Frailty in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia—Prevalence and Management, Where Are We? †
Abstract
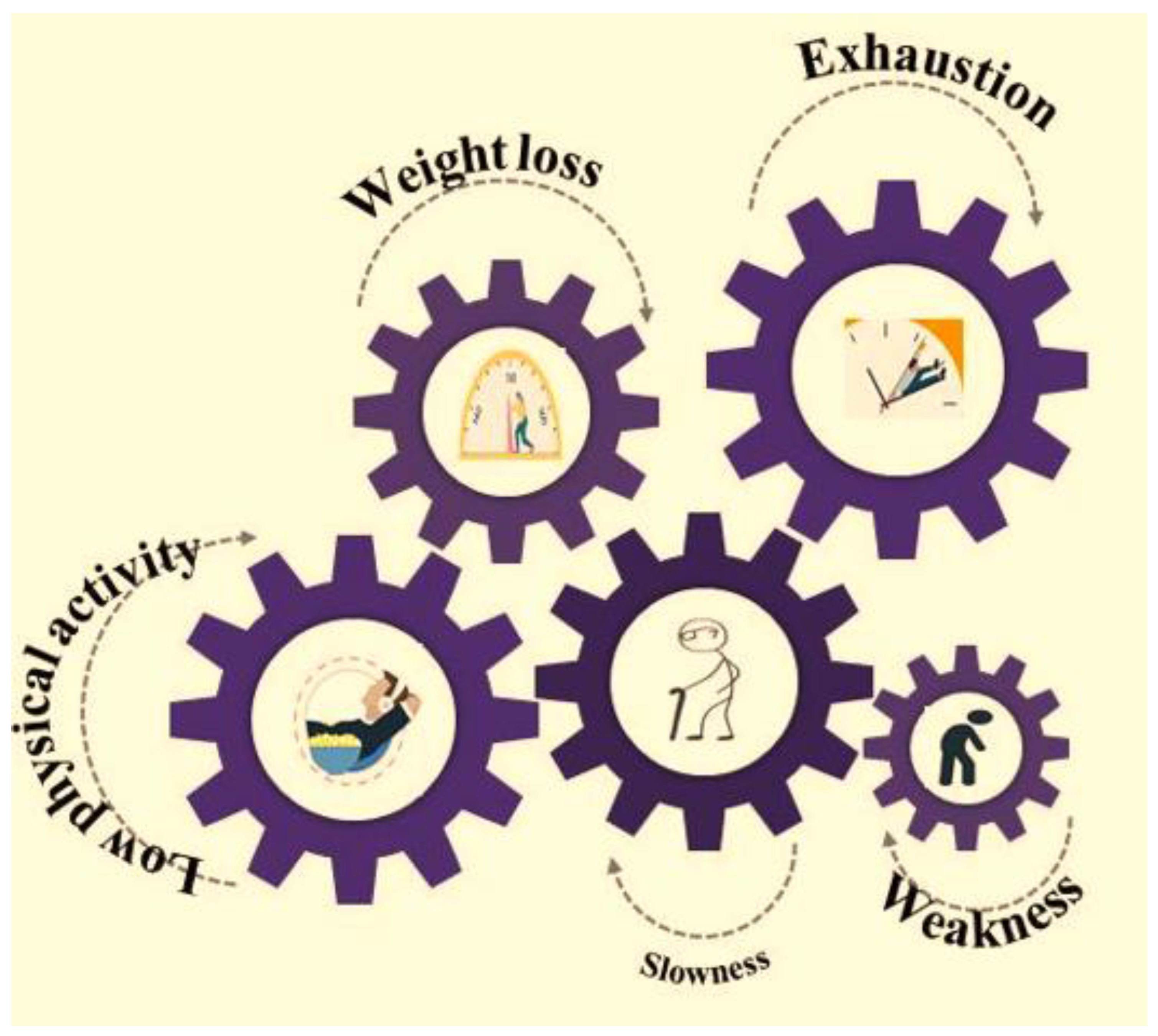
1. Frailty—Definition and Models Used for Its Prediction
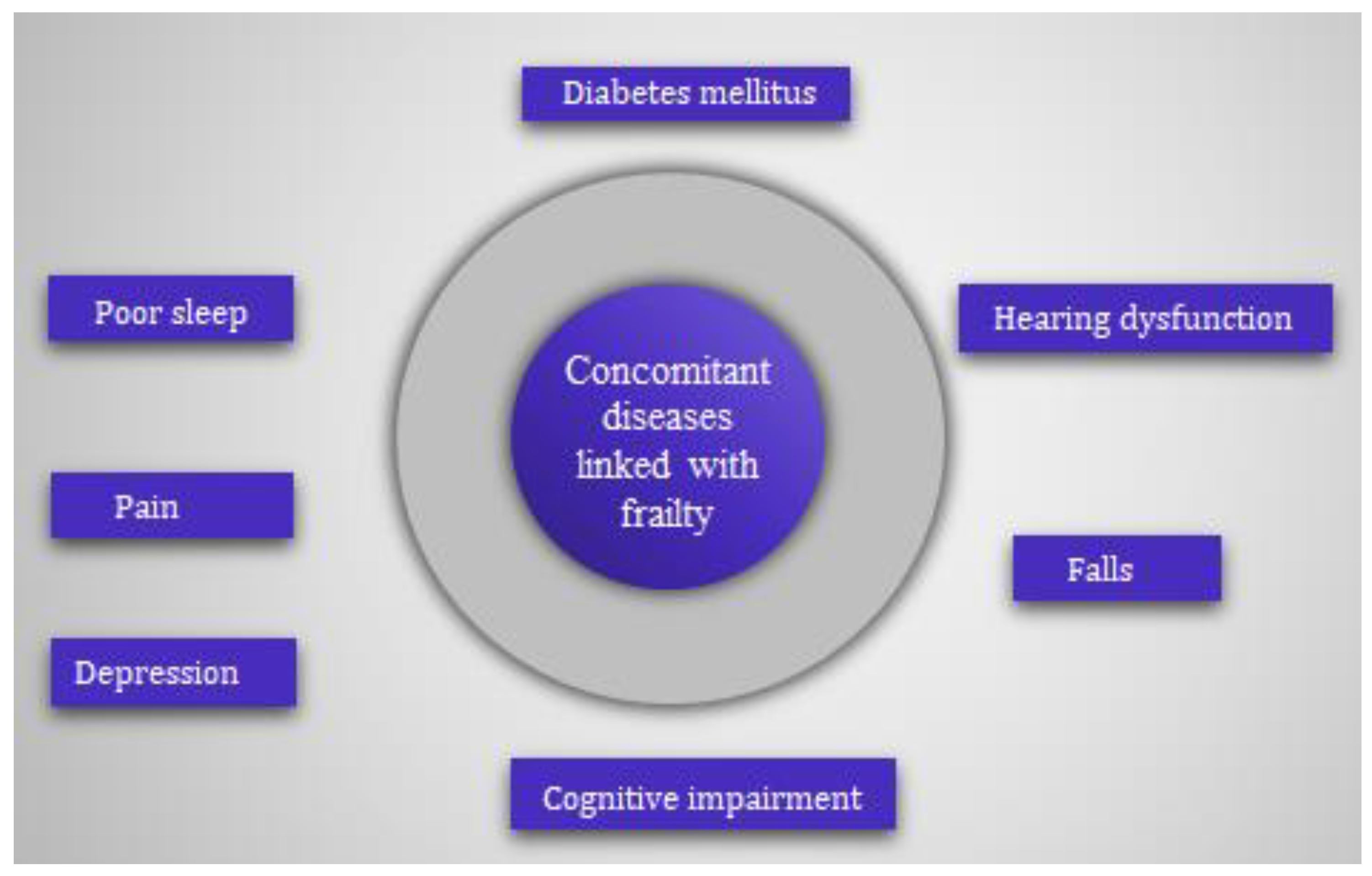
2. Association of Frailty with Concomitant Diseases
3. Research on Frailty in KSA until Present Day
3.1. Frailty Prevalence
3.2. Frailty and Sarcopenia
3.3. Frailty and Falls
4. Futuristic Management Plan—Author’s Opinion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Iriarte, E.; Cianelli, R.; De Santis, J.P.; Baeza, M.J.; Alamian, A.; Castro, J.G.; Matsuda, Y.; Araya, A.X. Frailty among older Hispanics living in the United States: A scoping review. Geriatr. Nurs. 2022, 48, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, R.; Stelmach-Mardas, M.; Bergmann, M.M.; Bernigau, W.; Weber, D.; Pischon, T.; Boeing, H. The accumulation of deficits approach to describe frailty. PLoS ONE 2019, 15, e0223449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, A.E.; Howlett, S.E. Sex differences in frailty: Comparisons between humans and preclinical models. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 198, 111546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinan, P. Frailty and old age. Linacre Q. 2016, 83, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midao, L.; Brochado, P.; Almada, M.; Duarte, M.; Paul, C.; Costa, E. Frailty status and polypharmacy predict all-cause mortality in community dwelling older adults in Europe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 30, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, C.S.; Labuschagne, H.A.; van Keulen, K. Polypharmacy, comorbidity and frailty: A complex interplay in older patients at the emergency department. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2022, 13, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshanberi, A.M. Recent updates on risk and management plans associated with polypharmacy in older population. Geriatrics 2022, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.K.; Canevelli, M.; Cesari, M.; Aprahamian, I. Frailty as a predictor of cognitive disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, J.K.H.; Chan, D.K. Frailty and sarcopenia-from theory to practice. Hong Kong Med. J. 2022, 28, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Physical frailty/sarcopenia as a key predisposing factor to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and its complications in older adults. Bio. Med. 2021, 1, 11–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.T.M.; Srivastava, S. Cross-sectional associations of physical frailty with fall, multiple falls and fall-injury among older Indian adults: Findings from LASI, 2018. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H.; Ding, H. Frailty as a predictor of future falls and disability: A four-year follow-up study of Chinese older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade, F.L.J.P.; Jerez-Roig, J.; Belem, L.N.M.; de Lima, K.C. Frailty among institutionalized older people: A cross-sectional study in Natal (Brazil). J. Frail. Sarcop. Falls 2019, 1, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhong, G.C.; Zhou, X. Frailty and risks of all-cause and cause-specific death in community-dwelling adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fhon, J.R.S.; Rodrigues, R.A.P.; Santos, J.L.F.; Diniz, M.A.; Santos, E.B.D.; Almeida, V.C.; Giacomini, S.B.L. Factors associated with frailty in older adults: A longitudinal study. Rev. Saude Publica 2018, 26, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Ghafar, M.Z.A.; O’Donovan, M.; Sezgin, D.; Moloney, E.; Rodrıguez-Laso, A.; Liew, A.; O’Caoimh, R. Frailty and diabetes in older adults: Overview of current controversies and challenges in clinical practice. Front. Clin. Diab. Health. 2022, 3, 895313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Abbatecola, A.M.; Woo, J. Management of comorbidities in older persons with type 2 diabetes. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, P.; Faure, I.; Corcoran, N.; Butterly, E.; Lewsey, J.; McAllister, D. Frailty measurement, prevalence, incidence and clinical implications in people with diabetes: A systematic review and study-level meta-analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2020, 1, e106–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Kim, K.I. Frailty and disability in diabetes. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2019, 23, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Almeida, O.P.; Jayakody, D.M.P.; Ford, A.H. Association between hearing loss and frailty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 25, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Trevenen, M.; Ford, A.H.; Jayakody, D.M.P.; Hankey, G.J.; Yeap, B.B.; Golledge, J.; Flicker, L.; Almeida, O.P. Hearing impairment and frailty in later life: The Health in Men Study HIMS). Maturitas 2022, 156, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Trevenen, M.; Ford, A.H. Hearing impairment and incident frailty in later life: The Health in Men Study (HIMS). J. Nutr. Health Ageing 2023, 27, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabricio, D.M.; Chagas, M.H.N.; Diniz, B.S. Frailty and cognitive decline. Transl. Res. 2020, 221, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Z.H.; Hang, A.L.; Xue, M.T.; Li, Q.Y.; Bai, Y.M.; Hu, G.H. Cognitive frailty as a predictor of adverse outcomes among older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e01926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigola, A.G.; Ottaviani, A.C.; Carvalho, D.H.T.; Oliveria, N.A.; Souza, E.N.; Pavarini, S.C.L. Association between cognitive impairment and criteria for frailty syndrome among older adults. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2020, 78, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Zhou, C.; Meng, Q. Associations of sleep quality and frailty among the older adults with chronic disease in China: The mediation effect of psychological distress. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 20, 5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, W. Evaluation of the correlation between frailty and sleep quality among elderly patients with osteoporosis: A cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.; Maharani, A.; Chandola, T.; O’Neill, T.W.; Todd, C.; Pendleton, N. A prospective analysis examining frailty remission and the association with future falls risk in older adults in England. Age Ageing 2023, 1, afad003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.L.; Chu, N.