Multiple Slip Impact on the Darcy–Forchheimer Hybrid Nano Fluid Flow Due to Quadratic Convection Past an Inclined Plane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Modeling
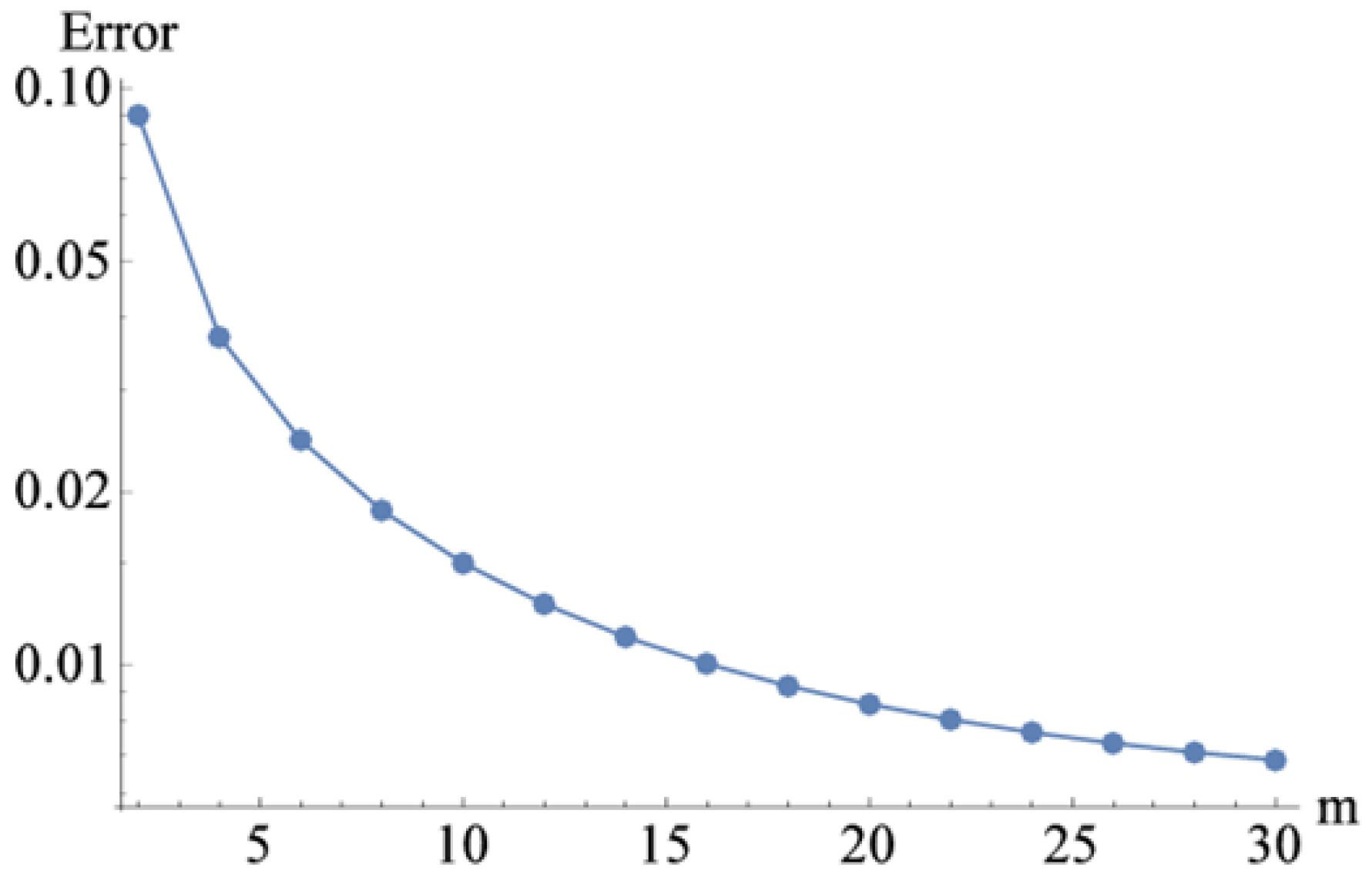
Method of Solution
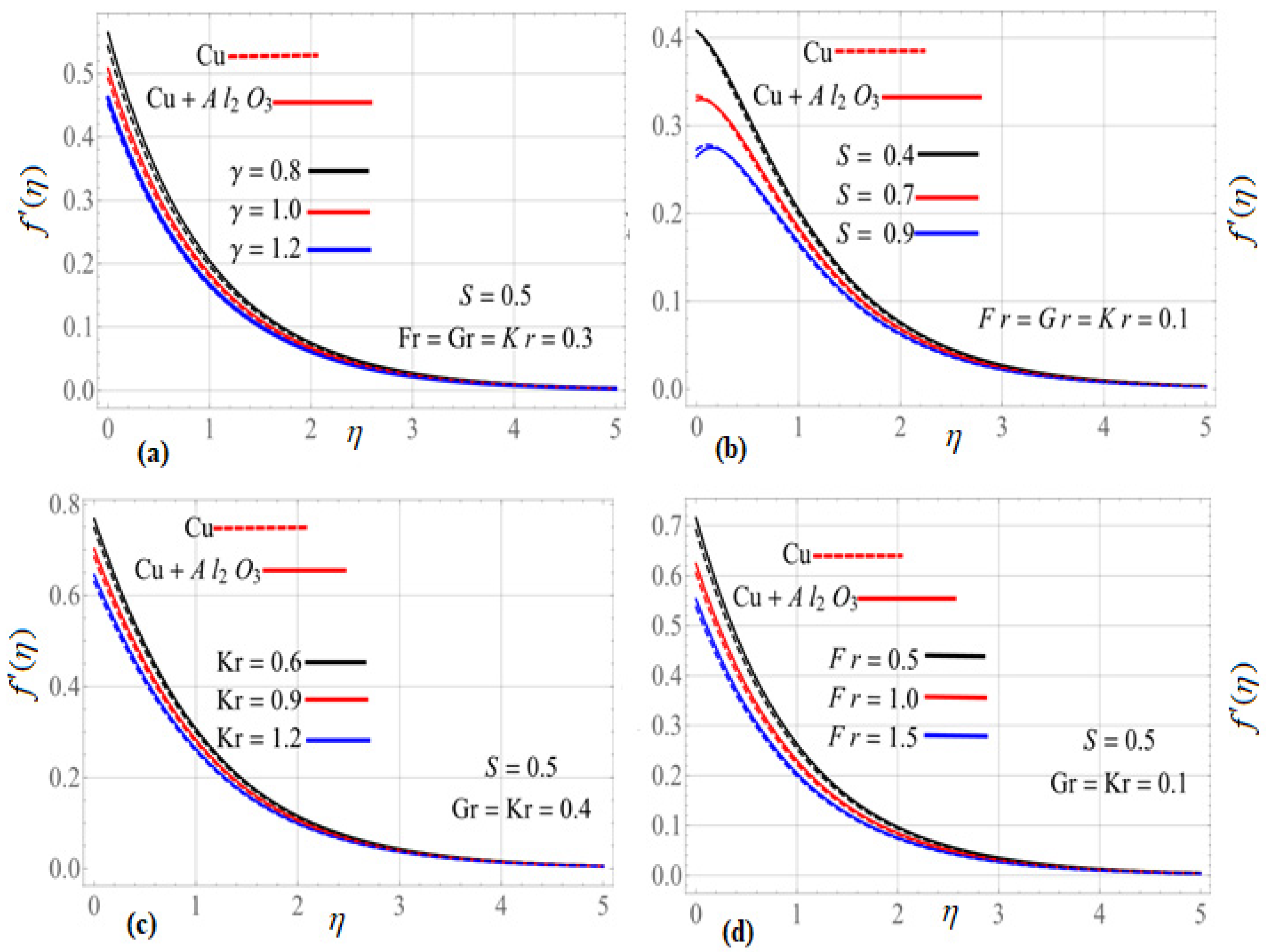
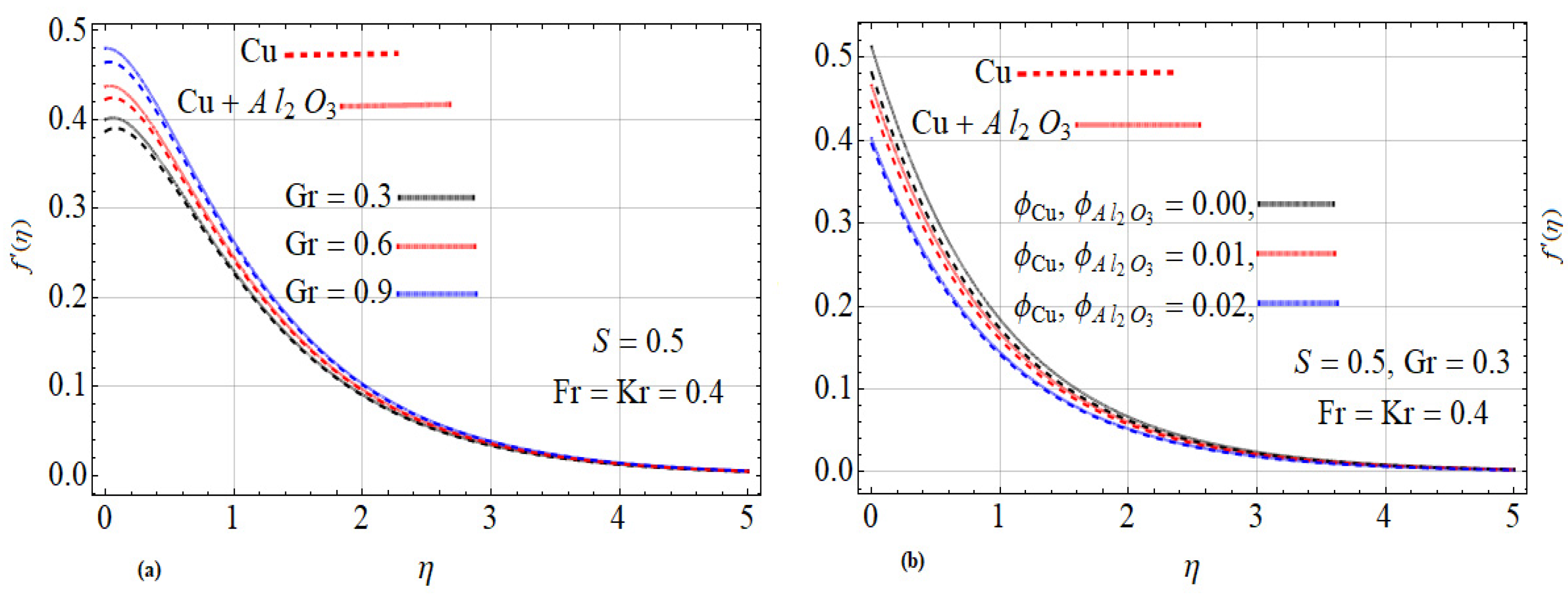
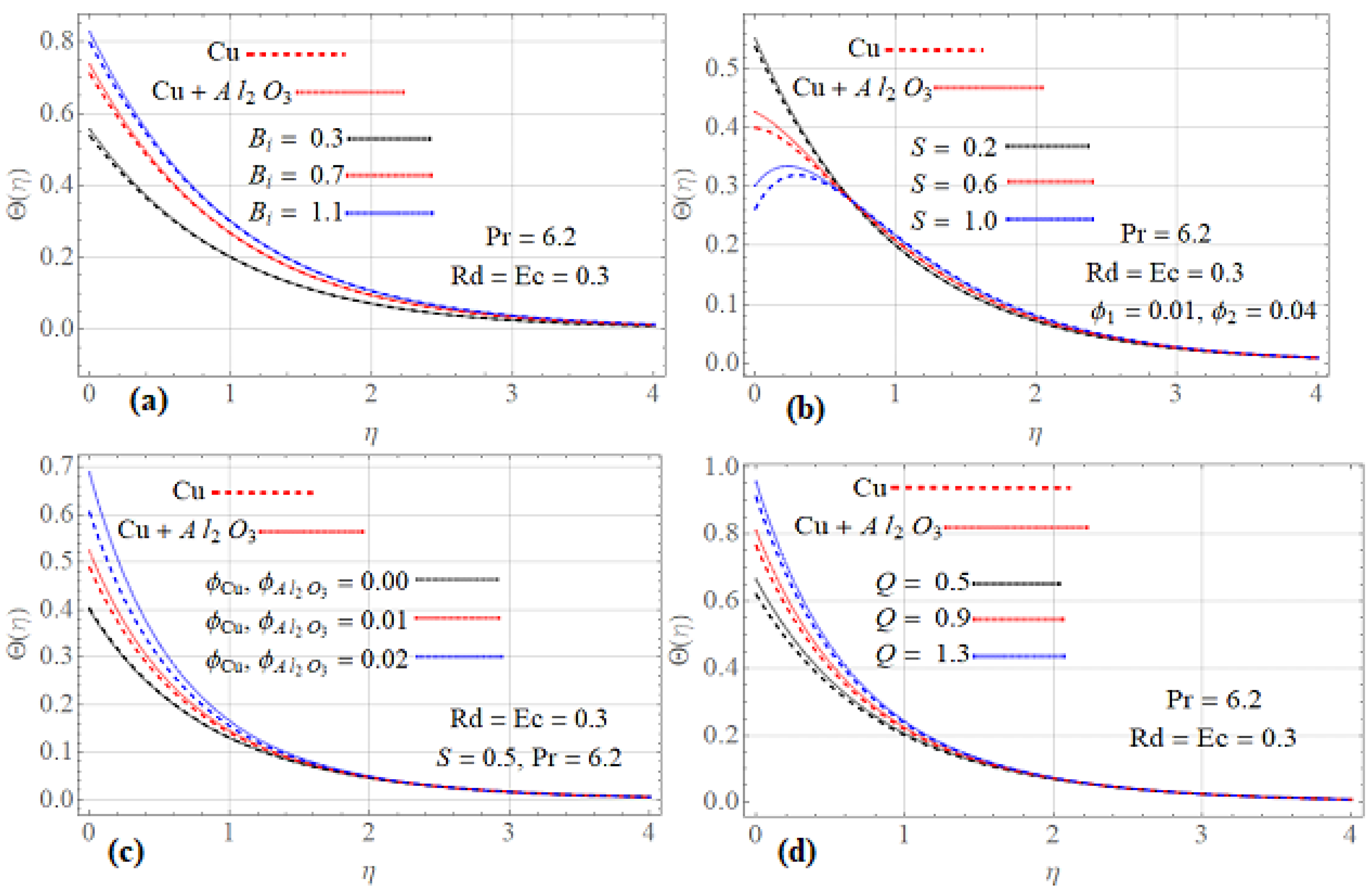
