Differences in Physical Activity Levels between Healthy and Transplanted Children: Who Needs More Tips?
Abstract
1. Introduction
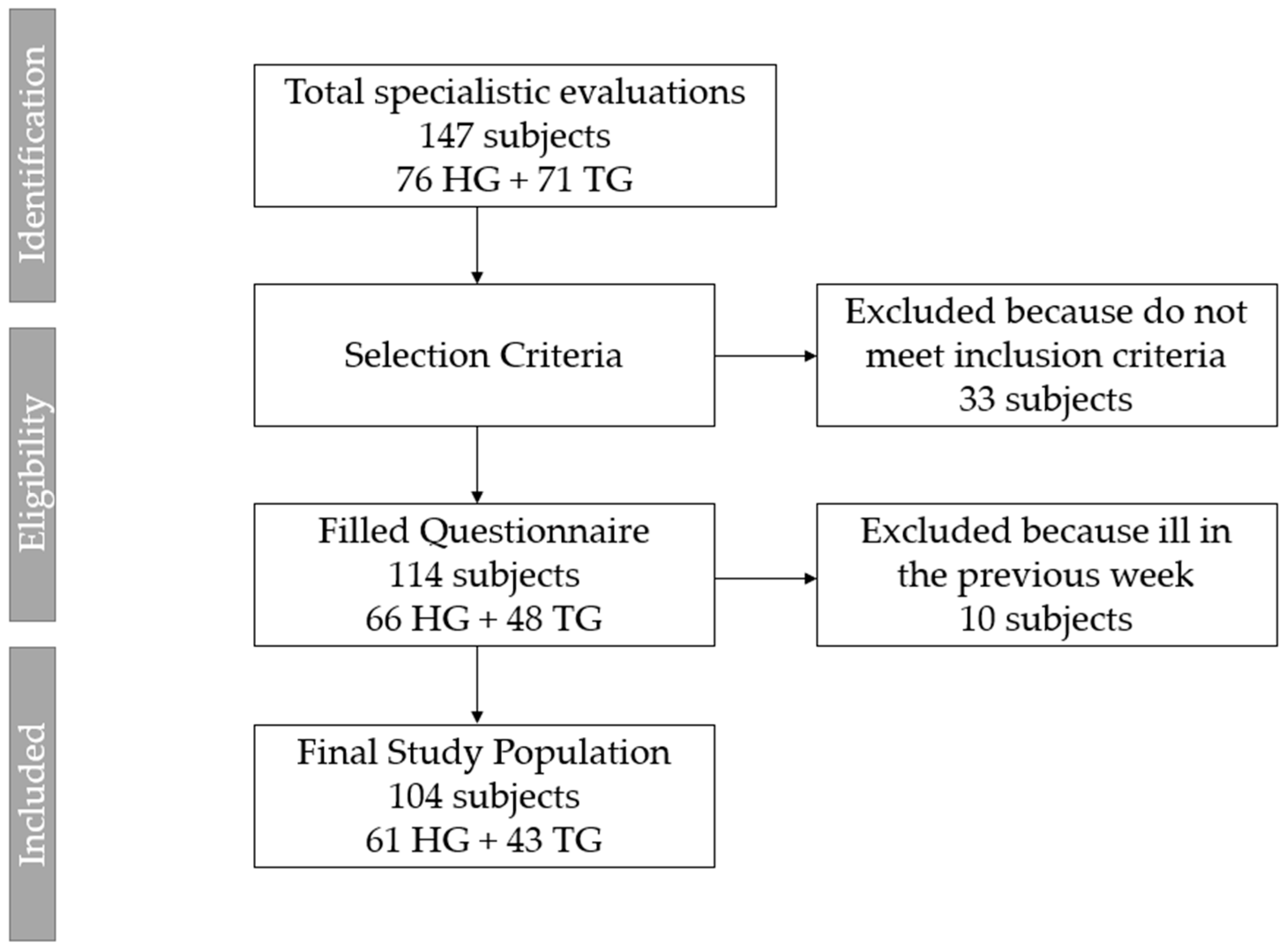
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects
- Aged between 8 and 18 years old;
- Underwent a solid organ transplant or undergoing to pre-participation screening for sport;
- At least 2 years elapsed since the kidney/liver transplant;
- No contraindications to practice sports activities;
- Stable clinical condition.
