Abstract
There is a substantial gap in our knowledge regarding the efficacy of exergames on the reduction of fall risk in older adults. This systematic review analyzes the findings of clinical trials describing the efficacy of exergames to improve balance or reduce the risk of falls in individuals above 60 years of age who are residents in community centers or nursing homes. We searched Google Scholar, PubMed, and Embase up to January 2023. Initially, 52,294 records were screened. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 20 studies were included in this systematic review. Meta-analyses revealed statistically significant reductions in the risk of falls and improvements in balance. Exergaming tended to produce positive benefits according to the results obtained using different instruments (TUG, PPA, BBS, and others), control groups, and times of intervention. Nevertheless, a substantial proportion of studies exhibited a high risk of bias and only one had a long follow-up period. Although a large body of evidence supports the view that exergaming is suitable for reducing fall risk and improving balance in older adults, some gaps remain in our knowledge about such benefits.
1. Introduction
The proportion of older adults within the population is growing in both developed and developing countries as a result of a decline in the rates of mortality and fertility together with an increase in life expectancy [1,2]. In 2017, individuals aged 60 years or more accounted for 12.3% of the world’s population, but this percentage is expected to increase to 21.3% by 2050 [3]. In this regard, it is imperative to understand and identify the priority problems of the older population in order to establish new policies and actions to ensure their security and to provide the health care that they need [4].
Accidental falls are the major causes of disability, morbidity, mortality, and institutionalization among older adult citizens, resulting in substantial social impacts especially in countries with a large aging population [5,6]. Recent research has shown that one in three individuals aged more than 65 years has at least one fall per year [7], the causes of which are associated with intrinsic (mobility, muscle strength, clinical, and cognitive conditions) or extrinsic (physical, social, and behavioral) factors [8].
In addition to the harm caused to physical health, falls in older adults are of particular concern as they engender changes in family structure and dynamics due to the need for specialized care, hospitalization, or institutionalization, all of which generate enormous pressure on health services [5,9].
In healthcare settings, the most significant impacts of falls are an increased demand for emergency care, ambulance services, medical consultations, and diagnostic tests. Additionally, treating fall-related injuries incurs high costs, including hospitalization expenses, surgery, medication, and rehabilitation. Within the family structure, falls generate additional costs both in terms of medical assistance and care for the elderly individual [5]. The responsibility of caring for older adults often falls on the family, which requires significant time, energy, and financial resources. Depending on the severity of their injuries, older adults may face temporary or permanent physical limitations, impacting their independence and mobility. As a result, adjustments to their home environment and daily routine are often necessary. Moreover, the fear of falling again can limit the individual’s participation in social and physical activities, leading to social isolation and a decline in mental health [5,9].
Thus, preventing the consequences of falls is the best way of securing a longer independent life with enhanced physical and emotional well-being for older adult citizens [10,11].
Although physical exercise is one of the most effective methods of preventing falls [10,11], the main barriers to adherence to exercise programs are reported to be a lack of time and inefficient and unsatisfactory exercises [10,12,13]. In this context, the application of exergames has been recommended for improving the physical and cognitive fitness of older adults since they offer a more positive experience with increased motivation in the practice of regular exercise. Moreover, exergaming is claimed to be an enjoyable, interesting, and inexpensive method for improving perceived self-sufficiency and facilitating healthy aging [14,15].
Exergames (combining the words exercise and game) can be defined as digital games that require body movement to be played. They provide an active experience, which functions as a form of physical exercise [16,17,18,19]. Despite the credible benefits of exergaming, there is a substantial gap in our knowledge regarding the efficacy of the intervention method on balance function and on the reduction of fall risk in the older population [20,21].
Currently, exergaming utilizes motion sensors, virtual and augmented reality, and artificial intelligence to create a more immersive exercise experience. Many emerging devices and games allow individuals to access personalized exercise routines, monitor their progress, set goals, and receive real-time feedback [22,23]. With these technological advances, it is possible to better understand variables related to performance in exergames and how they can be used more effectively to improve balance and decrease the risk of falls, in addition to improving the general health, quality of life, and well-being of older adults [23].
For older adults, exergames can provide overall health benefits, improve physical capacity and fitness, and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases. Additionally, exergames are valuable for motivating physical activity and are important for cognitive stimulation as they can enhance concentration and decision-making. However, exergames pose certain risks for elderly participants, such as injuries, and technological frustrations [22,23,24,25].
Other reviews have been published on the improvements in physical and cognitive function for older adults [20] or on the effectiveness of exergames only in community-dwelling individuals [22,23]. The present systematic review with a meta-analysis is the first to assess and combine different instruments to evaluate the risk of falls and balance and compare the performance of community-dwelling older adults and residents in nursing homes in addition to exploring possible sources of heterogeneity through subgroup analyses.
In this way, the aim of this systematic review was to compile and critically analyze the findings of published studies concerning the efficacy of exergames in improving balance and diminishing the risk of falls in older adults.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
The systematic literature review was based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses [24] (Supplementary Material file S1). We had an unpublished search-extraction protocol that did not change over the course of the study. The remit of the search was to include studies that employed exergames as an intervention method to reduce fall risk or the occurrence of falls or for improving the balance of older adults. The expected health-related outcomes were improved balance and/or risk of falls.
2.2. Bibliographic Search and Selection of Studies
The searches were performed up to January 2023 using English, Portuguese, and Spanish keyword combinations with Boolean operators (in the Google Scholar, Embase, and PubMed databases) and the PICO approach: population (individuals older than an average of 60 years; residents in community centers or nursing homes), intervention (exergame or electronic gaming platform), comparison (groups with no intervention or interventions with conventional therapies for balance training and/or risk of falls), and outcome (risk score for falls, balance in older adults, and/or the occurrence of falls during the training period) (Table 1). The searches were organized in the databases by the descriptors of each PICO item (Supplementary Material file S2).

