Influence of Game-Based Learning in Mathematics Education on Students’ Affective Domain: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
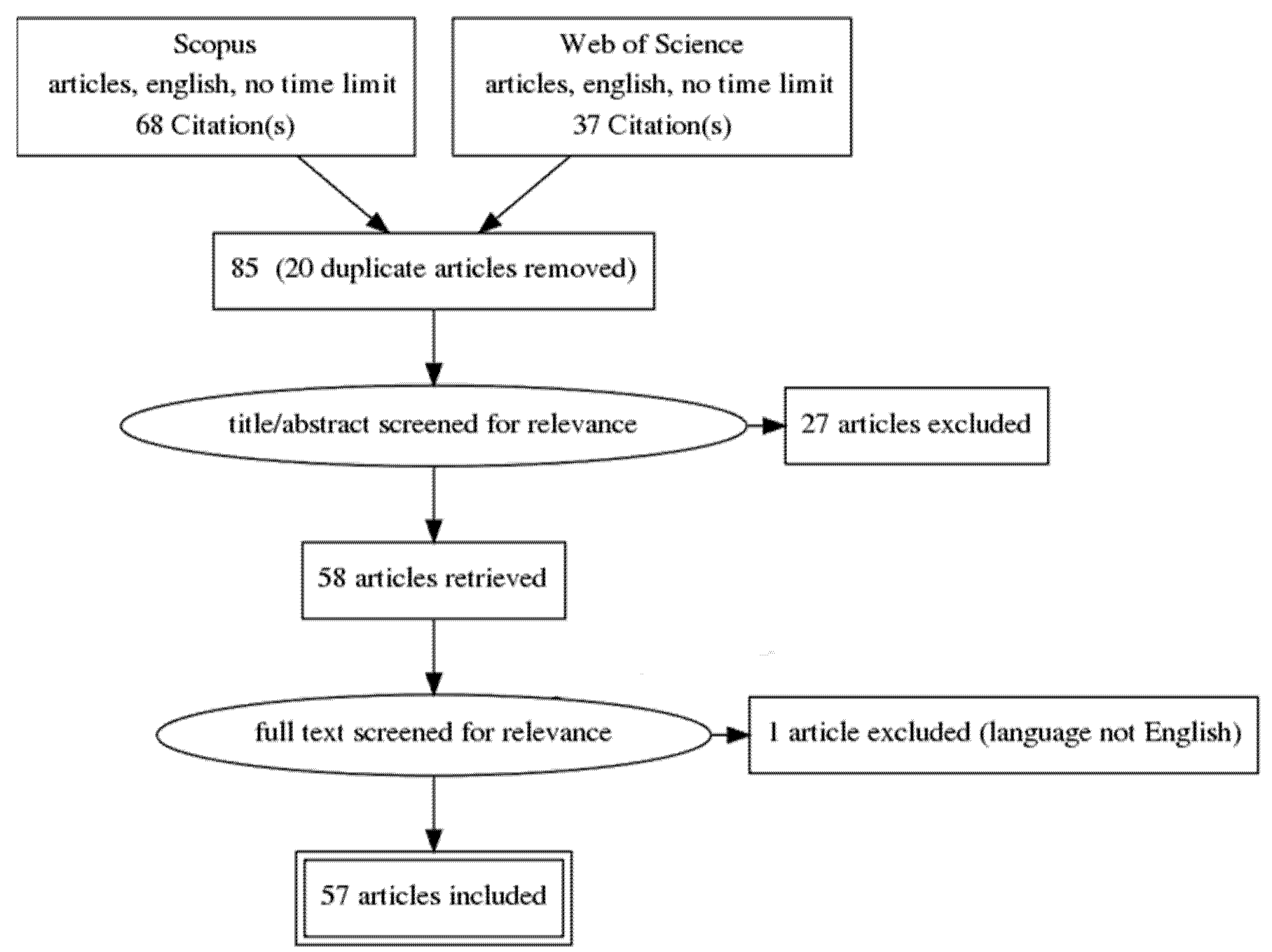
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
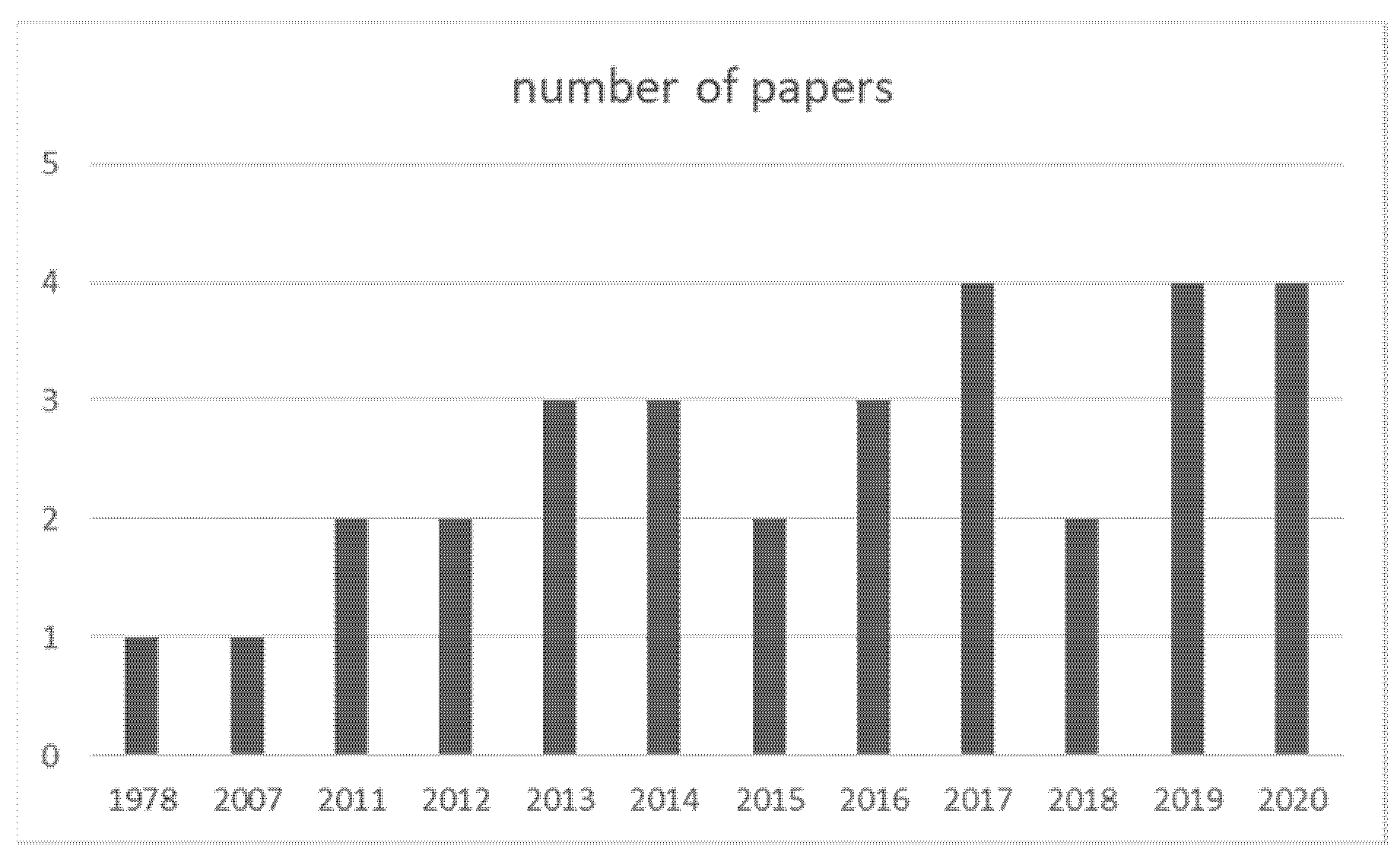
3.1. Extent of the Studies Considering the Affective Domain
3.2. Journals Publishing Studies Considering the Affective Domain
3.3. Influences of Game-Based Learning on the Affective Domain
3.4. Instruments Used to Measure the Influences of Game-Based Learning on the Affective Domain
4. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, D.B.; Tanner-Smith, E.E.; Killingsworth, S.S. Digital games, design, and learning: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 2016, 86, 79–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, O.; Dehghanzadeh, H.; Talaee, E. A systematic review on the impacts of game-based learning on argumentation skills. Entertain. Comput. 2020, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, M.; Holzinger, A. Successful implementation of user-centered game based learning in higher education: An example from civil engineering. Comput. Educ. 2007, 49, 873–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankúš, P. History and present of didactical games as a method of mathematics teaching. Acta Didact. Univ. Comen. Math. 2005, 5, 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Holzinger, A.; Nischelwitzer, A.; Meisenberger, M. Lifelong–Learning support by m-learning: Example scenarios. Elearn 2005, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divjak, B.; Tomic, D. The impact of Game-based learning on the achievement of learning goals and motivation for learning mathematics-literature review. J. Inf. Organ. Sci. 2011, 35, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, F.A. Qualitative Meta-Analysis of Computer Games as Learning Tools. In Handbook of Research on Effective Electronic Gaming in Education; Ferdig, R.E., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, J.M.; Morris, B.A.; Wetzel, C.D.; Whitehill, B.V. The Effectiveness of Games for Educational Purposes: A Review of Recent Research. Simul. Gaming. 1992, 23, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, R.T. The Effectiveness of Instructional Games: A Literature Review and Discussion; Naval Air Warfare Center: Orlando, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Abramovich, S. Topic in Mathematics for Elementary Teachers: A Technology-Enhanced Experiential Approach; Information Age Publishing, Inc.: Charlotte, NC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bottino, R.M.; Ferlino, L.; Ott, M.; Tavella, M. Developing strategic and reasoning abilities with computer games at primary school level. Comput. Educ. 2007, 49, 1272–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Chen, S.Y. Effects of gender differences and spatial abilities within a digital pentominoes game. Comput. Educ. 2010, 55, 1220–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R.; Durán, R. Do Multiple Representations Need Explanations? The Role of Verbal Guidance and Individual Differences in Multimedia Mathematics Learning. J. Educ. Psychol. 2004, 96, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokac, U.; Novak, E.; Thompson, C.G. Effects of game-based learning on students’ mathematics achievement: A meta-analysis. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2019, 35, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchino, M.I. Using Game-Based Learning to Foster Critical Thinking in Student Discourse. Interdiscip. J. Probl. Based Learn. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, C. Effects of attitudes and beliefs on mathematics achievement. Stud. Educ. Eval. 2000, 26, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloosterman, P. Beliefs About Mathematics and Mathematics Learning in the Secondary School: Measurement and Implications for Motivation. In Beliefs: A Hidden Variable in Mathematics Education? Mathematics Education Library; Leder, G.C., Pehkonen, E., Törner, G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, P.; Zan, R. Attitude towards mathematics: A bridge between beliefs and emotions. ZDM 2011, 43, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garris, R.; Ahlers, R.; Driskell, J.E. Games, Motivation, and Learning: A Research and Practice Model. Simul. Gaming 2002, 33, 441–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.F.; Vogel, D.S.; Cannon-Bowers, J.; Bowers, C.A.; Muse, K.; Wright, M. Computer gaming and interactive simulations for learning: A meta-analysis. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2006, 34, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Grabowski, B. Gameplaying for maths learning: Cooperative or not? Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2007, 38, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandercruysse, S.; Vandewaetere, M.; Clarebout, G. Game-Based Learning: A Review on the Effectiveness of Educational Games. In Handbook of Research on Serious Games as Educational, Business and Research Tools; Cruz-Cunha, M.M., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 628–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, L. Systematic reviewing. Soc. Res. Update 2008, 54, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan-Sharif, S.; Mura, P.; Wijesinghe, S.N.R. A systematic review of systematic reviews in tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2019, 39, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, T.M.; Lester, J.N. ATLAS.ti for conversation and discourse analysis studies. Int. J. Soc. Res. 2016, 19, 405–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljojo, N. The Design and Implementation of a Mathematics Game-Base Learning Application for Primary Students. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. 2018, 12, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broley, L.; Buteau, C.; Muller, E. E-Brock Bugs©: An Epistemic Mathematics Computer Game. J. Humanist. Math. 2015, 5, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Broley, L.; Buteau, C.; Muller, E. Struggles and Growth in Mathematics Education: Reflections by Three Generations of Mathematicians on The Creation of the Computer Game E-Brock Bugs. J. Humanist. Math. 2017, 7, 62–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carr, J.M. Does Math Achievement h APP en when iPads and Game-Based Learning Are Incorporated into Fifth-Grade Mathematics Instruction? JITE Res. 2012, 11, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.; Sauer, J.D. Video-Games Do Not Negatively Impact Adolescent Academic Performance in Science, Mathematics or Reading. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gris, G.; Alves, H.W.; Assis, G.J.A.; de Souza, S.R. The Use of Adapted Games for Assessment of Mathematics and Monetary Skills. Trends Psychol. Temas Em Psicol. 2017, 25, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyöngyösi-Wiersum, E.; Czapné, Z.; Makrides, G. Situation games to ease transition betweenabstract and real life mathematics forprimary school student teachers. Ann. Math. Inform. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, H.; Abd Halim, N.; Harun, J.; Arjunan, S. Exploring the Digital Game-Based Elements in Mathematics Education: A Meta-Analysis Review. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2019, 7, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa, S.P. Pedagogical Change in Mathematics Learning: Harnessing the Power of Digital Game-Based Learning. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2018, 21, 259–276. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, E.; Hanghøj, T. What’s the math in Minecraft? A Design-Based Study of Students’ Perspectives and Mathematical Experiences Across game and School Domains. Electron. J. Elearn. 2020, 18, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juric, P.; Brkic Bakaric, M.; Matetic, M. Design and Implementation of Anonymized Social Network-based Mobile Game System for Learning Mathematics. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2018, 13, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermani, H. Computer mathematics games and conditions for enhance young children’s learning of number sense. Malays. J. Learn. Instr. 2017, 14, 23–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, B.; Adams, D.; Mayer, R.; Forlizzi, J. A Computer-Based Game that Promotes Mathematics Learning More than a Conventional Approach. Int. J. Game Based Learn. 2017, 7, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer-Packenham, P.S.; Lommatsch, C.W.; Litster, K.; Ashby, J.; Bullock, E.K.; Roxburgh, E.K.; Shumway, J.F.; Speed, E.; Covington, B.; Hartmann, C.; et al. How design features in digital math games support learning and mathematics connections. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 91, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemu, N.; Zulkardi, Z. Building counting by traditional game: Mathematics Program for Young Children. J. Math. Educ. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkopodi, N.; Mosimege, M. Incorporating the indigenous game of morabaraba in the learning of mathematics. S. Afr. J. Educ. 2009, 29, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsubuga, E.S.; Cajigas, J.B.; Rombaoa, J.A.L.; Garcia, J.M.M.; Cruz, D.P.; Olfato, D.C.G.; Ca, C.M.E. Matherpiece: An Introduction to Math E-Learning PC Game Application for Grade 1 Pupils. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, E.W.; Chandrawati, T.B. Detection Hand Motion on Virtual Reality Mathematics Game with Accelerometer and Flex Sensors. Detect. Hand Motion Virtual Real. Math. Game Accelerometer Sens. 2018, 16, 2287–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, H.; Mangram, C. Wuzzit Trouble: The Influence of a Digital Math Game on Student Number Sense. Int. J. Serious Games 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukstrienwong, A. Animo Math: The Role-Playing Game in Mathematical Learning for Children. Tem J. 2018, 7, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, F.; Lam, W.; Shroff, R. Active Learning via Problem-Based Collaborative Games in a Large Mathematics University Course in Hong Kong. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, S.; Temur, Ö. The Effect of Game-Assisted Mathematics Education on Academic Achievement in Turkey: A Meta-Analysis Study. Int. Electron. J. Elem. Educ. 2017, 10, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyasari, W.; Sutopo, H.; Agustian, M. QR Code-based Learning Development: Accessing Math Game for Children Learning Enhancement. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. 2019, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, O.C.; Junaini, S.N.; Kamal, A.A.; Ibrahim, L. 1 Slash 100%: Gamification of mathematics with hybrid QR-based card game. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2020, 20, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalloo, V.; Mohan, P.; Kinshuk, D. A Technique for Mapping Mathematics Content to Game Design. Int. J. Serious Games 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Araya, R.; Jiménez, A.; Bahamondez, M.; Calfucura, P.; Dartnell, P.; Andrade, J.S. Teaching modeling skills using a massively multiplayer online mathematics game. World Wide Web 2012, 17, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, S.; O’Rourke, J. ‘New Directions for Traditional Lessons’: Can Handheld Game Consoles Enhance Mental Mathematics Skills? Aust. J. Teach. Educ. 2011, 36, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- O’Rourke, J.; Main, S.; Hill, S.M. Commercially available Digital Game Technology in the Classroom: Improving Automaticity in Mental-maths in Primary-aged Students. Aust. J. Teach. Educ. 2017, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.; Sutherland, L.M.; Norris, C.A.; Soloway, E. Effects of game technology on elementary student learning in mathematics. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2012, 43, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denham, A.R. Using the PCaRD digital game-based learning model of instruction in the middle school mathematics classroom: A case study. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2019, 50, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-Sajjade, A.; Paas, F. Educational theories and computer game design: Lessons from an experiment in elementary mathematics education. Educ. Tech. Res. Dev. 2020, 68, 2685–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katmada, A.; Mavridis, A.; Tsiatsos, T. Implementing a Game for Supporting Learning in Mathematics. Electron. J. Elearn. 2014, 12, 230–242. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, F.Y.; Hsieh, M.L. Role-Playing Game Based Assessment to Fractional Concept in Second Grade Mathematics. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2017, 13, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouze, A.Q.; Amit, M. Development of mathematical thinking through integration of ethnomathematic folklore game in math instruction. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2018, 14, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dele-Ajayi, O.; Strachan, R.; Pickard, A.J.; Sanderson, J.J. Games for Teaching Mathematics in Nigeria: What Happens to Pupils’ Engagement and Traditional Classroom Dynamics? IEEE Access 2019, 7, 53248–53261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drigas, A.; Pappas, M. On Line and Other Game-Based Learning for Mathematics. Int. J. Online Eng. 2015, 11, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernàndez, A.; Joanpere, M.; Gorgorió, N.; Albarracín, L. Mathematics learning opportunities when playing a Tower Defense Game. Int. J. Serious Games. 