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Kasper, J.D.; Xue, Q.L. Order of onset of physical frailty and cognitive impairment and risk of repeated falls in community-dwelling older adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2023, 24, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosch, P.S.; Kristensson, J.; McGuigan, F.E. Frailty and prediction of recurrent falls over 10 years in a community cohort of 75-year-old women. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriero, F.; Reid, M.C. Linking persistent pain and frailty in older adults. Pain Med. 2020, 1, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.; Crookes, K.; Seaman, K. Frailty and pain in an acute private hospital: An observational point prevalence study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, M.; Tang, R.; Wang, H.; Xiao, M.; Geng, G.; Xie, J.; Yan, H. A pathway model of chronic pain and frailty in older Chinese cancer patients: The mediating effect of sleep. Geriatr. Nurs. 2023, 50, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconcin, P.; Barak, S.; Ferrari, G.; Gouveia, E.R.; de Maio, N.M.; Willig, R.; Varela, M.; Marques, A. Prevalence of frailty and its association with depressive symptoms among european older adults from 17 countries: A 5-year longitudinal study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maștaleru, A.; Abdulan, I.M.; Ștefaniu, R.; Lefter, N.; Sandu, I.A.; Pislaru, A.I.; Leon-Constantin, M.M.; Alexa, I.D.; Ilie, A.C. Relationship between frailty and depression in a population from north-eastern romania. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Perez, D.; Sanchez-Flores, M.; Proietti, S.; Bonassi, S.; Costa, S.; Teixeira, J.P.; Fernandez-Tajes, J.; Pasaro, E.; Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B. Low Vitamin D levels and frailty status in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2020, 30, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Wanigatunga, A.A.; Mitchell, C.M.; Urbanek, J.K.; Miller, E.R.; Juraschek, S.P.; Michos, E.D.; Kalyani, R.R.; Roth, D.L.; Appel, L.J.; et al. The effects of vitamin D supplementation on frailty in older adults at risk for falls. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.J.; Ciarleglio, A.; Roose, S.P.; Montes Garcia, C.; Chung, S.; Fernandes, S.; Rutherford, B.R. Frailty and depression in late life: A high-risk comorbidity with distinctive clinical presentation and poor antidepressant response. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, V.A.C.; Berlezi, E.M.; Gross, C.B.; Colet, C.F. Antidepressant use and the components of the frailty syndrome. Rev. Bras. Geriatr. Gerontol. 2018, 21, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Hu, J.; Zhao, J.; Tao, H.; Chi, J.; Niu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Menopause and frailty: A scoping review. Menopause 2022, 27, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, G.; Taniguchi, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Aoyama, R.; Urano, T. Age at menopause is negatively associated with frailty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas 2022, 165, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, E. Association between menopausal hormone therapy and frailty: Cross-sectional study using national survey data in Korea. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori-Asenso, R.; Chin, K.L.; Mazidi, M.; Zomer, E.; Ilomaki, J.; Zullo, A.R.; Gasevic, D.; Ademi, Z.; Korhonen, M.J.; LoGiudice, D.; et al. Global incidence of frailty and pre-frailty among community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Net. Open. 2019, 2, e198398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs PD. World Population Ageing 2017; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/ageing/WPA2017_Highlights.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Care for the Elderly in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Available online: https://www.my.gov.sa/wps/portal/snp/careaboutyou/elderly/!ut/p/z0/04_Sj9CPykssy0xPLMnMz0vMAfIjo8zijQx93d0NDYz8LYIMLA0CQ4xCTZwN_Ay8Qgz1g1Pz9AuyHRUB-ivojg!!/ (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Alqahtani, B.A.; Alshehri, M.M.; Elnaggar, R.K.; Alsaad, S.M.; Alsayer, A.A.; Almadani, N.; Alhowimel, A.; Alqahtani, M.; Alenazi, A.M. Prevalence of frailty in the Middle East: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, B.A.; Nasser, T.A. Assessment of frailty in Saudi community-dwelling older adults: Validation of measurements. Ann. Saudi Med. 2019, 39, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, B.A.; Alenazi, A.M.; Alshehri, M.M.; Osailan, A.M.; Alsubaie, S.F.; Alqahtani, M.A. Prevalence of frailty and associated factors among Saudi community-dwelling older adults: A cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 17, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alodhayani, A.A.; Alsaad, S.M.; Almofarej, N.; Alrasheed, N.; Alotaibi, B. Frailty, sarcopenia and health related outcomes among elderly patients in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sc. 2021, 28, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghannam, A.F.; Almasud, A.A.; Alghnam, S.A.; Alharbi, D.S.; Aljubairi, M.S.; Altalhi, A.S.; Jan Am Alothman, S.A. Prevalence of sarcopenia among Saudis and its association with lifestyle behaviors: Protocol for cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almufarrih, A.; Almutairi, B.; Alblowi, N.; Asiri, S.; Alnashri, A.; Albattal, S.; Maher, M.; Kofi, M. The prevalence of frailty and its associated risk factors among the saudi elderly population in primary health care in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Act. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 5, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Ahmed, D.; Alfaris, M.; Holmes, A.; Aljizeeri1, A.; Al-Mallah, M.H. Prevalence and predictors of frailty in a high-income developing country: A cross-sectional study. Qatar Med. J. 2020, 2019, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almegbel, F.Y.; Alotaibi, I.M.; Alhusain, F.A.; Masuadi, E.M.; Al Sulami, S.L.; Aloushan, A.F.; Almuqbil, B.I. Period prevalence, risk factors and consequent injuries of falling among the Saudi elderly living in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, S.A.; Al Jabr, Q.M.; Alramadhan, Z.T.; Algharrash, Z.; Alyousif, A.J.A.; Alessa, A.N.; Al Butayan, H.A. Screening of diabetic patients for frailty with the frail scale: A comparison with the fried’s phenotype criteria in Saudi Arabia. Diab. Obes. Int. J. 2021, 6, 000244. [Google Scholar]
