The Influence of Fear Effect to a Discrete-Time Predator-Prey System with Predator Has Other Food Resource
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Existence of Equilibria
3. The Local Stability of Equilibria
- (1)
- If and , then the equilibrium point is called a sink and is locally asymptotical stable.
- (2)
- If and , then the equilibrium point is called a source and is unstable.
- (3)
- If and , then the equilibrium point is called a saddle.
- (4)
- If or , then the equilibrium point is called non-hyperbolic.
- (1)
- and if and only if and ;
- (2)
- and if and only if and ;
- (3)
- and if and only if ;
- (4)
- and if and only if and ;
- (5)
- and are the conjugate complex roots and if and only if and .
- (1)
- is a source if .
- (2)
- is a saddle if .
- (3)
- is non-hyperbolic if .
- (1)
- sink if and , then is stable.
- (2)
- saddle if one of the following conditions holds:
- (a)
- and ;
- (b)
- and .
- (3)
- source if and , then is unstable.
- (4)
- non-hyperbolic if or .
- (1)
- source if .
- (2)
- saddle if .
- (3)
- non-hyperbolic if .
- (1)
- sink if , or and ;
- (2)
- source if and , or and ;
- (3)
- saddle if and ;
- (4)
- non-hyperbolic if ;
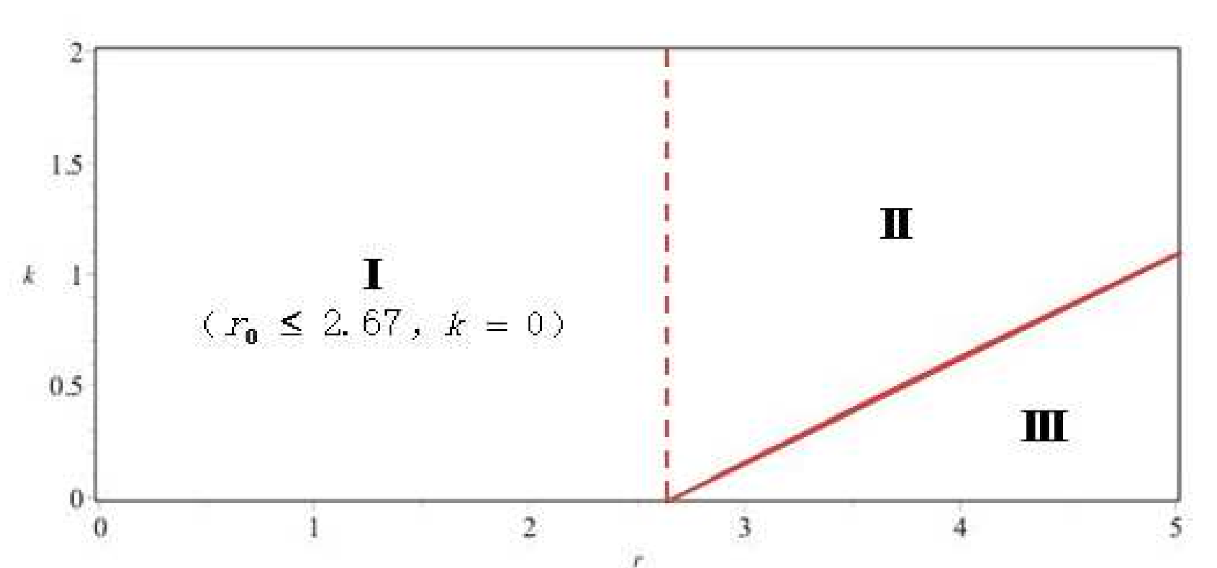
4. Global Stability of Interior Equilibrium
- (i)
- If , then .