Table 1.
Keywords used in the literature search.
In order to narrow the initial search results, the following filters (automatic tools) were applied to the databases: clinical trials, randomized controlled trials and quasi-experimental studies published in the last 11 years, and full texts (i.e., studies reported only as the abstracts were excluded). Finally, the reference list of the included studies was analyzed to check for further studies to be included. A restriction to studies carried out within the last decade was initiated because of the rapid technological evolution of Exergames. The selection of studies was performed by one researcher (JCL). After the studies were selected, two other researchers (RVF and IMS) analyzed the included studies to ensure proper inclusion. Discrepancies among the researchers who analyzed the studies were resolved by another researcher (VSB).
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The criteria for the inclusion of specified studies were: (i) clinical trials, randomized controlled trials, and quasi-experimental studies evaluating the efficacy of exergames on the fall risk and/or balance in individuals with an average age of 60 years or older who lived in older adult community centers or nursing homes; (ii) interventions with a duration of at least three weeks; (iii) blinded or non-blinded approaches; and (iv) unrestricted publication language. Relevant publications were selected on the basis of the eligibility criteria by reading the titles and abstracts. Following the removal of duplicated studies, the complete texts of the remaining articles were analyzed to select the studies to be included in this review (Figure 1) [24,25].
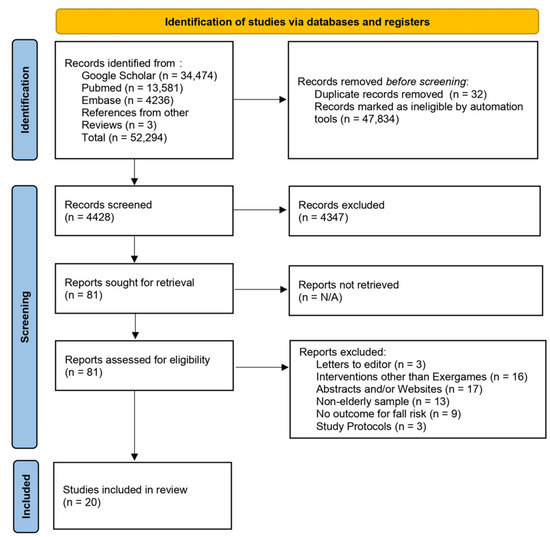
Figure 1.
PRISMA 2020 flow chart illustrating the systematic review process [24,25].
2.4. Data Extraction
Data from full texts of the included articles were extracted by two of the coauthors (JCL and IMS) and verified by all authors. The following information was recorded for each study: year, country, the duration of the experimental phase, population, experimental design, exposure, outcome, the diagnostic method employed in the assessment of balance and fall risk, confounding variables, adherence rate, results, measures of efficacy, discussion, and conclusion.
2.5. Data Quality
The Cochrane Collaboration tool was used to analyze the risk of bias from RCT studies [26,27,28,29,30,31]. This tool addresses seven specific domains, as detailed in Figure 2 and Figure 3, related to bias in selection, performance, detection, attrition, and reporting. For each domain, the studies were classified as presenting a low, unclear, or high risk of bias [32]. The risk of bias proportions were calculated as the ratio between the number of domains with a low, unclear, or high risk of bias by the total number of domains of the Cochrane collaboration tool.
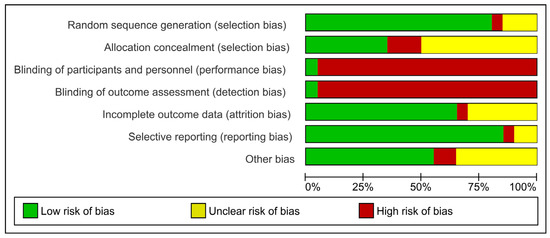
Figure 2.
Quality of studies and risk of bias according to the Cochrane Collaboration tool.
For the non-randomized study, the ROBINS-I tool was used [33,34]. The risk of bias was assessed by seven domains: bias due to confounding factors, in the selection of participants for the study, in the classification of interventions, due to deviations from the intended interventions, due to missing data, in the measurement of the outcomes and, in the selection of the reported result.
The small number of studies hindered the assessment of the occurrence of publication bias.
2.6. Quality of Evidence
To assess the quality of evidence, the GRADE approach was used [35], by means of the GRADEpro GDT [36]. Evidence was classified as “high”, “moderate”, “low”, and “very low”, depending on five criteria: (i) risk of bias; (ii) inconsistency of effect; (iii) indirect evidence; (iv) inaccuracy; and (v) publication bias. For this analysis, the risk of falls and balance groups were evaluated. Qualitative statements were standardized to describe the different combinations of effect size and certainty of evidence (Supplementary Material file S3) [37,38].
2.7. Data Analysis
The included studies were classified into two groups according to what they assessed: (i) risk of falls (studies that evaluated balance, and other capacities such as lower limb strength, sway speed, etc.) and (ii) balance-only studies.
The studies which used instruments to evaluate the risk of falls (group i) were divided into three categories: (a) the timed up and go (TUG) test, which assesses the normality and velocity of walking in addition to the ability to rise from a chair, ambulate, turn round, return, and sit in the chair again [39,40], (b) the physiological profile assessment (PPA), which involves a series of simple tests of vision, peripheral sensation, muscle force, reaction time, and postural sway and differentiates people who are at risk of falls (“fallers”) from people who are not at risk of falls (“non-fallers”) [41,42], and (c) other methods for the diagnosis of fall risk. The studies that used instruments that assessed balance (group ii) were divided into two categories: (d) Berg balance scale (BBS) studies, which determine static and dynamic balance during a series of predetermined tasks, including rising from a seated position and standing in a bipedal or unipedal stance until balance is lost, with higher scores indicating better balance [43,44], and (e) other instruments that evaluate balance (Supplementary Material file S4). The choice for these categories was based on the methods that assessed the risk of falls or the most prevalent balance in the studies included in this review.
