Classification Algorithms Used in Predicting Glaucoma Progression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Glaucoma
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Modeling Methodology
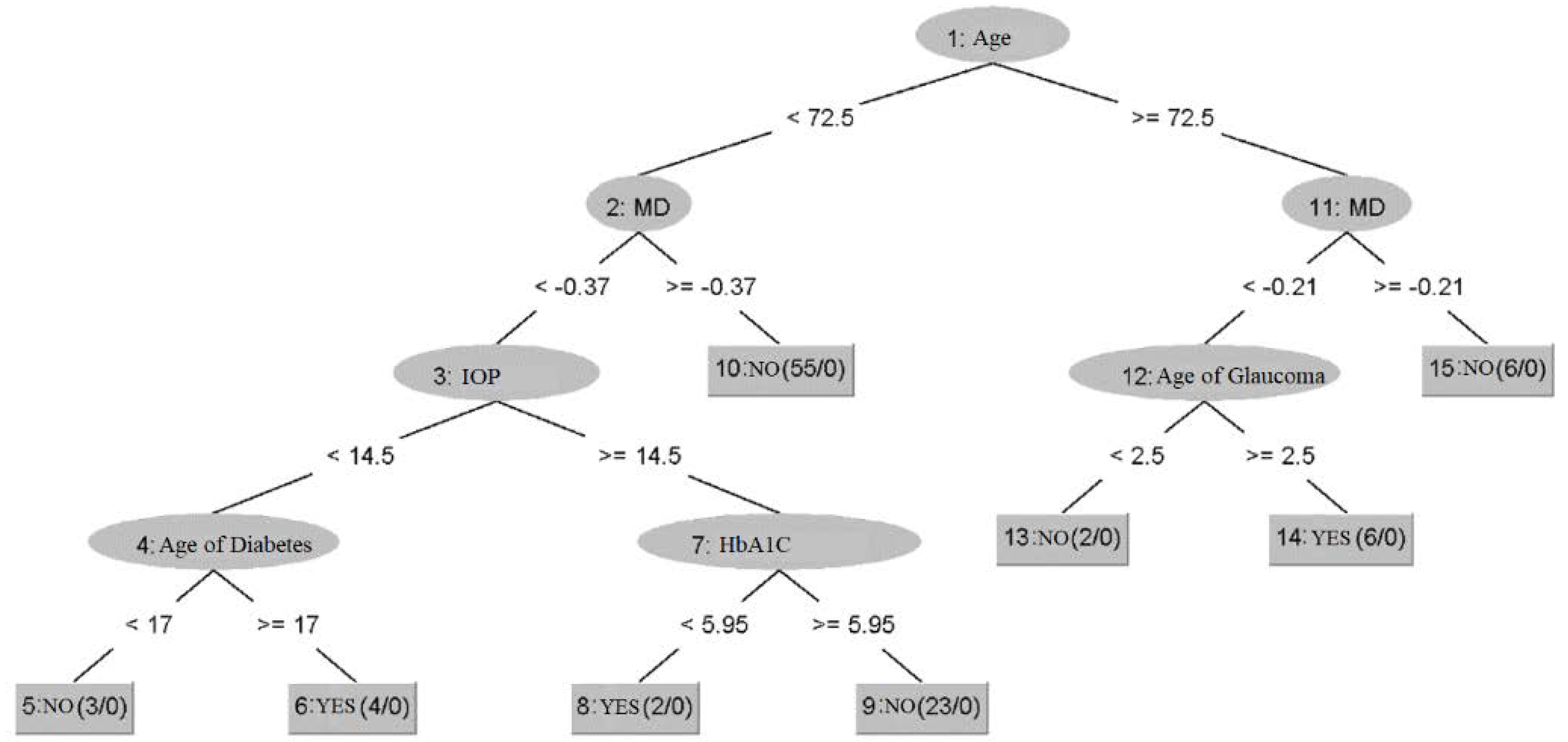
3. Results
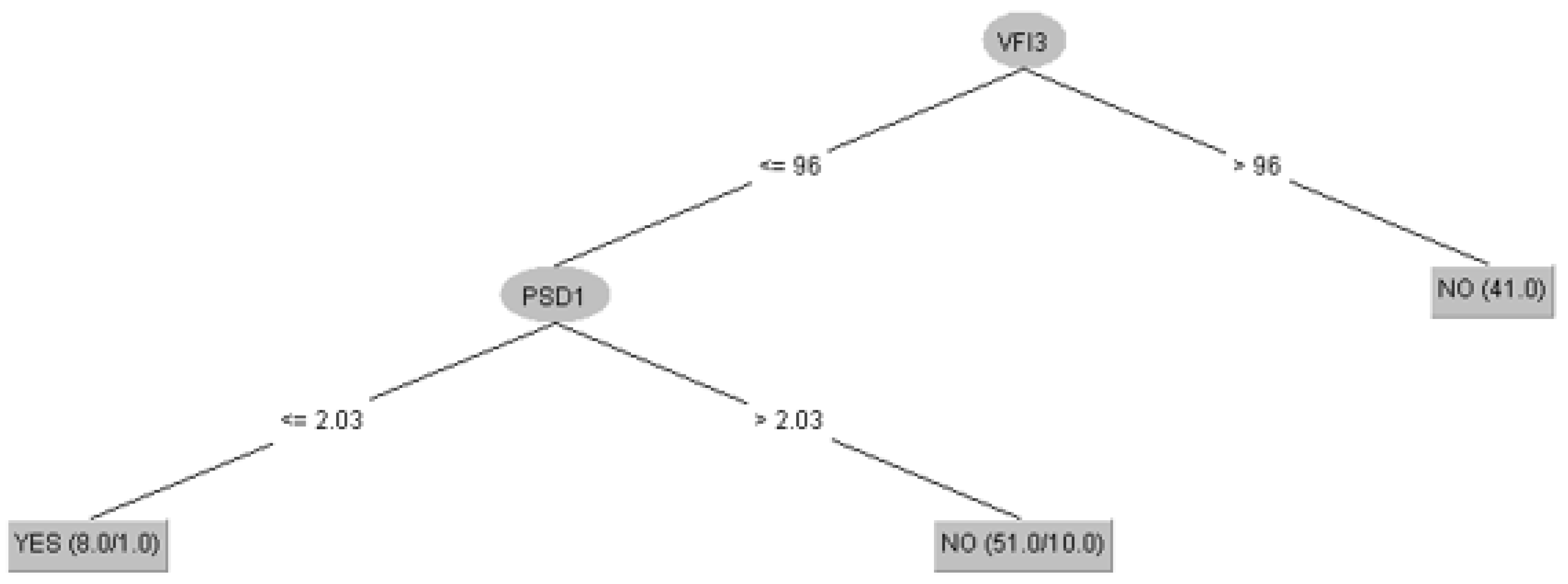
3.1. Prediction of Glaucoma Evolution Using Dataset 1
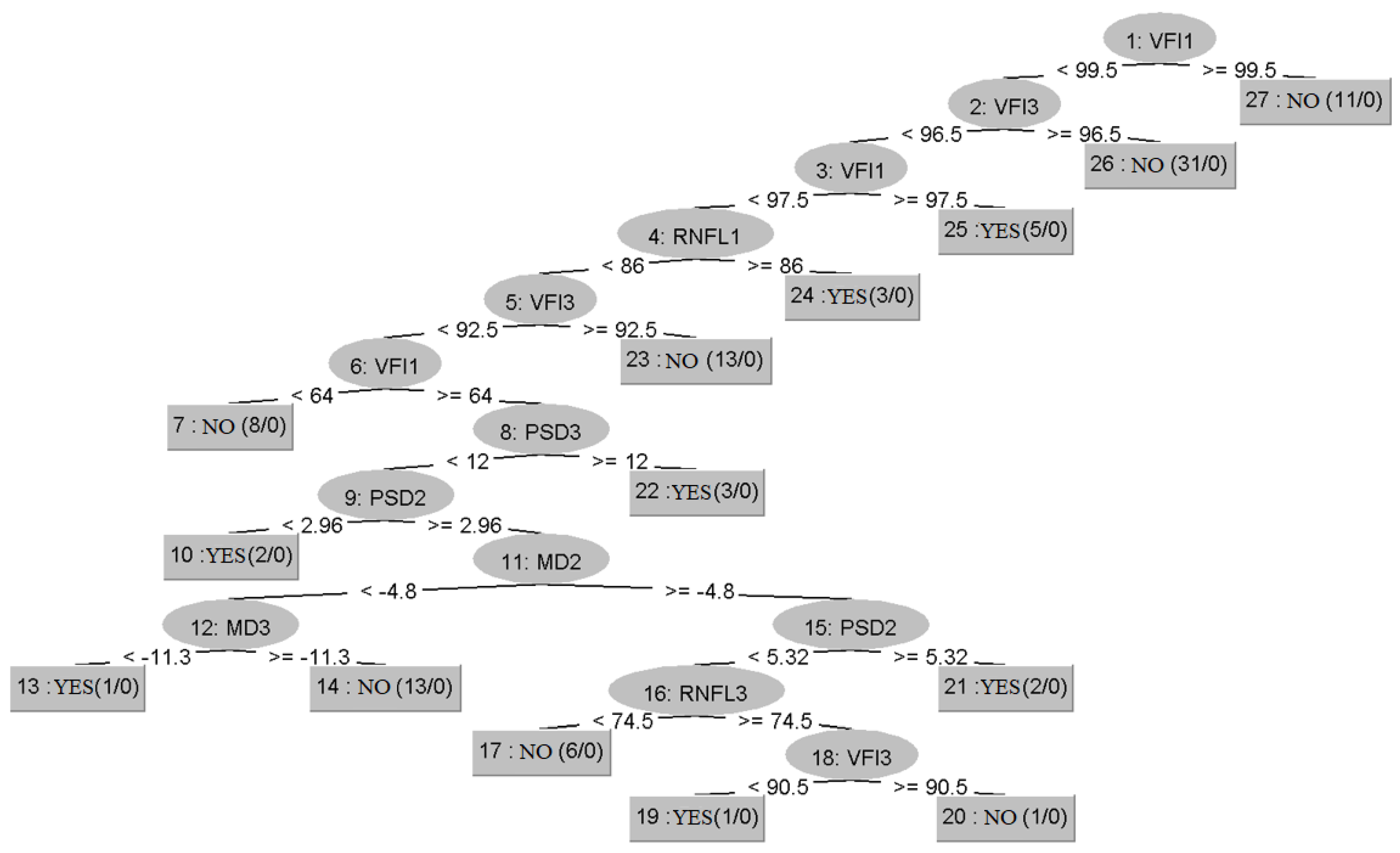
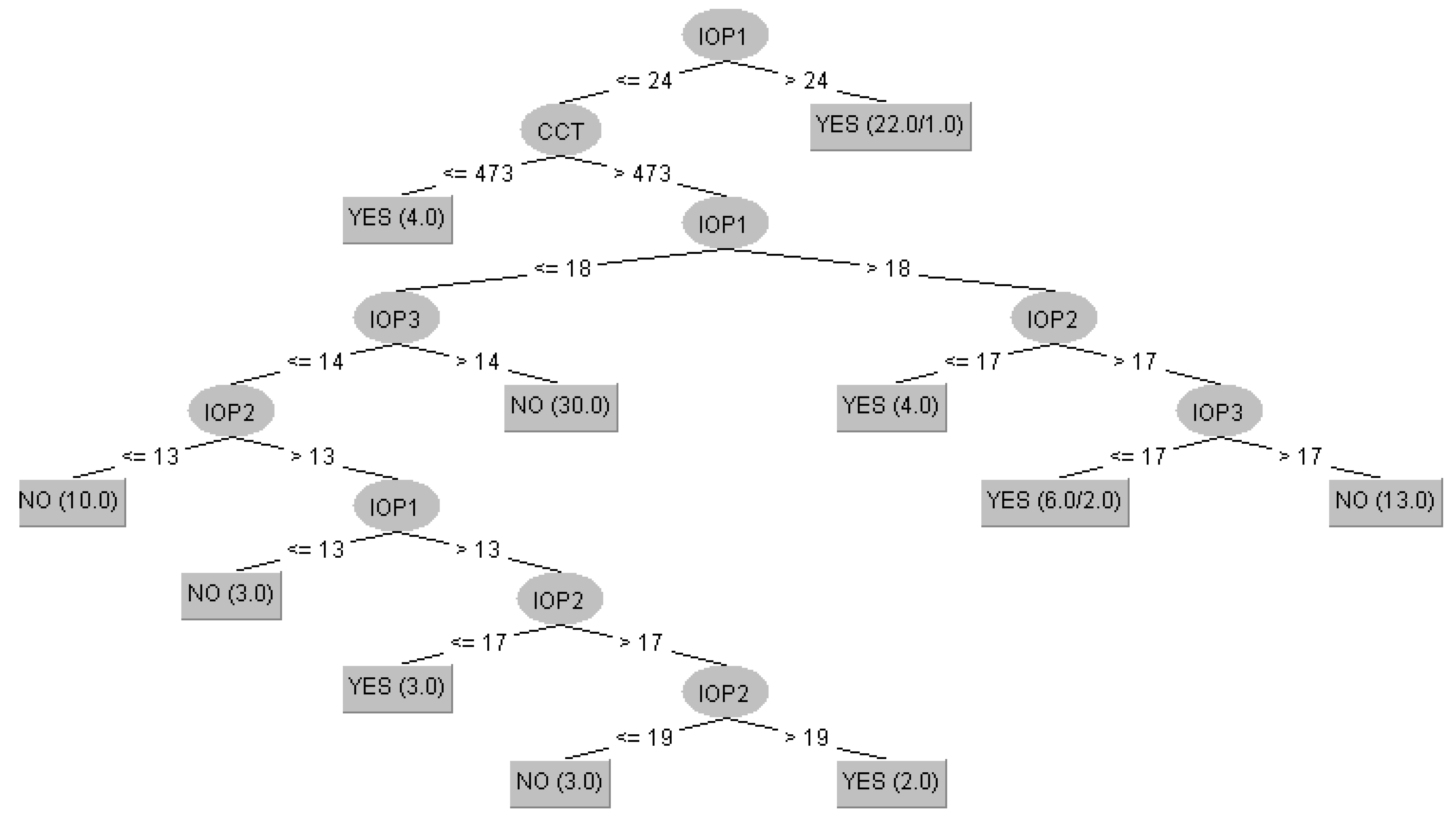
3.2. Prediction of Glaucoma Evolution Using Dataset 2
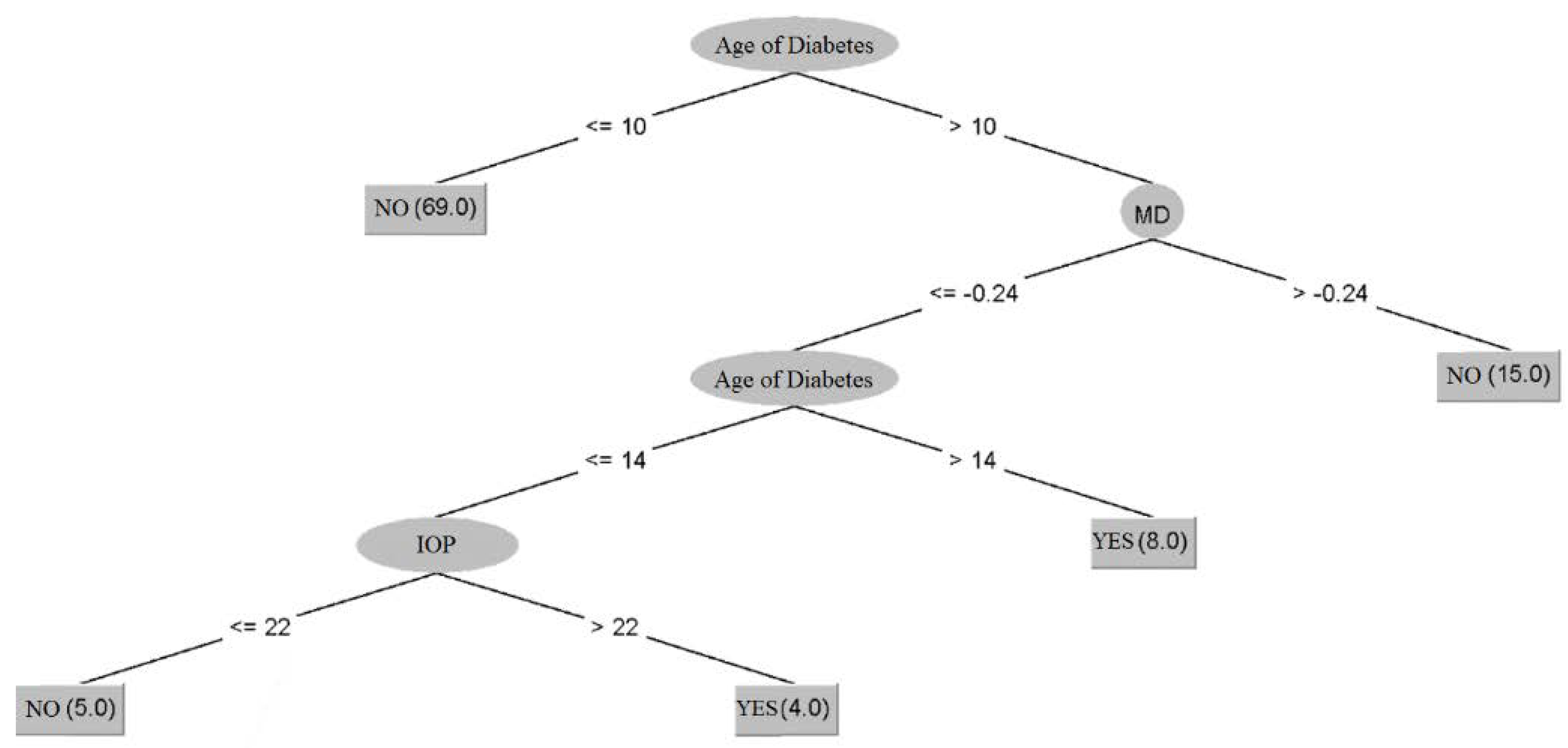
3.3. Prediction of Diabetic Retinopathy Status in Patients with Glaucoma Using Dataset 3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- Bryson, O.; Muata, K.; Kendall, G. An exploration of a set of entropy-based hybrid splitting methods for decision tree induction. J. Database Manag. 2004, 15, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, U.I.; Starkey, A. Review of classification algorithms with changing inter-class distances. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2021, 4, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Manolopoulos, Y. Nearest Neighbor Search: A Database Perspective; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.M. Bayesian Statistics: An Introduction, 3rd ed.; Peter, M., Ed.; Arnold Publishers: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, F. Decision Graphs. In Bayesian Networks and Decision Graphs; Statistics for Engineering and Information Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mira, J.; Álvarez, J. Computational Methods in Neural Modeling; IWANN 2003; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanciuc, O. Applications of Support Vector Machines in Chemistry. Comput. Chem. 2007, 23, 291–400. [Google Scholar]
