Abstract
The bullying of nurses in the workplace hurts the individuals and the work environment. Bullying can cause mental health problems, reduces the quality of nursing services, and reduces patient safety. The purpose of this study was to describe types of nursing interventions to reduce impact of bullying on nurses in the workplace. This study used the scoping review method to examine literature from the CINAHL, PubMed, and ProQuest databases. The keywords used in English are “bullying OR cyberbullying” AND “nurse” AND “workplace OR work-place” AND “nursing care OR nursing intervention”. The inclusion criteria were full text, randomized control trial or quasi-experiment design, English language, population of nurses, and the publication period of the last 10 years (2013–2022). We found nine articles that discussed nursing interventions designed to reduce the impact of bullying on nurses in the workplace. The sample in the study was in the range of 26–97 respondents. Most of the articles in this review used the quasi-experiment method. The study showed that nursing interventions to heal had negative effects on the bullying on nurses. There are three types of interventions employed to reduce the impact of bullying and aggression on nurses in the workplace, namely training programs, cognitive rehearsal programs, and education programs.
1. Introduction
Bullying is an aggressive behavior to someone that is intentionally and repeatedly in the form of physical or verbal abuse that causes another person to feel uncomfortable [1]. Bullying in nurses is a problem that often occurs in the workplace and needs serious handling. Bullying behavior in nurses occurs in the workplace with the aim of offending, humiliating, and debilitating, which is harmful, repetitive, and persistent, and is directed at one or more individuals [2,3]. Based on a previous study, 75% incidents of bullying happen in the workplace [4]. The reported prevalence of bullying behavior among nurses in European countries is 21.0–30.2% [5]. The reported frequency suggests a high prevalence in America, namely between 48.0 and 82.0% [6,7,8], while the reported prevalence of bullying behavior among nurses in Australia is around 37.3–61.0% [9,10]. In Korea, reported prevalence of bullying behavior in nurses reached 15.8%, and the reported incidence of bullying behavior in nurses in Indonesia reached 51.2% [11].
The causes of bullying in nurses include individuals, the work environment, and work-related factors. Individual factors in nurses include self-centeredness and immaturity [12], and work environment and organizational culture factors include values, customs, work rules, and shared habits [11,13,14,15]. Factors that can cause bullying in nurses in the workplace are job demands, support, work control, seniority, educational differences, patient rights, and poor leadership [13,14,15]. The previous study reported on perpetrators of bullying incidents in nurses conducted by supervisors 40.7%, managers (22%), colleagues 43%, patients 71%, and patients’ families 47% [12]. Regarding the form of bullying behavior that occurs in nurses, based on the results of the study, verbal bullying accounts for 40.4%, and includes behaviors such as insulting one’s personality, being humiliated in front of others, being blamed for something that is not one’s responsibility, and being treated disrespectfully [16]; moreover, physical bullying accounts for 43.3%, and includes behaviors such as the pushing, hitting, kicking, and of slapping nurses [17]. Bullying behaviors have a negative impact for nurses.
Bullying has negative effects on nurses in the workplace [18], including increased work pressure, decreased focus, physically tired, having trouble sleeping, and feeling uncomfortable [19]. Regarding the impact of bullying, mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorders, accounted for accounted for 29.9% of respondents; 8.7% reported physical health disorders such as palpitations, headaches, increased blood pressure, fatigue and insomnia; 81% reported lower work motivation; 1.27% reported an increase in absenteeism; and 3.24% reported overwork [20,21,22,23,24]. Bullying can decrease the quality of nursing services (2.11%) and patient safety (1.93%) [25,26,27].
Interventions were needed to reduce and prevent the bullying of nurses in the workplace, as it can have a physical and psychological impact [26] and can reduce the quality of nursing care [25,27,28,29]. Several studies have stated that interventions can be carried out to prevent bullying behavior in nurses, such as leadership support [2,20,23], educational interventions [28,29,30], cognitive exercises [31,32,33], and anti-bullying policies and regulations [32]. The results of previous studies indicate that education for all workers in hospitals can reduce the incidence of bullying in hospitals [16].