The adherence rate was calculated as the ratio of the number of participants who completed the intervention and/or control period by the number of participants recruited and/or who started the intervention. (Supplementary Material file S4).
Meta-analyses were performed separately for (i) the risk of falls and (ii) balance by recording the mean, standard deviation, and sample size values of the intervention and control groups and combining the standardized mean differences (SMD, Hedges’ g—95% confidence intervals) of individual studies in the following subgroups: categories (as previously indicated for risk of falls (“a”, “b”, and “c”) and balance (“d” and “e”)), the execution or not of the intervention in the control group, the place of execution (community centers or nursing homes), and the duration of the intervention. In situations in which the same study used more than one instrument, those which were most frequently used in the literature were kept in the meta-analyses.
Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistics were employed to quantify the heterogeneity among the results of the primary studies in the meta-analyses [45]. The Q test was used for the comparison of the effect sizes and the heterogeneity between the subgroups. The studies were combined within the subgroups by means of random effects models. For the execution or not of the intervention in the control group and for the duration of the intervention, there was also a combination of subgroups by means of mixed-effects models [46,47].
All analyses were performed with the aid of Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software version 13 (Biostat, Englewood, NJ, USA).
Since the numbers of studies that evaluated accidental falls among older adults were insufficient for the meta-analysis, the results were narratively discussed by indicating the strengths of associations and their statistical significance.
The materials employed and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.

Figure 3.
Summary of the analysis of the studies included in the review with respect to the risk of bias: low risk (+), unclear risk (?), and high risk (-) [12,13,16,17,19,42,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61].
3. Results
3.1. Studies Included
The bibliographic search resulted in 20 articles being selected for inclusion in the review (Figure 1) [25]. Studies conducted in 12 countries were included: four from the United States [12,48,49,50], three from Brazil [51,52,53], three from Taiwan [16,54,55], two from Australia [19,56], and one each from Hong Kong [57], Canada [58], South Korea [59], Japan [17], Spain [13], Turkey [60], Iran [61], and Thailand [42]. Six studies [12,13,50,59,62,63] were conducted in nursing homes. The remaining 14 studies were conducted with community-dwelling older adults (Supplementary Material file S4).
3.2. Quality of Evidence and Risk of Bias
Considering the risk of bias within the studies, it was observed that 49.62% of the information extracted presented a low risk, 19.55% presented an unclear risk, and 30.83% presented a high risk (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Only one article had a quasi-experimental design [51]. Four domains of ROBINS-I indicated a low risk of bias, and three domains indicated a moderate risk of bias (Supplementary Material file S5).
Regarding the quality of evidence evaluated by the mean of the GRADE, low quality was observed for the risk of falls and for balance (Supplementary Material file S3).
3.3. Participants
The total sample population comprised 1303 participants, with a median number of 65 per study. One study [62] had an intervention of 12 months, with an additional 12-month follow-up. The interventions in the other publications varied in duration, ranging from 3 to 16 weeks (with a mean of 7.15 weeks), occurring 2 to 3 times per week, and consisting of 9 to 36 sessions (with a mean of 18.57 sessions). Specifically, three studies [12,13,51] had interventions lasting 3 weeks, one study lasted 4 weeks [50], three studies lasted 5 weeks [53,55,57], five studies lasted 6 weeks [52,56,59,62,63], three studies lasted 8 weeks [54,60,61], one study lasted 9 weeks [19], three studies lasted 12 weeks [16,17,44], and one study lasted 16 weeks [58]. Ten studies implemented the interventions twice a week [12,13,17,19,51,53,55,57,60,63], while eight studies conducted the interventions three times a week [16,44,50,52,54,59,61,62]. One study applied the interventions five times a week [55], and one study did not provide information regarding the weekly frequency [58]. A total of 1117 participants completed the training period or returned for the final assessment. In general, the adherence rate was 85.72% (Supplementary Material file S4).
The ages ranged between 60.25 [54] and 85.47 years [13] in the experimental groups and between 67.2 [52] and 83.11 years in the control groups [13]. Rendon et al. (2012) [50] did not present the mean age of the participants but reported that their ages ranged between 60 and 95 years, and Batista et al. (2014) [51] studied participants with a mean age of 68.1 years. All studies involved both male and female participants except for that reported by Batista et al. (2014) [51], in which only women took part.
3.4. Interventions
The Nintendo Wii Fit Balance Board was the controller most frequently used in training programs (nine studies) [12,48,49,50,51,52,53,57,59]. The description of the controllers used in each study can be found in Supplementary Material file S4 under “Used Technology”. In seven studies, the control groups received no training [12,13,17,51,52,56,61], while the comparison group received some interventions, such as conventional balance training [62], conventional proprioception training [55], stationary bicycle exercises [54], aerobic exercises [54], usual care and/or routine activities [19,63], and interventions with educational material [44,58]. In six studies, the older adults received conventional training [16,50,57,59,60,62]. The mean duration of the interventions that assessed the risk of falls was 9.6 weeks, with a range between 3 and 52 weeks. The mean duration of the interventions that assessed balance was 9.2 weeks, with the same variation in the risk of falls.
To assess the risk of falls, TUG was the tool most frequently used, in 11 studies [12,16,19,42,52,54,55,58,60,61,63]. Another four studies used the PPA to assess the risk of falls [19,42,57,63]. In addition to TUG and the PPA, 11 other instruments were used to assess the risk of falls. To assess balance, the BBS was the most used instrument, appearing in 12 studies [12,16,17,48,49,51,52,53,54,58,60,61]. A further 10 different instruments were used to assess balance. In four instruments, balance was assessed with the participants with their eyes closed and eyes open. Of the included studies, 17 [12,13,16,17,19,41,47,48,49,51,54,55,56,57,58,59,60] were randomized clinical trials (RCTs). One study was a clinical trial (CT) [53] and two studies had a quasi-experimental design [50,52].
