Prevalence and Causes of Elective Surgical Cancellations: Findings from a Rural Tertiary Hospital in the Eastern Cape, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Setting
2.3. Patient Selection
- Elective surgical cases that were cancelled at NMAH main theatre from January 2019 to July 2019.
- Obstetric cases (cases carried out at labour ward theatre);
- Orthopaedic cases (cases carried out at an off-site orthopaedic unit);
- All emergency cases (cases carried out in a designated theatre).
2.4. Sampling Method and Data Source
2.5. Data Collection and Variables of Interest
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics of the Study Participants
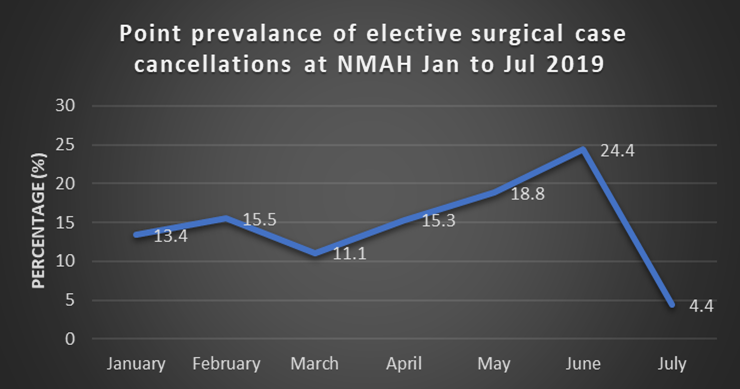
3.2. Prevalence Rate of Cancellation of Elective Surgical Cases
3.3. Causes of Cancellation of the Study Participants
3.3.1. Patient-Related Factors
3.3.2. Surgical-Related Factors
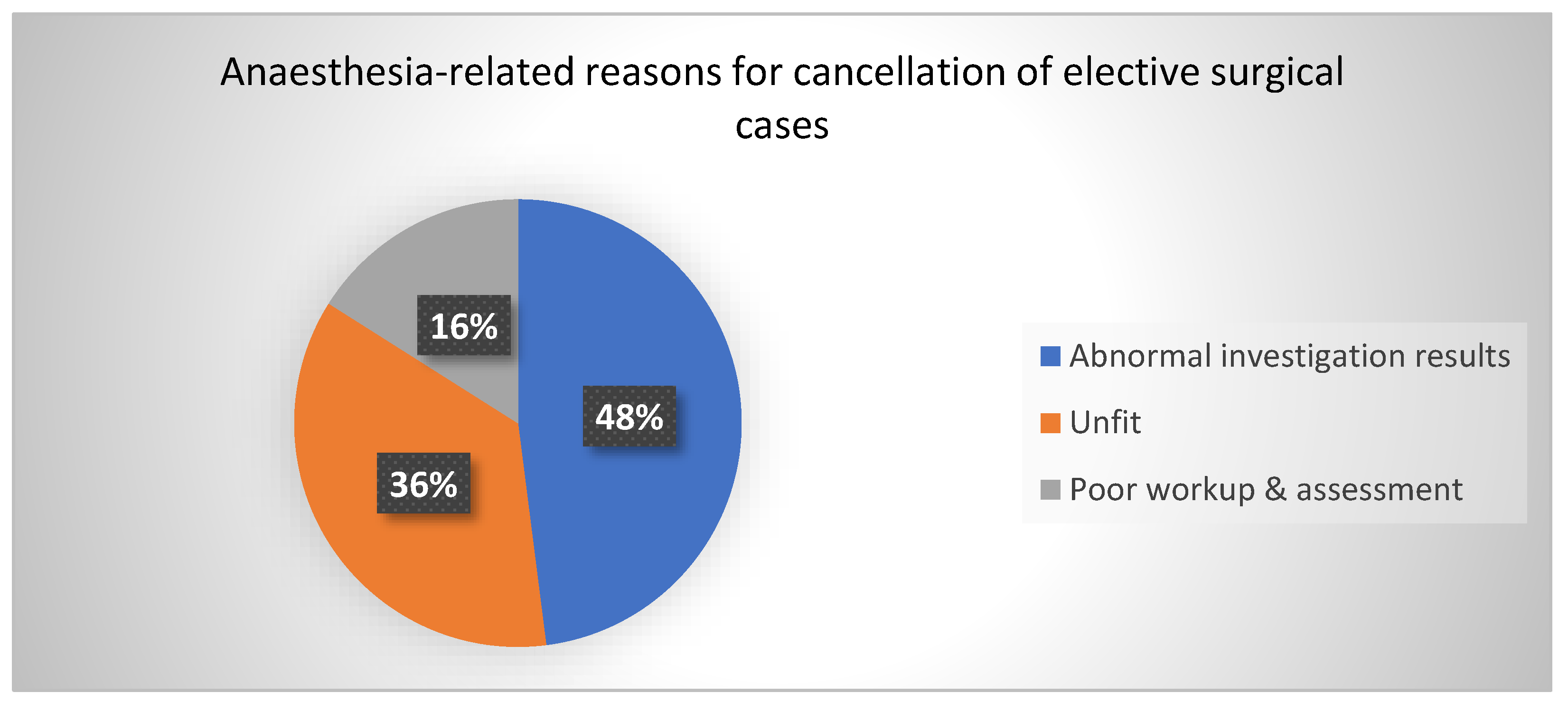
3.3.3. Anaesthesia-Related Factors
3.3.4. Facility-Related Factors
3.4. Avoidable and Unavoidable Reasons for Cancellation
3.5. Most Affected Surgical Departments, Surgical Procedures, and Frequently Cancelled Patients
3.5.1. Surgical Departments
3.5.2. Surgical Procedures
3.5.3. Sociodemographic Features of Frequently Cancelled Patients
3.6. Surgical Factors Per Category of Elective Surgical Cancellations
3.6.1. Surgical Department
3.6.2. Surgical Procedures
3.7. Causes of Cancellation Per Category of Elective Surgical Cancellations
4. Discussion
4.1. Prevalence of Elective Surgical Case Cancellation
4.2. Causes of Elective Surgical Case Cancellation
4.3. Avoidable vs. Unavoidable Category of Elective Surgical Cancellation
4.4. Surgical Disciplines and Procedures
5. Strengths and limitations
5.1. Strength
5.2. Limitations
6. Conclusions
7. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhuiyan, M.M.Z.U.; Mavhungu, R.; Machowski, A. Provision of an emergency theatre in tertiary hospitals is cost-effective: Audit and cost of cancelled planned elective general surgical operations at Pietersburg Hospital, Limpopo Province, South Africa. S. Afr. Med, J. 2017, 107, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankoandé, M.; Bonkoungou, P.K.K.; Kaboré, A.F.R.; Ouangré, E.; Savadogo, Y.; Bougouma, C.T.; Sanou, J.; Ouedraogo, N.; Pendeville, P. Economic and psychological burden of scheduled surgery cancellation in a sub-Saharan country (Burkina Faso). S. Afr. J. Anaesth. Analgesia. 