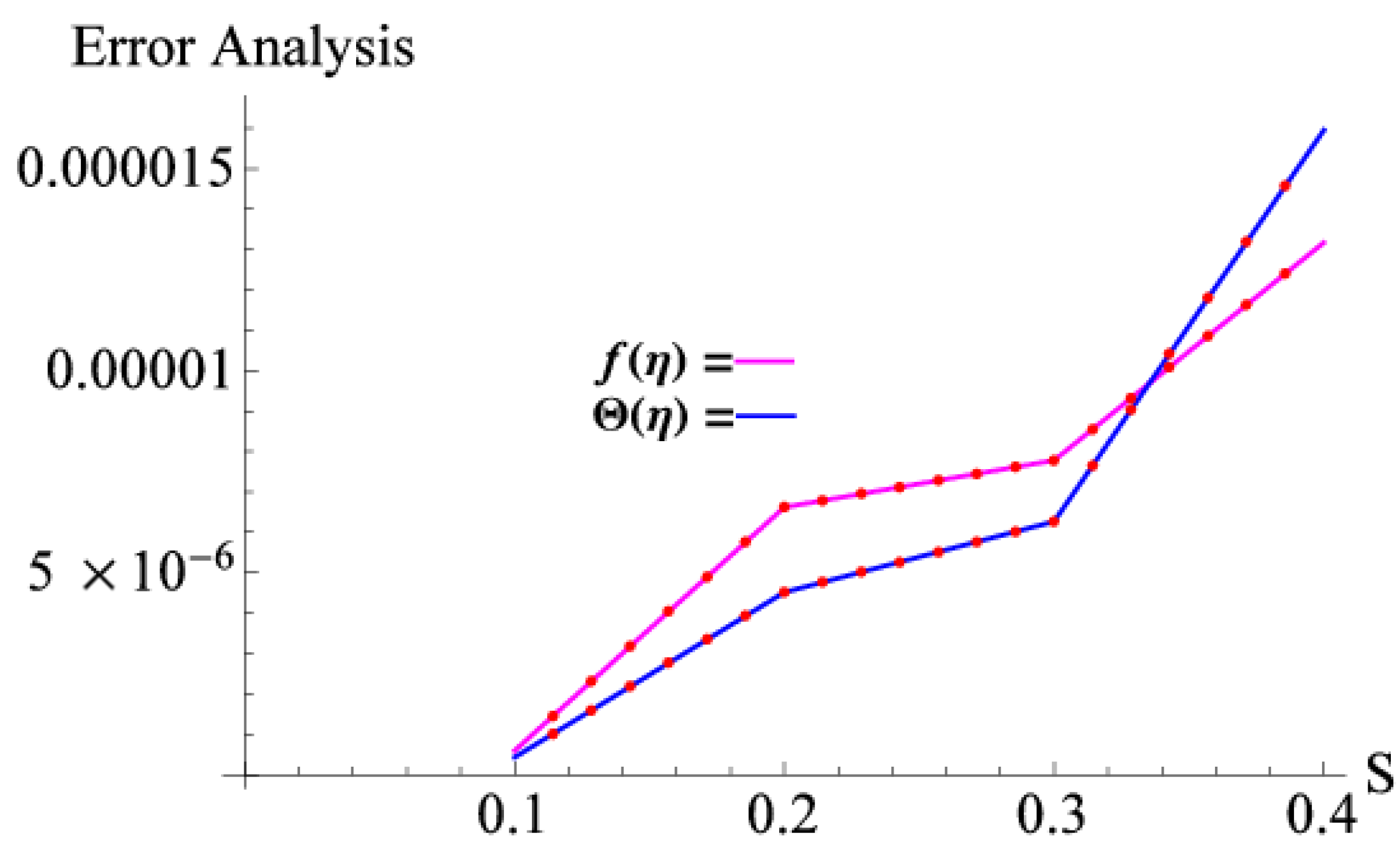
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- The velocity of the and nanofluids decrease with increasing the slip parameter .