3.5. Comparison
In seven studies, the control groups did not practice any other exercise [12,13,17,51,52,56,61]. In the other studies, the comparison groups practiced other exercises; most of them had traditional training for the risk of falls and/or balance.
3.6. Outcomes
For the risk of falls, a significant improvement in exergame groups was observed in relation to the control groups for TUG (Hedges’ g = 0.217, CI = 0.023; 0.411, p = 0.028), PPA (Hedges’ g = 0.382, CI = 0.004; 0.760, p = 0.048), and the other instruments (Hedges’ g = 0.216, CI = 0.040; 0.392, p = 0.016) (Figure 4). In the risk of falls outcome, significant heterogeneity was observed only in the PPA subgroup (I2 = 76.006%; p = 0.022). In the TUG groups (I2 = 25.71%; p = 0.191) and the other instruments (I2 = 13.241%; p = 0.318), no significant heterogeneity was observed. (Supplementary Material file S6).
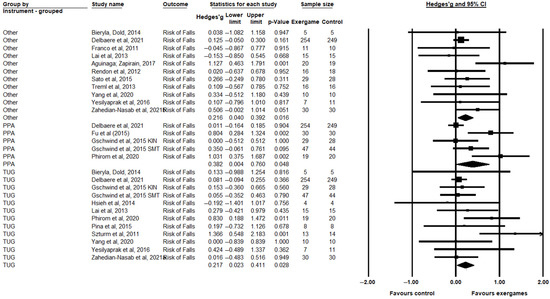
Figure 4.
Comparison between the intervention (exergaming) and control groups (conventional training or without intervention) evaluated regarding the risk of falls, in the time up and go (TUG), physiological profile assessment (PPA), and other categories, showing differences with standardized means (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) [12,13,16,17,19,42,49,50,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,60,61].
For balance, a significant improvement in exergame groups was observed in relation to the control groups for the BBS (Hedges’ g = 0.317, CI = 0.087; 0.546, p = 0.007) and the other instruments (Hedges’ g = 0.329, CI = 0.186; 0.472, p < 0.000) (Figure 5). In the balance outcome, significant heterogeneity was observed in both subgroups: the BBS (I2 = 61.892%; p = 0.034) and the other instruments (I2 = 74.055%, p = 0.0675).
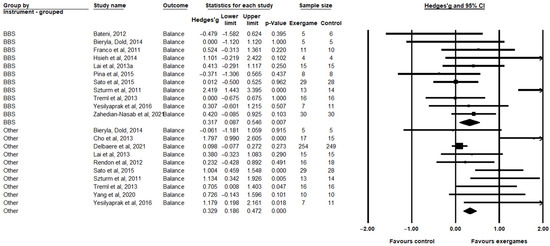
Figure 5.
Comparison between the intervention (exergaming) and control groups (conventional training or without intervention) evaluated regarding balance, in the Berg balance scale (BBS) categories and the other categories, showing the standardized mean differences (SMD) and confidence intervals (CI) of 95% [12,16,17,19,48,49,50,52,53,54,55,58,59,60,61].
Analyses of the other subgroups are presented in Supplementary Material file S6. In general, except for the subgroup that separated the studies on the risk of falls by place of execution (nursing homes or community centers), the adopted subgroups were not able to explain the heterogeneities in the individual studies. Significant heterogeneities remain within groups, which does not occur between groups. Although there were differences in the presence or absence of statistical significance, all subgroups, both for the risk of falls and for balance, showed positive results with the use of exergames. Only two studies [19,57] analyzed accidental falls among older adults. Fu et al. (2015) [57] reported that the incidence of falls was significantly lower in the exergame intervention group compared with the control group trained with conventional exercises (0.54 vs. 1.52 falls per person years, respectively). Delbaere et al. (2021) [19] reported that the risk of falls in the first 12 months of follow-up was lower (incidence rate ratio = 0.82) in their intervention group, although without statistical significance. Considering the 24-month follow-up, the difference (incidence rate ratio = 0.84) became statistically significant.
4. Discussion
The aim of this systematic review was to compile and critically analyze the findings of published studies concerning the efficacy of exergames in improving balance and reducing the risk of falls in older adults. The types of games, the outcome assessment tools, and the duration of intervention differed greatly between the studies, but the overall and subgroup results suggest that exergames have positive efficacy on balance and reduction of fall risks in older adults.
According to the meta-analysis, exergames were able to promote statistically significant positive effects on balance and the risk of falls in the groups submitted to intervention. Previous systematic reviews about the efficacy of exergames have already shown similar results [22,64,65]. The present review showed that the improvement occurs regardless of the instruments adopted to assess the results, the way in which the intervention was performed in the control groups, and the execution time in the short-term studies. However, care is needed with the interpretation of the results due to the low quality of the evidence. Despite this, it is important to note that only the study of Delbaere et al. (2021) [19] followed participants over a long period (24 months). In this study, the program significantly reduced the rate of falls after two years of follow-up. On the other side, meta-analysis of the present review showed that the reduction in the risk of falls was not significant after 12 weeks of follow-up. In this way, the results are not conclusive but indicate that exergames can be less effective in interventions designed to last for prolonged periods and this question must be better investigated.