- Non-cooperating children for the questionnaire due to age and/or psycho-physical limitations;
- Patients with a history of congenital heart disease;
- Patients with other comorbidities or multiple organ transplant;
- Children who reported having been ill in the previous week;
- Children with congenital heart disease or other comorbidities were not enrolled to avoid confounding effects of other pathologies on exercise practice.
2.3. Questionnaire
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Question | Response Scored 1 | Response Scored 2 | Response Scored 3 | Response Scored 4 | Response Scored 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Physical activity in your spare time: Have you done any of the following activities in the past 7 days (last week)? If yes, how many times? | No | 1–2 | 3–4 | 5–6 | 7 times or more |
| 2. In the last 7 days, during your physical education (PE) classes, how often were you very active (playing hard, running, jumping, throwing)? | I don’t do PE | Hardly ever | Sometimes | Quite often | Always |
| 3. In the last 7 days, what did you do most of the times at the access? | Sat down (talking, reading, doing schoolwork) | Stood around or walked around | Ran or played a little bit | Ran around and played quite a bit | Ran and played hard most of the time |
| 4. In the last 7 days, what did you normally do at lunch (besides eating lunch)? | Sat down (talking, reading, doing schoolwork) | Stood around or walked around | Ran or played a little bit | Ran around and played quite a bit | Ran and played hard most of the time |
| 5. In the last 7 days, on how many days right after school, did you do sports, dance, or play games in which you were very active? | None | 1 time last week | 2 or 3 times last week | 4 times last week | 5 times last week |
| 6. In the last 7 days, on how many evenings did you do sports, dance, or play games in which you were very active? | None | 1 time last week | 2 or 3 times last week | 4 or 5 last week | 6 or 7 times last week |
| 7. On the last weekend, how many times did you do sports, dance, or play games in which you were very active? | None | 1 time | 2 or 3 times | 4 or 5 times | 6 or more times |
| 8. Which one of the following describes you best for the last 7 days? | All or most of my free time was spent doing things that involve little physical effort | I sometimes (1–2 times last week) did physical things in my free time (e.g., played sports, went running, swimming, bike riding, did aerobics) | I often (3–4 times last week) did physical things in my free time | I quite often (5–6 times last week) did physical things in my free time | I very often (7 or more times last week) did physical things in my free time |
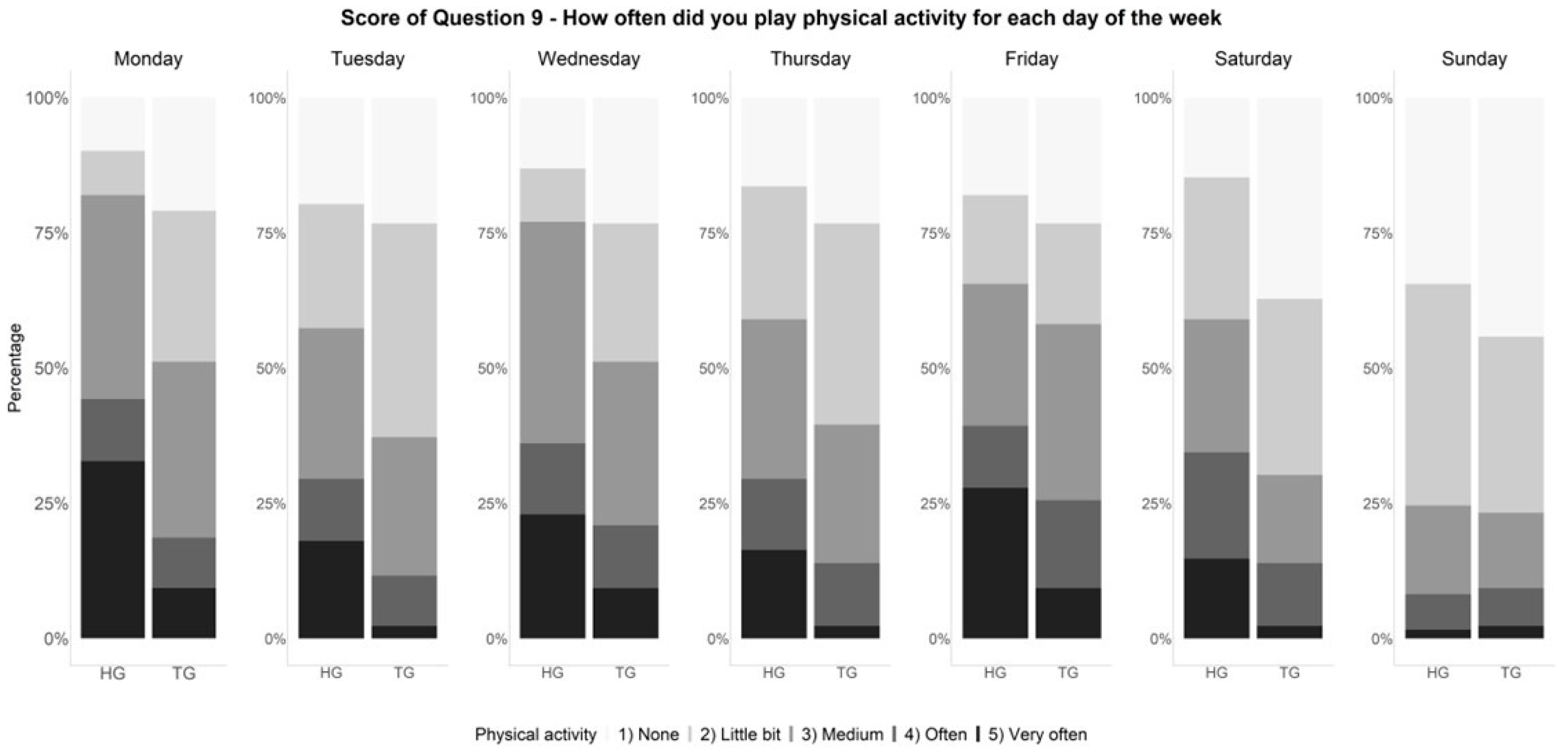
| 9. Mark how often you did physical activity (like playing sports, games, doing dance, or any other physical activity) for each day last week | None | Little bit | Medium | Often | Very often |
| 10. Were you sick last week, or did anything prevent you from doing your normal physical activities? | Non-evaluable score | Non-evaluable score | Non-evaluable score | Non-evaluable score | Non-evaluable score |
References