- Goldbaum, M.H.; Lee, I.; Jang, G.; Balasubramanian, M.; Sample, P.A.; Weinreb, R.N.; Liebmann, J.M.; Girkin, C.; Anderson, D.R.; Zangwill, L.M.; et al. Progression of patterns (POP): A machine classifier algorithm to identify glaucoma progression in visual fields. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 6557–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barella, K.A.; Costa, V.P.; Vidotti, G.V.; Silva, F.R.; Dias, M.; Gomi, E.S. Glaucoma Diagnostic Accuracy of Machine Learning Classifiers Using Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Optic Nerve Data from SD-OCT. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 2013, 789129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Witten, I.H. The WEKA Workbench. Online Appendix for “Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, 4th ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bizios, D.; Heijl, A.; Hougaard, J.; Bengtsson, B. Machine learning classifiers for glaucoma diagnosis based on classification of retinal nerve fibre layer thickness parameters measured by Stratus OCT. Acta Ophthalmol. 2010, 88, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Shen, H.; Lu, C.; Chen, S.; Chen, H. Comparison of Different Machine Learning Classifiers for Glaucoma Diagnosis Based on Spectralis OCT. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiseliță, D. Glaucomul Primitiv cu Unghi Deschis—Gânduri și Sinteze Practice, 2nd ed.; Iași: Thea, Cermi, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tham, Y.; Li, X.; Wong, T.; Quigley, H.A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatham, A.; Weinreb, R.; Medeiros, F. Strategies for improving early detection of glaucoma: The combined structure-function index. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2014, 8, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, R.; Aung, T.; Medeiros, F. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuman, J. Detection and diagnosis of glaucoma: Ocular imaging. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 2488–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Garway-Heath, D.F.; Leung, C.; Medeiros, F.A.; Liebmann, J. 10th Consensus Meeting: Diagnosis of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma; Kugler Publications: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, N.; Ayub, M.; Ali, M. Challenges in the management of glaucoma in developing countries. Taiwan J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 6, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devalla, S.K.; Liang, Z.; Pham, T.H.; Boote, C.; Strouthidis, N.G.; Thiery, A.H.; A Girard, M.J. Glaucoma management in the era of artificial intelligence. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 104, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Glaucoma Society. Terminology and Guidelines for Glaucoma, 5th ed.; PubliComm: Savona, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anton Apreutesei, N.; Tarcoveanu, F.; Cantemir, A.; Bogdanici, C.; Lisa, C.; Curteanu, S.; Chiseliţă, D. Predictions of ocular changes caused by diabetes in glaucoma patients. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 154, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- (ICO) TICoO. ICO Guidelines for Diabetic Eye Care. Updated 2017; International Council of Ophthalmology: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.; Frank, E. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools with Java Implementations; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning. Tools and Techniques Amsterdam; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, P. AI Qual Summary: Learning. 2000. Available online: http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/~pdoyle/quail/notes/pdoyle/learning.html (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Hamilton, H.; Gurak, E.; Findlater, L.; Olive, W. Knowledge Discovery in Databases. University of Regina, Canadal. 2002. Available online: http://www2.cs.uregina.ca/~hamilton/courses/831/notes/ml/dtrees/c4.5/tutorial.html (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Joshi, K.P. Analysis of Data Mining Algorithms. Available online: https://ebiquity.umbc.edu/_file_directory_/papers/457.html (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarcoveanu, F.; Apreutesei-Anton, N.; Chiselita, D.; Leon, F.; Curteanu, S. Configuratii Soft-Computing cu Aplicatii in Oftalmologie. Romanian Annual Ophthalmology Reunion Conference (RAO) Edition 58. 2021. Available online: https://online.eventernet.ro/virtual/rao-2021/830/entrance (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Anton, N.; Dragoi, E.; Tarcoveanu, F.; Ciuntu, R.; Lisa, C.; Curteanu, S.; Doroftei, B.; Ciuntu, B.; Chiseliţă, D.; Bogdănici, C. Assessing Changes in Diabetic Retinopathy Caused by Diabetes Mellitus and Glaucoma Using Support Vector Machines in Combination with Differential Evolution Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Algorithm | Training | Cross-Validation |
