Effect of Forward Head Posture on Resting State Brain Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
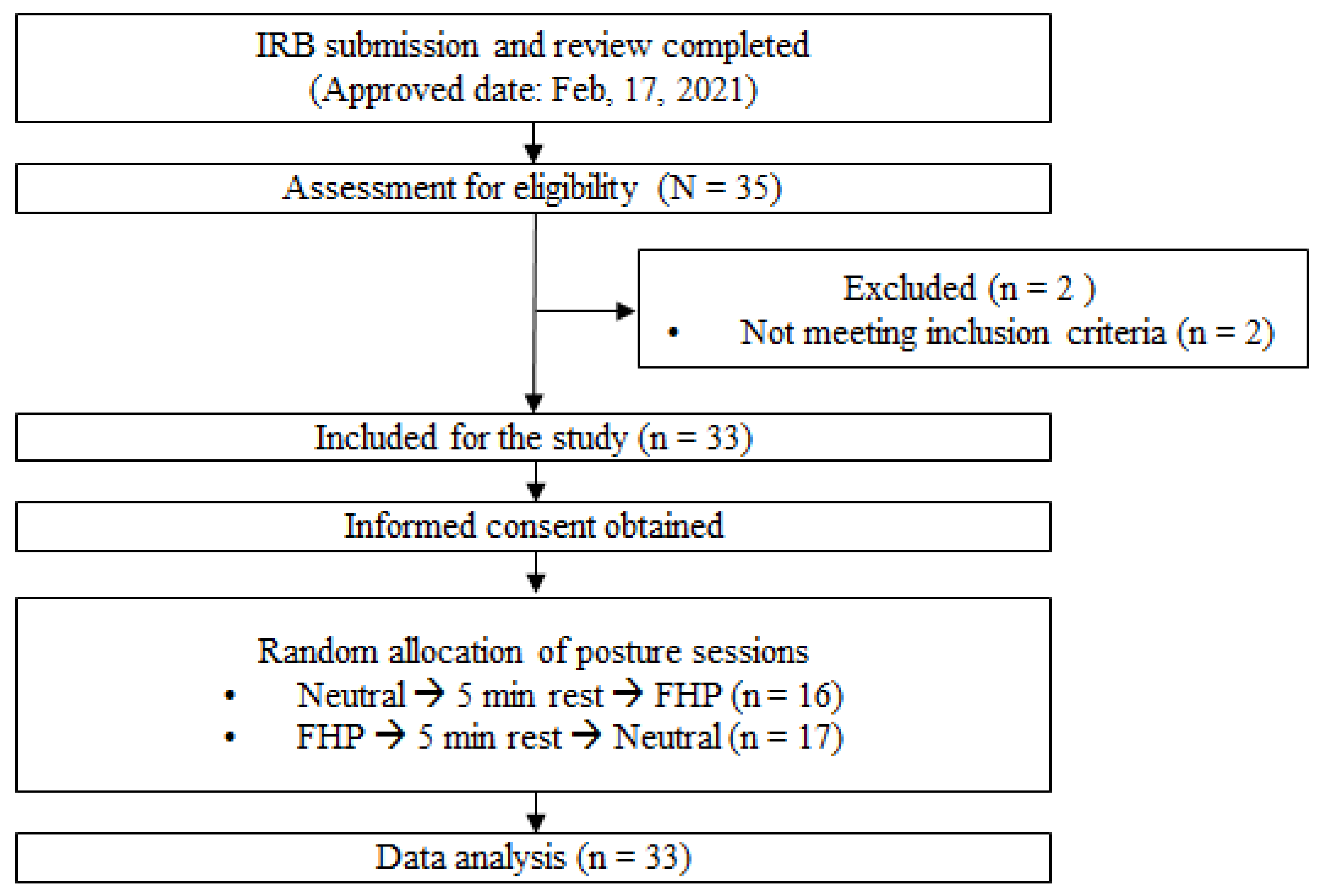
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Protocol and Intervention
2.3. Measurements
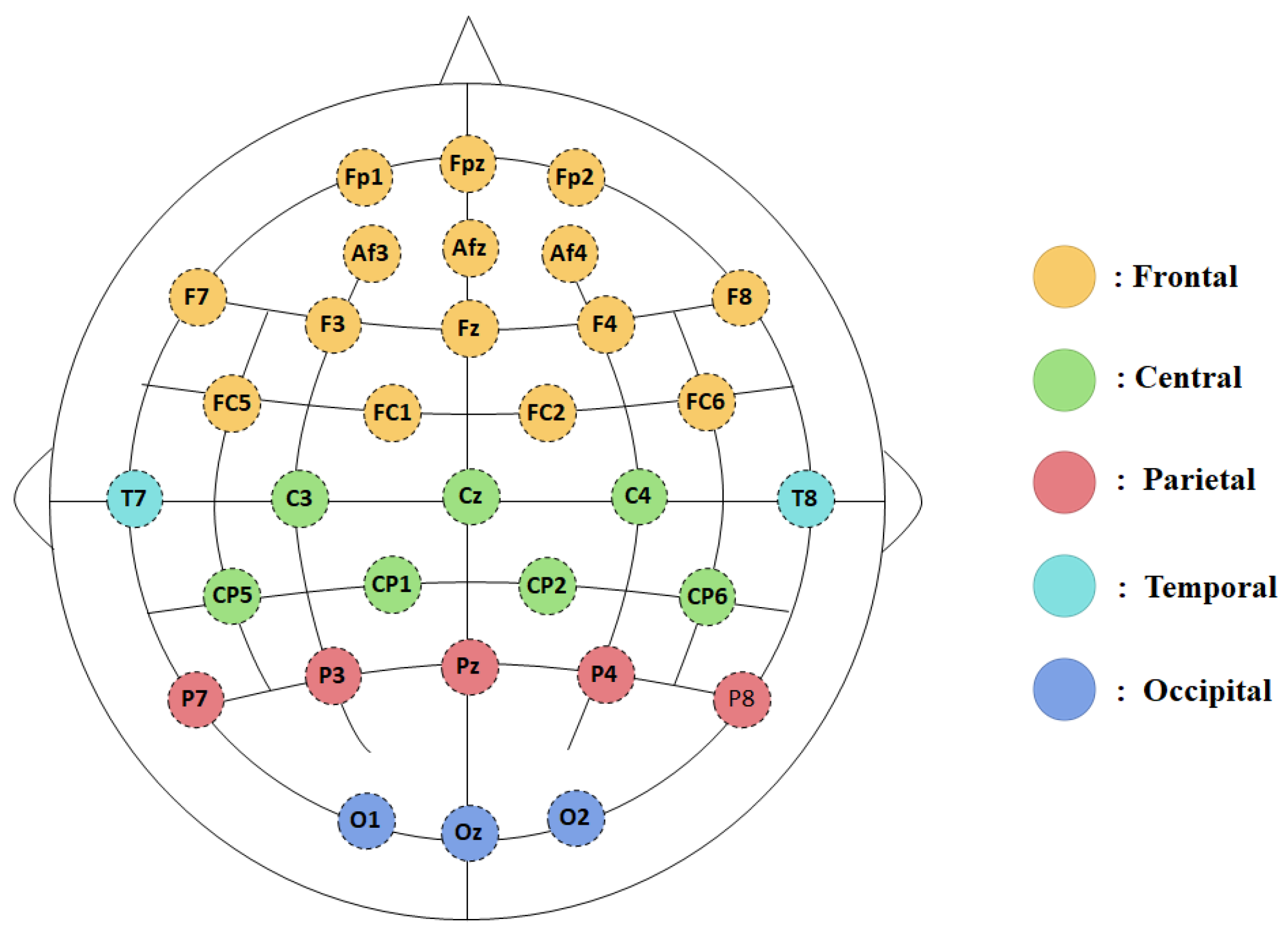
2.4. EEG Data Acquisition and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
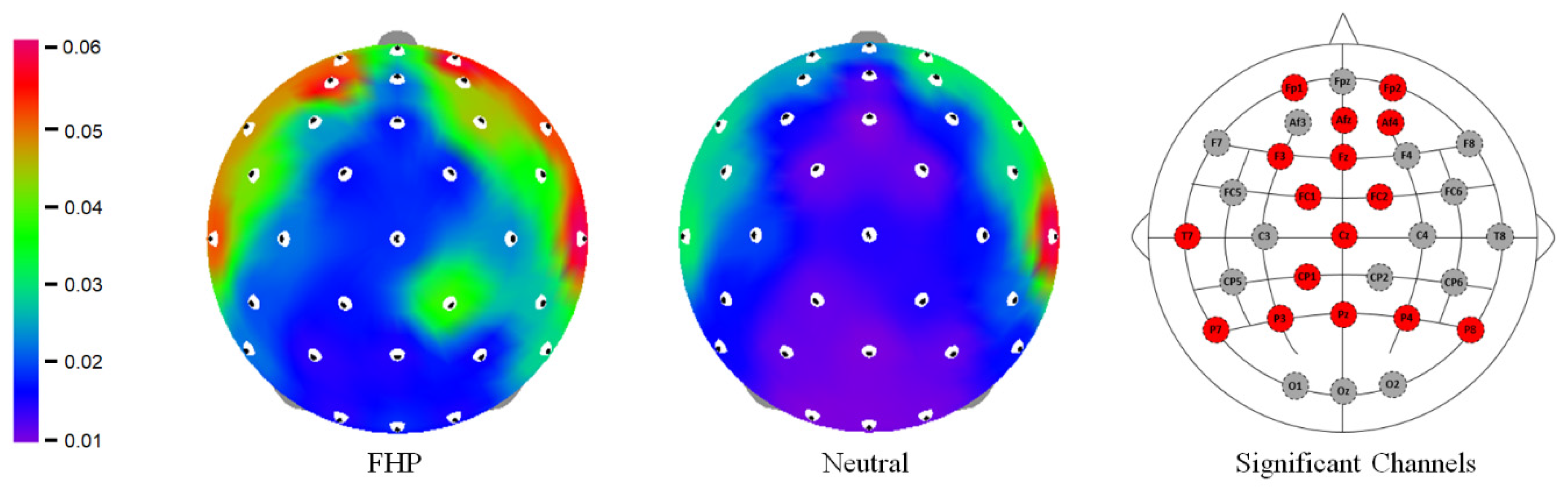
3.1. Relative Spectral Power Regional Variations
3.1.1. Frontal Region
3.1.2. Parietal Region
3.2. Biomechanical Changes between Neutral and Forward Head Postures
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Increased Gamma Activity in FHP
4.2. Muscular Stress in FHP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahmoud, N.F.; Hassan, K.A.; Abdelmajeed, S.F.; Moustafa, I.M.; Silva, A.G. The Relationship Between Forward Head Posture and Neck Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2019, 12, 562–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, E.C.P.; Lo, F.S.; Bhaumik, A. Plausible Impact of Forward Head Posture on Upper Cervical Spine Stability. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 2517–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuligowski, T.; Skrzek, A.; Cieślik, B. Manual Therapy in Cervical and Lumbar Radiculopathy: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arooj, A.; Aziz, A.; Khalid, F.; Iqbal, M.H.; Ashfaq, H.B. Forward Head Posture in Young Adults: A Systematic Review: Forward Head Posture in Young Adults. J. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2022, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, B.; Haight, A.; Maluf, K. Differential Effects of Mental Concentration and Acute Psychosocial Stress on Cervical Muscle Activity and Posture. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokaee, F.; Rezasoltani, A.; Manshadi, F.D.; Naimi, S.S.; Baghban, A.A.; Azimi, H. Comparison of Cervical Muscle Thickness between Asymptomatic Women with and without Forward Head Posture. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2017, 21, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocur, P.; Wilski, M.; Goliwąs, M.; Lewandowski, J.; Łochyński, D. Influence of Forward Head Posture on Myotonometric Measurements of Superficial Neck Muscle Tone, Elasticity, and Stiffness in Asymptomatic Individuals with Sedentary Jobs. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2019, 42, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-H.; Jung, J.-H.; Hahm, S.-C.; Oh, H.