the pragmatic critical care research group. Video versus direct laryngoscopy for tracheal intubation of critically ill adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumul, R.; Elvir-Lazo, O.L.; White, P.F.; Sloninsky, A.; Kaplan, M.; Kariger, R.; Naruse, R.; Parker, N.; Pham, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Comparison of three video laryngoscopy devices to direct laryngoscopy for intubating obese patients: A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Anesth. 2016, 31, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maassen, R.; Lee, R.; van Zundert, A.; Cooper, R. The videolaryngoscope is less traumatic than the classic laryngoscope for a difficult airway in an obese patient. J. Anesth. 2009, 23, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetzler, K.; Rivas, E.; Cohen, B.; Mosteller, L.; Martin, A.; Keebler, A.; Maheshwari, K.; Steckner, K.; Wang, M.; Praveen, C.; et al. McGrath video laryngoscope versus Macintosh direct laryngoscopy for intubation of morbidly obese patients: A randomized trial. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maassen, R.; Lee, R.; Hermans, B.; Marcus, M.; van Zundert, A. A comparison of three videolaryngoscopes: The Macintosh laryngoscope blade reduces, but does not replace, routine stylet use for intubation in morbidly obese patients. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 109, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treki, A.A.; Straker, T. Limitations of the videolaryngoscope: An anesthetic management reality. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2017, 55, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, S.Y.; Wong, T.G. Clinical uses of the Bonfils retromolar intubation fiberscope: A review. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 115, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.H.; Luk, H.N.; Qu, J.Z.; Shikani, A. An approach to improve the effectiveness of the video-assisted intubating stylet technique for tracheal intubation: A case series report. Healthcare 2023, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulds, L.T.; McGuire, B.E.; Shippey, B.J. A randomised cross-over trial comparing the McGrath(®) Series 5 videolaryngoscope with the Macintosh laryngoscope in patients with cervical spine immobilisation. Anaesthesia 2016, 71, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppan, L.; Tramèr, M.R.; Niquille, M.; Grosgurin, O.; Marti, C. Alternative intubation techniques vs Macintosh laryngoscopy in patients with cervical spine immobilization: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 116, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, B.N.; Morris, F.K.; Yet, B.; Buggy, D.J.; Perkins, Z.B. Effectiveness of intubation devices in patients with cervical spine immobilisation: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, H.; Park, H.P. Randomized crossover trial comparing cervical spine motion during tracheal intubation with a Macintosh laryngoscope versus a C-MAC D-blade videolaryngoscope in a simulated immobilized cervical spine. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; An, S.; Park, S.; Nahm, F.S.; Han, S.H.; Kim, J.H. Comparison of a new video intubation stylet and McGrath® MAC video laryngoscope for intubation in an airway manikin with normal airway and cervical spine immobilization scenarios by novice personnel: A randomized crossover study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4288367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, T.L.; Koay, K.P.; Hu, C.Y.; Luk, H.N.; Qu, J.Z.; Shikani, A. The use of the Shikani video-assisted intubating stylet technique in patients with restricted neck mobility. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eismann, H.; Sieg, L.; Etti, N.; Friedrich, L.; Schröter, C.; Mommsen, P.; Krettek, C.; Zeckey, C. Improved success rates using videolaryngoscopy in unexperienced users: A randomized crossover study in airway manikins. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2017, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.A.; Chaou, C.H.; Yu, S.R.; Kuan, J.T.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, H.P.; Chiu, T.F. Video assisted laryngoscope facilitates intubation skill learning in the emergency department. J. Acute Med. 2020, 10, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalubola, S.; Jin, E.; Drugge, E.D.; Weber, G.; Abramowicz, A.E. Video versus direct laryngoscopy in novice intubators: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 2022, 14, e29578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine-Brueggeney, M.; Greif, R.; Urwyler, N.; Wirthmüller, B.; Theiler, L. The