- The temperature profile was assessed using a higher number of and variables.
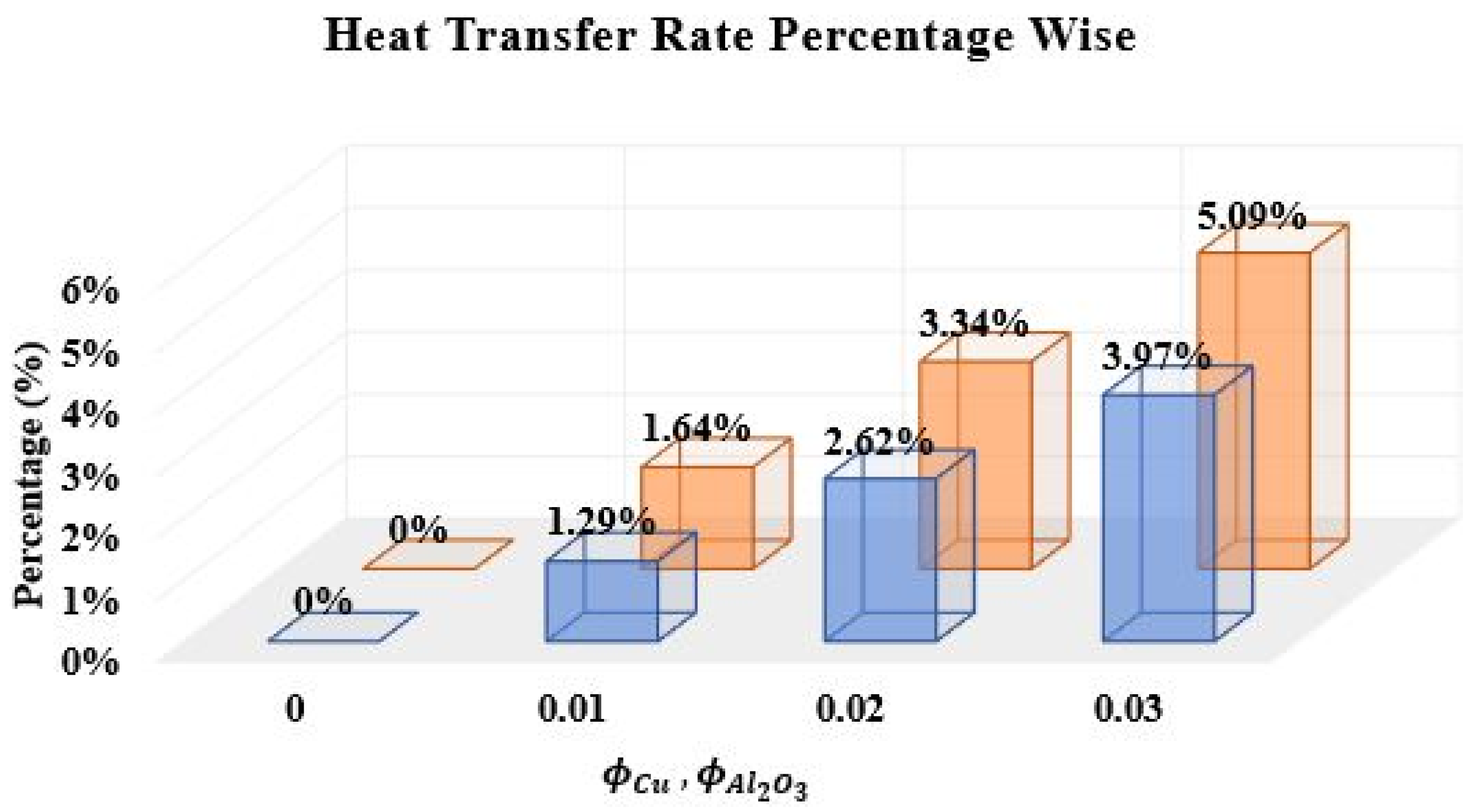
- The heat transfer rate accelerates as the scale of the thermal radiation parameter