Exergames were associated with an improvement in outcome measures that are used to predict the risk of falls. One study in particular showed that that the incidence of falls was lower in participants who trained with exergames [57]. Such an achievement may be explained by the visual and auditory stimuli provided by the games, which favor feedback mechanisms in the learning process and the retention of motor tasks performed in real-life situations [66]. The simultaneous feedback provided by exergames allows players to correct and synchronize their movement in real-time and, consequently, encourages better exercise performance and rehabilitation. In addition, the delivery and control of a dynamic stimulus is promoted by the exergaming environment [57]. Hence, the effectiveness of exergames, especially with respect to balance, can be explained by their efficiency and unpredictability. Another important aspect is that exergames seem to reduce the fear of falling in older individuals [61]. One of the advantages of exergames lies in the possibility of combining the specific tasks of the games used (sky slalom, sky jump, and soccer heading) with coaching instructions, such as bending forward, changing direction, and shifting weight. As a result, besides achieving balance control during the exercises, exergames allow participants to attain more effective movement or posture [20,67,68]. Older adults, due to the inherent characteristics of aging, experience reductions in muscle strength and balance. A lack of physical activity can exacerbate these losses, increasing the risk of falls. Therefore, exercise programs that involve balance training and muscle strengthening in sedentary older adults are expected to reduce the risk of falls [57].
One reason for the improvement observed in the groups that engaged in exergames is the greater appeal of interactive video games to older adults. This appeal contributes to increased performance in functional activities, which have been shown to effectively improve dynamic balance [57]. Other studies have also indicated that motivation and interest result in greater awareness and control of balance [69,70].
The duration of the intervention can play a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of exergaming. In this review, interventions lasting up to 12 weeks significantly reduced the risk of falls. However, interventions lasting 12 weeks or more were less common in the literature and did not show significant differences in fall risk reduction. This highlights the importance of considering longer interventions in future studies. A lack of physical activity can result in the weakening of the lower limbs and compromise balance. Thus, any intervention that includes physical activity can offer benefits for balance and reduce the risk of falls [55]. Our results show that the subjects taking part in exergaming had better results than those in the control groups with other exercises. However, the high heterogeneity, together with the low quality of the evidence, does not make it possible to say that exergames are superior to other practices. The publication of more studies will be useful for better clarification of this question.
Despite the benefits of exergaming, it is important to adopt safety measures and to always monitor participants, especially at the start of training, because the gaming platform and the screen may cause dizziness and disorientation which can cause accidents [66]. Moreover, as pointed out by Vojciechowski et al. (2018) [21], prescriptions of exercises involving exergaming typically lack specifications of, for example, the type of game, the number of sets and repetitions, and the duration, frequency, and intensity of training. Indeed, the studies included in this review varied considerably with respect to many of these parameters in addition to the outcomes analyzed, but none of the investigations examined training intensity.
Older adults in nursing homes often experience a rapid decline in daily functioning, leading to cognitive impairment, depression, and sleep disorders [71]. Despite the known benefits of physical activity and social interaction, these individuals spend a significant amount of time alone in their rooms without engaging in activities. This lack of physical activity and daily routine contributes to a significant functional deficit [71,72,73,74,75,76,77]. In our meta-analysis, the location where the interventions were conducted was the only subgroup that adequately explained the differences in the study results for fall risks. Minor variations were observed within the results of studies conducted in community centers or nursing homes, but significant variations were observed between these groups. This indicates that the specific characteristics of older adults living in each location contribute to differences in the effects of exergames.
Exergames have been found to be effective in significantly reducing fall risk and improving balance among older adults who live in community centers. However, there were no statistically significant effects on balance among individuals in the nursing homes group. This could be attributed to the lower statistical power of the analysis with studies conducted in nursing homes, which were less common in the literature. Therefore, although the findings suggest that exergames are important tools for improving balance, additional studies are still necessary.
Several reviews have examined the effectiveness of exercise in reducing the risk of falls and improving balance in older adults [22,38,39,78,79,80], all of which reported positive outcomes. However, only a couple of reviews [22,39] specifically discussed the use of exergames without comparing the issues analyzed in our review, such as the tools, interventions, duration of the interventions, and place of execution (community centers and nursing homes). Overall, the literature demonstrates that exercise is an important tool for reducing falls and improving balance in older adults, but it remains unclear whether exergames are superior to other exercise interventions [22,39]. Despite this, the published studies and the present review show that exergames are considered acceptable for community-dwelling older adults.
The assessment tools used in the studies evaluated a combination of balance, sway velocity, and lower limb strength, but these factors may not be sufficient to predict fall risk in older adult citizens [11]. Furthermore, some criticism may be justified with regard to the lack of blinding in the studies analyzed. Although it would be exceedingly difficult, if not impossible, to conceal the identities of the participants from the researchers who applied the tests, blinding could have been incorporated into the study design by masking the identities of the assessors from the individuals who performed the statistical analyses. In addition, many of the studies (~75%) employed small sample populations (≤40 participants) or were classified as having a high risk of bias (32.85%). The studies presented limited data on the socioeconomic characteristics, lifestyle, or health of the participants, while none of them analyzed the effectiveness of the exergame intervention according to age group. Another important limitation was the non-execution of publication bias analysis due to the small number of included studies.
In light of the above, future randomized clinical trials should encompass some fundamental protocols including: (i) increasing the sample size with blinding and division of participants into control, conventional training, and exergaming groups; (ii) standardizing the exergames by separating “commercial games” from specific health-related games aimed at training for balance and/or risk of falls; (iii) monitoring exercise intensity in all training groups; (iv) performing long-term interventions; (v) following up participants after the intervention to verify the retention of learning and physical gains obtained during the execution of the exergames and the ability to apply such information in daily life; (vi) analyzing variables such as prescribed medication, housing conditions, daily living habits, history of illnesses, and type of work which may impact on the intervention results; (vii) assessing the incidence of falls over time; (viii) monitoring participants according to their age group; (ix) performing better quality studies, using methods for blinding the participants and researchers; and (x) exploring various types of exergames (games and consoles) and examining other factors that may promote more effective effects of exergame use.
