Melanoma Detection Using Deep Learning-Based Classifications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We used an enhanced generative adversarial network with super-high resolution (ESRGAN) with 10,000 training photos to produce high-quality images for the Human Against Machine dataset (HAM10000 dataset [20]) to enhance the visibility of the images. ERSGAN improves the accuracy of Classification.
- Segmentation is performed for each image in the dataset to specify ROI to facilitate the learning process.
- We used Augmentation to ensure that the HAM10000 dataset had an even distribution of data.
- The feasibility of the suggested system is determined by a thorough comparative evaluation using numerous assessment measurements, such as accuracy, recall, precision, confusion matrix, top 1 accuracy, top 2 accuracy, and the F-score.
- Pre-trained networks’ weights are fine-tuned with the help of the HAM10000 dataset and a modified version of Resnet-50.
- The recommended technique’s overall effectiveness has been enhanced due to this change. Overfitting is prevented by using an alternative training process supported by applying various training strategies (e.g., batch size, learning rate, validation patience, and data augmentation).
2. Related Work
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Dataset Overview
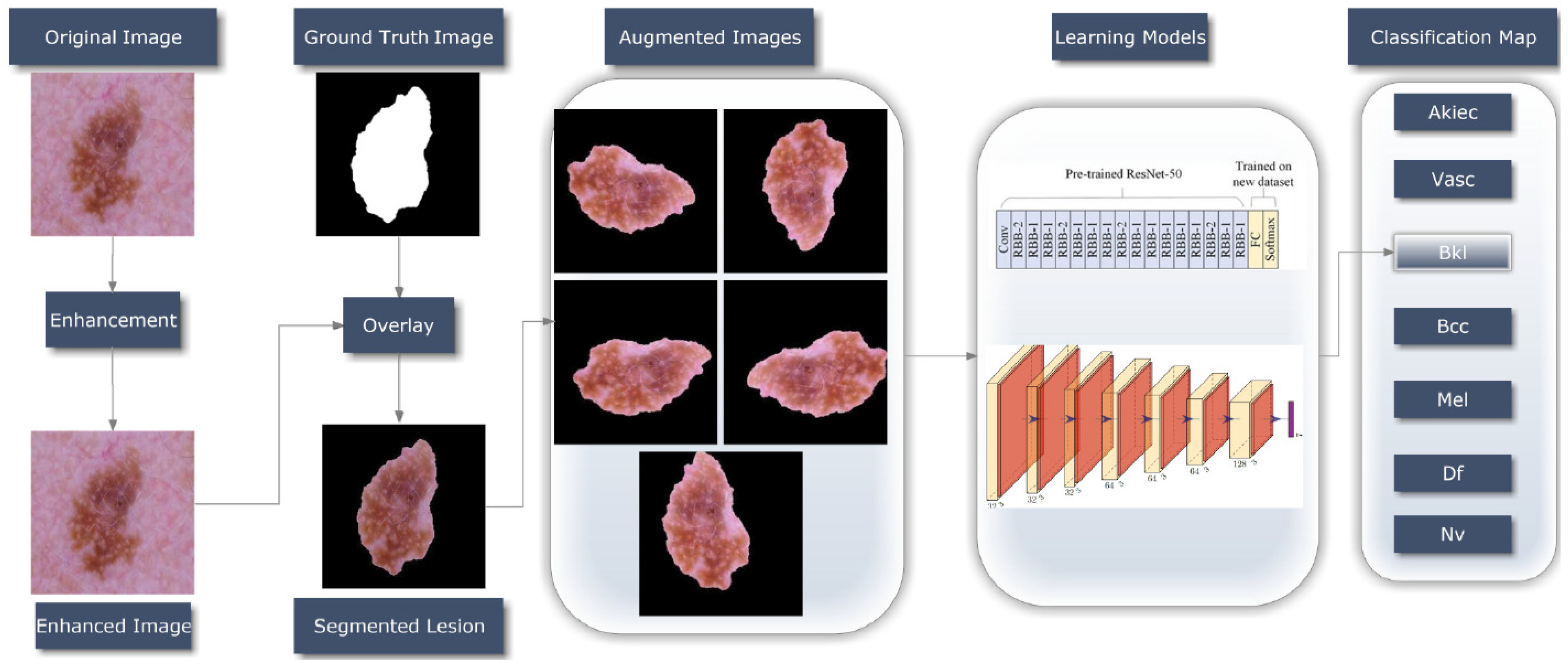
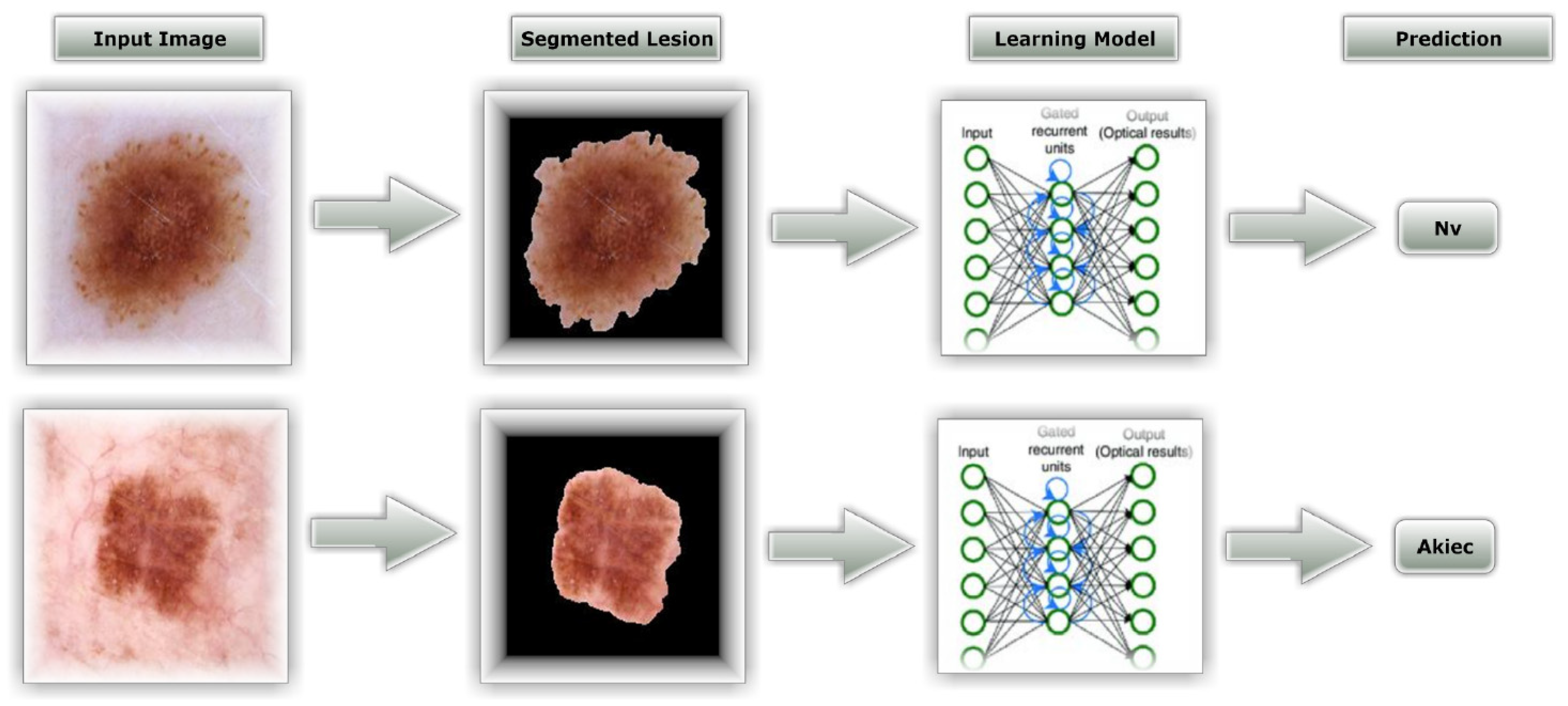
3.2. Proposed Methodology
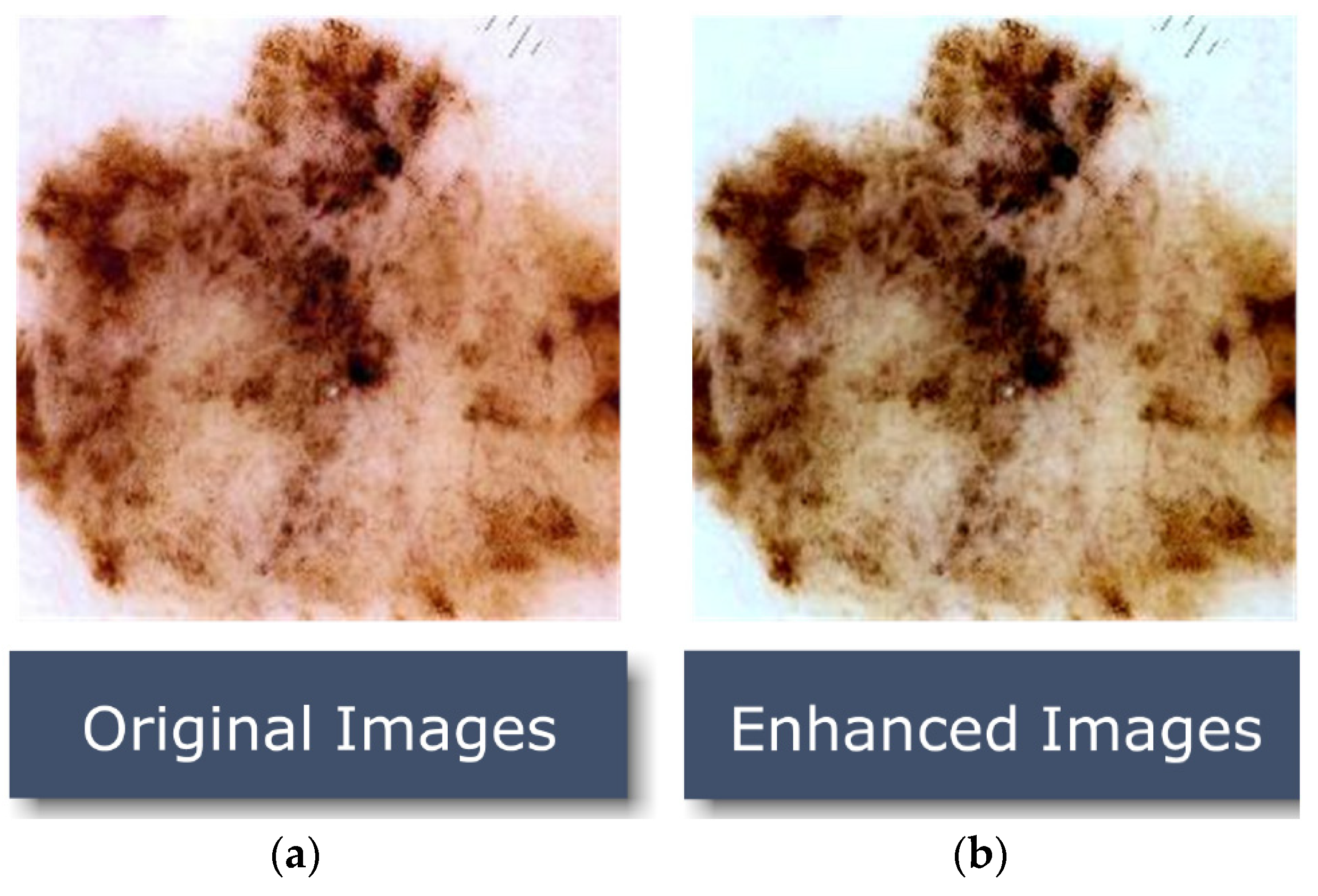
3.2.1. ESRGAN Preprocessing
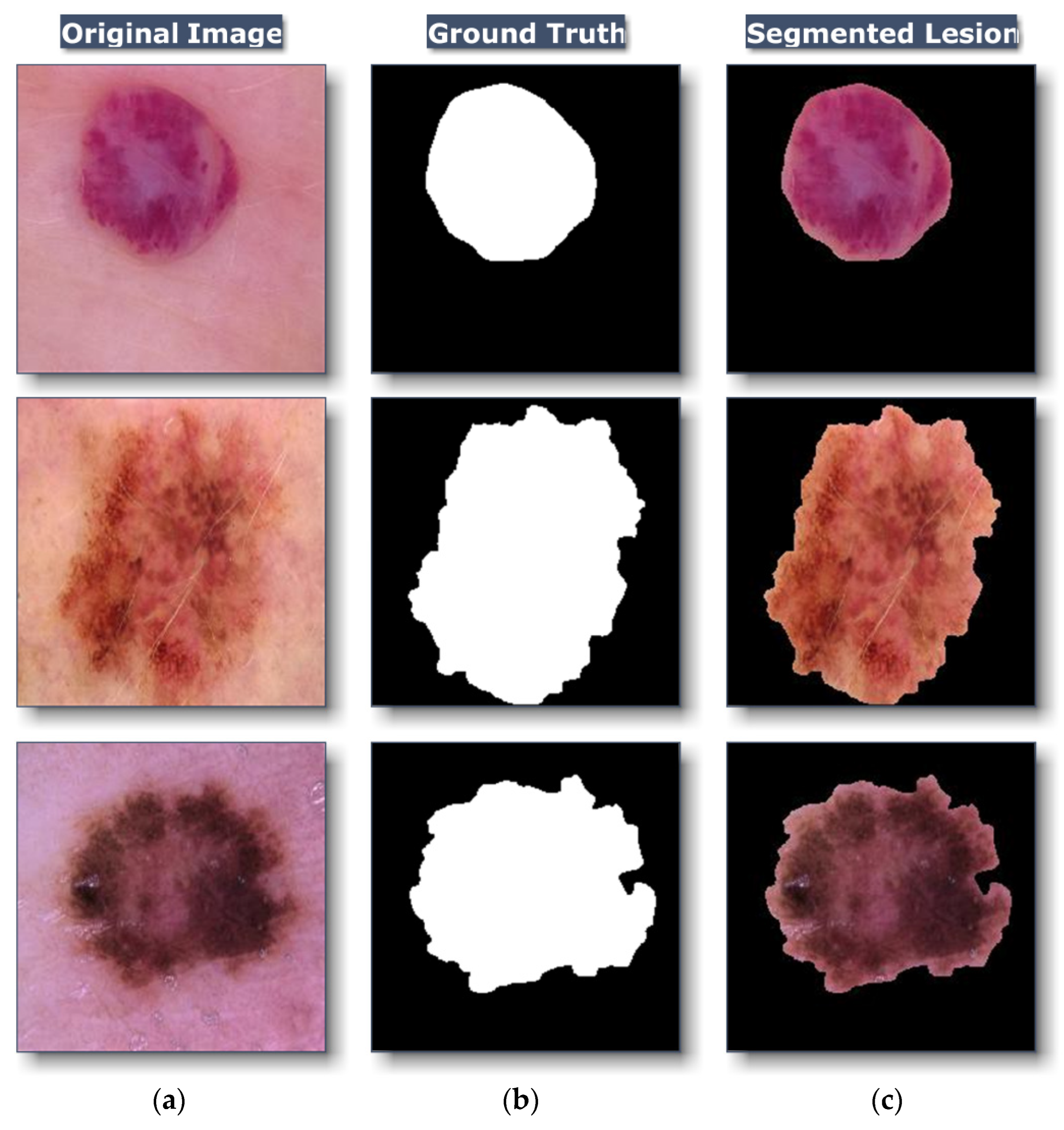
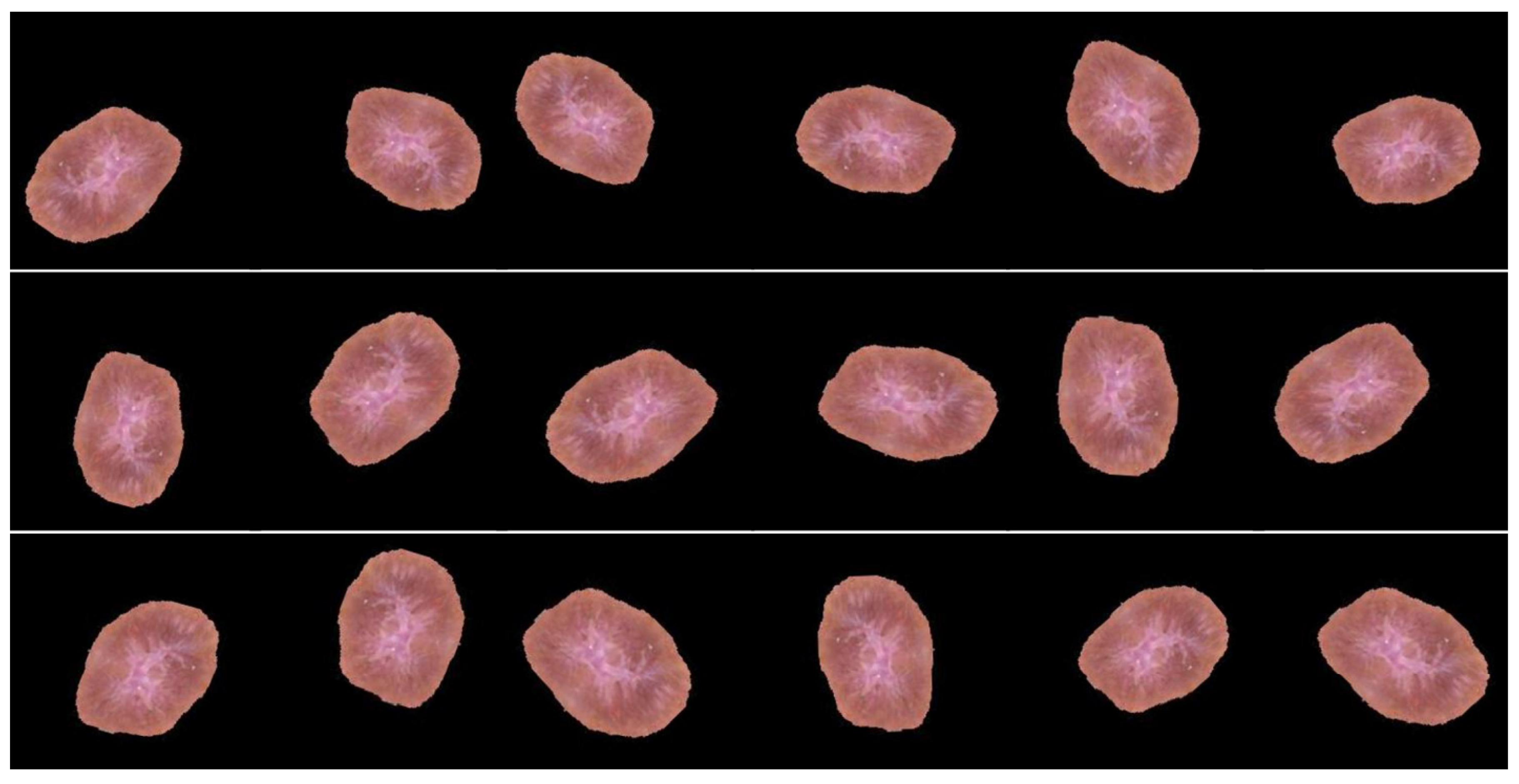
3.2.2. Segmentation
3.2.3. Data Augmentation
3.2.4. Learning Models
Model Training Using CNN
Model Training Using Modified Resnet-50
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Training and Configuration of Resnet-50 and the Proposed CNN
4.2. Set of Criteria for Evaluation
4.3. Performance of Various DCNN Models
4.4. Evaluation with Other Methods
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeed, J.; Zeebaree, S. Skin Lesion Classification Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Architectures. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends 2021, 2, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahar, M.A. Skin Lesion Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network with Novel Regularizer. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38306–38313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.U.; Aslam, N.; Anwar, T.; Aljameel, S.S.; Ullah, M.; Khan, R.; Rehman, A.; Akhtar, N. Remote Diagnosis and Tri-aging Model for Skin Cancer Using EfficientNet and Extreme Gradient Boosting. Complexity 2021, 2021, 5591614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitkina, A.I.; Bikmulina, P.Y.; Gafarova, E.R.; Kosheleva, N.V.; Efremov, Y.M.; Bezrukov, E.A.; Butnaru, D.V.; Dolganova, I.N.; Chernomyrdin, N.V.; Cherkasova, O.P.; et al. Terahertz radiation and the skin: A review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2021, 26, 043005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lu, C.; Berendt, R.; Jha, N.; Mandal, M. Automated analysis and classification of melanocytic tumor on skin whole slide images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2018, 66, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namozov, A.; Im Cho, Y. Convolutional neural network algorithm with parameterized activation function for mela-noma classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 17–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkan, I.A.; KOKLU, M. Skin lesion classification using machine learning algorithms. Int. J. Intelli-Gent Syst. Appl. Eng. 2017, 5, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamizhamuthu, R.; Manjula, D. Skin Melanoma Classification System Using Deep Learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 68, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, W. ABCD rule of dermatoscopy: A new practical method for early recognition of malignant melanoma. Eur. J. Der-Matol. 1994, 4, 521–527. [Google Scholar]
- Argenziano, G.; Fabbrocini, G.; Carli, P.; De Giorgi, V.; Sammarco, E.; Delfino, M. Epiluminescence microscopy for the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions: Comparison of the ABCD rule of dermatoscopy and a new 7-point checklist based on pattern analysis. Arch. Dermatol. 1998, 134, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehamberger, H.; Steiner, A.; Wolff, K. In vivo epiluminescence microscopy of pigmented skin lesions. I. Pattern analysis of pigmented skin lesions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1987, 17, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshma, G.; Al-Atroshi, C.; Nassa, V.K.; Geetha, B.; Sunitha, G.; Galety, M.G.; Neelakandan, S. Deep Learning-Based Skin Lesion Diagnosis Model Using Dermoscopic Images. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2022, 31, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.; Shen, S.; Xu, M.; Liu, P.; Zhang, F.; Xing, J.; Shao, P.; Kaffenberger, B.; Xu, R.X. Single model deep learning on im-balanced small datasets for skin lesion classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.01284. [Google Scholar]
- Adegun, A.; Viriri, S. Deep learning techniques for skin lesion analysis and melanoma cancer detection: A survey of state-of-the-art. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 54, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, X.; Liang, J.; Rosin, P.L. Clinical skin lesion diagnosis using representations inspired by dermatologist cri-teria. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Satheesha, T.Y.; Satyanarayana, D.; Prasad, M.N.G.; Dhruve, K.D. Melanoma Is Skin Deep: A 3D Reconstruction Technique for Computerized Dermoscopic Skin Lesion Classification. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2017, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschandl, P.; Rosendahl, C.; Kittler, H. The HAM10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.; MacNeil, S. State of the art in non-invasive imaging of cutaneous melanoma. Ski. Res. Technol. 2011, 17, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Ali Al-Jumaily, A. Computer aided diagnostic support system for skin cancer: A review of techniques and algorithms. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2013, 2013, 323268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimenko, M.; Ignatev, A.; Koshechkin, K. Review of medical image recognition technologies to detect melanomas us-ing neural networks. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, T.J.; Hekler, A.; Enk, A.H.; Klode, J.; Hauschild, A.; Berking, C.; Schilling, B.; Haferkamp, S.; Schadendorf, D.; Fröhling, S.; et al. A convolutional neural network trained with dermoscopic images performed on par with 145 derma-tologists in a clinical melanoma image classification task. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 111, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.G.; Krohling, R.A. The impact of patient clinical information on automated skin cancer detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 116, 103545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenssle, H.A.; Fink, C.; Schneiderbauer, R.; Toberer, F.; Buhl, T.; Blum, A.; Kalloo, A.; Hassen, A.B.H.; Thomas, L.; Enk, A.; et al. Man against machine: Diagnostic performance of a deep learning convolutional neural network for dermoscopic melanoma recognition in comparison to 58 dermatologists. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.F.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.J.; Xiong, N.N.; Du, Y.X.; Li, B.S. Deep learning in skin disease image recognition: A review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 208264–208280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadampur, M.A.; Al Riyaee, S. Skin cancer detection: Applying a deep learning based model driven architecture in the cloud for classifying dermal cell images. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 18, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinnai, S.; Yamazaki, N.; Hirano, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Ohe, Y.; Hamamoto, R. The Development of a Skin Cancer Classification System for Pigmented Skin Lesions Using Deep Learning. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.A.; Hosny, K.M.; Fouad, M.M. Skin lesions classification into eight classes for ISIC 2019 using deep convolu-tional neural network and transfer learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 114822–114832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekler, A.; Utikal, J.S.; Enk, A.H.; Hauschild, A.; Weichenthal, M.; Maron, R.C.; Berking, C.; Haferkamp, S.; Klode, J.; Schadendorf, D.; et al. Superior skin cancer classification by the combination of human and artificial intelligence. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, H.C.; Turk, V.; Khoshelham, K.; Kaya, S. InSiNet: A deep convolutional approach to skin cancer detection and seg-mentation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2022, 60, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.N.; Le, H.X.; Ngo, L.T.; Ngo, H.T. Transfer learning with class-weighted and focal loss function for automatic skin cancer classification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.05977. [Google Scholar]