Nurses, as health workers who provide comprehensive nursing care, have a role in reducing and preventing bullying. However, nurses only focus on reducing the impact of bullying on patients. Thus, the interventions taken to prevent and reduce bullying on nurses are not carried out. Therefore, the authors intend to conduct a systematic scoping review to describe interventions that can be carried out to reduce the impact of bullying on nurses.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This study was designed as a systematic scoping review. We used 5 core stages, namely the identification of research questions, identification of relevant study results, study selection, data mapping, compilation of results, and reporting of study results [33]. This literature review used the PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) to identify various topics that address interventions to reduce bullying behavior in nurses (Figure 1) [34].
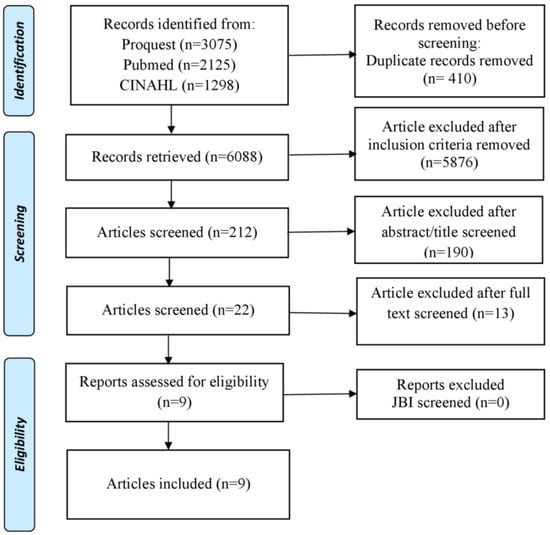
Figure 1.
PRISMA Flow Diagram.
2.2. Search Methods
The literature was collected from 3 databases, namely: CINAHL, PubMed, and ProQuest. The keywords used are: “bullying OR cyberbullying” AND “nurse” AND “workplace OR work-place” AND “nursing care OR nursing intervention”. The research question was: what are the interventions to reduce the impact and behavior of bullying on nurses in the workplace?
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Articles were selected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria of this study were: full text to be read by authors, randomized control trial or quasi-experiment design with nursing interventions, English language, that the population and samples were of nurses, and a publication period of the last 10 years (2013–2022) to analyze the latest research. The exclusion criteria of this study were studies that did not discuss interventions to reduce or prevent bullying or aggression in nurses in the workplace.
2.4. Data Extraction
The articles were manually extracted using tables by the authors. Before being included in the table, the author first analyzed and briefly summarized the contents of the reviewed study. In tabular form, it included the authors, year, country, study design, population and sample, procedures, interventions, and results of the study. Then, the authors described the results of the analysis, including an explanation of the interventions used to reduce the negative effects of bullying.
2.5. Quality Appraisal
Articles were analyzed using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) critical assessment method. The assessment checklist based on The JBI Critical Appraisal contains several questions to assess the quality of the study [35]. The assessment criteria were given a score of ‘yes’, ‘no’, ‘unclear’, or ‘not applicable’, and each criterion with a score of ‘yes’ was given one point and another score was zero, and each study score was then calculated and added up. JBI Critical Appraisal tools have been approved by the JBI Scientific Committee following extensive peer review. The standard of a good article was determined by a score of above 75%, based on criteria and topic relevance.
2.6. Data Analysis
The articles collected were then read in full and analyzed by all authors. The author then discusses the interventions carried out in overcoming bullying against nurses. After discussing, the authors make a summary of each article reviewed. After being analyzed, the interventions from the literature were classified based on similar interventions and then described.
3. Results
The number of articles obtained from the search was 6498. After removing duplicate articles, we had 6088 articles. Furthermore, after elimination based on the inclusion criteria, there were 212 articles left. Then, after checking the title and abstract, 22 articles were found. Then, the author conducted an overall full-text analysis of the article and found nine articles to analyze.
