Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire for Sleep Apnea in Newly Diagnosed Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
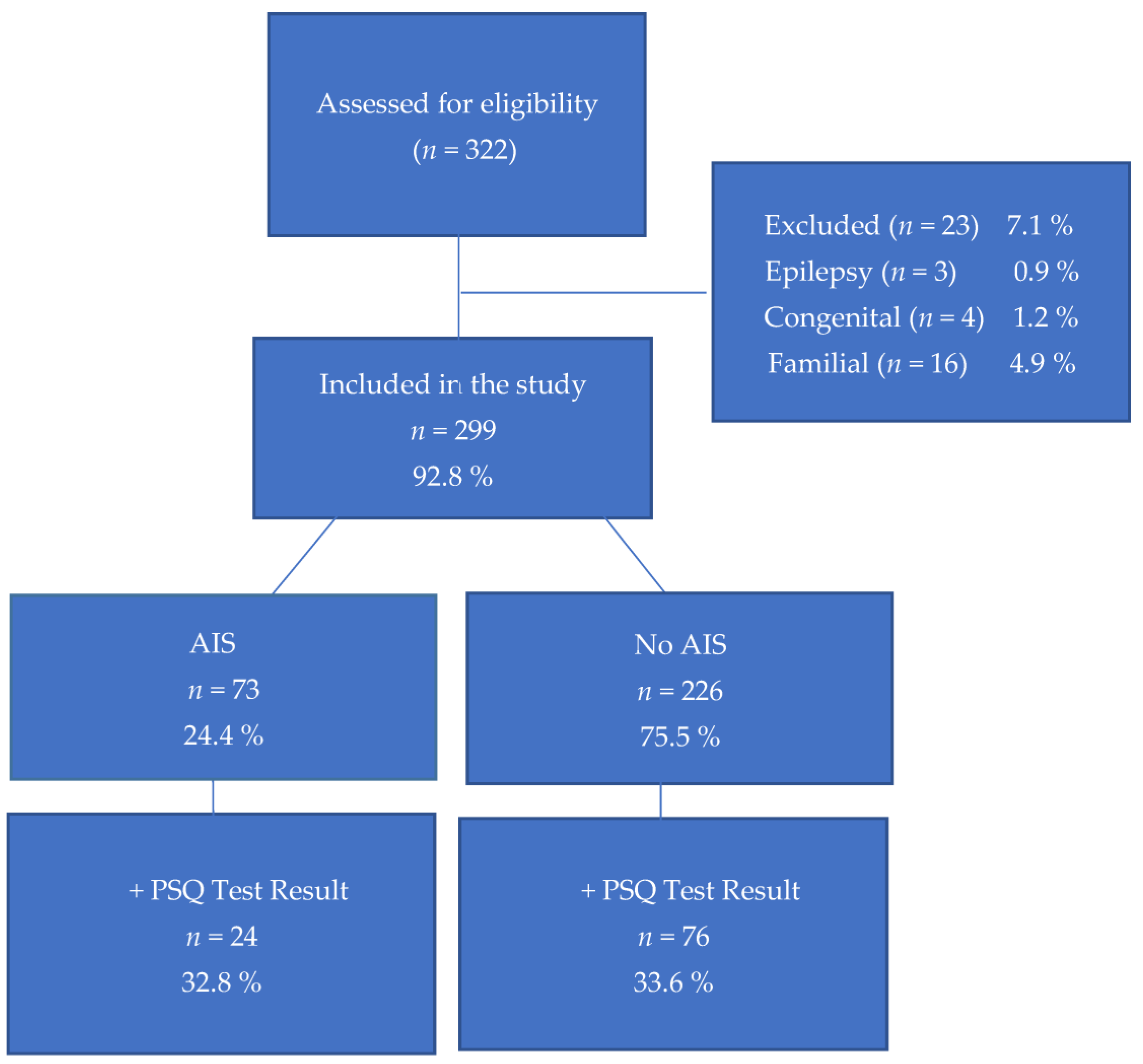
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
| AIS | Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis |
| EOS | Early onset scoliosis |
| IH | Intermittent hypoxia |
| PSG | Polysomnogram |
| PSQ | Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire |
| SDB | Sleep-disordered breathing |
References
- Konieczny, M.R.; Senyurt, H.; Krauspe, R. Epidemiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.-X.; Huang, C.-A.; Lin, J.-L.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Shi, Y.-F.; Chen, B.-D.; Zhang, H.-W.; Dai, Z.-Y.; Yu, X.-P. Prevalence of the thoracic scoliosis in children and adolescents candidates for strabismus surgery: Results from a 1935-patient cross-sectional study in China. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlösser, T.P.C.; Tsirikos, A.I.; Castelein, R.M. Aetiological process of idiopathic scoliosis: From a normal growing spine into a complex 3D spinal deformity. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 35, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.; Chae, H.-W.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.; Kwon, J.-W.; Lee, S.-B.; Moon, S.-H.; Lee, H.-M.; Lee, B.H. Incidence and surgery rate of idiopathic scoliosis: A nationwide database study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hresko, M.T. Clinical practice. Idiopathic Scoliosis in adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqsood, A.; Frome, D.K.; Gibly, R.F.; Larson, J.E.; Patel, N.M.; Sarwark, J.F. IS (Idiopathic Scoliosis) etiology: Multifactorial genetic research continues. A systematic review 1950 to 2017. J. Orthop. 2020, 21, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, M.C.; O’Brien, J.P. The Transformation of Spinal Curvature into Spinal Deformity: Pathological Processes and Implications for Treatment. Scoliosis 2006, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, W.K.; Cheung, J.P.Y.; Koljonen, P.A.; Kwan, K.Y.H.; Cheung, K.M.C.; Leung, V.Y.L. Slow Twitch Paraspinal Muscle Dysregulation in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Exhibiting HIF-2α Misexpression. JOR SPINE 2022, 5, e1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, M.; Yang, G.; Wang, L.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, H. Muscle Injury Associated Elevated Oxidative Stress and Abnormal Myogenesis in Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2584–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Meng, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Gao, R.; Zhou, X. Volumetric and Fatty Infiltration Imbalance of Deep Paravertebral Muscles in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrow, D.B.; Chapman, G.; Smith, A.J.; Mattar, M.Z.; Major, J.A.; O’Reilly, V.; Saga, Y.; Zackai, E.H.; Dormans, J.P.; Alman, B.A.; et al. A mechanism for gene-environment interaction in the etiology of congenital scoliosis. Cell 2012, 149, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivard, C.H. Effects of Hypoxia on the Embryogenesis of Congenital Vertebral Malformations in the Mouse. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1986, 208, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-R.; Ren, D.; Wu, H.-T.; Yao, S.-Q.; Song, Z.-H.; Geng, L.-D.; Wang, P.