- Hou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Zhong, S. Survival and Complication of Liver Transplantation in Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 628771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boenink, R.; Astley, M.E.; Huijben, J.A.; Stel, V.S.; Kerschbaum, J.; Ots-Rosenberg, M.; Åsberg, A.A.; Lopot, F.; Golan, E.; Castro de la Nuez, P.; et al. The ERA Registry Annual Report 2019: Summary and age comparisons. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 15, 452–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghelichi-Ghojogh, M.; Javanian, M.; Amiri, S.; Vali, M.; Sedighi, S.; Rajabi, A.; Shojaie, L.; Moftakhar, L.; Khezri, R.; Mohammadi, M.; et al. The survival rate of liver transplantation in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2022, 38, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenca, A.G.; Yeh, H. Improving patients outcomes following pediatric liver transplant: Current perspectives. Transpl. Res. Risk Manag. 2019, 11, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloh, T.; Barton, A.; Wheeler, J.; Pham, Y.; Hewitt, W.; Keegan, T.; Sanchez, C.; Bulut, P.; Goss, J. Immunosuppression in pediatric liver transplant recipients: Unique aspects. Liver Transpl. 2017, 23, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, S.; Dixon, S.N.; Paterson, J.M.; Dirk, J.; Hahn, E.; Kim, S.J.; Ng, V.; Solomon, M.; Vasilevska-Ristovska, J.; Banh, T.; et al. Incidence of cardiovascular disease and mortality in childhood solid organ transplant recipients: A population-based study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memaran, N.; Borchert-Mörlins, B.; Schmidt, B.M.W.; Sugianto, R.I.; Wilke, H.; Blöte, R.; Baumann, U.; Bauer, E.; von Wick, A.; Junge, N.; et al. High Burden of Subclinical Cardiovascular Target Organ Damage After Pediatric Liver Transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2019, 25, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondet, N.M.; Healey, P.J.; Hsu, E. Immunosuppression in the pediatric transplant recipient. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 26, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanik, E.L.; Smith, J.M.; Shiels, M.S.; Clarke, C.A.; Lynch, C.F.; Kahn, A.R.; Koch, L.; Pawlish, K.S.; Engels, E.A. Cancer risk after pediatric solid organ transplantation. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20163893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchlu, A.; Dixon, S.; Dirk, J.S.; Chanchlani, R.; Vasilevska-Ristovska, J.; Borges, K.; Dipchand, A.I.; Ng, V.L.; Hebert, D.; Solomon, M.; et al. Elevated risk of cancer after solid organ transplant in childhood. Transplantation 2019, 103, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Adrichem, E.J.; van de Zande, S.C.; Dekker, R.; Verschuuren, E.A.; Dijkstra, P.U.; van der Schans, C.P. Perceived Barriers to and Facilitators of Physical Activity in Recipients of Solid Organ Transplantation, a Qualitative Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masala, D.; Mannocci, A.; Unim, B.; Del Cimmuto, A.; Turchetta, F.; Gatto, G.; Santoro, R.; Ettorre, G.M.; Boccia, A.; La Torre, G. Quality of life and physical activity in liver transplantation patients: Results of a case-control study in Italy. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelle, D.M.; Corpeleijn, E.; Stolk, R.P.; de Greef, M.H.; Gans, R.O.; van der Heide, J.J.