The results showed articles from seven countries: there were two articles from Korea, two articles from Australia, and one article each from Turkey, Jordan, England, Iran, and the United States. The research designs used included five articles that used a quasi-experimental design and four articles that used a randomized control trial. Of the nine articles analyzed, there are three types of interventions that are effective in reducing the incidence and preventing bullying in nurses in the workplace: training program, cognitive rehearsal program, and education program.
Based on the results of the study, the training programs that can be carried out are assertiveness training, training programs, behavior management training, and workplace violence training programs. The training program focuses on training that involves all health workers in the workplace in preventing and reducing the incidence of bullying against nurses. Training is carried out over 4–8 weeks. The training is provided in the form of material delivery and demonstration. The cognitive rehearsal program includes several programs, namely the cognitive rehearsal program and the smartphone application for cognitive rehearsal intervention. Regarding cognitive rehearsal, the smartphone application-based program consists of introducing nonviolent conversation as standard communication, six web-toons on violent situations, and a bulletin board for questions and answers. The duration of the cognitive rehearsal program is 6–10 weeks. Moreover, the education program included education, a risk assessment checklist and prevention protocol, and clinical education. The education program is conducted from 2 days to 1 week. The form of the education about bullying provided is hybrid learning.
Articles were analyzed using the JBI Critical Appraisal Tool assessment method, with good article standards being denoted with scores above 75%, based on criteria and topic relevance (Table 1).

Table 1.
JBI Critical Appraisal Tool.
We found nine articles that discussed nursing intervention in reducing the impact and incidence of bullying on nurses in the workplace. We classified the interventions into three types, namely training programs, cognitive rehearsal programs, and education programs. The results of the analysis of the article are presented in tabular form as follows (Table 2):

Table 2.
Extracted data.
4. Discussion
We found nine articles that discussed nursing interventions employed to reduce the impact and incidence of bullying and aggression towards nurses in the workplace. Bullying towards nurses included both physical and verbal behavior. Physical aggression included being pushed, hit, kicked, thrown, pinched, grabbed, and elbowed, while verbal bullying included labeling, yelling, and psychological bullying. Bullying causes someone to feel uncomfortable, pressured, afraid, and disappointed.
The study showed that bullying had physical, social, and psychological impacts on nurses in the workplace. The physical effects felt include difficulty sleeping, dizziness, and palpitations [44]. The perceived social impacts are apathy and anti-social. Moreover, the psychological impacts felt include lack of confidence, low self-esteem, shame, anger, helplessness, sadness, fear, negative thoughts, and traumatic experiences [4].
Nurses have an important role in reducing the impact and incidence of bullying on nurses in the workplace. Everyone needs to collaborate in improving the welfare of workers. Holistic nursing care to improve human health status, including victims of bullying, should be employed to reduce the impact and incidence of bullying.
Based on the study, of the types of nursing intervention employed to reduce the impact and incidence of bullying, there were training programs, cognitive rehearsal programs, and education programs. A previous study showed that a training program which was conducted for 8 weeks included empathy training and people management training [18]. There was aim to increase respect and reduce the bullying of nurses in the workplace [45]. Meanwhile, another study on cognitive rehearsal programs showed that interventions packaged with theatrics could reduce the incidence of bullying among nurses in hospitals [27]. In the education program intervention, education about the impact of bullying can reduce the incidence of bullying on nurses in the workplace because there is an understanding related to bullying [46].
Education, cognitive training, leadership style and organizational policies can help nurses to deal with bullying behavior [19,47,48,49]. In education and role-playing programs, nurses can recognize and deal with bullying behavior [24,31,50]. Moreover, a previous study used teaching courses provided by nurses with intensive skills units to overcome and manage bullying behavior [30], and another study mentioned that education can reduce the incidence of bullying. They provided nurses with information about bullying, communication, and conflict resolution in the form of workshops that could reduce verbal violence rates from 90% to 76%; then, nurses’ opinions were respected, and the work atmosphere improved [28]. Educational interventions are effective in reducing bullying behavior. Cognitive interventions could manage and identify bullying behavior in the workplace [49]. This requires policies that are supported by the leadership and bullying procedures to prevent bullying by an organization [48].