- (ii)
- If , then
5. Global Stability of Prey Free Equilibrium
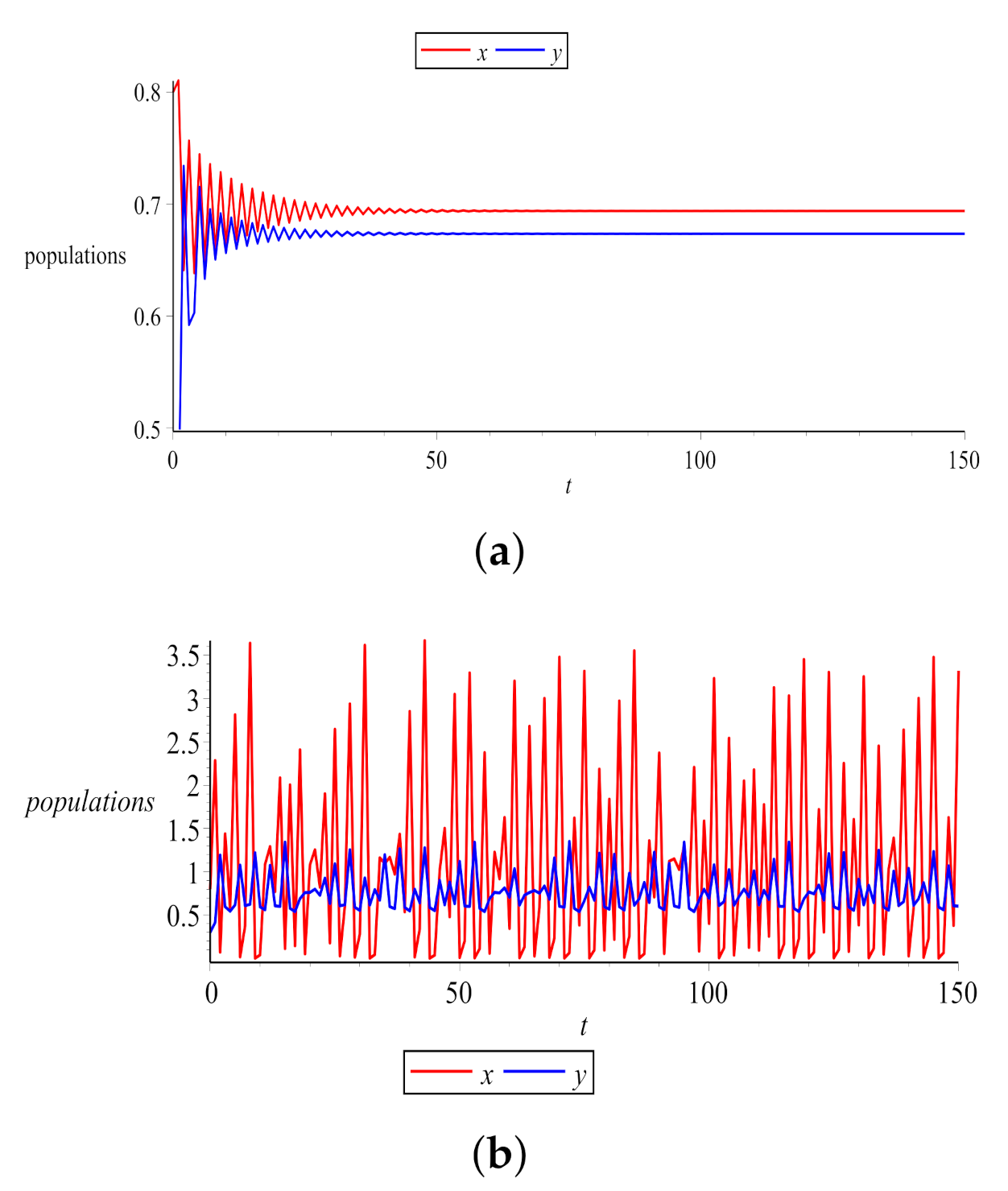
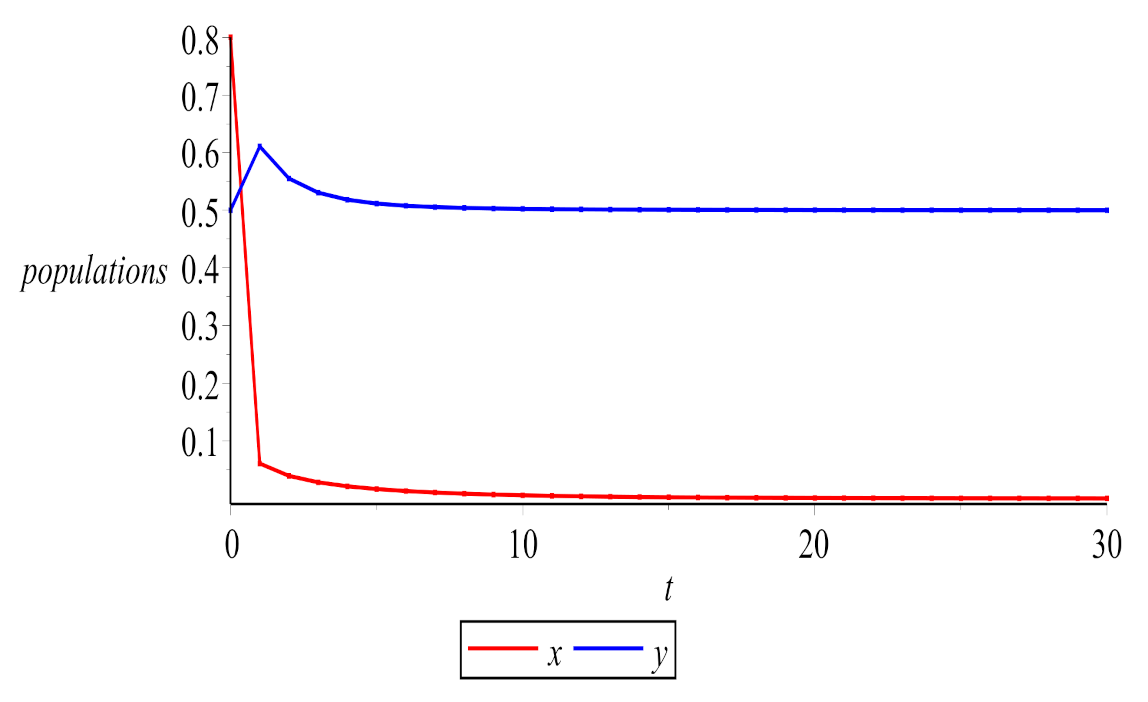
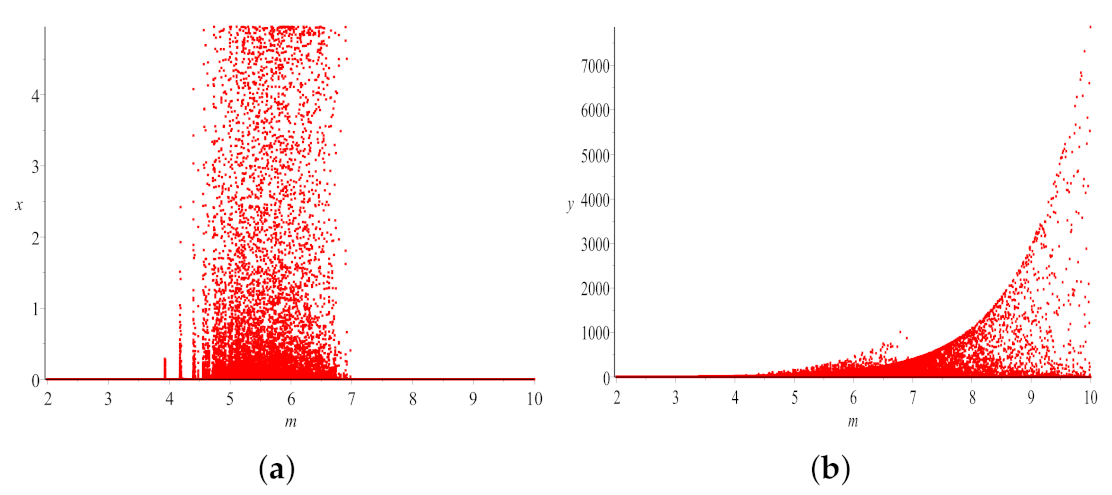
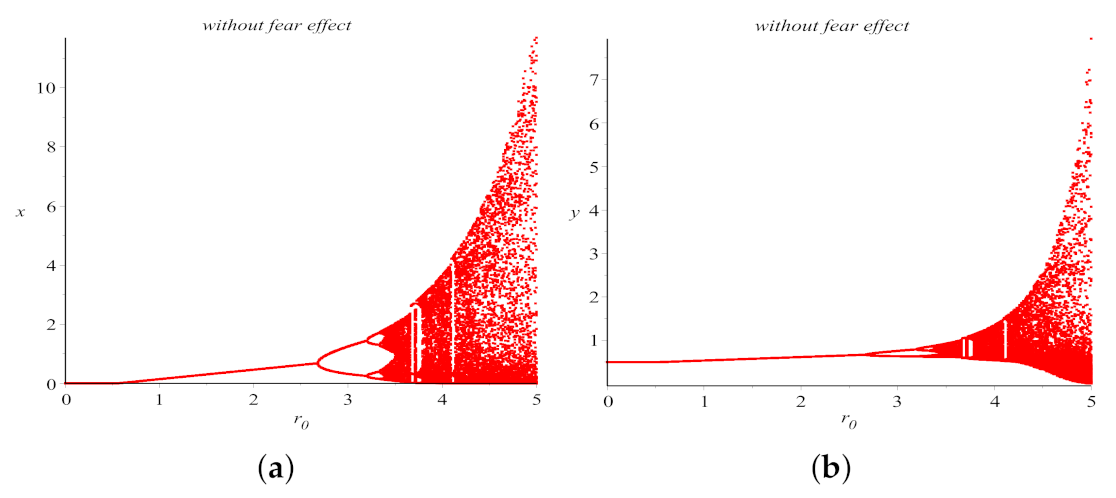
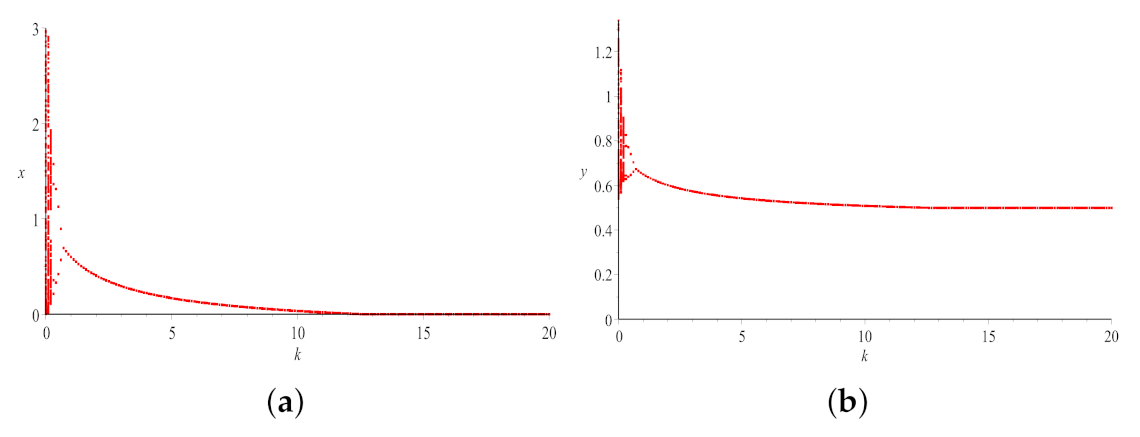
6. Numerical Simulations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.P.; Yang, W.S. Permanence of a discrete model of mutualism with infinite deviating arguments. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2010, 2, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.D.; Wu, H.L.; Xie, X.D. Global attractivity of a discrete cooperative system incorporating harvesting. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 2016, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, R.X.; Li, L. Permanence and global attractivity of discrete predator-prey system with Hassell-Varley type functional response. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2009, 2009, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.D.; Miao, Z.S.; Xue, Y.L. Positive periodic solution of a discrete Lotka-Volterra commensal symbiosis model. Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci. 2015, 2015. Available online: http://scik.org/index.php/cmbn/article/download/2118/1075 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Yue, Q. Extinction for a discrete competition system with the effect of toxic substances. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 2016, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.L.; Xie, X.D.; Chen, F.D.; Han, R.Y. Almost periodic solution of a discrete commensalism system. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Miao, Z.S.; Chen, F.D.; Xie, X.D. Influence of single feedback control variable on an autonomous Holling-II type cooperative system. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2016, 435, 874–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Teng, Z.D. On the stability in a discrete two-species competition system. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 38, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.G. Global attractivity of a discrete competition model. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Chen, F.D.; Lai, L.Y.; Li, Z. Dynamic behaviors of a discrete May type cooperative system incorporating Michaelis-Menten type harvesting. Int. J. Appl. Math. 2020, 50, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.S.; Zhang, H.Y. Bifurcation, chaos and pattern formation in a space- and time-discrete predator–prey system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2016, 91, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.M.; Yousef, A.M.; Elsadany, A.A. Stability, bifurcation analysis and chaos control of a discrete predator-prey system with square root functional response. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2016, 93, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.L.; Yu, L.P.; Siegmund, S. Bifurcations and chaos in a discrete predator–prey model with Crowley–Martin functional response. Nonlinear Dynam. 2017, 90, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Yan, Y. Stability and bifurcation analysis of a discrete predator–prey system with modified Holling–Tanner functional response. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 2018, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, P.K.; Mahapatra, G.S.; Phaijoo, G.R. Bifurcation and chaos of a discrete predator-prey model with Crowley–Martin functional response incorporating proportional prey refuge. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.L. Nonlethal effects in the ecology of predator-prey interactions. Bioscience 1998, 48, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creel, S.; Christianson, D. Relationships between direct predation and risk effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.L. Predators and the breeding bird: Behavioral and reproductive flexibility under the risk of predation. Biol. Rev. 2010, 84, 485–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresswell, W. Predation in bird populations. J. Ornithol. 