2015, 2, 2384–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nygren, E.; Blignaut, S.; Leendertz, V.; Sutinen, E. Quantitizing Affective Data as Project Evaluation on the Use of a Mathematics Mobile Game and Intelligent Tutoring System. Inform. Educ. 2019, 18, 375–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulz, A.; Londos, L.; Haake, M. Preschoolers’ Understanding of a Teachable Agent-Based Game in Early Mathematics as Reflected in their Gaze Behaviors—An Experimental Study. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2020, 30, 38–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.Y.S.; Tan, W.H.; Idris, M.Z. Digital Game-Based Learning for Remedial Mathematics Students: A New Teaching and Learning Approach in Malaysia. Int. J. Multimed. Ubiquitous Eng. 2014, 9, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellnhofer, K. All-in-One: Impact study of an online math game for educational purposes. Int. J. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2016, 8, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plass, J.; O’Keefe, P.; Homer, B.; Case, J.; Hayward, E.; Stein, M.; Perlin, K. The Impact of Individual, Competitive, and Collaborative Mathematics Game Play on Learning, Performance, and Motivation. J. Educ. Psychol. 2013, 105, 1050–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chu, H.; Chiang, L. Effects of a Progressive Prompting-based Educational Game on Second Graders’ Mathematics Learning Performance and Behavioral Patterns. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2018, 21, 322–334. [Google Scholar]
- Stebler, R.; Vogt, F.; Wolf, I.; Hauser, B.; Rechsteiner, K. Play-Based Mathematics in Kindergarten. A Video Analysis of Children’s Mathematical Behaviour While Playing a Board Game in Small Groups. J. Math. Didakt. 2013, 34, 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.M.; Huang, I.; Hwang, G.J. Effects of digital game-based learning on students’ self-efficacy, motivation, anxiety, and achievements in learning mathematics. J. Comput. Educ. 2014, 1, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, Z.; Sönmez, D. The Effect of Using Mathematical Games on Primary School 4th Grade Students’ Attitudes towards Mathematics Course and Their Visual Metaphorical Perceptions. J. Educ. E-Learn. Res. 2019, 6, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Liao, C.Y.; Cheng, H.; Yeh, C.; Chan, T.W. Influence of Game Quests on Pupils Enjoyment and Goal-pursuing in Math Learning. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2012, 15, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Kaune, C.; Nowinska, E.; Paetau, A.; Griep, M. Games for Enhancing Sustainability of Year 7 Maths Classes in Indonesia: Theory-Driven Development, Testing and Analyses of Lessons, and of Students Outcomes. J. Math. Educ. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, L. Students’ conflicting attitudes towards games as a vehicle for learning mathematics: A methodological dilemma. Math. Ed. Res. J. 2007, 19, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, D.; Vasconcelos, L.; Orey, M. Motivation and learning engagement through playing math video games. Malays. J. Learn. Instr. 