-K.; Jung, K.-S.; Cho, H.-Y. Effects of Lumbar Lordosis Assistive Support on Craniovertebral Angle and Mechanical Properties of the Upper Trapezius Muscle in Subjects with Forward Head Posture. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.M.; McKinnon, C.; Callaghan, J.P. Cervical Spine Joint Loading with Neck Flexion. Ergonomics 2020, 63, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, A.; Ashraf, H.S.; Sohail, M.; Akram, S.; Khan, M.; Azam, H. Prevalence of upper cross syndrome and associated postural deviations in computer operators; a qualitative study. Asian J. Allied Health Sci. 2022, 7, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Wilkinson, T. The Relationship between Forward Head Posture, Postural Control and Gait: A Systematic Review. Gait Posture 2022, 98, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.-Y.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kang, C.-K. Effects of a Traction Device for Head Weight Reduction and Neutral Alignment during Sedentary Visual Display Terminal (VDT) Work on Postural Alignment, Muscle Properties, Hemodynamics, Preference, and Working Memory Performance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseki, T.; Kakizaki, F.; Hayashi, S.; Nishida, N.; Itoh, M. Effect of Forward Head Posture on Thoracic Shape and Respiratory Function. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2019, 31, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulut, M.D.; Alpayci, M.; Şenköy, E.; Bora, A.; Yazmalar, L.; Yavuz, A.; Gülşen, İ. Decreased Vertebral Artery Hemodynamics in Patients with Loss of Cervical Lordosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, C.; Kydd, R.; Sagar, M.; Broadbent, E. Upright Posture Improves Affect and Fatigue in People with Depressive Symptoms. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 2017, 54, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, D.R.; Cuddy, A.J.C.; Yap, A.J. Power Posing: Brief Nonverbal Displays Affect Neuroendocrine Levels and Risk Tolerance. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 21, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.G.; Vasavada, A.N.; Wiest, M.M.; Schmitter-Edgecombe, M. Mobility and Upright Posture Are Associated with Different Aspects of Cognition in Older Adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.-J.; Lin, J.-F.; Lin, C.-F.; Wu, K.-T.; Wang, Y.-M.; Kuo, C.-D. Effect of Body Position on Bilateral EEG Alterations and Their Relationship with Autonomic Nervous Modulation in Normal Subjects. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 490, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-Y.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kang, C.-K. Brain Activity during a Working Memory Task in Different Postures: An EEG Study. Ergonomics 2020, 63, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, P.J.; Watson, B.O. Gamma Oscillations as a Biomarker for Major Depression: An Emerging Topic. Transl Psychiatry 2018, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, R.T.; Lifshitz, M.; Jones, J.M.; Raz, A. Posture Alters Human Resting-State. Cortex 2014, 58, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Oh, J.-S. Effects of Visual Display Terminal Works on Cervical Movement Pattern in Patients with Neck Pain. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, I.M.; Youssef, A.; Ahbouch, A.; Tamim, M.; Harrison, D.E. Is Forward Head Posture Relevant to Autonomic Nervous System Function and Cervical Sensorimotor Control? Cross Sectional Study. Gait Posture 2020, 77, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Hahm, S.-C.; Cho, H.-Y. Thermotherapy Plus Neck Stabilization Exercise for Chronic Nonspecific Neck Pain in Elderly: A Single-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, L.; Boswell, C.; Fryer, G. The Effects of High-Velocity, Low-Amplitude Manipulation and Muscle Energy Technique on Suboccipital Tenderness. Int. J. Osteopath. Med. 2007, 10, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, S.-E.; Seo, D. Correlation between Contraction Ratio, Endurance, and Muscle Tone of Cervical Muscles. Phys. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2020, 9, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Luz Cuadrado, M.; Pareja, J.A. Myofascial Trigger Points in the Suboccipital Muscles in Episodic Tension-Type Headache. Man. Ther. 2006, 11, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viir, R.; Virkus, A.; Laiho, K.; Rajaleid, K.; Selart, A.; Mikkelsson, M. Trapezius Muscle Tone and Viscoelastic Properties in Sitting and Supine Positions. SJWEH Suppl. 2007, 3, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kielar, A.; Joanisse, M.F. Graded Effects of Regularity in Language Revealed by N400 Indices of Morphological Priming. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 1373–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makeig, S.; Westerfield, M.; Jung, T.P.; Enghoff, S.; Townsend, J.; Courchesne, E.; Sejnowski, T.J. Dynamic brain sources of visual evoked responses. Science 2022, 295, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Li, F.; Liu, Q.; Wen, X.; Lai, Y.; Xu, P.; Yao, D. MATLAB Toolboxes for Reference Electrode Standardization Technique (REST) of Scalp EEG. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, A.; Zahediasl, S. Normality Tests for Statistical Analysis: A Guide for Non-Statisticians. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 10, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Cailliet, R.; Harrison, D.D.; Troyanovich, S.J.; Harrison, S.O. A Review of Biomechanics of the Central Nervous System—Part III: Spinal Cord Stresses from Postural Loads and Their Neurologic Effects. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 1999, 22, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastiani, L.; Simoni, A.; Gemignani, A.; Ghelarducci, B.; Santarcangelo, E.L. Human Hypnosis: Autonomic and Electroencephalographic Correlates of a Guided Multimodal Cognitive-Emotional Imagery. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 338, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandman, T.; Malach, R.; Simony, E. The Surprising Role of the Default Mode Network in Naturalistic Perception. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathewson, K.J.; Hashemi, A.; Sheng, B.; Sekuler, A.B.; Bennett, P.J.; Schmidt, L.A. Regional Electroencephalogram (EEG) Alpha Power and Asymmetry in Older Adults: A Study of Short-Term Test–Retest Reliability. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, A.D.; Griffis, J.C.; Visscher, K.M.; Dobbins, A.C.; Gawne, T.J.; DiFrancesco, M.W.; Szaflarski, J.P. Relationship Between Alpha Rhythm and the Default Mode Network: An EEG-fMRI Study. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 34, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ryu, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Choi, A.; Kim, D.-J.; Kim, S.N.; Choi, J.-S. Longitudinal Changes in Neural Connectivity in Patients With Internet Gaming Disorder: A Resting-State EEG Coherence Study. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Jung, H.Y.; Sohn, B.K.; Kim, D.J.; Choi, J.-S. Neural Connectivity in Internet Gaming Disorder and Alcohol Use Disorder: A Resting-State EEG Coherence Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oathes, D.J.; Ray, W.J.; Yamasaki, A.S.; Borkovec, T.D.; Castonguay, L.G.; Newman, M.G.; Nitschke, J. Worry, generalized anxiety disorder, and emotion: Evidence from the EEG gamma band. Biol. Psychol. 