2017, 23, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gandhi, R. Reasons for cancellation of operation on the day of intended surgery in a multidisciplinary 500 bedded hospital. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 28, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanjappa, N.; Kirti, K.; Kabeer, K.; Smile, S. Elective Surgical Case Cancellation–An Audit. Int. J. Curr. Res. Review. 2014, 6, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, S.V.; Dhulkhed, V.K.; Shinde, R.H. A prospective study on operation theater utilization time and most common causes of delays and cancellations of scheduled surgeries in a 1000-bedded tertiary care rural hospital with a view to optimize the utilization of operation theater. Anesth. Essays Res. 2018, 12, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macario, A. Are your hospital operating rooms "efficient"? A scoring system with eight performance indicators. Anesthesiology 2006, 105, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezike, H.; Ajuzieogu, V.; Amucheazi, A. Reasons for Elective Surgery Cancellation in a Referral Hospital. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2011, 1, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Desta, M.; Manaye, A.; Tefera, A.; Worku, A.; Wale, A.; Mebrat, A.; Gobena, N. Incidence and causes of cancellations of elective operation on the intended day of surgery at a tertiary referral academic medical center in Ethiopia. Patient Saf. Surg. 2018, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmal, I.I.; Keerath, K.; Cronje, L. An audit of operating theatre utilisation and day-of-surgery cancellations at a regional hospital in the Durban metropole. S. Afr. Med. J. 2019, 109, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogwal, A.; Oyania, F.; Nkonge, E.; Makumbi, T.; Galukande, M. Prevalence and Predictors of Cancellation of Elective Surgical Procedures at a Tertiary Hospital in Uganda: A Cross-Sectional Study. Surg. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, S.M.; Chekole, Y.A.; Minaye, S.Y.; Basu, B. Global prevalence and reasons for case cancellation on the intended day of surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. Open 2020, 26, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalya, P.L.; Gilyoma, J.M.; Mabula, J.B.; Simbila, S.; Ngayomela, I.H.; Chandika, A.B.; Mahalu, W. Incidence, causes and pattern of cancellation of elective surgical operations in a university teaching hospital in the Lake Zone, Tanzania. Afr. Health Sci. 2011, 11, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.H.; Lee, A.; Chui, P.T. Cancellation of elective operations on the day of intended surgery in a Hong Kong hospital: Point prevalence and reasons. Hong Kong Med. J. 2012, 18, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dhafar, K.O.; Ulmalki, M.A.; Felemban, M.A.; Mahfouz, M.E.; Baljoon, M.J.; Gazzaz, Z.J.; Baig, M.; Hamish, N.M.; AlThobaiti, S.A.; Al-Hothali, F.T. Cancellation of operations in Saudi Arabian hospitals: Frequency, reasons and suggestions for improvements. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 31, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.J.; McAvoy, J.; Dweik, D.; Ferrigno, M.; Macario, A.; Haisjackl, M. Cancellation of Elective Cases in a Recently Opened, Tertiary/Quaternary-Level Hospital in the Middle East. Obstet. Anesth. Dig. 2017, 125, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovlid, E.; Bukve, O.; Haug, K.; Aslaksen, A.B.; von Plessen, C. A new pathway for elective surgery to reduce cancellation rates. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2012, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänninen-Khoda, L.; Koljonen, V.; Ylä-Kotola, T. Patient-related reasons for late surgery cancellations in a plastic and reconstructive surgery department. JPRAS Open 2018, 18, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, I.U.; Gajida, A.U.; Nuhu, Y.N. Cancellations of elective surgical procedures performed at a Teaching Hospital in North-West Nigeria. J. Med. Trop. 2016, 18, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddoum, R.; Fadlallah, R.; Hitti, E.; El-Jardali, F.; Eid, G.E. Causes of cancellations on the day of surgery at a Tertiary Teaching Hospital. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2016, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van As, A.B.; Brey, Z.; Numanoglu, A. Improving Operating Theatre Efficiency in South Africa 2011. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.za/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0256-95742011000700008 (accessed on 22 December 2022).