5. Conclusions
Although there are many gaps in our knowledge about the benefits of exergaming, especially concerning long-term interventions and the effectiveness of exergames compared to other forms of exercise for older adults, we conclude that there is a low certainty of evidence that exergames are suitable for improving balance and reducing fall risk in older adults. Further studies on the use of exergames should be pursued and their use as a collective health strategy should be evaluated, especially in older adult recreational centers, nursing homes, and basic health units.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/healthcare11131872/s1. Supplementary Material file S1: Prisma 2020 Checklist; Supplementary Material file S2: Organization of searches; Supplementary Material file S3: Summary for analyzing the quality of evidence (GRADE); Supplementary Material file S4: Overview of the main characteristics of the studies retrieved from the systematic review; Supplementary Material file S5: Assessing risk of bias in the non-randomized study; Supplementary Material file S6: Other meta-analyses.
Author Contributions
J.C.L. participated in the conception and design of the study, the data collection, the analysis and interpretation of the data, and the drafting and editing of the paper; V.S.B. participated in the conception and design of the study, the data collection, the analysis and interpretation of the data, and the drafting and editing of the paper; I.M.S. participated in the conception and design of the study, the data collection, and the revising the article critically for important intellectual content; R.V.F. participated in the conception and design of the study, the data collection, and revising the article the for important intellectual content; S.N.d.M. participated in the conception and design of the study, the data collection, and critically revising the article for important intellectual content; E.S.d.S. participated in the conception and design of the study and critically revising the article for important intellectual content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001. The funding body had no role in the design of the study, the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data, or in writing of the manuscript. The APC was funded by the Federal University of São João del Rei.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the Supplementary Materials of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gawryszewski, V.P. The importance of falls on the same level among the elderly in São Paulo state. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2010, 56, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras, R. Fórum. Envelhecimento Populacional e as Informações de Saúde Do PNAD: Demandas e Desafios Contemporâneos. Introdução. Cad. Saude Publica 2007, 23, 2463–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.B.d.A.; Goldbaum, M. Challenges of Aging in the Context of Social Inequalities. Rev. Saude Publica 2018, 52, 1s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchôa, E. An Anthropological Approach to Senior Citizens’ Health Issues. Cad. Saude Publica 2003, 19, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, A.C.M.; Azevedo, R.C.d.S.; Reiners, A.A.O.; Mendes, P.A.; Segri, N.J. Factors Associated with Fall Prevention Practices in Older Adults. Esc. Anna Nery Rev. Enferm. 2017, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, J.K.H.; Chan, T.Y.; Chan, D.K.Y. Falls Prevention in the Elderly: Translating Evidence into Practice. Hong Kong Med. J. 2015, 21, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu-Ambrose, T.; Davis, J.C.; Khan, K.M. Exercise to Prevent Falls in Older Adults—Reply. JAMA 2019, 322, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messias, M.G.; Neves, F.d.F. A Influência de Fatores Comportamentais e Ambientais Domésticos Nas Quedas Em Idosos. Rev. Bras. Geriatr. Gerontol. 2009, 12, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.d.O.; Barbosa, J.B.; Lemos, T.; Oliveira, L.A.S.; Ferreira, A.d.S. Agreement and Predictive Performance of Fall Risk Assessment Methods and Factors Associated with Falls in Hospitalized Older Adults: A Longitudinal Study. Geriatr. Nurs. 2023, 49, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, N.D.; Kannus, P.; Khan, K.M. Exercise in the Prevention of Falls in Older People: A Systematic Literature Review Examining the Rationale and the Evidence. Sport. Med. 2001, 31, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, B.C.; Clark, R.A.; Pua, Y.H. Novel Use of the Wii Balance Board to Prospectively Predict Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Clin. Biomech. 2015, 30, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieryla, K.A.; Dold, N.M. Feasibility of Wii Fit Training to Improve Clinical Measures of Balance in Older Adults. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugueta-Aguinaga, I.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. FRED: Exergame to Prevent Dependence and Functional Deterioration Associated with Ageing. A Pilot Three-Week Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Chia, B.X.; Chen, X.; Pham, T.P.; Theng, Y.-L. Exergaming as a Community Program for Older Adults: The Effects of Social Interaction and Competitive Information. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2020, 29, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Alía, P.; Muñoz-Ortiz, L.; Jiménez-González, M.; Benedicto-Pañell, C.; Altimir-Losada, S.; López-Colomer, Y.; Prat-Rovira, J.; Amargant-Rubio, J.F.; Jastes, S.M.; Moreno-Buitrago, A.; et al. Study Protocol of a Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Primary Care Intervention Using the NintendoTM Wii Console to Improve Balance and Decrease Falls in the Elderly. BMC Geriatr. 2016, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.H.; Peng, C.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Huang, C.P.; Hsiao, Y.L.; Chen, S.C. Effects of Interactive Video-Game Based System Exercise on the Balance of the Elderly. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Kuroki, K.; Saiki, S.; Nagatomi, R. Improving Walking, Muscle Strength, and Balance in the Elderly with an Exergame Using Kinect: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Games Health J. 2015, 4, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Shimizu, K.; Shiko, Y.; Kawasaki, Y.; Orita, S.; Inage, K.; Shiga, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Sato, M.; Enomoto, K.; et al. Effects of Nintendo Ring Fit Adventure Exergame on Pain and Psychological Factors in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain. Games Health J. 2021, 10, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbaere, K.; Valenzuela, T.; Lord, S.R.; Clemson, L.; Zijlstra, G.A.R.; Close, J.C.T.; Lung, T.; Woodbury, A.; Chow, J.; McInerney, G.; et al. E-Health StandingTall Balance Exercise for Fall Prevention in Older People: Results of a Two Year Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ 2021, 373, n740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrington, C.; Fairhall, N.; Kwok, W.; Wallbank, G.; Tiedemann, A.