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J. Low physical activity and risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in renal transplant recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hecke, L.; Loyen, A.; Verloigne, M.; van der Ploeg, H.P.; Lakerveld, J.; Brug, J.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Ekelund, U.; Donnelly, A.; Hendriksen, I.; et al. Variation in population levels of physical activity in European children and adolescents according to cross-European studies: A systematic literature review within DEDIPAC. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermi, S.; Vecchiato, M.; Pennella, S.; Marasca, A.; Spinelli, A.; De Luca, M.; De Martino, L.; Fernando, F.; Sirico, F.; Biffi, A. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Childhood Obesity and Lifestyle—A Report from Italy. Pediatr. Rep. 2022, 14, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240015128 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Nunan, D.; Mahtani, K.R.; Roberts, N.; Heneghan, C. Physical activity for the prevention and treatment of major chronic disease: An overview of systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2013, 2, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Bruton, A.; Matute-Llorente, Á.; González-Agüero, A.; Casajús, J.A.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G. Plyometric exercise and bone health in children and adolescents: A systematic review. World J. Pediatr. 2017, 13, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammert, J.; Lubinski, J.; Gronwald, J.; Huzarski, T.; Armel, S.; Eisen, A.; Meschino, W.S.; Lynch, H.T.; Snyder, C.; Eng, C.; et al. Physical activity during adolescence and young adulthood and the risk of breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 169, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.C.; Lee, I.M.; Weiderpass, E.; Campbell, P.T.; Sampson, J.N.; Kitahara, C.M.; Keadle, S.K.; Arem, H.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Hartge, P.; et al. Association of Leisure-Time Physical Activity With Risk of 26 Types of Cancer in 1.44 Million Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, J.; Armstrong, M.J.; Fisher, J.; Mark, P.; Schmidtke, K.; Sharif, A.; Vlaev, I. Sport and Exercise in Improving Outcomes After Solid Organ Transplantation: Overview From a UK Meeting. Transplantation 2019, 103, S1–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leunis, S.; Vandecruys, M.; Cornelissen, V.; Van Craenenbroeck, A.H.; De Geest, S.; Monbaliu, D.; De Smet, S. Physical Activity Behaviour in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: Proposal of Theory-Driven Physical Activity Interventions. Kidney Dial. 2022, 2, 298–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranchita, E.; Cafiero, G.; Giordano, U.; Guzzo, I.; Labbadia, R.; Palermi, S.; Cerulli, C.; Candusso, M.; Spada, M.; Ravà, L.; et al. Preliminary Evaluation of Sedentary Lifestyle in Italian Children after Solid Transplant: What Role Could Physical Activity Play in Health? It Is Time to Move. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.C.; Crocker, P.R.; Donen, R.M. The physical activity questionnaire for older children (PAQ-C) and adolescents (PAQ-A) manual. Coll. Kinesiol. Univ. Sask. 2004, 87, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gobbi, E.; Elliot, C.; Varnier, M.; Carraro, A. Psychometric Properties of the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children in Italy: Testing the Validity among a General and Clinical Pediatric Population. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermi, S.; Sacco, A.M.; Belviso, I.; Romano, V.; Montesano, P.; Corrado, B.; Sirico, F. Guidelines for Physical Activity-A Cross-Sectional Study to Assess Their Application in the General Population. Have We Achieved Our Goal? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, S.; de Souza, A.; Sharma, A.; Fairbairn, J.; Schreiber, R.; Armstrong, K.; Blydt-Hansen, T. Physical activity and its correlates in a pediatric solid-organ transplant population. Pediatr. Transpl. 2020, 24, e13745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamiwka, L.A.; Cantell, M.; Crawford, S.; Clark, C.G. Physical activity and health related quality of life in children following kidney transplantation. Pediatr. Transpl. 2009, 13, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, C.; Ogunleye, A.A.; Sandercock, G.R. Physical Activity Questionnaire for children and adolescents: English norms and cut-off points. Pediatr. Int. 2013, 55, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.R.; Leem, Y.J.; Chiu, H.W.; Jeng, C. Impact of physical activity on heart rate variability in children with Tipe 1 Diabetes. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2008, 24, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossoni, A.; Vecchiato, M.; Brugin, E.; Tranchita, E.; Adami, P.E.; Bartesaghi, M.; Cavarretta, E.; Palermi, S. The eSports Medicine: Pre-Participation Screening and Injuries Management-An Update. Sport 2023, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, A.O. Cardiovascular complications after renal transplantation and their prevention. Transplantation 2006, 82, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dec, G.W.; Kondo, N.; Farrell, M.L.; Dienstag, J.; Cosimi, A.B.; Semigran, M.J. Cardiovascular complications following liver transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 1995, 9, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiorilli, G.; Buonsenso, A.; Di Martino, G.; Crova, C.; Centorbi, M.; Grazioli, E.; Tranchita, E.; Cerulli, C.; Quinzi, F.; Calcagno, G.; et al. Impact of Active Breaks in the Classroom on Mathematical Performance and Attention in Elementary School Children. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe. 2021 physical activity factsheets for the European Union Member States in the WHO European Region; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/345335 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Crocker, P.R.E.; Bailey, D.A.; Faulkner, R.A.; Kowalski, K.C.; McGrath, R. Measuring general levels of physical activity: Preliminary evidence for the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 1997, 29, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.L.; Upton, D. Psychometric properties of the physical activity questionnaire for older children (PAQ-C) in the UK. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2014, 15, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetsanou, F.; Emmanouilidou, K.; Soutos, K.; Sotiriou, S.A.; Bastida, L.; Moya, A.; Kambas, A. Towards a Functional Approach to the Assessment of Daily Life Physical Activity in Children: Are the PAQ-C and Fitbit Flex-2 Technically Adequate? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roi, G.S.; Mosconi, G.; Totti, V.; Angelini, M.L.; Brugin, E.; Sarto, P.; Merlo, L.; Sgarzi, S.; Stancari, M.; Todeschini, P.; et al. Renal function and physical fitness after 12-mo supervised training in kidney transplant recipients. World J. Transplant. 2018, 8, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupo, C.; Boccia, G.; Ungureanu, A.N.; Mulasso, A.; De Pasquale, P.; Mancini, A.; Buono, P.; Rainoldi, A.; Brustio, P.R. The Cut-Off Value for Classifying Active Italian Children Using the Corresponding National Version of the Physical Activity Questionnaire. Sports 2022, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gender (n = 104) | Age | BMI (kg/m2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | (Mean ± SD) | (Mean ± SD) | |
| Healthy group | 35 | 26 | 12.75 ± 2.8 | 20.1 ± 3.65 |
| Transplant Group | 18 | 25 | 12.86 ± 3.5 | 19.47 ± 3.46 |
| Total | 53 | 51 | 12.8 ± 3.16 | 19.84 ± 3.57 |
| Population | Score of PAQs Questionnaire (Mean ± SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy group | 2.69 ± 0.65 | 0.08 |
| Transplant Group | 2.42 ± 0.88 | |
| Competitive Group | 2.82 ± 0.59 | 0.09 |
| Not Competitive Group | 2.53 ± 0.70 | |
| Tx Liver | 2.51 ± 0.91 | 0.21 |
| Tx Kidney | 2.16 ± 0.75 |
| Population | Score of Question 2 of the PAQs Questionnaire (Mean ± SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy group | 3.66 ± 1.58 | 0.05 * |
| Transplant Group | 3.05 ± 1.59 | |
| Competitive Group | 3.97 ± 1.33 | 0.08 |
| Non-Competitive Group | 3.26 ± 1.58 | |
| Tx Liver | 3.12 ± 1.70 | 0.53 |
| Tx Kidney | 2.82 ± 1.25 |
| Population | Score of Question 8 of the PAQs Questionnaire (Mean ± SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy group | 3.13 ± 1.02 | 0.02 * |
| Transplant Group | 2.63 ± 1.22 | |
| Competitive Group | 3.47 ± 0.75 | 0.005 ** |
| Non-Competitive Group | 2.7 ± 1.17 | |
| Tx Liver | 2.75 ± 1.22 | 0.26 |
| Tx Kidney | 2.27 ± 1.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tranchita, E.; Cafiero, G.; Giordano, U.; Palermi, S.; Gentili, F.; Guzzo, I.; Spada, M.; Morolli, F.; Drago, F.; Turchetta, A. Differences in Physical Activity Levels between Healthy and Transplanted Children: Who Needs More Tips? Healthcare 2023, 11, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111610
Tranchita E, Cafiero G, Giordano U, Palermi S, Gentili F, Guzzo I, Spada M, Morolli F, Drago F, Turchetta A. Differences in Physical Activity Levels between Healthy and Transplanted Children: Who Needs More Tips? Healthcare. 2023; 11(11):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111610
Chicago/Turabian StyleTranchita, Eliana, Giulia Cafiero, Ugo Giordano, Stefano Palermi, Federica Gentili, Isabella Guzzo, Marco Spada, Federica Morolli, Fabrizio Drago, and Attilio Turchetta. 2023. "Differences in Physical Activity Levels between Healthy and Transplanted Children: Who Needs More Tips?" Healthcare 11, no. 11: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111610
APA StyleTranchita, E., Cafiero, G., Giordano, U., Palermi, S., Gentili, F., Guzzo, I., Spada, M., Morolli, F., Drago, F., & Turchetta, A. (2023). Differences in Physical Activity Levels between Healthy and Transplanted Children: Who Needs More Tips? Healthcare, 11(11), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11111610