| Variables | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) (n = 425) γ | ||
| 0–1 | 14 | 3.29 |
| 2–12 | 24 | 5.65 |
| 13–18 | 16 | 3.76 |
| 19–35 | 84 | 19.76 |
| 36–64 | 164 | 38.59 |
| >65 | 123 | 28.94 |
| Mean (SD) | 47.72 ± 23.24 years | |
| Gender (n = 137) γ | ||
| Female | 237 | 55.37 |
| Male | 191 | 44.63 |
| Ratio | 1.24: 1 | |
| γ = Missing Values applicable | ||
| Variables | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Months | n = 2962 |
| January | 216 |
| February | 386 |
| March | 449 |
| April | 404 |
| May | 453 |
| June | 480 |
| July | 574 |
| Variables | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Patient-related (n = 167) γ | ||
| Failure to show up | 123 | 73.65 |
| Uncontrolled hypertension | 17 | 10.18 |
| Patient eating | 11 | 6.59 |
| Upper or lower respiratory tract infection | 6 | 3.59 |
| Patient refusal | 4 | 2.40 |
| Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus | 2 | 1.20 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 1 | 0.60 |
| Collapsed | 1 | 0.60 |
| Deteriorated condition | 1 | 0.60 |
| Asthma | 1 | 0.60 |
| γ = Missing Values applicable | ||
| Variables | Frequency | Percentage |
| Surgical-related (n = 114) γ | ||
| Overbooking | 39 | 33.21 |
| Malfunction or lack of equipment | 21 | 18.42 |
| Postponed | 17 | 14.91 |
| Change of diagnosis | 16 | 14.03 |
| Poor workup | 10 | 8.70 |
| Cancelled by surgeon | 6 | 5.26 |
| Surgical staff unavailable | 3 | 2.63 |
| Does not belong to the firm | 1 | 0.87 |
| Late start | 1 | 0.87 |
| γ = Missing Values applicable |
| Variables | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Facility-related (n = 123) γ | ||
| Time factor | 57 | 46.34 |
| No steam | 25 | 20.33 |
| No nursing staff | 15 | 12.20 |
| No Linen | 6 | 4.88 |
| Unavailability of pre- or post-op beds | 6 | 4.88 |
| Prioritisation of other cases including emergencies | 4 | 3.25 |
| Unavailable or malfunctioning equipment | 3 | 2.44 |
| Delay due to death on the table | 3 | 2.44 |
| No water | 1 | 0.81 |
| 1 | 0.81 | |
| Air-conditioning malfunction | 1 | 0.81 |
| Given clexane (enoxaparin) in ward | 1 | 0.81 |
| γ = Missing Values applicable |
| Variables | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Category of cancellation | ||
| Avoidable | 174 | 40.65 |
| Unavoidable | 254 | 59.35 |
| Variables | Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Procedures | ||
| Avastin injection | 77 | 17.99 |
| Excisional biopsy | 45 | 10.51 |
| Small incision cataract surgery and intraocular lens (SICS & IOL) | 36 | 8.41 |
| Total abdominal hysterectomy | 18 | 4.21 |
| Thoracotomy | 16 | 3.74 |
| Dilatation and curettage (D&C) | 15 | 3.50 |
| Optical urethrotomy | 11 | 2.57 |
| Cauterisation of corneal vessels | 9 | 2.10 |
| Cone biopsy | 9 | 2.10 |
| Examination under anaesthesia (EUA) of anus | 9 | 2.10 |
| Transurethral resection prostate (TURP) | 9 | 2.10 |
| Orchidopexy | 8 | 1.87 |
| Herniotomy | 5 | 1.17 |
| Laparotomy and dye test | 5 | 1.17 |
| Others | 156 | 36.44 |
| Variables | Category of Elective Surgical Cancellations (Freq %) | Total | Chi-Square, p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avoidablen n = 174 | Unavoidablen n = 254 | |||
| Age | χ2 = 4.53, p = 0.476 | |||
| 0–1 yrs | 8 (57.14) | 6 (42.86) | 14 (100.0) | |
| 2–12 yrs | 7 (29.17) | 17 (70.83) | 24 (100.0) | |
| 13–18 yrs | 7 (43.75) | 9 (56.25) | 16 (100.0) | |
| 19–35 yrs | 38 (45.24) | 46 (54.76) | 84 (100.0) | |
| 36–64 yrs | 61 (37.20) | 103 (62.80) | 164 (100.0) | |
| >65 yrs | 51 (41.46) | 72 (58.54) | 123 (100.0) | |
| Gender | χ2 = 0.00, p = 0.976 | |||
| Male | 78 (40.84) | 113 (59.16) | 191 (100.0) | |
| Female | 96 (40.51) | 141 (59.49) | 237 (100.0) | |