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Ng, C.A.C.M.; Bauman, A. Evidence on Physical Activity and Falls Prevention for People Aged 65+ Years: Systematic Review to Inform the WHO Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojciechowski, A.S.; Biesek, S.; Filho, J.M.; Rabito, E.I.; Amaral, M.P.d.; Gomes, A.R.S. Effects of Physical Tr aining with the Nintendo Wii Fit Plus® and Protein Supplementation on Musculoskeletal Function and the Risk of Falls in Pre-Frail Older Women: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial (the WiiProtein Study). Maturitas 2018, 111, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, L.; Rössler, R.; Faude, O. Effects of Virtual Reality Training (Exergaming) Compared to Alternative Exercise Training and Passive Control on Standing Balance and Functional Mobility in Healthy Community-Dwelling Seniors: A Meta-Analytical Review. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.-Y.; Li, H.-J. Effects of Exergame and Video Game Training on Cognitive and Physical Function in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Appl. Ergon. 2022, 101, 103690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated Guidance and Exemplars for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R Package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-Compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armijo-Olivo, S.; Stiles, C.R.; Hagen, N.A.; Biondo, P.D.; Cummings, G.G. Assessment of Study Quality for Systematic Reviews: A Comparison of the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias Tool and the Effective Public Health Practice Project Quality Assessment Tool: Methodological Research. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2012, 18, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morissette, K.; Tricco, A.C.; Horsley, T.; Chen, M.H.; Moher, D. Blinded versus Unblinded Assessments of Risk of Bias in Studies Included in a Systematic Review. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 2011, MR000025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savović, J.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; Turner, L.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; Higgins, J.P. Evaluation of the Cochrane Collaboration’s Tool for Assessing the Risk of Bias in Randomized Trials: Focus Groups, Online Survey, Proposed Recommendations and Their Implementation. Syst. Rev. 2014, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmucker, C.; Meerpohl, J.J.; Blümle, A. Bias in Kontrollierten Studien. Radiologe 2019, 59, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.P.V.; Silva, V.G.A. Avaliação Do Risco de Viés de Ensaios Clínicos Randomizados Pela Ferramenta Da Colaboração Cochrane. Diagnóstico Trat. 2013, 18, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (Robvis): An R Package and Shiny Web App for Visualizing Risk-of-bias Assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GRADE Working Group. Grading Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations. BMJ 2004, 328, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRADEpro. GDT GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool; GRADEpro: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil, M. Diretrizes Metodológicas: Sistema GRADE—Manual de Graduação Da Qualidade Da Evidência e Força de Recomendação Para Tomada de Decisão Em Saúde; Ministério da Saúde Brasília: Brasília, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington, C.; Fairhall, N.J.; Wallbank, G.K.; Tiedemann, A.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Howard, K.; Clemson, L.; Hopewell, S.; Lamb, S.E. Exercise for Preventing Falls in Older People Living in the Community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD012424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchet, O.; Fantino, B.; Allali, G.; Muir, S.W.; Montero-Odasso, M.; Annweiler, C. Timed up and Go Test and Risk of Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2011, 15, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlo, D.; Richardson, S. The Timed “Up & Go”: A Test of Basic Functional Mobility for Frail Elderly Persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, S.R.; Menz, H.B.; Tiedemann, A. A Physiological Profile Approach to Falls Risk Assessment and Prevention. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phirom, K.; Kamnardsiri, T.; Sungkarat, S. Beneficial Effects of Interactive Physical-Cognitive Game-Based Training on Fall Risk and Cognitive Performance of Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, S. The Berg Balance Scale. J. Physiother. 2015, 61, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-S. The Diagnostic Accuracy of the Berg Balance Scale in Predicting Falls. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2017, 39, 1502–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamato, T.; Maher, C.; Saragiotto, B.; Hancock, M.; Ostelo, R.; Cabral, C.; Costa, L.; Costa, L. Pilates for Low Back Pain ( Review) Pilates for Low Back Pain. Cochrane Collab. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Jain, K. Meta-Analysis of Fixed, Random and Mixed Effects Models. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2019, 4, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Higgins, J.P.T. Meta-Analysis and Subgroups. Prev. Sci. 2013, 14, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateni, H. Changes in Balance in Older Adults Based on Use of Physical Therapy vs the Wii Fit Gaming System: A Preliminary Study. Physiotherapy 2012, 98, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.R.; Jacobs, K.; Inzerillo, C.; Kluzik, J. The Effect of the Nintendo Wii Fit and Exercise in Improving Balance and Quality of Life in Community Dwelling Elders. Technol. Heal. Care 2012, 20, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, A.A.; Lohman, E.B.; Thorpe, D.; Johnson, E.G.; Medina, E.; Bradley, B. The Effect of Virtual Reality Gaming on Dynamic Balance in Older Adults. Age Ageing 2012, 41, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, J.S.; Wibelinger, L.M.; De Marchi, A.C.B.; Pasqualotti, A. Evaluation and Physiotherapeutic Intervention in Older with Deficit Balance through the Scale of Berg and Wii Balance Board Platform. Fisioter. em Mov. 2014, 27, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, J.M.S.; Santana, M.C.d.S.; Duarte, G.P.; Gomes Neto, M.; Ribeiro, N.M.d.S.; Ferraz, D.D. Estudo Comparativo Dos Efeitos de Exercícios Realizados Com Nintendo Wii Comparado a Exercícios Aeróbicos Convencionais No Equilíbrio e Risco de Quedas de Idosos: Um Ensaio Clínico Randomizado Piloto. Fisioterapia 2015, 10, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Treml, C.J.; Filho, F.A.K.; Ciccarino, R.F.L.; Wegner, R.S.; Saita, C.Y.d.S.; Correa, A.G. The Balance Board Plataform Used as a Physiotherapy Resource in Elderly. Rev. Bras. Geriatr. Gerontol. 