Interventions to reduce the impact of bullying on nurses need to be performed in collaboration with other professionals. This requires cooperation and coordination between various parties, especially health workers. Other professionals need to respect each other, increasing cooperation, and should not look down on the nursing profession. They should also work to improve policies to equalize work wages and ensure the quality of life of health workers in the workplace, especially nurses. Indeed, Intervention should not only be applied by and for nurses, as it requires collaboration and cooperation at the workplace level.
Limitations
The limitations of this study were its small sample size taken from the literature. The article was limited to the last 10 years, therefore it does not discuss interventions carried out before then. The articles were only analyzed in English because of the author’s limitations in understanding other languages. The interventions reported were only carried out by nurses even though the cooperation between various parties in carrying out interventions to reduce the impact and incidence of bullying on nurses in the workplace is required. The discussion on how to reduce the impact of bullying and aggression is not comprehensive as the previous studies with the same theme are limited.
5. Conclusions
Nursing intervention can reduce the incidence and impact of bullying on nurses in the workplace. There are three types of nursing intervention, namely through a training program, cognitive rehearsal program, and an education program. Programs can be conducted online, hybrid, and offline for nurses and other employees in the workplace. These three types of interventions can be used as a basis for nurses in providing nursing care to prevent and reduce bullying in nurses in the workplace. In addition, nursing intervention can also improve the welfare and confidence of nurses. The recommendation in this study for further research was related to the effectiveness of nursing intervention to reduce the incidence and impact of bullying on nurses in the workplace.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.Y., R.H. and A.M.; methodology, I.Y. and R.H.; resources, R.H.; data curation, I.Y., A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, I.Y., R.H., A.M.; writing—review and editing, I.Y., R.H., A.M.; visualization, I.Y. and A.M.; supervision, I.Y.; project administration, I.Y. and R.H.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
All authors thank the Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Padjadjaran, Bandung, Indonesia which has helped us in facilitating the database for us to review the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- American Psychological Association. Bullying. 2022. Available online: https://www.apa.org/topics/bullying (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Giorgi, G.; Ando, M.; Arenas, A.; Shoss, M.K.; Leon-Perez, J.M. Exploring personal and organizational determinants of workplace bullying and its prevalence in a Japanese sample. Psychol. Violence 2013, 3, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.; Vickers, M.H.; Wilkes, L.; Jackson, D. A typology of bullying behaviours: The experiences of Australian nurses. J. Clin. Nurs. 2010, 19, 2319–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyaemni, A.; Alhudaithi, H. Workplace violence against nurses in the emergency departments of three hospitals in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional survey. NursingPlus Open 2016, 2, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, F.D.; Levy, H.; Khalaila, R.; Arad, D.; Bennaroch, K.; Kolpak, O.; Drori, Y.; Benbinishty, J.; Raanan, O. Bullying and Its Prevention Among Intensive Care Nurses. J. Nurs. Sch. 2015, 47, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, P.A.; Gillespie, G.; Gates, D.; Schafer, J. Novice Nurse Productivity Following Workplace Bullying. J. Nurs. Sch. 2012, 44, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, B.C.; Meisinger, S.; Whitacre, M.J.; Corbin, G. Nursing2012. Horizontal violence survey report. Nursing 2012, 42, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etienne, E. Exploring Workplace Bullying in Nursing. Work. Health Saf. 2014, 62, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, B.C.; Holland, P.; Reynolds, R. The effect of bullying on burnout in nurses: The moderating role of psychological detachment. J. Adv. Nurs. 2015, 71, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reknes, I.; Pallesen, S.; Magerøy, N.; Moen, B.E.; Bjorvatn, B.; Einarsen, S. Exposure to bullying behaviors as a predictor of mental health problems among Norwegian nurses: Results from the prospective SUSSH-survey. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2014, 51, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Kang, J. Relationship between Organizational Culture and Workplace Bullying among Korean Nurses. Asian Nurs. Res. 2016, 10, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatziioannidis, I.; Bascialla, F.G.; Chatzivalsama, P.; Vouzas, F.; Mitsiakos, G. Prevalence, causes and mental health impact of workplace bullying in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit environment. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e018766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, D.; Rodwell, J. Psychosocial Antecedents and Consequences of Workplace Aggression for Hospital Nurses. J. Nurs. Sch. 2012, 44, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granstra, K. Nurse Against Nurse: Horizontal Bullying in the Nursing Profession. J. Health Manag. 2015, 60, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogh, A.; Hoel, H.; Carneiro, I.G. Bullying and employee turnover among healthcare workers: A three-wave prospective study. J. Nurs. Manag. 2011, 19, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyrek, H.; Ekici, D. Nurses’ Perception of Organisational Justice and its Effect on Bullying Behaviour in the Hospitals of Turkey. Hosp. Pract. Res. 2017, 2, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, A.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J. Workplace violence against nurses: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2017, 72, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, M.; Suzuki, M.; Takai, Y.; Igarashi, A.; Noguchi-Watanabe, M.; Yamamoto-Mitani, N. Workplace bullying among nurses and their related factors in Japan: A cross-sectional survey. J. Clin. Nurs. 2016, 25, 2478–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambur, M.; Vadi, M. Workplace bullying and organizational culture in a post-transitional country. Int. J. Manpow. 2012, 33, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, C.S.; Kovner, C.T.; Obeidat, R.F.; Budin, W.C. Positive work environments of early-career registered nurses and the correlation with physician verbal abuse. Nurs. Outlook 2013, 61, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budin, W.C.; Brewer, C.S.; Chao, Y.-Y.; Kovner, C. Verbal Abuse from Nurse Colleagues and Work Environment of Early Career Registered Nurses. J. Nurs. Sch. 2013, 45, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipps, E.M.; McRury, M. The Development of an Educational Intervention to Address Workplace Bullying: A Pilot Study. J. Nurses Prof. Dev. 2012, 28. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/jnsdonline/Fulltext/2012/05000/The_Development_of_an_Educational_Intervention_to.2.aspx (accessed on 1 June 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laschinger, H.K.S. Impact of Workplace Mistreatment on Patient Safety Risk and Nurse-Assessed Patient Outcomes. JONA J. Nurs. Adm. 2014, 44, 284–290. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Fulltext/2014/05000/Impact_of_Workplace_Mistreatment_on_Patient_Safety.9.aspx (accessed on 1 June 2022). [CrossRef]
- Roche, M.; Diers, D.; Duffield, C.; Catling, C. Violence Toward Nurses, the Work Environment, and Patient Outcomes. J. Nurs. Sch. 2010, 42, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, W.; Khatri, N. Bullying among nursing staff: Relationship with psychological/behavioral responses of nurses and medical errors. Health Care Manag. Rev. 2015, 40. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/hcmrjournal/Fulltext/2015/04000/Bullying_among_nursing_staff__Relationship_with.6.aspx (accessed on 1 June 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.; Kang, J. Influencing Factors and Consequences of Workplace Bullying among Nurses: A Structural Equation Modeling. Asian Nurs. Res. 2018, 12, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.M.S. Management of work place bullying in hospital: A review of the use of cognitive rehearsal as an alternative management strategy. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2016, 3, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceravolo, D.J.; Schwartz, D.G.; Foltz-Ramos, K.M.; Castner, J. Strengthening communication to overcome lateral violence. J. Nurs. Manag. 