|---|---|---|
| SVM (PUK kernel, C = 100) | 0.9990 | 0.7963 |
| kNN (k = 1, wi = 1/di) | 0.9999 | 0.7168 |
| Random Forest (n = 100) | 0.9839 | 0.8558 |
| C4.5 (unpruned) | 0.8905 | 0.7279 |
| NNGE | 0.9558 | 0.6931 |
| Inputs | Weights |
|---|---|
| Age | 0.109 |
| Sex | 0.055 |
| Glaucoma age | 0.111 |
| Diabetes age | 0.088 |
| HbAIc | 0.066 |
| Baseline IOP | 0.150 |
| IOP on this visit | 0.072 |
| IOL presence | 0.0006 |
| CCT | 0.089 |
| Algorithm | Training | Cross-Validation |
|---|---|---|
| SVM (PUK kernel, C = 100) | 0.9988 | 0.8039 |
| kNN (k = 1, wi = 1/di) | 0.9999 | 0.7331 |
| Random Forest (n = 100) | 0.9882 | 0.8800 |
| C4.5 | 0.9365 | 0.7252 |
| NNGE | 0.9630 | 0.7461 |
| Inputs | Weights |
|---|---|
| Age | 0.127 |
| Sex | 0.062 |
| Glaucoma age | 0.109 |
| Diabetes age | 0.101 |
| HbAIc | 0.079 |
| Baseline IOP | 0.231 |
| IOP on this visit | 0.054 |
| IOL presence | 0.096 |
| CCT | 0.148 |
| Algorithm | Training | Cross-Validation |
|---|---|---|
| SVM (PUK kernel, C = 100) | 0.9957 | 0.7790 |
| kNN (k = 3, wi = 1/di) | 0.9992 | 0.7893 |
| Random Forest (n = 100) | 0.9870 | 0.8620 |
| C4.5 (pruned) | 0.7962 | 0.6418 |
| NNGE | 0.9369 | 0.6842 |
| Inputs | Weights |
|---|---|
| Age | 0.086 |
| Sex | 0.027 |
| Glaucoma age | 0.079 |
| Diabetes age | 0.042 |
| HbAIc | 0.024 |
| Baseline IOP | 0.073 |
| IOP on this visit | 0.059 |
| IOL presence | 0.0009 |
| CCT | 0.138 |
| Algorithm | Training | Cross-Validation |
|---|---|---|
| SVM (PUK kernel, C = 100) | 0.9996 | 0.8184 |