- Alqahtani, B.A. Association between physical frailty and sleep quality among saudi older adults: A community-based, cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaad, S.M.; AlEraij, S.; Alsaad, A.M.; AlSaif, H.I.; Bawazeer, G. Potentially inappropriate medications among elderly with frailty in a tertiary care academic medical centre in saudi arabia. Healthcare 2022, 31, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkeridy, W.A.; Aljasser, A.; Alayed, K.M.; Alsaad, S.M.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Lim, C.A.; Alamri, S.H.; Mekkawy, D.Z.; Al-Sofiani, M. Predictors of mortality in home health care service: Data from Saudi Arabia. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2022, 2022, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaad, S.M.; Alghamdi, K.A.; Alghamdi, S.A.; Alsahli, N.A.; Alshamrani, S.A.; Alodhayani, A.A. Frailty and its associated factors among hospitalized older patients in an academic hospital using the FRAIL scale. Int. J. Gerontol. 2022, 16, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Gobbens, R.J.; Boersma, P.; Uchmanowicz, I.; Santiago, L.M. The Tilburg Frailty Indicator (TFI): New Evidence for Its Validity. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 21, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| S. No. | Type of Study | Scale | Setting | Sample Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cross-section | FFI | Outpatient | 47 | [47] |
| 2 | Cross-section | Fried frailty phenotype | Residence | 486 | [48] |
| 3 | Descriptive | Edmonton frail and SARC-F scale | Residence | 498 | [49] |
| 4 | Analytical | Global physical activity questionnaire, PSQI, Euro QOL five-dimensional questionnaire | Lifestyle and health research center at Princess Norah bint Abdulrehman University, Riyadh | 1532 | [50] |
| 5 | Observational | FRAIL scale and Mini-Cog test | Outpatient | 228 | [51] |
| 6 | Descriptive | Fried clinical frailty scale | Cardiac patients | 876 | [52] |
| 7 | Cross-sectional study by convenient sampling | Data collection form | Questionnaire | 1182 | [53] |
| 8 | Cross-section | Cardiovascular Health study index and FRAIL | Outpatient | 78 | [54] |
| 9 | Cross-section | PSQI and FFI | Community-based | 270 | [55] |
| 10 | Retrospective | Beers and FRAIL | Inpatient | 358 | [56] |
| 11 | Retrospective | Clinical frailty scale | King Saud University Medical Complex, Riyadh | 555 | [57] |
| 12 | Analytical | FRAIL | King Saud University Medical Complex, Riyadh | 367 | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshanberi, A.M. Frailty in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia—Prevalence and Management, Where Are We? Healthcare 2023, 11, 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121715
Alshanberi AM. Frailty in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia—Prevalence and Management, Where Are We? Healthcare. 2023; 11(12):1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121715
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshanberi, Asim Muhammed. 2023. "Frailty in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia—Prevalence and Management, Where Are We?" Healthcare 11, no. 12: 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121715
APA StyleAlshanberi, A. M. (2023). Frailty in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia—Prevalence and Management, Where Are We? Healthcare, 11(12), 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11121715