| Variables | Category of Elective Surgical Cancellations (Freq %) | Total | Fisher’s Exact p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avoidablen n = 174 | Unavoidablen n = 254 | |||
| Surgical Department | p = 0.001 µ* | |||
| Ophthalmology | 41 (23.03) | 137 (76.97) | 178 (100.0) | |
| Gynaecology | 45 (62.50) | 27 (37.50) | 72 (100.0) | |
| General Surgery | 27 (56.26) | 21 (43.75) | 48 (100.0) | |
| Urology | 24 (63.16) | 14 (36.84) | 38 (100.0) | |
| Ear, nose, and throat surgery (ENT) | 13 (39.39) | 20 (60.61) | 33 (100.0) | |
| Neurosurgery | 9 (42.86) | 12 (57.14) | 21 (100.0) | |
| Cardiothoracic surgery | 6 (33.33) | 12 (66.67) | 18 (100.0) | |
| Paediatric surgery | 4 (33.33) | 8 (66.67) | 12 (100.0) | |
| Maxillofacial surgery | 4 (66.67) | 2 (33.33) | 6 (100.0) | |
| Plastic surgery | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | 2 (100.0) | |
| Variables | Category of Elective Surgical Cancellations (Freq %) | Total | Fisher’s Exact p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avoidablen n = 174 | Unavoidablen n = 254 | |||
| Surgical Procedure | p = 0.001 µ* | |||
| Avastin injection | 10 (12.99) | 67 (87.01) | 77 (100.0) | |
| Excisional biopsy | 8 (17.78) | 37 (82.22) | 45 (100.0) | |
| SICS and IOL | 19 (52.78) | 17 (47.22) | 36 (100.0) | |
| Total abdominal hysterectomy | 10 (55.56) | 8 (44.44) | 18 (100.0) | |
| Thoracotomy | 5 (31.25) | 11 (68.75) | 16 (100.0) | |
| DD&C | 12 (80.0) | 3 (20.0) | 15 (100.0) | |
| Optical urethrotomy | 8 (72.73) | 3 (27.27) | 11 (100.0) | |
| Cauterisation of corneal vessels | 2 (22.22) | 7 (77.78) | 9 (100.0) | |
| Cone biopsy | 3 (33.33) | 6 (66.67) | 9 (100.0) | |
| EUA anus | 6 (66.67) | 3 (33.33) | 9 (100.0) | |
| TURP | 6 (66.67) | 3 (33.33) | 9 (100.0) | |
| Orchidopexy | 4 (50.0) | 4 (50.0) | 8 (100.0) | |
| Herniotomy | 2 (40.0) | 3 (60.0) | 5 (100.0) | |
| Laparotomy and dye | 5 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (100.0) | |
| Variables | Category of Elective Surgical Cancellations (Freq %) | Total | Fisher’s Exact p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avoidablen n = 174 | Unavoidablen n = 254 | |||
| Causes of cancellation | p = 0.001 µ* | |||
| Patient-related | 16 (9.58) | 151 (90.42) | 167 (100.0) | |
| Surgical-related | 113 (99.12) | 1 (0.88) | 114 (100.0) | |
| Anaesthesia-related | 16 (66.67) | 8 (33.3) | 24 (100.0) | |
| Facility-related | 29 (23.57) | 94 (76.42) | 123 (100.0) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukwana, A.; Mrara, B.; Oladimeji, O. Prevalence and Causes of Elective Surgical Cancellations: Findings from a Rural Tertiary Hospital in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Healthcare 2023, 11, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020270
Sukwana A, Mrara B, Oladimeji O. Prevalence and Causes of Elective Surgical Cancellations: Findings from a Rural Tertiary Hospital in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Healthcare. 2023; 11(2):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020270
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukwana, Abongile, Busisiwe Mrara, and Olanrewaju Oladimeji. 2023. "Prevalence and Causes of Elective Surgical Cancellations: Findings from a Rural Tertiary Hospital in the Eastern Cape, South Africa" Healthcare 11, no. 2: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020270
APA StyleSukwana, A., Mrara, B., & Oladimeji, O. (2023). Prevalence and Causes of Elective Surgical Cancellations: Findings from a Rural Tertiary Hospital in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Healthcare, 11(2), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020270