performance of rigid scopes for tracheal intubation: A randomised, controlled trial in patients with a simulated difficult airway. Anaesthesia 2016, 71, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, L.; Greif, R.; Bütikofer, L.; Arheart, K.; Kleine-Brueggeney, M. The skill of tracheal intubation with rigid scopes-a randomised controlled trial comparing learning curves in 740 intubations. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.S.; Corey, T.; Luk, H.N.; Qu, J.Z.; Shikani, A. Combined styletubation with videolaryngoscopy for tracheal intubation in patients undergoing thyroidectomy with intraoperative neuromonitoring. Anesth. Res. 2024, 1, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.C.; Wu, Z.F.; Lai, M.F.; Lai, H.C. Combination use of laryngoscope, jaw thrust, and trachway for improving difficult tracheal intubation in obese. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 42, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhuang, B.J.; Luk, H.N.; Qu, J.Z.; Shikani, A. Video-twin technique for airway management, combining video-intubating stylet with videolaryngoscope: A case series report and review of the literature. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Kim, J.A.; Ahn, H.J.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, D.K.; Cho, E.A. Double-lumen tube tracheal intubation using a rigid video-stylet: A randomized controlled comparison with the Macintosh laryngoscope. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, K.Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, R.H. Comparison of video laryngoscope, video stylet, and flexible videoscope for transoral endotracheal intubation in patients with difficult airways: A randomized, parallel-group study. Trials 2023, 24, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, H.; Liu, M.; Feng, D.; Wei, J.; Min, K.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Y.; Lv, X. A randomized study of rigid video stylet versus Macintosh laryngoscope for double-lumen endobronchial tube intubation assistance in thoracoscopic pulmonary surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaszynski, T.; Pietrzyk, M.; Szewczyk, T.; Gaszynska, E. A comparison of performance of endotracheal intubation using the Levitan FPS optical stylet or Lary-Flex videolaryngoscope in morbidly obese patients. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 207591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
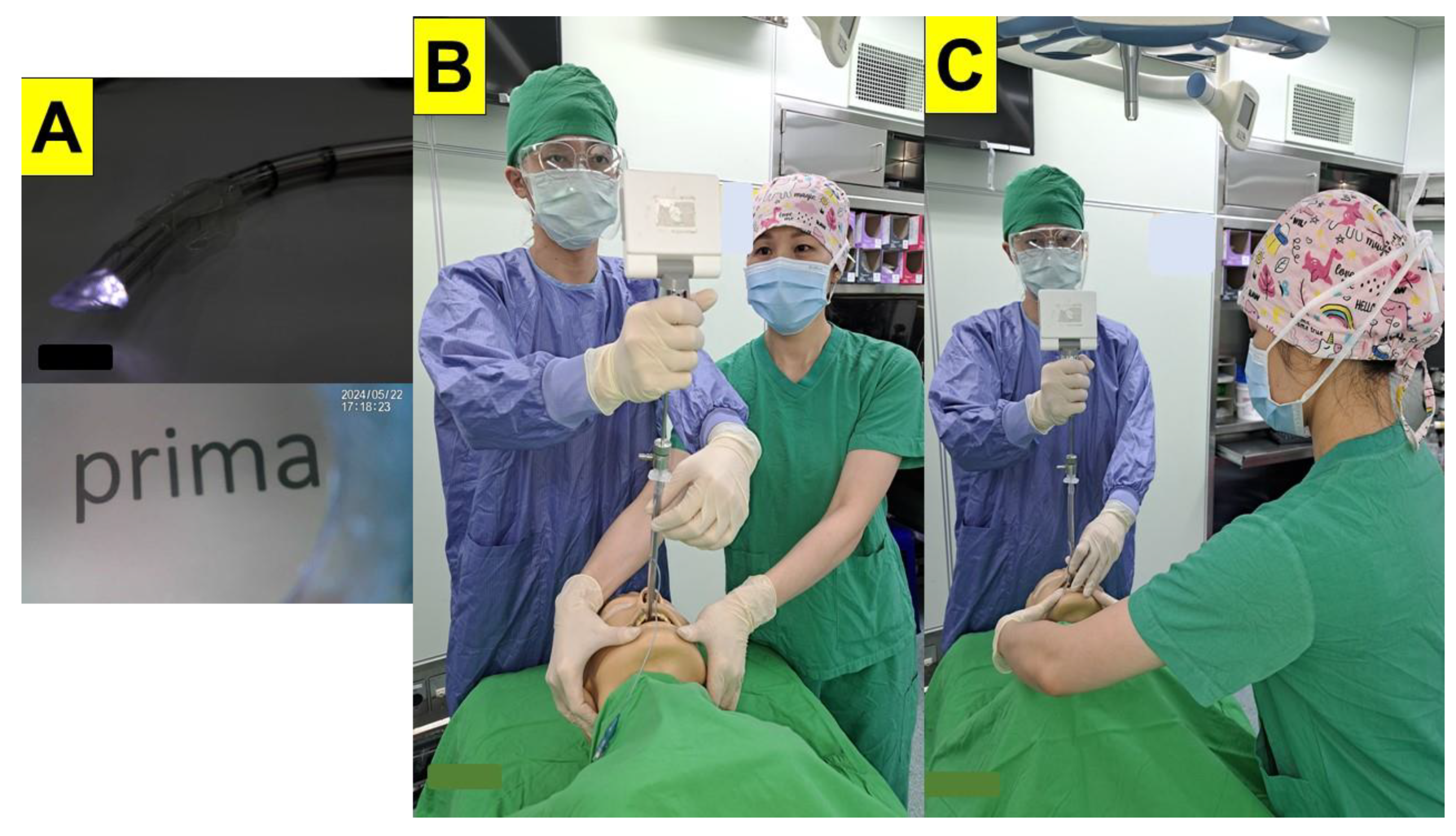
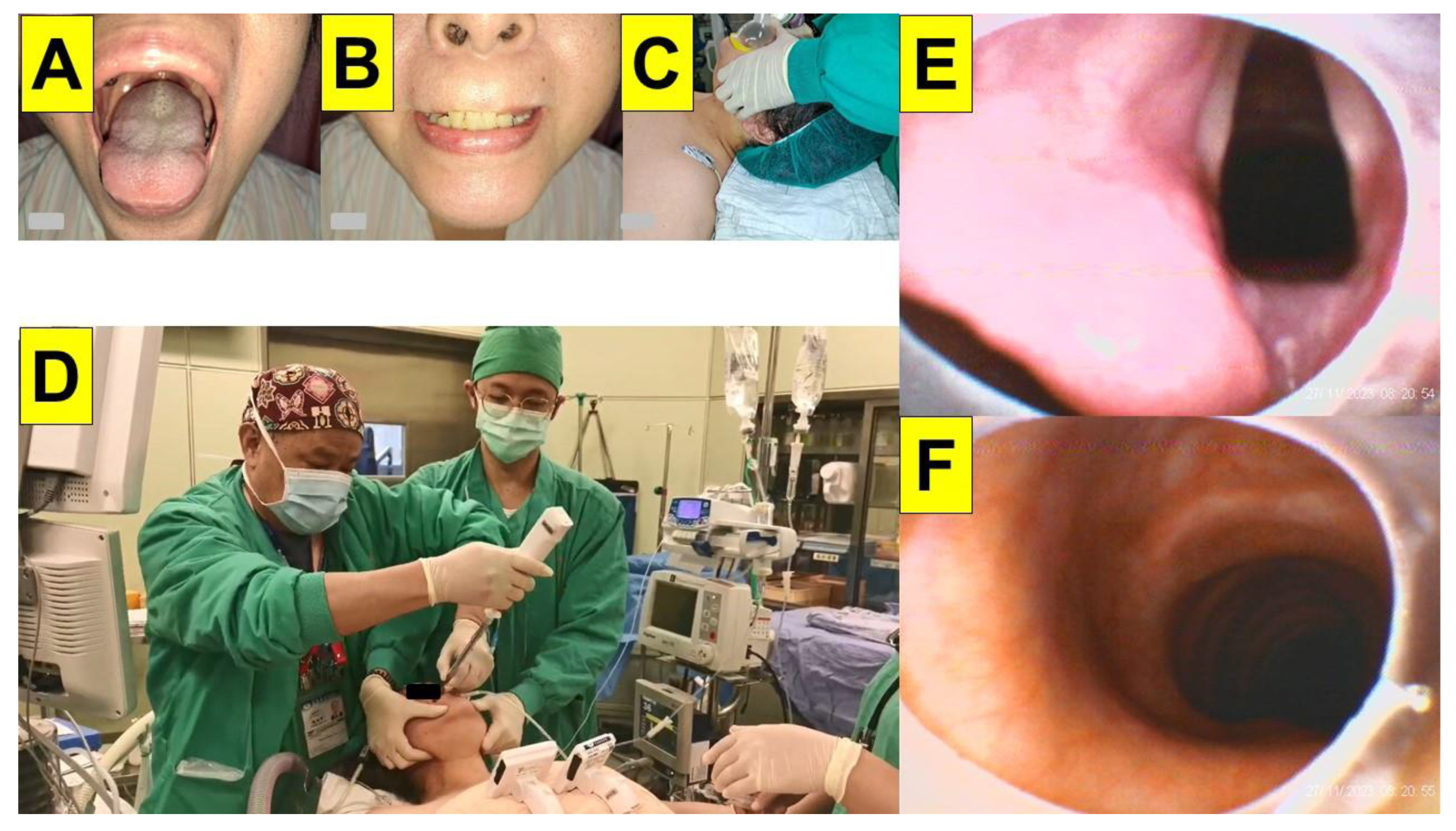


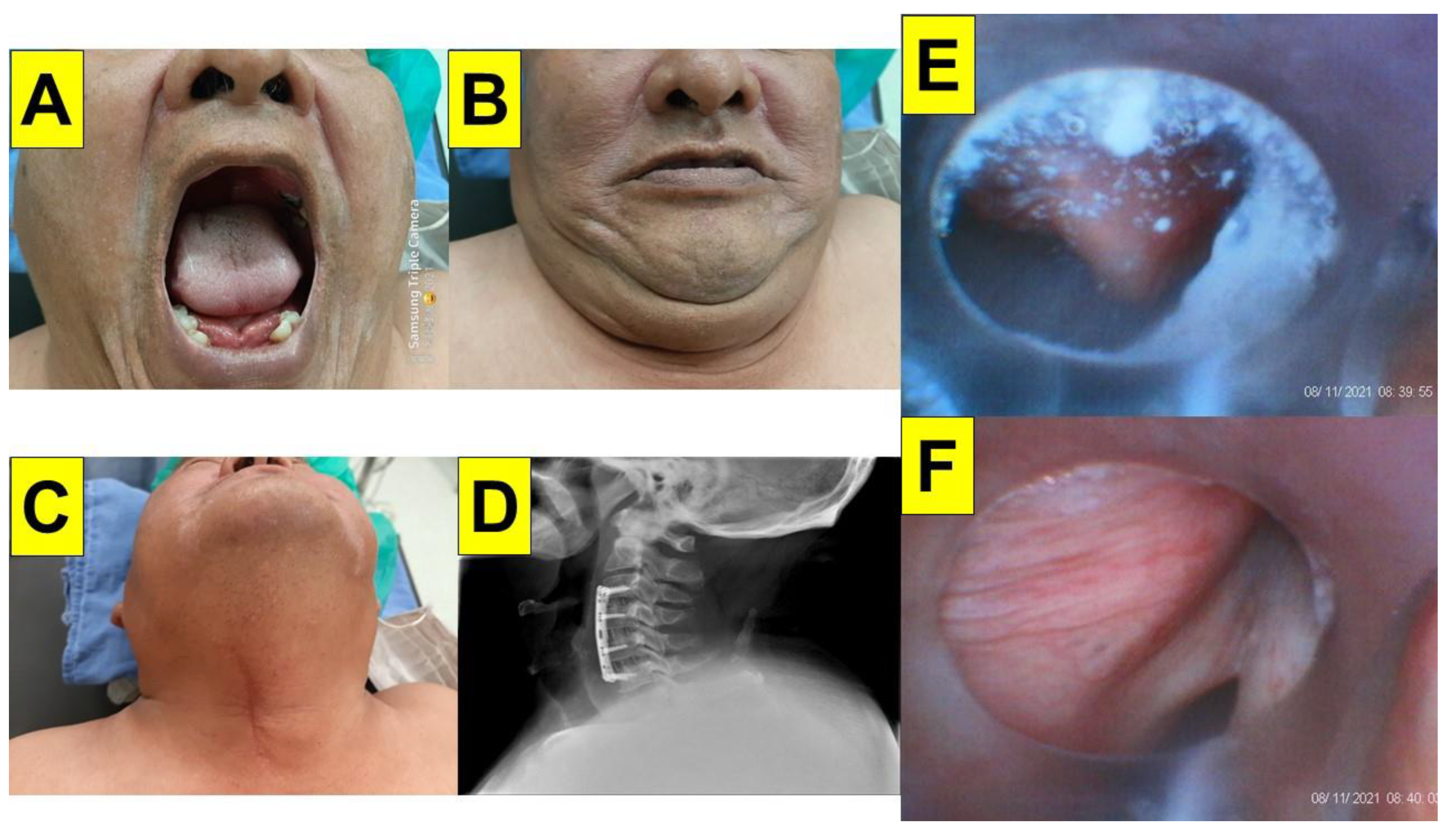
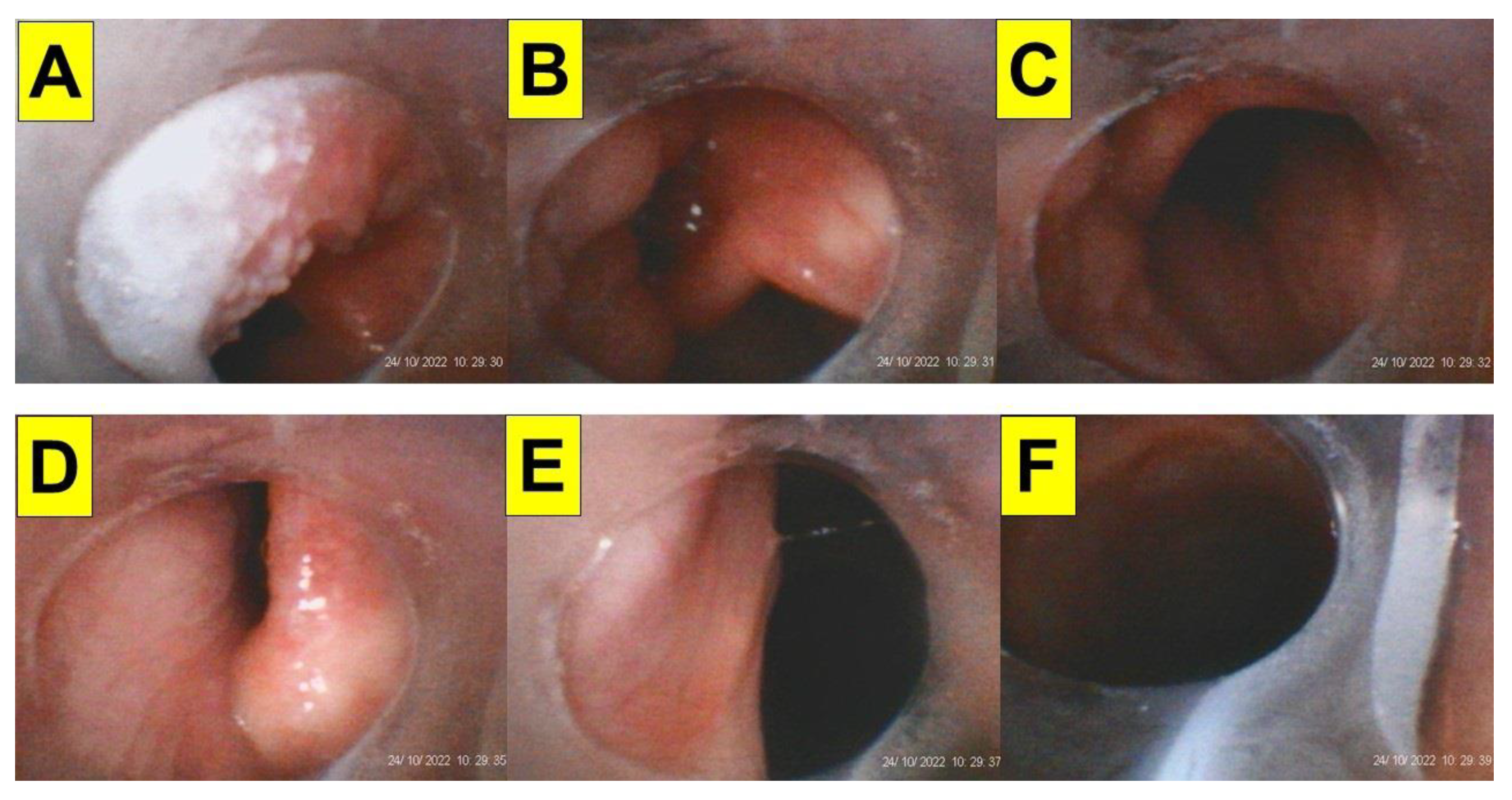
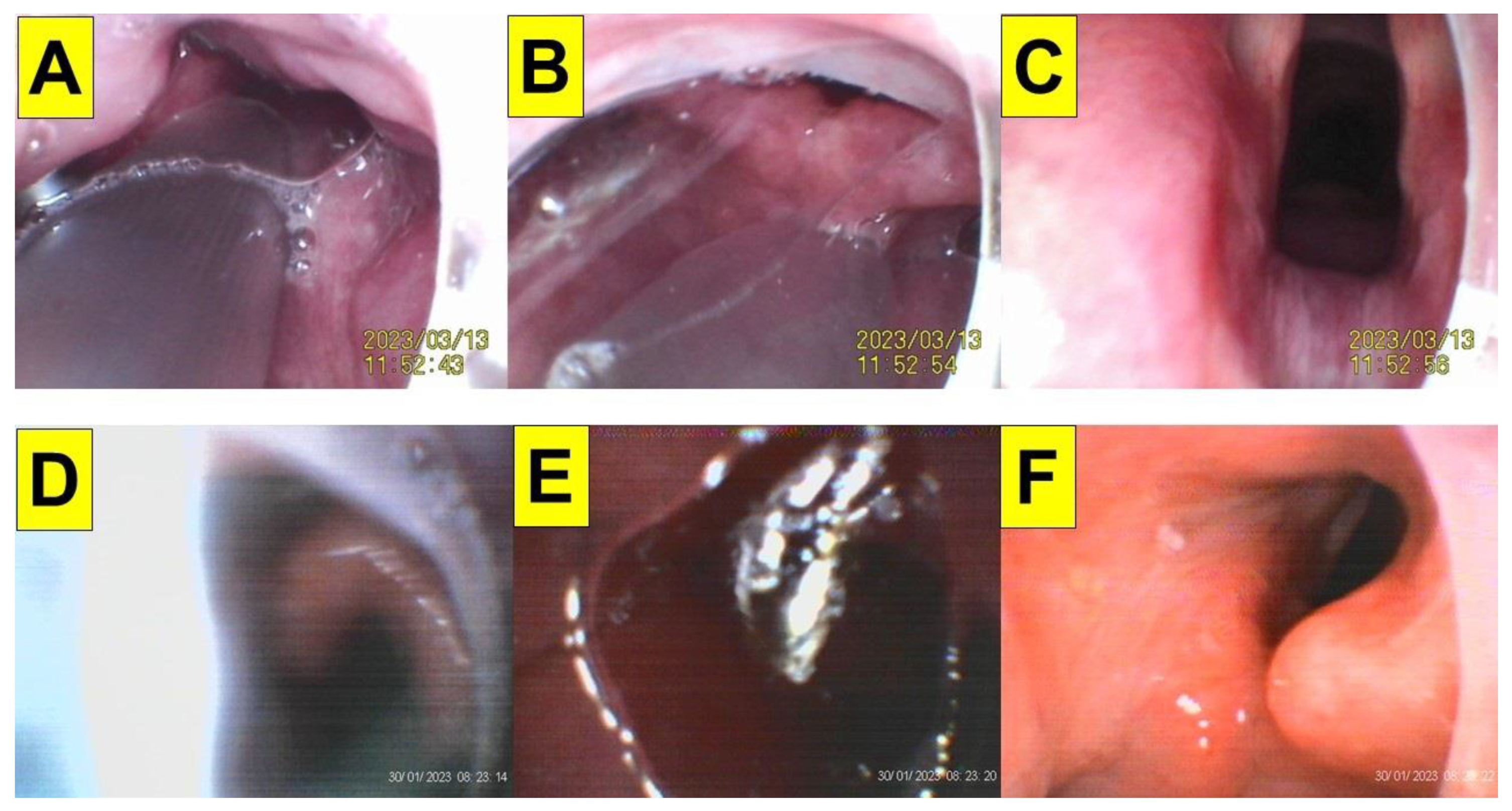
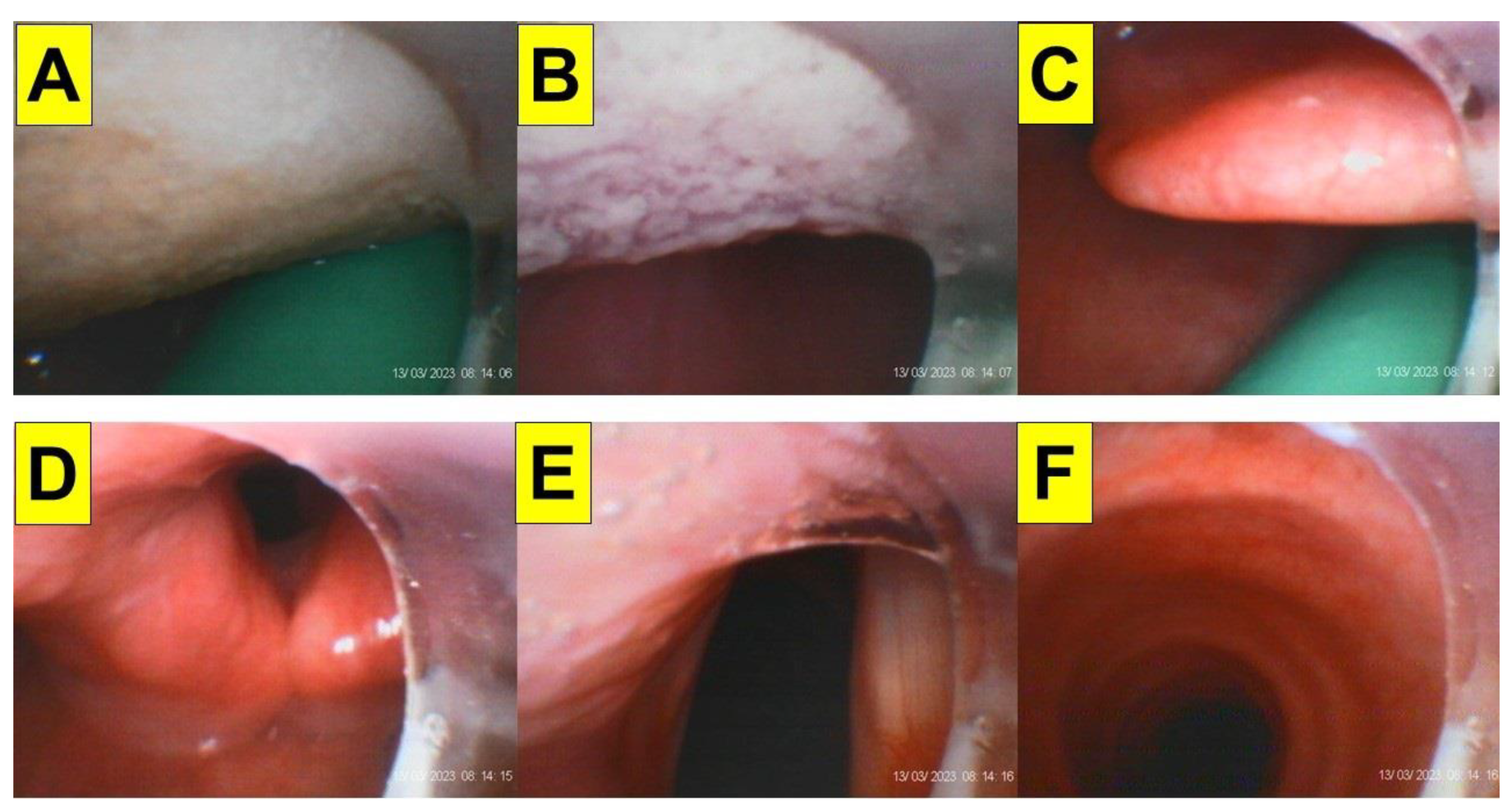
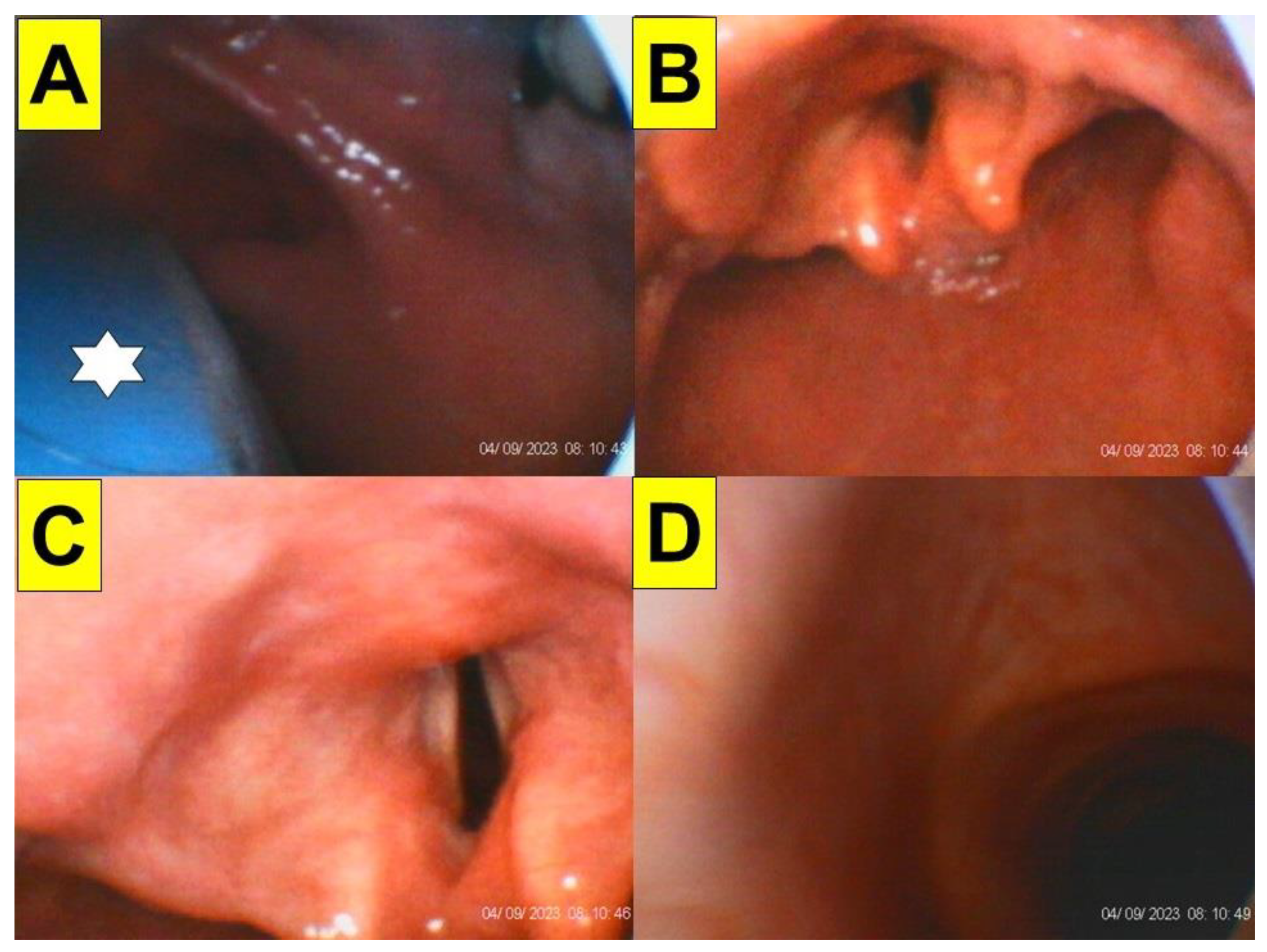
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 6 | Case 7 | Case 8 | Case 9 | Case 10 | Case 11 | Case 12 | Case 13 | Case 14 | Case 15 | Case 16 | Case 17 | Case 18 | Case 19 | Case 20 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age/Gender (years old) | 33/M | 42/M | 42/F | 49/M | 57/F | 51/F | 26/F | 45/M | 32/F | 37/F | 23/M | 56/M | 41/F | 26/M | 48/M | 56/M | 38/M | 42/M | 40/M | 58/F |