| kNN (k = 1, wi = 1/di) | 1.0000 | 0.8674 |
| Random Forest (n = 100) | 0.9896 | 0.9015 |
| C4.5 (pruned) | 0.8779 | 0.7724 |
| NNGE | 0.9144 | 0.6980 |
| Inputs | Weights |
|---|---|
| Age | 0.092 |
| Sex | 0.015 |
| Glaucoma age | 0.142 |
| Diabetes age | 0.050 |
| HbAIc | 0.037 |
| Baseline IOP | 0.141 |
| IOP on this visit | 0.073 |
| IOL presence | 0.077 |
| CCT | 0.074 |
| Algorithm | Correctly Classified Instances | Incorrectly Classified Instances | Kappa Statistic | Mean Absolute Error | Root Mean Squared Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Tree | 74 | 26 | 0.192 | 0.26 | 0.5099 |
| Random Forest | 85 | 15 | 0.3268 | 0.2116 | 0.3217 |
| C4.5 | 83 | 17 | 0.1889 | 0.2006 | 0.3768 |
| NNGE | 81 | 19 | 0.1949 | 0.19 | 0.4359 |
| kNN | 86 | 14 | 0.4527 | 0.1478 | 0.3702 |
| MLP | 92 | 8 | 0.7165 | 0.1006 | 0.2724 |
| SVM | 83 | 17 | 0 | 0.17 | 0.4123 |
| Predicted Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| YES | NO | ||
| Actual Class | YES | 13 | 4 |
| NO | 4 | 79 | |
| Algorithm | Correctly Classified Instances | Incorrectly Classified Instances | Kappa Statistic | Mean Absolute Error | Root Mean Squared Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Tree | 65 | 35 | 0.2757 | 0.35 | 0.5916 |
| Random Forest | 84 | 16 | 0.6497 | 0.2742 | 0.3541 |
| C4.5 | 79 | 21 | 0.5329 | 0.2353 | 0.4285 |
| NNGE | 83 | 17 | 0.6298 | 0.17 | 0.4123 |
| kNN | 80 | 20 | 0.5379 | 0.2065 | 0.4425 |
| MLP | 86 | 14 | 0.7029 | 0.1436 | 0.3445 |
| SVM | 62 | 38 | 0 | 0.38 | 0.6164 |
| AdaBoost | 85 | 15 | 0.6664 | 0.2312 | 0.361 |
| Performance Indicator | Value |
|---|---|
| Correctly classified instances | 95 (94.0594%) |