2011, 152, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanette, L.Y.; Clinchy, M. Perceived predation risk reduces the number of offspring songbirds produce per year. Science 2011, 334, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zou, X.F. Modeling the fear effect in predator-prey interactions with adaptive avoidance of predators. Bull. Math. Biol. 2017, 79, 1325–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, S. Population dynamics with multiple Allee effects induced by fear factors induced by fear factors-a mathematical study on prey-predator. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 64, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Pal, N.; Samanta, S.; Chattopadhyay, J. Effect of hunting cooperation and fear in apredator-prey model. Ecol. Complex. 2019, 39, 100770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cai, Y.L.; Fu, S.M.; Wang, W.M. The effect of the fear factor on the dynamics of a predator-prey model incorporating the prey refuge. Chaos 2019, 29, 083109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.W.; Li, Z. Stability analysis of a mutual interference predator-prey model with the fear effect. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2019, 22, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Zhang, M. Integrability and multiple limit cycles in a predator-prey system with fear effect. J. Funct. Space. 2019, 2019, 3948621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.S.; Cai, Y.L.; Fu, S.M.; Wang, W.M. Impact of the fear effect in a prey-predator model incorporating a prey refuge. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 356, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Pal, N.; Samanta, S.; Chattopadhay, J. Fear effect in prey and hunting cooperation among predators in a Leslie-Gower model. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 5146–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.W.; Xie, X.D.; Xue, Y.L. Stability and bifurcation in a Holling type II predator-prey model with Allee effect and time delay. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 2018, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zanette, L.; Zou, X.F. Modelling the fear effect in predator-prey interactions. J. Math. Biol. 2016, 73, 1179–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, K.; Pal, S.; Samanta, S.; Sen, A.; Pal, N. Impact of fear effect in a discrete-time predator-prey system. Bull. Calcutta Math. Soc. 2018, 110, 245–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Wu, R.X.; Lai, L.Y.; Yu, X.Q. The influence of fear effect to the Lotka–Volterra predator–prey system with predator has other food resource. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, M. Ordinary Difference Equation; Xinjiang University Press: Xinjiang, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.D. Permanence and global attractivity of a discrete multi-species Lotka–Volterra competition predator–prey systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2006, 182, 3–12. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; He, X.; Chen, F. The Influence of Fear Effect to a Discrete-Time Predator-Prey System with Predator Has Other Food Resource. Mathematics 2021, 9, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9080865
Chen J, He X, Chen F. The Influence of Fear Effect to a Discrete-Time Predator-Prey System with Predator Has Other Food Resource. Mathematics. 2021; 9(8):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9080865
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jialin, Xiaqing He, and Fengde Chen. 2021. "The Influence of Fear Effect to a Discrete-Time Predator-Prey System with Predator Has Other Food Resource" Mathematics 9, no. 8: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9080865
APA StyleChen, J., He, X., & Chen, F. (2021). The Influence of Fear Effect to a Discrete-Time Predator-Prey System with Predator Has Other Food Resource. Mathematics, 9(8), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9080865