2008, 79, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, A.K.; Fries, P. Beta-Band Oscillations—Signalling the Status Quo? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Caneda, E.; Cadaveira, F.; Correas, A.; Crego, A.; Maestú, F.; Rodríguez Holguín, S. The Brain of Binge Drinkers at Rest: Alterations in Theta and Beta Oscillations in First-Year College Students with a Binge Drinking Pattern. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeto, G.P.Y.; Straker, L.M.; O’Sullivan, P.B. A Comparison of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Office Workers Performing Monotonous Keyboard Work—2: Neck and Shoulder Kinematics. Man. Ther. 2005, 10, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, W.; Yi, C.; Cho, S.; Jeon, H.; Cynn, H.; Choi, H. Effects of the Height of Ball-Backrest on Head and Shoulder Posture and Trunk Muscle Activity in VDT Workers. Ind. Health 2008, 46, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; James, C.; Edwards, S.; Snodgrass, S.J. Differences in Posture Kinematics between Using a Tablet, a Laptop, and a Desktop Computer in Sitting and in Standing. Work 2018, 61, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P.; Frank, C.C.; Lardner, R. Assessment and Treatment of Muscle Imbalance: The Janda Approach, 1st ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-7360-7400-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rosario, J.L.; Bezerra Diógenes, M.S.; Mattei, R.; Leite, J.R. Differences and Similarities in Postural Alterations Caused by Sadness and Depression. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2014, 18, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 33) | Men (n = 17) | Women (n = 16) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 22.18 ± 1.88 | 22.88 ± 2.26 | 21.44 ± 0.96 |
| Height (cm) | 169.95 ± 8.15 | 176.26 ± 5.56 | 162.80 ± 2.93 |
| Weight (kg) | 67.14 ± 12.43 | 74.50 ± 10.60 | 59.33 ± 9.14 |
| Functional CVA (°) | 39.65 ± 6.31 | 36.94 ± 5.94 | 42.52 ± 5.49 |
| Regions | Variables | Forward Head (Mean ± SD) | Neutral (Mean ± SD) | T | FDR_p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal | FP1 | 7.027 ± 7.737 | 4.528 ± 4.669 | 2.631 | 0.037 |
| FP2 | 7.836 ± 8.029 | 4.597 ± 4.255 | 2.465 | 0.037 | |
| F3 | 6.109 ± 6.181 | 4.023 ± 3.851 | 2.876 | 0.031 | |
| AF4 | 8.443 ± 7.381 | 5.324 ± 4.777 | 2.800 | 0.031 | |
| AFz | 4.972 ± 5.136 | 3.347 ± 3.638 | 2.976 | 0.031 | |
| Fz | 3.89 ± 3.778 | 2.535 ± 2.116 | 2.925 | 0.031 | |
| FC1 | 3.581 ± 3.487 | 2.571 ± 2.026 | 2.315 | 0.049 | |