2013, 16, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, W.M.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, S.C.; Tan, S.Y.; Hwang, Y.S.; Chen, S.C.; Lai, J.S.; Chen, Y.L. Virtual Reality System Based on Kinect for the Elderly in Fall Prevention. Technol. Heal. Care 2014, 22, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-M.; Hsieh, J.S.C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Yang, S.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.K. Effects of Kinect Exergames on Balance Training among Community Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicine 2020, 99, e21228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwind, Y.J.; Eichberg, S.; Marston, H.R.; Ejupi, A.; Rosario, H.d.; Kroll, M.; Drobics, M.; Annegarn, J.; Wieching, R.; Lord, S.R.; et al. ICT-Based System to Predict and Prevent Falls (IStoppFalls): Study Protocol for an International Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Geriatr. 2014, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, A.S.; Gao, K.L.; Tung, A.K.; Tsang, W.W.; Kwan, M.M. Effectiveness of Exergaming Training in Reducing Risk and Incidence of Falls in Frail Older Adults with a History of Falls. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szturm, T.; Betker, A.L.; Moussavi, Z.; Desai, A.; Goodman, V. Effects of an Interactive Computer Game Exercise Regimen on Balance Impairment in Frail Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys. Ther. 2011, 91, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.H.; Hwangbo, G.; Shin, H.S. The Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Balance Training on Balance of the Elderly. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilyaprak, S.S.; Yildirim, M.Ş.; Tomruk, M.; Ertekin, Ö.; Algun, Z.C. Comparison of the Effects of Virtual Reality-Based Balance Exercises and Conventional Exercises on Balance and Fall Risk in Older Adults Living in Nursing Homes in Turkey. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2016, 32, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedian-Nasab, N.; Jaberi, A.; Shirazi, F.; Kavousipor, S. Effect of Virtual Reality Exercises on Balance and Fall in Elderly People with Fall Risk: A Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrens, M.; Tiedemann, A.; Delbaere, K.; Alley, S.; Vandelanotte, C. The Effect of EHealth-Based Falls Prevention Programmes on Balance in People Aged 65 Years and over Living in the Community: Protocol for a Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e031200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwind, Y.J.; Schoene, D.; Lord, S.R.; Ejupi, A.; Valenzuela, T.; Aal, K.; Woodbury, A.; Delbaere, K. The Effect of Sensor-Based Exercise at Home on Functional Performance Associated with Fall Risk in Older People—A Comparison of Two Exergame Interventions. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, L.; Hou, H.-Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, H.-J. The Effect of Exergame Training on Physical Functioning of Healthy Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Games Health J. 2022, 11, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.D.; Guo, L.; Kang, D.; Xiong, S. Exergame Technology and Interactive Interventions for Elderly Fall Prevention: A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Ergon. 2017, 65, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, G.C.V.; Simões, M.d.S.; Lin, S.M.; Bacha, J.M.R.; Viveiro, L.A.P.; Varise, E.M.; Junior, N.C.; Lange, B.; Filho, W.J.; Pompeu, J.E. Feasibility, Safety, Acceptability, and Functional Outcomes of Playing Nintendo Wii Fit PlusTM for Frail Older Adults: A Randomized Feasibility Clinical Trial. Maturitas 2018, 118, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Pua, Y.-H.; Fortin, K.; Ritchie, C.; Webster, K.E.; Denehy, L.; Bryant, A.L. Validity of the Microsoft Kinect for Assessment of Postural Control. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Diest, M.; Stegenga, J.; Wörtche, H.J.; Postema, K.; Verkerke, G.J.; Lamoth, C.J.C. Suitability of Kinect for Measuring Whole Body Movement Patterns during Exergaming. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, J.-W.; Chou, C.-X.; Hsieh, Y.-W.; Wu, W.-C.; Yu, M.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Chang, H.-F.; Ding, S.-E. Randomized Comparison Trial of Balance Training by Using Exergaming and Conventional Weight-Shift Therapy in Patients With Chronic Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSANG, W.W.N.; HUI-CHAN, C.W.Y. Effects of Exercise on Joint Sense and Balance in Elderly Men: Tai Chi versus Golf. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2004, 36, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A.; Lambley, R.; Hardy, J.; Young, J.; Smith, J.; Green, J.; Burns, E. Rehabilitation for Older People in Long-Term Care. In The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; Forster, A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ice, G.H. Daily Life in a Nursing Home. J. Aging Stud. 2002, 16, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, S.; Winsby, M. A Relational Perspective on Autonomy for Older Adults Residing in Nursing Homes. Heal. Expect. 2011, 14, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.A.; Gooneratne, N.; Cole, C.S.; Kleban, M.H.; Kalra, G.K.; Richards, K.C. Exercise and Social Activity Improve Everyday Function in Long-Term Care Residents. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2012, 20, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, M.M.Y.; Tang, S.K.; Wan, V.T.C.; Vong, S.K.S. The Effectiveness of Physical Exercise Training in Pain, Mobility, and Psychological Well-Being of Older Persons Living in Nursing Homes. Pain Manag. Nurs. 2014, 15, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, G.I.; Hastie, C.L.; Morris, J.N.; Fries, B.E.; Ankri, J. Measuring Change in Activities of Daily Living in Nursing Home Residents with Moderate to Severe Cognitive Impairment. BMC Geriatr. 2006, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, S.; Nayak, U.S.; Isaacs, B. Balance in Elderly Patients: The “Get-up and Go” Test. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1986, 67, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Thomas, S.M.; Veroniki, A.A.; Hamid, J.S.; Cogo, E.; Strifler, L.; Khan, P.A.; Robson, R.; Sibley, K.M.; MacDonald, H.; et al. Comparisons of Interventions for Preventing Falls in Older Adults. JAMA 2017, 318, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautzenberg, L.; Beglinger, S.; Tsokani, S.; Zevgiti, S.; Raijmann, R.C.M.A.; Rodondi, N.; Scholten, R.J.P.M.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Di Nisio, M.; Emmelot-Vonk, M.; et al. Interventions for Preventing Falls and Fall-related Fractures in Community-dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 2973–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Min, L.; Xu, N.; Huang, L.; Li, X. The Effect of Exercise Intervention on Reducing the Fall Risk in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).