2017, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloo, A.; Md-Ali, R.; Chairany, S. Using Cooperative Teams-Game-Tournament in 11 Religious School to Improve Mathematics Understanding and Communication. Malays. J. Learn. Instr. 2016, 13, 97–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleros, C.B.; Guerrero-García, J.; Navarro-Rangel, Y. UvaMate: A Serious Game for Learning Mathematics for Children with ADHD: Usability Evaluation. Rev. Colomb. Comput. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.E.; Jackson, G.; Ross, J.; White, S. What Counts Is How the Game Is Scored: One Way to Increase Achievement in Learning Mathematics. Simul. Gaming 1978, 9, 371–392. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo, K.; Chamberlin, B.; Wiburg, K.; Armstrong, A. Measurement in Learning Games Evolution: Review of Methodologies Used in Determining Effectiveness of Math Snacks Games and Animations. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2016, 21, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieftje, K.; Pendergrass, T.; Kyriakides, T.; Gilliam, W.; Fiellin, L. An Evaluation of an Educational Video Game on Mathematics Achievement in First Grade Students. Technologies 2017, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi; Sri, L.; Thompson, J. Simulation and Games Based Learning Model for Learning Math in Higher Education. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 8, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husman, J.; Derryberry, W.P.; Crowson, H.M.; Lomax, R. Instrumentality, task value, and intrinsic motivation: Making sense of their independent interdependence. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2004, 29, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criterion | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Document type | Published journal article (both empirical and review) | Book, book chapter, conference presentation, or other type of non-peer-reviewed or unpublished publication |
| Language | English | Articles not written in English |
| Accessibility | Open-access version of the article | Source with no open-access version available |
| Database | Search String and Limits |
|---|---|
| Scopus | TITLE ((“game” OR “game-based”) AND (“mathematics” OR “math”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (PUBSTAGE, “final”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (OA, “all”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “ar”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, “English”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (SRCTYPE, “j”)) |
| Web of Science | TI = ((“game” OR “game-based”) AND (“mathematics” OR “math”))) AND LANGUAGE: (English) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article) Refined by: Open Access: (OPEN ACCESS) Timespan: All years. Indexes: SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, A&HCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH, BKCI-S, BKCI-SSH, ESCI, CCR-EXPANDED, IC. |
| Ref. | Journal | Influence on MRAF 1 [Positive/Negative/Mixed] | Measured Aspects of Affective Domain | Instruments to Measure MRAF 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [53] | Aust. J. Teach. Educ. | positive | motivation, engagement, state of flow, self-efficacy | questionnaire, video data |