2012, 20, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasater, K.; Mood, L.; Buchwach, D.; Dieckmann, N.F. Reducing Incivility in the Workplace: Results of a Three-Part Educational Intervention. J. Contin. Educ. Nurs. 2015, 46, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.; Clark, C.M. Revisiting Cognitive Rehearsal as an Intervention Against Incivility and Lateral Violence in Nursing: 10 Years Later. J. Contin. Educ. Nurs. 2014, 45, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagg, S.J.; Sheridan, D.; Jones, R.A.; Speroni, K.G. Evaluation of a Workplace Bullying Cognitive Rehearsal Program in a Hospital Setting. J. Contin. Educ. Nurs. 2011, 42, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M. Preventing workplace mobbing and bullying with effective organizational consultation, policies, and legislation. Consult. Psychol. J. Pract. Res. 2009, 61, 242–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury-Jones, C.; Aveyard, H.; Herber, O.R.; Isham, L.; Taylor, J.; O’Malley, L. Scoping reviews: The PAGER framework for improving the quality of reporting. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2022, 25, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JBI. Checklist for Systematic Reviews and Research Syntheses. 2017. Available online: http://joannabriggs.org/research/critical-appraisal-tools.html (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Karakaş, S.A.; e Okanli, A. The Effect of Assertiveness Training on the Mobbing That Nurses Experience. Work. Health Saf. 2015, 63, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ali, N.M.; Al Faouri, I.; Al-Niarat, T.F. The impact of training program on nurses’ attitudes toward workplace violence in Jordan. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2016, 30, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Kim, J.-I.; Yun, S. Effects of a Cognitive Rehearsal Program on Interpersonal Relationships, Workplace Bullying, Symptom Experience, and Turnover Intention among Nurses: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 2017, 47, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Jeong, Y.J. Effects of a smartphone application for cognitive rehearsal intervention on workplace bullying and turnover intention among nurses. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2019, 25, e12786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, M.; Schoenfisch, A.; Wadsworth, B.; Foresman-Capuzzi, J. Impact of Behavior Management Training on Nurses’ Confidence in Managing Patient Aggression. JONA J. Nurs. Adm. 2019, 49, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Shahoei, R.; Nouri, B.; Almvik, R.; Valiee, S. Effect of an education program, risk assessment checklist and prevention protocol on violence against emergency department nurses: A single center before and after study. Int. Emerg. Nurs. 2020, 50, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.; Knowles, A.; Irons, G.; Roddy, A.; Ashworth, J. Assessing the effectiveness of clinical education to reduce the frequency and recurrence of workplace violence. Aust. J. Adv. Nurs. 2017, 34, 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lamont, S.; Brunero, S. The effect of a workplace violence training program for generalist nurses in the acute hospital setting: A quasi-experimental study. Nurse Educ. Today 2018, 68, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleassa, H.; Megdadi, O.D. Workplace Bullying and Unethical Behaviors: A Mediating Model. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2014, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tuna, R.; Kahraman, B.; Dalli, B. Workplace bullying: A qualitative study on experiences of Turkish nurse managers. J. Nurs. Manag. 2019, 27, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, D.E.; Gillespie, G.L.; Smith, C.R. Interventions against bullying of prelicensure students and nursing professionals: An integrative review. Nurs. Forum 2018, 54, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Ji, X.-Z.; Meng, L.-N.; Cai, Y.-J. Effects of Modified Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) on the Psychological Health of Adolescents with Subthreshold Depression: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, E.S.; Moya-Gale, G.; Chang, Y.H.M.; Freeman, K.; Forrest, K.; Brin, M.F.; Ramig, L.A. The effects of intensive speech treatment on intelligibility in Parkinson’s disease: A randomised controlled trial. eClinicalMedicine 2020, 24, 100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikstaitis, T.; Simko, L.C. Incivility Among Intensive Care Nurses. Dimens. Crit. Care Nurs. 2014, 33, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiper, J. Nurse against nurse. Nursing 2005, 35, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).