| Height (cm) | 158 | 165 | 161 | 180 | 153 | 160 | 160 | 171 | 157 | 162 | 176 | 159 | 158 | 166 | 175 | 170 | 178 | 166 | 174 | 166 |
| Weight (kg) | 258 | 172 | 165 | 175 | 120 | 131 | 130 | 147 | 119 | 126 | 146 | 115 | 111 | 121 | 124 | 112 | 120 | 101 | 109 | 96 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 103 | 63.1 | 63.6 | 54 | 51.2 | 51.1 | 50.7 | 50.2 | 48.2 | 48 | 47.1 | 45.4 | 44.4 | 43.9 | 40.4 | 38.7 | 37.8 | 36.6 | 36 | 34.8 |
| Surgery | LSG | OAGB | OAGB | LSG | LSG | OAGB | LSG | LSG | OAGB | OAGB | LSG | LSG | LSG | LSG | LSG | OAGB | LSG | LSG | LSG | LSG |
| Comorbidity | HTN/DM/OSAS | HTN/DM/OSAS | HTN/OSAS | HTN/OSAS | HTN/CAD/cirrhosis of liver | HTN/OSAS | Obesity/OSAS | CAD/CVA/OSAS | OSAS | HTN/DM | OSAS | HTN/DM/CVA | DM/asthma | OSAS | OSAS | HTN/DM/CAD | OSAS | OSAS/COPD | HTN/DM/OSAS | HTN/DM |
| ASA class | III | III | II | II | III | II | II | III | II | III | II | III | II | II | II | III | II | II | III | III |
| MMT | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Interincisor distance | 4.5 | 5.5 | 5 | 5.5 | 5 | 4.5 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4 | 5 | 5.5 | 4.5 | 5 | 4.5 | 4 | 4.5 |
| ULBT | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Thyromental distance (cm) | 8 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 8 |
| Sternomental distance (cm) | 17 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 16 | 18 | 13 | 16 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 18 |