| [54] | Aust. J. Teach. Educ. | positive | motivation, attitudes | interview |
| [55] | Br J Educ Technol | positive | motivation, attitudes | questionnaire |
| [56] | Br. J. Educ. Technol. | positive | motivation, engagement | observations |
| [57] | Education Tech. Research Dev. | mixed | motivation | questionnaire |
| [58] | EJEL | positive | attitudes | questionnaire |
| [59] | Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. | mixed | attitudes, anxiety | questionnaire |
| [60] | Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. | positive | motivation | unspecified |
| [61] | IEEE Access | positive | motivation, engagement, attitudes | questionnaire |
| [62] | iJOE | positive | motivation | literature review |
| [63] | IJSG | positive | motivation | video data |
| [64] | Informatics Educ. | positive | motivation, engagement, enjoyment | questionnaire, interview |
| [65] | Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. | positive | motivation | unspecified |
| [66] | Int. J. Multimedia Ubiquitous Eng. | positive | motivation | literature review |
| [67] | Int. J. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. | positive | state of flow | questionnaire |
| [68] | J Educ Psychol | positive | motivation, engagement, attitudes | questionnaire |
| [69] | J Educ Techno Soc | positive | self-efficacy, state of flow | questionnaire |
| [70] | J Math Didakt | positive | motivation, engagement | video data |
| [71] | J. Comput. Educ. | positive | motivation, self-efficacy, attention | questionnaire |
| [72] | J. Educ. E-Learn. Res. | mixed | attitudes | questionnaire |
| [73] | J. Educ. Techno. Soc. | positive | motivation, enjoyment, engagement | questionnaire, active participation |
| [74] | J. Inf. Organ. Sci. | positive | motivation, attitudes | literature review |
| [75] | J. Math. Educ. | positive | attitudes | questionnaire |
| [6] | Math. Ed. Res. J. | mixed | attitudes | questionnaire, interview, game data |
| [76] | MJLI | mixed | motivation | video data |
| [77] | MJLI | positive | motivation | unspecified |
| [78] | Rev. Colomb. Comput. | positive | motivation | questionnaire |
| [79] | Simul. Gaming | positive | motivation | active participation |
| [80] | Technol. Knowl. Learn. | positive | enjoyment | game data |
| [81] | Technologies | positive | engagement, enjoyment | questionnaire |
| [82] | Univers. J. Educ. Res. | positive | motivation | questionnaire |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vankúš, P. Influence of Game-Based Learning in Mathematics Education on Students’ Affective Domain: A Systematic Review. Mathematics 2021, 9, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9090986
Vankúš P. Influence of Game-Based Learning in Mathematics Education on Students’ Affective Domain: A Systematic Review. Mathematics. 2021; 9(9):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9090986
Chicago/Turabian StyleVankúš, Peter. 2021. "Influence of Game-Based Learning in Mathematics Education on Students’ Affective Domain: A Systematic Review" Mathematics 9, no. 9: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9090986
APA StyleVankúš, P. (2021). Influence of Game-Based Learning in Mathematics Education on Students’ Affective Domain: A Systematic Review. Mathematics, 9(9), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9090986