increases, and as a result, the Nusselt number rises.
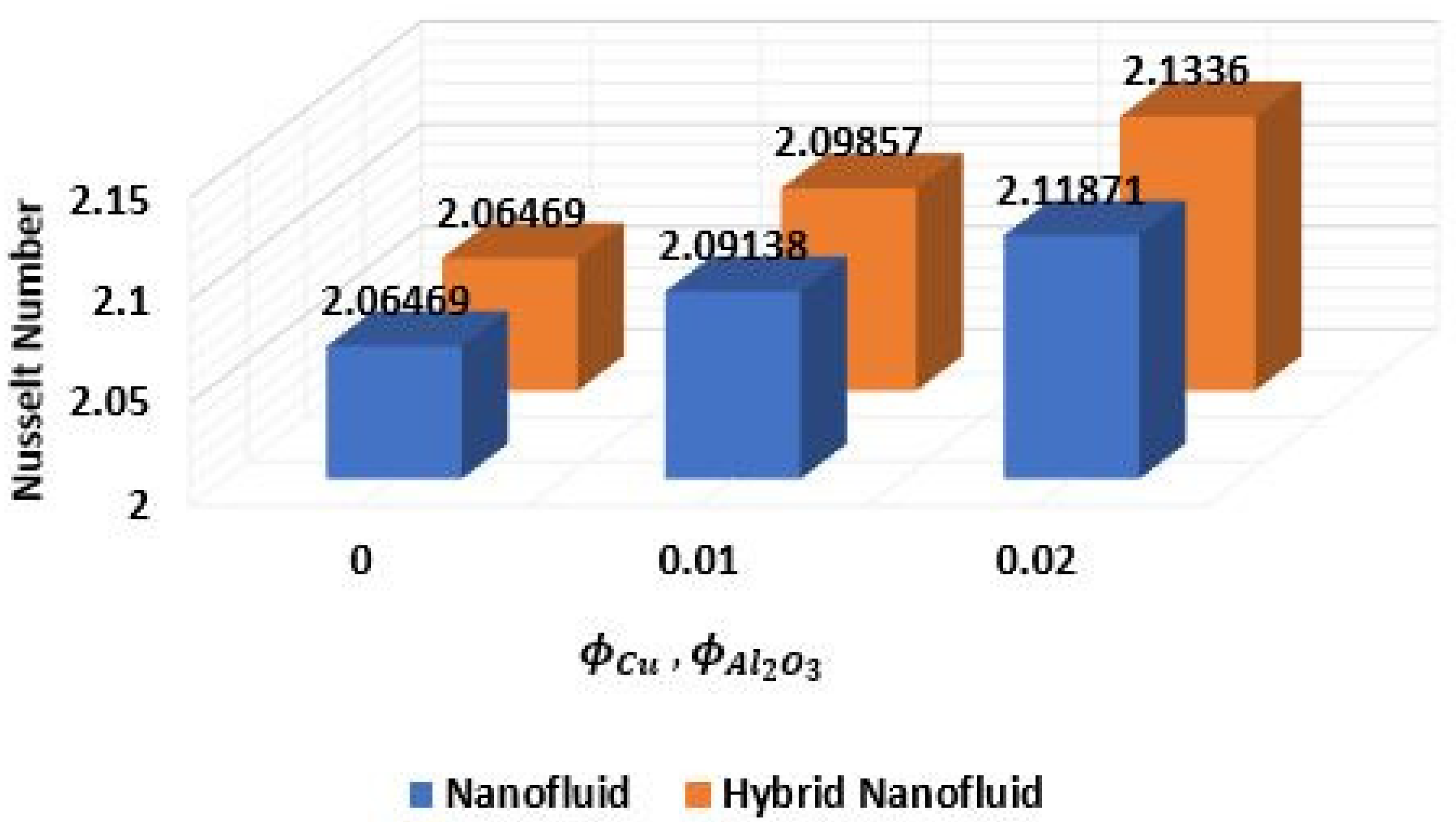
- The heat transfer rate of hybrid nanofluid () seems to be higher than that of nanofluid ().