| Neck circumference (cm) | 54 | 54 | 42 | 50 | 37 | 47 | 39 | 48 | 45 | 39 | 50 | 49 | 45 | 47 | 44 | 46 | 44 | 41 | 44 | 38 |
| Neck fat deposition/soft tissue loading on the upper airway | moderate | moderate | mild | moderate | moderate | moderate | Mild | mild | mild | Mild | mild | moderate | mild | mild | mild | mild | mild | mild | mild | mild |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 200 | 166 | 155 | 150 | 142 | 155 | 132 | 143 | 142 | 133 | 143 | 133 | 114 | 124 | 140 | 115 | 124 | 112 | 119 | 110 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 202 | 154 | 158 | 148 | 144 | 150 | 146 | 126 | 156 | 134 | 148 | 126 | 140 | 128 | 124 | 115 | 118 | 120 | 120 | 126 |
| LQS grading | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| POGO (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Time to intubation | 12 s | 14 s | 18 s | 22 s | 6 s | 10 s | 8 s | 11 s | 5 s | 5 s | 11 s | 13 s | 9 s | 6 s | 18 s | 8 s | 12 s | 22s | 20 s | 5 s |
| Expected cause of prolonged time of tracheal intubation | Performed by a third- year resident | Prior cervical spine surgery, copious secretions | For demonstration purpose | For demonstration purpose | ||||||||||||||||
| First-pass success | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Subjective easiness | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy | easy |
| Airway-related complications | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none |