- Murugan, A.; Nair, S.A.H.; Preethi, A.A.P.; Kumar, K.P.S. Diagnosis of skin cancer using machine learning techniques. Microprocess. Microsystems 2020, 81, 103727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Miah, M.S.; Haque, J.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.K. An enhanced technique of skin cancer classification using deep convolutional neural network with transfer learning models. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2021, 5, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, G.; Agrawal, S.; Raut, G.; Vishvakarma, S.K. An accurate and noninvasive skin cancer screening based on imaging technique. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2022, 32, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani, P.; Padole, M. Deep learning to detect skin cancer using google colab. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. Regul. Issue 2019, 8, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, D.B.; da Silva, N.C. Skin lesions classification using convolutional neural networks in clinical images. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.02316. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Akram, T.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Sharif, M. Attributes based skin lesion detection and recognition: A mask RCNN and transfer learning-based deep learning framework. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 143, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, R.; Pourkazemi, A. DenseNet approach to segmentation and classification of dermatoscopic skin lesions images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.04632. [Google Scholar]
- Thapar, P.; Rakhra, M.; Cazzato, G.; Hossain, M.S. A novel hybrid deep learning approach for skin lesion segmentation and classification. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1709842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Qiao, Y.; Change Loy, C. Esrgan: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur-Martineau, A. The relativistic discriminator: A key element missing from standard GAN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.00734. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y. Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series. Handb. Brain Theory Neural Netw. 1995, 3361, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation Applied to Handwritten Zip Code Recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.S.; Dubey, S.R.; Pulabaigari, V.; Mukherjee, S. Impact of fully connected layers on performance of convolutional neural networks for image classification. Neurocomputing 2019, 378, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, F.; Guedria, S.; De Palma, N.; Vuillerme, N. Variability and reproducibility in deep learning for medical image segmentation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameri, A. A deep learning approach to skin cancer detection in dermoscopy images. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2020, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sae-Lim, W.; Wettayaprasit, W.; Aiyarak, P. Convolutional neural networks using MobileNet for skin lesion classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Joint Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE), Chonburi, Thailand, 10–12 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gouda, W.; Almurafeh, M.; Humayun, M.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. Detection of COVID-19 Based on Chest X-rays Using Deep Learning. Healthcare 2022, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salian, A.C.; Vaze, S.; Singh, P.; Shaikh, G.N.; Chapaneri, S.; Jayaswal, D. Skin lesion classification using deep learning architectures. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Communication System, Computing and IT Applications (CSCITA), Mumbai, India, 3–4 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, E.Z.; Jiang, H. From deep learning towards finding skin lesion biomarkers. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.C.; Tran, G.S.; Nghiem, T.P.; Doucet, A.; Luong, C.M.; Hoang, V.D. A comparative study for classification of skin cancer. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), Dong Hoi, Vietnam, 20–21 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Polat, K.; Koc, K.O. Detection of skin diseases from dermoscopy image using the combination of convolutional neural network and one-versus-all. J. Artif. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Ami, A.M. A transfer learning based approach for skin lesion classification from imbalanced data. In Proceedings of the 2020 11th International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (ICECE), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–19 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasu, P.N.; SivaSai, J.G.; Ijaz, M.F.; Bhoi, A.K.; Kim, W.; Kang, J.J. Classification of skin disease using deep learning neural networks with MobileNet V2 and LSTM. Sensors 2021, 21, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
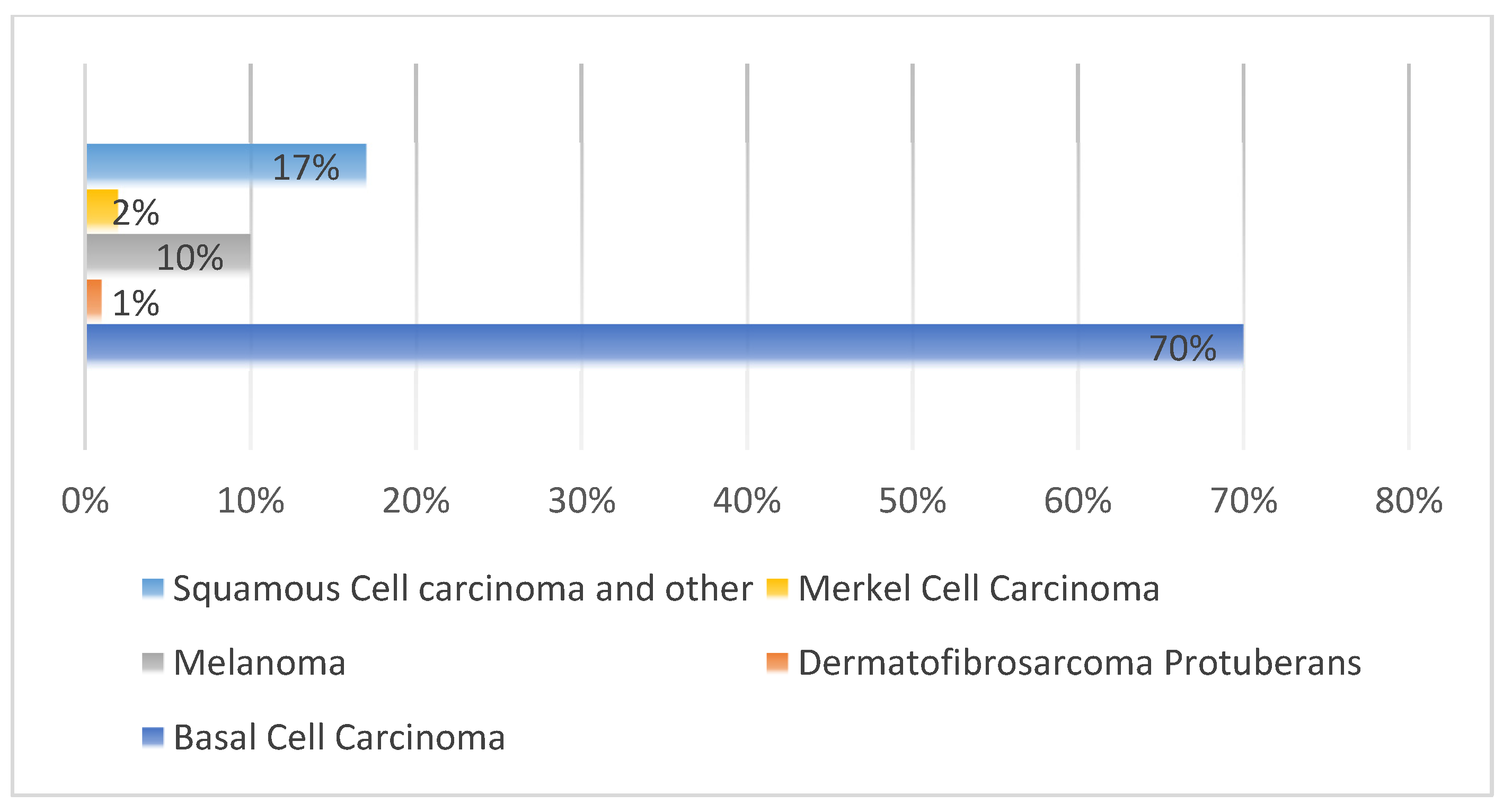





| Notable Designs | Size | Dataset | Methods | # Classes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [3] | 2298 | PAD-UFES-20 | EfficientNetB3 + Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGB) | 6 |
| [19] | 1600 | ISIC-2017 | swarm intelligence (SI) | 2 |
| 1600 | ISIC-2018 | |||
| 1000 | PH-2 | |||
| [33] | 300 | HAM10000 | CNN + XGBoost | 5 |
| [34] | 1323 | HAM10000 | InSiNet | 2 |
| [35] | 7470 | HAM10000 | ResNet50 | 7 |
| [36] | 1000 | ISIC | RF + Support Vector Machine (SVM) | 8 |
| [37] | 6705 | HAM10000 | CNN | 2 |
| [38] | 10,015 | HAM10000 | AlexNet | 7 |
| [39] | 10,015 | HAM10000 | CNN | 7 |
| [40] | 4753 | Atlas | ResNet-152 | 12 |
| [41] | 10,015 | HAM10000 | MASK-RCNN | 7 |
| [42] | 10,015 | HAM10000 | DenseNet121 | 7 |
| Class | Number of Training Images |
|---|---|
| Akiec | 5684 |
| Bcc | 5668 |
| Mel | 5886 |
| Vasc | 5570 |
| Nv | 5979 |
| Df | 4747 |
| Bkl | 5896 |
| Total | 39,430 |
| Acc | Top-2 Accuracy | Top-3 Accuracy | Pre | Rec | Fsc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8598 | 0.9400 | 0.9726 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.8598 |
| Acc | Top-2 Accuracy | Top-3 Accuracy | Pre | Rec | Fsc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8526 | 0.9329 | 0.9695 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.8526 |
| Pre | Rec | Fsc | Total Images | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
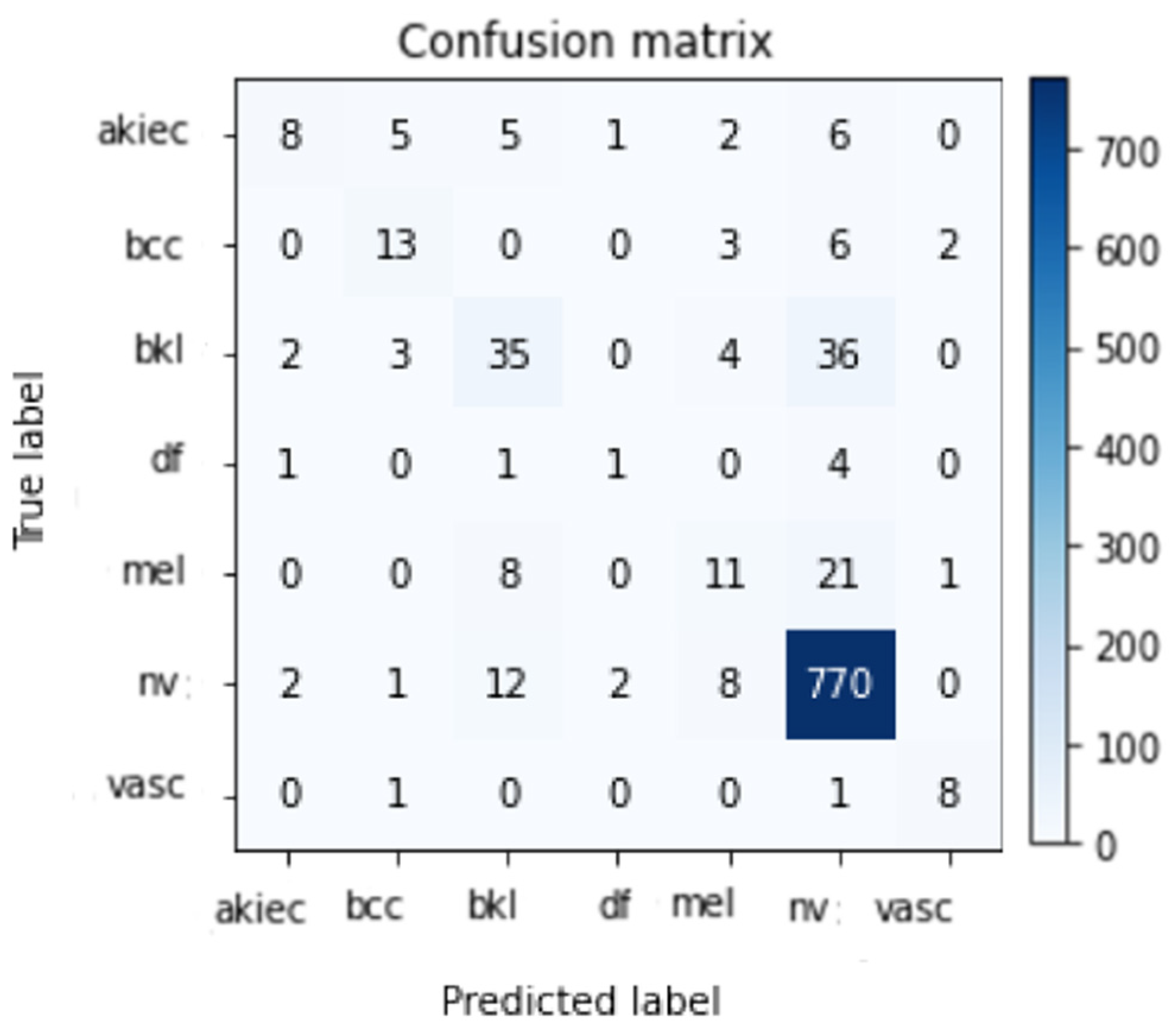
| Akiec | 0.62 | 0.30 | 0.4 | 27 |
| Bcc | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 24 |
| Bkl | 0.57 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 80 |
| Df | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 7 |
| Mel | 0.39 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 41 |
| Nv | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 795 |
| Vasc | 0.73 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 10 |