| Incorrectly classified instances | 6 (5.9406%) |
| Kappa statistic | 0.7354 |
| Mean absolute error | 0.0583 |
| Root mean squared error | 0.2349 |
| Algorithm | Correctly Classified Instances | Incorrectly Classified Instances | Kappa Statistic | Mean Absolute Error | Root Mean Squared Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 100 99.0099% | 1 0.9901% | 0.9509 | 0.055 | 0.1094 |
| SVM | 88 87.1287% | 13 12.8713% | −0.0186 | 0.1287 | 0.3588 |
| MLP | 97 96.0396% | 4 3.9604% | 0.8109 | 0.0558 | 0.1749 |
| Random Tree | 98 97.0297% | 3 2.9703% | 0.8631 | 0.0297 | 0.1723 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarcoveanu, F.; Leon, F.; Curteanu, S.; Chiselita, D.; Bogdanici, C.M.; Anton, N. Classification Algorithms Used in Predicting Glaucoma Progression. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10101831
Tarcoveanu F, Leon F, Curteanu S, Chiselita D, Bogdanici CM, Anton N. Classification Algorithms Used in Predicting Glaucoma Progression. Healthcare. 2022; 10(10):1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10101831
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarcoveanu, Filip, Florin Leon, Silvia Curteanu, Dorin Chiselita, Camelia Margareta Bogdanici, and Nicoleta Anton. 2022. "Classification Algorithms Used in Predicting Glaucoma Progression" Healthcare 10, no. 10: 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10101831
APA StyleTarcoveanu, F., Leon, F., Curteanu, S., Chiselita, D., Bogdanici, C. M., & Anton, N. (2022). Classification Algorithms Used in Predicting Glaucoma Progression. Healthcare, 10(10), 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10101831