| FC2 | 4.295 ± 4.314 | 2.582 ± 2.067 | 2.549 | 0.037 | |
| Central | CP1 | 3.082 ± 2.778 | 2.131 ± 1.713 | 2.498 | 0.037 |
| Cz | 2.993 ± 2.582 | 2.083 ± 1.624 | 2.471 | 0.037 | |
| Temporal | T7 | 10.404 ± 8.506 | 7.158 ± 7.036 | 2.984 | 0.031 |
| Parietal | P7 | 4.746 ± 3.821 | 2.937 ± 2.299 | 4.420 | 0.002 |
| P8 | 4.509 ± 3.809 | 2.793 ± 2.45 | 4.294 | 0.002 | |
| P3 | 3.262 ± 2.417 | 2.335 ± 1.669 | 2.754 | 0.031 | |
| P4 | 3.569 ± 3.035 | 2.374 ± 1.759 | 2.840 | 0.031 | |
| Pz | 2.663 ± 2.204 | 1.880 ± 1.493 | 2.476 | 0.037 |
| Variables | Forward Head (Mean ± SD) | Neutral (Mean ± SD) | T | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVA (°) | 39.564 ± 6.39 | 55.105 ± 4.947 | −13.165 | <0.001 |
| Tone_R_LS (Hz) | 17.925 ± 1.7 | 17.206 ± 1.527 | 2.598 | 0.014 |
| Tone_L_LS (Hz) | 18.25 ± 1.708 | 17.503 ± 1.922 | 3.498 | 0.001 |
| Stiffness_R_SCM (N/m) | 209.485 ± 27.188 | 196.848 ± 18.226 | 3.399 | 0.002 |
| Elasticitiy_R_Platysma | 1.421 ± 0.243 | 1.352 ± 0.2 | 2.158 | 0.039 |
| Elasticity_L_Platysma | 1.398 ± 0.198 | 1.335 ± 0.142 | 2.526 | 0.017 |
| CVA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regions | Variables | Pearson’s r | p | Regions | Variables | Pearson’s r | p |
| Frontal | FP1 | −0.132 | 0.322 | Central | CP1 | −0.174 | 0.193 |
| FP2 | −0.190 | 0.152 | Cz | −0.174 | 0.192 | ||
| F3 | −0.122 | 0.361 | Temporal | T7 | −0.144 | 0.281 | |
| AF4 | −0.152 | 0.255 | Parietal | P7 | −0.266 | 0.044 * | |
| AFz | −0.121 | 0.366 | P8 | −0.370 | 0.004 * | ||
| Fz | −0.132 | 0.324 | P3 | −0.170 | 0.201 | ||
| FC1 | −0.078 | 0.559 | P4 | −0.216 | 0.104 | ||
| FC2 | −0.212 | 0.110 | Pz | −0.157 | 0.240 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-B.; Kang, C.-K. Effect of Forward Head Posture on Resting State Brain Function. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12121162
Jung J-Y, Lee Y-B, Kang C-K. Effect of Forward Head Posture on Resting State Brain Function. Healthcare. 2024; 12(12):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12121162
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Ju-Yeon, Yeong-Bae Lee, and Chang-Ki Kang. 2024. "Effect of Forward Head Posture on Resting State Brain Function" Healthcare 12, no. 12: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12121162
APA StyleJung, J.-Y., Lee, Y.-B., & Kang, C.-K. (2024). Effect of Forward Head Posture on Resting State Brain Function. Healthcare, 12(12), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12121162