| Supplemental video-clips | Video S1 | Video S2 | Video S3 | Video S4 | Video S5 | Video S6 | Video S7 | Video S8 | Video S9 | Video S10 | Video S11 | Video S12 | NA | Video S13 | Video S14 | Video S15 | Video S16 | Video S17 | Video S18 | Video S19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-C.; Wu, B.-G.; Chen, B.-C.; Luk, H.-N.; Qu, J.Z. Structured Routine Use of Styletubation for Oro-Tracheal Intubation in Obese Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgeries—A Case Series Report. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12141404
Lee H-C, Wu B-G, Chen B-C, Luk H-N, Qu JZ. Structured Routine Use of Styletubation for Oro-Tracheal Intubation in Obese Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgeries—A Case Series Report. Healthcare. 2024; 12(14):1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12141404
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hsiang-Chen, Bor-Gang Wu, Bo-Cheng Chen, Hsiang-Ning Luk, and Jason Zhensheng Qu. 2024. "Structured Routine Use of Styletubation for Oro-Tracheal Intubation in Obese Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgeries—A Case Series Report" Healthcare 12, no. 14: 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12141404
APA StyleLee, H.-C., Wu, B.-G., Chen, B.-C., Luk, H.-N., & Qu, J. Z. (2024). Structured Routine Use of Styletubation for Oro-Tracheal Intubation in Obese Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgeries—A Case Series Report. Healthcare, 12(14), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12141404