-C. Reparative Effects of Chronic Intermittent Hypobaric Hypoxia Pre-Treatment on Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafont, J.E. Lack of Oxygen in Articular Cartilage: Consequences for Chondrocyte Biology. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2010, 91, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risbud, M.V.; Schipani, E.; Shapiro, I.M. Hypoxic Regulation of Nucleus Pulposus Cell Survival: From Niche to Notch. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKintosh, E.W.; Ho, M.; White, K.K.; Krengel, W.; Bompadre, V.; Chen, M.L.; Redding, G.J. Referral Indications and Prevalence of Sleep Abnormalities in Children with Early Onset Scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2020, 8, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.-L.; Gozal, D.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L. Obstructive sleep apnea in children: A critical update. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2013, 25, 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Dewan, N.A.; Nieto, F.J.; Somers, V.K. Intermittent hypoxemia and OSA: Implications for comorbidities. Chest 2015, 147, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakut, Y.; Pelin, Z.; Yagci, G. An investigation of sleep profiles in individuals with idiopathic scoliosis. Sleep Sci. 2022, 15, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardo, M.; Bettini, N.; Dema, E.; Cervellati, S. The role of melatonin in the pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (ais). Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20 (Suppl. S1), S68–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chervin, R.D.; Hedger, K.; Dillon, J.E.; Pituch, K.J. Pediatric sleep questionnaire (PSQ): Validity and reliability of scales for sleep-disordered breathing, snoring, sleepiness, and behavioral problems. Sleep Med. 2000, 1, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umano, G.R.; Rondinelli, G.; Luciano, M.; Pennarella, A.; Aiello, F.; Mangoni di Santo Stefano, G.S.R.C.; Di Sessa, A.; Marzuillo, P.; Papparella, A.; Miraglia del Giudice, E. Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire Predicts Moderate-to-Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children and Adolescents with Obesity. Children 2022, 9, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, H.; Söğüt, A.; Yılmaz, O.; Kutluay, E. Reliability and validity of the Turkish version of the pediatric sleep questionnaire: A tool for prediction of sleep related breathing disorder. Tuberk Toraks 2011, 59, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznia, A.L.; Hernandez, A.K.; Lee, L.U. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Common questions and answers. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 101, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, A.; Askin, G. Paediatric scoliosis: Update on assessment and treatment. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2020, 49, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfair, D.; Flemming, A.K.; Dvorak, M.F.; Munk, P.L.; Vertinsky, A.T.; Heran, M.K.; Graeb, D.A. Radiographic evaluation of scoliosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194 (Suppl. S3), S8–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonini, F.; Zucchini, L.; Pellitteri, F.; Palone, M.; Lombardo, L. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Developmental Age: 22-Item Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire for an Observational Descriptive Investigation. Children 2023, 10, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.C.; Galland, B.C.; Smith, L.A.; Maessen, S.E.; Haszard, J.J.; Schaughency, E.A.; Dawes, P.J. Can sleep questionnaires predict outcome in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy for sleep disordered breathing? Aust. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, C.L.; Brooks, L.J.; Draper, K.A.; Gozal, D.; Halbower, A.C.; Jones, J.; Schechter, M.S.; Sheldon, S.H.; Spruyt, K.; Ward, S.D.; et al. Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e714–e755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzarella, V.; Giuliana, G.; Spinuzza, P.; La Mantia, G.; Maniscalco, L.; Pizzo, G.; Matranga, D. Paediatric Sleep Questionnaire for Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Syndrome Screening: Is Sleep Quality Worthy of Note? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Su, S.; Liang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Shu, Y.; Ding, L. Analysis of the risk factors associated with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in Chinese children. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 900216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupper, A.J.; Nation, J.; Pransky, S. Adenoidectomy in children: What is the evidence and what is its role? Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2018, 6, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneuer, F.J.; Bell, K.J.; Dalton, C.; Elshaug, A.; Nassar, N. Adenotonsillectomy and adenoidectomy in children: The impact of timing of surgery and post-operative outcomes. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2022, 58, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Dubousset, J.; Imamura, Y.; Iwaya, T.; Yamada, T.; Kimura, J. Role of melatonin deficiency in the development of scoliosis in pinealectomised chickens. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1995, 77, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikanloo, S.R.; Tarpada, S.P.; Cho, W. Etiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A literature review. Asian Spine J. 2019, 13, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanduri, J.; Semenza, G.L.; Prabhakar, N.R. Epigenetic changes by DNA methylation in chronic and intermittent hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L1096–L1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Lin, T.; Liang, S.; Gao, R.; Jiang, H.; Shao, W.; Yang, F.; Zhoua, X. Value of DNA methylation in predicting curve progression in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n = 299 | Descriptive Statistics |
|---|---|
| Is there, adenoid hypertrophy? | |
| Yes | 13 (4.3%) |
| No | 217 (72.6%) |
| Dont know | 69 (23%) |
| Is there, tonsil hypertrophy? | |
| Yes | 48 (16%) |
| No | 240 (80.3%) |
| Dont know | 11 (3.6%) |
| Has the patient undergone adenoid and tonsil surgery? | |
| Yes | 37 (12.3%) |
| No | 260 (87.1%) |
| Dont know | 2 (0.6%) |
| PSQ score ≥ 0.33 | 100 (33.4%) |
| 13 (4.3%) |
| Cobb < 5° | Cobb 5–9° | Cobb ≥ 10° | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 12 (10–14) | 11.50 (10–15) | 12 (10–16) | 0.090 * |
| PSQ total score | 0.22 (0–0.93) | 0.23 (0–0.59) | 0.20 (0–0.73) | 0.980 * |
| Gender | ||||
| ♂ | 40 (31%) | 30 (30.2%) | 16 (22.9%) | 0.457 ** |
| ♀ | 89 (69%) | 70 (69.8%) | 54 (77.1%) | |
| PSQ score | ||||
| <0.33 | 99 (72.3%) | 62 (69.7%) | 49 (67.1%) | 0.718 ** |
| ≥0.33 | 38 (27.7%) | 27 (30.3%) | 24 (32.9%) |
| Cobb < 5° | Cobb 5–9° | Cobb ≥ 10° | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Is there, adenoid hypertrophy? | ||||