| Average | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 984 |
| Pre | Rec | Fsc | Total Images | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
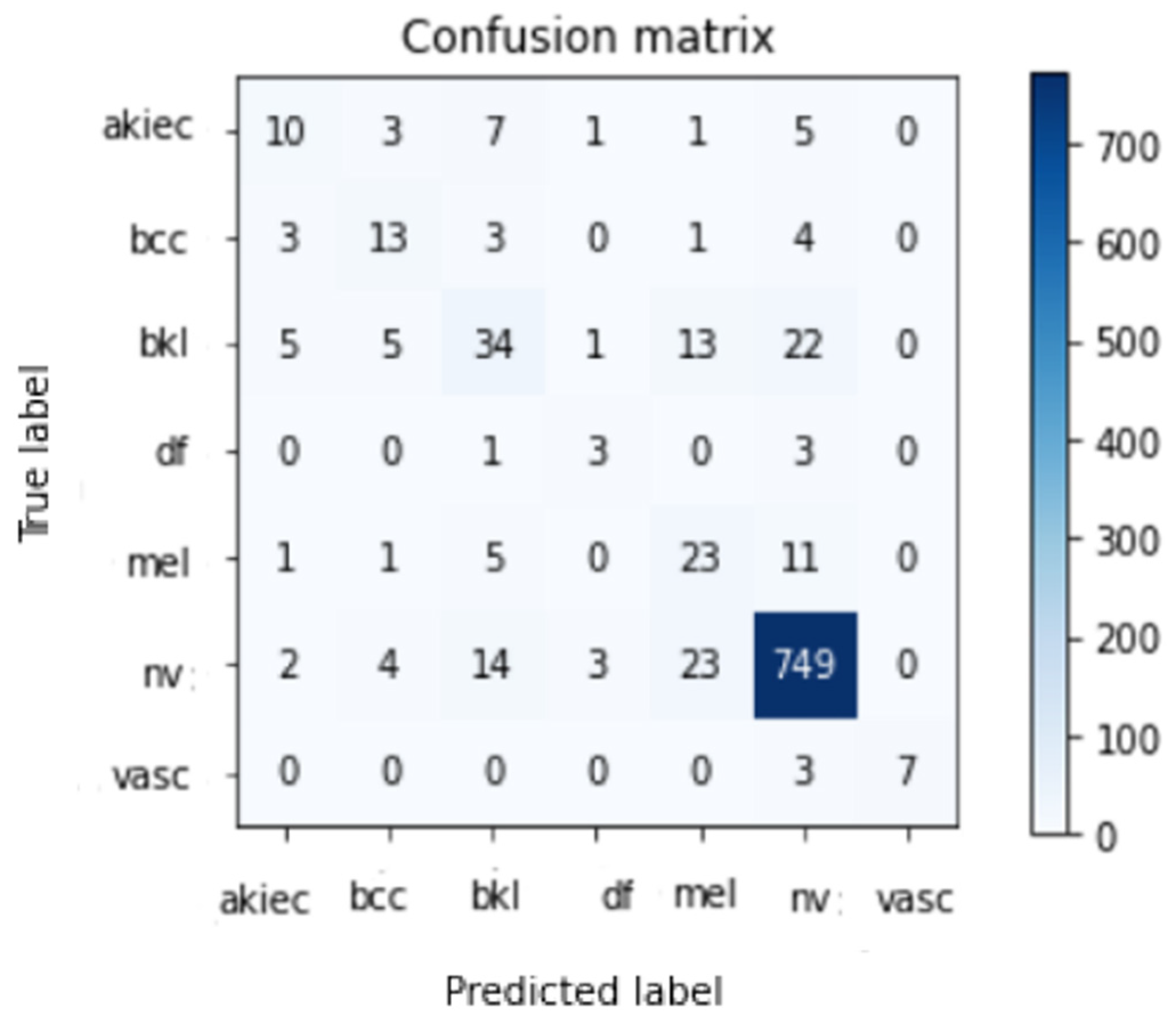
| Akiec | 0.48 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 27 |
| Bcc | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 24 |
| Bkl | 0.55 | 0.42 | 0.48 | 80 |
| Df | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.40 | 7 |
| Mel | 0.37 | 0.59 | 0.45 | 41 |
| Nv | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 795 |
| Vasc | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.82 | 10 |
| Average | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 984 |
| Reference | Dataset | Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | HAM10000 | RegNetY-3.2GF | 85.8% |
| [49] | HAM10000 | AlexNet | 84% |
| [50] | HAM10000 | MobileNet | 83.9% |
| [51] | ISIC2018 | CNN | 83.1% |
| [51] | ISIC2018 | Resnet-50 | 83.6% |
| [52] | HAM10000 | MobileNet, VGG-16 | 80.61% |
| [53] | ISIC2018 | Resnet-50 | 85% |
| [54] | HAM10000 | Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), AdaBoost (Adaptive Boosting), Balanced Bagging (BB) and Balanced Random Forest (BRF) | 74.75% |
| [55] | HAM10000 | CNN | 77% |
| [56] | HAM10000 | ResNet, Xception, and DenseNet | 78%, 82%, 82% |
| [57] | HAM10000 | MobileNet and LSTM | 85% |
| Proposed | HAM10000 | CNN | 86% |
| Proposed | HAM10000 | Modified Resnet-50 | 85.3% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alwakid, G.; Gouda, W.; Humayun, M.; Sama, N.U. Melanoma Detection Using Deep Learning-Based Classifications. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122481
Alwakid G, Gouda W, Humayun M, Sama NU. Melanoma Detection Using Deep Learning-Based Classifications. Healthcare. 2022; 10(12):2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122481
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlwakid, Ghadah, Walaa Gouda, Mamoona Humayun, and Najm Us Sama. 2022. "Melanoma Detection Using Deep Learning-Based Classifications" Healthcare 10, no. 12: 2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122481
APA StyleAlwakid, G., Gouda, W., Humayun, M., & Sama, N. U. (2022). Melanoma Detection Using Deep Learning-Based Classifications. Healthcare, 10(12), 2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122481