- Although nanofluids are more sticky than ordinary fluids, their boiling point is greater than that of conventional base liquids. It could help to increase the heat transfer capacity of the solar panel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, U.S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. AS-MEFED 1995, 231, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Izadi, A.; Siavashi, M.; Xiong, Q. Impingement jet hydrogen, air and Cu–H2O nanofluid cooling of a hot surface covered by porous media with non-uniform input jet velocity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15933–15948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Vafai, K. A review on the applications of nanofluids in solar energy field. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, H.T.; Sivaraj, R.; Reddy, A.S.; Chamkha, A. SWCNH/diamond ethylene glycol nanofluid flow over a wedge, plate and stagnation point with induced magnetic field and nonlinear radiation-solar energy application. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2019, 228, 2531–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siavashi, M.; Joibary, S.M.M. Numerical performance analysis of a counter-flow double-pipe heat exchanger with using nanofluid and both sides partly filled with porous media. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 135, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. Fabrication of microencapsulated phase change materials based on n-octadecane core and silica shell through interfacial polycondensation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 389, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebarek-Oudina, F. Convective heat transfer of Titania nanofluids of different base fluids in cylindrical annulus with discrete heat source. Heat Transf.-Asian Res. 2019, 48, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Saleem, S.; Shafee, A.; Chamkha, A.J.; Du, S. Analytical investigation of nanoparticle migration in a duct considering thermal radiation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 135, 1629–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, G.G. Experimental investigation of mixed convection with water-Al2O3 & hybrid nanofluid in inclined tube for laminar flow. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 2, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zaim, A.; Aissa, A.; Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Mahanthesh, B.; Lorenzini, G.; Sahnoun, M.; El Ganaoui, M. Galerkin finite element analysis of magneto-hydrodynamic natural convection of Cu-water nanoliquid in a baffled U-shaped enclosure. Propuls. Power Res. 2020, 4, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M. Magnetic field influence on CuO—H2O nanofluid convective flow in a permeable cavity considering various shapes for nanoparticles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19611–19621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, T.; Nasir, S.; Islam, S.; Shah, Z.; Khan, M.A. Effective Prandtl Number Model Influences on the γAl2O3-H2O and γAl2O3-C2H6O2 Nanofluids Spray Along a Stretching Cylinder. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, T.; Nadeem, S. Heat transfer enhancement with Ag–CuO/water hybrid nanofluid. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A.J.; Miroshnichenko, I.V.; Sheremet, M.A. Numerical analysis of unsteady conjugate natural convection of hybrid waterbased nanofluid in a semicircular cavity. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2017, 9, 041004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Jamshed, W.; Ali, Y.; Shams, M. Heat transfer and entropy analysis of Maxwell hybrid nanofluid including effects of inclined magnetic field, Joule heating and thermal radiation. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst.-S 2020, 13, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali Lunda, L.; Omara, Z.; Khan, I.; Sherif, E.S.M. Dual solutions and stability analysis of a hybrid nanofluid over a stretching/shrinking sheet executing MHD flow. Symmetry 2020, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwesigye, A.; Huan, Z. Thermodynamic analysis and optimization of fully developed turbulent forced convection in a circular tube with water–Al2O3 nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 89, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Lunda, L.; Omara, Z.; Khan, I.; Seikh, A.; El-Sayed, H.; Sherif, M.; Nisar, K.S. Stability analysis and multiple solution of Cu–Al2O3/ H2O nanofluid contains hybrid nanomaterials over a shrinking surface in the presence of viscous dissipation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Naz, R.; Abdelsalam, S.I. On the onset of entropy generation for a nanofluid with thermal radiation and gyrotactic microorganisms through 3D flows. Phys. Scr. 2020, 95, 045206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladdin, N.A.L.; Bachok, N.; Pop, I. Cu-Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid flow over a permeable moving surface in presence of hydromagnetic and suction effects. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapen, P.T.; Ketchate, C.G.N.; Fokwa, D.; Tchuen, G. Linear stability analysis of (Cu-Al2O3)/water hybrid nanofluid flow in porous media in presence of hydromagnetic, small suction and injection effects. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, H.; Ahmad, I.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Tahir, M.B.; Shoaib, M. Neuro-intelligent mappings of hybrid hydro-nanofluid Al2O3–Cu–H2O model in porous medium over rotating disk with viscous dissolution and Joule heating. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 28298–28326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S. Impact of Cattaneo–Christov Heat Flux On Al2O3–Cu/H2O–(CH2OH)2 Hybrid Nanofluid Flow Between Two Stretchable Rotating Disks. In Energy Systems and Nanotechnology; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 329–368. [Google Scholar]
- Forchheimer, P.H. Wasserbewegung durch boden. Z. Ver. Deutsch. Ing. 1901, 45, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Muskat, M. The Flow of Homogeneous Fluids Through Porous Media; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1946. [Google Scholar]
- Saif, R.S.; Hayat, T.; Ellahi, R.; Muhammad, T.; Alsaedi, A. Darcy-Forchheimer flow of nanofluid due to a curved stretching surface. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 29, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Shafiq, A.; Khalique, C.M.; Zhang, T. Magnetohydrodynamic Darcy-Forchheimer nanofluid flow over a nonlinear stretching sheet. Phys. Scr. 2019, 94, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.A.; Haider, F.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A. Partial slip in Darcy-Forchheimer carbon nanotubes flow by rotating disk. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 116, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Arabkoohsar, A.; Ismail, K.A.R. Entropy analysis for a nanofluid within a porous media with magnetic force impact using non-Darcy model. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 112, 104488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Khan, S.A.; Alsaedi, A.; Fardoun, H.M. Heat transportation in electro-magnetohydrodynamic flow of Darcy-Forchheimer viscous fluid with irreversibility analysis. Phys. Scr. 2020, 95, 105214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Haider, F.; Alsaedi, A. Darcy-Forchheimer flow with nonlinear mixed convection. Appl. Math. Mech. 2020, 41, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.G.; Rahimi-Gorji, M.; Reddy, M.G.; Chamkha, A.J.; Alarifi, I.M. Enhancement of heat transfer in a convergent/divergent channel by using carbon nanotubes in the presence of a Darcy–Forchheimer medium. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.A.; Ali, F.; Khan, I.; Gohar, M. A theoretical study on the performance of a solar collector using CeO2 and Al2O3 water-based nanofluids with inclined plate: Atangana–Baleanu fractional model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 115, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.K.; Ullah, M.Z.; Alshomrani, A.S.; Gul, T. Hybrid nanofluid flow in a Darcy-Forchheimer permeable medium over a flat plate due to solar radiation. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 26, 100955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.L. Combined electrical MHD heat transfer thermal extrusion system using Maxwell fluid with radiative and viscous dissipation effects. Appl. Ther. Engr. 2017, 112, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M. Micropolar flow of EMHD nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation and slip effects. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Tlili, I.; Waqas, H.; Imran, M. Effects of nonlinear thermal radiation and activation energy on modified second-grade nanofluid with Cattaneo–Christov expressions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 143, 175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorla, R.S.R.; Sidawi, I. Free convection on a vertical stretching surface with suction and blowing. Appl. Sci. Res. 1994, 52, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.J. The Proposed Homotopy Analysis Method for the Solution of Nonlinear Problems. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.J. An optimal homotopy-analysis approach for strongly nonlinear differential equations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 8, 2003–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Liao, S.J. Advances in the Homotopy Analysis Method, Chapter 7; World Scientific Press: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, T.; Ferdous, K. The experimental study to examine the stable dispersion of the graphene nanoparticles and to look at the GO–H2O nanofluid flow between two rotating disks. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 8, 1711–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Shah, Z.; Tassaddiq, A.; Kumam, P.; Roy, P. Entropy generation in MHD Casson fluid flow with variable heat conductance and thermal conductivity over nonlinear bi-directional stretching surface. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y. Free convection on a vertical stretching surface. ZAMM-J. Appl. Math. Mech. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 1989, 69, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
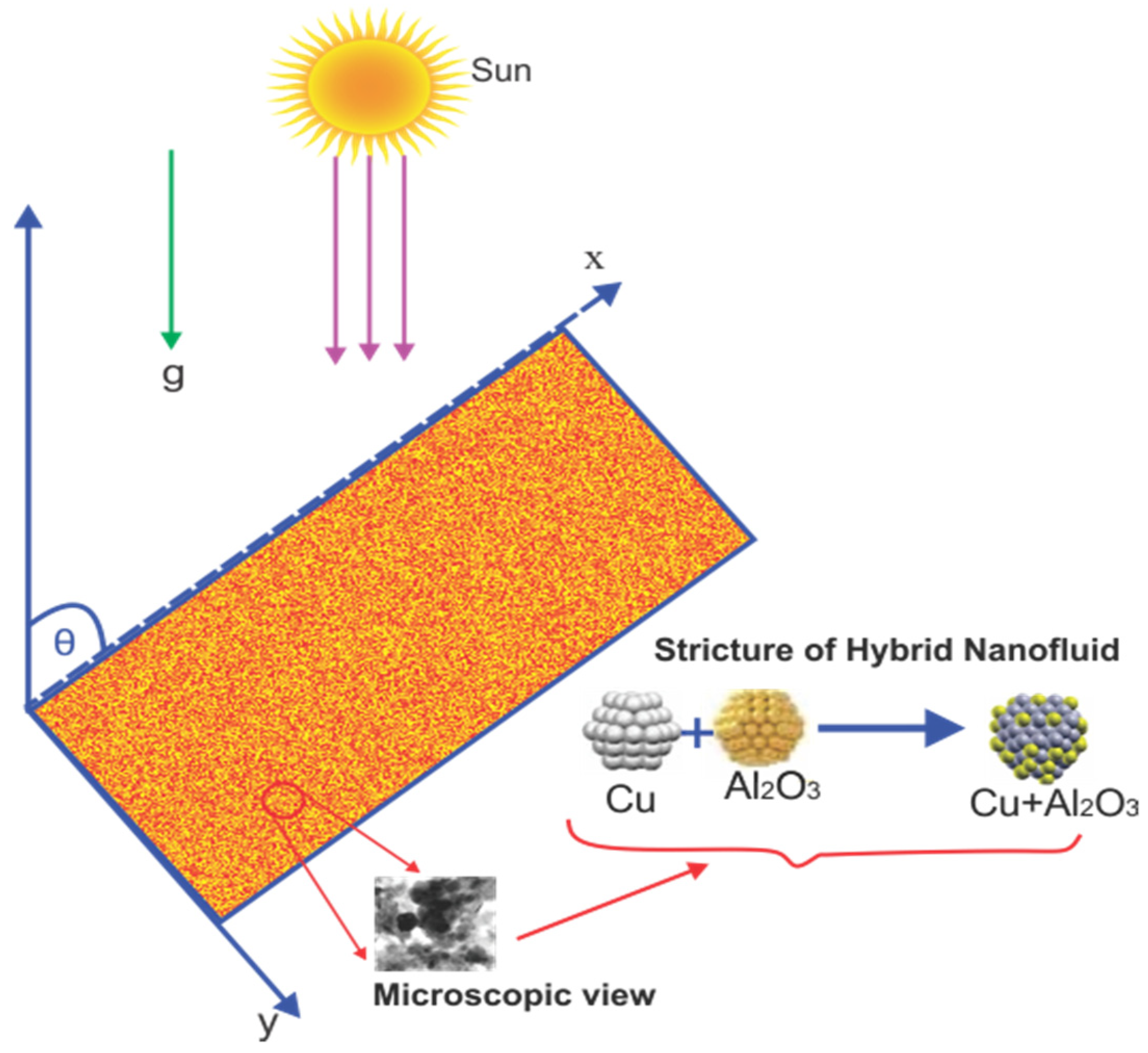
| Nanofluid | Hybrid Nanofluid |
|---|---|
where |
| Property | H2O | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 997.1 | 3970 | 8933 | |
| 4179 | 765 | 385 | |
| 0.6071 | 40 | 400 | |
| 21 | 1.67 | 0.85 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.02363 | 1.0237 |
| 0.2 | 0.938348 | 0.938522 | |||||
| 0.3 | 0.866086 | 0.866346 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.02363 | 1.0237 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.0301 | 1.03477 | |||||
| 0.3 | 1.03681 | 1.04096 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.02363 | 1.0237 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.03567 | 1.03569 | |||||
| 0.3 | 1.03845 | 1.04041 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.02363 | 1.0237 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.04186 | 1.04622 | |||||
| 0.3 | 1.05064 | 1.05453 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.02363 | 1.0237 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.01474 | 1.01592 | |||||
| 0.3 | 1.0053 | 1.00765 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.02363 | 1.0237 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.020214 | 1.02013 | |||||
| 0.3 | 1.016310 | 1.016281 |
| 1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1.013145 | 1.05777 |
| 1.1 | 1.15634 | 1.16634 | |||||
| 1.2 | 1.18005 | 1.21031 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.013145 | 1.05777 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.00395 | 1.01158 | |||||
| 0.3 | 0.902247 | 0.965545 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.013145 | 1.05777 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.12721 | 1.1701 | |||||
| 0.3 | 1.19808 | 1.23711 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.013145 | 1.05777 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.07488 | 1.09531 | |||||
| 0.3 | 1.08934 | 1.10979 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.013145 | 1.05777 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.17754 | 1.19043 | |||||
| 0.3 | 1.21896 | 1.25974 | |||||
| 0.1 | 1.013145 | 1.05777 | |||||
| 0.2 | 1.19876 | 1.21804 | |||||
| 0.3 | 1.26676 | 1.29415 |
Nanofluid | Hybrid Nanofluid | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 2.06469 (0% Increase) | 2.06469 (0% Increase) |
| 0.01 | 2.09138 (1.29% Increase) | 2.09857 (1.64% Increase) |
| 0.02 | 2.11871 (2.62% Increase) | 2.13360 (3.34% Increase) |
| 0.03 | 2.14671 (3.97% Increase) | 2.16984 (5.09% Increase) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mallawi, F.O.; Ullah, M.Z. Multiple Slip Impact on the Darcy–Forchheimer Hybrid Nano Fluid Flow Due to Quadratic Convection Past an Inclined Plane. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222934
Mallawi FO, Ullah MZ. Multiple Slip Impact on the Darcy–Forchheimer Hybrid Nano Fluid Flow Due to Quadratic Convection Past an Inclined Plane. Mathematics. 2021; 9(22):2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222934
Chicago/Turabian StyleMallawi, Fouad Othman, and Malik Zaka Ullah. 2021. "Multiple Slip Impact on the Darcy–Forchheimer Hybrid Nano Fluid Flow Due to Quadratic Convection Past an Inclined Plane" Mathematics 9, no. 22: 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222934
APA StyleMallawi, F. O., & Ullah, M. Z. (2021). Multiple Slip Impact on the Darcy–Forchheimer Hybrid Nano Fluid Flow Due to Quadratic Convection Past an Inclined Plane. Mathematics, 9(22), 2934. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222934