| No | 97 (70.8%) | 72 (80.9%) | 51 (69.9%) | 0.050 ** |
| Yes | 6 (4.4%) | 2 (2.2%) | 5 (6.8%) | |
| Dont know | 34 (24.8%) | 15 (16.9%) | 17 (23.3%) | |
| Is there, tonsil hypertrophy? | ||||
| No | 113 (82.5%) | 70 (78.6%) | 59 (80.8%) | 0.941 ** |
| Yes | 21 (15.3%) | 16 (17.9%) | 11 (15.1%) | |
| Dont know | 3 (2.2%) | 3 (3.4%) | 3 (2.2%) | |
| Has the patient undergone adenoid and tonsil surgery? | ||||
| No | 118 (86.1%) | 78 (87.6%) | 66 (90.4%) | 0.684 ** |
| Yes | 19 (13.9%) | 12 (12.1%) | 6 (8.2%) | |
| Dont know | 1 (0.7%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.4%) |
| Question | Total Positive Responses |
|---|---|
| 1: Snores more than half of the time | 47 |
| 2: Always snores | 8 |
| 3: Snores loudly | 17 |
| 4: Has “heavy” or loud breathing | 37 |
| 5: Has trouble breathing, or struggles to breathe | 64 |
| 6: Seen your child stop breathing during the night | 16 |
| 7: Tends to breathe through the mouth during the day | 81 |
| 8: Has a dry mouth on waking up in the morning | 172 |
| 9: Occasionally wets the bed | 26 |
| 10: Wakes up feeling un-refreshed in the morning | 162 |
| 11: Has problems with sleepiness during the day | 114 |
| 12: Complains that they are sleepy during the day | 75 |
| 13: It is hard to wake them up in the morning | 115 |
| 14: Wakes up with headaches in the morning | 38 |
| 15: Has stopped growing at a normal rate at any time since birth | 30 |
| 16: Is overweight | 58 |
| 17: Does not seem to listen when spoken to directly | 97 |
| 18: Has difficulty organizing tasks and activities | 91 |
| 19: Easily distracted by extraneous stimuli | 140 |
| 20: Fidgets with hands or feet or squirms in seat | 123 |
| 21: “On the go” or acts as if “driven by a motor” | 62 |
| 22: Interrupts or intrudes on other (i.e., interferes with conversations/games) | 95 |
| Question | Positive Responses | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Has a dry mouth on waking up in the morning | 172 |
| 2 | Wakes up feeling un-refreshed in the morning | 162 |
| 3 | Easily distracted by extraneous stimuli | 140 |
| 4 | Fidgets with hands or feet or squirms in seat | 123 |
| 5 | Interrupts or intrudes on other (i.e., interferes with conversation/games) | 115 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ugur, F.; Topal, K.; Albayrak, M.; Taskin, R. Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire for Sleep Apnea in Newly Diagnosed Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2506. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11182506
Ugur F, Topal K, Albayrak M, Taskin R. Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire for Sleep Apnea in Newly Diagnosed Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients. Healthcare. 2023; 11(18):2506. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11182506
Chicago/Turabian StyleUgur, Fatih, Kubra Topal, Mehmet Albayrak, and Recep Taskin. 2023. "Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire for Sleep Apnea in Newly Diagnosed Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients" Healthcare 11, no. 18: 2506. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11182506
APA StyleUgur, F., Topal, K., Albayrak, M., & Taskin, R. (2023). Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire for Sleep Apnea in Newly Diagnosed Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients. Healthcare, 11(18), 2506. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11182506





